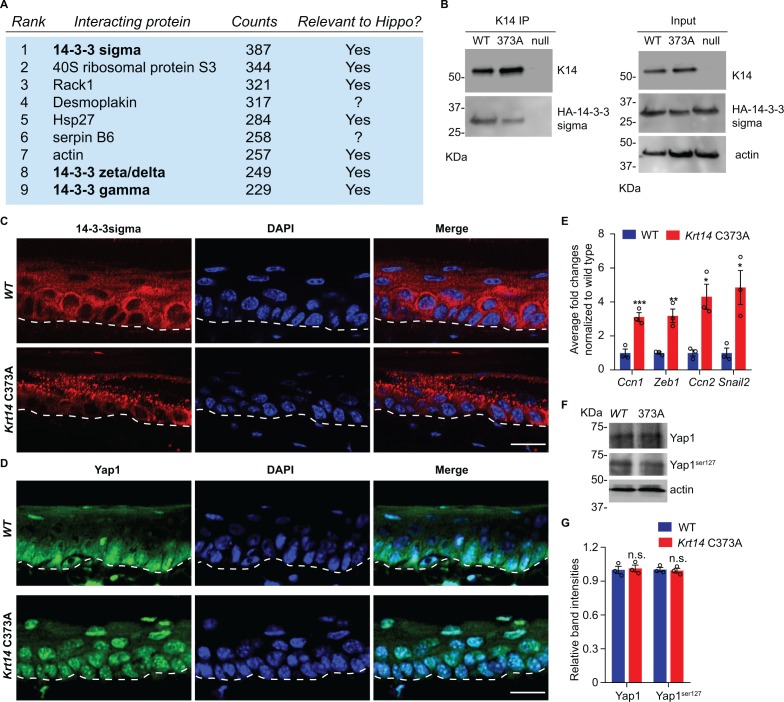
Figure 4. 14-3-3σ interacts with K14, and abnormal localization 14-3-3σ and YAP in Krt14 C373A epidermis.
(A) Top nine most abundant non-keratin entries from a mass spectrometry screen for proteins interacting with K14 in WT newborn skin keratinocytes (primary culture,1 mM calcium, 4 days). Spectral counts and known relevance to Hippo signaling are indicated. See Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for full listing. (B) Immunoprecipitation of K14 from WT or Krt14 C373A skin keratinocytes in primary culture. Both K14 WT and, albeit to a lesser extent, the 373A mutant interact with HA-tagged 14-3-3σ. KDa, kilodalton. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence for 14-3-3σ in WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin sections. Dashed lines depict the dermo-epidermal interface. (D) Indirect immunofluorescence for YAP in WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin sections. (E) Relative mRNA levels (qRT-PCR) for YAP target genes Ccn1, Zeb1, Ccn2, and Snail2 in adult WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin. N = 3 biological replicates per genotype. (F) Immunoblotting analysis for total YAP and YAPSer127 in WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin protein lysates. (G) Quantification of relative protein levels shown in frame d. Data are mean ± SEM from three biological replicates. Student’s t test: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.005; n.s., no statistical difference. Scale bars, 20 µm.