Abstract
Background
Surgical smoke is a well-recognized hazard in the operating room. At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, surgical societies quickly published guidelines recommending avoiding laparoscopy or to consider open surgery because of the fear of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 through surgical smoke or aerosol. This narrative review of the literature aimed to determine whether there are any differences in the creation of surgical smoke/aerosol between laparoscopy and laparotomy and if laparoscopy may be safer than laparotomy.
Methods
A literature search was performed using the Pubmed, Embase and Google scholar search engines, as well as manual search of the major journals with specific COVID-19 sections for ahead-of-print publications.
Results
Of 1098 identified articles, we critically appraised 50. Surgical smoke created by electrosurgical and ultrasonic devices has the same composition both in laparoscopy and laparotomy. SARS-CoV-2 has never been found in surgical smoke and there is currently no data to support its virulence if ever it could be transmitted through surgical smoke/aerosol.
Conclusion
If laparoscopy is performed in a closed cavity enabling containment of surgical smoke/aerosol, and proper evacuation of smoke with simple measures is respected, and as long as laparoscopy is not contraindicated, we believe that this surgical approach may be safer for the operating team while the patient has the benefits of minimally invasive surgery. Evidence-based research in this field is needed for definitive determination of safety.
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Laparoscopy, Risk, Viral transmission, Safety
Surgical smoke may harbor particulates of blood fragments, viable cellular material, bacteria and viruses, as well as toxic gas vapors, all of which can negatively affect surgical staff [1]. Consequently, it was feared that surgical smoke may contain viable SARS-CoV-2 [2–4] and all too quickly, major surgical learned societies published guidelines, statements and recommendations, not only to stop elective surgery but favoring laparotomy over laparoscopy [5–7]. In turn, societies [8] and surgeons [9, 10] dedicated to Minimally Invasive Surgery challenged these statements, underscoring that these risks were largely over-estimated and unjustified because of the low quality of evidence [9, 10].
Even if other societies [11] progressively nuanced their initial recommendations and statements, they no longer take any clear stand for or against, only to generate more confusion among surgeons on whether laparotomy or laparoscopy was more appropriate during the pandemic.
In this narrative review, we aimed to critically appraise the literature with regard to the quandary of surgical smoke safety, to determine whether there are any differences in the creation of surgical smoke and aerosol between laparoscopy and laparotomy, whether they contain and/or diffuse viruses such as the SARS CoV-2 and why perfect containment and proper evacuation systems should make laparoscopy safer than laparotomy.
Materials and methods
Although this was a narrative review, we searched Medline/PubMed, Embase and Google Scholar according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [12], with the following search word chains: ("covid19" OR "coronavirus" OR "sars cov 2") AND ("surgery" OR "laparoscopy" OR "laparotomy") AND ("recommendations" OR "indications" OR "guidelines" OR "statements") AND ("2019/12/01"[Date—Publication]: "3000"[Date—Publication]), (“COVID19 surgery laparoscopy laparotomy”), and ('covid19′ OR 'coronavirus'/exp OR 'coronavirus' OR 'sars cov 2′) AND ('surgery'/exp OR 'surgery' OR 'laparoscopy'/exp OR 'laparoscopy' OR 'laparotomy'/exp OR 'laparotomy') AND ('recommendations'/exp OR 'recommendations' OR 'indications' OR 'guidelines'/exp OR 'guidelines' OR 'statements') AND [1-12-2019]/sd NOT [2-5-2020]/sd AND [2020–2020]/py).
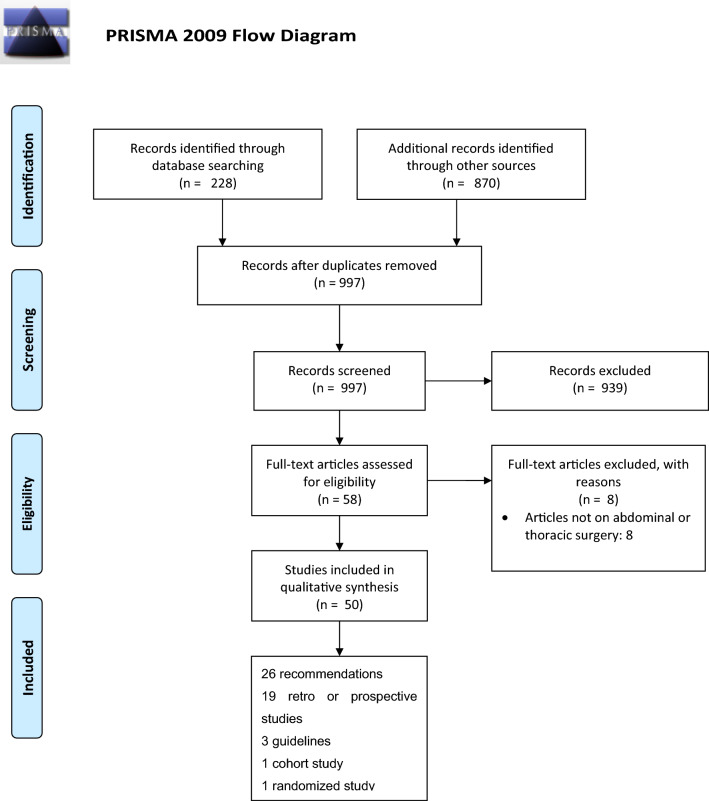
In addition, we searched the major journals with specific COVID-19 sections (NEJM, BJS, BMJ, Annals of Surgery, The Lancet, JAMA Surgery, JACS) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
PRISMA 2009 flow diagram
Eligibility criteria
Studies that compared indications and contra-indications to laparoscopy with regard to laparotomy or studied surgical smoke/aerosol as to the creation and/or diffusion of viral particles, or dealt with protective measures with the context of COVID-19 (patients, pandemic) or other infectious diseases were deemed eligible for inclusion.
Study selection and data extraction
Three authors (RB, AA, AF) performed the search independently. A fourth author (YM) arbitrated any disagreements on inclusion or exclusion of studies. The reference lists of the included studies were searched manually. Special attention was paid to indications for the use of laparoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic, with respect to both patient and surgical team safety. Specific questions we aimed to answer were as follows:
Is there any difference in the surgical smoke created between laparoscopy and laparotomy?
Do surgical smoke and/or aerosols contain and diffuse viruses such as the CoV-2?
Will perfect containment and proper evacuation systems make laparoscopy safer than laparotomy?
Results
A total of 1098 articles were identified through search engines, or after manual search in journals with specific COVID-19 sections. We excluded 1048 articles leaving 50 relevant for our aim (Fig. 1). Of these, 26 consisted of recommendations, 19 were retro or prospective studies, three were guidelines and one cohort and one randomized study. Out of these 50 articles, six favored avoiding laparoscopy, 13 were in favor of laparoscopy over laparotomy if surgical expertise and adequate equipment were available, while 31 were neutral for the use laparoscopy.
Is there any difference in the surgical smoke created between laparoscopy and laparotomy?
In agreement with Liu et al. [13], we use the term surgical smoke, although not formally correct in all cases, that encompasses the terms, used interchangeably, for the gaseous byproducts produced by energy-based surgical instruments such as “plume,” “aerosols,” “cautery smoke,” “diathermy plume” and “smoke plume.”
Surgical smoke is the result of tissue vaporization released when energy-generating devices raise the intracellular temperature to at least 100 ºC (212 ºF). Surgical smoke is an iatrogenic aerosol (short for aero-solution), composed of 95% water and 5% of a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or other gas, and can include cellular material, blood fragments, bacteria, and viruses [14, 15].
The size of particles differs according to the energy source: electrosurgery (ES) (monopolar and bipolar energy devices) dissection releases 0.07 µm size particles [16], while laser tissue coagulation produces larger particles [17]. Ultrasonic (US) energy devices release the largest (0.35–6.5 µm), but also cooler particles (due to the vibration mechanism involved rather than heat only in the tissue desiccation process of ES energy) [4, 14]. Substantial differences were also found regarding smoke particulate size depending on the type of tissue dissected. Particulate diameter ranges from 7 nm to 10 µm with the highest originating from the liver and the lowest from skin, brain matter and subcutaneous fat. The number of particles produced are highest in operations such as abdominoplasty (3900 particles/cm3), thereby resulting in higher exposure of surgical team [18–20].
Once formed, the smoke diffuses according to pressure gradients, gravity, and eventually suction or other air movements. This differs obviously when patients undergoing laparotomy (the abdomen is in direct communication with the ambient air) or laparoscopy (the abdominal cavity is closed).
The analysis of the literature by the Association of periOperative Registered Nurses (AORN) demonstrated that during open surgery the smoke spreads evenly throughout the operating room exposing all surgical staff to the same particle concentrations [15], based on the speed and dispersion of particles generated by laser scalpel [21]. Field drift experiments suggest that aerosol-born particles can travel up to 20 m [22]. Of note, the OR environment is substantially different compared to these experimental conditions.
The issue of creation and disposal of surgical smoke arose quickly after the introduction of laparoscopy [23, 24]. As smoke in laparoscopy can hamper visualization, in the past, surgeons used to release pneumoperitoneum through port valves to clear the field of vision. Although many reports then flourished on the dangers of such maneuvers, many surgeons ignored the risks. A recent report study measured the cumulation and concentration of particles in surgical smoke in 30 patients undergoing laparoscopy or laparotomy at different timings and different areas during the although in laparoscopic operation. While the authors did not find any statistically significant differences in either 0.3 or 0.5 μm particles when compared to open surgery, the cumulative count was higher in laparoscopy than laparotomy after 10 min of the treatment. This study suggests that proper surgical smoke evacuation equipment and regulations are necessary [25]. One randomized controlled trial, comparing the visibility during laparoscopic hysterectomy in patients using either an US energy-based surgical device or monopolar energy, found the degree of surgical smoke or vapor created by US was nearly one fourth of that created by monopolar energy; the difference was highly statistically significant (p < 0.001) [26]. Today there are several systems available to capture and/or filter and/or eliminate the CO2 desufflation [10, 27].
In sum, there is no difference in the creation of surgical smoke between laparoscopy and laparotomy. The only differences concern the aerosol composition, related to the source of energy, or target organ, and aerosol diffusion, which will be dealt with later.
Does surgical smoke and/or aerosols contain and diffuse viruses such as the SARS-CoV-2?
Until the current crisis, the phenomenon of transmission of bacteria and viral particles in infected patients were disregarded and/or neglected by surgeons due to the relative rarity of these patients and low infectivity rate of surgical staff dealing with these patients. While we still lack evidence whether SARS-CoV-2 can be found in smoke/aerosol generated within the peritoneal cavity, the theoretical risks may be extrapolated from previous pandemics and viral infections [28]. In the current COVID crisis, the main question is whether surgical smoke or aerosols created by energy-driven devices can contain SARS-CoV-2, whether they are stable, viable and transmissible and lastly, whether they are virulent which is related to the viral replication and dissemination within hosts (within-host fitness).
Publications before the current COVID-19 pandemic have indicated that surgical smoke may contain viruses such as Corynebacterium [29], Hepatitis B [30], Human papilloma virus (HPV) [31, 32] and Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [29, 33, 34]. Virus-laden small (< 5 μm) aerosolized droplets can remain in the air and travel long distances, > 1 m [35]. Of note, most of these reports concerned open laser-generated plumes, open electrocautery (coagulation or cutting mode), high-speed bone cutting router, an oscillating bone saw, and a wound irrigation syringe jet [29, 34].
Johnson et al. concluded that HIV may be able to remain viable in cool aerosols generated by certain surgical power tools [33]. They suggested that this raises the possibility of HIV transmission to medical personnel exposed to patient procedures in which such equipment is used. They recognized, however, that these laboratory experiments do not establish a risk of HIV transmission to personnel by aerosols generated under clinical conditions such as in the operating room.
At least six cases of would-be HPV transmission have been documented, three in gynecologists that treated HPV-positive patients with laser ablation, one in a nurse that assisted such operations [13], and two ENT surgeons, also after laser ablation [31]. No cases of HIV or HBV transmission have been documented [36]. Of note, most of these reports were case reports or case series, and no causality between the presence of virus or particles and the reported consequences could be established.
Viral-laden aerosol generated by ultrasonic plumes has never been reported in clinical practice [14].
Van Doremalen et al. [37] reported experimental results of stability of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols, concluding that aerosol and fomite transmission of SARS-CoV-2 was “plausible.” Nevertheless, it is not clear if stability can be correlated to viability and whether these two characteristics are sustainable after aerosol transmission. While the authors stated that the virus remained “viable” and “infectious” in aerosols for hours and on surfaces up to days (depending on the inoculum shed), the aerosols were contained within a Goldberg drum at 65% relative humidity, and not dispersed in free air. The current standard on operating room relative humidity levels is set to be between 20 and 60% by the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air Conditioning. Moreover, the ideal temperature in OR is in the United States, is an air temperature of 70 to 75 °F (21 to 24 °C.) The temperature was not mentioned in the experimental drum. Last, no cultures were mentioned to affirm the viability or infectious character of the aerosol.
HBV was detected by nested PCR determinations in surgical smoke in 10 of the 11 laparoscopic procedures (laparoscopic colorectal resections in 5 cases, laparoscopic gastrectomies in three cases and laparoscopic hepatic wedge resections in another three cases); all patients were proven HBV-positive [26]. However, the nested PCR method used is well-known for its high false-positive rates, and nothing was mentioned about their viability or replication potential nor their infectibility.
In answer to our question, to the best of our knowledge, SARS-CoV-2 has never been found in surgical smoke.
Moreover, even if SARS-CoV-2 can be found in blood, lungs or peritoneal fluid of patients who are COVID-positive, there is no compelling data to support that disease can be transmitted through surgical plume or aerosolized gas [38] or even that if they were, that the virus can replicate, and once again, there is no evidence that the surgical plume or aerosol be different between laparotomy and laparoscopy.
Will perfect containment and proper evacuation systems make laparoscopy safer than laparotomy?
We have seen that there are very little differences related to surgical smoke generated in laparoscopic surgery compared to open surgery: only the space of smoke aerosol dispersion differs. Aerosols created in laparotomy are directly in communication with the ambient air in the OR. Conversely, in a laparoscopic operation the closed abdominal cavity space is separated from the open operating room space by the abdominal wall. While these two spaces are independent in terms of pressure, temperature, humidity as well as the composition of intraabdominal gas vs. the OR air, but according to our review, the effect of these parameters with regard to SARS-CoV-2 has not yet been explored.
In laparoscopic surgery, continuity between the two above-mentioned distinct spaces occurs under several circumstances. Opening the trocar cannulas for smoke evacuation to improve visibility should always be avoided as the smoke is spread into the OR under high pressure, with no control. The potential dangers arise in cases of inadvertent release of the peritoneum, but also, during the exchange of instruments, and last, the planned release of the peritoneum whether for specimen retrieval or wound closure. If ever the aerosol via pneumoperitoneum escapes during laparoscopy or laparotomy, the operating room should be considered one of the safest places in the hospital to avoid COVID-19 exposure, given the dilution into the operating room air, the air filtration/circulation in most standard ORs, the sterile field, and the fact that surgeons and anesthesiologists are well protected by protective personal equipment (PPE), more or less at distance from the source [39, 40].
Protective measures have been widely reported. Protective personal equipment, even the most recent, for protection from bodily fluids is insufficient against fumes. For open surgery, smoke evacuator/suction device should be placed at a maximum distance of 5 cm away from the smoke origin, otherwise 50% of the smoke will still be present in the operating room [27]. When this form of particle spread occurs, all OR surfaces including personnel garments are contaminated, and potential transmission of viable particles is thereby increased [40]. To reduce this smoke hazard risk, downward were found to be better than upward types [40].
Suggestions for smoke control under laparoscopy were outlined by Zheng et al. following the Chinese and Italian experience with the coronavirus outbreak [9]; as well, filter and closed evacuation systems, advocated by Kwak et al. [30], were elaborated by the Technology Committee of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery [10]. To attenuate particle load in laparoscopic surgery, continuous flow of fresh CO2 during activation of electrosurgical devices, rather than active release of smoke only when view is compromised, has been advocated [29].
To answer the last question, we suggest that laparoscopy might be safer than laparotomy, in particular when lengthy or repeated energy-driven dissection, or bowel resection/transection because laparoscopy is performed in a closed cavity separated from the open operating room space by the abdominal wall, and surgical plumes will be contained inside the abdominal cavity until properly evacuated, not possible in open surgery.
Discussion
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the fear of transmission of infection by COVID-19-positive patients during laparoscopy has led to contradicting and/or vague statements and recommendations published by several learned societies regarding laparoscopy. These statements and recommendations have caused much confusion, compounded by the constant revisions and updates, becoming more and more cautious.
Surgical smoke exists both in open surgery and in laparoscopy; however, while smoke cannot be controlled appropriately during open surgery, the closed cavity in laparoscopy enables smoke control when the necessary precautions are taken. Evacuation of smoke only through filters, complete evacuation of pneumoperitoneum prior to specimen extraction or conversion to open surgery, clamping both sides of intestine before transection to avoid exposure of stools as well as smart use of energy instruments are key factors of safe smoke hazard control. Moreover, in laparoscopy unintentional spurting of potentially contaminated blood in the surgeons’ face never occurs.
After critical analysis of the literature regarding surgical smoke, we consider that there is no high-level evidence to routinely contra-indicate laparoscopic surgery just because of the risk of aerosol contamination. In particular, there is no evidence that surgical smoke produced by monopolar scalpel, bipolar and monopolar coagulation forceps, lasers, ultrasound dissectors, cavitronic ultrasound surgical aspirator and radiofrequency devices contain or vehicles the SARS-CoV-2. The mechanism by which such viruses can be part of the aerosol remains somewhat mysterious especially since the release from desiccated tissue involves high temperatures that may influence its virulence [25].
The current quandary on the risk of transmission of virions via the aerosol is akin to the flood of publications on the risk of port-site metastatic deposits that plagued the early days of laparoscopic treatment of cancer [41, 42]. Once it was recognized that the prevalence was not that much different from metastatic involvement of laparotomy scars, that precautions were necessary to avoid the “chimney effect” [43] by sudden release of pneumoperitoneum, that adequate and proper carcinological precautions were necessary as in open surgery, the possibility of port-site metastasis was no longer considered a contra-indication to laparoscopic surgery.
Limitations
There were no randomized and only one comparative trial comparing surgical smoke created in laparoscopy and laparotomy; therefore, the level of evidence is low and does not apply evidence-to-decision. Moreover, several of the guidelines, statements and recommendations that appeared were geared on orthopedics and urology or gynecology, and not general surgery.
There is a wide variability of terms employed in the literature (smoke, vapor, aerosol, plume) [13, 15]; this may have added to the confusion. Moreover, the search strings for PubMed and Embase are probably not broad enough to address the study aims, as they combine key words with the terms ‘statements’, ‘recommendations’ …. using the Boolean operator AND.
Conclusion
In agreement with SAGES, EAES and the Australian College of Surgeons, we endorse laparoscopy for all surgical procedures performed during the COVID-19 crisis as long as patient condition allows [44, 45]. Because laparoscopy unfolds in a closed peritoneal cavity that can be adequately contained during surgery, and if all intra-peritoneal airborne particles can be safely eliminated through closed and filtered evacuation systems, the patient will benefit from the well-recognized advantages of laparoscopy and protection of the OR staff may actually be better. In an effort to ensure that the pneumoperitoneum is contained during the operation and released in a closed, filtered circuit, and thus ensure the safety of the operating room team, the authors have indicated all the “tricks and tips” they use in Table 1.
Table 1.
Authors tricks and tips to ensure aerosol safety during laparoscopic surgery
| Hand-assisted laparoscopic surgery should be discouraged |
|---|
| As SARS-CoV-2 was found in stools of about 50% of COVID-19 + patientsa [47, 48], if the digestive tract is open (perforation or spillage), abundant lavage with proper closed evacuation of lavage fluid should be performed. If gastrointestinal resection is planned, the up and downstream segments should be adequately sealed off (stapler better than clamp?) and division of the gastrointestinal tract with energy-driven devices should be avoided (not to create potentially virus-laden smoke) |
| Port site and trocars |
| Trocar stopcocks should not be opened during surgery and can be sealed by a protective cap |
| One or two dedicated trocar(s) should be connected continuously to a filter by the Luer lock mechanism and open to evacuate the smoke which will be filtered before exiting into the OR space or ideally, another evacuation system |
| Instrument shafts should be inserted and withdrawn, swiftly, with precise and regular movements, parallel to the trocar shaft |
| As little torque as possible should be exercised on trocars (this means that insertion sites should be well planned to provide the optimal elevation angle for the organ under dissection) [49] |
| To ensure complete evacuation of pneumoperitoneum, several different ports can be utilized for desufflation, and whenever possible through the most anti-gravity port 25 |
| Port-site closure should be commenced only after complete desufflation |
| Check air-tightness of trocars before each operation. Disposable trocars should be preferred over reusables |
| Evacuation energy created smoke should be evacuated through filters continuously and not only when smoke compromises visualization |
| Complete evacuation of the pneumoperitoneum should be obtained through filters before laparotomy for specimen extraction or conversion |
| If the Airseal port® is used, it should be connected to another smoke evacuator with an ULPA filter or used in Smoke Evacuation Mode where the tube set is connected to two standard trocars in a “closed loop” configuration, one for insufflation and one for active smoke evacuation through a 0.01 micron ULPA filter |
| Pneumoperitoneal pressure should be as low as possible without compromising surgical view and safe maneuvers (10 mm Hg); the Trendelenburg position should be avoided (or at least not more than 10–15°) [50] |
| Energy-driven devices |
| Bipolar energy should be preferred |
| Use the lower possible power needed |
| Keep pulses short and avoid long use of energy on the same tissue area |
| If a drain is indicated, it should be tubular, inserted through an airtight skin incision, and clamped closed until the abdomen is complete desufflated as above |
| All instruments should be cleaned by the scrub nurse after each use and exchange |
| All OR personnel should wear a highly efficient tight seal-fit mask when in the OR |
However, although we were unable to find evidence of any particular risk in laparoscopic surgery, this does not mean that the risk does not exist: similar to statistics, “absence of evidence is not evidence of absence” [46] and caution is warranted (“precautionary principle”) as long as uncertainty of surgical smoke or aerosol virulence of SARS Cov-2 exists.
Last, we want to highlight that this report focuses on the possibility of virus transmission related to different surgical approaches. It does not pretend to be a justification of one approach over another, but simply aims to show that laparoscopy does not, in itself and with the above-mentioned precautions, increase the risk of airborne transmission.
There is an urgent need to promote evidence-based research in this field leading to evidence-based recommendations in the near future.
Compliance of ethical standards
Disclosures
Yoav Mintz MD, Alberto Arezzo MD, Luigi Boni MD, Ludovica Baldari MD, Ronit Brodie MPAS, Elisa Cassinotti MD, Selman Uranues MD, Min Hua Zheng MD, and Abe Fingerhut have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Alberto Arezzo, Email: alberto.arezzo@mac.com.
Luigi Boni, Email: luigi.boni@unimi.it.
Abe Fingerhut, Email: abefingerhut@aol.com.
References
- 1.Pierce JS, Lacey SE, Lippert JF, et al. Laser-generated air contaminants from medical laser applications: a state-of-the-science review of exposure characterization, health effects, and control. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2011;8(7):447–466. doi: 10.1080/15459624.2011.585888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brown J. Surgical decision making in the era of COVID-19: a new set of rules. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2020.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Novara G, Giannarini G, De Nunzio C, et al. Risk of sars-cov-2 diffusion when performing minimally invasive surgery during the covid-19 pandemic. Eur Urol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Veziant J, Bourdel N, Slim K. Risks of viral contamination in healthcare professionals during laparoscopy in the Covid-19 pandemic. J Visceral Surg. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2020.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.American College of Surgeons (2020) Clinical Guidance for Surgeons. https://www.facs.org/covid-19/clinical-guidance/surgeon-protection
- 6.Royal College of Surgeons (2020) Optimal surgical approach during the Sars-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic 2020. Updated 29 March 2020. https://umbraco.surgeons.org/media/5136/optimal-surgical-approach-during-the-covid-19-pandemic_updated-version.pdf
- 7.Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) and European Association of Endoscopic Surgery (EAES) (2020) Recommendations for Surgical Response to COVID 19 Crisis. https://www.sages.org/recommendations-surgical-response-covid-19/
- 8.Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) (2020) Resources for Smoke & Gas Evacuation during open, laparoscopic and endoscopic Procedures. Updated March 29, 2020. https://www.sages.org/resources-smoke-gas-evacuation-during-open-laparoscopic-endoscopic-procedures/
- 9.Zheng MH, Boni L, Fingerhut A. Minimally invasive surgery and the novel coronavirus outbreak: lessons learned in China and Italy. Ann Surg. 2020 doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mintz Y, Arezzo A, Boni L, et al. A low cost, safe and effective method for smoke evacuation in laparoscopic surgery for suspected coronavirus patients. Ann Surg. 2020 doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Royal College of Surgeons (2020) England Covid-19 Statements. https://www.asgbi.org.uk/covid-19/covid-19-statements. Accessed 27 Apr 2020
- 12.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu Y, Song Y, Hu X, Yan L, Zhu X. Awareness of surgical smoke hazards and enhancement of surgical smoke prevention among the gynecologists. J Cancer. 2019;10(12):2788–2799. doi: 10.7150/jca.31464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Alp E, Bijl D, Bleichrodt RP, et al. Surgical smoke and infection control. J Hosp Infect. 2006;62(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2005.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ulmer BC. The hazards of surgical smoke. AORN J. 2008;87(4):721–734. doi: 10.1016/j.aorn.2007.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Heinsohn P, Jewett DL. Exposure to blood-containing aerosols in the operating room: a preliminary study. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1993;54:446–453. doi: 10.1080/15298669391354946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nezhat C, Winer WK, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, Forrest D, Reeves WG. Smoke from laser surgery: is there a health hazard? Lasers Surg Med. 1987;7:376–382. doi: 10.1002/lsm.1900070414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brüske-Hohlfeld I, Preissler G, Jauch KW, Pitz M, Nowak D, Peters A, Wichmann HE. Surgical smoke and ultrafine particles. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2008;3:31. doi: 10.1186/1745-6673-3-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karjalainen M, Kontunen A, Saari S, Rönkkö T, Lekkala J, Roine A, Oksala N. The characterization of surgical smoke from various tissues and its implications for occupational safety. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(4):e0195274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ragde SF, Jorgensen R, Foreland S. Characterisation of exposure to ultrafine particles from surgcial smoke by use of a fast mobility particle sizer. Ann Occup Hyg. 2016;60:860–874. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/mew033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nicola JH, Nicola EM, Vieira R, et al. Speed of particles ejected from animal skin by CO2 laser pulses, measured by laser Doppler velocimetry. Phys Med Biol. 2002;47(5):847–856. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/47/5/311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nuyttens D, Schampheleire M, Baetens D, Dekeyser B. Sonck, direct and indirect drift assessment means. Part 3: Field drift experiments. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2008;73:763–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Champault G, Taffinder N, Ziol M, Riskalla H, Catheline JM. Cells are present in the smoke created during laparoscopic surgery. Br J Surg. 1997;84(7):993–995. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800840724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nduka CC, Poland N, Kennedy M, Dye J, Darzi A. Does the ultrasonically activated scalpel release viable airborne cancer cells? Surg Endosc. 1998;12(8):1031–1034. doi: 10.1007/s004649900774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li CI, Pai JY, Chen CH. Characterization of smoke generated during the use of surgical knife in laparotomy surgeries. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2020;70(3):324–332. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2020.1717675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Choi C, Do IG, Song T. Ultrasonic versus monopolar energy-based surgical devices in terms of surgical smoke and lateral thermal damage (ULMOST): a randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc. 2018;32(11):4415–4421. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barrett WL, Garber SM. Surgical smoke: a review of the literature. Is this just a lot of hot air? Surg Endosc. 2003;17(6):979–987. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-8584-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mallick R, Odejinmi F, Clark TJ. Covid 19 pandemic and gynaecological laparoscopic surgery: knowns and unknowns. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2020;12(1):3–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Capizzi PJ, Clay RP, Battey MJ. Microbiologic activity in laser resurfacing plume and debris. Lasers Surg Med. 1998;23(3):172–174. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9101(1998)23:3<172::AID-LSM7>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kwak HD, Kim S-H, Seo YS, Song KJ. Detecting hepatitis B virus in surgical smoke emitted during laparoscopic surgery. Occup Environ Med. 2016;73:857–863. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2016-103724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rioux M, Garland A, Webster D, Reardon E. HPV positive tonsillar cancer in two laser surgeons: case reports. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;42(1):54. doi: 10.1186/1916-0216-42-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sawchuck WS, Weber PJ, Lowy DR, Dzubow LM. Infectious papillomavirus in the vapor of warts treated with carbon dioxide laser or electrocoagulation: detection and protection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21:41–49. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(89)70146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Johnson GK, Robinson WS. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) in the vapors of surgical power instruments. J Med Virol. 1991;33(1):47–50. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890330110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Garden JM, O’Banion MK, Bakus AD, Olson C. Viral disease transmitted by laser-generated plume (aerosol) Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1303–1307. doi: 10.1001/archderm.138.10.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fernstrom A, Goldblatt M. Aerobiology and its role in the transmission of infectious diseases. J Pathog. 2013 doi: 10.1155/2013/493960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bree K, Barnhill S, Rundell W. The dangers of electosurgical smoke to operating room personnel: a review. Workplace Health Saf. 2017;65(11):517–526. doi: 10.1177/2165079917691063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH, et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. NEJM. 2020;382(16):1564–1567. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2004973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Morris SM, Nickles Fader A, Milad MP, Dionisi HJ. Understanding the "scope" of the problem: why laparoscopy is considered safe during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2020.04.00. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Judson SD, van Doremalen N, Munster VJ. Stability and viability of SARS-CoV-2 Reply. N Engl J Med. 2020;13:382. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2007942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Romano F, Gusten J, De Antonellis S, et al. Electrosurgical smoke: ultrafine particle measurements and work environment quality in different operating theatres. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 doi: 10.3390/ijerph14020137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Curet MJ. Port site metastatses. Am J Surg. 2004;187(6):705–712. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ishida H, Murata N, Yamada H, Nomura T, Shimomura K, Fujioka M, Idezuki Y. Influence of trocar placement and CO2 pneumoperitoneum on port site metastasis following laparoscopic tumor surgery. Surg Endosc. 2000;14(2):193–197. doi: 10.1007/s004649900099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ramirez PT, Wolf JK. Levenback C Laparoscopic port-site metastases: etiology and prevention. Gynecol Oncol. 2003;91:179–189. doi: 10.1016/S0090-8258(03)00507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Francis N, Dort J, Cho E, Feldman L, Keller D, Lim R, Mikami D, Phillips E, Spaniolas K, Tsuda S, Wasco K, Arulampalam T, Sheraz M, Morales S, Pietrabissa A, Asbun H, Pryor A. SAGES and EAES recommendations for minimally invasive surgery during COVID-19 pandemic. Surg Endosc. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07565-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Optimal surgical approach during the Sars-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic 29th March 2020. https://umbraco.surgeons.org/media/5136/optimal-surgical-approach-during-the-covid-19-pandemic_updated-version.pdf
- 46.Altman D, Bland J. Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence. BMJ. 1995 doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7003.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tian Y, Rong L, Nian W, He Y. Review article: gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of fecal transmission. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;51(9):843–851. doi: 10.1111/apt.15731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wu Y, Guo C, Tang L, Hong Z, Zhou J, Dong X, Yin H, Xiao Q, Tang Y, Qu X, Kuang L, Fang X, Mishra N, Lu J, Shan H, Jiang G, Huang X. Prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in fecal samples. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(5):434–435. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30083-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fingerhut A, Hanna GB, Veyrie N, Ferzli G, Millat B, Alexakis N, Leandros E. Optimal trocar placement for ergonomic intracorporeal sewing and knotting in laparoscopic hiatal surgery. Am J Surg. 2010;200:519–528. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Park JS, Ahn EJ, Ko DD, Kang H, Shin HY, Baek CH, Jung YH, Woo UC, Kim JY, Koo GH. Effects of pneumoperitoneal pressure and position changes on respiratory mechanics during laparoscopic colectomy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012;63:419–424. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.5.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]