Figure 6:
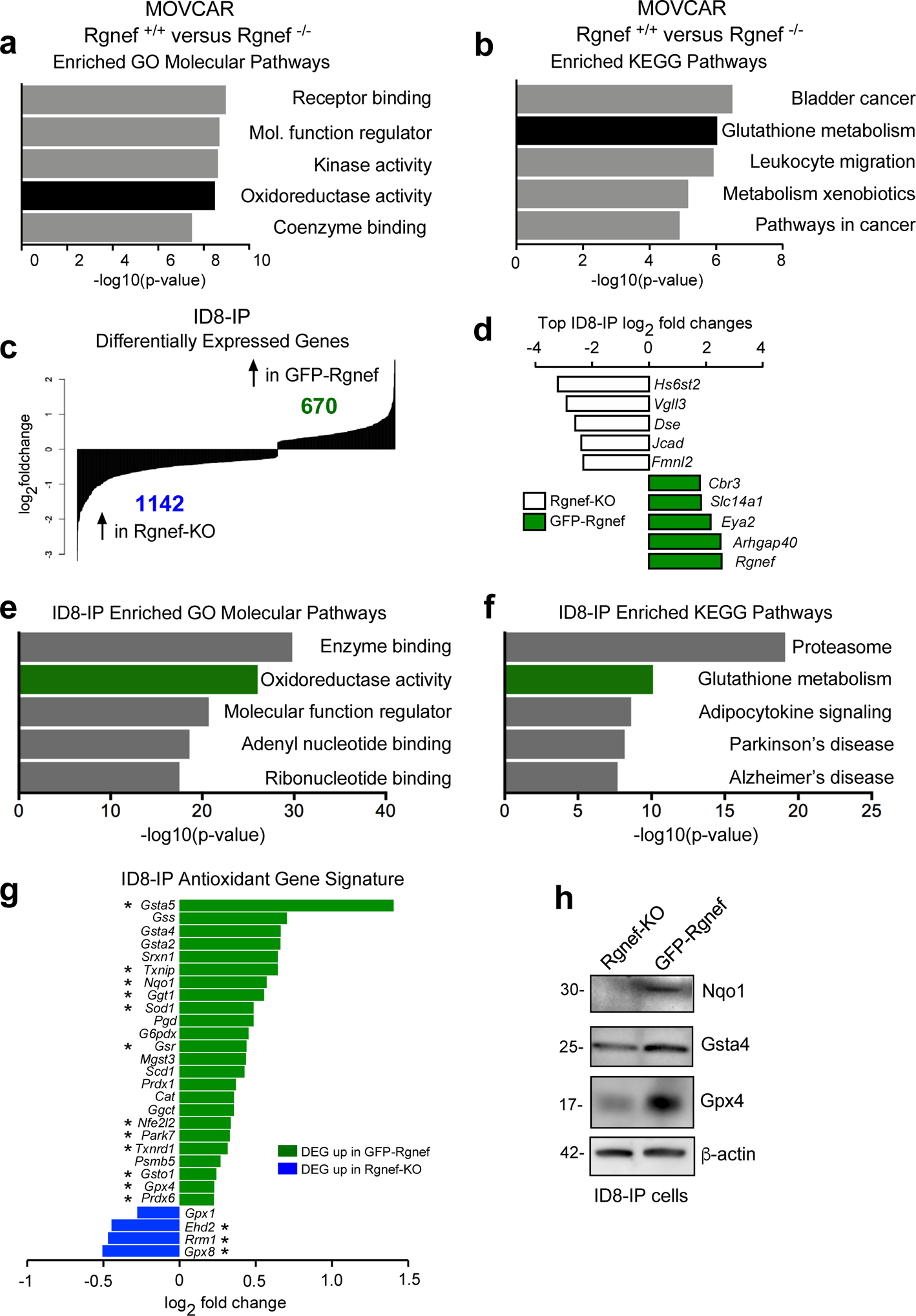
Rgnef promotes an antioxidant gene signature. (a) Differentially upregulated mRNAs in MOVCAR Rgnef+/+ as compared to Rgnef−/− were determined using Illumina BeadChip Array and processed by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). Top 5 most enriched GO molecular function (a) or KEGG pathways (b) in the set of 313 upregulated transcripts are shown. (c) RNA sequencing was used to determine differential mRNA levels in Rgnef-KO and GFP-Rgnef re-expressing ID8-IP cells. 670 targets were upregulated in the GFP-Rgnef re-expressing, and 1142 targets were upregulated in Rgnef-KO cells. (d) The top log2 fold changes in the ID8-IP Rgnef-KO or GFP-Rgnef re-expressing cells are shown. (e) Top 5 most enriched GO molecular function or (f) KEGG pathways in the set of 670 upregulated genes in the ID8-IP GFP-Rgnef re-expressing cells. Enrichment score was determined using GSEA. (g) Differentially expressed genes were compared to a curated list of antioxidant genes (Supplemental Table 2). Genes differentially upregulated (green) or downregulated (blue) in ID8-IP GFP-Rgnef cells vs Rgnef-KO cells are shown. (h) Immunoblotting shows increased levels of Nqo1, Gsta4, and Gpx4 in lysates of anchorage-independent (5 days) ID8-IP GFP-Rgnef cells with β-actin as a loading control.
