Abstract
Background
Rotaviruses (RVs) are recognized as a major cause of acute gastroenteritis (AGE) in infants and young children worldwide. Here we summarize the virology, disease burden, prevalence, distribution of genotypes and seasonality of RVs, and the current status of RV vaccination in Southeast Asia (Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) from 2008 to 2018.
Methods
Rotavirus infection in Children in Southeast Asia countries was assessed using data from Pubmed and Google Scholars. Most countries in Southeast Asia have not yet introduced national RV vaccination programs. We exclude Brunei Darussalam, and Timor Leste because there were no eligible studies identified during that time.
Results
According to the 2008–2018 RV surveillance data for Southeast Asia, 40.78% of all diarrheal disease in children were caused by RV infection, which is still a major cause of morbidity and mortality in children under 5 years old in Southeast Asia. Mortality was inversely related to socioeconomic status. The most predominant genotype distribution of RV changed from G1P[8] and G2P[4] into the rare and unusual genotypes G3P[8], G8P[8], and G9P[8]. Although the predominat strain has changed, but the seasonality of RV infection remains unchanged. One of the best strategies for decreasing the global burden of the disease is the development and implementation of effective vaccines.
Conclusions
The most predominant genotype distribution of RV was changed time by time. Rotavirus vaccine is highly cost effective in Southeast Asian countries because the ratio between cost per disability-adjusted life years (DALY) averted and gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is less than one. These data are important for healthcare practitioners and officials to make appropriate policies and recommendations about RV vaccination.
Keywords: Rotavirus, Disease burden, Genotypes, Vaccination, Southeast Asia
Introduction
Rotavirus (RV) history
RV was first identified in cattle in 1969 [1]. The virus appeared similar to those that cause diarrhea in mice [2], calves [3], and a virus identified from a rectal swab of a healthy monkey [4]. In May 1973, Bishop, Davidson, Holmes, and Ruck examined ultrathin sections of duodenal mucosa from children with acute gastroenteritis (AGE) by electron microscopy (EM), and found abundant viral particles in the epithelial cell linings of the upper villous surface which were similar in appearance to the RVs discovered in animals before [5]. EM also revealed 70-nm particles in negatively stained fecal extracts [6, 7]. The viral particle was initially identified by several names including reovirus-like, orbivirus-like, duovirus, infantile gastroenteritis virus, or a “new” virus. The wheel-like structure observed on EM eventually led to the naming concensus of Rotavirus (rota is Latin for wheel) [8]. RVs have now been shown to be a cause of diarrhea in the young of many mammalian and avian species [9].
RV morphology
RVs are 70-nm, non-enveloped RNA viruses belonging to the family Reoviridae. The RV genome consists of 11 segments of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) surrounded by a triple-layered capsid. Each genomic fragment encodes protein of different function. The outer layer proteins (viral protein [VP] 4 and VP7) mediate attachment and penetration; the inner layer is composed of VP2 protein and encloses the viral genome and the minor protein VP1, the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and VP3, the viral capping enzyme. The middle layer is composed of VP6 which interacts with and stabilized the inner and outer layer [9]. VP6 defines species/group and subgroup specificities [10–12]. All RNA segments, except for segment 11, are monocistronic, encoding either structural viral proteins (VP1 to VP4, VP6, and VP7) or non-structural proteins (NSP1 to NSP5). Genome segment 11 codes for two proteins: NSP5 and NSP6 [9]. RVs can be differentiated by a dual classification system, based on the two outer capsid proteins, VP7 and VP4, that determine the G (VP7, glycoprotein) and P (VP4, protease-sensitive) genotypes [13]. At least 36 G types and 51 P types have so far been identified in humans and animals [14].
A whole genome-based genotyping system was recently proposed for RV Group A (RVA) based on the genotype assignment of all 11 gene segments [15]. The genome of individual RV strains is given the complete descriptor of Gx-P [x]-Ix-Rx-Cx-Mx-Ax-Nx-Tx-Ex-Hx to identify the genotypes of the VP7-VP4-VP6-VP1-VP2-VP3-NSP1-NSP2-NSP3-NSP4-NSP5/6 encoding RNA segments, respectively. Most strains demonstrate either a Wa-like (G1-P[8]-I1-R1-C1-M1-A1-N1-T1- E1-H1), DS-1 (G2-P[4]-I2-R2-C2-M2-A2-N2-T2-E2-H2), or AU-1-related (G3-P[3]-I3-R3-C3-M3-A3/A12-N3-T3-E3-H3/H6) genotype constellation [16, 17].
Indirect immunofluorescence techniques targeting VP6 are used to differentiate RV species. RVs are currently differentiated into at least nine species, designated A to I and a tentative tenth species, J. RVA infects in birds and mammals; RVB, RVC, RVE, RVH, and RVI have been detected in one or more mammalian hosts; RVD, RVF, and RVG have been detected only in birds; RVJ infects bats [18–20]. Table 1 shows rotavirus groups and its host.
Table 1.
Rotavirus groups and hosts
| Rotavirus Group | Host |
|---|---|
| A | Human, Pig [21], Cattle, Horse [22], Rabbit [23], Alpaca [24], Turkey, Pheasant, Bat, Sugar Glider, Camel, Vicugna, Velvet Scoter, Fox, Common Gull, Chicken, Shrew, Racoon, Mouse [1, 16, 25] |
| Sheep, Partridge, Panda, Monkey, Mussel, Oyster, Shellfish, Salmon, Shark, Trout, Deer, Mosquito, Cormorant, Fly, Moth, Tick, Tasmanian Devil, Leafhopper, Buffalo, Antelope, Dog, Civet, Cat [26] Giraffe [27] Pigeon, Guanaco, Macaques [28] | |
| B | Human, Cattle, Pig, Rat, Goat [29] |
| C | Human [30], Dog, Bear, Ferret, Pig [31] |
| D | Chicken, Duck, Pigeon, Guinea Fowl [25, 32] |
| E | Pig [33] |
| F | Pig, Chicken, Teal, Partridge [25, 32] |
| G | Chicken, Duck, Pigeon, Turkey, Partridge, Gull, Avaret, Teal [25, 32] |
| H | Human, Pig, Bat [34, 35] |
| I | Cat [36], Dog [19] |
| J | Bat [20] |
RV infection burden
RVs were recognized as a major cause of AGE in infants and young children in 1973 [2, 7]. RV is the leading cause of diarrhea-associated mortality among children younger than 5 years, although the burden of RV has decreased during the past decade. RV infections were responsible for approximately 128,515 deaths annually among children younger than 5 years. RV constitutes 1 of the 13 diarrhea etiologic agents measured in the 2016 Global Burden of Disease Study [37]. It is the most prevalent agent causing severe diarrhea in both developed and developing countries [38, 39]. After RV vaccine introduction in developed countries, norovirus become the predominant viral pathogen that caused AGE in children. Norovirus prevalence remained stable or increased, whereas rotavirus activity dramatically decreased [40–42]. Nevertheles, from 2000 to 2013 in Southeast Asia, approximately 50.7% (n = 10,765) of total diarrhea mortality was associated with RV disease [43].
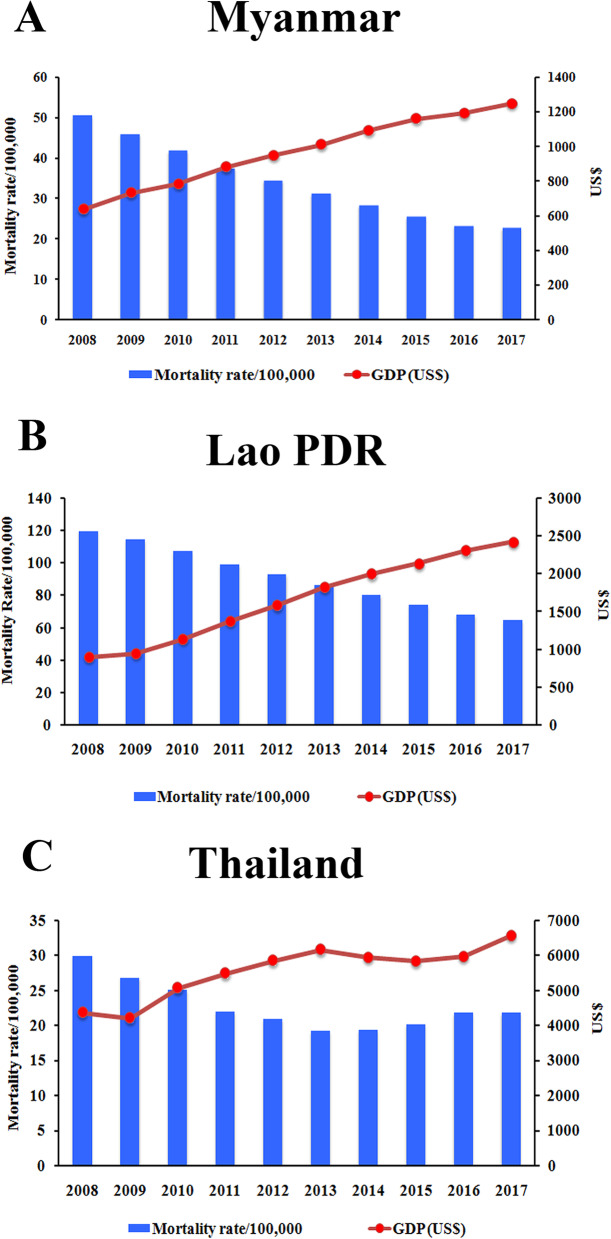
Figure 1 shows the prevalence and death caused by diarrheal disease and RV in children under 5 years old from 1990 to 2017 in Southeast Asia. The prevalence of diarrheal diseases in Southeast Asia countries varies, but the mortality trend associated with diarrhea and especially RV infection has been decreasing in recent years. Lao People’s Democratic Republic [PDR] reports one of the highest death rates in this period. However, improvement in hygiene and sanitation combined with the introduction of the rotavirus vaccine has contributed to decreasing RV infection [46].
Fig. 1.
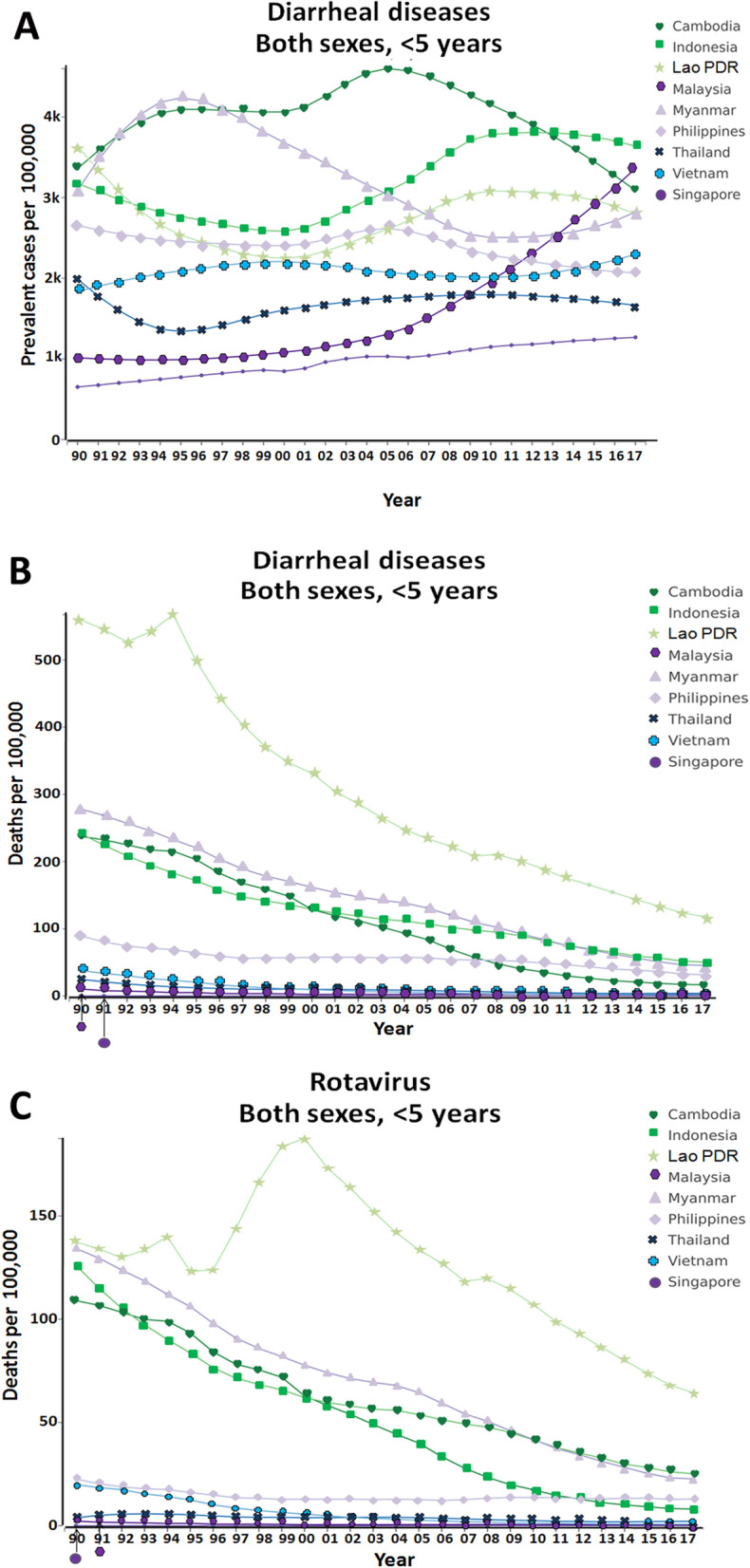
Diarrhea diseases in children under 5 years old in Southeast Asian countries from 1990 to 2017. a Prevalence of diarrhea; b diarrhea-associated mortality; c mortality attributed specifically to rotavirus [44, 45]
We collected RV surveillance data from 9 countries in Southeast Asia (Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) for the years 2008–2018 to estimate the proportion of RV gastroenteritis (RVGE) (Table 2). A total of 52,579 stool samples were collected of which 21,444 (40.78%) were RV positive. Acute diarrheal disease caused by RV is still a major cause of morbidity and mortality in children under 5 years old in developing countries, which may be attributed to the regions’ lower standards of living and hygiene conditions [46]. However, our study revealed that as the gross domestic product (GDP) per capita increases, and the economic status of Southeast Asian countries improves, the RV mortality rate steadily declines (Fig. 2). Higher socioeconomic status (SES) can improve sanitation, hygiene practices, and healthcare facilities to support better living conditions and decrease the RV mortality in children.
Table 2.
The annual incidence of rotavirus in children under 5 years old in Southeast Asian countries, 2007–2018
| Country | Region | Year | Study Design | Number of Stool Sample | Number of Rotavirus Positive | Percentage (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cambodia | Phnom Penh | 2010–2016 | Active hospital surveillance | 7007 | 3473 | 49.56 | [47] |
| Indonesia | Bandung, Yogyakarta, Mataram, Denpasar | 2009–2010 | Hospital-based surveillance | 4235 | 2220 | 52.42 | [48] |
| Yogyakarta | 2009 | Hospital-based surveillance | 104 | 57 | 54.81 | [49] | |
| Denpasar | 2009–2011 | Hospital-based surveillance | 656 | 327 | 49.85 | [50] | |
| Bandung | 2009–2012 | Prospective cross-sectional study | 135 | 92 | 68.15 | [51] | |
| Mataram | 2010 | Cross-sectional study | 328 | 210 | 64.02 | [52] | |
| Surabaya | 2013 | Cross-sectional study | 220 | 88 | 40 | [53] | |
| Pekanbaru | 2015 | Cross-sectional study | 71 | 42 | 59.15 | [54] | |
| Indonesia | 2010–2015 | National surveillance | 4013 | 1950 | 48.59 | [55] | |
| Surabaya | 2015–2016 | Hospital-based surveillance | 134 | 42 | 31.34 | [56] | |
| Central Java | 2013–2016 | Hospital-based surveillance | 1649 | 105 | 6.37 | [57] | |
| Jawa Timur | 2015–2018 | Hospital-based surveillance | 432 | 137 | 31.71 | [58] | |
| Lao PDR | Vientiane | 2009–2015 | Hospital-based surveillance | 1772 | 928 | 52.37 | [59] |
| Malaysia | Malaysia | 2008–2010 | Hospital-based surveillance | 822 | 279 | 33.94 | [60] |
| Myanmar | Yangon | 2009–2014 | Prospective active surveillance | 3724 | 1860 | 49.95 | [61] |
| Philippines | Palawan | 2012 | Not specified | 45 | 25 | 55.56 | [62] |
| Philippines | 2013–2015 | National Surveillance | 5229 | 2024 | 38.1 | [63] | |
| Zamboanga city | 2016 | Hospital-based surveillance | 93 | 56 | 60.22 | [64] | |
| Singapore | Singapore | 2008 | Hospital-based surveilance | 285 | 167 | 58.60 | [65] |
| Singapore | 2008 | Randomized clinical trial | 58 | 11 | 18.97 | [66] | |
| Thailand | Bangkok, Khon Kaen, Nahon Ratchasima, Tak | 2007–2009 | Hospital-based surveillance | 557 | 158 | 28.37 | [67] |
| Chiang Rai, Nakhon Ratchasima, Surat Thani, Phitsanulok, | 2008–2010 | Regional surveillance | 3470 | 458 | 13.20 | [68] | |
| Khon Kaen & Bangkok | 2009–2011 | Hospital-based surveillance | 562 | 250 | 44.48 | [69] | |
| Thailand | 2010–2013 | Active surveillance | 1032 | 184 | 17.83 | [70] | |
| Khon Kaen, Bangkok | 2011–2014 | Hospital-based surveillance | 688 | 204 | 29.65 | [71] | |
| Chiang Mai | 2012 | Hospital-based surveillance | 186 | 35 | 18.82 | [72] | |
| Nonthaburi | 2012–2014 | Hospital-based surveillance | No Data | 73 | – | [73] | |
| Sukhothai, Petchabun | 2013–2014 | Regional surveillance | 2754 | 666 | 24.18 | [74] | |
| Thailand | 2014–2016 | Hospital-based surveillance | 1867 | 514 | 27.53 | [75] | |
| Chiang Rai | 2015–2016 | Hospital-based surveillance | 270 | 91 | 33.70 | [76] | |
| Vietnam | Ho Chi Min | 2009–2010 | Hospital-based surveillance | 1419 | 664 | 46.79 | [77] |
| Vietnam | 2012–2015 | National Surveillance | 8689 | 4054 | 46.66 | [78] |
Fig. 2.
The mortality of rotavirus-associated acute gastroenteritis per 100,000 children under 5 years old and the national gross domestic product (GDP) per capita between 2008 to 2017 in lower-middle income countries; a Myanmar and b Lao PDR, and in the upper-middle income country; c Thailand [44, 79]. The bar graphs represent the mortality rate per 100,000 populations. The red dots represent the GDP per capita in US$
RV genotype distribution
Among the data from Southeast Asia countries examined, the most predominant genotype distribution of RV has changed except in Lao PDR and Malaysia. In 2009–2013, G1P[8] and G2P[4] were the most predominant genotypes, but starting 2014, it changed into the rare and unusual genotypes G3P[8], G8P[8], and G9P[8]. Several uncommon RV genotypes such as G2P[8], G8P[6], G5P[19], G9P[4], G9P[6], and G1P7[5] were identified in the surveillance data. The presence of such diversity among RV isolates provides insight into the evolution of these strains, which can arise due to point mutations, genetic rearrangements, reassortment events, and interspecies transmission [13, 80, 81]. Circulating RV strain appears diverse despite RV vaccination, which may enable the increase in the prevalence of non-vaccine strains. Thus, the circulation of strains in which vaccines have lower efficacy eventually impairs vaccine effectiveness [82]. In the Philippines, where the Rotarix® vaccine was introduced in July 2012, the frequency of RVGE cases caused by G1P[8] decreased while the circulation of G9P[8] increased significantly [83]. The genotype distribution of RV in Southeast Asia is shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
The distribution of rotavirus genotype in Southeast Asian countries based on the surveillance data from 2008 to 2018a
| Genotype | Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017/2018 | |
| Cambodia | ||||||||||
| G1P[8] | 118 | 109 | 190 | 107 | 52 | 81 | 8 | |||
| G2P[4] | 2 | 12 | 199 | 88 | ||||||
| G3P[8] | 21 | 50 | 5 | 4 | 43 | 101 | ||||
| G8P[8] | 2 | 1 | 4 | 42 | 118 | 8 | ||||
| G9P[8] | 2 | 4 | 1 | 29 | 29 | |||||
| Others | 19 | 3 | 34 | 52 | 18 | 17 | 14 | |||
| Indonesia | ||||||||||
| G1P[4] | 30 | 11 | 16 | 30 | ||||||
| G1P[6] | 33 | 38 | 8 | 33 | 1 | |||||
| G1P[8] | 64 | 219 | 98 | 138 | 202 | 2 | 1 | 12 | ||
| G1P[UT] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 6 | ||||||
| G2P[4] | 35 | 25 | 17 | 1 | 36 | 1 | ||||
| G2P[6] | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 5 | ||||
| G2P[8] | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||||||
| G3P[4] | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| G3P[6] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 19 | |||||
| G3P[8] | 2 | 6 | 8 | 47 | 54 | 126 | 98 | |||
| G3P[9] | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| G3P[UT] | 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| G9P[8] | 1 | |||||||||
| G12P[8] | 8 | |||||||||
| Thailand | ||||||||||
| G1P[4] | 8 | 4 | ||||||||
| G1P[8] | 14 | 217 | 63 | 146 | 87 | 236 | 447 | 42 | 3 | |
| G2P[4] | 38 | 107 | 3 | 5 | 109 | 152 | 3 | |||
| G2P[8] | 1 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 1 | |||||
| G3P[8] | 1 | 22 | 20 | 156 | 26 | 4 | 19 | 125 | 44 | |
| G3P[9] | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| G4P[6] | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| G8P[8] | 1 | 58 | 164 | 8 | ||||||
| G9P[8] | 7 | 58 | 7 | 13 | 1 | 5 | 77 | |||
| G9P[UT] | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||||||
| G12P[6] | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||
| G12P[8] | 24 | 5 | ||||||||
| Untypeable | 5 | 1 | ||||||||
| Myanmarb | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||||
| G1P[6] | 15 | 7 | 2 | 30 | 31 | 3 | ||||
| G1P[8] | 3 | 2 | ||||||||
| G2P[4] | 1 | 1 | 14 | 9 | 22 | 3 | 1 | |||
| G2P[6] | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| G2P[8] | 1 | |||||||||
| G3P[8] | 5 | |||||||||
| G9P[4] | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||
| G9P[8] | 7 | 1 | 20 | 20 | ||||||
| G12P[6] | 6 | 50 | 103 | 45 | 1 | |||||
| G12P[8] | 3 | 7 | 8 | 37 | 2 | |||||
| Mixed | 6 | 5 | 2 | 11 | 1 | |||||
| Partially typed | 4 | 4 | 7 | 26 | 1 | 14 | 10 | |||
| Untypeable | 7 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |||||
| Lao PDR | ||||||||||
| G1P[4] | 6 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| G1P[8] | 53 | 32 | 47 | 15 | 96 | 14 | 145 | |||
| G2P[4] | 66 | 44 | 2 | 6 | 57 | 76 | 3 | |||
| G2P[8] | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| G3P[4] | 2 | |||||||||
| G3P[8] | 7 | 32 | 80 | 92 | 7 | |||||
| G3P[9] | 1 | |||||||||
| G4P[4] | 1 | |||||||||
| G4P[6] | 1 | |||||||||
| G8P[8] | 1 | |||||||||
| G9P[4] | 1 | |||||||||
| G9P[8] | 40 | 6 | 1 | |||||||
| G10P[4] | 1 | |||||||||
| G12P[6] | 1 | |||||||||
| Mixed | 19 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| Untypeable | 11 | 1 | ||||||||
| Philippines | ||||||||||
| G1P[8] | 232 | 543 | 417 | 587 | ||||||
| G2P[4] | 55 | 101 | 400 | 187 | ||||||
| G9P[8] | 19 | 51 | 43 | 360 | ||||||
| Untypeable | 8 | 22 | 7 | 133 | ||||||
| Mixed | 3 | 7 | 28 | 13 | ||||||
| Unusual | 5 | 28 | 40 | |||||||
| G1P[6], G2P[6], G1P[9] | 9 | 13 | ||||||||
| Vietnam | ||||||||||
| G1P[4] | 12 | 12 | 9 | |||||||
| G1P[8] | 934 | 985 | 391 | 125 | ||||||
| G2P[4] | 58 | 108 | 306 | 234 | ||||||
| G3P[8] | 47 | 24 | 68 | 50 | ||||||
| G8P[8] | 9 | 259 | ||||||||
| Mixed | 23 | 12 | 34 | 58 | ||||||
| Untypeable | 93 | 48 | 26 | 92 | ||||||
| Others | 12 | 9 | 17 | |||||||
| Malaysia | ||||||||||
| 2008–2010 | ||||||||||
| G1P[8] | 206 | |||||||||
| G2P[4] | 19 | |||||||||
| G9P[8] | 16 | |||||||||
| G12P[8], G3P[9], G9P[9], G3P[8] | 10 | |||||||||
| Singaporea | ||||||||||
| 2005–2008 | ||||||||||
| G1P[4] | 4 | |||||||||
| G1P[8] | 125 | |||||||||
| G1P[11] | 1 | |||||||||
| G2P[4] | 49 | |||||||||
| G2P[8] | 5 | |||||||||
| G3P[4] | 1 | |||||||||
| G3P[8] | 61 | |||||||||
| G9P[4] | 5 | |||||||||
| G4P[8] | 1 | |||||||||
| G9P[8] | 68 | |||||||||
aIn Singapore, the available data was between 2005 to 2008
bMyanmar: Surveillance data were collected during the intervals defined as 1. January – June 2009; 2. July 2009 – June 2010; 3. July 2010 – June 2011; 4. July 2011 – June 2012; 5. July 2012 – June 2013; 6. July 2013 – June 2014; 7. July – December 2014
Differences in the predominance of RV genotypes and newly emerging strains were identified over the surveillance period in Cambodia. The G1P[8] genotype was predominant in 2010, 2011, and 2012 (74, 66, and 79%, respectively), whereas genotype G2P[4] predominated between 2013 (54%) and 2014 (44%). The previously uncommon strain G8P[8] also emerged in 2014 (21%). The proportion of G8P[8] genotype detections increased further in 2015 (41%), in conjunction with the emergence of G9P[8] (10%). By 2016, the detection of genotype G9P[8] had increased to 18%, and G3P[8] became the most prevalent genotype (responsible for 63% of detections) [47].
In Indonesia, the surveillance results demonstrated a changing trend for the most prevalent genotype, from G1P[8] in 2009–2013 to G3P[8] in 2014–2018. From 2009– to 2013, G1P[8] was the most prevalent genotype circulating, which accounted for 38, 73.7, 67.5, 85.7, and 60.1% each year, respectively. G3P[8] became the most predominant strain in 2013, and this continued to 2015, accounting for 49,7, 82.5%, and 84,4%, respectively [49, 53, 55–57]. Another study reported that G3P[8]/[6] was also the predominant strain during 2015–2018 [58].
During the 7-year surveillance period in Lao PDR, the most predominant genotypes identified by year were G2P[4] (40%) and G1P[8] (32%) in 2009; G2P[4] (28%) and G9P[8] (26%) in 2010; G3P[8] (61%) and G1P[8] (36%) in 2011; G3P[8] (81%) in 2012; G1P[8] (57%) and G2P[4] (34%) in 2013; G2P[4] (81%) in 2014; and G1P[8] (96%) in 2015 [59].
From 2008 to 2010, the most common genotype in Malaysia was G1P[8] (82%). Other genotypes identified were G2P[4] (7.6%) and G9P[8] (6.3%). Approximately 4% of the samples were either mixed or untypeable (G12P[8], G3P[9], G9P[9], G3P[8]) [60]. A 2006 preliminary report in Sabah State showed that approximately 33% of samples were positive for RV, of which 33% were of genotype G4P [9, 84].
In Myanmar, the most common strains in 2009 were G1P [8] (28.3%) and G12P [8] (28.3%). G12P [8] was detected from 2009 to 2012, ranging from 28.3% in 2009 to 70% in 2011. G2P[4] became the most predominant strain in 2012–2013, followed by G1P[8] in 2013–2014. G9P[8] comprised only 1% of the RV strains in 2011 and increased to 97.5% in 2014. While in 2015, the majority (90%) of RV strains comprised G9P[8] (54%) and G3P[8] (36%). G9P[8] emerged in Myanmar in 2011 and was the most common strain in 2014 and 2015 [61, 85].
In the Philippines, 1949 (98.5%) RVA-positive stool specimens were successfully typed. The most common genotypes identified were G1P[8] (60.3%), G2P[4] (28.1%), and G9P[8] (5.7%). The frequencies of RVGE cases due to G1P[8] were similar in 2013 (72.0%) and 2014 (75.1%), but it decreased to 44.7% in 2015. Likewise, the frequencies of cases due to G2P[4] were similar in 2013 (17.1%) and 2014 (14.1%) but increased to 42.9% in 2015. The proportion of RVGE cases caused by G9P[8] did not change appreciably from 2013 (5.9%) to 2014 (6.9%) or 2015 (4.6%). Mixed genotypes, unusual strains, and animal strains were detected in specimens from 38 (1.9%), 22 (1.1%), and 10 (0.5%) children with RVGE,. Rare and unusual genotype combinations identified include three G1P[4], eight G2P[8], seven G8P [6], two G8P[8], and two G9P[4] strains. Also, animal strains were detected in specimens from 10 children, including 1 G3P[9] feline-like and nine G4P[6] porcine-like strains [63].
The predominant strain observed in Singapore was G1P[8] (18,3%), while G9P[8] (9,9%) was the second most common type observed among children in Singapore [65, 66].
In Thailand, G2P[4] was the most common genotype in 2008 (53,5%). G1P[8] was the predominant genotype in 2009, 2010, 2012, 2013, and 2014, accounting for 47.3, 35.8, and 63.9%, 60.4, and 56.2%, respectively. In 2011 (68.7%), 2015 (47.3%), and 2016 (89.8%), most RV strains were G3P[8]. Uncommon genotypes found were G1P7[5], G5P[19], G9P[4], and G9P[6], adding to the existing list of uncommon genotypes reported to circulate in Thailand [67–71, 73–76].
Based on RV diarrhea data from four sentinel hospitals in Vietnam from 2012 to 2015, G1P[8] was the most prevalent strain during 2012 and 2013, accounting for 80 and 82% of total genotyped samples, respectively. G2P[4] was found in 5% of samples in 2012 and 9% in 2013. In 2014 and 2015, the proportion of RVGE caused by G2P[4] increased to 36 and 28%, respectively. G8P[8] was not detected in 2012 and 2013, it accounted for only 1% of specimens in 2014, and it became predominant (31%) in 2015 [78].
RV seasonality
Meteorological conditions have an indirect yet important impact on the epidemiology of human rotavirus infection. Weather-related low indoor relative humidity and indoor crowding may be key factors in the epidemiology of rotavirus disease. Hospitalizations for rotavirus gastroenteritis tended to be more common after a cold or dry month than after a warm or wet corresponding calendar month [86].
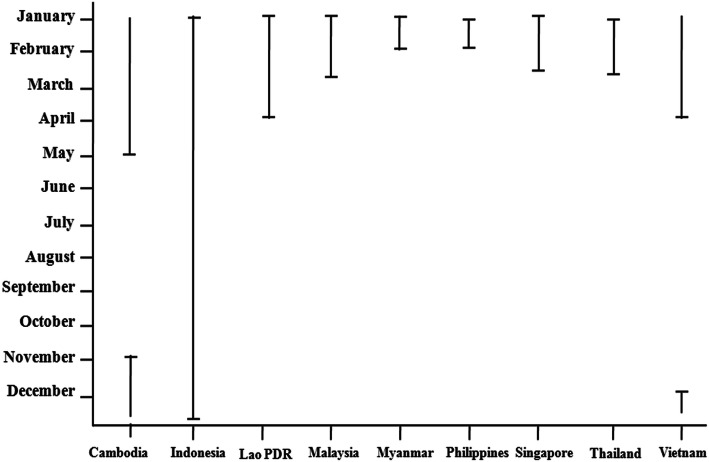
The temporal trend of Cambodian RV infection shows substantial year-round transmission with prominent peaks during colder, dry months. Peaks typically occurred between November and May [47]. In Indonesia, RV infection was present throughout the year and did not demonstrate clear annual seasonality [55]. Conversely, infection generally peaks during the rainy season in Singapore and Malaysia. An outbreak of RV infection was observed from January to March [65, 87]. Positive RV cases increased in number and proportion during the dry season (January–April) each year in Lao PDR [88]. In Myanmar and the Philippines, RV infection has a strong seasonal peak in colder, drier months, as seen in other Asian countries. The highest rate of RV infection occurred in January and February [61, 63]. RV cases in Thailand were most prevalent during the cooler months, specifically from January to March, but RV was detected every month in the northern part of Thailand, where the weather is relatively cooler compared to the rest of the country [68]. In Vietnam, RV was detected every month, but most RV gastroenteritis (GE) cases occurred between December and May [78]. Figure 3 shows the RV seasonality in Southeast Asian countries.
Fig. 3.
Seasonality of rotavirus in Southeast Asian countries
The seasonal pattern in RV varies by climatic region and is also associated with local weather. A reduction in RV rates was associated with increased temperature and precipitation [89]. There is a significant association between increased numbers of estimated positive RV cases and lower humidity, rain, and temperature. In children younger than 2 years old, RV was the pathogen most frequently identified in the winter, dry, or cool/dry seasons [90]. In tropical climates, the higher temperature was associated with a greater decrease in RV than in humid mid-latitude climates [91]. It had been suggested that the seasonal pattern may be driven by airborne transmission of the disease [92].
RV vaccination
One of the best strategies for decreasing the global burden of disease is the development and implementation of effective vaccines [43]. RV is the most common cause of vaccine-preventable severe diarrhea [93]. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommended that RV vaccines be included in immunization programs in the European region and the Americas in 2006. In 2009, following efficacy studies in low-income countries (LICs) and lower-middle-income countries (LMICs) in Africa and Asia, the WHO recommended the use of RV vaccines in all National Immunization Programs (NIPs) [94]. RV vaccines had been introduced in 101 countries by the end of 2018, and global coverage was estimated to be at 35% [95]. Most countries in Southeast Asia have not yet introduced national RV vaccination programs. Among Asian countries, only the Philippines, and recently Thailand have introduced the vaccines on a limited basis [96].
The Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunizations (GAVI), also known as the Vaccine Alliance, actively supports RV vaccination by subsidizing the cost in eligible countries. In LMIC, the budget impact is an important criterion for funding new interventions, particularly for large public health investments such as new vaccines. By the end of 2018, GAVI had funded RV vaccine introductions in 45 countries [97].
RV vaccine history
Research to develop a safe, effective RV vaccine began in the mid-1970s when investigators demonstrated that previous infection with animal RV strains protected laboratory animals from experimental infection with human RVs [98]. The first multivalent live oral reassortant vaccine developed was RotaShield® (a rhesus RV tetravalent [RRV-TV] vaccine) in the late 1980s [99]. The RRV-TV vaccine was licensed in August 1998 for routine use in children in the United States at 2, 4, and 6 months of age due to its proven efficacy [100]. In 1999, RotaShield® was voluntarily withdrawn from the U.S. market due to an increased risk of intussusception within 3 to 14 days after the first dose in infants < 3 months of age [101].
Due to the past association of intussusception and the earlier RV vaccine, large safety studies were performed both for RV1 and RV5 before market authorization [102]. Rotarix® vaccine were highly efficacious in protecting infants against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis [66, 103] and were not associated with an increased risk of intussusception [104–106]. The pentavalent rotavirus vaccine (RotaTeq®) was highly efficacious against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis and provided substantial protection against rotavirus gastroenteritis of any severity. A significantly increased risk of intussusception in vaccine recipients was not detected [107]. In February 2014, WHO reviewed global intussusception data and found that the risk of intussusception following current rotavirus vaccines remains small compared to the benefits of preventing the impact of severe diarrhea [108].
At the end of 2018 there are four globally available WHO-prequalified oral vaccines (Rotarix® and RotaTeq®, Rotavac® and Rotasiil®) [109], one rotavirus vaccine licensed in China (Lanzhou lamb RV vaccine), one in Vietnam (Rotavin-M1), and there are several candidates in development [110].
Two RV vaccines, Rotarix® and RotaTeq®, have been developed by Glaxo Smith Kline and Merck, respectively. Rotarix® is a live attenuated monovalent vaccine derived from the most common human RV strain, G1P[8]. RotaTeq® is a live attenuated pentavalent vaccine containing mono-reassortant strains with genes encoding the human G1, G2, G3, G4, and P[8] protein in the genetic background of a bovine RV strains [39, 100]. These vaccines are highly effective for the global prevention of severe diarrhea and are included in the NIPs or phased subnational introductions in 101 countries by the end of 2018 [95, 111].
Rotavac® (Bharat Biotech International Limited) is a monovalent human-bovine RV vaccine. The vaccine consists of the 116E RV strain, which is a naturally occurring reassortant strain G9P[11], containing 1 bovine RV gene P[11] and 10 human RV genes [112]. Rotavac® is the first to be introduced into a public vaccination program as of April 2016 when it was introduced in four states in India [113]. Rotasiil® is a live attenuated human-bovine reassortant pentavalent RV vaccine that contains genes encoding the VP7 of serotypes G1, G2, G3, G4, and G9. In March and September 2018 Rotavac® and Rotasiil®, respectively achieved WHO prequalification. Rotavac® has a vaccine efficacy of 53.6% for severe RV diarrhea in India [112], while Rotasiil® has efficacies of 60.5 to 66.7% in India [114] and Niger respectively [115]. Rotasiil® can safely be delivered with decreased dependence on the availability of a cold chain [116].
The Lanzhou Institute of Biological Products manufactures the Lanzhou Lamb RV vaccine (LLR). It is a monovalent lamb vaccine strain G10P[12], attenuated by cell passage [117], and was licensed in China in 2000. When given to children between 9 and 35 months old, one dose of the LLR vaccine conferred partial protection [118]. Vaccine effectiveness in children under 5 years of age was recently estimated at 35% (13 to 52%) against RV diarrhea and 53% (15 to 75%) against moderate-to-severe RV diarrhea based on a large case-controlled study [119].
Rotavin-M1 vaccine is manufactured by the Center for Research and Production of Vaccines and Biologicals and was licensed for use in Vietnam in 2012. The vaccine was derived from an attenuated strain, G1P[8], isolated from a Vietnamese child. A clinical trial found the vaccine to be safe and immunogenic in Vietnamese infants [120].
Another candidate RV vaccine, RV3-BB, was developed from a neonatal strain G3P[6] identified in Australia, with ongoing early clinical studies conducted in New Zealand and now underway in Indonesia. It was also successfully implemented for vaccination of neonates [121]. Table 4 describes the comparison of all oral RV vaccines developed and used so far.
Table 4.
Comparison of oral rotavirus vaccines
| Rotavirus Vaccines | Rotarix® (GSK) [100] | RotaTeq® (Merck) [100] | Rotavac® (Bharat Biotech) [112] | RotaSIIL® (Serum) [116] | Rotavin (Polyvac) [120] | LLR (Lanzhou) [118, 119] | RV3-BB (Bio Farma) [121] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Licensure | Several countries, 2006 | Several countries, 2006 | India, 2014 | India, 2017 | Vietnam, 2012 | China, 2000 | Clinical trial phase IIb |
| Prequalification | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Strains | Monovalent, human derived G1P[8] | Pentavalent, WC3 G6P[5] bovine reassortant G1–4,P8 | Monovalent, human neonatal derived G9P[11] | Pentavalent, UK Bovine G6P[5], reassortant G1–4, G9 | Monovalent, human G1P[8] | Monovalent, Lamb G10P[12] | Monovalent, human neonatal G3P[6] |
| Number of doses | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Age, first dose | 6 weeks | 6 weeks | 6 weeks | 6 weeks | 6 weeks | 2 months | New born: 0–5 days Infant: 8 weeks |
| Age, last dose | 10 weeks | 14 weeks | 14 weeks | 14 weeks | 14 weeks | 36 months | New born: 14 week Infant: 18 weeks |
| Dosage | 106 median CCID50 of live attenuated human G1P[8] RV | 2.0–2.8 × 106 infectious units per reassortant | 105 fluorescent focus unit (FFU) of live rotavirus | 105.6 infectious units per reassortant | 106.3 FFU/dose of live attenuated human G1P[8] particles | > 5.5 log CCID50 | 8.3–8.7 × 106 FCFU/ml |
| UNICEF price per course for GAVI-supported countries, 2020 [122] | $4.58 | $9.60 (RotaTeq is no longer an option available to GAVI-supported countries) | $2.55 | $4.65 (1-dose vial) $2.85 (2-dose vial) | $17.60 | $72 for the three-dose series |
Intussusception, neutralizing antibodies present in breast milk, as well as the lower vaccine effectiveness in less developed settings has stimulated interest in an alternative, parenteral approach to immunization [123–126]. The inactivated rotavirus particles, protein sub-units or virus-like particles (VLPs, structurally-similar to live virus) are being investigated as rotavirus vaccine candidates [125, 127, 128].
Three types of animal models have been used to evaluate protective efficacy of VLPs: infection models (adult mice and rabbits), disease models (gnotobiotic piglets), and models evaluating passive protection (neonatal mice and calves) [129]. Gnotobiotic pig was used to assessed the immunogenicity and protection of a candidate inactivated rotavirus vaccine (IRV), the human strain CDC-9 (G1P[8] [130] and attenuated Wa human rotavirus [AttHRV] or non replicating Wa 2/6 rotavirus-like particles [131]. Mice, rabbits, and piglets were used to evaluate the efficacy of VPL such as 2/6-VLPs (consisting of VP2 and VP6) [129] and RF 8–2/6/7-VLPs [132]. Human clinical trial recently assessed in South African toddlers and infants was done for the subunit vaccine P2-VP8-P[8] [133, 134].
Vaccine efficacy
RV vaccination does not completely protect young children against infection, but it reduce the severity of RVGE [135]. RV vaccines are highly effective in preventing severe gastroenteritis in young children during the first 5 years of their life, particularly in developed countries [136]. The SES of a country seems to influence RV vaccine effectiveness [137]. Vaccination was predicted to prevent 93, 86, and 51% of severe RVGE in high, middle, and low SES, respectively [126]. Analysis of the data for the Asia region found median vaccine effectiveness of 94% in low child mortality countries, 64% in medium child mortality countries, and 49% in high child mortality countries [138]. Factors that might contribute to this phenomenon including gut microbiota, genetic factors, transplacental antibodies, enteric pathogens, and environmental enteropathy [139, 140]. Evidence suggests that vaccine efficacy may vary by setting, due to regional differences in circulating RV vaccine strains and reduced efficacy of oral vaccines in settings with a high prevalence of malnutrition and gastrointestinal infections [141]. Pooled efficacy estimate of Rotarix® and RotaTeq® against severe RVGE in industrialized countries is 88% during the first year of age and 83% during the second year. However, RV vaccine efficacy is much lower in countries where the mortality rate for children under 5 years of age is high [142]. The efficacy of Rotarix® and RotaTeq® in the U.S. depends on the level of exposure during the RV season [143]. It can be concluded that vaccine efficacy is affected by individual factors such as nutritional level, gut microbiota, genetic factor, transplacental antibody and environmental enteropathy and external factors including SES, circulating vaccine strain, childhood mortality rate, and RV season in each country.
Additionally, RV vaccination confers herd protection among infants and children under 5 years old who had not been vaccinated [144–146]. In developing countries with lower RV vaccine efficacy and coverage, indirect protection gain from herd immunity is more significant than in industrialized countries where vaccine efficacy and coverage exceed 90% [142].
Vaccine introduction in Southeast Asia
Many countries in Southeast Asia have not implemented national RV vaccination programs including Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam. One reason is because of uncertainties regarding the cost-effectiveness of incorporating RV vaccination into the NIP. In addition, the vaccine’s decreased efficacy in LIC settings has discouraged its introduction. Prevention of diarrhea in these countries has focused on patient treatment and the management of water quality, sanitation, and hygiene [84].
In Indonesia, the RV vaccine has been commercially available since 2011. Indonesia’s national vaccine manufacturer, PT. Bio Farma, Bandung, is developing an RV vaccine using G3P[6] strain in collaboration with the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne, Australia [125]. Bio Farma is currently driving clinical development, intending to introduce the vaccine into the Indonesian NIP by 2021, and eventually develop a product for the global market [128].
Currently Rotarix® and RotaTeq® are commercially available in Malaysia through private health providers [147]. However, RV vaccine is not included in Malaysia NIP because it is not considered permissible under Islamic shariah law (halal) [84]. The current oral rotavirus vaccines use porcine trypsin in the manufacturing process [148]. There are also concerns about competing public health priorities and price [84]. The Health Ministry recently said the RV vaccine would be included in NIP if the associated mortality rate for children aged 5 and below exceeded 10%. However, the childhood mortality rates in Malaysia was 0.5% in 2014 and 2.9% in 2015 [149].
In Myanmar and Lao PDR where individual incomes are relatively low, international assistance will support for the RV vaccine introduction in 2020. The total amount of GAVI support for Myanmar is $4,088,000 [150]. Lao PDR is also planning RV vaccine introductions into the NIP in near future and assistance will be provided the Asian Development Bank and GAVI through an accelerated transition program [84].
In July 2012, the Philippines became the first Asian country to introduce RV vaccines into its NIP. The Philippines has initially focus on immunizing children living in the poorest communities, which have the highest child morbidity and mortality rates from the diarrheal disease [151]. The target population was identified by the Department of Social Welfare and Development, but there were challenges with nationwide vaccine distribution. In 2014, vaccine introduction was limited to the Caraga region, where it was co-administered with oral polio vaccine and the pentavalent vaccine. By 2015, vaccine coverage was close to 90% in the province of Agusan del Sur within this region but subsequently decreased due to a supply shortage [84]. In Agusan del Sur, the RV vaccine became available to the poorest quintile in September 2012; in January 2013, availability was expanded to all age-eligible children in two municipalities, San Francisco and Prosperidad; it was available to the entire province in July 2014. RV vaccine introduction was associated with a substantial decline in diarrheal hospitalizations and outpatient consultations for diarrhea in Agusan del Sur, Philippines [152].
Two live-attenuated, orally administrable RV vaccines Rotarix® and RotaTeq® were licensed in Singapore in October 2005 and July 2007, respectively [106]. To date, RV vaccination is optional in Singapore [65].
The National Vaccine Committee of Thailand considered the introduction of an RV vaccine in 2010 in Sukhothai and Petchabun. Sukhothai province began a routine immunization program with an RV vaccine in October 2011. Evaluation of the first introduction was completed in 2017 and concluded that RV vaccine was highly effective in preventing diarrheal hospitalizations and conferring herd protection among older children who had not been vaccinated [144]. Therefore, universal RV vaccination for infants has been implemented in Thailand since January 2020.
Vietnam is located in a region of high RV infection incidence and eligible for financial support to introduce vaccines into the expanded program of immunization (EPI) from the GAVI [153]. In 2012, the local vaccine manufacturer Polyvac licensed Rotavin-M1, which is based on an attenuated G1P[8] strain. Rotavin-M1 will be offered to children less than 1 year through a two-dose schedule, vaccinating infants at 2 and 4 months [120]. Rotarix® and RotaTeq® are also licensed in Vietnam and are available in the private sector, with approximately 590,000 doses imported since 2017. That same year, the Government approved the introduction of RV vaccination into Vietnam’s NIP by September 2019 with GAVI support. In 2021, the national government will pay for 80% of the vaccine cost, while GAVI will cover the remaining 20% and all operational costs. By 2022, all costs will be covered by the government [84].
Health and economic impacts of RV vaccination
In LMICs, understanding the short- and long-term impact of intervention adoption on national budgets is critical for ensuring program sustainability [154]. Both budget impact and cost effectiveness are key criteria, among others, for policy makers deciding how to allocate limited resources [155].. Vaccination would be considered a worthwhile investment for improving general childhood development and health levels in most LIC. The highest reduction in burden would be achieved in countries with a high disease burden (≥200 RV deaths per 100,000 children under 5 years old), but a similar reduction would be achieved in countries with a medium burden (100–200 RV deaths per 100,000 children under 5 years old) because disease burden reduction also depends heavily on population size and country-specific vaccine efficacy adjusted for local RV serotype distributions [156].
For GAVI non-eligible countries, the price for Rotarix® is $2.49–7.27, and for RotaTeq® is $3.65–5.09 [157]. For GAVI-eligible countries, the price per dose will depend on the country’s gross national income per capita averaged over the previous 3 years. As such Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand are fully not eligible for GAVI vaccine prices and will have to rely on self-financing [158]. For LIC in Asia, introducing vaccines would halve RV-related deaths and medical visits, leading to significant cost reductions [159].
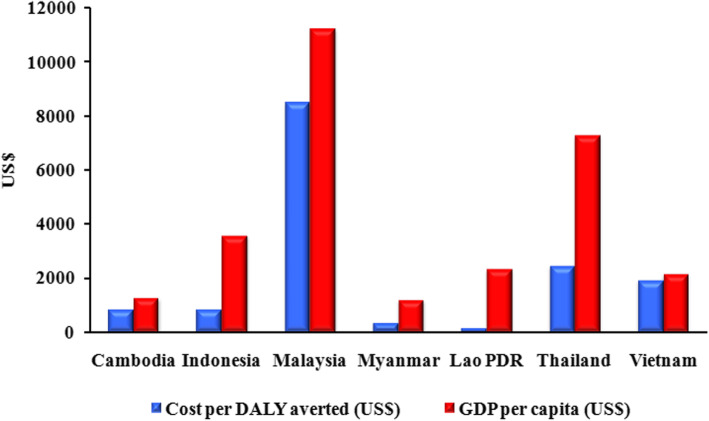
WHO-CHOICE (CHOosing Interventions that are Cost-Effective) uses the GDP as an indicator to develop the following widely referenced categories of cost-effectiveness. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) averted is a widely used indicator that allows easy comparison with a ‘no vaccination’ strategy and with others public health interventions. The ratio between costs per DALY averted and GDP per capita less than one is defined as highly cost effective. The ratio between 1 to < 3 and ≥ 3 are defined as cost effective and not cost effective, respectively [160]. The lowest and highest GDP values were in Myanmar with $1326 and Malaysia with $11,239, respectively [79]. Figure 4 shows the comparison between costs per DALY averted with each country’s GDP in 2018. We excluded the Philippines because the RV vaccine already included in the country’s NIP and Singapore because Singapore is a high-income country. According to categories of cost-effectiveness, RV vaccine introduction into Southeast Asia countries is highly cost-effective because the ratio between costs per DALY averted and GDP per capita it is less than one.
Fig. 4.
Comparison between cost per DALY averted and GDP per capita in Southeast Asia. Introducing the rotavirus vaccine in Southeast Asia is highly cost-effective because the ratio is less than one [79, 107, 137, 161]
Conclusions
According to 2008–2018 RV surveillance data for Southeast Asia, 40.78% of all diarrheal cases were causes by RV. Acute diarrheal disease caused by RV is still a major cause of morbidity and mortality in children under 5 years old in Southeast Asia. Among all assessed countries, the most predominant genotype distribution of RV changed from G1P[8] and G2P[4] into the rare and unusual genotypes G3P[8], G8P[8], and G9P[8]. Although the predominant RV strain has been changed, but the seasonality of RV infection remains unchanged. Continuous surveillance is necessary to determine whether they are regional genotype differences. Epidemiological data on RV prevalence will greatly facilitate vaccine development. In the mean time, the development of new vaccines will be needed if RVs are able to evade current vaccine immunity. More effective vaccines may also further decrease RV infection in children in LIC and LMIC, where currently available vaccines provide moderate efficacy. RV vaccine efficacy is affected by individual factors and external factors. Although most countries in Southeast Asia have not yet introduced national RV vaccination programs, such introduction is projected to be highly cost-effective because the ratio between costs per DALY averted and GDP per capita it is less than one.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AGE
Acute gastroenteritis
- DALY
Disability-adjusted life year
- EM
Electron microscopy
- G
Glycoprotein
- GAVI
Global Alliance for Vaccine and Immunization
- GDP
Gross domestic product
- LIC
Low-income countries
- LMIC
Low-middle income countries
- NIP
National Immunization Program
- NSP
Non-structural protein
- P
Protease
- RV
Rotavirus
- RVGE
Rotavirus gastroenteritis
- SES
Socioeconomic status
- VP
Viral protein
- WHO
World Health Organization
Authors’ contributions
FBL drafted the manuscript. FBL and YP wrote the article and prepared the figures. SV, NW, and YP revised and finished the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Fajar Budi Lestari is a doctoral student at the Inter-Department of Biomedical Science, Faculty of Graduate School, at Chulalongkorn University, in Bangkok. Her primary research interests are zoonotic diseases and molecular epidemiology and evolution of rotavirus in humans and animals.
Funding
This study was funded by the Beasiswa Pendidikan Pascasarjana Luar Negeri (BPP-LN) Scholarship from the Ministry of Education and Culture from the Indonesian Government to Fajar Budi Lestari; the Research Chair Grant from the National Science and Technology Development Agency (P-15-50004); Center of Excellence in Clinical Virology at Chulalongkorn University; MK Restaurant Group Public Company Limited and Charoen Pokphand Group Co., Ltd.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Fajar Budi Lestari, Email: Fajar.budi.l@mail.ugm.ac.id.
Sompong Vongpunsawad, Email: Sompong.Vo@chula.ac.th.
Nasamon Wanlapakorn, Email: Nasamon.W@chula.ac.th.
Yong Poovorawan, Email: Yong.P@chula.ac.th.
References
- 1.Dodet B, Heseltine E, Mary C, Saliou P. Rotaviruses in human and veterinary medicine. Sante. 1997;7(3):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Adam WR, Kraft LM. Epizootic diarrhea of infant mice: indentification of the etiologic agent. Science. 1963;141(3578):359–360. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3578.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mebus CA, Underdahl NR, Rhodes MB, Twiehaus MJ. Historical Research Bulletins of the Nebraska Agricultural Experiment Station. 1969. Calf Diarrhea (Scours): Reproduced with a Virus from a Field Outbreak; pp. 1913–1993. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Malherbe HH, Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bishop RF, Davidson GP, Holmes IH, Ruck BJ. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bishop RF, Davidson GP, Holmes IH, Ruck BJ. Detection of a new virus by electron microscopy of faecal extracts from children with acute gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1974;1(7849):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Flewett TH, Bryden AS, Davies H. Letter: virus particles in gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973;2(7844):1497. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92760-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Flewett TH, Bryden AS, Davies H, Woode GN, Bridger JC, Derrick JM. Relation Between Viruses From Acute Gastroenteritis of Children and Newborn Calves. Lancet. 1974;304(7872):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Greenberg HB, et al. Rotaviruses. In: Estes MK, Knipe DM, Howley PM, et al., editors. Fields Virology. 6. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/ Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2013. pp. 1347–1401. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen JZ, Settembre EC, Aoki ST, Zhang X, Bellamy AR, Dormitzer PR, et al. Molecular interactions in rotavirus assembly and uncoating seen by high-resolution cryo-EM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(26):10644–10648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904024106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li Z, Baker ML, Jiang W, Estes MK, Prasad BV. Rotavirus architecture at subnanometer resolution. J Virol. 2009;83(4):1754–1766. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01855-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Settembre EC, Chen JZ, Dormitzer PR, Grigorieff N, Harrison SC. Atomic model of an infectious rotavirus particle. EMBO J. 2011;30(2):408–416. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kirkwood CD. Genetic and antigenic diversity of human rotaviruses: potential impact on vaccination programs. J Infect Dis. 2010;202(Suppl):S43–S48. doi: 10.1086/653548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.RCWG . List of Accepted Genotypes. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Heiman E, Arijs I, Delbeke T, McDonald SM, et al. Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J Virol. 2008;82(7):3204–3219. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02257-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, McDonald SM, Attoui H, Bányai K, Brister JR, et al. Uniformity of rotavirus strain nomenclature proposed by the rotavirus classification working group (RCWG) Arch Virol. 2011;156(8):1397–1413. doi: 10.1007/s00705-011-1006-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Matthijnssens J, Van Ranst M. Genotype constellation and evolution of group a rotaviruses infecting humans. Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2(4):426–433. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Matthijnssens J, Otto PH, Ciarlet M, Desselberger U, Van Ranst M, Johne R. VP6-sequence-based cutoff values as a criterion for rotavirus species demarcation. Arch Virol. 2012;157(6):1177–1182. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mihalov-Kovács Eszter, Gellért Ákos, Marton Szilvia, Farkas Szilvia L., Fehér Enikő, Oldal Miklós, Jakab Ferenc, Martella Vito, Bányai Krisztián. Candidate New Rotavirus Species in Sheltered Dogs, Hungary. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2015;21(4):660–663. doi: 10.3201/eid2104.141370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bányai K, Kemenesi G, Budinski I, Földes F, Zana B, Marton S, et al. Candidate new rotavirus species in Schreiber's bats, Serbia. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;48:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Phan MVT, Anh PH, Cuong NV, Munnink BBO, van der Hoek L, My PT, et al. Unbiased whole-genome deep sequencing of human and porcine stool samples reveals circulation of multiple groups of rotaviruses and a putative zoonotic infection. Virus Evol. 2016;2(2):vew027. doi: 10.1093/ve/vew027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Matthijnssens J, Miño S, Papp H, Potgieter C, Novo L, Heylen E, et al. Complete molecular genome analyses of equine rotavirus a strains from different continents reveal several novel genotypes and a largely conserved genotype constellation. J Gen Virol. 2012;93(Pt 4):866–875. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.039255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schoondermark-van de Ven E, Van Ranst M, de Bruin W, Van den Hurk P, Zeller M, Matthijnssens J, et al. Rabbit colony infected with a bovine-like G6P[11] rotavirus strain. Vet Microbiol. 2013;166(1–2):154–164. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rojas M, Gonçalves JL, Dias HG, Manchego A, Pezo D, Santos N. Whole-genome characterization of a Peruvian alpaca rotavirus isolate expressing a novel VP4 genotype. Vet Microbiol. 2016;196:27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pickett BE, Sadat EL, Zhang Y, Noronha JM, Squires RB, Hunt V, et al. ViPR: an open bioinformatics database and analysis resource for virology research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D593–D598. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pietsch C, Liebert UG. Evidence for presumable feline origin of sporadic G6P[9] rotaviruses in humans. Infect Genet Evol. 2018;63:180–194. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.05.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.O'Shea H, Mulherin E, Matthijnssens J, McCusker MP, Collins PJ, Cashman O, et al. Complete genomic sequence analyses of the first group a giraffe rotavirus reveals close evolutionary relationship with rotaviruses infecting other members of the Artiodactyla. Vet Microbiol. 2014;170(1–2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Matthijnssens J, Taraporewala ZF, Yang H, Rao S, Yuan L, Cao D, et al. Simian rotaviruses possess divergent gene constellations that originated from interspecies transmission and reassortment. J Virol. 2010;84(4):2013–2026. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02081-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marthaler D, Rossow K, Gramer M, Collins J, Goyal S, Tsunemitsu H, et al. Detection of substantial porcine group B rotavirus genetic diversity in the United States, resulting in a modified classification proposal for G genotypes. Virology. 2012;433(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Trovão NS, Shepherd FK, Herzberg K, Jarvis MC, Lam HC, Rovira A, et al. Evolution of rotavirus C in humans and several domestic animal species. Zoonoses Public Health. 2019;66(5):546–557. doi: 10.1111/zph.12575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Collins PJ, Martella V, O'Shea H. Detection and characterization of group C rotaviruses in asymptomatic piglets in Ireland. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(9):2973–2979. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00809-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dhama K, Saminathan M, Karthik K, Tiwari R, Shabbir MZ, Kumar N, et al. Avian rotavirus enteritis - an updated review. Vet Q. 2015;35(3):142–158. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2015.1046014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pedley S, Bridger JC, Chasey D, McCrae MA. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hull JJ, Marthaler D, Rossow S, Ng TFF, Montmayeur AM, Magana L, et al. Genomic sequence of the first porcine rotavirus group H strain in the United States. Genome Announc. 2016;4(2):e01763–e01715. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01763-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yinda CK, Ghogomu SM, Conceição-Neto N, Beller L, Deboutte W, Vanhulle E, et al. Cameroonian fruit bats harbor divergent viruses, including rotavirus H, bastroviruses, and picobirnaviruses using an alternative genetic code. Virus Evol. 2018;4(1):vey008. doi: 10.1093/ve/vey008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Phan TG, Leutenegger CM, Chan R, Delwart E. Rotavirus I in feces of a cat with diarrhea. Virus Genes. 2017;53(3):487–490. doi: 10.1007/s11262-017-1440-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Troeger C, Khalil IA, Rao PC, Cao S, Blacker BF, Ahmed T, et al. Rotavirus vaccination and the global burden of rotavirus diarrhea among children younger than 5 years. JAMA Pediatr. 2018;172(10):958–965. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Steele AD, Duque J, Parashar UD. WHO-coordinated global rotavirus surveillance network. 2008 estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12(2):136–141. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Parashar UD, Gibson CJ, Bresee JS, Glass RI. Rotavirus and severe childhood diarrhea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12(2):304–306. doi: 10.3201/eid1202.050006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Koo HL, Neill FH, Estes MK, Munoz FM, Cameron A, DuPont HL, et al. Noroviruses: the Most common pediatric viral enteric pathogen at a Large University hospital after introduction of rotavirus vaccination. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2013;2(1):57–60. doi: 10.1093/jpids/pis070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Payne DC, Vinjé J, Szilagyi PG, Edwards KM, Staat MA, Weinberg GA, et al. Norovirus and medically attended gastroenteritis in U.S. children. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(12):1121–1130. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1206589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hemming M, Räsänen S, Huhti L, Paloniemi M, Salminen M, Vesikari T. Major reduction of rotavirus, but not norovirus, gastroenteritis in children seen in hospital after the introduction of RotaTeq vaccine into the National Immunization Programme in Finland. Eur J Pediatr. 2013;172(6):739–746. doi: 10.1007/s00431-013-1945-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Parashar UD. World Health Organization–Coordinated Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network. Global, Regional, and National Estimates of Rotavirus Mortality in Children <5 Years of Age, 2000–2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(Suppl 2):S96–S105. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.IHME . GBD Compare. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Troeger C, Blacker B, Khalil IA, Rao PC, Cao J, Zimsen SRM, et al. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(11):1211–1228. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30362-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Carvalho MF, Gill D. Rotavirus vaccine efficacy: current status and areas for improvement. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(6):1237–1250. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1520583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Angkeabos N, Rin E, Vichit O, Chea C, Tech N, Payne DC, et al. Pediatric hospitalizations attributable to rotavirus gastroenteritis among Cambodian children: seven years of active surveillance, 2010-2016. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7856–7861. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.03.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nirwati H, Wibawa T, Aman AT, Wahab A, Soenarto Y. Detection of group a rotavirus strains circulating among children with acute diarrhea in Indonesia. Springerplus. 2016;5:97. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-1724-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nirwati H, Hakim MS, Aminah S, Dwija IBNP, Pan Q, Aman AT. Identification of rotavirus strains causing Diarrhoea in children under five years of age in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Malays J Med Sci. 2017;24(2):68–77. doi: 10.21315/mjms2017.24.2.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Salim H, Karyana IP, Sanjaya-Putra IG, Budiarsa S, Soenarto Y. Risk factors of rotavirus diarrhea in hospitalized children in Sanglah Hospital, Denpasar: a prospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-14-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Prasetyo D, Sabaroedin IM, Ermaya YS, Soenarto Y. Association between Severe Dehydration in Rotavirus Diarrhea and Exclusive Breastfeeding among Infants at Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital, Bandung, Indonesia. J Trop Med. 2015;2015:862578. doi: 10.1155/2015/862578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Parwata WSS, Wayan S, Abdul W, Yati S. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of rotavirus diarrhea in Mataram, Lombok, Indonesia. Paediatr Indones. 2016;56(2):118–123. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sudarmo SM, Shigemura K, Athiyyah AF, Osawa K, Wardana OP, Darma A, et al. Genotyping and clinical factors in pediatric diarrhea caused by rotaviruses: one-year surveillance in Surabaya, Indonesia. Gut Pathog. 2015;7:3. doi: 10.1186/s13099-015-0048-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Djojosugito F, Maya S, Dewi A, Andani E. Identification of the P genotypes of rotavirus in children with acute diarrhea in Pekanbaru, Indonesia. Malays J Microbiol. 2017;13:67–72. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mulyani NS, Prasetyo D, Karyana IPG, Sukardi W, Damayanti W, Anggraini D, et al. Diarrhea among hospitalized children under five: a call for inclusion of rotavirus vaccine to the national immunization program in Indonesia. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7826–7831. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.05.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Utsumi T, Wahyuni RM, Doan YH, Dinana Z, Soegijanto S, Fujii Y, et al. Equine-like G3 rotavirus strains as predominant strains among children in Indonesia in 2015-2016. Infect Genet Evol. 2018;61:224–228. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cowley D, Nirwati H, Donato CM, Bogdanovic-Sakran N, Boniface K, Kirkwood CD, et al. Molecular characterisation of rotavirus strains detected during a clinical trial of the human neonatal rotavirus vaccine (RV3-BB) in Indonesia. Vaccine. 2018;36(39):5872–5878. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.08.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Athiyyah AF, Utsumi T, Wahyuni RM, Dinana Z, Yamani LN, Soetjipto, et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Rotavirus Infection Among Pediatric Patients in East Java, Indonesia During 2015–2018: Dynamic Changes in Rotavirus Genotypes From Equine-Like G3 to Typical Human G1/G3. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:940. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.SoukAloun D, Douangbouphaa V, Phetsouvanh R, Sibounheuang B, Vongsouvat M, Chanmala K, et al. Rotavirus diarrhea in hospitalized children under 5 years of age in Vientiane, Lao PDR, 2009-2015. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7878–7882. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lee WS, Lim BT, Chai PF, Kirkwood CD, Lee JK. Rotavirus genotypes in Malaysia and universal rotavirus vaccination. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2012;8(10):1401–1406. doi: 10.4161/hv.21577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Theingi WM, Hlaing MT, Ye MK, Khin MA, Mo MW, Htin L, et al. Sentinel surveillance for rotavirus in children <5 years of age admitted for diarrheal illness to Yangon Children's hospital, Myanmar, 2009-2014. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7832–7835. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yamamoto D, Tandoc A, 3rd, Mercado E, Quicho F, Lupisan S, Obata-Saito M, et al. First detection of DS-1-like G1P[8] human rotavirus strains from children with diarrhoea in the Philippines. New Microbes New Infect. 2017;18:54–57. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2017.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bonifacio J, Lupisan S, Roque V, Jr, Ducusin MJ, Grabovac V, Batmunkh N, et al. Molecular characterization of rotavirus diarrhea among children aged under five years in the Philippines, 2013-2015. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7888–7893. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.08.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rebato ND, de Los Reyes VCD, Sucaldito MNL, Marin GR. Is your drinking-water safe? A rotavirus outbreak linked to water refilling stations in the Philippines, 2016. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2019;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.5365/wpsar.2017.8.1.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Phua KB, Tee N, Tan N, Ramakrishnan G, Teoh YL, Bock H, et al. A hospital-based surveillance of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children <5 years of age in Singapore. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013;32(12):e426–e431. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31829f2cb0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Phua KB, Lim FS, Lau YL, Nelson EAS, Huang LM, Quak SH, et al. Rotavirus vaccine RIX4414 efficacy sustained during the third year of life: a randomized clinical trial in an Asian population. Vaccine. 2012;30(30):4552–4557. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Khananurak K, Vutithanachot V, Simakachorn N, Theamboonlers A, Chongsrisawat V, Poovorawan Y. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of rotavirus genotypes in Thailand between 2007 and 2009. Infect Genet Evol. 2010;10(4):537–545. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2010.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sakpaisal P, Silapong S, Yowang A, Boonyasakyothin G, Yuttayong B, Suksawad U, et al. Prevalence and genotypic Distribution of rotavirus in Thailand: a multicenter study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(5):1258–1265. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Maiklang O, Vutithanachot V, Vutithanachot C, Hacharoen P, Chieochansin T, Poovorawan Y. Prevalence of group a genotype human rotavirus among children with dirarrhea in Thailand, 2009-2011. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2012;43(4):904–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yodmeeklin A, Khamrin P, Kumthip K, Malasao R, Ukarapol N, Ushijima H, et al. Increasing predominance of G8P[8] species a rotaviruses in children admitted to hospital with acute gastroenteritis in Thailand, 2010-2013. Arch Virol. 2018;163(8):2165–2178. doi: 10.1007/s00705-018-3848-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Chieochansin T, Vutithanachot V, Phumpholsup T, Posuwan N, Theamboonlers A, Poovorawan Y. The prevalence and genotype diversity of human rotavirus a circulating in Thailand, 2011-2014. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;37:129–136. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Saikruang W, Khamrin P, Malasao R, Kumthip K, Ushijima H, Maneekarn N. Complete genome analysis of a rare G12P[6] rotavirus isolated in Thailand in 2012 reveals a prototype strain of DS-1-like constellation. Virus Res. 2016;224:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Intamaso U, Poomipak W, Chutoam P, Chotchuang P, Sunkkham W, Srisopha S, et al. Genotype Distribution and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rotaviruses in Thailand and Emergence of Uncommon Genotypes. Arch Clin Microbiol. 2017;8(4):60. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Guntapong R, Tacharoenmuang R, Singchai P, Upachai S, Sutthiwarakom K, Komoto S, et al. Predominant prevalence of human rotaviruses with the G1P[8] and G8P[8] genotypes with a short RNA profile in 2013 and 2014 in Sukhothai and Phetchaboon provinces, Thailand. J Med Virol. 2017;89(4):615–620. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Tacharoenmuang R, Komoto S, Guntapong R, Upachai S, Singchai P, Ide T, et al. High prevalence of equine-like G3P[8] rotavirus in children and adults with acute gastroenteritis in Thailand. J Med Virol. 2020;92(2):174–186. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chan-It W, Chanta C. Emergence of G9P[8] rotaviruses in children with acute gastroenteritis in Thailand, 2015-2016. J Med Virol. 2018;90(3):477–484. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.My PV, Rabaa MA, Donato C, Cowley D, Phat VV, Dung TT, et al. Novel porcine-like human G26P[19] rotavirus identified in hospitalized paediatric diarrhoea patients in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. J Gen Virol. 2014;95(Pt 12):2727–2733. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.068403-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Huyen DTT, Hong DT, Trung NT, Hoa TTN, Oanh NK, Thang HV, et al. Epidemiology of acute diarrhea caused by rotavirus in sentinel surveillance sites of Vietnam, 2012-2015. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7894–7900. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.World Bank . GDP Per Capita. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Jain S, Vashistt J, Changotra H. Rotaviruses: is their surveillance needed? Vaccine. 2014;32(27):3367–3378. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Gentsch JR, Laird AR, Bielfelt B, Griffin DD, Banyai K, Ramachandran M, et al. Serotype diversity and reassortment between human and animal rotavirus strains: implications for rotavirus vaccine programs. J Infect Dis. 2005;192(Suppl 1):S146–S159. doi: 10.1086/431499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Leshem E, Lopman B, Glass R, Gentsch J, Bányai K, Parashar U, et al. Distribution of rotavirus strains and strain-specific effectiveness of the rotavirus vaccine after its introduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(9):847–856. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70832-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bonifacio J, Igoy MA, Tandoc A. Reassortment of human rotavirus gene segments into G9P[8] rotavirus strain over a four year period: 2013-2016. Int J Infect Dis. 2018;73:195. [Google Scholar]
- 84.WHO. Rotavirus Disease Prevention through Immunization in the Western Pacific Region, Manila, Philippines, 11–12 December 2018 : meeting report. Manila; 2018. p. 36.
- 85.Giri S, Priya HR, Arumugam R, Sherchand JB, Thu HM, Galagoda G, et al. Molecular epidemiology of rotaviruses in the south-east Asian region from 2009 to 2015. Vaccine. 2018;36(51):7851–7855. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.02.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Brandt CD, Kim HW, Rodriguez WJ, Arrobio JO, Jeffries BC, Parrott RH. Rotavirus gastroenteritis and weather. J Clin Microbiol. 1982;16(3):478–482. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.478-482.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lee WS, Rajasekaran G, Pee S, Karunakaran R, Hassan HH, Puthucheary SD. Rotavirus and other enteropathogens in childhood acute diarrhoea: a study of two centres in Malaysia. J Paediatr Child Health. 2006;42(9):509–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2006.00913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Aloun DS, Nyambat B, Phetsouvanh R, Douangboupha V, Keonakhone P, Xoumphonhphakdy B, et al. Rotavirus diarrhoea among children aged less than 5 years at Mahosot hospital, Vientiane, Lao PDR. Vaccine. 2009;27(Suppl 5):F85–F88. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.08.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Levy K, Hubbard AE, Eisenberg JN. Seasonality of rotavirus disease in the tropics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2009;38(6):1487–1496. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Chao DL, Roose A, Roh M, Kotloff KL, Proctor JL. The seasonality of diarrheal pathogens: a retrospective study of seven sites over three years. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(8):e0007211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Jagai JS, Sarkar R, Castronovo D, Kattula D, McEntee J, Ward H, et al. Seasonality of rotavirus in South Asia: a meta-analysis approach assessing associations with temperature, precipitation, and vegetation index. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ansari SA, Springthorpe VS, Sattar SA. Survival and vehicular spread of human rotaviruses: possible relation to seasonality of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13(3):448–461. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Walker CLF, Rudan I, Liu L, Nair H, Theodoratou E, Bhutta ZA, et al. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet. 2013;381(9875):1405–1416. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60222-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.WHO Rotavirus vaccines: an update. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2009;84(50):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.WHO . Rotavirus Immunization coverage. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Abou-Nader AJ, Sauer MA, Steele AD, Tate JE, Atherly D, Parashar UD, et al. Global rotavirus vaccine introductions and coverage: 2006–2016. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018;14(9):2281–2296. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1470725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.GAVI . Rotavirus Vaccine Support. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Zissis G, Lambert JP, Marbehant P, Marissens D, Lobmann M, Charlier P, et al. Protection studies in colostrum-deprived piglets of a bovine rotavirus vaccine candidate using human rotavirus strains for challenge. J Infect Dis. 1983;148(6):1061–1068. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Kapikian AZ, Hoshino Y, Chanock RM, Pérez-Schael I. Efficacy of a quadrivalent rhesus rotavirus-based human rotavirus vaccine aimed at preventing severe rotavirus diarrhea in infants and young children. J Infect Dis. 1996;174(Suppl 1):S65–S72. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.supplement_1.s65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Dennehy PH. Rotavirus vaccines: an overview. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008;21(1):198–208. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00029-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Murphy TV, Gargiullo PM, Massoudi MS, Nelson DB, Jumaan AO, Okoro CA, et al. Rotavirus intussusception investigation team. Intussusception among infants given an oral rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(8):564–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200102223440804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kollaritsch H, Kundi M, Giaquinto C, Paulke-Korinek M. Rotavirus vaccines: a story of success. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(8):735–743. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Phua KB, Lim FS, Quak SH, Lee BW, Teoh YL, Suryakiran PV, et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of a human rotavirus vaccine RIX4414 in Singaporean infants. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2016;45(2):44–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Yung CF, Chan SP, Soh S, Tan A, Thoon KC. Intussusception and Monovalent Rotavirus Vaccination in Singapore: Self-Controlled Case Series and Risk-Benefit Study. J Pediatr. 2015;167(1):163–168.e161. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Ruiz-Palacios GM, Perez-Schael I, Velazquez FR, Abate H, Breuer T, Clemens SC, et al. Safety and efficacy of an attenuated vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(1):11–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Tan N, Teoh YL, Phua KB, Quak SH, Lee BW, Teo HJ, et al. An update of paediatric intussusception incidence in Singapore: 1997-2007, 11 years of intussusception surveillance. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2009;38(8):690–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Vesikari T, Matson DO, Dennehy P, Van Damme P, Santosham M, Rodriguez Z, et al. Safety and efficacy of a pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(1):23–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.WHO. Update on intussusception following rotavirus vaccine administration: World Health Organization; 2014. Available from: http://www.who.int/vaccine_safety/committee/topics/rotavirus/rotarix_and_rotateq/dec_2013/en/.
- 109.Debellut F, Clark A, Pecenka C, Tate J, Baral R, Sanderson C, et al. Re-evaluating the potential impact and cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in 73 Gavi countries: a modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(12):e1664–e1674. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30439-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Deen J, Lopez AL, Kanungo S, Wang XY, Anh DD, Tapia M, et al. Improving rotavirus vaccine coverage: can newer-generation and locally produced vaccines help? Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018;14(2):495–499. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1403705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.World Health Organization. Rotavirus Immunization Coverage. available from: https://www.who.int/gho/immunization/rotavirus/en/. Cited March, 3, 2020.
- 112.Bhandari N, Rongsen-Chandola T, Bavdekar A, John J, Antony K, Taneja S, et al. India rotavirus vaccine group. Efficacy of a monovalent human-bovine (116E) rotavirus vaccine in Indian infants: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383(9935):2136–2143. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62630-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.International Vaccine Access Center . VIEW-hub report: global vaccine introduction and implementation. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kulkarni PS, Desai S, Tewari T, Kawade A, Goyal N, Garg BS, et al. A randomized phase III clinical trial to assess the efficacy of a bovine-human reassortant pentavalent rotavirus vaccine in Indian infants. Vaccine. 2017;35(45):6228–6237. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Isanaka S, Guindo O, Langendorf C, Matar Seck A, Plikaytis BD, Sayinzoga-Makombe N, et al. Efficacy of a low-cost, heat-stable Oral rotavirus vaccine in Niger. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(12):1121–1130. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Naik SP, Zade JK, Sabale RN, Pisal SS, Menon R, Bankar SG, et al. Stability of heat stable, live attenuated rotavirus vaccine (ROTASIIL®) Vaccine. 2017;35(22):2962–2969. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Chen B, Shen S. Selection and characterization of strain LLR-85 for oral rotavirus live vaccine. Chin J Biol. 1994;7(2):49–52. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Fu C, Dong Z, Shen J, Yang Z, Liao Y, Hu W, et al. Rotavirus gastroenteritis infection among children vaccinated and unvaccinated with rotavirus vaccine in southern China: a population-based assessment. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(4):e181382. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Zhen SS, Li Y, Wang SM, Zhang XJ, Hao ZY, Chen Y, et al. Effectiveness of the live attenuated rotavirus vaccine produced by a domestic manufacturer in China studied using a population-based case-control design. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2015;4(10):e64. doi: 10.1038/emi.2015.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Dang DA, Nguyen VT, Vu DT, Nguyen TH, Nguyen DM, Yuhuan W, et al. Rotavin-M1 Vaccine Trial Group. A dose-escalation safety and immunogenicity study of a new live attenuated human rotavirus vaccine (Rotavin-M1) in Vietnamese children. Vaccine. 2012;30(Suppl 1):A114–A121. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.07.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Bines JE, At Thobari J, Satria CD, Handley A, Watts E, Cowley D, et al. Human neonatal rotavirus vaccine (RV3-BB) to target rotavirus from birth. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(8):719–730. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Council R . Current and Upcomming Rotavirus Vaccine. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Velasquez DE, Parashar U, Jiang B. Decreased performance of live attenuated, oral rotavirus vaccines in low-income settings: causes and contributing factors. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018;17(2):145–161. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2018.1418665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Clarke E, Desselberger U. Correlates of protection against human rotavirus disease and the factors influencing protection in low-income settings. Mucosal Immunol. 2015;8(1):1–17. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kirkwood CD, Ma L-F, Carey ME, Steele AD. The rotavirus vaccine development pipeline. Vaccine. 2019;37(50):7328–7335. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.03.076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Lopman BA, Pitzer VE, Sarkar R, Gladstone B, Patel M, Glasser J, et al. Understanding reduced rotavirus vaccine efficacy in low socio-economic settings. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Steele D, Kirkwood C, Ma LF. WHO Product Development for Vaccines Advisory Committee. 2018. Next generation rotavirus vaccine. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Burke RM, Tate JE, Kirkwood CD, Steele AD, Parashar UD. Current and new rotavirus vaccines. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2019;32(5):435–444. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Blutt SE, Warfield KL, O’Neal CM, Estes MK, Conner ME. Host, viral, and vaccine factors that determine protective efficacy induced by rotavirus and virus-like particles (VLPs) Vaccine. 2006;24(8):1170–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.08.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Wang Y, Azevedo M, Saif LJ, Gentsch JR, Glass RI, Jiang B. Inactivated rotavirus vaccine induces protective immunity in gnotobiotic piglets. Vaccine. 2010;28(33):5432–5436. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Azevedo MSP, Gonzalez AM, Yuan L, et al. An oral versus intranasal prime/boost regimen using attenuated human rotavirus or VP2 and VP6 virus-like particles with immunostimulating complexes influences protection and antibody-secreting cell responses to rotavirus in a neonatal gnotobiotic pig model. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010;17(3):420–428. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00395-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Istrate C, Hinkula J, Charpilienne A, et al. Parenteral administration of RF 8-2/6/7 rotavirus-like particles in a one-dose regimen induce protective immunity in mice. Vaccine. 2008;26(35):4594–4601. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.05.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Fix AD, Harro C, McNeal M, Dally L, Flores J, Robertson G, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a parenterally administered rotavirus VP8 subunit vaccine in healthy adults. Vaccine. 2015;33(31):3766–3772. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Groome MJ, Koen A, Fix A, Page N, Jose L, Madhi SA, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a parenteral P2-VP8-P[8] subunit rotavirus vaccine in toddlers and infants in South Africa: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17(8):843–853. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30242-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Kim SY, Goldie SJ, Salomon JA. Cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in Vietnam. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Suwantika AA, Tu HA, Postma MJ. Cost-effectiveness of rotavirus immunization in Indonesia: taking breastfeeding patterns into account. Vaccine. 2013;31(32):3300–3307. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Gosselin V, Généreux M, Gagneur A, Petit G. Effectiveness of rotavirus vaccine in preventing severe gastroenteritis in young children according to socioeconomic status. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016;12(10):2572–2579. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1189038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Burnett E, Parashar U, Tate J. Rotavirus vaccines: effectiveness, safety, and future directions. Paediatr Drugs. 2018;20(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/s40272-018-0283-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Desselberger Ulrich. Differences of Rotavirus Vaccine Effectiveness by Country: Likely Causes and Contributing Factors. Pathogens. 2017;6(4):65. doi: 10.3390/pathogens6040065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Parker EP, Ramani S, Lopman BA, Church JA, Iturriza-Gómara M, Prendergast AJ, et al. Causes of impaired oral vaccine efficacy in developing countries. Future Microbiol. 2018;13:97–118. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2017-0128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Munos MK, Walker CL, Black RE. The effect of rotavirus vaccine on diarrhoea mortality. Int J Epidemiol. 2010;39(Suppl 1):i56–i62. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyq022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Patel MM, Steele D, Gentsch JR, Wecker J, Glass RI, Parashar UD. Real-world impact of rotavirus vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30(1 Suppl):S1–S5. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181fefa1f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Premkumar PS, Parashar UD, Gastanaduy PA, McCracken JP, de Oliveira LH, Payne DC, et al. Reduced rotavirus vaccine effectiveness among children born during the rotavirus season: a pooled analysis of 5 case-control studies from the Americas. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60(7):1075–1078. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Tharmaphornpilas P, Jiamsiri S, Boonchaiya S, Rochanathimoke O, Thinyounyong W, Tuntiwitayapun S, et al. Evaluating the first introduction of rotavirus vaccine in Thailand: moving from evidence to policy. Vaccine. 2017;35(5):796–801. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.12.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Lopman BA, Curns AT, Yen C, Parashar UD. Infant rotavirus vaccination may provide indirect protection to older children and adults in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2011;204(7):980–986. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Pollard SL, Malpica-Llanos T, Friberg IK, Fischer-Walker C, Ashraf S, Walker N. Estimating the herd immunity effect of rotavirus vaccine. Vaccine. 2015;33(32):3795–3800. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.06.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Loganathan T, Lee WS, Lee KF, Jit M, Ng CW. Household catastrophic healthcare expenditure and impoverishment due to rotavirus gastroenteritis requiring hospitalization in Malaysia. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Padmawati RS, Heywood A, Sitaresmi MN, Atthobari J, Maclntyre CR, Soenarto Y, et al. Religious and community leaders' acceptance of rotavirus vaccine introduction in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6706-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Arumugam T. Rotavirus: Govt urged to protect kids with vaccine. In: New Straits Times. Malaysia; 2017. Available from: https://www.nst.com.my/news/2017/02/211628/rotavirus-govt-urged-protect-kids-vaccine. Cited October 10, 2019.
- 150.GAVI . GAVI Country Hub: Myanmar. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 151.PATH, Rotavirus Disease and Vaccines in Asia. 2014; available from: https://www.path.org/resources/rotavirus-disease-and-vaccines-in-asia/. Cited November 1, 2019.
- 152.Lopez AL, Daag JV, Esparagoza J, Bonifacio J, Fox K, Nyambat B, et al. Effectiveness of monovalent rotavirus vaccine in the Philippines. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32595-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Tu HA, Rozenbaum MH, Coyte PC, Li SC, Woerdenbag HJ, Postma MJ. Health economics of rotavirus immunization in Vietnam: potentials for favorable cost-effectiveness in developing countries. Vaccine. 2012;30(8):1521–1528. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Ngcobo NJ, Cameron NA. The decision making process on new vaccines introduction in South Africa. Vaccine. 2012;30(Suppl 3):C9–13. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.04.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Carvalho N, Jit M, Cox S, Yoong J, Hutubessy RCW. Capturing budget impact considerations within economic evaluations: a systematic review of economic evaluations of rotavirus vaccine in low- and middle-income countries and a proposed assessment framework. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018;36(1):79–90. doi: 10.1007/s40273-017-0569-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Kim SY, Sweet S, Slichter D, Goldie SJ. Health and economic impact of rotavirus vaccination in GAVI-eligible countries. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:253. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Portnoy A, Ozawa S, Grewal S, Norman BA, Rajgopal J, Gorham KM, et al. Costs of vaccine programs across 94 low- and middle-income countries. Vaccine. 2015;33(Suppl 1):A99–108. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.12.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Council R . Rotavirus: common, severe, devastating, preventable. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 159.Rheingans RD, Antil L, Dreibelbis R, Podewils LJ, Bresee JS, Parashar UD. Economic costs of rotavirus gastroenteritis and cost-effectiveness of vaccination in developing countries. J Infect Dis. 2009;200(Suppl 1):S16–S27. doi: 10.1086/605026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.WHO. Guidelines for estimating costs of introducing new vaccines into the national immunization system. Geneva; 2002. Available from: https://archives.who.int/vaccines-documents/DocsPDF02/www665.pdf. Accessed 3 Nov 2019.
- 161.Saokaew S, Prasitsuebsai W, Bibera GL, Kengkla K, Zhang XH, Oh KB, et al. Economic evaluation of human rotavirus vaccine in Thailand. Infect Dis Ther. 2019;8(3):397–415. doi: 10.1007/s40121-019-0246-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.