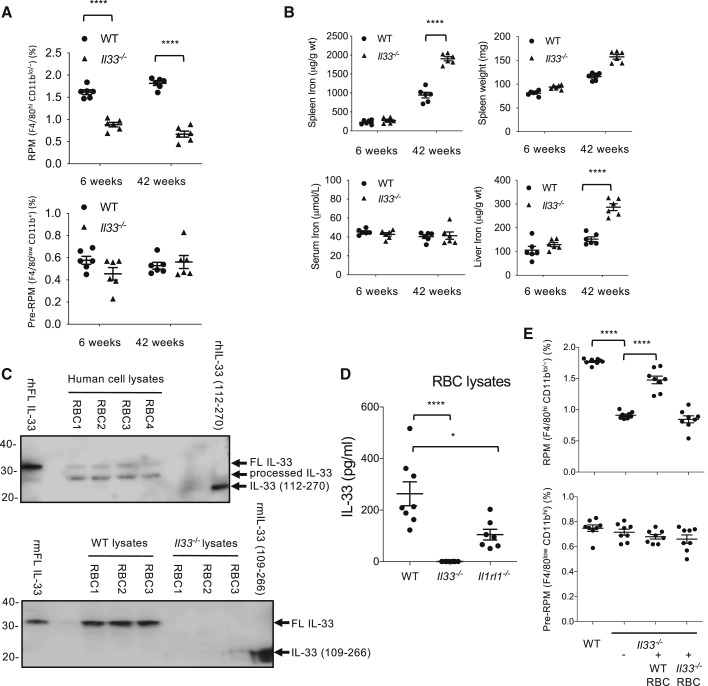
Figure 5.
Red-Blood-Cell-Derived IL-33 Controls the Development of Splenic Red Pulp Macrophages (RPMs)
(A) Quantification of RPMs and pre-RPMs (percentage among CD11clow Ly6Glow NK1.1low SSC-Alow cells) in spleens of young (6 weeks) and old (42 weeks) WT and Il33−/− mice.
(B) Quantification of serum iron, spleen weight, spleen iron, and liver iron in young (6 weeks) and old (42 weeks) WT and Il33−/− mice.
(C) Detection of IL-33 in human (top panel) and mouse (lower panel) red blood cell (RBC) lysates using western blotting. Recombinant full-length and processed human and mouse IL-33 are included as positive controls. RBC lysates from Il33−/− mice are included as negative controls. Each lane is from a separate mouse or individual, representative of at least five independent experiments.
(D) Quantification of IL-33 protein in RBC lysates of WT, Il33−/− (negative control), and Il1rl1−/− mice.
(E) Quantification (percentage among CD11clow Ly6Glow NK1.1low SSC-Alow cells) of splenic pre-RPMs (CD11bhi F4/80lo) and RPMs (CD11blo/− F4/80hi) by flow cytometry in WT and Il3−/− mice. Some Il33−/− mice were reconstituted with either WT or Il33−/− RBCs (see STAR Methods) prior to assessment of splenic pre-RPMs and RPMs.
Each dot in (A), (B), (D), and (E) represents a separate mouse. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001. Please also see Figure S5 and S6.