Abstract
High-resolution ultrasonography (US) is a valuable tool in breast imaging. Nevertheless, US is an operator-dependent technique: to overcome this issue, the American College of Radiology (ACR) has developed the breast imaging-reporting and data system (BI-RADS) US lexicon. Despite this effort, the variability in the assessment of focal breast lesions (FBLs) with the use of BI-RADS US lexicon is still an issue. Within this framework, evidence shows that computer-aided image analysis may be effective in improving the radiologist’s assessment of FBLs. In particular, S-Detect is a newly developed image-analytic computer program that provides assistance in morphologic analysis of FBLs seen on US according to the BI-RADS US lexicon. This pictorial essay describes state-of-the-art of sonographic characterization of FBLs by using S-Detect.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms, Ultrasonography, BI-RADS, Problem-solving, Decision-making, Computer-assisted diagnosis
Introduction
High-resolution ultrasonography (US) is a valuable tool in breast imaging, and it is currently considered a useful adjunct to mammography and magnetic resonance (MR) [1, 2].
Nevertheless, US is operator dependent and the American College of Radiology (ACR) developed the breast imaging-reporting and data system (BI-RADS) US lexicon, firstly released in 2003, aiming to standardize image interpretation, reporting and teaching breast imaging [3].
Spiculated margin, irregular shape, and nonparallel orientation are sonographic BI-RADS descriptors highly predictive for malignancy, whereas circumscribed margin, parallel orientation, and oval shape are highly predictive of benign FBLs [4].
Despite this effort, the variability in the assessment of focal breast lesions (FBLs) with the use of BI-RADS US lexicon is still an issue, in particular for some of the descriptors, such as margin and echo pattern of the lesion [5].
Within this framework, evidence shows that computer-aided image analysis may be effective in improving the radiologist’s assessment of FBLs [6]. Shen WC et al. have demonstrated the feasibility of computer-aided classification system for breast US, showing statistically significant improvement of accuracy and specificity (5.91% and 8.85%, respectively) in comparison with radiologists [7]. In particular, S-Detect is a newly developed image-analytic computer program that provides assistance in morphologic analysis of FBLs seen on US according to the BI-RADS US lexicon [8]. Some preliminary studies have showed that the use of S-Detect can lead to an increase in the number of correctly characterized breast masses, especially for less experienced radiologist [9, 10]. In 2013 BI-RADS US lexicon underwent revision and S-Detect software was improved accordingly [11].
This pictorial essay describes state-of-the-art of sonographic characterization of FBLs by using S-Detect.
Materials and methods
Ultrasonography
All cases presented in this article were assessed with an ultrasound unit provided with a 3–12 MHz linear multi-frequency transducer (RS80A with Prestige, Samsung Medison, Co. Ltd.). We retrospectively evaluated 570 US examinations of breast performed between 2017 and 2018 and selected ten patients with additional S-Detect assessment to show the spectrum of advantages provided by this technique in the categorization of FBLs.
Computer-guided decision-making support software
S-Detect™ is a built-in, commercially available dedicated software installed and running on the ultrasound system RS80A. The software is licensed for clinical use: by placing an operator-defined marker within a FBL, it draws the contour of the lesion, analyses it according to the BI-RADS US descriptors and provides a categorization into possibly benign or possibly malignant. The sonographer can either accept the indications as provided by the software or choose and record the most appropriate term for each descriptor as deemed necessary, including the final categorization [8].
Features used for US feature analysis in S-Detect are as follows: shape differences, echo and texture features using spatial grey-level dependence matrices, intensity in the mass area, gradient magnitude in the mass area, orientation, depth-width ratio, distance between mass shape and best t ellipse, average gray changes or histogram changes between tissue/mass area, comparison of grey value of left, posterior, and right under the lesion, the number of lobulated areas/protuberances/depressions, lobulation index, and elliptic-normalized circumference [12].
Results
S-Detect aided US BI-RADS classification of FBLs
Category 0: incomplete—need additional imaging evaluation
Category 0 is assigned to an incomplete examination, usually for the need for additional imaging evaluation and/or prior images for comparison.
Category 1: negative
Category 1 is assigned to a negative, normal examination. Essentially 0% likelihood of malignancy.
Category 2: benign
Category 2 is assigned to any lesion lacking US signs of malignancy. As category BI-RADS 1, there is essentially 0% likelihood of malignancy. The implication for management is to perform routine screening.
Simple cysts (Fig. 1);
Intramammary lymphnodes;
Postsurgical fluid collections;
Breast implants;
Complicated cysts/probable fibroadenomas that are unchanged for at least 2 or 3 years.
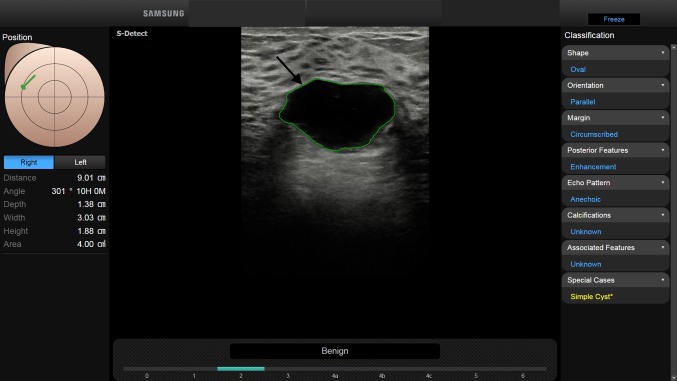
Fig. 1.
BI-RADS 2. In a 28-year-old-woman, with palpable right breast lump, B-mode US depicts a 3 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was classified as oval-shaped, with parallel orientation and circumscribed margins (arrow). The echo pattern was judged anechoic, with enhancement as posterior feature. Final diagnosis: simple cyst
Category 3: probably benign (98%)
Category 3 is assigned to any lesion or specific imaging findings known to have > 0% but ≤ 2% likelihood of malignancy. For US, there is robust evidence that a solid mass with a circumscribed margin, oval shape, and parallel orientation (most commonly fibroadenoma), and an isolated complicated cyst have a likelihood of malignancy in the defined (≤ 2%) probably benign range (Figs. 2, 3) [3]. Similar data have been reported for clustered microcysts, but these data are less strong because they involve many fewer cases (Fig. 4). The recommended management for these lesions is short-interval (6-month) follow-up sonography and then periodic sonographic surveillance.
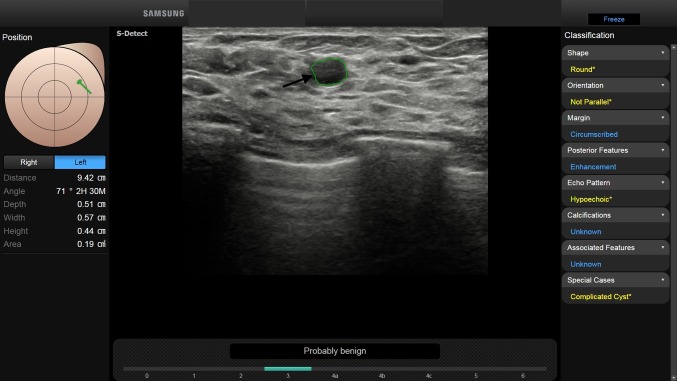
Fig. 2.
BI-RADS 3. In a 35-year-old-woman, B-mode US shows a 6 mm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was assessed as round-shaped, with not parallel orientation and circumscribed margins (arrow). The echo pattern was assessed as hypoechoic, with enhancement as posterior feature. Final diagnosis: complicated cyst
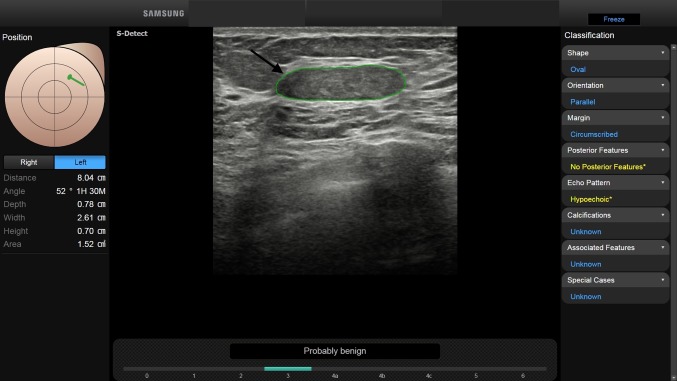
Fig. 3.
BI-RADS 3. In a 32-year-old-woman, with palpable right breast lump, B-mode US depicted a 2.6 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was classified as oval-shaped, with parallel orientation and circumscribed margins (arrow). The echo pattern was assessed as hypoechoic, with no posterior features. Final diagnosis: fibroadenoma
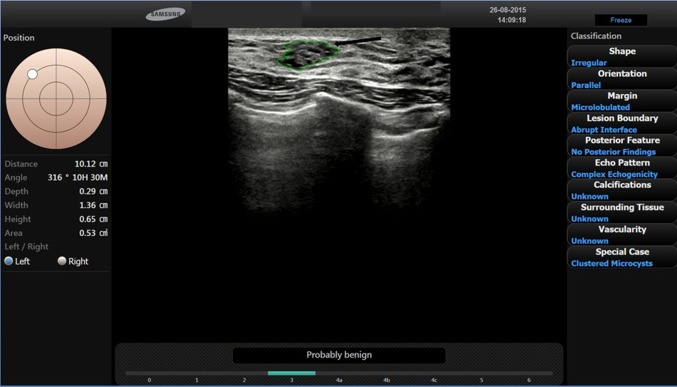
Fig. 4.
BI-RADS 3. In a 38-year-old-woman, B-mode US showed a 1.3 cm FBL in her left breast. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was classified as irregular-shaped, with parallel orientation and microlobulated margins. The echo pattern was assessed as complex echogenicity, with no posterior features. Final diagnosis: clustered microcysts
Category 4: suspicious
This category is reserved for findings that do not have the classic appearance of malignancy but are sufficiently suspicious to justify a recommendation for biopsy. The ceiling for category 3 assessment is a 2% likelihood of malignancy, and the floor for category 5 assessment is 95%, so category 4 assessments cover the wide range of likelihood of malignancy in between [3].
Category 4 may be further subdivided into:
4A (low suspicion for malignancy: > 2 to ≤ 10% likelihood of malignancy) (Figs. 5, 6),
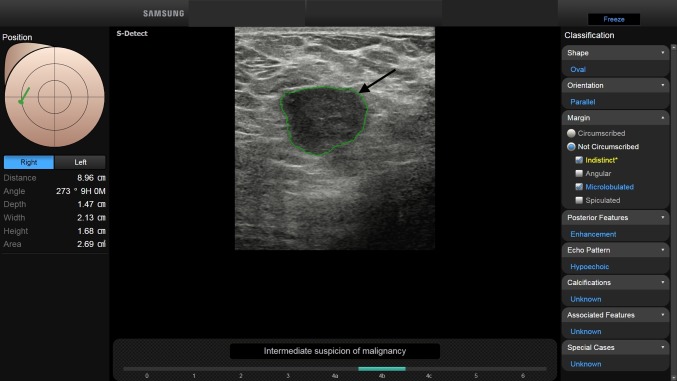
4B (moderate suspicion for malignancy: > 10 to ≤ 50% likelihood of malignancy) (Fig. 7);
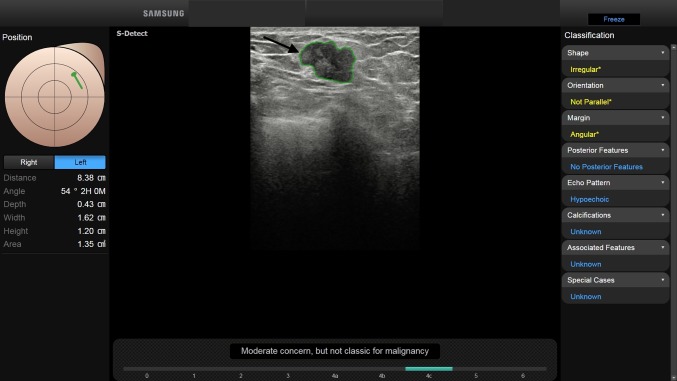
4C (high suspicion for malignancy: > 50 to < 95% likelihood of malignancy) (Fig. 8).
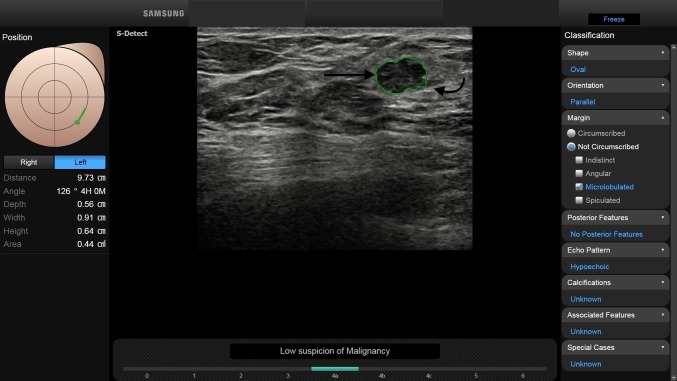
Fig. 5.
BI-RADS 4a. In a 40-year-old-woman, with a history of multiple bilateral fibroadenomas and a new palpable left breast lump, B-mode US showed a 9 mm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was evaluated as an oval-shaped hypoechoic mass with parallel orientation (arrow). Margins were partially circumscribed (< 75%) and partially microlobulated (curved arrow). Core-needle biopsy proved the mass to be a fibroadenoma
Fig. 6.
BI-RADS 4a. In a 47-year-old-woman, with a palpable left breast lump, B-mode US showed a 3.4 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was described as an oval-shaped hypoechoic mass with parallel orientation and enhancement as posterior feature (arrow). Margins were partially circumscribed (< 75%) and partially indistinct. Core-needle biopsy proved the mass to be a mucinous carcinoma
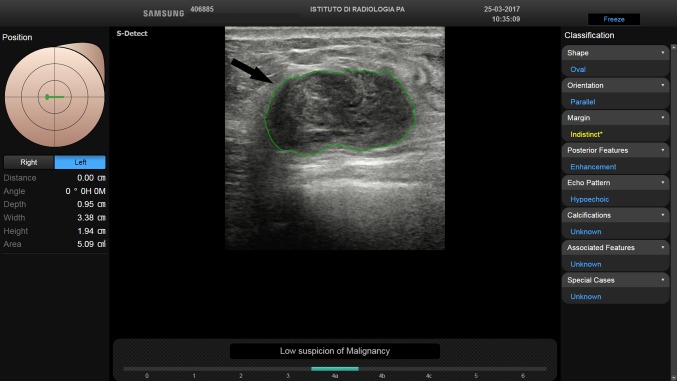
Fig. 7.
BI-RADS 4b. In a 43-year-old-woman, with a palpable left breast lump, B-mode US depicted a 2 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was assessed as an oval-shaped hypoechoic mass with parallel orientation and enhancement as posterior feature (arrow). Margins were not circumscribed, indistinct and microlobulated. Core-needle biopsy proved the mass to be a medullary breast carcinoma
Fig. 8.
BI-RADS 4c. In a 50-year-old-woman, with a palpable left breast lump, B-mode US depicted a 1.6 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was judged as an irregular-shaped hypoechoic mass with angular margins, not parallel orientation and no posterior features (arrow). Core-needle biopsy proved the mass to be an invasive ductal breast carcinoma
Category 5: highly suggestive of malignancy
At US, a solid mass with irregular shape, spiculated margins, not parallel orientation presents a very high probability (≥ 95%) of malignancy (Figs. 9, 10).
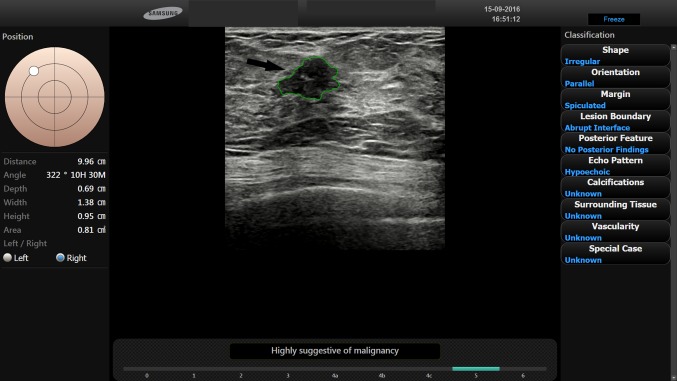
Fig. 9.
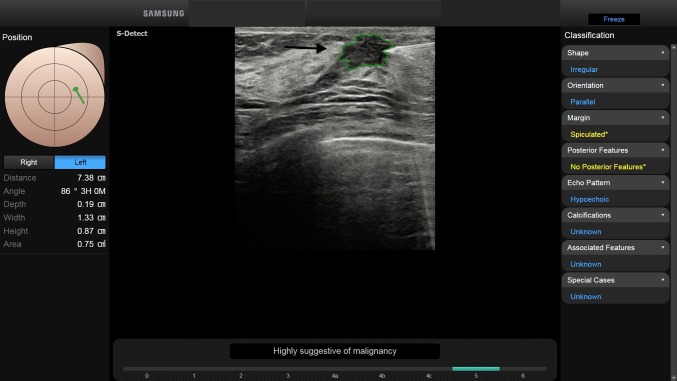
BI-RADS 5. In a 41-year-old-woman, with a palpable left breast lump, B-mode US showed a 1.3 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was classified as an irregular-shaped hypoechoic mass with spiculated margins, not parallel orientation and no posterior features (arrow). Core-needle biopsy proved the mass to be an invasive ductal breast carcinoma.
Fig. 10.
BI-RADS 5. In a 55-year-old-woman, with a palpable left breast lump, B-mode US depicted a 1.4 cm FBL. According to BI-RADS lexicon, with S-Detect (green line contour) this FBL was judged as an irregular-shaped hypoechoic mass with spiculated margins, parallel orientation and no posterior features (arrow). Core-needle biopsy proved the mass to be an invasive ductal breast carcinoma
As for category 4, the recommended management for category 5 is tissue sampling.
Category 6: known biopsy-proven malignancy
This category is reserved for examinations performed after biopsy proof of malignancy and the implication for management is surgical excision when clinically appropriate.
Discussion
Breast ultrasound (US) is a widespread imaging tool, often used as an adjunct to mammography with the aim to characterize FBLs, thus improving cancer detection rates and reducing the number of false negatives for breast cancer diagnosis [1, 13–15]. However, breast US requires extensive experience, considering that it is an operator-dependent procedure and presents lower reproducibility, specificity and positive predictive value than mammography [16]. The introduction of a categorization system based on sonographic criteria, such as the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), has proved useful for describing and classifying both benign and malignant breast lesions [3]. However, the limited reproducibility of the system in determining the exact likelihood of malignancy of suspicious breast lesions (category 4), with variability ranging from 3 to 94%, leaves unchanged the need for more invasive and expensive diagnostic procedures, such as biopsy [2].
As an attempt to overcome these drawbacks at least in part, image analysis systems such as S-Detect may represent an useful adjunct tool either for physicians or sonographers. Previous studies have shown that the use of S-Detect can lead to a change in the final BI-RADS classification with a significant rate of correct re-classification either in experienced or less experienced breast radiologists [8, 9, 17]. Considering that BI-RADS classification directly influences the management plan it is crucial to achieve a precise and robust assessment. To this latter purpose, an improvement in both interobserver and intra-observer agreement with the use of S-Detect has been reported [18].
Conclusion
In conclusion, S-Detect can be used as an effective computer-aided decision-making tool for characterization of FBLs according to BI-RADS US lexicon, in order to improve the diagnostic performance of ultrasound and better orientate patient management.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by research equipment from SAMSUNG MEDISON Co., Ltd.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
Tommaso Vincenzo Bartolotta is lecturer and scientific advisor for Samsung. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was granted for the use of all data in this study. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Hooley RJ, Scoutt LM, Philpotts LE. Breast ultrasonography: state of the art. Radiology. 2013;268(3):642–659. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13121606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bartolotta TV, Ienzi R, Cirino A, Genova C, Ienzi F, Pitarresi D, Safina E, Midiri M. Characterisation of indeterminate focal breast lesions on grey-scale ultrasound: role of ultrasound elastography. Radiol Med. 2011;116(7):1027–1038. doi: 10.1007/s11547-011-0648-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mendelson EB, Böhm-Vélez M, Berg WA, et al. ACR BI-RADS® atlas, breast imaging reporting and data system. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2013. ACR BI-RADS® urltrasound. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hong AS, Rosen EL, Soo MS, Baker JA. BI-RADS for sonography: positive and negative predictive values of sonographic features. Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(4):1260–1265. doi: 10.2214/ajr.184.4.01841260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Raza S, Goldkamp AL, Chikarmane SA, Birdwell RL. US of breast masses categorized as BI-RADS 3, 4, and 5: pictorial review of factors influencing clinical management. Radiographics. 2010;30(5):1199–1213. doi: 10.1148/rg.305095144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jalalian A, Mashohor SB, Mahmud HR, Saripan MI, Ramli AR, Karasfi B. Computer-aided detection/diagnosis of breast cancer in mammography and ultrasound: a review. Clin Imaging. 2013;37(3):420–426. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2012.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shen WC, Chang RF, Moon WK. Computer aided classification system for breast ultrasound based on Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007;233(11):1688–1698. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim K, Song MK, Kim EK, Yoon JH. Clinical application of S-Detect to breast masses on ultrasonography: a study evaluating the diagnostic performance and agreement with a dedicated breast radiologist. Ultrasonography. 2017;36(1):3–9. doi: 10.14366/usg.16012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bartolotta TV, Orlando A, Cantisani V, Matranga D, Ienzi R, Cirino A, Amato F, Di Vittorio ML, Midiri M, Lagalla R. Focal breast lesion characterization according to the BI-RADS US lexicon: role of a computer-aided decision-making support. Radiol Med. 2018;123(7):498–506. doi: 10.1007/s11547-018-0874-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Di Segni M, De Soccio V, Cantisani V, Bonito G, Rubini A, Di Segni G, Lamorte S, Magri V, De Vito C, Migliara G, Bartolotta TV, Metere A, Giacomelli L, De Felice C, D'Ambrosio F. Automated classification of focal breast lesions according to S-Detect: validation and role as a clinical and teaching tool. J Ultrasound. 2018;21(2):105–118. doi: 10.1007/s40477-018-0297-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mercado CL. BI-RADS update. Radiol Clin N Am. 2014;52(3):481–487. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2014.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee JH, Seong YK, Chang CH, Ko EY, Cho BH, Ku J et al (2013) Computer- aided lesion diagnosis in B-mode ultrasound by border irregularity and multiple sonographic features. In: Proc. SPIE 8670, Medical Imaging 2013: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 86701, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 28 Feb 2013
- 13.Catalano O, Varelli C, Sbordone C, et al. A bump: what to do next? Ultrasound imaging of superficial soft-tissue palpable lesions. J Ultrasound. 2019 doi: 10.1007/s40477-019-00415-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carlino G, Rinaldi P, Giuliani M, et al. Ultrasound-guided preoperative localization of breast lesions: a good choice. J Ultrasound. 2019;22:85–94. doi: 10.1007/s40477-018-0335-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Alikhassi A, Azizi F, Ensani F. Imaging features of granulomatous mastitis in 36 patients with new sonographic signs. J Ultrasound. 2020;23:61–68. doi: 10.1007/s40477-019-00392-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abdullah N, Mesurolle B, El-Khoury M, Kao E. Breast imaging reporting and data system lexicon for US: interobserver agreement for assessment of breast masses. Radiology. 2009;252(3):665–672. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2523080670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Park HJ, Kim SM, La Yun B, Jang M, Kim B, Jang JY, Lee JY, Lee SH. A computer-aided diagnosis system using artificial intelligence for the diagnosis and characterization of breast masses on ultrasound: added value for the inexperienced breast radiologist. Medicine. 2019;98(3):e14146. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee YJ, Choi SY, Kim KS, Yang PS. Variability in observer performance between faculty members and residents using Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-ultrasound. Iran J Radiol. 2016;13(3):e28281. doi: 10.5812/iranjradiol.28281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]