Abstract
CRISPR-Cas9 has proven as a very powerful gene editing tool for Actinomyces, allowing scarless and precise genome editing in selected strains of these biotechnologically relevant microorganisms. However, its general application in actinomycetes has been limited due to its inefficacy when applying the system in an untested strain. Here, we provide evidence of how Cas9 levels are toxic for the model actinomycetes Streptomyces coelicolor M145 and Streptomyces lividans TK24, which show delayed or absence of growth. We overcame this toxicity by lowering Cas9 levels and have generated a set of plasmids in which Cas9 expression is either controlled by theophylline-inducible or constitutive promoters. We validated the targeting of these CRISPR-Cas9 system using the glycerol uptake operon and the actinorhodin biosynthesis gene cluster. Our results highlight the importance of adjusting Cas9 expression levels specifically in strains to gain optimum and efficient gene editing in Actinomyces.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s10295-020-02277-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Streptomyces, CRISPR-Cas9, Theophylline riboswitch, Genome editing, Glycerol
Introduction
Since its first biotechnological application, CRISPR-Cas-based technology has marked a turning point in synthetic biology [1, 2]. Thus, the diversity in applications and the range of organisms genetically modified using CRISPR-Cas9 system have increased exponentially during the past few years ([3, 4] for detailed reviews). However, this breakthrough technology is still in its infancy, especially in actinobacteria, with numerous proof-of-concept studies supporting its wide applicability but hindering its routine use, where it is often unsuccessful.
Actinobacteria, with Streptomyces as its major representative, are G-C rich Gram-positive bacteria renowned for their natural ability to produce a plethora of pharmacologically active and industrially relevant natural products. In fact, they are known to produce over two-thirds of all known secondary metabolites [5]. To combat antimicrobial resistance it is pertinent to elucidate novel bioactive compounds. The current search for new natural products is focused on the awakening of sleeping biosynthesis gene clusters that are found through genome sequences of many microbes [6]. To awaken these potential biosynthesis gene clusters, it will be much faster and efficient to be able to genetically engineer the genome. However, genetic engineering of these bacteria remains challenging. CRISPR-Cas9 has emerged as a very promising alternative [7]. The endonuclease Cas9, guided by a customer-designed short RNA guide transcript, generates a double strand break (DSB) in a specific point of the DNA target. This, combined with homology-directed repair (HDR) system in Streptomyces, allows rapid, precise and efficient scarless genetic edition [4].
The four most widely used CRISPR-Cas9 toolkits to perform in vivo genome editing in Streptomyces are pCRISPomyces-2 [8], pKCcas9dO [9], pCRISPR-Cas9 [10] and pWHU2653 [11] (for a detailed and critical review of these toolkits features and their successful application to a wide range of actinomycetes, see Alberti and Corre [12]). However, these and other authors reported a series of crucial drawbacks in its application in Streptomyces, ranging from the absolute absence of exconjugants [13] to the opposite situation with zero genome-edited colonies among all exconjugants obtained [14]. There are several factors that might affect CRISPR-Cas9 system efficacy, for some of which specific solutions have been adopted. (1) The pSG5 origin of replication, present in most of CRISPR-Cas9 bearing plasmids, can promote integration of the plasmid into the chromosome when repeated regions are targeted. This problem can be solved by using the defective pIJ101 origin of replication instead [15]. (2) The guide RNA selection plays an important role in the outcome of the recombination event, as different guide RNAs targeting the same gene can lead to differences in Cas9 cleaving efficiency [10]. This issue can be addressed by testing several protospacers for each target [9]. (3) The DSBs caused by Cas9 can lead to genome instability, a problem that has recently been addressed by using a nickase version of Cas9 fused to a cytidine or adenosine deaminase-based editor [16]. (4) Cas9 expression may be toxic for the bacteria, as previously suggested by other authors [8, 16, 17]. Recently, a multi-layer control of Cas9 activity coupled with ATP-synthase over expression has been successfully adopted by Wang and colleagues, to increase transformation efficiency in S. coelicolor, showing different levels of genome editing efficiency depending on the condition [17]. In their study, Cas9 levels are controlled at transcription, translation and protein level, by using thiostrepton, theophylline and blue light as respective inductors. Only by addition of the three inducers, the authors were able to achieve values higher than 10% editing efficiency.
In this work, we investigated the effect of Cas9 expression on cell viability in the model actinomycete S. coelicolor M145 and the related S. lividans TK24, confirming Wang and colleagues’ previous observations. Unlike them, we performed a set of experiments that clearly and rapidly showed the range of tolerance to Cas9 levels for each strain, in regard to both survival and Cas9 activity. We also produced a new plasmid toolkit to perform CRISPR-Cas9 mediated recombination in which Cas9 expression is either tightly translationally regulated by theophylline or controlled by a relatively weak promoter for both strains. The advantages of using each of the proposed systems are further discussed. All experiments conducted showed clear differences between the level of inductor required by each strain, emphasizing the importance of adjusting Cas9 levels to each strain to achieve the optimum balance between survival and editing efficiency. We believe that this study highlights the importance of pre-exploring the tolerance to Cas9 expression when this technology is intended to be applied in a new specie and provides with tools that can be accordingly adapted for genome editing the targeted strain.
Methods
Bacterial strains and culture conditions.
Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), M145 [18] and Streptomyces lividans TK24 [19] were used as source of DNA and for conjugation experiments. Streptomyces strains were grown on solid soy flour mannitol (SFM) [18], liquid tryptic soy broth (TSB) (Oxoid) and MYG medium [8] for conjugation efficiency and CRISPR-Cas9 induction experiments; and on solid minimal medium (SMM) [18] prepared with glucose or glycerol as sole carbon source for the screening of positive recombinants targeting the glycerol uptake operon. A 40-mM stock of theophylline-anhydrous (Sigma Aldrich) was prepared in distilled water and, after filter-sterilisation, added to the media at concentrations between 0.5–12 mM. E. coli DH5α (NEB) was used for routine cloning, and E. coli ET12567[pUZ8002] [19, 20] was used as donor in the intergeneric conjugation from E. coli to Streptomyces. E. coli strains were grown in Luria–Bertani (LB) broth (Formedium). All bacterial strains used in this work are listed in Table 1. When required antibiotics were added to the media as follows: apramycin (50 μg ml−1), chloramphenicol (25 μg ml−1), kanamycin (50 μg ml−1) and nalidixic acid (25 μg ml−1) for all media condition and for Streptomyces and E. coli.
Table 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Genotype/characteristics | Use | Reference(s) or source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strains | |||
| Escherichia coli DH5α | fhuA2 Δ(argF-lacZ)U169 phoA glnV44 ϕ80Δ(lacZ)M15 gyrA96 recA1 relA1 endA1 thi-1 hsdR17 | Cloning | NEB |
| Escherichia coli ET12567[pUZ8002] | dam13::Tn9 dcm6 hsdM hsdR recF143 zjj201::Tn10 galK2 galT22 ara14 lacY1 xyl5 leuB6 thi1 tonA31 rpsL136 hisG4 tsx78 mtli glnV44 F − , carries plasmid pUZ8002 | Intergenic conjugation | [18, 19] |
| Streptomyces coelicolor M145 | Wild type | [17] | |
| Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) | Wild type | [17] | |
| Streptomyces lividans TK24 | Wild type | [17] | |
| Plasmids | |||
| pCRISPomyces-2 | oriT, rpsLp (XC)-cas9 | [8] | |
| pSET152 | oriT-traJ | Source of oriT-traJ | [24] |
| pCRISPomyces-ptc | oriT, ermEp1-TheoR-cas9 | Source of TheoR | A. Rodríguez-García (unpublished) |
| pCM4.4 | oriT-traJ, ermE*p-cas9 | This work | |
| pCM4.4-Act-KO | oriT-traJ, ermE*p-cas9, spacer sequence, DNA repair template | CRISPR-Cas9-mediated deletion of actinorhodin positive transcriptional regulator | This work |
| pCM2.1 | oriT-traJ, rpsLp (XC)-cas9 | Test effect of traJ lack | This work |
| pCMU | oriT-traJ, rpsLp(XC)-TheoR-cas9 | Test effect of Cas9 levels | This work |
| pCMU-4 | oriT-traJ, D4-TheoR-cas9 | Test effect of Cas9 levels | This work |
| pCMUtuf | pCMU, tufprot | Control of Cas9 activity | This work |
| pCMU-4tuf | pCMU-4, tufprot | Control of Cas9 activity | This work |
| pCM(-cas9) | pCMU-4, Δcas9 | Control of Cas9 expression | This work |
| pCMU-4dGly | pCMU-4, glyprot, DNA repair template | CRISPR-Cas9-mediated interruption of glycerol uptake operon | This work |
DNA manipulation and vectors
DNA manipulations were performed according to standard procedures for E. coli [21] and Streptomyces [18]. Fragment amplifications for plasmid construction were carried out with PrimeSTAR Max DNA polymerase (Takara) whilst amplifications from spores were performed with Terra polymerase (Takara). Constructs were assembled by Gibson Isothermal Assembly with NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix (New England Biolabs, NEB), following the manufacturer’s instructions. When plasmid DNA was used as template for fragment amplification, a DpnI restriction digest was performed after PCR in order to remove all methylated (template) DNA. When indicated, unique nucleotide sequences (UNS) were added as overlapping regions to increase the efficiency of the Gibson assembly [22]. The correct assembly was assessed by restriction digest and Sanger sequencing (Eurofins Genomics). The gBlocks fragments were ordered from Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT).
Plasmid construction
pCM2.1 is a derivative of pCRISPomyces-2 [8] in which traJ was cloned between oriT and rpsLp (XC). It was constructed by 2-fragment Gibson assembly: a 6,665-bp fragment containing gapdhp-lacZ-gRNA-tracr-ColE1ori-aac3(IV)-pSG5rep-oriT-traJ and a 4,476-bp fragment containing rpsLp(XC)-cas9. The former was amplified from pCM4.4 (this manuscript) using primers oriT rev Gibson and pCM fw Gibson; whilst the latter was amplified from pCRISPomyces-2 with primers rpsLp fw Gibson and Cas9 rev Gibson.
pCMU is a derivative of pCM2.1 in which the theophylline riboswitch (TheoR) was cloned between rpsLp(XC) and the ribosome binding site (RBS) of cas9. It was constructed by 2-fragment Gibson assembly: a 6,939-bp fragment containing gapdhp-lacZ-gRNA-tracr-ColE1ori-aac3(IV)-pSG5rep-oriT-traJ-rpsLp(XC) and a 4,535-bp fragment containing TheoR-cas9. The former was amplified from pCM2.1 using primers rpsLp rev Gibson and pCM fw Gibson; whilst the latter was amplified from pCRISPomyces-ptc (A. Rodríguez-García, unpublished) with primers Cas9 fw Gibson and Cas9 rev Gibson.
pCMU-4 is a derivative of pCMU in which the rpsLp(XC) was replaced by D4 promoter [23]. For that purpose, D4 sequence was inserted de novo as an overlapping region by including its sequence to the corresponding primers. It was constructed by 2-fragment Gibson assembly: a 6686-bp fragment containing gapdhp-lacZ-gRNA-tracr-ColE1ori-aac3(IV)-pSG5rep-oriT-traJ-D4 and a 4280-bp fragment containing D4-TheoR-cas9. Both fragments were amplified from pCMU, the former using primers pCM fw Gibson and pCMU-4 Gibson rev, whilst the latter used primers pCMU-4 Gibson fw and Cas9 rev Gibson.
pCMUtuf and pCMU-4tuf were used as controls of Cas9 activity. CRISPy-web [24] was used to obtain a list of protospacers within tuf1 coding sequence, and 2 protospacers cutting at both ends of the gene were selected. For that purpose, a synthetic dsDNA gBlocks containing 2 protospacers targeting S. coelicolor tuf1 (SCO4662) was designed with the configuration of (BbsaI site-protospacer1-tracRNA-T7terminator-gapdhp-protospacer2-BbsaI site) (Table S1) and sourced to IDT. The tuf1prot synthetic DNA was cloned into pCMU and pCMU-4tuf by a BbsI-mediated Golden Gate assembly to give rise to pCMUtuf and pCMU-4tuf, respectively. Correct insertion was verified by Sanger sequencing with primer Fragment seq rev.
pCM(-cas9) is a derivative of pCMU-4 in which the cas9 coding region has been removed. For that purpose, the 6,686-bp fragment used to construct pCMU-4 was 5′-phosphorylated with T4 PNK (NEB) and subsequently re-ligated with T4 DNA ligase (NEB).
pCMU-4dGly is a derivative of pCMU-4 designed to disrupt the glycerol uptake operon by CRISPR-Cas9. Both protospacer and homology arms were assembled in one step via 5-fragment Gibson assembly. To facilitate the efficiency of the reaction, UNS sequences were added to every overlapping region except the one with the protospacer. Thus, a 2,305-bp comprising protospacer-gRNA-tracr-aac3(IV)-UNS1 was amplified with primers dgly GA Prot1 fw and dgly GA UNS1 rev. A 1,312-bp fragment containing UNS1-5′ homologous arm-UNS3 was amplified with primers dgly F1 UNS1 fw and dgly F1 UNS3 rev, whereas UNS3-3′ homologous arm-UNS9 was amplified as a 1,222-bp fragment with primers dgly F2.1 UNS3 fw and dgly F2 UNS9 rev. A 2,501-bp fragment comprising UNS9-pSG5rep-UNS2 was amplified with primers dgly GA UNS9 fw and dgly GA UNS2 rev. Finally, a 5442-bp fragment containing UNS2-oriT-traJ-D4-TheoR-cas9-gapdhp-protospacer was amplified with primers dgly GA UNS2 fw and dgly GA Prot1 rev. All fragments were amplified from pCMU-4, with the exception of the ones corresponding to the homology arms, for which S. coelicolor M145 genomic DNA was used as template.
pCM4.4 is a derivative of pCRISPomyces-2 in which Cas9 promoter rpsLp(XC) was replaced with ermE* promoter and a new RBS sequence, and full traJ sequence was cloned between oriT and ermE*. First, a 461-bp dsDNA synthesized gBlocks fragment containing ter-ermE*p-RBS, and a section of cas9 gene was cloned into a 10,453-bp fragment created by digestion of pCRISPomyces-2 by restriction enzyme SbfI using 2-fragment Gibson assembly. The full traJ and oriT sequence was then amplified from plasmid pSET152 [25] by PCR and cloned into the previously constructed vector digested by restriction enzymes AvrII and NheI using 2-fragment Gibson assembly to yield the final pCM4.4 construct.
pCM4.4-Act-KO is a derivative of pCM4.4 designed to knock out the positive pathway regulator for actinorhodin biosynthetic gene cluster. The gRNA spacer sequence was assembled into the plasmid as described before [8]. The 1.5-kB homology arms were amplified from S. coelicolor A3(2) genomic DNA by PCR. pCM4.4 containing gRNA sequence was linearized by XbaI and the homology arms were assembled into the plasmid using 3-fragment Gibson assembly.
All plasmids used in this work are summarized in Table 1 and the corresponding map can be found in supplementary Fig. S1. Primers are listed in Table S1.
Intergeneric conjugation and CRISPR-Cas9 system induction
Plasmids were delivered into Streptomyces by intergeneric conjugation according to standard procedures [19]. An overnight culture of E. coli ET12567[pUZ8002] containing the corresponding plasmid was diluted 1:100 into fresh LB with antibiotics and grown to an OD600 of 0.6. Then, 1 mL of the culture was washed twice and resuspended in the same volume of fresh LB without antibiotics. The washed cells were mixed with 108 of pre-germinated spores in a 5:1 volume ratio. 100 μL from the mixture was spread on SFM supplemented with 0, 0.5, 1 or 2 mM of theophylline. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 16 h, subsequently overlaid with 1 mL of distilled water containing nalidixic acid (25 μg ml−1) and apramycin (50 μg ml−1) and incubated at 30 °C. All plates were photographed 6 days after conjugation and the number of exconjugants counted. The conjugation efficiency was calculated per conjugation by multiplying the number of exconjugants per plate by the dilution factor.
For the glycerol uptake operon disrupted by CRISPR-Cas9 mediated recombination, 5 exconjugants from the uninduced conjugation plate (0 mM of theophylline) were pooled together in 400 μL of TSB, thoroughly mixed by vortexing and 100 μL of the mixture was used to inoculate 10 mL of TSB containing apramycin (50 μg ml−1), nalidixic acid (25 μg ml−1) and 4, 8 or 12 mM of theophylline. Cultures were incubated at 30 °C and 220 rpm for 4 days and afterwards re-streaked on SFM for single colonies. Ten colonies from each condition were randomly picked, subcultured twice for single colonies on SFM and subjected to further screening.
Screening of mutants
To determine the Cas9 editing of glycerol uptake operon, screening was conducted by both phenotype and DNA verification by analysing ten independent mutants. For each screened colony, half of the colony was picked and plated out on SMM containing either glycerol or glucose. Plates were incubated at 30 °C and photographed after 6 days. The other half of the colony was subjected to PCR directly from spores with two pairs of primers. The set of primers ‘dGly’ (‘dGly SCO check fw’ and ‘dGly SCO check rev’) can amplify a region containing the deleted sequence, exclusively from the chromosome, as ‘dGly SCO check fw’ anneals outside of the fragment used as the 5′ homologous arm for the recombination (Fig. S2). Thus, a 1360-bp fragment was expected from the mutant strain in contrast to the 3032-bp fragment expected from the wild type. A second pair of primers, ‘SCO1660′ (‘SCO1660 check fw’ and ‘SCO1660 check rev’), amplified a 775-bp fragment within the deleted region. Therefore, no amplification was expected from the mutant strain (Fig. S2).
To determine the Cas9 editing of actinorhodin positive regulator gene, act II-ORF4, eight exconjugants were picked and streaked on SFM plates supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1). The plates were incubated at 37 °C so that the editing plasmid is lost. After 3 days of incubation, spores from each exconjugant were picked and transferred into 3 mL liquid MYG medium. The cells were incubated at 37 °C for 2 days and their genomic DNA was extracted using Wizard genomic DNA extraction kit (Promega) following the manufacturer’s protocol. 50 ng of genomic DNA was used as template for genotyping PCR. For positive PCR primer pair of ‘Act-edit-F’, and ‘Act-edit-R’ were used. For negative controls, primer pairs (‘Act-edit-F’, ‘Act-WT-R’) and (‘Act-edit-R’, ‘Act-WT-F’) were used.
Results and discussions
Effect of Cas9 expression on conjugation efficiency
Our previous attempts to deliver plasmid pCRISPomyces-2 [8] into either Streptomyces coelicolor M145 or Streptomyces lividans TK24 through intergeneric conjugation appeared to be unsuccessful. There are published reports from other authors of failed attempts to obtain exconjugants with the same plasmid in S. coelicolor [13], Streptomyces sp. KY 40–1 [26], Streptomyces sp. NRRL S-244 and S. roseosporus NRRL 15,998 [27]. All these together suggested an existing issue with the plasmid that prevented any exconjugant from growing.
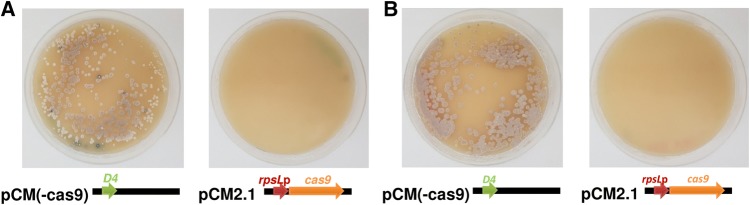
An analysis of pCRISPomyces-2 nucleotide sequence revealed that traJ gene coding sequence in this plasmid is incomplete, encoding a truncated and likely non-functional protein. TraJ positively regulates the expression of transfer genes that are involved in the conjugal transfer of DNA between bacterial cells [28]. Despite not being essential for the process, previous observations indicated that its absence in the conjugable plasmid greatly affects the efficiency of the conjugation process [29]. Therefore, traJ sequence was amended to encode for a complete TraJ in pCRISPomyces-2 to create plasmid pCM2.1. However, as was the case with the parental pCRISPomyces-2 plasmid, no exconjugants grew after conjugations with both S. coelicolor and S. lividans, ruling out the absence of functional TraJ as the reason for the lack of exconjugants. Multiple exconjugants were observed from conjugation with only pCM(-cas9) plasmid, a pCMU-4 derivative lacking cas9, suggesting that the problem of not obtaining the exconjugants may be due to Cas9 expression (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Plates incubated for 6 days after conjugation with pCM2.1 (pCRISPomyces-2 derivative with traJ amended and rpsLp promoter in front of cas9) and pCM(-cas9) (control plasmid with D4 promoter but lacking cas9) in aS. coelicolor and bS. lividans
In pCRISPomyces-2, cas9 expression is under the control of rpsLp (XC), the promoter from 30 s ribosomal protein S12 of Xylanimonas cellulosilytica, which had been proved to be the strongest promoter among a collection of natural promoters from Streptomyces griseus and other Actinobacteria, tested in S. lividans [30]. In fact, it showed more than 100-fold increased activity compared to the commonly used ermE*p. In order to test if rpsLp (XC) is driving the expression levels of cas9 so high that it might become toxic for the cell, plasmid pCMU was built by cloning the theophylline riboswitch [31] between rpsLp (XC) and the RBS of cas9. This enabled the cas9 expression to be inducible by theophylline. Plasmid pCMUtuf, containing two protospacers targeting tuf1 but no homology repair template, was used as a control to analyse the Cas9 activity. This gene encodes the elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), which is an essential protein involved in protein translation [32]. A conjugation in parallel with pCM(-cas9) was performed as a positive control of the conjugation process.
When pCMU was delivered into S. coelicolor, exconjugants were observed in all conditions, indicating that Cas9 levels had been reduced to non-toxic levels for the cell. A negative correlation between the number of exconjugants and the concentration of theophylline is observed: 13,200 exconjugants in the uninduced condition, 8208 at 0.5 mM, 7044 at 1 mM and 3780 at 2 mM of theophylline. Considering the number of exconjugants observed in the uninduced condition as 100% survival, induction with 0.5 mM of theophylline reduced survival to 62%, 1 mM to 53% and 2 mM to 28% (Table 2, Fig. S3a). The same trend was also observed with pCM(-cas9): 10,140 (100%) in the uninduced condition, 5640 (55%) at 0.5 mM, 6000 (59%) at 1 mM and 1800 (17%) at 2 mM of theophylline (Table 2, Fig. S3a); suggesting that that negative effect observed with pCMU and pCM(-cas9) may be mainly caused by the toxicity of theophylline to S. coelicolor rather than Cas9, which has not been reported previously. When Cas9 activity was tested with pCMUtuf, no exconjugants were observed in any of the conditions assayed, included the uninduced condition. This suggests that the inducible theophylline riboswitch system is leaky and basal activity of Cas9 is high enough to be lethal for the cells.
Table 2.
Number of exconjugantsa and percentage of survivalb from Cas9 tolerance experiments
| Plasmid | Theophylline concentration (mM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | |
| Streptomyces coelicolor M145 | ||||
| pCM2.1 | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| pCM(-cas9) | 10,140a/100b | 5,640/55 | 6,000/59 | 1,800/17 |
| pCMU | 13,200/100 | 8,208/62 | 7,044/53 | 3,780/28 |
| pCMUtuf | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pCMU-4 | 11,760/100 | 8,124/69 | 5,712/49 | 1,440/12.2 |
| pCMU-4tuf | 10,560/100 | 36/0.003 | 0 | 0 |
| Streptomyces lividans TK24 | ||||
| pCM2.1 | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| pCM(-cas9) | 19,320/100 | 16,920/88 | 12,960/67 | 3,276/17 |
| pCMU | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pCMUtuf | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pCMU-4 | 18,000/100 | 12,516/70 | 9,516/53 | 1,560/9 |
| pCMU-4tuf | 20,304/100 | 5,760/28 | 3,480/17 | 240/0.01 |
aNumber of exconjugants expressed as number of colony-forming units (CFUs) per conjugation
bPercentage of survival considering number of CFUs in the uninduced condition (0 mM theophylline) as 100%
In case of S. lividans, no exconjugants were observed 6 days after conjugation with pCMU, including the uninduced condition (Table 2, Fig. S3b). This suggests that in this organism, and unlike in S. coelicolor, basal expression of Cas9 is toxic at this level. However, small colonies started to appear when plates were incubated for 10 days (Fig. S5). This indicates that for S. lividans toxicity leads to delayed growth instead of lethality. Even though S. lividans can eventually overcome Cas9 negative effects, and, therefore, plasmids like pCRISPomyces-2 can be successfully used for genome editing as previously reported [8, 33], it requires a very long time. It would be better if editing system can be completed in a shorter timeframe.
Lowering Cas9 levels to obtain a tightly regulated Cas9 expression system.
In light of the results from pCMU, it became clear that Cas9 expression needed to be further lowered. Therefore, plasmid pCMU-4 was created, in which rpsLp (XC) promoter was replaced by D4 promoter [24]. D4 promoter was shown as the weakest promoter among all 200 natural and synthetic promoters reviewed by Myronovskyi and Luzhetskyy [34]. As with pCMU, control conjugations in parallel with pCMU-4tuf (pCMU-4 containing two protospacers targeting tuf1, but no homology repair template) and pCM(-cas9) were performed.
As seen in previous experiments with pCMU in S. coelicolor, when cas9 expression was reduced by pCMU-4, exconjugants were observed from all conditions: 11,760 (100%) in the uninduced condition, 8124 (69%) at 0.5 mM, 5712 (49%) at 1 mM and 1440 (12.2%) at 2 mM of theophylline (Table 2, Fig. S4a). pCMU-4tuf gave rise to 10,560 exconjugants (100%) in the uninduced condition, meaning that the basal expression of active Cas9 was most likely not toxic to the cells. Induction with 0.5 mM theophylline seemed to be enough to fully activate the system, as only 36 exconjugants (0.003%) were observed (Table 2, Fig. S4a).
When the same experiments were performed with S. lividans, a similar behaviour with pCMU-4 was observed. By using the low-strength promoter, the cells were able to grow at all conditions: 18,000 (100%) in the uninduced condition, 12,516 (88%) at 0.5 mM, 9516 (53%) at 1 mM and 1560 (9%) at 2 mM of theophylline (Table 2, Fig. S4b). When Cas9 activity was tested by using pCMU-4tuf, 20,304 exconjugants (100%) were observed from the uninduced condition, suggesting that basal activity of Cas9 is also low. However, unlike S. coelicolor, higher concentrations of theophylline seemed to be needed to fully induce the system, as 240 exconjugants (0.01%) were still observed at 2 mM of theophylline (the highest concentration tested) (Table 2, Fig. S4b). Higher concentration of theophylline was not tested as only 9% of S. lividans colonies survived with 2 mM theophylline induction of pCMU-4, indicating that even higher concentration will be too toxic to the cells on solid media.
Conjugation for both Streptomyces species tested was successful. The observed differences in efficiency between plasmids pCMU and pCMU-4 depending on the species (S. coelicolor versus S. lividans), highlight the importance of previously determining the strain tolerance to Cas9 to select an appropriate toolkit before genome editing can be conducted. Without further modifications, the set of experiments and plasmids (pCM2.1, pCM(-cas9), pCMU, pCMUtuf, pCMU-4 and pCMU-4tuf) described in this study could potentially be applied to other actynomycetes in order to test their range of tolerance to Cas9. As tuf1 is a very conserved gene across species, is very likely that at least one of the two protospacers contained in pCMUtuf and pCMU-4tuf will find its matching sequence in the targeted strain.
Interruption of glycerol uptake operon using pCMU-4
Once the toxicity of Cas9 levels had been overcome by modifying the promoter strength and a tightly regulated and inducible system was developed for both S. coelicolor and S. lividans by adjusting the concentration of theophylline, the CRISPR-Cas9 mediated recombination efficiency of this system was tested. For this purpose, the glycerol uptake operon was chosen as a target. This operon comprises four genes: gylA (glycerol uptake protein), gylB (glycerol kinase) and gylC (glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) are dedicated to the uptake and catabolism of glycerol, while gylR encodes a regulatory protein. Inactivation of gylB has been shown to be lethal for S. lividans when grown on a glycerol-containing medium [35], allowing a screening of CRISPR-Cas9 mediated disruption of the glycerol uptake operon by growth phenotype with and without glycerol. Thus, plasmid pCMU-4dGly was built as described in “Methods” in order to delete a fragment of the chromosome containing 1202 nucleotides of gylB coding region and the first 402 nucleotides of the gylC coding sequence (Fig. S2). After conjugation, induction on solid media was performed at 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 mM of theophylline. Ten exconjugants from each condition were selected for phenotypic screening by plating out on SMMS with glucose (control) or glycerol as sole carbon source, and for PCR verification with two set of primers, ‘dGy’ and ‘SCO1660′ (Fig. S2, Table S1). Based on previous results with pCMU-4tuf, positive recombinants were expected at 0.5 mM theophylline for S. coelicolor and at 2 mM for S. lividans. However, all screened colonies were shown to be wild type (data not shown), even at 2 mM for S. coelicolor, suggesting that higher concentrations of theophylline might be needed. Therefore, a CRISPR-Cas9 induction in liquid TSB containing 4, 8 and 12 mM theophylline was conducted as described in “Methods” and ten exconjugants from each condition were assessed by both phenotype and PCR.
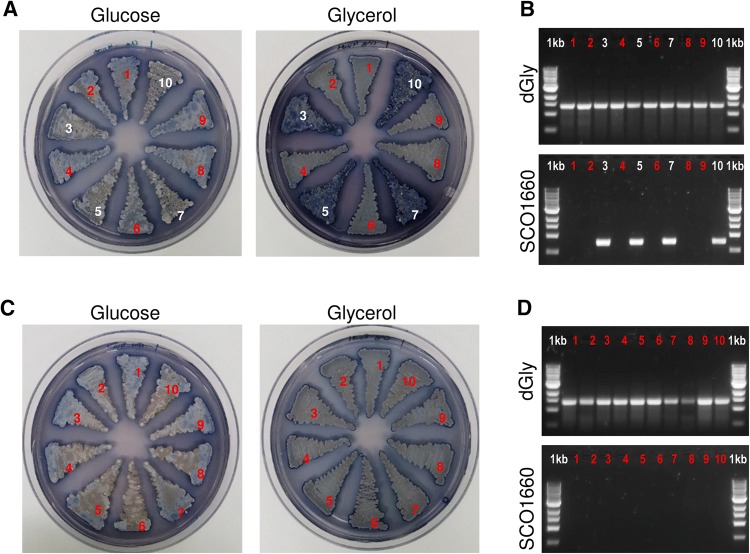
For S. coelicolor, growth in glycerol was observed for all the ten screened colonies after induction with 4 and 8 mM theophylline, suggesting that the recombination had failed. However, when those colonies were verified by PCR, 6 out of 10 colonies from 4 mM and all 10 out of 10 colonies from 8 mM showed to have the deletions designed in gylB and gylC (Fig. 2b and d). Though all the exconjugants were able to grow with glycerol, an antibiotic production phenotype was observed between wild-type and positive recombinants, as the former seemed to be producing remarkably more actinorhodin in glycerol. Interestingly, in glucose, despite being less apparent, the situation seemed to be the opposite, with the wild type producing less actinorhodin than the positive exconjugants (Fig. 2a and c).
Fig. 2.
Phenotypic and genotypic screening of S. coelicolor colonies after conjugation with pCMU-4dGly and induction with a 4 mM and c 8 mM of theophylline. PCR verification with set of primers ‘dGly’ and ‘SCO1660 check’ of colonies after induction with b 4 mM and d 8 mM of theophylline. Positive recombinants are shown in red
Unlike S. lividans, S. coelicolor possesses two operons dedicated to the glycerol catabolism: the targeted gylABC operon (SCO1658-1661) that is glucose repressible and actively uptakes glycerol, and a second less efficient operon that is not under glucose regulation and uses diffusible glycerol [36]. This second operon might be the one allowing S. coelicolor mutants to grow in glycerol.
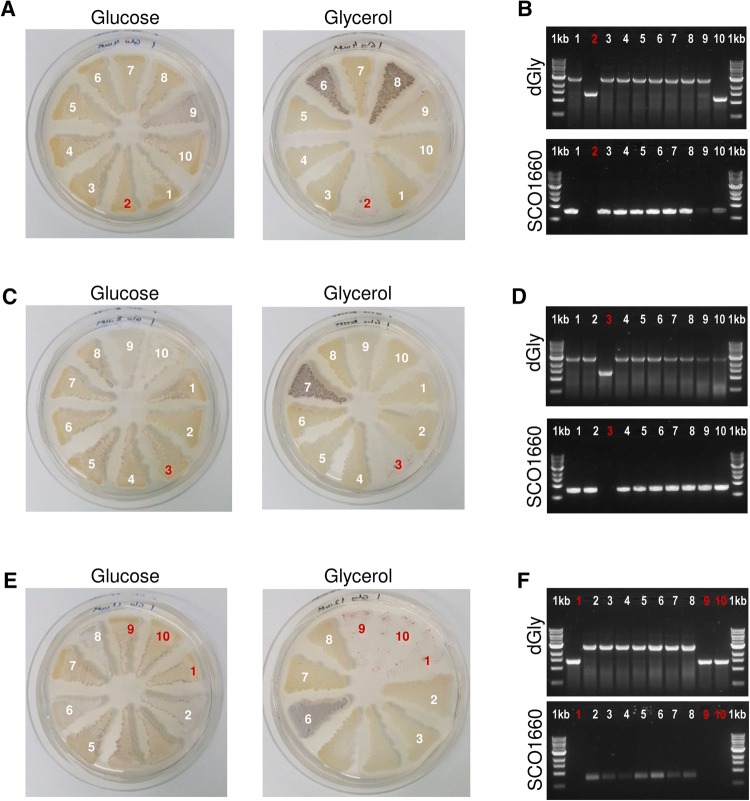
For S. lividans, the phenotypic screening revealed those with the correct deletion of the glycerol operon, which are 1 out of 10 recombinants from both 4 mM and 8 mM theophylline induction, and 3 out of 10 recombinants from the 12 mM theophylline induction (Fig. 3a, c and e). In this case, all the positive recombinants showed the expected phenotype where the exconjugants were unable to grow on glycerol after the disruption of the glycerol uptake operon. This was further confirmed by PCR (Fig. 3b, d and f).
Fig. 3.
Phenotypic and genotypic screening of S. lividans colonies after conjugation with pCMU-4dGly and induction with a 4 mM, c 8 mM and e 12 mM of theophylline. PCR verification with set of primers ‘dGly’ and ‘SCO1660 check’ of colonies after induction with b 4 mM, d 8 mM and f 12 mM of theophylline. Positive recombinants are shown in red
The pCMU-4 plasmid constructed in this manuscript has been successfully applied for the disruption of the glycerol uptake operon in both S. coelicolor and S. lividans. This system has been shown as inducible and dose dependent, as the recombination efficiency increases with higher concentrations of theophylline. The recombination efficiency is also strain-dependent, with 100% of positive recombinants from S. coelicolor after induction with 8 mM theophylline versus 10% from S. lividans in the same condition. These observations are in agreement with results from pCMU-4/pCMU-4tuf, from which S. lividans was predicted to require higher induction compared to S. coelicolor.
pCM4.4, an ermE*p-cas9-driven expression, as an alternative plasmid
While we were able to achieve successful gene editing in both S. coelicolor and S. lividans using pCMU-4 plasmid, our system still has some drawbacks: (1) As we have an extra step needed for system induction, gene editing occurs in long time frames; (2) Although we were able to use theophylline in sub-lethal concentrations to induce Cas9 expression in both S. coelicolor and S. lividans, theophylline toxicity might inhibit successful gene editing in other Actinomycetes. To address these potential drawbacks, a new plasmid called pCM4.4 was constructed. As high levels of Cas9 expression from plasmid pCRISPomyces-2 led to Cas9 toxicity in S. coelicolor, we replaced Cas9 promoter with a weaker constitutive promoter, ermE*p, to test whether decreasing Cas9 expression could solve Cas9 toxicity issues in this strain. Plasmid pCM4.4 without a gRNA sequence was delivered into S. coelicolor by conjugation and we were able to observe thousands of exconjugants after 4 days of incubation at 30 °C. As shown above, we were not able to observe any exconjugants from plasmids pCRISPomyces-2 and pCM2.1, this result suggests the possibility of using constitutive promoters for Cas9 expression, as long as the expression levels are kept on levels which are not toxic to the cells.
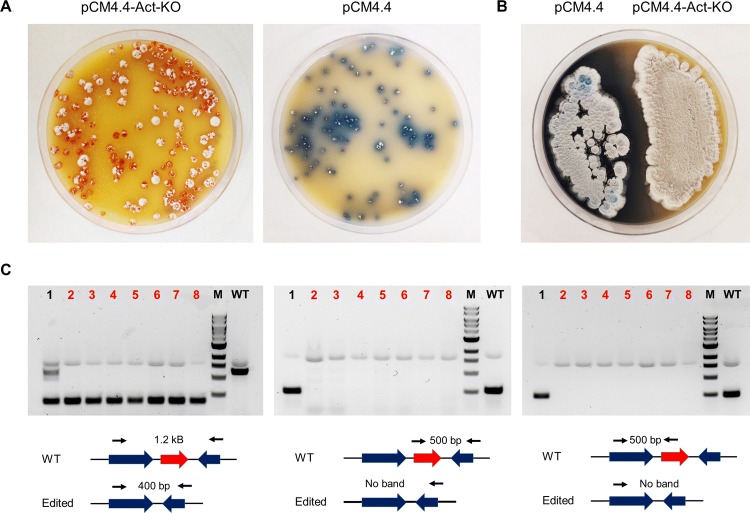
We next evaluated pCM4.4 for genome editing in S. coelicolor by attempting to knock out an 852-bp DNA sequence corresponding to the actinorhodin biosynthetic gene cluster positive transcriptional regulator actII-ORF4 (SCO5085). As titration of this regulator could abolish actinorhodin production in S. coelicolor [37], we sought to use actinorhodin production as an indicator for successful genome editing. To perform gene editing, we designed a single gRNA sequence which would lead to Cas9 cleavage in the middle of regulator gene. Two homology arms (~ 1.5 kB in size) on each side of the 852-bp DNA sequence were also provided as template for homologous recombination. The editing plasmid pCM4.4-Act-KO was delivered into S. coelicolor by conjugation and an empty pCM4.4 plasmid was also included as control. After conjugation, 100-fold less exconjugants were observed from pCM4.4-Act-KO compared to pCM4.4 which suggests successful Cas9 chromosomal cleavage. As shown in Fig. 4a, none of the exconjugants from pCM4.4-Act-KO showed actinorhodin production (blue pigment) while almost all exconjugants from pCM4.4 showed actinorhodin production. To further confirm this phenotype, single exconjugants from both edited and non-edited cells were streaked on SFM medium (Fig. 4b) which confirmed lack of actinorhodin production in edited cells. Finally, genotyping was performed on eight exconjugants to assess correct gene editing (Fig. 4c). Out of eight exconjugants analysed, seven showed successful deletion of the 852-bp sequence while one exconjugant showed a mixture of edited and non-edited cells resulting in 87.5% editing efficiency.
Fig. 4.
Phenotypic and genotypic screening of S. coelicolor exconjugants after conjugation with pCM4.4-Act-KO, pCM4.4. a Image of conjugation plates after 5 days of incubation at 30 °C. pCM4.4-Act-KO exconjugants do not show actinorhodin (blue pigment) production. b Re-streaked exconjugants for both pCM4.4 and pCM4.4-Act-KO confirm lack of actinorhodin production for edited exconjugants. c Genotypic screening of 8 exconjugants confirm deletion of 852 bp target for 7 colonies
In summary, we have demonstrated that high levels of Cas9 can be toxic for the cells, translated in a drastically reduced (to even zero) transformation efficiency. Reducing Cas9 levels can remarkably increase transformation efficiency but can also be insufficient for efficient Cas9 activity. Therefore, Cas9 levels should be perfectly balanced within a range that would compromise high transformation efficiency with successful genome editing. Moreover, this range of tolerance is strain dependent and should be experimentally determined. We have developed a set of 5 plasmids (pCM(-cas9), pCMU, pCMUtuf, pCMU-4 and pCMU-4tuf) which have rapidly and easily showed the different range of tolerance to Cas9 expression and activity of S. coelicolor and S. lividans. Pre-exploration of the range of tolerance with this set of plasmids could be potentially used with any other actinomycete and would be certainly advisable in order to save time and uncertainties when establishing CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in a new strain. The different range of tolerance to Cas9 activity of S. coelicolor and S. lividans was further confirmed in the genome editing experiments carried out with plasmid pCMU-4. With this plasmid, Cas9 expression is tightly regulated, allowing optimum transformation efficiency in an initial step with no inductor, followed by successful genome editing by modulation of Cas9 expression with different levels of an inducer. Thus, this plasmid was customised for each strain. The adaptability of this plasmid would be potentially useful for performing CRISPR-Cas9 based genome editing in any other actinomycete, being particularly convenient for those strains especially sensitive to Cas9 expression levels. Alternatively, and for other strains more tolerant to Cas9 levels, we have developed plasmid pCM4.4, in which Cas9 expression has been lowered by using a weaker constitutive promoter. This way, no induction step is necessary, shortening the timeframe of the experiment and avoiding the potential toxicity of theophylline. This work will help to rationally implement CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing to strains in which this technology has been reported as unsuccessful as well as to new actinomycete strains.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We thank Antonio Rodríguez-García for kindly providing us with plasmid pCRISPomyces-ptc.
Author contributions
Investigation, visualization and validation: SY and BE. Conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources and supervision: HZ and ET. Writing—original draft: SY and BE. Writing—review and editing: all authors.
Funding
ET received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme under Grant Agreement No. 720793 TOPCAPI—thoroughly Optimised Production Chassis for Advanced Pharmaceutical Ingredients. SY was funded from H2020 TOPCAPI. HZ received funding from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) under Award No. AI144967.
Compliance with ethical standards
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu PD, Wu X, Jiang W, Marraffini LA, Zhang F. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas9 systems. Science. 2013;339(6121):819–823. doi: 10.1126/science.1231143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo JE, Norville J, Church GM. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science. 2013;339(6121):823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.1232033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tong Y, Weber T, Lee SY. CRISPR/Cas9-based genome engineering in natural product discovery. Nat Prod Rep. 2018;36(9):1262–1280. doi: 10.1039/c8np00089a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yao R, Liu D, Jia X, Zheng Y, Liu W, Xiao Y. CRISPR-Cas9/Cas12a biotechnology and application in bacteria. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2018;3(3):135–149. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2018.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bilyk O, Luzhetskyy A. Metabolic engineering of natural product biosynthesis in actinobacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016;42:98–107. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sekurova ON, Schneider O, Zotchev SB. Novel bioactive natural products from bacteria via bioprospecting, genome mining and metabolic engineering. Microb Biotechnol. 2019 doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tao W, Anna Y, Deng Z, Sun Y. CRISPR/Cas9-based editing of Streptomyces for discovery, characterization, and production of natural products. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1660. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cobb RE, Wang Y, Zhao H. High-efficiency multiplex genome editing of Streptomyces species using an engineered CRISPR/Cas9 system. ACS Synth Biol. 2015;4(6):723–728. doi: 10.1021/sb500351f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang H, Zheng G, Jiang W, Hu H, Lu Y. One-step high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in Streptomyces. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2015;47(4):231–243. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tong Y, Charusanti P, Zhang L, Weber T, Lee SY. CRISPR-Cas9 based engineering of actinomycetal genomes. ACS Synth Biol. 2015;4(9):1020–1029. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.5b00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zheng H, Wen S, Xu W, He Z, Zhai G, Liu Y, Deng Z, Sun Y. Highly efficient editing of the actinorhodin polyketide chain length factor gene in Streptomyces coelicolor M145 using CRISPR/Cas9-CodA(sm) combined system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99(24):10575–10585. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6931-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Alberti F, Corre C. Editing streptomycete genomes in CRISPR/Cas9 age. Nat Prod Rep. 2019;36(9):1237–1248. doi: 10.1039/c8np00081f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alberti F, Leng DJ, Wilkening I, Song L, Tosin M, Corre C. Triggering the expression of a silent gene cluster from genetically intractable bacteria results in scleric acid discovery. Chem Sci. 2019;10(2):453–463. doi: 10.1039/c8sc03814g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Low ZJ, Pang LM, Ding Y, Cheang QW, Le Mai HK, Thi Trai H, Li J, Liu XW, Kanagasundaram Y, Yang L, Liang ZX. Identification of a biosynthetic gene cluster for polyene macrolactam sceliphrolactam in a Streptomyces strain isolated from mangrove sediment. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1594. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20018-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mo J, Wang S, Zhang W, Li C, Deng Z, Zhang L, Qu X. Efficient editing DNA regions with high sequence identity in actinomycetal genomes y a CRISPR-Cas9 system. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2019;4(2):86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2019.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tong Y, Whitford CM, Robertsen HL, Blin K, Jorgensen TS, Klitgaard AK, Gren T, Jiang X, Weber T, Lee SY. Highly efficient DSB-free base editing for streptomycetes with CRISPR-Best. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116(41):20366–20375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913493116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang K, Zhao Q-W, Liu Y-F, Sun C-F, Chen X-A, Burchmore R, Burgess K, Li Y-Q, Mao X-M. Multi-layer controls of Cas9 activity coupled with ATP synthase over-expression for efficient genome editing in Streptomyces. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:304. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kieser T, Bibb JM, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation.
- 19.MacNeil DJ, Gewain KM, Ruby CL, Dezeny G, Gibbons PH, MacNeil T. Analysis of Streptomyces avermitilis genes required for avermectin biosynthesis utilizing a novel integration vector. Gene. 1992;111:61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90603-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Paget MS, Chamberlin L, Atrih A, Foster SJ, Buttner MJ. Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma sigma factor sigma E is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) J Bacteriol. 1999;181(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.1.204-211.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
- 22.Torella JP, Lienert F, Boehm CR, Chen JH, Way JC, Silver PA. Unique nucleotide sequence (UNS)-guided assembly of repetitive DNA parts for synthetic biology applications. Nat Protoc. 2016;9(9):2075–2089. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Siegl T, Tokovenko B, Myronovskyi M, Luzhetskyy A. Design, construction and characterization of a synthetic promoter library for fine-tuned gene expression in actinomycetes. Metab Eng. 2013;19:98–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2013.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Blin K, Pedersen LE, Weber T, Lee SY. CRISPy-web: an online resource to design sgRNAs for CRISPR applications. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2016;1(2):118–121. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2016.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE. Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene. 1992;116(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90627-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Salem SM, Weidenbach S, Rohr J. A putative glycosyltransferase complex is responsible for the sugar diversity of saquayaycins isolated from Streptomyces sp. KY 40–1. ACS Chem Biol. 2017;12(10):2529–2534. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yeo WL, Heng E, Tan LL, Lim YW, Lim YH, Hoon S, Zhao H, Zhang MM, Wong FT. Characterization of Cas proteins for CRISPR-Cas9 editing in streptomycetes. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019 doi: 10.1002/bit.27021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fowler Tim, Taylor Linda, Thompson Russell. The control region of the F plasmid transfer operon: DNA sequence of the traJ and traY genes and characterisation of the traY → Z promoter. Gene. 1983;26(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Guiney DG, Yakobson E. Location and nucleotide sequence of the transfer origin of the broad host range plasmid RK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1983;80(12):3595–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shao Zengyi, Rao Guodong, Li Chun, Abil Zhanar, Luo Yunzi, Zhao Huimin. Refactoring the Silent Spectinabilin Gene Cluster Using a Plug-and-Play Scaffold. ACS Synthetic Biology. 2013;2(11):662–669. doi: 10.1021/sb400058n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rudolph MM, Vockenhuber MP, Suess B (2013) Synthetic riboswitches for the conditional control of gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 80(12):3595–3598. 159(Pt 7):1416–22. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.067322–0 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 32.Sprinzl M. Elongation factor Tu: a regulatory GTPase with an integrated effector. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19(6):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90149-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang MM, Wong FT, Wang Y, Luo S, Lim YH, Heng E, Yeo WL, Cobb RE, Enghiad B, Ang EL, Zhao H. CRISPR-Cas9 strategy for activation of silent Streptomyces biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:607–609. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Myronovskyi Maksym, Luzhetskyy Andriy. Native and engineered promoters in natural product discovery. Natural Product Reports. 2016;33(8):1006–1019. doi: 10.1039/C6NP00002A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Clerc-Bardin S, Karray F, Frostegard A, Pernodet JL, Simonet P. Development of a conditional lethal system for a Streptomyces lividans strain and its use to investigate conjugative transfer in soil. FEMS Mirobiol Ecol. 2001;38(2–3):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2001.tb00889.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hodgson DA. Glucose repression of carbon source uptake and metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and its perturbation in mutant resistant to 2-deoxyglucose. J Gen Microbiol. 1982;128:2417–2430. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Arias P, Fernández-Moreno MA, Malpartida F. Characterization of the pathway-specific positive transcriptional regulator for actinorhodin biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2) as a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1999;181(22):6958–6968. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.22.6958-6968.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.