Abstract
Despite advances in targeted anticancer therapies, there are still no small molecule-based therapies available that specifically target colorectal cancer development and progression, the second-leading cause of cancer deaths. We previously disclosed the discovery of TASIN-1 (Truncating APC-Selective Inhibitor), a small molecule that specifically targets colorectal cancer cells lines with truncating mutations in the Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) tumor suppressor gene through inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis. Here, we report a medicinal chemistry evaluation of a collection of TASIN analogs and activity against colon cancer cell lines and an isogenic cell line pair reporting on the status of APC-dependent selectivity. A number of potent and selective analogs were identified, including compounds with good metabolic stability and PK properties. The compounds reported herein represent a first-in-class genotype-selective series that specifically target apc mutations present in the majority of CRC patients, and serves as a translational platform towards a targeted therapy for colon cancer.
Keywords: Adenomatous Polyposis Coli, colon cancer, bipiperidines, arylsulfonamides, structure-activity relationships, antiproliferative
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
Colorectal Cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths resulting in ~600,000 deaths world-wide every year (49,700 in the U.S. and 152,000 in the E.U.).1 Despite the fact that the disease etiology for the majority of CRCs is fairly well understood, there are still no therapies available that specifically target oncogenotypes that drive CRC development and progression.2–4 In addition to early detection (colonoscopy and genetic testing) and surgical removal of precancerous adenomatous polyps (adenomas), current treatment options for advanced CRC include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.2–4 A large body of studies have shown that the primary initiating event in both Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) and sporadic CRC is a loss of function of the Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) tumor suppressor gene leading to aberrant crypts and early adenomas.5–7 According to the model of Fearon and Vogelstein, these early events in the adenoma to adenocarcinoma sequence cause genomic instability leading to the acquisition of additional mutations in various oncogenes such as KRAS or BRAF, SMAD4, TGF-b, and frequently in the tumor suppressor TP53.8,9 Although the full spectrum of biological pathways regulated by the large multifunctional apc protein remains a topic of debate,10 it is now commonly accepted that wild-type APC (APCwt) is essential for intestinal cell differentiation and crypt homeostasis at least in part via regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway.11,12 It is estimated that mutations in the APC gene occur in >80% of patients diagnosed with CRC with >90% of those mutations targeting the Mutation Cluster Region (MCR) leading to defined truncated APC (APCTR) gene products.13–15,5,6 While loss of tumor suppressive function of APC mutations is believed to be important for CRC tumorigenesis,8,9 increasing evidence suggests that the truncated form of the mutant APCTR protein also endows these tumors with gain-of-function properties.10,16–19 For instance, a recent paper co-authored by some of us documented that apc-truncations relief the autoinhibition of C-terminal activation of Asef (APC-selective guanine exchange factor) leading to downstream Golgi fragmentation via activation of an Asef-ROCK-MLC2 signaling pathway.20
In light of the above, we reasoned that small molecule cytotoxins that specifically target colon cancer cell lines with APCTR while sparing normal cells with APCWT would provide for a potential highly selective therapy for the vast majority of CRC patients. This approach is further supported by a recent study demonstrating that introduction of APCWT in colon cancer models reestablishes normal intestinal crypt homeostasis and function, even in the presence of potent oncogenic drivers such as Kras and p53.21 We recently described a potent small molecule that selectively kills CRC cells with truncated apc protein termed TASIN-1 (Truncated APC-Selective Inhibitor 1) using a 200,000 compound high throughput screen (HTS) to identify small molecules with selective cytotoxic activity against an experimentally developed human colonic epithelial cell line (HCEC) with introduced oncogenes (KRAS, CDK4, TERT), coupled with loss of tumor suppressor function (p53) and expressing a mutant apc protein truncated at amino acid residue AA1309 (1CTRPA A1309).22 TASIN-1 was not toxic against the isogenic HCEC cell line that expressed the wild type apc protein (1CTRPA), and selectivity for apc-truncating mutations was retained in every human cell line (normal and cancer) that we tested. Based on serum and sterol rescue experiments, we postulated that TASIN-1 exerts its cytotoxic effects through inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis at the level of Emopamil Binding Protein (EBP), the enzyme that isomerizes a Δ8,9 to a Δ7,8 double bond.22 Furthermore, TASIN-1 inhibited the growth of human tumor xenografts in mice implanted with tumors derived from DLD-1 or HT29 (APCTR), but not HCT116 (APCWT) CRC cell lines.22 Also, TASIN-1 treatment significantly reduced the number of polyps and tumor size in the colons of a genetically engineered mouse apc inactivation model of colonic adenoma-carcinoma progression (CPC;APC mice).23 In addition, TASIN-treated mice (90-day treatment), gained weight and did not show any signs of overt toxicity (histopathology, liver function, kidney function, blood cell counts all look normal).22 Given these promising initial results with TASIN-1, we further characterized the TASIN chemotype and present herein our results related to an extensive medicinal chemistry program that delineates the Structure Activity Relationships (SAR) within this scaffold. A number of very potent and selective analogs were identified, including compounds with good metabolic stability against murine microsomal fractions (S9) and PK properties. The small molecules reported herein thus represent a first-in-class genotype-selective series that specifically target apc mutations present in the vast majority of CRC patients, and therefore serves as a translational platform towards a potential targeted therapy for colon cancer. Finally, although we speculate that TASINs targets the cholesterol biosynthesis enzyme EBP, we have no direct evidence for this interaction. Therefore, the current SAR studies are also essential for the development of photoactivatable probe reagents for pull-down studies in an unbiased search for the molecular target of TASINs, efforts that are currently being pursued in our laboratory.
Results and Discussion
SAR Design and Primary Assays
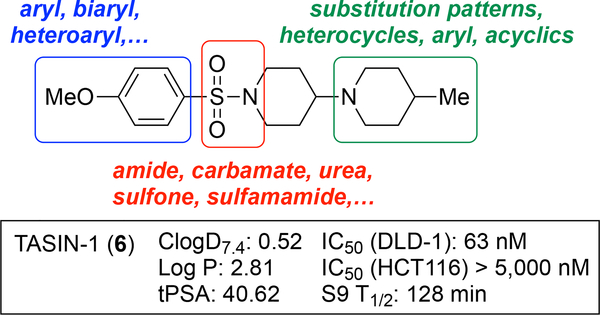
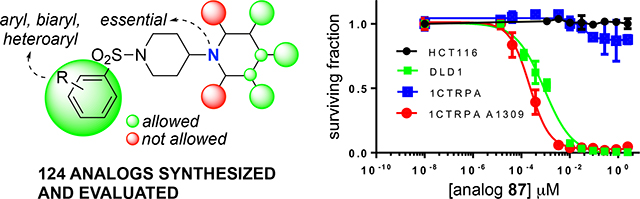
The starting point for the described SAR studies is the HTS hit-compound TASIN-1.22 TASIN-1 (6) is typified by an arylsulfonamide attached to a 1,4’-bipiperidine (Figure 1). The objectives for the enclosed SAR studies encompassed optimization for potency, selectivity, and ADME properties via exploration of the following structural characteristics: (i) functionalization and substitution patterns in the sulfonylated aromatic ring, or replacement with biaryl or heteroaryl groups; (ii) substitution patterns in the terminal piperidine ring; (iii) replacement of the terminal piperidine ring with other heterocycles, aromatic rings, or acyclic substituents; (iv) replacement of the central sulfonylated piperidine ring with other ring systems or an acyclic tether; (v) replacement of the sulfonamide with an amide, carbamate, urea, sulfone, or a sulfamamide. All new compounds were initially evaluated in a cell proliferation assay (CellTiter-Glo®; Promega) using two human colorectal cancer cell lines, one with a truncating mutation in the APC gene (DLD-1) and one with wildtype APC status (HCT116). The assay was performed under low serum conditions (HCEC medium supplemented with 0.2% Fetal Bovine Serum) as described before.22 A select set of compounds was additionally evaluated against another human CRC cell line with truncating mutations in the APC gene (HT29), and a pair of diploid isogenic HCEC-derived cell lines (CTRPA, APCWT; CTRPA A1309, APCTR).22 Finally, select compounds were evaluated for in vitro metabolic stability using mouse liver S9 fractions and in vivo PK properties.
Figure 1.
Structure, properties, and analog design of TASIN-1 (6).
Synthesis
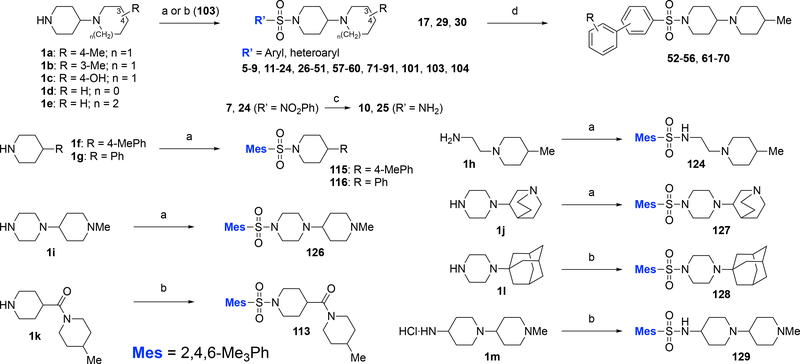
The synthesis of analogs 5-91, 101, 103, 104, 113, 115, 116, 124, 126-129 is shown in scheme 1. Standard sulfonylation of substituted 1,4’-bipiperidines 1a-c, 4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)piperidine (1d), or 1-(piperidin-4-yl)azepane (1e) with a variety of commercially available aryl- or heteroarylsulfonyl chlorides at room temperature provided analogs 5-9, 11-24, 26-51, 57-60, 71-91, 101, 103, and 104.24 A subsequent hydrogenolysis of nitro-substituted analogs 7 and 24 over Pd/C at room temperature yielded aniline analogs 10 and 25. The 2-, 3-, or 4-bromophenylsulfonamide analogs 17, 29, and 30 offered viable starting materials for further diversification toward biaryl-substituted congeners 52-56 and 61-70 via Suzuki cross-coupling with commercially available arylboronic acids.25 Variants in the bipiperidinyl moiety were prepared via reaction of the corresponding heterocyclic amines 1f-l with 2,4,6-trimethylphenylsulfonyl chloride under the same standard sulfonylation conditions.24
Scheme 1. Synthesis of aromatic and heteroaromatic sulfonamide analogs via sulphonylation / cross-couplinga.
aReagents and conditions: (a) amine 1a-d, 1f-j, RSO2Cl, iPr2NEt, CH2Cl2, rt; (b) amine 1e, 1k-m, RSO2Cl, K2CO3, CHCl3/H2O (1/1), rt; (c) Pd/C, H2, MeOH, rt; (d) ArB(OH)2, Pd(PPh3)4 (10 mol%), aq. Na2CO3 (2 M)/THF (1/10), reflux. Mes, mesitylene, 2,4,6-Me3Ph.
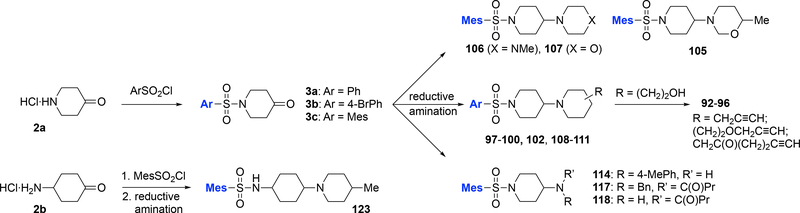
Additional sulfonamide analogs not directly available from direct sulfonylation of commercially available amines were synthesized via procedures outlined below in Scheme 2. First, reaction of piperidine-4-one (2a) or 4-aminocyclohexan-1-one (2b) with phenyl-, 4-bromophenyl-, or 2,4,6-trimethylphenylsulfonyl chloride provided intermediate sulfonamides 3a-c and 2,4,6-trimethyl-N-(4-oxocyclohexyl)benzenesulfonamide (not shown, derived from 2b).24 Subsequent reductive amination (NaBH(OAc)3 or NaCNBH3) of these materials with a variety of amines yielded analogs 97-100, 102, 106-111, 114, and 123.26 Analog 105 was obtained after an additional condensation of the intermediate 4-((1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)amino)butan-2-ol with paraformaldehyde. Analogs 117 derived from acylation of intermediate N-benzyl-1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-amine, which upon subsequent hydrogenolysis yielded analog 118. Analog 96 was made from hydroxyethyl-substituted analog 100 (R = −4-(CH2)2OH) via a sequence of reactions including Swern oxidation, addition of (4-(trimethylsilyl)but-3-yn-1-yl)magnesium bromide, silyl-deprotection, and oxidation to the ketone with Dess-Martin periodinane. Analogs 92-94 are derived after reductive amination of arylsulfonylpiperidinone 3a or 3b with 2- or 4-(hydroxyethyl)piperidine, followed by alkylation with propargyl bromide (→94, 95). Alternatively, the same reductive amination products were oxidized to the aldehyde, followed by Gilbert-Seyferth (→92) or Corey-Fuchs alkynylation (→93).
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of sulfonamide analogs via sulphonylation / reductive amination
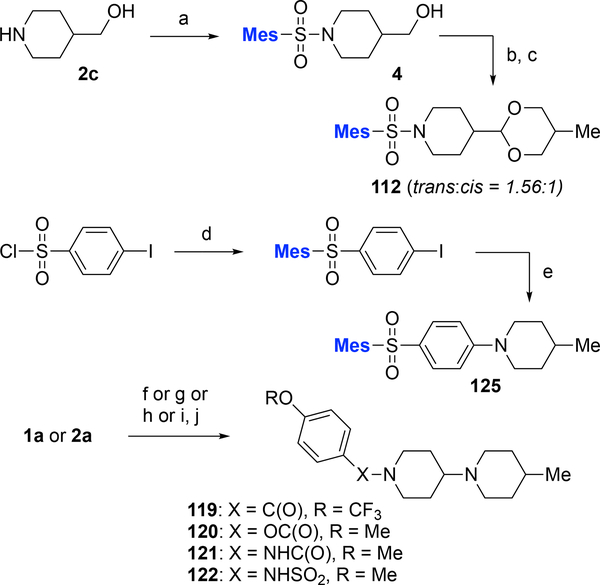
The 1,3-dioxanyl-containg analog 112 (1.56:1 mixture of cis:trans isomers) was synthesized from 4-hydroxymethyl-piperidine 2c via sulfonylation (→4), followed by Swern oxidation and condensation with 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol (Scheme 3). The synthesis of analog 125 relied on a copper-catalyzed Buchwald amination of 1-iodo-4-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylsulfonyl)benzene with 4-methylpiperidine.27 We also explored analogs wherein the sulfonamide linker is replaced with various other functionality. As shown in Scheme 3, condensation of 4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine with 4-trifluoromethoxybenzoic acid provided amide analog 119, whereas reaction with 4-methoxyphenyl carbonochloridate or 4-methoxyphenylisocyanate yielded carbamate analog 120 and urea analog 121, respectively. Finally, reaction of piperidinone 2b with (4-methoxyphenyl)sulfamoyl chloride, followed by reductive amination with 4-methylpiperidine furnished analog 122.
Scheme 3. Synthesis of analogs 112, 125, and analogs 119–122a.
aReagents and conditions: (a) amine 2c, RSO2Cl, iPr2NEt, CH2Cl2, rt; (b) (COCl)2, DMSO, CH2Cl2; then −78 °C, Et3N, −78 °C → rt; (c) MeC(CH2OH)2, cat. PPTS, MgSO4, PhMe, reflux; (d) AlCl3, CH2Cl2, rt; (e) 4-Me-piperidine, CuI, proline, K2CO3, DMSO, 90 °C; (f) 1a, 4-CF3OPhCO2H, EDC·HCl, DMAP, CH2Cl2, rt; (g) 1a, 4-MeOPhOC(O)Cl, K2CO3, Et2O, 0 °C → rt; (h) 1a, 4-MeOPhNCO, CH2Cl2, 0 °C → rt; (i) 2a, 4-MeOPhNHSO2Cl, Et3N, Na2SO4, CH2Cl2, rt; (j) 4-Me-piperidine, NaBH(OAc)3, AcOH, DCE, rt. DCE, 1,2-dichloroethane; DMAP, N,N-dimetylaminopyridine; EDC, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide; Mes, 2,4,6-Me3Ph; PPTS, pyridinium para-toluenesulfonic acid.
SAR of Monocyclic Functionalized Arylsulfonamides
Our SAR studies initiated with an evaluation of the arylsulfonamide moiety. As shown in Table 1, compared to the parent 4-methoxyphenyl-substituted comparator TASIN-1 (6), replacement with an unsubstituted phenyl ring (→ 5) led to about a 5-fold reduction in antiproliferative activity. A survey of various para-substituents indicated that strongly electron-withdrawing (−NO2, 7; −CO2Me, 8; or −CN, 9) or polar hydrophilic substituents (−NH2, 10) were not tolerated. Increasing the size of the 4-alkoxy substituent from methoxy (6) to a propoxy (18), butoxy (19) or benzyloxy (20) also led to a significant drop in activity. That steric hindrance in the para-position might be the culprit was in agreement with the observation that the 4-methyl substituted analog 11 yielded single-digit nanomolar activity (IC50 = 9.1 nM), whereas increasing the size of the 4-alkyl substituent (ethyl, 12; isopropyl, 13, or t-butyl, 14) abrogated activity in the DLD-1 cell line. Replacement of the 4-methoxy group with fluorinated congeners (−OCF3, 21; −OCHF2, 22) or halides (−Cl, 16; −Br, 17) improved potency 4- to 28-fold, in agreement with smaller hydrophobic Van Der Waals-interacting substituents being preferred at this position. An exception was noted for the 4-trifluoromethylphenyl analog 15, which was 20-fold less active than the corresponding 4-methylphenyl analog 11. Although less extensively explored, single meta-substituents that improved activity versus the unsubstituted parent 5 were restricted to methyl (26, IC50 = 25 nM) and bromine (29, IC50 = 3.2 nM), whereas 3-methoxy, 3-nitro, 3-amino, 3-trifluoromethyl, and 3-chloro substitution (23-25, 27, 28) led to a virtual complete loss of antiproliferative activity. Ortho-bromo substitution (30) also provided high potency (IC50 = 3 nM). Trends for a series of disubstituted arylsulfonamides were less clear. Addition of a 2-methoxy substituent to the 4-methylphenyl analog 11 (IC50 = 9.1 nM) yielded an inactive compound 34, whereas 2-methoxy substitution did not diminish activity in combination with 3-bromo (33 versus 29), and dramatically increased potency of an otherwise inactive monosubstituted meta-methoxyphenyl analog (32, IC50 = 4.5 nM versus 23). The 2,4-dimethoxyphenyl analog (31) lost about 2-fold in potency versus the 4-methoxyphenyl comparator (6). Interestingly, a 3-trifluoromethyl group enhanced significantly the activity of the otherwise inactive para-nitrophenyl analog (35, IC50 = 56 nM versus 7, IC50 = 981 nM), but diminished the activity of the para-chlorophenyl parent (39, IC50 = 17 nM versus 16, IC50 = 2.2 nM). Additional introduction of an ortho-ethyl or -chloride substituent slightly enhanced activity (38, IC50 = 0.6 nM and 41, IC50 = 1 nM versus 17, IC50 = 3.1 nM and 16, IC50 = 2.2 nM respectively), whereas a 2-trifluoromethoxy group had minimal effect (45, IC50 = 5 nM versus 17, IC50 = 3.1 nM). When attaching an additional methyl, trifluoromethyl, or chlorine to the meta-position, the potency of the corresponding monosubstituted para-methyl, -trifluoromethyl, -chloro, or -bromo analogs was diminished 1.3- to 7.7-fold (37, IC50 = 24 nM; 39, IC50 = 17 nM; 40, IC50 = 2.9 nM; 43, IC50 = 12 nM versus 11, IC50 = 9.1 nM; 16, IC50 = 2.2 nM; 17, IC50 = 3.1 nM). The 2-cyano-5-methylphenyl analog 36 was 11-fold less active than ortho-methylphenyl comparator 26. The 3,5-dichlorophenyl analog 42 displayed very weak activity, unlike other dihalo substitution patterns (40, 41, 43). Based on the moderate activity of compounds 44 and 50, fluorine substitution did not appear beneficial.
Table 1.
SAR of Arylsulfonamide Analogs 5–50
| Cpd | R | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | S9 T1/2 (min)b | ClogD7.4c | Cpd | R | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | S9 T1/2 (min)b | ClogD7.4c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | H | 294 ± 7.6 | NA | 0.69 | 28 | 3-Cl | >5,000 | NA | 1.31 |
| 6 | 4-MeO | 63 ± 5.6 | 182 | 0.52 | 29 | 3-Br | 3.2 ± 0.06 | 13 | 1.47 |
| 7 | 4-NO2 | 981 ± 22.6 | NA | 0.66 | 30 | 2-Br | 3 ± 0.25 | 6 | 1.48 |
| 8 | 4-MeO2C | >5,000 | NA | 0.72 | 31 | 3,4-(OMe)2 | 138 ± 12 | NA | 0.37 |
| 9 | 4-CN | 2,800 | NA | 2.28 | 32 | 2,5-(OMe)2 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 9.4 | 0.41 |
| 10 | 4-NH2 | >5,000 | NA | −0.17 | 33 | 2-MeO, 5-Br | 2 ± 0.006 | 9 | 1.33 |
| 11 | 4-Me | 9.1 ± 0.6 | 19 | 1.2 | 34 | 2-MeO, 4-Me | >5,000 | NA | 1.06 |
| 12 | 4-Et | >5,000 | NA | 1.64 | 35 | 3-CF3, 4-NO2 | 56 ± 1.6 | NA | 1.55 |
| 13 | 4-iPr | 685 ± 24 | NA | 1.93 | 36 | 2-CN, 5-Me | 285 ± 3.9 | NA | 1.09 |
| 14 | 4-iBu | >5,000 | NA | 2.23 | 37 | 3,4-Me2 | 24 ± 1.2 | NA | 1.71 |
| 15 | 4-CF3 | 185 ± 8.7 | NA | 1.57 | 38 | 2-Et, 4-Br | 0.6 ± 0.02 | 9.1 | 2.47 |
| 16 | 4-Cl | 2.2 ± 0.04 | 41 | 1.3 | 39 | 3-CF3, 4-Cl | 17 ± 1.2 | 32 | 2.18 |
| 17 | 4-Br | 3.1 ± 0.08 | 32 | 1.46 | 40 | 3,4-Cl2 | 2.9 ± 0.34 | 33 | 1.91 |
| 18 | 4-PrO | 452 ± 2.6 | NA | 1.4 | 41 | 2,4-Cl2 | 1 ± 0.002 | 15 | 1.93 |
| 19 | 4-BuO | 2,300 | NA | 1.85 | 42 | 3,5-Cl2 | 3,400 | NA | 1.92 |
| 20 | 4-BnO | 385 ± 9.4 | NA | 2.25 | 43 | 3-Cl, 4-Br | 12 ± 0.5 | 43 | 2.08 |
| 21 | 4-CF3O | 16 ± 0.7 | NA | 2.12 | 44 | 2,4-F2 | 102 ± 3.5 | NA | 1.02 |
| 22 | 4-CHF2O | 4.8 ± 0.5 | >240 | 1.46 | 45 | 2-CF3O, 4-Br | 5 ± 0.07 | 5 | 2.93 |
| 23 | 3-MeO | >5,000 | NA | 0.54 | 46 | 2-Me, 4-MeO, 5-iPr | 3 ± 0.23 | 8 | 2.27 |
| 24 | 3-NO2 | >5,000 | NA | 0.67 | 47 | 2,4,6-Me3 | 0.03 ± 0.0001 | 5 | 2.2 |
| 25 | 3-NH2 | 3,400 | NA | −0.14 | 48 | 2,4-Cl2, 5-Me | 2 ± 0.05 | 6.5 | 2.44 |
| 26 | 3-Me | 25 ± 2.1 | NA | 1.2 | 49 | 2,4-Cl2, 6-Me | 0.6 ± 0.01 | 7.2 | 2.43 |
| 27 | 3-CF3 | >5,000 | NA | 1.58 | 50 | 3,5-F2, 4-Br | 107 ± 5.3 | NA | 1.78 |
IC50 values represent the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration as determined in the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay. Error represents SD (n = 3). All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the HCT116 cell line (IC50 > 5 μM).
T1/2 values represent the half life for compound phase I metabolic stability using female ICR/CD-1 mouse liver S9 fractions. NA = Not Assayed.
Calculated using MarvinSketch (version 6.3.0).
Although not perfect and with some exceptions (e.g. 16, 17, 37, 42), the SAR-patterns of substituted arylphenylsulfonamide analogs correlated best with a Hansch-type π-σ parameter dependency,28,29 in addition to steric restrictions at the 4-position. Specifically, potent analogs in this series are characterized by substitution with relatively apolar substituents with low electron-withdrawing ability (Br, Cl, alkyl, MeO, CF3O, CHF2O), particular beneficial at the ortho- and para-positions, but restricted in size at the 4-position. Combining these features in a set of trisubstituted arylsulfonamides resulted in a series of very potent compounds (46-49, IC50 = 0.03–3.0 nM). Overall, fifteen analogs displayed IC50-values below 5 nM against the DLD-1 colon cancer cell line, with two breaking the picomolar barrier (47, IC50 = 30 pM and 49, IC50 = 600 pM). None of the compounds tested registered any activity in the corresponding colon cancer cell line with wild-type APC status (HCT116), attesting to their highly specific genotype-selective mode-of-action. Unfortunately, eleven were rapidly metabolized with half-lives between 5 and 30 minutes when subjected to murine S9 microsomal fractions, and another 3 with half-lives between 32 and 41 minutes. Only the 4-difluoromethoxyphenyl analog 22 retained very potent cellular activity (IC50 = 4.8 nM) while exhibiting excellent microsomal stability (T1/2 >240 min). The 3-chloro-4-bromophenyl analog 43 was slightly less potent (IC50 = 12 nM) but also exhibited acceptable microsomal stability (T1/2 = 43 min). Not surprisingly given the bipiperidinyl moiety, the ClogD7.4 value for all potent analogs was below 2.93 (range 0.41–2.93; ClogP range 3.21–4.91). Other parameters such as rotatable bonds, hydrogen bond donors and acceptors, total polar surface area (tPSA, range 40.62–59.08) and MW (range 336–485) are also within the range of drug-like properties for orally available small molecules.
SAR of Biaryl Sulfonamides
Next, we decided to briefly explore ortho-, meta-, and para-aryl substituted phenylsulfonamides (biaryl analogs, Table 2). In the ortho-series, only the unsubstituted biphenyl analog 51 displayed potent selective cytotoxicity against the DLD-1 cell line with truncating APC-mutations. Ortho-biphenyl analogs with additional substituents at the 4’-position (52-55) were >120-fold less active, indicating a potential size restriction along the 4’-vector. For para-biphenyls, the unsubstituted biphenyl analog 56 and those with additional 4’-substitution (57, 58) where significantly less potent than those with additional 2’-substituents (59, 60). We had previously observed that bulkier substituents in the para-position of the arylsulfonamide was dendrimental to activity (Table 1, 12-14 and 18-20). However, given the potent activity of 59 and 60, both containing a large aryl group in the para-position, one might speculate that this size-restriction is limited to 3-dimensional substituents, and space is allowed for a flat properly oriented aryl ring. For the biaryl series of analogs, the meta-position appears to be the sweet spot for connecting the additional aromatic ring, and all meta-biaryl analogs 61-70 displayed potent activity with IC50’s between 2 and 41 nM. The biaryl series of analogs also appeared to provide opportunities to improve metabolism. Indeed, with the exception of analogs 51, 66, and 67 all other potent biaryl analogs had acceptable half-lives between 31 and 289 min in the in vitro murine S9 microsomal stability assay. Despite these initial promising results within the biaryl series, we decided not to further pursue them in light of the significant price to be paid in terms of increased molecular weight and lipophilicity (ClogD7.4 range 2.19–3.37; ClogP range 4.8–5.7; ClipE range 3.58–6.67).
Table 2.
SAR of Biaryl Sulfonamide Analogs 51–70
| Cpd | Ar | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | S9 T1/2 (min)b | ClogD7.4c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 | 2-Ph | 0.96 ± 0.002 | <6 | 2.35 |
| 52 | 2-(4’-ClPh) | 202 ± 7.6 | NA | 2.95 |
| 53 | 2-(4’-MeOPh) | 1,000 | NA | 2.19 |
| 54 | 2-(4’-MePh) | 366 ± 9.6 | NA | 2.86 |
| 55 | 2-(4’-CF3Ph) | 122 ± 8.6 | NA | 3.22 |
| 56 | 4-Ph | 258 ± 14 | NA | 2.34 |
| 57 | 4-(4’-ClPh) | 105 ± 7.6 | NA | 2.94 |
| 58 | 4-(4’-MeOPh) | 263 ± 25 | NA | 2.18 |
| 59 | 4-(2’-MeOPh) | 26 ± 0.5 | 289 | 2.19 |
| 60 | 4-(2’-FPh) | 5 ± 0.06 | 210 | 2.49 |
| 61 | 3-Ph | 2 ± 0.3 | 31 | 2.34 |
| 62 | 3-(4’-ClPh) | 15 ± 2.1 | 147 | 2.95 |
| 63 | 3-(4’MeOPh) | 23 ± 0.9 | 144 | 2.19 |
| 64 | 3-(4’-MePh) | 11 ± 1.0 | 115 | 2.86 |
| 65 | 3-(4’-FPh) | 12 ± 0.6 | 77 | 2.49 |
| 66 | 3-(2’-MeOPh) | 21 ± 0.2 | 15 | 2.19 |
| 67 | 3-(2’-FPh) | 10 ± 0.9 | 17 | 2.49 |
| 68 | 3-(2’-CF3Ph) | 10 ± 0.03 | 37 | 3.22 |
| 69 | 3-(3’,5’-Me2Ph) | 41 ± 1.1 | >240 | 3.37 |
| 70 | 3-(2’-naphthyl) | 2 ± 0.0001 | 204 | 3.33 |
IC50 values represent the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration as determined in the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay. Error represents SD (n = 3). All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the HCT116 cell line (IC50 > 5 μM).
T1/2 values represent the half life for compound phase I metabolic stability using female ICR/CD-1 mouse liver S9 fractions. NA = Not Assayed.
Calculated using MarvinSketch (version 6.3.0).
SAR of Heterocyclic and Fused Bicyclic Sulfonamides
In our search for heterocyclic and fused bicyclic replacements for the arylsulfonamide ring, it became quickly apparent that the more desirable (drug-like properties) heterocyclic ring systems such as pyridines, imidazoles, thiazoles, and isoxazoles were not a fruitful avenue of pursuit (see Table 3). With the exception of thiazole 81, all such heterocyclic replacements led to inactive compounds (71-80, 82). Interestingly, whereas the methyl-substituted chlorothiazole 81 was very potent (IC50 = 1.6 nM), removing the methyl-substituent (80), or replacement with an isopropyl (82) largely abolished activity of these chlorothiazoles. Despite the potency and excellent ClogD7.4 of 0.63 (ClipE 8.17), the chlorothiazole analog 81 was rapidly metabolized in murine S9 microsomal fractions (T1/2 = 10 min). On the other hand, activity results for the relatively apolar fused benzodioxoles and dihydrobenzofurans were more in alignment with results displayed in Table 1. Whereas benzodioxole 83 displayed mediocre activity (IC50 = 853 nM), the corresponding isomeric benzodioxole 84 exhibited a 14-fold improvement (IC50 = 62 nM). Bromo-dihydrobenzopyran 86 was of intermediate potency (IC50 = 96 nM), while introduction of additional methyl-groups led to the very potent and metabolically stable analog 85 (IC50 = 1.2 nM; T1/2 (S9) = 67 min) but increased lipophilicity (ClogD7.4 = 2.78; ClogP = 5.4; ClipE = 6.14). Finally, lipophilic naphtyl analogs 87 and 88 were very potent (0.1–0.65 nM; ClipE 7.50–7.70) but metabolically labile (T1/2 <5–14 min) while the more polar acetamidonaphtyl and isoquinoline analogs 89 and 90 largely lost activity.
Table 3.
SAR of Heterocyclic and Fused Bicyclic Sulfonamide Analogs 71–90
| Cpd | R | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | S9 T1/2 (min)b | ClogD7.4c | Cpd | R | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | S9 T1/2 (min)b | ClogD7.4c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71 | 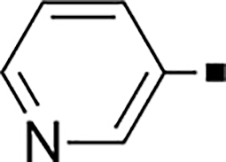 |
2,400 | NA | −0.49 | 81 | 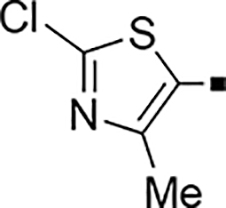 |
1.6 ± 0.03 | 10 | 0.63 |
| 72 |  |
>5,000 | NA | 0.35 | 82 |  |
>5,000 | NA | 1.42 |
| 73 |  |
>5,000 | NA | 0.08 | 83 |  |
853 ± 43 | NA | 0.35 |
| 74 | 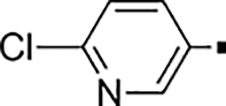 |
3,700 | NA | 0.33 | 84 | 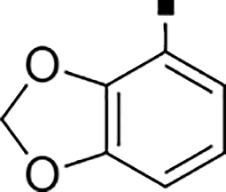 |
62 ± 4.3 | NA | 0.32 |
| 75 | 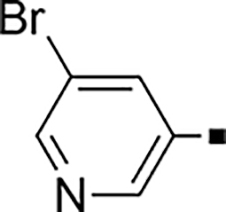 |
>5,000 | NA | 0.28 | 85 | 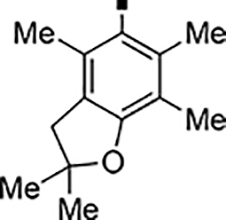 |
1.2 ± 0.03 | 67 | 2.78 |
| 76 | 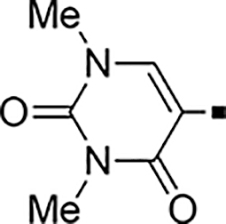 |
>5,000 | NA | −1.71 | 86 | 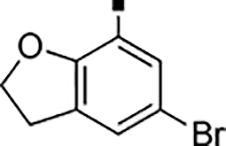 |
96 ± 7.3 | 5 | 1.37 |
| 77 | 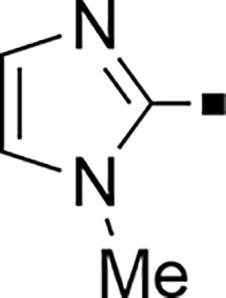 |
>5,000 | NA | −0.5 | 87 | 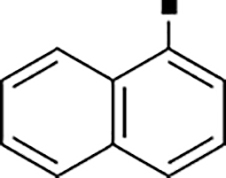 |
0.65 ± 0.002 | <5 | 1.69 |
| 78 | 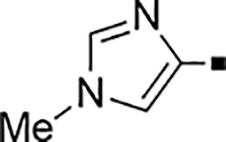 |
>5,000 | NA | −0.55 | 88 | 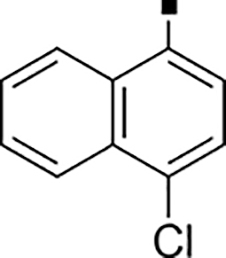 |
0.1 ± 0.02 | 14 | 2.3 |
| 79 | 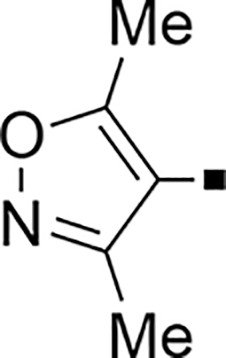 |
>5,000 | NA | −0.53 | 89 | 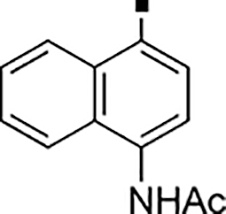 |
1,100 | NA | 0.93 |
| 80 | 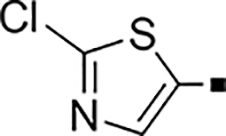 |
1,800 | NA | 0.53 | 90 | 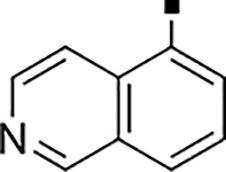 |
225 ± 13 | NA | 0.47 |
IC50 values represent the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration as determined in the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay. Error represents SD (n = 3). All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the HCT116 cell line (IC50 > 10 μM).
T1/2 values represent the half life for compound phase I metabolic stability using female ICR/CD-1 mouse liver S9 fractions. NA = Not Assayed (compounds 71–80 were also not assayed for microsomal stability).
Calculated using MarvinSketch (version 6.3.0).
SAR of the Terminal Piperidine Ring
With a rather extensive survey of the arylsulfonamide moiety completed, the next phase entailed evaluation of the terminal piperidine ring. As shown in Table 4, moving the terminal methyl group from the 4- to the 3-position as in analog 91 reduced activity ~20-fold versus the comparator 22 (105 vs 4.8 nM). Replacement of the 4-methyl with a propargyl (92) or propargyloxyethyl (94) increased activity significantly versus comparators 17 and 5 (0.2 and 85 nM vs 3.1 and 294 nM). Moving those two substituents to the 2-position as in analogs 93 and 95 on the other hand was not tolerated. Other groups that were tolerated in the 4-position in decreasing order of potency are isopropyl (98, 0.3 nM), benzyl (108, 3.5 nM), 2-oxohex-5-yn-1-yl (96, 3 nM), (4-fluorophenyl)methyl (110, 18 nM), 2-hydroxyethyl (100, 19 nM), (2-fluorophenyl)methyl (109, 74 nM), and hydroxy (101, 106 nM). A phenyl (111) or 2-cyanoethyl (99) in that position greatly diminished activity (865 to 7,400 nM). The unsubstituted piperidine 102 lost almost all activity, whereas the 3,5-Me2-substituted analog 97 was active at 17 nM. When other nitrogen-containing ring systems were evaluated, it was revealed that pyrrolidine 104, morpholine 107, and piperazine 106 all lost activity, whereas 1,3-oxazinane 105 was of intermediate potency (IC50 = 92 nM). Only azepane 103 retained single-digit nanomolar potency. Removing the ring-nitrogen altogether, such as in 1,3-dioxane analog 112 and phenyl or tolyl analogs 115 and 116 led to a complete loss of activity.
Table 4.
SAR of Terminal Piperidine Ring Analogs 91–118
 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cpd | R | Ar | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | ClogD7.4c | Cpd | R | Ar | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | ClogD7.4c |
| 91 |  |
4-CFH2OPh | 105 ± 21 | 1.41 | 105 | 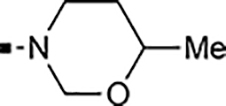 |
Mes | 92 ± 1.23 | 2.94 |
| 92 | 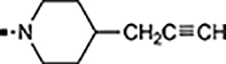 |
4-BrPh | 0.2 ±0.03 | 1.55 | 106 | 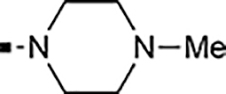 |
Mes | 1,100 | 1.57 |
| 93 | 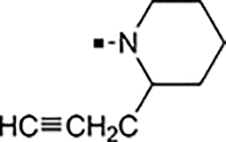 |
Ph | >5,000 | 1.05 | 107 | 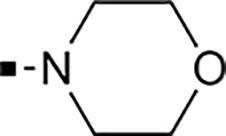 |
Mes | 3,100 | 2.32 |
| 94 | 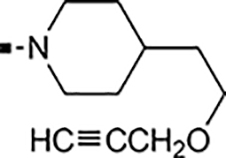 |
Ph | 85 ± 6.8 | 0.67 | 108 |  |
Mes | 3.5 ± 0.03 | 3.76 |
| 95 | 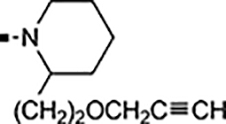 |
Ph | >5,000 | 0.44 | 109 | 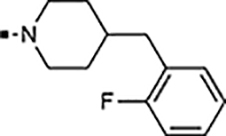 |
Mes | 74 ± 4.5 | 4.04 |
| 96 | 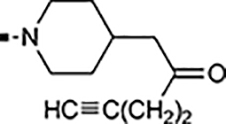 |
Mes | 3 ± 0.04 | 3.21 | 110 | 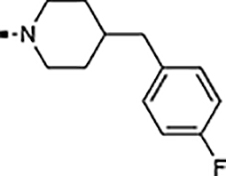 |
Mes | 18 ± 0.7 | 3.93 |
| 97 | 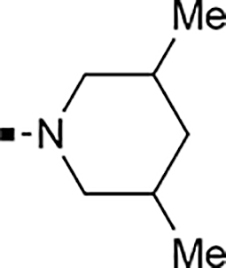 |
Mes | 17 ± 0.9 | 2.22 | 111 | 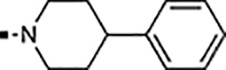 |
Mes | 865 ± 89 | 3.44 |
| 98 | 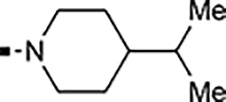 |
Mes | 0.3 ± 0.002 | 2.83 | 112 | 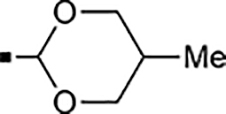 |
Mes | >5,000 | 3.52 |
| 99 | 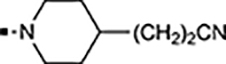 |
Mes | >5,000 | 1.97 | 113 | 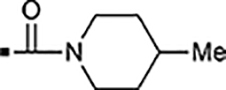 |
Mes | >5,000 | 3.42 |
| 100 | 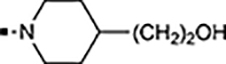 |
Mes | 19 ± 0.8 | 1.31 | 114 | 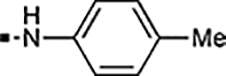 |
Mes | 2,900 | 4.36 |
| 101 | 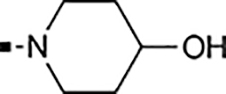 |
Mes | 106 ± 7.9 | 1.01 | 115 | 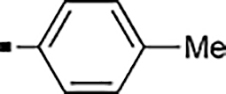 |
Mes | 2,200 | 5.35 |
| 102 | 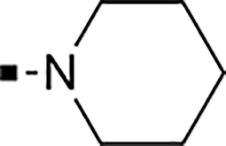 |
Mes | 2,200 | 2.1 | 116 | 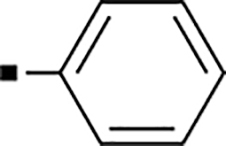 |
Mes | >5,000 | 4.85 |
| 103 | 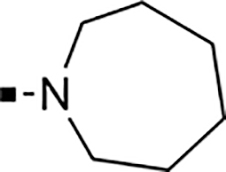 |
Mes | 5.3±2.0b | 2.09 | 117 | 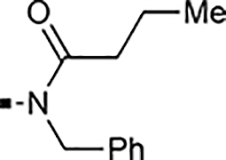 |
Mes | >5,000 | 4.69 |
| 104 | 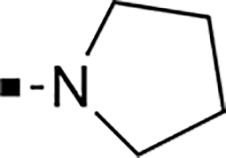 |
4-MeOPh | 3,203 | −0.15 | 118 |  |
Mes | >5,000 | 2.74 |
IC50 values represent the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration as determined in the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay. Error represents SD (n = 3).
Error represents SD (n = 2). All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the HCT116 cell line (IC50 > 5 μM).
Calculated using MarvinSketch (version 6.3.0).
Introducing a carbonyl between the two piperidine ring systems (113), or replacing the terminal piperidine ring with acyclic substituents such as aniline 114, or amides 117 and 118 were also unproductive. To conclude this section, the above results indicate that a basic nitrogen within a six to seven-membered ring (piperidine or azepine) is crucial for retaining cellular activity. A number of substituents, mostly hydrophobic in nature that can include aliphatic, hydroxylated alkyl, propargylic, ether, ketone, or benzylic substitution are well tolerated. Introduction of an additional polar nitrogen or oxygen in the terminal azacycle is contraindicated for bioactivity. Of the single-digit nanomolar compounds, azepane 103 had the lowest ClogD7.4 (2.09) and an acceptable ClipE of 6.19. Other analogs within this series with similar ClipE values are 94, 98, and 100 (ClipE 6.40–6.69). The alkyne-containing analog 92 displayed the best lipophilic efficiency (ClipE 8.15) within this series and is only matched by analogs 47 and 81 (see Table 6).
Table 6.
Antiproliferative Activity of Selected Analogs in Cell Lines with Truncated APC
| Cpd. | IC50 ±
(nM)a |
CLipE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLD-1 | HT-29 | CTRPA A1309b | ||
| 6 | 63 ± 5.6 | 53 ± 2.3 | 122±6.5 | 6.68 |
| 22 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 2±0.1 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 6.86 |
| 29 | 3.2 ± 0.06 | 1.2 ± 0.07 | 6.9±0.8 | 7.02 |
| 30 | 3 ± 0.25 | 3 ± 0.05 | 2.8 ±0.03 | 7.04 |
| 32 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 4±0.1 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 7.94 |
| 33 | 2 ± 0.006 | 2 ± 0.004 | 0.7 ± 0.02 | 7.37 |
| 38 | 0.6 ± 0.02 | 0.5±0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.03 | 6.75 |
| 40 | 2.9 ± 0.34 | 2.2 ± 0.06 | 8.2±0.63 | 6.63 |
| 45 | 5 ± 0.07 | 4 ± 0.02 | 9.6 ± 0.3 | 5.37 |
| 46 | 3 ± 0.23 | 2.2±0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 6.25 |
| 47 | 0.03 ± 0.0001 | 0.9 ± 0.08 | 0.04 ± 0.002 | 8.32 |
| 48 | 2 ± 0.05 | 1.1 ± 0.04 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | 6.26 |
| 49 | 0.6 ± 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.7 ± 0.05 | 6.79 |
| 51 | 0.96 ± 0.002 | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 1.2 ± 0.06 | 6.67 |
| 60 | 5 ± 0.06 | 6 ± 0.07 | 10.2 ± 0.8 | 5.81 |
| 61 | 2 ± 0.3 | 2 ± 0.07 | 1.6 ±0.3 | 6.36 |
| 81 | 1.6 ± 0.03 | 1.5 ± 0.03 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 8.17 |
| 85 | 1.2 ± 0.03 | 0.8 ± 0.03 | 1.5 ±0.08 | 6.14 |
| 87 | 0.65 ± 0.002 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ±0.01 | 7.50 |
| 92 | 0.2 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.9±0.07 | 8.15 |
| 96 | 3 ± 0.04 | 2.1±0.07 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 5.31 |
| 98 | 0.3 ± 0.002 | 0.2 ± 0.001 | 0.6 ± 0.003 | 6.69 |
| 108 | 3.5 ± 0.03 | 3 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 4.70 |
IC50 values represent the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration as determined in the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay. Error represents SD (n = 3). All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the HCT116 cell line with wild-type APC status (IC50 > 5 μM).
All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the isogenic CTRPA cell line with wild-type APC status (IC50 > 5 μM).
Miscellaneous SAR
The final structural attributes to be explored are the role of the sulfonamide functionality and the central piperidine ring. As shown in Table 5, replacement of the sulfonamide linker with an amide (119, IC50 = 426 nM), urea (121, IC50 = 1,360 nM), or sulfamamide linker (122, IC50 = 814 nM ) led to a significant 13 to 90 fold reduction in activity when compared to their sulfonamide congeners 22 and 6 (IC50 = 4.8 and 63 nM). The carbamate replacement 120 fared better with a more marginal 4-fold drop versus sulfonamide 6 – a modification that further lowered the ClogD7.4 to 0.5. Substitution of the central piperidine ring with an aminocyclohexyl (123), aminoethyl (124), or phenyl linker (125) led to a substantial or complete loss of activity. Finally, replacement of the bipiperidine with an amino-bipiperidine (129), N-(N-methylpiperidin-4-yl)piperazine (126), or adamantanylpiperazine (128) led to compounds with mediocre potency. Of interest for future analog design, a quinuclidine analog 127 with altered position of the tertiary nitrogen retained significant activity (IC50 = 83 nM), was metabolically stable (S9 T1/2 = 193 min) and decreased ClogD7.4 significantly to 0.87.
Table 5.
Miscellaneous SAR
| Compound | DLD-1 IC50 (nM)a | ClogD7.4b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 119 | 426 ± 24.5 | 1.54 | |
| 120 | 256 ± 10 | 0.5 | |
| 121 | 1,360 | 0.03 | |
| 122 | 814 ± 21 | −0.27 | |
| 123 | 380 ± 3.5 | 2.45 | |
| 124 | 1,900 | 3.06 | |
| 125 | >5,000 | 5.71 | |
| 126 | 426 ± 42 | 0.75 | |
| 127 | 84 ± 7.6 | 0.87 | |
| 128 | 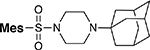 |
231 ± 4.4 | 3.8 |
| 129 | 958 | 0.43 |
IC50 values represent the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration as determined in the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay. Error represents SD (n = 3). All compounds were inactive when counter-screened against the HCT116 cell line (IC50 > 5 μM).
Calculated using MarvinSketch (version 6.3.0).
Activity in Other Cell Lines
As disclosed previously, TASIN-1 (6) was identified as a selective cytotoxin that specifically kills colon cancer cell lines with truncating mutations in the APC tumor suppressor gene. Above we described an extensive medicinal chemistry effort to identify analogs of TASIN-1 with improved potency and physicochemical properties. To ensure that these analogs remained on target, we have additionally counter-screened them for activity against the HCT-116 cell line with wild-type APC. In Table 6 below, we represent additional cytotoxicity data for a selection of 23 analogs that displayed single-digit nanomolar activity against the DLD-1 cell line. All 23 analogs were found to be equally effective against another human colon cancer cell line with truncating APC-mutations (HT29). Given the heterogenous genetic background between all these cultured human colon cancer cell lines (DLD-1, HT29, HCT116), we further evaluated these analogs against an isogenic cell line pair derived from primary human colonic epithelial (HCEC) cells. As disclosed previously,30 introduction of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), telomerase (T) into primary HCEC cells was sufficient to produce an immortalized, nontransformed diploid cell line (CT) with multipotent stem-like characteristics that can differentiate in three dimensional culture conditions. Additional introduction of oncogenic KRASV12, mutant TP53 (key-alterations in CRC), and knockdown of APC established the CTRPA cell line.22 Additional ectopic expression of mutant APC truncated at amino acid 1309 led to the isogenic APCmut cell line (CTRPA A1309).22 As can be seen from data in Table 6, all compounds retained exquisite selectivity for cells with truncating APC mutations with low nanomolar IC50’s in CTRPA A1309 and no apparent effect on the isogenic cell line CTRPA (IC50 >5 μM).
PK Properties of Select Compounds
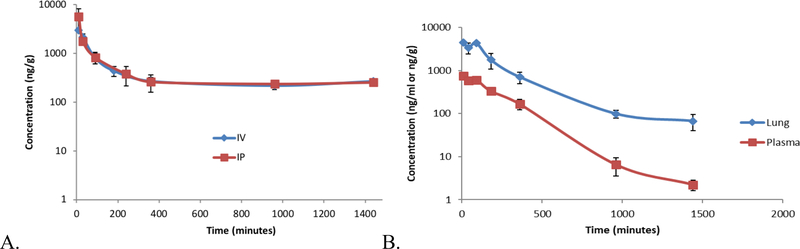
As a prelude for future in vivo efficacy studies in xenografts and genetic models of CRC,22 we selected compounds 16, 22, and 92 for in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis because of their cellular potency (IC50 <5 nM) and low microsomal clearance (murine S9 T1/2 41–240 min; CLint 2.9–16.9 μL/min/mg protein). As can be seen from the data compiled in Table 7, the PK characteristics of analogs 16, 22, and 92 mirrored those of the previously characterized TASIN-1 (6).22 When dosed intravenously (i.v.), analogs 16 (5 mg/kg), 22 (10 mg/kg), and 92 (10 mg/kg) had low to moderate plasma clearance between 0.58 and 10.6 mL/min, a half-life between 1.35 and 2.8 h, and a Cmax between 191 and 742 ng/mL 10 to 30 min after dosing. Plasma exposure for analogs 16 and 92, while good, was significantly lower than for analog 22 and TASIN-1 (6). Intraperitoneal (i.p.) dosing led to similar plasma clearance, Cmax, terminal half-life and exposure as for the i.v. route. The % plasma protein binding was determined using ultrafiltration (22, 69% bound) or rapid equilibrium dialysis (92, 83% bound; 6, 8% bound). We selected compound 22 for oral bioavailablity, which was determined to be excellent (52%, 20 mg/kg) and leading to higher plasma and intestinal exposures than when dosed i.v. at 5 mg/kg. Future efficacy studies will include evaluation of select compounds in a genetically engineered mouse apc inactivation model of colonic adenoma-carcinoma progression (CPC;APC mice).22 Therefore, we assessed the PK of these compounds in the large intestine, the intended target organ. Gratifyingly, large intestinal exposure was excellent, irrespective of the delivery method and between 2.6–23 fold higher than the plasma exposure. The Tmax was achieved 10 min after dosing with a the terminal half-life between 8–15 h except analog 16 with an extraordinary long half-life of 231 h. Examination of the concentration-time curves indicated that elimination reached a plateau phase after an initial seemingly normally decaying half-life, an example which is provide in Figure 2A. This behavior results in the apparent high AUC numbers for this class of compounds. The observed accumulation in the large intestine is likely not limited to this organ. For example, a PK analysis of analog 22 indicated similar levels of accumulation in the lung (5.7-fold higher than plasma), and probably other highly perfused organs (Fig. 2B). As a result, the volume of distribution for analogs 22, 16, and 92 was large, ranging from 5.87 to 63 L/kg. This phenomenon is not unexpected as many lipohilic amine drugs (e.g.) are known to be deposited in highly perfused, lysosome-rich organs via lysosomal trapping.31,32 Together with their ability to bind phospholipids, this lysosomal trapping contributes to presystemic extraction and the large volume of distribution of many cationic amphiphilic drugs including imipramine, tamoxifen, propranolol, and others.32,33 Although we have not yet experimentally assessed lysosomal trapping for the analogs described herein, a future evaluation is warranted as lysosomal accumulation has in some instances been implicated as a cause for phospholipidosis.34 These studies will include a comprehensive histological evaluation of tissues after repeat dosing experiments as part of a full toxicological evaluation of potential lead compounds.
Table 7.
Pharmacokinetics of Compounds 6, 16, 22, and 92 in Mousea
| Cpd | route | dose(mg/kg) | Plasma PK |
Large Intestinal PK |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1/2 (min) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (min) | AUClast (ng·min/mL) | Vz (mL) | CL (mL/min) | T1/2 (min) | Cmax (ng/g) | Tmax (min) | AUClast (ng·min/g) | |||
| 6 | ip | 10 | 48 | 2,390 | 10 | 104,103 | 162 | 2.32 | 570 | 10,678 | 10 | 737,709 |
| 22 | iv | 5 | 162 | 742 | 10 | 197,571 | 135 | 0.58 | 912 | 1,816 | 10 | 511,878 |
| 22 | ip | 10 | 168 | 1,117 | 10 | 205,914 | 156 | 0.64 | 903 | 10,146 | 10 | 790,425 |
| 22 | po | 20 | 182 | 691 | 10 | 328,296 | 153 | 0.58 | 506 | 3,252 | 10 | 890,969 |
| 16 | iv | 10 | 81 | 191 | 30 | 21,581 | 1243 | 10.6 | 13,861 | 1,414 | 10 | 262,874 |
| 92 | iv | 10 | 135 | 303 | 10 | 39,146 | 1152 | 5.92 | 504 | 2,974 | 10 | 559,037 |
| 92 | ip | 10 | 171 | 145 | 10 | 27,904 | 1390 | 5.64 | 678 | 5,754 | 10 | 633,289 |
Elimination half-life (T1/2), maximum observed concentration (Cmax), time to Cmax (Tmax), apparent volume of distribution during terminal phase (Vz), area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to the last measured concentration (AUClast), clearance (CL), intravenous (i.v.), intraperitoneal (i.p.), per os (p.o.).
Figure 2.
A. Concentration-time curve in the large intestine for analog 92 when dosed 10 mg/kg i.v. or i.p. B. Concentration-time curve in the plasma and lung for analog 22 when dosed 5 mg/kg i.v.
Conclusions
There are currently no small molecule therapeutics that target specifically oncogenotypes that drive the development and progression of colorectal cancers. Germline truncating mutations in the APC tumor suppressor gene lead to Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) and early development of CRC, whereas somatic truncating APC mutations are observed in the vast majority of sporadic CRC patients. We previously disclosed the discovery of TASIN-1, a small molecule that selectively targets human colorectal cancer cell lines expressing mutant-APC with high specificity through inhibition of endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis.22 Here, we reported an extensive Structure-Activity Relationship study through the design of analogs of TASIN-1 exploring the structural determinants responsible for cellular activity and selectivity. This study identified several very potent analogs with good drug-like properties that inhibit CRC cells with mutant APC in the single-digit nanomolar to picomolar range, while being innocuous for cells with wildtype APC. Several of these potent analogs exhibited acceptable metabolically stability in murine microsomal fractions, and excellent in vivo exposure whether dosed i.v., i.p. or orally. The high intestinal exposure and half-life of this class bodes well for future efficacy studies in genetic or orthotopic animal models of CRC. However, we note that this significant intestinal accumulation and long half-life could indicate a potential lysosomal trapping of these lipophilic amines, an issue that will be explored in future studies. Lipophilic basic amine drugs are also potentially liable for off-target activity against potassium and sodium channels. Given that our SAR studies indicate that a protonatable amine is absolutely essential for activity, we will have to evaluate our compound collection against these and other potential off-target interactions. In this context, future studies will focus on analogs that perturb the pKa to the 7.5–8.5 range, which is known to limit potassium and sodium channel activity and also may limit the effect of lysosomal accumulation. The SAR studies described herein have not attempted to address these specific issues yet, but indicate that the TASINs represents an excellent scaffold for such SAR-driven optimization, and we are therefore confident that ongoing studies will enable the identification of novel translatable leads for a potential targeted therapy for colorectal cancer.
Experimental Section
Cytotoxicity assay
Activity of each analog was evaluated as described before.22 Briefly, DLD-1, HT29, HCT116, CTRPA, or CTRPA A1309 cells were seeded in 96-well plate in triplicate at a density of 3,000 cells/well in HCEC medium supplemented with 0.2% fetal bovine serum and treated with compound at 9-point 3-fold dilution series for 72 hours. Cell viability was determined using the CellTiter-Glo® (Promega) assay per manufacturer’s instruction. Each value was normalized to cells treated with DMSO and the IC50 values were calculated using Graphpad Prism software.
In vitro liver S9 stability
Female ICR/CD-1 mouse S9 fractions were purchased from Bioreclamation/IVT (Chestertown, MD). 0.025 mL (0.5 mg) of S9 protein was added on ice to a 15 mL glass screw cap tube followed by 0.350 mL of a 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5 solution, containing the compound of interest. The tube was then placed in a 37 °C shaking water bath for 5 min and 0.125 mL of an NADPH-regenerating system (1.7 mg/mL NADP, 7.8 mg/mL glucose 6-phosphate, 6 U/mL glucose 6- phosphate dehydrogenase in 2% w/v NaHCO3/10 mm MgCl2) was added for analysis of phase I metabolism. After addition of all reagents, the final concentration of compound was 2 μM and S9 protein 1 mg/ml. At varying time points after addition of phase I cofactors, the reaction was stopped by the addition of 0.5 mL of methanol containing 0.2% formic acid and either tolbutamide or n-benzylbenzamide as internal standard. Time 0 samples were stopped prior to placing the samples at 37 °C and the NADPH-regenerating system was added immediately thereafter. The samples were incubated for 10 min at rt and then spun at 16,100g for 5 min in a microcentrifuge. The supernatant was analyzed by LC−MS/MS using a Sciex 3200 or 4000 Qtrap mass spectrometer coupled to a Shimadzu Prominence LC with the mass spectrometer in MRM (multiple reaction monitoring) mode. The method described by McNaney et al35 was used with modification for determination of metabolic stability half-life by substrate depletion. A “% remaining” value was used to assess metabolic stability of a compound over time. The LC−MS/MS peak area of the incubated sample at each time point was divided by the LC−MS/MS peak area of the time 0 (T0) sample and multiplied by 100. The natural logarithm (ln) of the % remaining of compound was then plotted versus time (in min) and a linear regression curve plotted going through y-intercept at ln(100). The metabolism of some compounds failed to show linear kinetics at a later time point, so those time points were excluded. The half-life (T1/2) was calculated as T1/2 = 0.693/slope. Compound stability was also evaluated at 0 and 240 min in reaction buffer only minus S9 protein to determine chemical stability.
Protein Binding
Protein binding was determined using either ultrafiltration (22) or rapid equilibrium dialysis (RED; 92) as described in Wang et al.36 Binding in plasma was evaluated using undiluted plasma and plasma diluted with 1 part plasma and 3 parts PBS, while binding in large intestine was evaluated using large intestinal tissue homogenates prepared using a 3-fold volume of PBS. Values were corrected for dilution as described37 using the following equation:
Mouse PK analysis
Animal work for the pharmacokinetic studies described in this manuscript has been approved and conducted under the oversight of the UT Southwestern Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. UT Southwestern uses the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” when establishing animal research standards. Seven PK experiments are reported in the manuscript. Each PK experiment utilized 24 female CD1 mice at 5–6 weeks of age (obtained from Charles River) which were euthanized in groups of three at eight time points for collection of blood and tissues. Thus, a total of 168 mice were used. The animals were housed in standard microisolator cages and were administered inhibitor compounds in 0.2 mL by IP (10 mg/kg) or IV (5 or 10 mg/kg) injection or oral gavage (20 mg/kg) formulated as follows: 16 and 92: 10% DMSO / 10% PEG-400 / 80% 50 mM citrate buffer, pH 5.4; 22: 10% ethanol / 10% PEG-400 / 80% 50 mM citrate buffer, pH 4.4. Animals were euthanized by inhalation overdose of CO2 in groups of 3 at 10, 30, 90, 180, 360, 960, and 1440 min post dose and blood collected by cardiac puncture, using acidified citrate dextrose (ACD) as the anticoagulant. In some cases, large intestine was also isolated, intestinal contents flushed, and the tissue snap frozen. Plasma was isolated from blood by centrifugation at 9600g for 10 min and stored at −80 °C until analysis. Tissues were homogenized in a 3-fold volume of PBS (final homogenate volume in ml = weight of tissue in g × 4). 0.1 mL of plasma or tissue homogenate was precipitated with 0.2 mL of an organic crash solution containing either methanol or acetonitrile, 0.15% formic acid, and an internal standard (n-benzylbenzamide). Extraction conditions were optimized prior to PK analysis for efficient and reproducible recovery over a 3 log range of concentrations. The solution was centrifuged twice at 16,100g twice for 5 min. The final supernatant was analyzed by LC−MS/MS as described above, and compound concentrations were determined in reference to a standard curve prepared by addition of the appropriate compound to blank plasma or tissue homogenate. A value of 3× above the signal obtained in the blank plasma was designated the limit of detection (LOD). The limit of quantitation (LOQ) was defined as the lowest concentration at which back calculation yielded a concentration within 20% of the theoretical value and above the LOD signal. The LOQ values were as follows: 0.5 ng/ml for 16, and 92; and 5 ng/ml for 22. Compound concentrations in large intestine were calculated by subtracting the amount of compound in the residual blood in that tissue based on reference values for large intestinal vasculature.38 Pharmacokinetic parameters were determined using the noncompartmental analysis tool in Phoenix WinNonlin (Certara, Corp., Princeton, NJ).
Chemistry
General Information
Unless otherwise specified, all commercially available reagents were used as received. All reactions using dried solvents were carried out under an atmosphere of argon in flame-dried glassware with magnetic stirring. Dry solvent was dispensed from a solvent purification system that passes solvent through two columns of dry neutral alumina. Silica gel chromatographic purifications were performed by flash chromatography with silica gel (Sigma, grade 60, 230–400 mesh) packed in glass columns (the eluting solvent was determined by thin layer chromatography, TLC), or with an Isco Combiflash system using Redisep®Rf Flash columns with size ranging from 4 to 80 grams. Analytical TLC was performed on glass plates coated with 0.25 mm silica gel using UV or by iodide or KMnO4 staining for visualization. Melting points are uncorrected. Routine 1H and proton-decoupled 13C NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker 400 MHz NMR spectrometer. Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in parts per million (ppm) from low to high field relative to residual solvent. Multiplicities are given as: s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), dd (doublet of doublets), m (multiplet). All synthetic compounds exhibited >95% purity as determined by LC-MS analysis performed on an Agilent 1100 HPLC system using an Eclipse XDB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm; Agilent) that was coupled to an Agilent G1956A (or 6120) ESI mass spectrometer run in the positive mode with a scan range of 100 to 1,100 m/z. Liquid chromatography was carried out at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min at 20 °C with a 5 μL injection volume, using the gradient elution with aqueous acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid. The gradient was adjusted based on the different polarity of different compounds. HRMS data were obtained from the Shimadzu Center for Advanced Analytical Chemistry (SCAAC) at U.T. Arlington.
General procedure A for the preparation of sulfonamides 4–9, 11–24, 26–51, 57, 58, 71–91, 104, 115, 116, 124, and 126–128 from sulfonyl chlorides and amines
A mixture of amine (1.0 eq.), sulfonyl chloride (1.1 eq.), and N,N-diisopropyl ethylamine (1.5 eq.) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL/mmol amine) was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction solution was then poured into a saturated aqueous NaHCO3 solution (20 mL/mmol amine) and extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 20 mL/mmol amine). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified through flash chromatography or Isco Combiflash (MeOH/CH2Cl2, or MeOH/EtOAc eluent mixture; gradient adjusted based on the different polarity of different compounds), or by recrystallization to provide the corresponding sulfonamides with >95% purity.
General procedure B for the preparation of sulfonamides 3a-c, 103, and 113 from sulfonyl chlorides and amine hydrochloride salts
A biphasic mixture of sulfonyl chloride (1.2 eq.), amine hydrochloride salt (1.0 eq.) and K2CO3 (2.5 eq.) in CHCl3 (2 mL/mmol amine hydrochloride salt) and water (2 mL/mmol amine hydrochloride salt) was stirred vigorously at room temperature for 20 h followed by the addition of saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (25 mL/mmol of amine hydrochloride salt). The resulting solution was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 20 mL/mmol of amine hydrochloride salt) and the combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified through flash chromatography or Isco Combiflash (MeOH/CH2Cl2, or hexanes/EtOAc eluent mixture; gradient adjusted based on the different polarity of different compounds) to provide the corresponding sulfonamides with >95% purity.
General procedure C for the preparation of biarylsulfonamides 52–56 and 59–70 via Suzuki cross-coupling
To a flame-dried flask equipped with a reflux condenser were added bromophenylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (1.0 eq.), phenylboronic acid (1.58 eq.), Pd(PPh3)4 (0.1 eq.), THF (14.5 mL/mmol sulfonamide) and aqueous Na2CO3 (2 M; 1.45 mL/mmol sulfonamide). The mixture was degassed through freeze-pump-thaw cycling and was refluxed for 3–12 h. After being cooled down to room temperature, the reaction suspension was diluted with water (45.5 mL/mmol sulfonamide), stirred for 10 min and was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 54.5 mL/mmol sulfonamide). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified through flash chromatography or Isco Combiflash (MeOH/CH2Cl2, or MeOH/EtOAc eluent mixture; gradient adjusted based on the different polarity of different compounds) to provide the corresponding biarylsulfonamides with >95% purity.
General procedure D for the reductive amination of N-arylsulfonyl-piperidin-4-ones 3a-c, or N-mesitylsulphonyl-4-aminocyclohexanone
A mixture of ketone (1.0 eq.), amine (1.0 e.q), AcOH (1.0 eq.), and CH2Cl2 (or DCE) (5 ml/mmol amine) was stirred at room temperature for 15 min before NaBH(OAc)3 (1.5 eq.) was added. The resulting suspension was stirred at room temperature with a reaction time ranging from 20 h to 89 h. The reaction was then quenched by dropwise addition of saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (30 mL/mmol of amine) at 0 °C and the resulting biphasic solution was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 30 ml/mmol amine). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified through flash chromatography or Isco Combiflash (MeOH/CH2Cl2, or hexanes/EtOAc eluent mixture; gradient adjusted based on the different polarity of different compounds) to provide the corresponding reductive amination product with >95% purity.
1-(Phenylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (3a)
Reaction of amine hydrochloride salt 2a with benzenesulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 3a as a white solid (93%); mp 105–108 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85–7.73 (m, 2H), 7.66–7.58 (m, 1H), 7.58–7.48 (m, 2H), 3.39 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 2.52 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 205.6, 136.3, 133.2, 129.3, 127.5, 45.9, 40.7. The analytical data were consistent with the literature report.39
1-(4-Bromophenylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (3b)
Reaction of amine hydrochloride salt 2a with 4-bromobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 3b as a white solid (82%); mp 155–158 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.79–7.57 (m, 4H), 3.39 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 4H), 2.54 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 4H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 205.1, 135.5, 132.6, 128.9, 128.4, 45.8, 40.6.
1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (3c)
Reaction of amine hydrochloride salt 2a with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 3c as a white solid (95%); mp 102–105 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.95 (s, 2H), 3.50 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.52 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 2.29 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 201.6, 138.3, 135.6, 127.4, 126.8, 39.6, 36.3, 18.1, 16.2. LC-MS (ESI) calcd for C14H20NO3S [M + H]+ 282.1, found 282.1.
(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)methanol (4)
Reaction of amine 2c with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 4 as a white solid (78%); mp 85–88 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 3.56 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 3.43 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.71 (td, J = 12.3, 2.6 Hz, 2H), 2.57 (s, 6H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.00–1.80 (m, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 13.6, 2.9 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.48 (m, 1H), 1.18 (qd, J = 11.9, 4.3 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.3, 131.9, 131.7, 67.0, 44.1, 38.3, 28.1, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C15H23NO3SNa [M + Na]+ 320.1291, found 320.1280.
4-Methyl-1’-(phenylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (5)
Reaction of amine 1a with PhSO2Cl (Procedure A) yielded 5 as a pale yellow solid (92%); mp 154–156 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.77 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.65–7.58 (m, 1H), 7.54 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 3.87 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 2.32–2.20 (m, 3H), 2.14 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.59 (m, 4H), 1.40 – 1.28 (m, 1H), 1.27–1.12 (m, 2H), 0.91 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 136.0, 132.7, 129.0, 127.6, 61.3, 49.1, 46.1, 33.9, 30.8, 26.9, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H27N2O2S [M + H]+ 323.1788, found 323.1774.
1’-((4-Methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (6)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 6 as a white solid (94%); mp 109–112 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.67 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.97 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.83–3.74 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.28–2.04 (m, 5H), 1.88–1.75 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.23–1.08 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.9, 129.8, 127.6, 114.1, 61.5, 55.6, 49.5, 46.2, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H29N2O3S [M + H]+ 353.1893, found 353.1883.
4-Methyl-1’-((4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (7)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-nitrobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 7 as a yellow solid (76%); mp 165–168 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.35 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.31 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.21 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 2.10 (td, J = 11.5, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 1.62 (qd, J = 12.0, 4.0 Hz, 4H), 1.38–1.21 (m, 1H), 1.14 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.1, 142.4, 128.7, 124.3, 61.2, 49.5, 46.1, 34.5, 30.9, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26N3O4S [M + H]+ 368.1639, found 368.1633.
Methyl 4-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)benzoate (8)
Reaction of amine 1a with methyl 4-(chlorosulfonyl)benzoate (Procedure A) yielded 8 as a white solid (54%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.16 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.80 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 3.84 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.38–2.02 (m, 5H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.6, 140.2, 133.8, 130.2, 127.6, 61.4, 52.6, 49.4, 46.1, 34.4, 30.9, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H29N2O4S [M + H]+ 381.1843, found 381.1843.
4-((4-Methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)benzonitrile (9)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-cyanobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 9 as a white solid (92%); mp 184–186 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.84 (q, J = 8.5 Hz, 4H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.31 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (tt, J = 11.6, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (t, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 1.85 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.25–1.10 (m, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.9, 132.8, 128.1, 117.3, 116.4, 61.2, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H26N3O2S [M + H]+ 348.1740, found 348.1737.
4-((4-Methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)aniline (10)
To a 50 mL flask were added 4-methyl-1’-((4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine 7 (0.1004 g, 0.33 mmol), methanol (3 mL) and Pd/C (1 spatula, 10% on active carbon). The reaction flask was sealed by a septum and after the removal of air using vacuum, a hydrogen balloon was fitted on the top of the septum. The reaction suspension was then stirred at room temperature for 22 h and was filtered through a pad of celite. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired product (0.09 g, >95%) as a colorless gel. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.41 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.84–3.63 (m, 2H), 2.83 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.31–2.06 (m, 5H), 1.87 (d, J = 14.5 Hz, 2H), 1.62 (d, J = 14.1 Hz, 2H), 1.51 (qd, J = 12.2, 4.1 Hz, 2H), 1.41–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 12.4, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ 153.1, 129.4, 121.2, 112.9, 61.3, 49.1, 45.9, 33.7, 30.7, 26.9, 20.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H27N3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 360.1716, found 360.1719.
4-Methyl-1’-tosyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (11)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 11 as a white solid (67%); mp 139–142 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.59 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 3.80 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 2H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.30–2.07 (m, 5H), 1.84 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.40–1.09 (m, 3H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 143.5, 132.9, 129.6, 127.7, 61.6, 49.4, 46.0, 34.1, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7, 21.5. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H29N2O2S [M + H]+ 337.1944, found 337.1937.
1’-((4-Ethylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (12)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 12 as a brown solid (>95%); mp 108–110 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.31 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 3.82 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.70 (q, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (t, J = 12.1 Hz, 3H), 2.12 (t, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 1.62 (td, J = 12.3, 8.2 Hz, 4H), 1.39–1.08 (m, 6H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 149.5, 133.3, 128.4, 127.8, 61.5, 49.4, 46.1, 34.4, 30.9, 28.8, 27.2, 21.8, 15.1. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H31N2O2S [M + H]+ 351.2101, found 351.2093.
1’-((4-Isopropylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (13)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-isopropylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 13 as a yellow solid (79%); mp 144–147 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 3.81 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.94 (p, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.75 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.31–2.15 (m, 3H), 2.09 (td, J = 11.7, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 1.80 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 1.68–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.03 (m, 3H), 1.24 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 154.1, 133.4, 127.8, 127.0, 61.4, 49.4, 46.1, 34.5, 34.1, 30.9, 27.2, 23.6, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H33N2O2S [M + H]+ 365.2257, found 365.2247.
1’-((4-(Tert-butyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (14)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-(tert-butyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 14 as a yellow solid (85%); mp 173–176 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.64, 7.49 (ABq, JAB = 8.6 Hz, 4H), 3.83 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.31–2.18 (m, 3H), 2.13 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.31 (s, 9H), 1.30–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.24–1.11 (m, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.4, 133.1, 127.5, 125.9, 61.5, 49.4, 46.1, 35.1, 34.3, 31.1, 30.9, 27.1, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H35N2O2S [M + H]+ 379.2414, found 379.2418.
4-Methyl-1’-((4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (15)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 15 as a yellow solid (87%); mp 175–178 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.86, 7.77 (ABq, JAB = 8.2 Hz, 4H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 3H), 2.19 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.09 (td, J = 11.3, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.62 (qd, J = 12.4, 4.0 Hz, 4H), 1.38–1.21 (m, 1H), 1.14 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.0, 134.4 (q, J = 33.1 Hz), 128.1, 126.2 (q, J = 3.7 Hz), 123.2 (q, J = 272.9 Hz), 61.3, 49.4, 46.1, 34.4, 30.9, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H26F3N2O2S [M + H]+ 391.1662, found 391.1654.
1’-((4-Chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (16)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-chlorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 16 as a white solid (67%); mp 152–155 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.66 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 3.93–3.69 (m, 2H), 2.80 (dt, J = 11.6, 3.4 Hz, 2H), 2.23 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 3H), 2.15 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.42–1.26 (m, 1H), 1.25–1.12 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.3, 134.6, 129.3, 129.0, 61.4, 49.4, 46.0, 34.2, 30.8, 27.2, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26ClN2O2S [M + H]+ 357.1398, found 357.1393.
1’-((4-Bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (17)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-bromobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 17 as a white solid (83%); mp 165–168 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–7.45 (m, 4H), 3.81 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.38–1.96 (m, 5H), 1.81 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 1.73–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.22 (m, 1H), 1.22–1.06 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 135.2, 132.3, 129.1, 127.7, 61.3, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26 BrN2O2S [M + H]+ 401.0893, found 401.0886.
4-Methyl-1’-((4-propoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (18)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-propoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 18 as a white solid (>95%); mp 118–121°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.65 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 3.95 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 3.80 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 2.15 (dt, J = 37.1, 11.5 Hz, 5H), 1.88–1.72 (m, 4H), 1.71–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.15 (q, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 1.03 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.5, 129.7, 127.3, 114.5, 69.9, 61.5, 49.5, 46.2, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 22.4, 21.9, 10.5. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 381.2206, found 381.2210.
1’-((4-Butoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (19)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-butoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 19 as a pink solid (82%); mp 137–139 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.64 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.99 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 3.80 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 2.27–2.06 (m, 5H), 1.88–1.72 (m, 4H), 1.70–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.47 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.39–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.24–1.10 (m, 2H), 0.96 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.5, 129.7, 127.2, 114.5, 68.1, 61.6, 49.4, 46.1, 34.4, 31.0, 30.9, 27.2, 21.8, 19.1, 13.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H35N2O3S [M + H]+ 395.2363, found 395.2361.
1’-((4-(Benzyloxy)phenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (20)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-(benzyloxy)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 20 as a white solid (84%); mp 157–159 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.67 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.48–7.27 (m, 4H), 7.04 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 5.10 (s, 2H), 3.81 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 2.31–2.04 (m, 5H), 1.89–1.76 (m, 2H), 1.68–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.08 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.1, 135.8, 129.8, 128.7, 128.4, 127.9, 127.5, 115.0, 70.4, 61.5, 49.5, 46.2, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 429.2206, found 429.2195.
4-Methyl-1’-((4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (21)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 21 as a yellow solid (>95%); mp 168–170 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.79 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.35–2.19 (m, 3H), 2.13 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.39–1.11 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 152.1 (q, J = 1.8 Hz), 134.7, 129.7, 120.8 (q, J = 1.1 Hz), 120.2 (q, J = 259.5 Hz), 61.3, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H26 F3N2O3S [M + H]+ 407.1611, found 407.1615.
1’-((4-(Difluoromethoxy)phenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (22)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-(difluoromethoxy)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 22 as a light orange solid (69%); mp 132–135 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.76 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2 H), 6.61 (t, J = 72.6 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.33–2.16 (m, 3 H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.6, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.52 (m, 4 H), 1.30 (dddt, J = 13.3, 9.7, 6.5, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 154.1 (t, J = 2.9 Hz), 132.9, 129.8, 119.3, 115.2 (t, J = 262.5 Hz), 61.4, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H26 F2N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 411.1524, found 411.1529.
1’-((3-Methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (23)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 23 as a yellow solid (85%); mp 81–83 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.40 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (ddd, J = 7.7, 1.6, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (dd, J = 2.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (ddt, J = 8.3, 2.6, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.82 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.25 (td, J = 12.0, 2.6 Hz, 3H), 2.18–2.07 (m, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.13 (m, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.8, 137.2, 130.0, 119.7, 118.8, 112.5, 61.5, 55.6, 49.4, 46.1, 34.3, 30.9, 27.2, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H29N2O3S [M + H]+ 353.1893, found 353.1898.
4-Methyl-1’-((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (24)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3-nitrobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 24 as a yellow solid (77%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.55 (s, 1H), 8.42 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.86 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.19 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.09 (td, J = 11.6, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.20 (m, 1H), 1.13 (qd, J = 12.1, 4.0 Hz, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 148.3, 138.8, 133.0, 130.4, 127.1, 122.6, 61.2, 49.5, 46.1, 34.5, 31.0, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26N3O4S [M + H]+ 368.1639, found 368.1630.
3-((4-Methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)aniline (25)
This compound was prepared as a yellow gel (55%) by hydrogenation of 24 in the same manner as for the preparation of 10. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.24 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (dddd, J = 23.6, 8.1, 2.0, 1.0 Hz, 2H), 3.76 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 3.29 (p, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 2.83 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (td, J = 12.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.23–2.07 (m, 3H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 1.62 (dd, J = 13.3, 3.5 Hz, 2H), 1.52 (qd, J = 12.3, 4.1 Hz, 2H), 1.40–1.23 (m, 2H), 1.16 (qd, J = 12.1, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ 149.1, 136.3, 129.3, 118.5, 115.4, 112.5, 61.2, 49.1, 45.9, 33.7, 30.7, 26.9, 20.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H27N3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 360.1716, found 360.1703.
4-Methyl-1’-(m-tolylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (26)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 26 as a yellow solid (86%); mp 90–93 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.62–7.43 (m, 2H), 7.41–7.31 (m, 2H), 3.81 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.34–2.06 (m, 5H), 1.85 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.68–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.13 (m, 3H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.2, 135.8, 133.5, 128.8, 127.9, 124.8, 61.6, 49.4, 46.0, 34.1, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7, 21.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H29N2O2S [M + H]+ 337.1944, found 337.1937.
4-Methyl-1’-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (27)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 27 as a pink solid (90%); mp 123–125 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.92 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.83 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.27 (tt, J = 11.8, 3.7 Hz, 3H), 2.19–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.48 (m, 4H), 1.35–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.18 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.6, 131.8 (q, J = 33.4 Hz), 130.8, 129.9, 129.4 (q, J = 3.5 Hz), 124.5 (q, J = 3.7 Hz), 121.8, 61.3, 49.4, 46.0, 34.2, 30.8, 27.2, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H26F3N2O2S [M + H]+ 391.1661, found 391.1666.
1’-((3-Chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (28)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3-chlorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 28 as a yellow solid (74%); mp 122–124 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (td, J = 11.8, 2.5 Hz, 3H), 2.15 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.56 (m, 4H), 1.40–1.14 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 138.0, 135.3, 132.8, 130.3, 127.5, 125.7, 61.4, 49.4, 46.1, 34.2, 30.8, 27.2, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26ClN2O2S [M + H]+ 357.1398, found 357.1386.
1’-((3-Bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (29)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3-bromobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 29 as a white solid (65%); mp 125–126 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.66 (dd, J = 13.3, 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.37 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 3.80 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.16 (dt, J = 73.4, 11.4 Hz, 5H), 1.81 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 1.60 (td, J = 12.4, 8.1 Hz, 4H), 1.34–1.22 (m, 1H), 1.20–1.02 (m, 2H), 0.85 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 138.2, 135.7, 130.5, 130.3, 126.1, 123.1, 61.3, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.4, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26BrN2O2S [M + H]+ 401.0893, found 401.0886.
1’-((2-Bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (30)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-bromobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 30 as a white solid (>95%); mp 82– 84 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.05 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.70 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (dtd, J = 24.2, 7.5, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 2.91–2.62 (m, 4H), 2.33 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.80 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 1.65–1.50 (m, 4H), 1.35–1.22 (m, 1H), 1.15 (qd, J = 12.2, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 138.0, 135.7, 133.5, 132.2, 127.4, 120.4, 61.7, 49.5, 45.6, 34.6, 31.0, 27.8, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H26BrN2O2S [M + H]+ 401.0893, found 401.0891.
1’-((3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (31)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3,4-dimethoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 31 as a white solid (78%); mp 132–134 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.34 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 3.91 (s, 3H), 3.90 (s, 3H), 3.80 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.30–2.04 (m, 5H), 1.82 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 12.1, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H), 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 152.5, 148.9, 127.8, 121.5, 110.5, 110.1, 61.5, 56.2, 56.1, 49.5, 46.2, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H31N2O4S [M + H]+ 383.1999, found 383.1991.
1’-((2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (32)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,5-dimethoxybenzenesulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 32 as a white solid (95%); mp 75–78 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39 (d, J = 3.1 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (dd, J = 9.0, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.57 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.27 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 1H), 2.10 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.77 (d, J = 13.8 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.47 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.22 (m, 1H), 1.21–1.08 (m, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 152.9, 151.0, 127.3, 120.0, 115.9, 113.9, 61.9, 56.6, 56.0, 49.5, 45.9, 34.6, 31.0, 27.9, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H31N2O4S [M + H]+ 383.1999, found 383.1991.
1’-((5-Bromo-2-methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (33)
Reaction of amine 1a with 5-bromo-2-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 33 as a yellow solid (92%); mp 98–102 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.01 (d, J = 2.6, Hz, 1H), 7.59 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 3.96–3.88 (d, J = 13.6 Hz, 2H), 3.90 (s, 3H), 2.84 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 2.64 (td, J = 12.5, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.38 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 2.17 (t, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 1.85 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 1.68–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.40–1.14 (m, 3H), 0.91 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.9, 136.8, 133.8, 128.7, 114.1, 112.3, 61.8, 56.3, 49.5, 45.9, 34.6, 31.0, 28.0, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H27BrN2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 453.0818, found 453.0805.
1’-((2-Methoxy-4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (34)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-methoxy-4-methylphenylsulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 34 as a yellow solid (88%); mp 95–98 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.70 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.85–6.69 (m, 2H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.78 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 2H), 2.54 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 2.27 (tt, J = 11.8, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (td, J = 11.5, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 1.78 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.47 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.22–1.08 (m, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.8, 145.5, 131.6, 123.5, 121.0, 112.9, 61.9, 55.8, 49.5, 45.9, 34.5, 31.0, 27.9, 21.9, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H31N2O3S [M + H]+ 367.2050, found 367.2061.
4-Methyl-1’-((4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (35)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 35 as a yellow solid (86%); mp 175–178 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.15 (s, 1H), 8.08 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.38 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.25 (tt, J = 11.4, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.4, 2.6 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.73–1.56 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 11.7, 3.5 Hz, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.0, 141.4, 132.2, 127.1 (q, J = 5.2 Hz), 125.9,124.7 (d, J = 35.3 Hz). 121.1 (d, J = 274.2 Hz), 61.0, 49.5, 46.0, 34.5, 30.9, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H25F3N3O4S [M + H]+ 436.1512, found 436.1515.
4-Methyl-2-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)benzonitrile (36)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-cyano-5-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 36 as a light pink solid (94%); mp 118–121 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 3.92 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (t, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 2.47 (s, 3H), 2.31 (t, J = 11.7 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 14.5 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.17 (q, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 144.4, 140.3, 135.4, 133.2, 130.8, 116.5, 107.8, 61.5, 49.5, 45.8, 34.5, 31.0, 27.5, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H28N3O2S [M + H]+ 362.1897, found 362.1885.
1’-((3,4-Dimethylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (37)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3,4-dimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 37 as a yellow solid (89%); mp 87–89 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.47 (s, 1H), 7.45 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.30 (s, 6H), 2.16 (m, 5H), 1.82 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.17 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.6 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.2, 137.7, 133.1, 130.1, 128.4, 125.3, 61.5, 49.4, 46.2, 34.4, 30.9, 27.2, 21.8, 19.9, 19.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H31N2O2S [M + H]+ 351.2101, found 351.2091.
1’-((4-Bromo-2-ethylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (38)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-bromo-2-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 38 as a white solid (92%); mp 87–91 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.73 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.75 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.96 (q, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.83 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.60 (td, J = 12.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.40–2.27 (m, 1H), 2.20–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.68–1.48 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.13 (m, 6H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 145.2, 134.8, 133.9, 131.7, 129.0, 127.8, 61.6, 49.5, 45.1, 34.4, 30.9,27.7, 25.9, 21.8, 15.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H30Br N2O2S [M + H]+ 429.1206, found 429.1202.
1’-((4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (39)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 39 as a light brown solid (>95%); mp 118–120 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03 (s, 1H), 7.84 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 2H), 2.37–2.18 (m, 3H), 2.12 (td, J = 11.5, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.17 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.3, 135.7, 132.4, 131.7, 129.5 (q, J = 32.6 Hz), 126.7 (q, J = 5.3 Hz), 122.0 (q, J = 274.1 Hz), 61.3, 49.4, 45.9, 34.1, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H25ClF3N2O2S [M + H]+ 425.1261, found 425.1272.
1’-((3,4-Dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (40)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3,4-dichlorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 40 as a light brown solid (86%); mp 160–162 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.81 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.44 (m, 2H), 3.81 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.29 (td, J = 11.9, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.20 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.10 (td, J = 11.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.62 (ddt, J = 16.3, 12.5, 5.6 Hz, 4H), 1.36–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.15 (qd, J = 11.8, 11.2, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.5, 136.2, 133.8, 131.1, 129.4, 126.6, 61.3, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H25Cl2N2O2S [M + H]+ 391.1008, found 391.1018.
1’-((2,4-Dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (41)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,4-dichlorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 41 as a light orange solid (88%); mp 75–78 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.94 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.71 (td, J = 12.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.37 (tt, J = 11.7, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.14 (td, J = 11.0, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.67–1.47 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.25–1.11 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.2, 135.2, 133.2, 132.9, 131.8, 127.2, 61.6, 49.5, 45.6, 34.4, 30.9, 27.8, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H25Cl2N2O2S [M + H]+ 391.1008, found 391.1013.
1’-((3,5-Dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (42)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3,5-dichlorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 42 as a pink solid (92%); mp 128–131 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.61 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 7.57 (t, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 3.92–3.76 (m, 2H), 2.83 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 2H), 2.47–2.25 (m, 3H), 2.17 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.90 (d, J = 14.2 Hz, 2H), 1.65 (td, J = 12.6, 4.1 Hz, 4H), 1.37–1.27 (m, 1H), 1.27–1.13 (m, 2H), 0.90 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.3, 136.1, 132.7, 125.8, 61.3, 49.5, 46.0, 34.2, 30.8, 27.2, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H25Cl2N2O2S [M + H]+ 391.1008, found 391.1001.
1’-((4-Bromo-3-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (43)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-bromo-3-chlorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 43 as a white solid (95%); mp 169–171 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.87–7.70 (m, 2H), 7.46 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 2.29 (t, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.20 (tt, J = 11.5, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 2.15–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.74–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.22–1.07 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 136.9, 135.8, 134.4, 129.1, 127.9, 126.6, 61.3, 49.5, 46.1, 34.6, 31.0, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H25ClBrN2O2S [M + H]+ 435.0503, found 435.0515.
1’-((2,4-Difluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (44)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,4-difluorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 44 as a white solid (88%); mp 165–168 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.89–7.73 (m, 2H), 7.63 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (td, J = 8.7, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 7.05–6.83 (m, 2H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.31 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.27–2.17 (m, 1H), 2.12 (td, J = 11.6, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.24–1.09 (m, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.9 (dd, J = 251.0, 11.9 Hz), 159.8 (dd, J = 251.8, 11.9 Hz), 139.4 (d, J = 1.6 Hz), 135.4, 131.5 (dd, J = 9.6, 4.6 Hz), 129.4 (d, J = 3.1 Hz), 127.9, 123.5 (dd, J = 13.3, 3.9 Hz), 112.0 (dd, J = 21.3, 3.8 Hz), 104.7 (t, J = 10.0 Hz), 61.4, 49.5, 46.2, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. MS (ESI) calcd for C17H25F2N2O2S [M + H]+ 359.2, found 359.2.
1’-((4-Bromo-2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (45)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-bromo-2-(trifluoromethoxy)benzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 45 as a yellow solid (67%); mp 108–110 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.83 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 7.58–7.45 (m, 2H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (dt, J = 11.9, 3.3 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (td, J = 12.5, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.29 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (dt, J = 12.7, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.45 (m, 4H), 1.40–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.23–1.05 (m, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 146.2, 132.7, 130.1, 129.8, 127.9, 123.90, 121.3, 61.5, 49.5, 45.7, 34.59, 31.0, 27.8, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H25BrF3N2O3S [M + H]+ 485.0716, found 485.0724.
1’-((5-Isopropyl-4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (46)
Reaction of amine 1a with 5-isopropyl-4-methoxy-2-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 46 as a brown solid (94%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.65 (s, 1H), 6.71 (s, 1H), 3.88–3.84 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.02 (p, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.51 (td, J = 12.5, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.34–2.26 (m, 1H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 2.15 (td, J = 11.4, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.80 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 1.67–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.11 (m, 3H), 1.16 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 6H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 154.3, 142.3, 139.1, 128.0, 123.8, 114.1, 62.0, 56.0, 49.4, 45.8, 34.3, 30.9, 28.7, 27.7, 23.2, 21.8, 19.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C22H37N2O3S [M + H]+ 409.2519, found 409.2511.
1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (47)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 47 as a yellow solid (>95%); mp 62–65 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 3.62 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 2.85 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.34 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 1H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 2.12 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 2H), 1.63 (d, J = 13.4 Hz, 2H), 1.50 (qd, J = 12.3, 4.0 Hz, 2H), 1.39–1.27 (br, 1H), 1.27–1.13 (m, 2H), 0.90 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 140.4, 131.8, 131.7, 61.8, 49.6, 44.0, 34.6, 31.0, 27.7, 22.8, 21.9, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H33N2O2S [M + H]+ 365.2257, found 365.2252.
1’-((2,4-Dichloro-5-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (48)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,4-dichloro-5-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 48 as a white solid (83%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.49 (s, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 2.82 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.71 (td, J = 12.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 2.36–2.26 (m, 1H), 2.15 (t, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.65–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.39–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.06 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.3, 135.5, 134.6, 133.6, 132.0, 129.9, 61.7, 49.5, 45.6, 34.5, 31.0, 27.7, 21.8, 19.6. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H27Cl2N2O2S [M + H]+ 405.1165, found: 405.1165.
1’-((2,4-Dichloro-6-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (49)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,4-dichloro-6-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 49 as a white solid (93%); mp 89–91 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (dd, J = 2.3, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 2.93–2.73 (m, 4H), 2.67 (s, 3H), 2.45–2.27 (m, 1H), 2.14 (td, J = 11.3, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (dd, J = 12.3, 3.4 Hz, 2H), 1.57 (dtd, J = 24.4, 11.6, 4.0 Hz, 4H), 1.30 (ddt, J = 12.8, 6.4, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 1.18 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.9 Hz, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 143.7, 137.7, 135.3, 134.2, 131.6, 130.2, 61.7, 49.5, 45.0, 34.6, 31.0, 27.9, 24.0, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H27Cl2N2O2S [M + H]+ 405.1165, found 405.1161.
1’-((4-Bromo-3,5-difluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (50)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-bromo-3,5-difluorobenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 50 as a white solid (73%); mp 161–163 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36–7.27 (m, 2H), 3.81 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.34 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (tt, J = 11.4, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.10 (td, J = 11.5, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.85 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 11.8, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.9 (dd, J = 255.0, 3.8 Hz), 137.9 (t, J = 7.6 Hz), 111.0 (m), 103.9, 103.7 (t, J = 96.4 Hz), 61.2, 49.5, 46.1, 34.5, 31.0, 27.4, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H24BrF2N2O2S [M + H]+ 437.0704, found 437.0695.
1’-([1,1’-Biphenyl]-2-ylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (51)
Reaction of amine 1a with [1,1’-biphenyl]-2-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 51 as a yellow solid (>95%); mp 106–109 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.12 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (td, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.46 (td, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.43–7.36 (m, 5H), 7.30 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 3.29 (d, J = 12.8, 2H), 2.71 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (td, J = 12.6, 2.5 Hz, 3H), 2.09 (t, J = 10.4 Hz, 2H), 1.90–1 49 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.13 (m, 5H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.6, 139.7, 137.1, 133.0, 132.2, 130.3, 129.6, 127.7, 127.5, 61.7, 49.3, 44.4, 34.4, 31.0, 27.2, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H31N2O2S [M + H]+ 399.2101, found: 399.2101.
1’-((4’-Chloro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-2-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (52)
Reaction of 30 with 4-chlorophenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 52 as a black gel (66%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.08 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (td, J = 7.5, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (td, J = 7.8, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (s, 4H), 7.26 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 3.32 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.70 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.36–2.15 (m, 3H), 2.08 (td, J = 11.7, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.60 (s, 4H), 1.38–1.02 (m, 5H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.3, 138.1, 137.0, 133.8, 132.8, 132.4, 131.0, 130.3, 127.8, 127.6, 61.5, 49.3, 44.6, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. LC-MS (ESI) calcd for C23H30ClN2O2S [M + H]+ 433.2, found 433.2.
1’-((4’-Methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-2-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (53)
Reaction of 30 with (4-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 53 as a black gel (59%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.08 (dd, J = 7.9, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (td, J = 7.5, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.44–7.40 (m, 1H), 7.35–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.23 (m, 1H), 6.93–6.87 (m, 2H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.31 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 2.68 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.34–2.12 (m, 3H), 2.06 (td, J = 11.6, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 1.57 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 4H), 1.39–1.01 (m, 5H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.2, 141.4, 137.1, 133.2, 132.2, 132.0, 130.9, 130.3, 128.5, 128.4, 127.2, 112.9, 61.6, 55.3, 49.3, 44.6, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 429.2206, found 429.2199.
4-Methyl-1’-((4’-methyl-[1,1’-biphenyl]-2-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (54)
Reaction of 30 with p-tolylboronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 54 as a brown gel (23%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.08 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (td, J = 7.5, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (td, J = 7.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 3H), 7.18 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 3.33 (d, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H), 2.84 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 2.43 (t, J = 12.6 Hz, 1H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 2.22 (td, J = 12.6, 2.4 Hz, 4H), 1.76–1.58 (m, 4H), 1.47–1.19 (m, 5H), 0.90 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.7, 137.5, 136.9, 136.7, 133.1, 132.3, 130.2, 129.4, 128.2, 127.3, 62.0, 49.1, 44.2, 33.4, 30.6, 26.7, 21.5, 21.2. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O2S [M + H]+ 413.2257, found 413.2264.
4-Methyl-1’-((4’-(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1’-biphenyl]-2-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (55)
Reaction of 30 with (4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 55 as a black solid (12%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.10 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.59 (tt, J = 7.5, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.56–7.49 (m, 3H), 7.29 (dd, J = 7.7, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 3.30 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 2.73 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.31 (td, J = 12.6, 2.4 Hz, 3H), 2.10 (t, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.64 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 4H), 1.35–1.12 (m, 5H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 143.4, 140.1, 136.9, 132.7, 132.5, 130.3, 130.1, 130.0, 129.8, 128.2, 124. 4 (q, J = 3.7 Hz), 61.6, 49.3, 44.5, 34.3, 30.9, 27.1, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H30F3N2O2S [M + H]+ 467.1975, found 467.1967.
1’-([1,1’-Biphenyl]-4-ylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (56)
Reaction of 17 with phenylboronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 56 as a white solid (21%); mp 178–181 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.81 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.64–7.56 (m, 2H), 7.52–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.45–7.37 (m, 1H), 3.90 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.84 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (td, J = 12.1, 2.5 Hz, 3H), 2.20 (t, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.91 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 1.77–1.57 (m, 4H), 1.42–1.12 (m, 3H), 0.90 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 145.6, 139.2, 134.6, 129.1, 129.1, 128.5, 128.2, 127.6, 127.3, 61.6, 49.4, 46.1, 34.1, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H31N2O2S [M + H]+ 399.2101, found 399.2097.
1’-((4’-Chloro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (57)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4’-chloro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 57 as a white solid (87%); mp 205–207 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.88–7.75 (m, 2H), 7.67 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.51 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 2.41–2.02 (m, 5H), 1.83 (dd, J = 12.3, 3.6 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.46 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.05 (m, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 144.2, 137.7, 135.1, 134.7, 129.2, 128.5, 128.3, 127.4, 61.4, 49.5, 46.2, 34.6, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H30ClN2O2S [M + H]+ 433.1711, found 433.1706.
1’-((4’-Methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (58)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4’-methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 58 as a white solid (92%); mp 195–198 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85–7.72 (m, 2H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.04–6.88 (m, 2H), 3.88 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 2.76 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.40–1.95 (m, 5H), 1.83 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.48 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.23–1.04 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 160.0, 145.1, 133.9, 131.6, 128.4, 128.2, 126.9, 114.5, 61.5, 55.4, 49.5, 46.2, 34.6, 31.0, 27.4, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 429.2206, found 429.2203.
1’-((2’-Methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (59)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2’-methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 59 as a colorless gel (88%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.74 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.07–6.91 (m, 2H), 3.86 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (tt, J = 11.6, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (t, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 1.73–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.16 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.3, 143.2, 134.2, 130.7, 130.0, 129.8, 128.6, 127.3, 121.0, 111.3, 61.4, 55.5, 49.4, 46.1, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 429.2206, found 429.2205.
1’-((2’-Fluoro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (60)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2’-fluoro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 60 as a colorless gel (73%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85–7.76 (m, 2H), 7.72–7.64 (m, 2H), 7.42 (td, J = 7.7, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.39–7.33 (m, 1H), 7.24 (dd, J = 6.3, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.22–7.12 (m, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.42–2.17 (m, 3H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 13.6 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.24–1.09 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.6 (d, J = 249.1 Hz), 140.3 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 135.2, 130.6 (d, J = 3.1 Hz), 130.2 (d, J = 8.3 Hz), 129.5 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 127.8, 127.2 (d, J = 13.0 Hz), 124.7 (d, J = 3.7 Hz), 116.3 (d, J = 22.6 Hz), 61.4, 49.4, 46.2, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H30FN2O2S [M + H]+ 417.2007, found 417.1995.
1’-([1,1’-Biphenyl]-3-ylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (61)
Reaction of 29 with phenylboronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 61 as a black gel (58%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.94 (t, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (ddd, J = 7.8, 1.9, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (ddd, J = 7.8, 1.8, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.55 (m, 3H), 7.50–7.43 (m, 1H), 7.43–7.36 (m, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.20 (td, J = 8.1, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.37–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.17 (qd, J = 12.1, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.3, 139.2, 136.7, 131.3, 129.4, 129.1, 128.3, 127.2, 126.2, 126.1, 61.4, 49.4, 46.2, 34.4, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H31N2O2S [M + H]+ 399.2101, found 399.2096.
1’-((4’-Chloro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (62)
Reaction of 29 with 4-chlorophenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 62 as a pink solid (58%); mp 124–126 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.89 (t, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (ddt, J = 15.7, 7.9, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.54–7.48 (m, 2H), 7.45–7.39 (m, 2H), 3.86 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (dt, J = 11.5, 3.1 Hz, 2H), 2.27 (td, J = 12.1, 2.4 Hz, 3H), 2.13 (t, J = 10.6 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.14 (m, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.1, 137.6, 136.9, 134.5, 131.1, 129.6, 129.2, 128.5, 126.5, 125.8, 61.5, 49.4, 46.1, 34.2, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H30ClN2O2S [M + H]+ 433.1711, found 433.1705.
1’-((4’-Methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (63)
Reaction of 29 with (4-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 63 as a yellow solid (44%); mp 107–109 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.58–7.47 (m, 3H), 6.98 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 2.80 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.27 (td, J = 12.0, 2.4 Hz, 3H), 2.15 (t, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 1.75–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.19 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.9, 141.9, 136.6, 131.6, 130.8, 129.4, 128.3, 125.6, 125.5, 114.5, 61.5, 55.4, 49.4, 46.1, 34.2, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 429.2206, found 429.2206.
4-Methyl-1’-((4’-methyl-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (64)
Reaction of 29 with p-tolylboronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 64 as a yellow solid (95%); mp 103–105 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 3.87 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.40 (s, 3H), 2.31–2.20 (m, 3H), 2.17 (t, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 1.74–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.40–1.12 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.2, 138.3, 136.6, 136.3, 131.1, 129.8, 129.4, 127.0, 125.9, 125.8, 61.5, 49.4, 46.1, 34.1, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7, 21.1. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O2S [M + H]+ 413.2257, found 413.2258.
1’-((4’-Fluoro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (65)
Reaction of 29 with (4-fluorophenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 65 as a white solid (63%); mp 131–134 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.76–7.66 (m, 2H), 7.60–7.50 (m, 3H), 7.14 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 3.86 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (td, J = 12.1, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.18 (tt, J = 11.5, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.09 (td, J = 11.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.20 (m, 1H), 1.21–1.06 (m, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.94 (d, J = 248.1 Hz), 141.27, 136.89, 135.39 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 131.11, 129.53, 128.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz), 126.26, 125.88, 116.02 (d, J = 21.6 Hz), 61.40, 49.47, 46.20, 34.58, 31.01, 27.36, 21.86. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H30FN2O2S [M + H]+ 417.2007, found 417.2018.
1’-((2’-Methoxy-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (66)
Reaction of 29 with (2-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 66 as an orange gel (53%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.73 (dt, J = 7.8, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (dt, J = 8.0, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.39–7.27 (m, 2H), 7.08–6.94 (m, 2H), 3.86 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.43–2.17 (m, 3H), 2.13 (t, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.52 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.24–1.10 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.3, 139.5, 135.5, 133.7, 130.7, 129.6, 128.7, 128.6, 128.5, 125.8, 121.0, 111.3, 61.5, 55.5, 49.4, 46.2, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H33N2O3S [M + H]+ 429.2206, found 429.2192.
1’-((2’-Fluoro-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (67)
Reaction of 29 with (2-fluorophenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 67 as a yellow gel (74%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.89 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.79–7.68 (m, 2H), 7.57 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (td, J = 7.7, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.38–7.31 (m, 1H), 7.25–7.18 (m, 1H), 7.14 (ddd, J = 10.8, 8.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 3.86 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 2.29 (td, J = 12.1, 2.5 Hz, 3H), 2.21–2.08 (m, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.46 (m, 4H), 1.39–1.05 (m, 3H), 0.86 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.58 (d, J = 248.6 Hz), 136.83, 136.38, 133.19 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 132.03 (d, J = 9.9 Hz), 130.55 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 130.06 (d, J = 8.3 Hz), 129.15, 127.94 (d, J = 3.1 Hz), 126.64, 124.69 (d, J = 3.7 Hz), 116.27 (d, J = 22.5 Hz), 61.50, 49.38, 46.06, 34.11, 30.78, 27.10, 21.71. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H30FN2O2S [M + H]+ 417.2007, found 417.1999.
4-Methyl-1’-((2’-(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (68)
Reaction of 29 with (2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 68 as a yellow solid (37%); mp 110–112 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.80–7.68 (m, 3H), 7.61–7.47 (m, 4H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.82 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.35–2.18(m, 3H), 2.13 (td, J = 11.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.25–1.12 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.7, 139.3 (q, J = 2.1 Hz), 135.8, 133.2, 131.8, 131.7, 128.6, 128.2, 128.1 (q, J = 1.6 Hz), 126.9, 126.2 (q, J = 5.3 Hz), 124.0 (q, J = 274.0 Hz), 61.5, 49.4, 46.1, 34.3, 30.9, 27.2, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H30F3N2O2S [M + H]+ 467.1975, found 467.1981.
1’-((3’,5’-Dimethyl-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (69)
Reaction of 29 with (3,5-dimethylphenyl)boronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 69 as a yellow solid (45%); mp 120–123 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.77 (dt, J = 7.7, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (dd, J = 7.8, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (s, 2H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 3.86 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 2.37 (s, 6H), 2.33–2.16 (m, 3H), 2.11 (t, J = 11.1 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (dt, J = 12.2, 3.1 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.39–1.08 (m, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 139.2, 138.7, 136.5, 131.3, 129.9, 129.3, 126.1, 125.1, 61.4, 49.4, 46.2, 34.4, 30.9, 27.2, 21.8, 21.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C25H35N2O2S [M + H]+ 427.2414, found 427.2407.
4-Methyl-1’-((3-(naphthalen-2-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (70)
Reaction of 29 with naphthalen-2-ylboronic acid (Procedure C) yielded 70 as a yellow gel (29%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.06 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 2H), 7.96–7.82 (m, 4H), 7.72 (ddd, J = 10.5, 8.2, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 7.62 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.56–7.47 (m, 2H), 3.90 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.38–2.20 (m, 3H), 2.13 (t, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 1.74–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.39–1.13 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.2, 136.8, 136.5, 133.5, 132.9, 131.5, 129.6, 128.9, 128.3, 127.7, 126.7, 126.6, 126.3, 126.3, 125.0, 61.5, 49.4, 46.2, 34.3, 30.9, 27.2, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C27H33N2O2S [M + H]+ 449.2257, found 449.2254.
4-Methyl-1’-(pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (71)
Reaction of amine 1a with pyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 71 as a yellow solid (86%); mp 144–147 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.98 (s, 1H), 8.82 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (dd, J = 8.0, 4.9 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (td, J = 12.0, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (tt, J = 11.6, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (t, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.75–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.17 (qd, J = 12.0, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 153.3, 148.4, 135.2, 133.1, 123.7, 61.3, 49.5, 46.0, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H25ClN3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 346.1560, found 346.1566.
1’-((2-Chloropyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (72)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-chloropyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 72 as a white solid (71%); mp 122–124 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.55 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 8.38 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 7.8, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 3.92 (d, J = 13.0 Hz, 2H), 2.83 (t, J = 12.5 Hz, 4H), 2.38 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 1H), 2.15 (t, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 1.86 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H)., 1.72–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.26 (m, 1H), 1.25–1.13 (m, 2H), 0.90 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 148.4, 144.5, 136.9, 130.5, 118.5, 57.6, 45.6, 41.9, 30.7, 27.1, 24.0, 17.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H24ClN3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 380.1170, found 380.1160.
1’-((2-Fluoropyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (73)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-fluoropyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 73 as a white solid (>95%); mp 120–123 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.41 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 8.29 (dd, J = 9.2, 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (dd, J = 7.6, 4.9 Hz, 1H), 3.96 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H),, 2.67 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.34 (ddd, J = 11.5, 8.0, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.15 (t, J = 10.4 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.74–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.32 (ddt, J = 10.3, 6.9, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 1.27–1.11 (m, 2H), 0.91 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 154.75 (d, J = 244.0 Hz), 147.68 (d, J = 14.3 Hz), 138.2, 118.2, 117.9, 57.5, 45.6, 41.9, 30.7, 27.1, 23.8, 17.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H24FN3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 364.1465, found 364.1462.
1’-((6-Chloropyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (74)
Reaction of amine 1a with 6-chloropyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 74 as a white solid (80%); mp 178–182 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.75 (s, 1H), 7.99 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.51 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 2.35 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.25 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 2.14 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.89 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.75–1.58 (m, 4H), 1.33 (br, 1H), 1.28–1.10 (m, 2H), 0.91 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.6, 148.6, 137.7, 132.1, 124.7, 61.3, 49.5, 46.0, 34.4, 30.9, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H24ClN3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 380.1170, found 380.1171.
1’-((5-Bromopyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (75)
Reaction of amine 1a with 5-bromopyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 75 as a white solid (79%); mp 171–173 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.81 (s, 2H), 8.18 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.39 (td, J = 12.0, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.25 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 1H), 2.14 (t, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.90 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 1.78–1.57 (m, 4H), 1.43–1.29 (m, 1H), 1.28–1.11 (m, 2H), 0.91 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 154.4, 146.2, 137.4, 134.5, 121.0, 61.2, 49.5, 46.0, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H24BrN3O2SNa [M + Na]+ 424.0665, found 424.0668.
1,3-Dimethyl-5-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione (76)
Reaction of amine 1a with 1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 76 as a white solid (78%); mp 212–215 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.07 (s, 1H), 3.94 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 3.50 (s, 3H), 3.35 (s, 3H), 2.93 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.85 (t, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 2.56 (t, J = 11.7 Hz, 1H), 2.26 (t, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.92 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.75–1.58 (m, 4H), 1.48–1.20 (m, 3H), 0.93 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 158.2, 150.8, 148.1, 112.6, 61.6, 49.2, 46.0, 37.9, 33.8, 30.7, 28.3, 27.5, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H28N4O4SNa [M + Na]+ 407.1723, found 407.1725.
4-Methyl-1’-((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (77)
Reaction of amine 1a with 1-methyl-1H-imidazole-2-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 77 as a white solid (51%); mp 153–156 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.03 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 3.96 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 3.05 (t, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 2.89 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 2.54 (s, 1H), 2.24 (s, 2H), 1.94 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 1.81–1.58 (m, 4H), 1.31 (s, 3H), 1.06–0.79 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.8, 128.2, 124.4, 61.8, 49.4, 46.6, 34.8, 34.1, 30.9, 27.3, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C15H26N4O2SNa [M + Na]+ 349.1669, found 349.1673.
4-Methyl-1’-((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (78)
Reaction of amine 1a with 1-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 78 as a yellow solid (61%); mp 139–142 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.48 (s, 1H), 7.42 (s, 1H), 3.90 (d, J = 13.0 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 2.80 (d, J = 9.9 Hz, 2H), 2.57 (t, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.26 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 1H), 2.13 (t, J = 10.5 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.57 (m, 4H), 1.31 (br, 1H), 1.26–1.12 (m, 2H), 0.90 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.0, 138.3, 124.4, 61.7, 49.5, 46.3, 34.6, 34.0, 31.1, 27.4, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C15H26N24O2SNa [M + Na]+ 349.1669, found 349.1660.
3,5-Dimethyl-4-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)isoxazole (79)
Reaction of amine 1a with 3,5-dimethylisoxazole-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 79 as a white solid (28%); mp 158–161 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.78 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.61 (s, 3H), 2.50 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 2.27 (tt, J = 11.4, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.14–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.50 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.25–1.09 (m, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.5, 158.0, 113.7, 61.3, 49.6, 45.4, 34.6, 31.0, 27.5, 21.9, 13.0, 11.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H28N3O3S [M + H]+ 342.1846, found 342.1854.
2-Chloro-5-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)thiazole (80)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-chlorothiazole-5-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 80 as a pale yellow solid (51%); mp 141–143 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.87 (s, 1H), 3.82 (d, J = 10.4 Hz, 2H), 2.83 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 2.45 (td, J = 12.3, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 2.16 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.92 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.74–1.56 (m, 4H), 1.39–1.13 (m, 3H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 157.2, 144.9, 134.4, 61.2, 49.5, 46.0, 34.2, 30.8, 27.1, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C14H22ClN3O2S2Na [M + Na]+ 386.0734, found 386.0745.
2-Chloro-4-methyl-5-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)thiazole (81)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2-chloro-4-methylthiazole-5-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 81 as a white solid (64%); mp 117–119 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.85 (d, J = 13.5 Hz, 2H), 2.82 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.60 (s, 3H), 2.53 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.34 (t, J = 11.9 Hz, 1H), 2.15 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 1.91 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 1.65 (m, 4H), 1.45–1.29 (m, 1H), 1.28–1.12 (m, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.4, 154.4, 128.9, 61.3, 49.5, 46.0, 34.3, 30.9, 27.3, 21.8, 16.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C15H25ClN3O2S2 [M + H]+ 378.1071, found 378.1060.
2-Chloro-4-cyclopropyl-5-((4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)thiazole (82)
2-Chloro-4-cyclopropylthiazole (0.3531 g, 2.21 mmol; see SI for synthesis) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (7 mL) at −78 °C, followed by dropwise addition of n-BuLi (2.5 M in hexane, 1.0 mL, 2.50 mmol) under argon in 10 min. The solution mixture was stirred for 20 min at −78 °C and anhydrous SO2 gas (generated from dropwise addition of sodium sulfite to concentrated aq. HCl; the generated SO2 gas was passed through concentrated H2SO4) was bubbled through the reaction solution at −78 °C for 10 min and then at room temperature for 1 h. Upon the evaporation of solvents, the residue was dissolved in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (6 mL) and NCS (0.4726 g, 3.54 mmol) was added. The resulting suspension was stirred at room temperature for 16 h. The suspension was then filtered and the filtrate was concentrated to about 10 mL, followed by addition of DIPEA (1.0 mL, 5.75 mmol) and 4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine 1a (0.4998 g, 2.75 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5.5 h and then poured into saturated NaHCO3 solution (60 mL). The biphasic solution was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 60 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified through flash chromatography on silica gel (1:19 CH3OH/CH2Cl2), followed by recrystallization from a mixture of CH2Cl2 and hexane to afford the desired product as a yellow solid (0.5398 g, 60% over two steps); mp 139–141 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.85 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.62–2.44 (m, 3H), 2.31 (tt, J = 11.6, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (td, J = 11.6, 2.6 Hz, 2H), 1.88 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.24 (m, 1H), 1.18 (qd, J = 11.8, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 1.11–0.99 (m, 4H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.2, 154.6, 126.3, 61.2, 49.4, 46.1, 34.4, 30.9, 27.3, 21.8, 11.4, 10.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H27ClN3O2S2 [M + H]+ 404.1228, found 404.1226.
1’-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-4-ylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (83)
Reaction of amine 1a with benzo[d][1,3]dioxole-4-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 83 as a yellow solid (86%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.12 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 6.89 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.06 (s, 2H), 3.88 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.43 (td, J = 12.3, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (tt, J = 11.6, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.13 (td, J = 11.6, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 14.8 Hz, 2H), 1.71–1.50 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.19 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 148.9, 145.2, 121.7, 121.5, 118.8, 112.5, 102.2, 61.6, 49.4, 45.9, 34.3, 30.9, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H27N2O4S [M + H]+ 367.1686, found 367.1686.
1’-((3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (84)
Reaction of amine 1a with benzo[d][1,3]dioxole-5-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 84 as a light orange solid (82%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.28 (dt, J = 8.2, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (t, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.05 (s, 2H), 3.78 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.30–2.04 (m, 5H), 1.82 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.53 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.23 (m, 1H), 1.22–1.08 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 151.3, 148.1, 129.3, 123.2, 108.2, 107.9, 102.3, 61.5, 49.5, 46.2, 34.5, 31.0, 27.3, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H27N2O4S [M + H]+ 367.1681, found 367.1686.
4-Methyl-1’-((2,2,4,6,7-pentamethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)sulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (85)
Reaction of amine 1a with 2,2,4,6,7-pentamethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 85 as a pale yellow oil (95%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.63 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.97 (s, 2H), 2.89 (br, 2H), 2.75 (dt, J = 12.0, 4.0 Hz, 2H), 2.50 (s, 3H), 2.46 (s, 3H), 2.41 (br, 1H), 2.14 (br, 2H), 2.10 (s, 3H), 1.90 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 1.64 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 1.58–1.43 (m, 2H), 1.48 (s, 6H), 1.40–1.08 (m, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.9, 140.8, 135.3, 125.8, 125.0, 117.9, 86.8, 61.9, 49.6, 43.9, 43.1, 34.5, 31.0, 28.6, 27.7, 21.8, 19.2, 17.6, 12.5. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C24H39N2O3S [M + H]+ 435.2676, found 435.2664.
1’-((5-Bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (86)
Reaction of amine 1a with 5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 86 as a white solid (86%); mp 128–132 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.62 (s, 1H), 7.43 (s, 1H), 4.70 (t, J = 8.9 H z, 2H), 3.89 (d, J = 12.3Hz, 2H), 3.24 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.50 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.27 (tt, J = 11.7, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 1.67–1.51 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.25 (m, 1H), 1.17 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.4, 132.3, 132.2, 130.7, 121.0, 111.8, 73.0, 61.7, 49.5, 46.0, 34.6, 31.0, 29.0, 27.6, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H28Br N2O3S [M + H]+ 443.0999, found 443.0989.
4-Methyl-1’-(naphthalen-1-ylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (87)
Reaction of amine 1a with naphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 87 as a yellow gel (79%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.74 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.69–7.44 (m, 3H), 3.91 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 2.53 (td, J = 12.3, 2.1 Hz, 2H), 2.20 (tt, J = 11.3, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.06 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.80 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.65–1.43 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.21 (m, 1H), 1.22–1.06 (m, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 134.3, 133.0, 130.4, 128.9, 128.8, 128.0, 126.8, 125.2, 124.1, 61.5, 49.5, 45.5, 34.6, 31.0, 27.7, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) (ESI) calcd for C21H28N2O2S [M + H]+ 373.1950, found: 373.1944.
1’-((4-Chloronaphthalen-1-yl)sulfonyl)-4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (88)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-chloronaphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 88 as a white solid (71%); mp 129–132 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.80–8.72 (m, 1H), 8.43–8.36 (m, 1H), 8.11 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.69 (dd, J = 6.6, 3.3 Hz, 2H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.55 (td, J = 12.2, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.23 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 2.06 (t, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.81 (d, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H), 1.66–1.45 (m, 4H), 1.35–1.21 (m, 1H), 1.15 (dd, J = 13.4, 9.6 Hz, 2H), 0.87 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 138.4, 132.3, 131.5, 130.1, 130.0, 128.7, 127.9, 125.7, 125.4, 124.6, 61.5, 49.5, 45.5, 34.5, 31.0, 27.7, 21.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H28ClN2O2S [M + H]+ 407.1555, found: 407.1551.
N-(4-((4-Methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)naphthalen-1-yl)acetamide (89)
Reaction of amine 1a with 4-acetamidonaphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 89 as a yellow solid (64%); mp 113–117 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.51 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.17–8.05 (m, 2H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.57–7.37 (m, 2H), 3.86 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.52 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.36 (t, J = 12.8 Hz, 1H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 2.15 ( t, J = 11.6 Hz, 3H), 1.83 (d, J =13.6 Hz, 2H), 1.66–1.45 (m, 4H), 1.35–1.20 (m, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 169.5, 133.3, 133.2, 130.6, 129.5, 129.4, 128.1, 127.7, 124.3, 123.9,123.4, 61.6, 49.3, 45.3, 33.7, 30.7, 27.2, 24.0, 21.6. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C23H32N3O3S [M + H]+ 430.2159, found: 430.2165.
5-((4-Methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)sulfonyl)isoquinoline (90)
Reaction of amine 1a with isoquinoline-5-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 90 as a white solid (51%); mp 123–126 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.33 (s, 1H), 8.66 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.48 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.36 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.69 (dd, J = 8.2, 7.4 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 2H), 2.51 (td, J = 12.0, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.26–2.15 (m, 1H), 2.12–2.03 (m, 2H), 1.81 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.45 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.20 (m, 1H), 1.19–1.06 (m, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 153.2, 145.1, 134.0, 133.7, 132.6, 131.9, 129.1, 125.8, 117.7, 61.4, 49.9, 45.6, 34.5, 31.0, 27.7, 21.6. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H28N3O2S [M + H]+ 396.1716, found 396.1710.
1’-((4-(Difluoromethoxy)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (91)
Reaction of amine 1b with 4-(difluoromethoxy)benzenesulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 91 as a pale yellow solid (76%); mp 88–91 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.77 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.60 (t, J = 72.6 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 2.85–2.56 (m, 2H), 2.37–2.15 (m, 3H), 2.04 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.78–1.42 (m, 7H), 0.90–0.73 (m, 1H), 0.82 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 154.1, 133.0, 129.8, 119.3, 115.2 (t, J = 262.7 Hz), 61.5, 57.6, 49.5, 46.2, 33.3, 31.5, 27.2, 27.1, 25.9, 19.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H26N2O3F2S [M + H]+ 389.1699, found: 389.1705.
1’-((4-Bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (92)
The synthesis of 92 is described in the Supporting Information. mp 161–164 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.78–7.54 (m, 4H), 3.83 (d, J = 12.0, 2H), 2.83 (dt, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 2.33–2.17 (m, 3H), 2.19 – 2.04 (m, 4H), 1.96 (t, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 1.88–1.73 (m, 4H), 1.64 (qd, J = 12.2, 4.1 Hz, 2H), 1.53–1.37 (m, 1H), 1.37–1.17 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 135.2, 132.3, 129.1, 127.8, 82.7, 69.4, 61.3, 49.2, 46.1, 35.5, 31.9, 27.3, 25.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H26BrN2O2S [M + H]+ 425.0893, found 425.0894.
1’-(Phenylsulfonyl)-2-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (93)
The synthesis of 93 is described in the Supporting Information. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.82–7.70 (m, 2H), 7.63–7.57 (m, 1H), 7.57–7.50 (m, 2H), 3.85 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.78–2.57 (m, 3H), 2.36–2.19 (m, 4H), 1.94 (t, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 1.89–1.39 (m, 9H), 1.35–1.19 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 136.2, 232.7, 129.0, 127.6, 82.1, 70.0, 56.4, 55.5, 46.5, 46.0, 45.2, 31.8, 30.1, 26.0, 24.2, 23.2, 21.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H27N2O2S [M + H]+ 347.1788, found 347.1799.
1’-(Phenylsulfonyl)-4-(2-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)ethyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (94)
To a solution of 2-(1’-(phenylsulfonyl)-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-yl)ethanol (0.0585 g, 0.17 mmol; prepared from 3a with 4-piperidineethanol, see SI) in anhydrous THF (1 mL) was added a suspension of KH (30% in mineral oil, 0.0275 g, 0.21 mmol) in anhydrous THF (0.5 mL) via syringe at room temperature. After stirring for 45 min, propargyl bromide (80% in toluene, 0.038 mL, 0.43 mmol) was added dropwise via syringe, and the solution was stirred at room temperature for 7.5 h. After the evaporation of solvents, the residue was purified by flash chromatography (1/19 CH3OH/CH2Cl2) to afford the desired product 94 as a yellow gel (0.0072 g, 11%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.83–7.69 (m, 2H), 7.63–7.57 (m, 1H), 7.57–7.49 (m, 2H), 4.11 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 2H), 3.95–3.80 (m, 2H), 3.53 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 2.85 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 2.41 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 2.30–2.13 (m, 5H), 1.87 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 1.79–1.59 (m, 4H), 1.52 (q, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 1.45–1.36 (m, 1H), 1.32–1.22 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 136.1, 132.7, 129.0, 127.6, 79.9, 74.2, 67.6, 61.6, 58.1, 49.3, 46.1, 35.9, 32.6, 32.2, 27.1. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H30N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 413.1869, found 413.1863.
1’-(Phenylsulfonyl)-2-(2-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)ethyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (95)
To a solution of 2-(1’-(phenylsulfonyl)-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-2-yl)ethan-1-ol (0.0830 g, 0.24 mmol; prepared from 3a with 2-piperidineethanol, see SI) in anhydrous THF (2 mL) was added NaH (60%, 0.0192 g, 0.48 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction solution was stirred at 0 °C for 15 min and propargyl bromide (80% in toluene, 0.075 ml, 0.67 mmol) was added via syringe. The reaction solution was stirred at 0 °C for another 30 min and was allowed to warm up to room temperature and stirred for 3 h before a second portion of NaH (60%, 0.0175 g, 0.44 mmol) in anhydrous THF (1 mL) was introduced. The reaction solution was then stirred for 18 h at room temperature and water (10 mL) was added to quench the reaction, followed by the extraction with CH2Cl2 (3 × 10 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. After the purification by flash chromatography (1/19 CH3OH/CH2Cl2), the product 95 was obtained as a yellow gel (0.0132 g, 18%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.82–7.69 (m, 2H), 7.64–7.56 (m, 1H), 7.56–7.48 (m, 2H), 4.06 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 3.83 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 3.58–3.37 (m, 2H), 2.73 (dd, J = 39.3, 10.5 Hz, 3H), 2.35 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 2.33–2.16 (m, 3H), 1.88–1.70 (m, 4H), 1.69–1.19 (m, 8H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 136.0, 132.8, 129.1, 127.6, 79.6, 74.4, 67.1, 58.2, 55.5, 55.0, 46.4, 45.9, 45.4, 30.3, 29.8, 29.7, 25.6, 24.2, 23.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H31N2O3S [M + H]+ 391.2050, found 391.2048.
1-(1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-yl)hex-5-yn-2-one (96)
The synthesis of 96 is described in the Supporting Information. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 3.61 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 2.88 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 2.71 (td, J = 12.2, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.63–2.58 (m, 2H), 2.57 (s, 6H), 2.41 (qd, J = 8.4, 7.0, 3.5 Hz, 3H), 2.32 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.19 (t, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.90 (t, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 3H), 1.67 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 2H), 1.49 (qd, J = 12.2, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.34–1.22 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 207.7, 142.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.6, 83.0, 68.7, 61.8, 49.2, 43.9, 41.9, 32.0, 31.7, 27.4, 22.8, 20.9, 12.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C25H37N2O3S [M + H]+ 445.2519, found 445.2524.
1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-3,5-dimethyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (97)
Reaction of 3c with 3,5-dimethylpiperidine (Procedure D) yielded 97 as a colorless oil (37%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.92 (s, 2H), 3.61 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.87–2.66 (m, 4H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.47–2.29 (m, 1H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.82 (d, J = 13.6 Hz, 2H), 1.74–1.39 (m, 7H), 0.81 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 6H), 0.47 (q, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 140.4, 131.8, 131.8, 61.8, 57.2, 44.1, 42.3, 31.4, 27.5, 22.8, 20.9, 19.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H35N2O2S [M + H]+ 379.2414, found 379.2406.
4-Isopropyl-1’-(mesitylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (98)
Reaction of 3c with 4-isopropylpiperidine (Procedure D) yielded 98 as a yellow oil (46%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 3.60 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 2.90 (dd, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.72 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 6H), 2.38–2.29 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 2.06 (t, J = 10.6 Hz, 2H), 1.85 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 1.63 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 2H), 1.49 (td, J = 12.1, 4.1 Hz, 2H), 1.44–1.32 (m, 1H), 1.30–1.14 (m, 2H), 1.01–0.87 (m, 1H), 0.83 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 140.4, 131.8, 131.7, 61.8, 50.0, 44.0, 42.6, 32.4, 29.6, 27.7, 22.8, 20.9, 19.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C22H37N2O2S [M + H]+ 393.2570, found 393.2567.
3-(1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-yl)propanenitrile (99)
Tert-butyl 4-(2-cyanoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (S10, 0.328 g, 1.38 mmol, see SI for synthesis) was stirred with HCl (1 mL) in 1,4-dioxane (4 mL) at room temperature for 2 hours. After the evaporation of the solvents, the 4-(2-cyanoethyl)piperidine hydrochloride acid salt was neutralized by shaking with saturated NaHCO3 solution at 0 °C, followed by extraction with CH2Cl2 (3 × 25 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to provide 3-(piperidin-4-yl)propanenitrile which was used for the next step without further purification. Reaction of the above prepared 3-(piperidin-4-yl)propanenitrile and 1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (3c) (Procedure D) yielded 99 as a white gel. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 3.63 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.90 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (td, J = 12.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.60 (s, 6H), 2.35 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 2.14 (t, J = 9.6 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 1.71 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.34 (m, 5H), 1.27–1.16 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.7, 119.7, 61.8, 49.2, 44.0, 34.8, 31.8, 31.7, 27.6, 22.8, 21.0, 14.6. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C22H34N3O2S [M + H]+ 404.2366, found 404.2361.
2-(1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-yl)ethanol (100)
Reaction of 3c with 4-piperidineethanol (Procedure D) yielded 100 as a white solid (66%); mp 82–85 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.93 (s, 2H), 3.66 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 3.62 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 2.86 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.73 (td, J = 12.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.60 (s, 6H), 2.40–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 2.11 (td, J = 11.6, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 1.69 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H), 1.63 (s, 1H), 1.55–1.33 (m, 5H), 1.21 (qd, J = 11.7, 11.0, 3.8 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 140.4, 131.9, 131.7, 61.8, 60.4, 49.5, 44.0, 39.4, 32.6, 32.5, 27.7, 22.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H35N2O3S [M + H]+ 395.2363, found 395.2365.
1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-ol (101)
To a mixture of [1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-ol (1c, 0.2075 g, 1.13 mmol), and iPr2NEt (0.27 ml, 1.55 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (3 mL) was dropwise added 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (0.2154 g, 0.98 mmol, in 2 mL CH2Cl2) over 10 min. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight and then poured into saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (20 ml). The bi-phasic solution was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 20 ml). The combined organic layers were dried by Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified via flash chromatography (1/19 MeOH/CH2Cl2) to afford the desired product (0.214 g, 65%) as a white solid; mp 120–123 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.92 (s, 2H), 3.74–3.59 (br, 1H), 3.60 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 2.85–2.65 (m, 4H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.46–2.22 (m, 3H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.78 (m, 4H), 1.64–1.30 (m, 5H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.3, 131.9, 131.6, 67.6, 61.4, 46.7, 43.9, 34.5, 27.6, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H31N2O3S [M + H]+ 367.2050, found 367.2058.
1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (102)
Reaction of 3c with piperidine (Procedure D) yielded 102 as a colorless gel (67%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.93 (s, 2H), 3.62 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (t, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.60 (s, 6H), 2.47 (s, 4H), 2.38–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.85 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.52–1.60 (m, 4H), 1.52–1.44 (m, 2H), 1.44–1.37 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 140.4, 131.8, 131.8, 62.2, 50.2, 44.1, 27.5, 26.3, 24.6, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H30N2O2SNa [M + Na]+ 373.1920, found 373.1910.
1-(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)azepane (103)
Reaction of amine hydrochloride salt 1e with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 103 as an orange gel (90%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 3.71 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 3.62 (br, 1H), 3.18–2.89 (br, 4H), 2.77 (t, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 2.10 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 1.82 (s, 4H), 1.76–1.54 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.8, 140.3, 132.0, 132.0, 132.0, 131.5, 63.3, 51.2, 43.8, 26.9, 26.6, 26.4, 22.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H33N2O2S [M + H]+ 365.2257, found 365.2253.
1-((4-Methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl)-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)piperidine (104)
Reaction of amine 1d with 4-methoxybenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 104 as a pale yellow oil (70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.68 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 6.97 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.68 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.51 (s, 4H), 2.36 (dt, J = 12.0, 4.0 Hz, 2H), 2.04–1.86 (m, 3H), 1.75 (s, 4H), 1.61 (q, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.9, 129.8, 127.8, 114.1, 60.8, 55.6, 51.3, 45.0, 30.4, 23.2. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C16H25N2O3S [M + H]+ 325.1580, found 325.1571.
3-(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)-6-methyl-1,3-oxazinane (105)
Reaction of 3c with 4-aminobutan-2-ol (Procedure D) yielded 4-((1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)amino)butan-2-ol as a white solid (82%); mp 105–108 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.95 (s, 2H), 3.96 (ddd, J = 8.9, 5.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 3.55 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 3.05 (dt, J = 11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 2.83 (tt, J = 12.5, 3.3 Hz, 2H), 2.76 (td, J = 11.1, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 2.61 (s, 7H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 1.96 (t, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 1.63 (d, J = 14.9 Hz, 1H), 1.53–1.42 (m, 1H), 1.39–1.27 (m, 2H), 1.16 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.6, 140.4, 131.9, 131.6, 69.5, 54.4, 45.5, 43.1, 43.0, 37.0, 31.8, 31.5, 23.6, 22.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H30N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 377.1869, found 377.1856.
A solution of the above prepared 4-((1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)amino)butan-2-ol (0.119 g, 0.34 mmol), paraformaldehyde (0.0143 g, 0.48 mmol), Mg2SO4 (0.2091 g, 1.74 mmol), and pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate (PPTS) (0.0025 g, 0.01 mmol) in anhydrous toluene (4 mL) was refluxed for 3 h and then cooled to room temperature. The suspension was poured into saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (30 mL) and extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified via flash chromatography (1/19 MeOH/CH2Cl2) to provide the desired product 105 as a colorless gel (0.0555 g, 45%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 4.61 (dd, J = 10.0, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 4.16 (d, J = 10.1 Hz, 1H), 3.63–3.50 (m, 3H), 3.11 (ddt, J = 13.4, 4.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 2.89–2.68 (m, 4H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.92 (dp, J = 12.2, 2.8 Hz, 2H), 1.65–1.29 (m, 4H), 1.15 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.6, 81.6, 73.6, 55.0, 46.5, 43.4, 30.3, 29.8, 29.2, 22.8, 21.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H30N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 389.1869, found 389.1874.
1-(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)-4-methylpiperazine (106)
Reaction of 3c with 1-methylpiperazine (Procedure D) yielded 106 as a colorless gel (74%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 3.59 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 2.73 (t, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.55 (s, 4H), 2.49–2.35 (br, 4H), 2.36–2.29 (s, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 1.84 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.59–1.34 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.4, 131.8, 131.7, 61.2, 55.3, 48.9, 45.9, 43.7, 27.8, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C19H32N3O2S [M + H]+ 366.2210, found 366.2199.
4-(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)morpholine (107)
Reaction of 3c with morpholine (Procedure D) yielded 107 as a colorless gel (74%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.92 (s, 2H), 3.68 (s, 4H), 3.60 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (t, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.50 (s, 4H), 2.27 (s, 4H), 1.87 (d, J = 14.5 Hz, 2H), 1.46 (qd, J = 11.6, 3.4 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.4, 140.4, 131.9, 131.6, 67.1, 61.5, 49.7, 43.6, 27.7, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H29N2O3S [M + H]+ 353.1893, found 353.1889.
4-Benzyl-1’-(mesitylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (108)
Reaction of 3c with 4-benzylpiperidine (Procedure D) yielded 108 as a light brown oil (68%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36–7.22 (m, 2H), 7.21–7.06 (m, 3H), 6.92 (s, 2H), 3.61 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.92 (s, 2H), 2.72 (td, J = 12.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.50 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 2.40–2.26 (br, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 2.08 (t, J = 17.9 Hz, 1H), 1.85 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 1.64 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 1.49 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 3H), 1.41–1.12 (br, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.7, 129.1, 128.2, 125.8, 61.9, 49.6, 44.0, 43.1, 38.1, 32.3, 27.6, 22.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C26H37N2O2S [M + H]+ 441.2570, found 441.2567.
4-(2-Fluorobenzyl)-1’-(mesitylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (109)
To a solution of 1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (3c, 0.2855 g, 1.02 mmol) and 4-(2-fluorobenzyl)piperidine (0.1936 g, 1.00 mmol) in anhydrous DCE (6 mL) was added Ti(Oi-Pr)4 (0.60 mL, 2.05 mmol) and the solution was stirred at 80 °C for 6.5 h. After cooling 0 °C, NaBH4 (0.1271 g, 3.34 mmol) in EtOH (6 mL) was added dropwise at the solution was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (30 mL), extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 30 mL), dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified via flash chromatography (1/19 MeOH/CH2Cl2 then 100% EtOAc) to afford the product 109 as a light brown gel (0.1444 g, 35%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.17–7.05 (m, 2H), 7.03–6.92 (m, 2H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 3.59 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 2.86 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.70 (td, J = 12.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.57 (s, 6H), 2.55–2.48 (m, 2H), 2.44–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 2.09 (td, J = 11.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 14.5 Hz, 2H), 1.61 (d, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H), 1.58–1.41 (m, 3H), 1.39–1.22 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.2 (d, J = 244.6 Hz), 142.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.7, 131.5 (d, J = 5.1 Hz), 127.6 (d, J = 8.1 Hz), 127.2 (d, J = 16.2 Hz), 123.7 (d, J = 3.5 Hz), 115.1 (d, J = 22.5 Hz), 61.8, 49.4, 43.9, 36.8, 35.9, 32.0, 27.5, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C26H36FN2O2S [M + H]+ 459.2476, found 459.2470.
4-(4-Fluorobenzyl)-1’-(mesitylsulfonyl)-1,4’-bipiperidine (110)
Reaction of 3c and 4-(4-fluorobenzyl)piperidine in the same manner as for the preparation of 109 yielded 110 as a colorless gel (31%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.09–7.00 (m, 2H), 6.97–6.87 (m, 4H), 3.60 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 2H), 2.86 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.72 (td, J = 12.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.46 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 2.35 (t, J = 11.8 Hz, 1H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.08 (dd, J = 12.8, 10.2 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.61 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 1.55–1.36 (m, 3H), 1.34–1.15 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 161.2 (d, J = 243.4 Hz), 142.5, 140.4, 136.1 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 131.9, 131.7, 130.3 (d, J = 7.7 Hz), 114.9 (d, J = 21.0 Hz), 61.8, 49.5, 44.0, 42.2, 38.1, 32.2, 27.6, 22.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C26H36FN2O2S [M + H]+ 459.2476, found 459.2477.
1’-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-4-phenyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (111)
Reaction of 3c with 4-phenylpiperidine (Procedure D) yielded 111 as a white solid (90%); mp 141–144 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.34–7.26 (m, 2H), 7.25–7.16 (m, 3H), 6.95 (s, 2H), 3.66 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 3.03 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (t, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 2.62 (s, 6H), 2.54–2.37 (m, 2H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 2.30–2.20 (m, 2H), 1.99–1.66 (m, 6H), 1.56 (qd, J = 12.2, 4.3 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.5, 131.9, 131.7, 128.4, 126.8, 126.2, 61.9, 50.0, 44.0, 42.9, 33.7, 27.7, 22.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C25H35N2O2S [M + H]+ 427.2414, found 427.2405.
1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-4-(5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-2-yl)piperidine (112)
The synthesis of compound 112, obtained as a mixture of cis:trans isomers (1:1.56), is described in the Supporting Information. Trans: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 4.16 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 3.97 (dd, J = 11.8, 4.7 Hz, 2H), 3.55 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 2H), 3.20 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.70 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.07–1.90 (m, 1H), 1.77 (d, J = 14.4 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.54 (m, 1H), 1.42–1.24 (m, 2H), 0.66 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.3, 140.5, 140.4, 131.8, 103.4, 71.8, 44.0, 40.3, 29.5, 26.1, 22.8, 20.9, 12.3. Cis: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 4.26 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 3.74 (d, J = 10.1 Hz, 2H), 3.55 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 2H), 2.70 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.77 (d, J = 14.4 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.54 (m, 1H), 1.54–1.47 (m, 1H), 1.42–1.24 (m, 2H), 1.20 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.3, 140.5, 140.4, 103.9, 73.2, 44.0, 40.3, 29.1, 25.9, 22.8, 20.9, 15.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) (ESI) calcd for C19H29NO4SNa [M + Na]+ 390.1710, found 390.1706.
(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)methanone (113)
Reaction of amine 1k (see SI for synthesis) with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 113 as a light brown solid (86%); mp 122–124 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.89 (s, 2H), 4.49 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 1H), 3.77 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.53 (dt, J = 12.1, 3.6 Hz, 2H), 2.94 (td, J = 12.5, 11.6, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 2.85–2.70 (m, 2H), 2.56 (s, 6H), 2.54–2.38 (m, 2H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.82–1.45 (m, 7H), 1.08–0.92 (m, 2H), 0.88 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.1, 142.6, 140.5, 131.8, 131.3, 45.7, 43.6, 42.2, 38.0, 34.9, 33.8, 31.1, 28.1, 27.8, 22.7, 21.6, 20.9; HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H32N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 415.2026, found 415.2017.
1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-N-(p-tolyl)piperidin-4-amine (114)
Reaction of 3c with p-toluidine (Procedure D) yielded 114 as a white solid (61%); mp 148–151 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.03–6.89 (m, 4H), 6.51 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 3.56 (dt, J = 13.2, 3.5 Hz, 2H), 3.36 (tt, J = 10.1, 3.9 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (ddd, J = 12.8, 11.2, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.06 (dd, J = 13.2, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 1.54–1.32 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 144.0, 142.6, 140.5, 131.9, 131.6, 129.9, 127.2, 113.8, 50.0, 43.2, 31.8, 22.8, 21.0, 20.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H28N2O2SNa [M + Na]+ 395.1764, found 395.1771.
1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-4-(p-tolyl)piperidine (115)
Reaction of amine 1f with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 115 as a pale yellow solid (73%); mp 87–90 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.08 (q, J = 8.1 Hz, 4H), 6.95 (s, 2H), 3.69 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.86 (t, J = 12.5 Hz, 2H), 2.64 (s, 6H), 2.62 – 2.51 (m, 1H), 2.30 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 6H), 1.86 (d, J = 13.0 Hz, 2H), 1.67 (dtd, J = 13.4, 12.2, 4.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 142.1, 140.5, 136.0, 131.9, 131.8, 129.2, 126.6, 44.9, 41.8, 32.7, 22.9, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H27NO2SNa [M + Na]+ 380.1655, found 380.1652.
1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-4-phenylpiperidine (116)
Reaction of amine 1g with 2,4,6trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 116 as a yellow solid (93%); mp 88–90 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36–7.26 (m, 2H), 7.23–7.14 (m, 3H), 6.96 (s, 2H), 3.71 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.87 (t, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 2.65 (s, 6H), 2.64–2.54 (m, 1H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 1.88 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H), 1.70 (dtd, J = 13.7, 12.1, 4.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 145.1, 142.5, 140.5, 131.9, 131.8, 128.5, 126.7, 126.5, 44.9, 42.2, 32.6, 22.9, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H25NO2SNa [M + Na]+ 366.1498, found 366.1489.
N-Benzyl-N-(1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyramide (117)
Reaction of 3c with benzylamine (Procedure D) yielded N-benzyl-1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-amine as a yellow oil (>95%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.45–7.19 (m, 5H), 6.92 (s, 2H), 3.77 (s, 2H), 3.52 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 2H), 3.52 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 2H), 2.68–2.58 (m, 1H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.90 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 1.45–1.22 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.0, 127.8, 127.1, 53.7, 50.8, 42.9, 31.7, 22.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H29N2O2S [M + H]+ 373.1944, found 373.1942.
A mixture of the above prepared N-benzyl-1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-amine (0.4135 g, 1.11 mmol), butyryl chloride (0.13 mL, 1.24 mmol), and iPr2NEt (0.28 mL, 1.70 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (4 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 23 h. CH2Cl2 (25 mL) was added and the solution was washed with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (25 mL). The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified via flash chromatography (1/9 MeOH/CH2Cl2) to afford the desired product 117 as a yellow gel (4:1 ratio of two rotamers; 0.2351 g, 48%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 at 50 °C) δ 7.62–7.18 (m, 3H), 7.15 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 4.70–4.35 (m, 1H), 4.48 (s, 2H), 3.63 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.96–2.68 (m, 2H), 2.56 (s, 6H), 2.35–2.10 (br, 2H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.65 (s, 6H), 0.89 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) Major Rotamer δ 174.0, 142.5, 140.2, 138.1, 131.9, 131.8, 128.8, 127.3, 125.7, 51.7, 46.9, 44.2, 35.7, 29.1, 22.8, 20.9, 18.7, 13.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C25H34N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 465.2182, found 465.2190.
N-(1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyramide (118)
To a solution of N-benzyl-N-(1-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyramide 117 (0.1338 g, 0.30 mmol) in methanol (4 mL) was added palladium on carbon (10 wt%). The flask was evacuated by vacuum and refilled by a hydrogen balloon. This evacuation/refill was repeated three times and the reaction suspension was stirred under hydrogen at room temperature for 18 h. The reaction suspension was then filtered through a pad of celite and washed with methanol. Upon evaporation of the solvent compound 118 was obtained as a yellow solid (0.0662 g, 62%); mp 144–147 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 5.82–5.25 (br, 1H), 3.95 (s, 1H), 3.58 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 2.90 (s, 2H), 2.60 (s, 6H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 2.25–2.06 (br, 2H), 1.95 (s, 2H), 1.73–1.59 (br, 2H), 1.58–1.40 (br, 2H), 1.04–0.83 (br, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.5, 142.6, 140.3, 132.0, 131.7, 46.1, 43.4, 39.0, 31.7, 22.9, 21.0, 19.3, 13.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H28N2O3SNa [M + Na]+ 375.1713, found 375.1715.
(4-Methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-1’-yl)(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)methanone (119)
A mixture of 4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzoic acid (0.2024 g, 0.98 mmol), DMAP (0.0200 g, 0.16 mmol), and EDC hydrochloride (0.2166 g, 1.13 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (6 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 0.5 h. 4-Methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (0.1847 g, 1.01 mmol) was added and the resulting solution was stirred at room temperature for 26.5 h. The reaction solution was diluted with CH2Cl2 (60 mL), washed with brine (60 mL) and saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (60 mL). The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (1:19 MeOH/CH2Cl2) to afford compound 119 (0.2434 g, 67%) as a white solid; mp 72–75 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.42 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.23 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 4.73 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 1H), 3.75 (d, J = 13.6 Hz, 1H), 3.00 (s, 1H), 2.87 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (s, 1H), 2.50 (t, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 2.14 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (d, J = 49.0 Hz, 2H), 1.70–1.28 (m, 5H), 1.20 (qd, J = 11.8, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 0.90 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 168.8, 149.9 (q, J = 1.8 Hz), 134.7, 128.7, 120.9, 120.3 (q, J = 258.0 Hz), 62.1, 49.8 and 49.5 (rotamers), 47.4 and 42.0 (rotamers), 34.6, 31.0, 29.2 and 27.8 (rotamers), 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) (ESI) calcd for C19H25N2O2F3 [M + Na]+ 393.1754, found: 393.1760.
4-Methoxyphenyl 4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidine]-1’-carboxylate (120)
To a solution of 4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (0.1831g, 1.01 mmol), and K2CO3 (0.1522 g, 1.10 mmol) in Et2O (15 mL) was added at 0 °C 4-methoxyphenyl carbonochloridate (0.15 mL, 1.00 mmol). The resulting suspension was allowed to warm up to room temperature gradually and stirred for 5 h. The suspension was then poured into H2O (30 mL), extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (9/1 CH2Cl2/CH3OH) to afford compound 120 as a white solid (0.2647 g, 79%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.97 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 2H), 6.83 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 2H), 4.33 (s, 2H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.09 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.93 (s, 1H), 2.79 (t, J = 11.8 Hz, 2H), 2.41 (s, 2H), 2.05 (s, 2H), 1.84–1.37 (m, 7H), 0.94 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.9, 153.8, 144.8, 122.5, 114.3, 62.7, 55.6, 49.6, 49.2, 43.7, 32.8, 30.3, 27.5, 26.8, 21.4. HRMS (ESI-TOF) (ESI) calcd for C19H29N2O3 [M + H]+ 333.2173, found 333.2189.
N-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidine]-1’-carboxamide (121)
To a 15 mL flame-dried flask were added 4-methyl-1,4’-bipiperidine (0.1889 g, 1.04 mmol), DCM (6 mL) and 1-isocyanato-4-methoxybenzene (0.1674 g, 1.12 mmol) at 0 °C sequentially. The resulting solution was then allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 22 hours. After the evaporation of solvents, the residue was purified through flash chromatography on silica gel (1:19 MeOH/CH2Cl2) to afford the entitled product as a white solid (0.2032 g, 59%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.21 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.80 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.38 (s, 1H), 4.08 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 2.93–2.72 (m, 4H), 2.53–2.33 (m, 1H), 2.14 (t, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 2H), 1.64 (d, J = 13.8 Hz, 1H), 1.49 (qd, J = 12.4, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.42–1.26 (m, 1H), 1.20 (qd, J = 11.9, 3.5 Hz, 2H), 0.90 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.7, 155.4, 132.2, 122.3, 114.0, 62.2, 55.5, 49.6, 44.0, 34.7, 31.1, 28.0, 21.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) (ESI) calcd for C19H30N3O2 [M + H]+ 332.2333, found 332.2326.
N-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4-oxopiperidine-1-sulfonamide (122)
A solution of 4-methoxyaniline (1.8932 g, 15.39 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (18 mL) was cooled to −10 °C and chlorosulfonic acid (0.34 mL, 5.13 mmol) was added dropwise in 10 min. The resulting suspension was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 3 h. After filtration, the solid was dried under reduced pressure and suspended in toluene (15 mL), followed by addition of PCl5 (1.0239 g, 4.92 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at 75 °C for 3.5 h and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford 4-MeOPhNHSO2Cl which was used without further purification.
A suspension of piperidin-4-one hydrochloride hydrate (2a, 0.7689 g, 5.03 mmol), Na2SO4 (1.2132 g, 7.19 mmol), and Et3N (2.9 mL, 2.1054 g, 20.85 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (15 mL) was stirred vigorously, followed by addition of 4-MeOPhNHSO2Cl as prepared above. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 20 h and poured into 0.5 N aqueous HCl (50 mL) and extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 50 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (1/1 EtOAc/hexane) to afford N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxopiperidine-1-sulfonamide as a brown gel (0.1552 g, 11% over two steps). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.17 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.02 (s, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.53 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 2.42 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 206.4, 157.7, 129.2, 124.2, 114.6, 55.5, 46.0, 40.8. MS (ESI) calcd for C12H17N2O4S [M + H]+ 285.1, found 285.1.
Reaction of the above prepared N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxopiperidine-1-sulfonamide (0.1102 g, 0.39 mmol) with 4-methylpiperidine (Procedure D) yielded 122 as a pale yellow gel (0.0217 g, 15%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.21 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.3 Hz, 2H), 3.88 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 2H), 3.79 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 3H), 3.16 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 2.92 (s, 1H), 2.74 (t, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 2.50 (t, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 2.13–1.93 (m, 3H), 1.88–1.56 (m, 6H), 1.55–1.39 (m, 1H), 0.97 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 157.2, 130.1, 123.9, 114.4, 62.3, 55.5, 49.0, 45.5, 31.4, 29.6, 25.9, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C18H30N3O3S [M + H]+ 368.2002, found 368.1991.
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-(4-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)cyclohexyl)benzenesulfonamide (123)
A mixture of tert-butyl (4-oxocyclohexyl)carbamate (0.4296 g, 2.02 mmol), HCl (37%, 2 mL) and 1,4-dioxane (6 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 3.5 hours. Upon evaporation of solvents, the residue (2b) was reacted with 2-mesitylenesulfonyl chloride according to Procedure B to yield 2,4,6-trimethyl-N-(4-oxocyclohexyl)benzenesulfonamide as a light yellow gel (83%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (s, 2H), 5.36–5.26 (br, 1H), 3.64–3.40 (m, 1H), 2.63 (s, 6H), 2.40–2.31 (m, 2H), 2.30–2.20 (m, 5H), 2.04–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.79–1.67 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 138.9, 134.3, 132.1, 49.6, 38.4, 32.2, 22.9, 20.9.
Reaction of the above prepared 2,4,6-trimethyl-N-(4-oxocyclohexyl)benzenesulfonamide with 4-methylpiperidine (Procedure D) yielded 123 as a light yellow gel (13%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 6.36 (s, 1H), 3.45–3.20 (m, 3H), 3.02 (t, J = 11.7, 1H), 2.74 (dt, J = 13.9, 7.9 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.10–1.65 (m, 10H), 1.62–1.35 (m, 3H), 0.94 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 139.0, 133.7, 132.1, 64.0, 49.1, 47.1, 30.9, 29.9, 23.0, 20.9, 20.8. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H35N2O2S [M + H]+ 379.2414, found 379.2427.
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-(2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)ethyl)benzenesulfonamide (124)
Reaction of amine 1h with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 124 as a yellow gel (>95%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 2.86 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.52 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 2H), 2.28 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.82 (td, J = 11.9, 2.6 Hz, 2H), 1.52 (d, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H), 1.36–1.20 (m, 1H), 1.07 (qd, J = 12.5, 3.7 Hz, 2H), 0.86 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.0, 139.0, 133.3, 131.8, 55.8, 53.3, 39.0, 34.2, 30.6, 22.9, 21.8, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C17H29N2O2S [M + H]+ 325.1944, found 325.1947.
1-(4-(Mesitylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4-methylpiperidine (125)
On the basis of a literature report,40 a mixture of 4-iodobenzenesulfonyl chloride (0.9232 g, 3.02 mmol), mesitylene (120 mg, 3.09 mmol), and AlCl3 (0.4956 g, 3.73 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (15 mL) was stirred for 3 h at room temperature. The mixture was then poured into 45 mL of 5% aqueous HCl and extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic layers were concentrated under reduced pressure to about 50 mL and were then washed with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (45 mL) and brine (45 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (10/1 hexane/EtOAc) to give the desired product 2-((4-iodophenyl)sulfonyl)-1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (0.5707 mg, 48%) as pale yellow solid. mp 118–121 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.91–7.72 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.57–7.35 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 6.93 (s, 2H), 2.56 (s, 6H), 2.27 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 143.7, 143.2, 140.0, 138.1, 133.3, 132.3, 127.6, 99.9, 22.8, 21.0.
To a solution of the above prepared 2-((4-iodophenyl)sulfonyl)-1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (0.2879 g, 0.75 mmol), CuI (0.0145 g, 0.076 mmol), L-proline (0.0176 g, 0.15 mmol), and K2CO3 (0.2160 g, 1.57 mmol) in DMSO (6 mL) was added 4-methylpiperidine (0.18 mL, 1.52 mmol) and the reaction suspension was stirred vigorously at 90 °C for 67 h. After cooling to room temperature, water (30 mL) was added followed by extraction with CH2Cl2 (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated, and the residue was purified by flash chromatography (10/1 hexane/EtOAc) to afford the title compound 125 as a white solid (0.0636 g, 24%); mp 103–105 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.62 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 3.79 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 2H), 2.84 (t, J = 13.4 Hz, 2H), 2.61 (s, 6H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.71 (d, J = 13.0 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.47 (m, 1H), 1.25 (q, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 0.96 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 139.6, 135.3, 132.0, 128.2, 113.7, 48.1, 33.5, 30.7, 22.9, 21.8, 21.0. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C21H27NO2SNa [M + Na]+ 380.1655, found 380.1660.
1-(Mesitylsulfonyl)-4-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)piperazine (126)
Reaction of amine 1i with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 126 as a colorless gel (>95%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (s, 2H), 3.23–3.04 (m, 4H), 2.85 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.57–2.48 (m, 4H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 2.22–2.15 (m, 1H), 1.89 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 1.69 (d, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 1.51 (qd, J = 12.3, 3.9 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.5, 140.4, 131.9, 131.3, 61.4, 55.3, 48.4, 46.1, 44.7, 28.0, 23.0, 21.0. LC-MS (ESI) calcd for C19H32N3O2S [M + H]+ 366.2, found 366.2.
3-(4-(Mesitylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)quinuclidine (127)
Reaction of amine 1j with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (Procedure A) yielded 127 as a white solid (42%); mp >300 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.96 (s, 2H), 3.34–3.12 (m, 9H), 3.04 (dd, J = 12.0, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 2.60 (s, 6H), 2.45 (s, 5H), 2.30 (s, 4H), 2.16–1.95 (m, 2H), 1.85–1.75 (m, 1H), 1.74–1.62 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.8, 140.5, 132.0, 131.0, 59.1, 52.8, 50.3, 46.6, 45.6, 44.1, 23.0, 22.9, 22.1, 20.9, 17.7. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H32N3O2S [M + H]+ 378.2210, found: 378.2200.
1-(Adamantan-1-yl)-4-(mesitylsulfonyl)piperazine (128)
Reaction of amine 1l with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 128 as a yellow solid (70%); mp 182–184 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.92 (s, 2H), 3.20–3.02 (m, 4H), 2.68–2.61 (m, 4H), 2.60 (s, 6H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.70–1.49 (m, 14H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.4, 140.4, 131.9, 131.4, 54.0, 45.2, 43.7, 38.5, 36.8, 29.5, 23.1, 20.9. HRMS calcd for C23H35N2O2S [M + H]+ 403.2414, found 403.2407.
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-(1’-methyl-[1,4’-bipiperidin]-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide (129)
Reaction of amine hydrochloride salt 1m with 2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1-sulfonyl chloride (Procedure B) yielded 128 as a yellow gel (81%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.89 (s, 2H), 4.73 (s, 1H), 3.04 (s, 1H), 2.84 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.69 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 2.59 (s, 6H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 2.19–2.05 (m, 3H), 1.87 (t, J = 10.6 Hz, 2H), 1.76–1.59 (m, 4H), 1.50 (qd, J = 12.2, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 1.44–1.31 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.0, 138.7, 135.0, 131.9, 61.4, 55.4, 50.7, 47.6, 46.0, 33.2, 27.7, 22.9, 20.9. HRMS (ESI-TOF) calcd for C20H34N3O2S [M + H]+ 380.2366, found 380.2359.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (grants RP130189 and RP160180). J.K.D.B. acknowledges the support of the Welch Foundation (Grant I-1422). N.S.W. and the Preclinical Pharmacology Core were supported in part by institutional funds from the Institute for Innovations in Medicine. HRMS data were obtained from the Shimadzu Center for Advanced Analytical Chemistry (SCAAC) at U.T. Arlington. J.K.D.B. holds the Julie and Louis Beecherl, Jr., Chair in Medical Science and J.W.S. holds the distinguished Southland Financial Corporation Chair in Geriatrics Research. The authors thank Karen MacMillan for the synthesis of select analogs.
Abbreviations
- APC
adenomatous polyposis coli
- CRC
colorectal cancer
- FAP
familial adenomatous polyposis
- HCEC
human colonic epithelial cell
- HTS
high throughput screen
- MCR
mutation cluster region
- PK
pharmacokinetics
- SAR
structure activity relationship
- TASIN
truncated APC-selective inhibitor
Footnotes
J.W.S and J.K.D.B are scientific co-founders of Barricade Therapeutics, Inc. whom holds the license to the TASIN class of compounds.
References
- 1.https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html accessed on March 26, 2019.
- 2.Martini G; Troiani T; Cardone C; Vitiello P; Sforza V; Ciardiello D; Napolitano S; Della Corte CM; Morgillo F; Raucci A; Cuomo A; Selvaggi F; Ciardiello F; Martinelli E Present and future of metastatic colorectal cancer treatment: A review of new candidate targets. World J. Gastroenterol 2017, 23(26), 4675–4688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Akhtar R; Chandel S; Sarotra P; Medhi B Current status of pharmacological treatment of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol 2014, 6(6), 177–183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moriarity A; O’Sullivan J; Kennedy J; Mehigan B; McCormick P Current targeted therapies in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol 2016, 8(4), 276–293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rowan AJ; Lamlum H; Ilyas M; Wheeler J; Straub J; Papadopoulou A; Bicknell D; Bodmer WF; Tomlinson IPM APC mutations in sporadic colorectal tumors: A mutational “hotspot” and interdependence of the “two hits”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000, 97, 3352–3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nieuwenhuis MH; Vasen HFA Correlations between mutation site in APC and phenotype of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): A review of the literature. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol 2007, 61, 153–161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lamlum H; Ilyas M; Rowan A; Clark S; Johnson V; Bell J; Frayling I; Efstathiou J; Pack K; Payne S; Roylance R; Gorman P; Sheer D; Neale K; Phillips R; Talbot I; Bodmer W; Tomlinson I The type of somatic mutation at APC in familial adenomatous polyposis is determined by the site of the germline mutation: A new facet to Knudson’s ‘two-hit’ hypothesis. Nat. Med 1999, 5, 1071–1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Poiwell SM; Zilz N; Beazer-Barclay Y; Bryan TM; Hamilton SR; Thibodeau SN; Vogelstein B; Kinzler KW APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature 1992, 359, 235–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fearon ER; Vogelstein B A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990, 61, 759–767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aoki K; Taketo MM Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC): a multi-functional tumor suppressor gene. J. Cell Sci 2007, 120, 3327–3335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Roberts DM; Pronobis MI; Poulton JS; Waldmann JD; Stephenson EM; Hanna S; Peifer M Deconstructing the β-catenin destruction complex: Mechanistic roles for the tumor suppressor APC in regulating Wnt signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1845–1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.van de Wetering M; Sancho E; Verweij C; de Lau W; Oving I; Hurlstone A; van der Horn K; Batlle E; Coudreuse D; Haramis A-P; Tjon-Pon-Fong M; Moerer P; van den Born M; Soete G; Pals S; Eilers M; Medema R; Clevers H The β-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell 2002, 111, 241–250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goss KH; Groden J Biology of the adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1967–1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Polakis P The adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1332, F127–F147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mori Y; Nagse H; Ando H; Horii A; Ichii S; Nakatsuru S; Aoki T; Miki Y; Mori T; Nakamura Y Somatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: Mutation cluster region in the APC gene. Hum. Mol. Genet 1992, 1, 229–233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kawasaki Y; Sato R; Akiyama T Mutated APC and Asef are involved in the migration of colorectal tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol 2003, 5, 211–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kawasaki Y; Senda T; Ishidate T; Koyama R; Morishita T; Iwayama Y; Higuchi O; Akiyama T Asef, a link between the tumor suppressor APC and G-protein signaling. Science 2000, 289, 1194–1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Green RA; Kaplan KB Chromosome instability in colorectal tumor cells is associated with defects in microtubule plus-end attachments caused by a dominant mutation in APC. J. Cell Biol 2003, 163, 949–961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tighe A; Johnson VL; Taylor SS Truncating APC mutations have dominant effects on proliferation, spindle checkpoint control, survival and chromosome stability. J. Cell Sci 2004, 117, 6339–6353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim SB; Zhang L; Yoon J; Lee J; Min J; Li W; Grishin NV; Moon Y-A; Wright WE; Shay JW Truncated adenomatous polyposis coli mutation induces Asef-activated Golgi fragmentation. Mol. Cell. Biol 2018, 38, e00135–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dow LE; O’Rourke KP; Simon J; Tschaharganeh DF; van Es JH; Clevers H; Lowe SW Apc restoration promotes cellular differentiation and reestablishes crypt homeostasis in colorectal cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1539–1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang L; Theodoropoulos PC; Eskiocak U; Wang W; Moon Y-A; Posner B; Williams NS; Wright WE; Kim SB; Nijhawan D; De Brabander JK; Shay JW Selective targeting of mutant adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) in colorectal cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 361ra140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hinoi T, Akyol A; Theisen BK; Ferguson DO; Greenson JK; Williams BO; Cho KR; Fearon ER Mouse model of colonic adenoma-carcinoma progression based on somatic Apc inactivation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9721–9730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Engler TA; Wanner J Lewis acid-directed cyclocondensation of piperidone enol ethers with 2-methoxy-4-(N-phenylsulfonyl)-1,4-benzoquinoneimine: A new regioselective synthesis of oxygenated carbolines. J. Org. Chem 2000, 65, 2444–2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Han Q; Dominquez C; Stouten PFW; Park JM; Duffy DE; Galemmo RA; Rossi KA; Alexander RS; Smallwood AM; Wong PC; Wright MM; Luettgen JM; Knabb RM; Wexler RR Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent and selective amidino bicyclic factor xa inhibitors. J. Med. Chem 2000, 23, 4398–4415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abdel-Magid AF; Carson KG; Harris BD; Maryanoff CA; Shah RD Reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones with sodium triacetoxyborohydride. Studies on direct and indirect reductive amination procedures. J. Org. Chem 1996, 61, 3849–3862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ma D; Cai Q; Zhang H Mild method for UIImann coupling reaction of amines and aryl halides. Org. Lett 2003, 14, 2453–2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Topliss JG Utilization of operational schemes for analog synthesis in drug design. J. Med. Chem 1972, 15, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Topliss JG A manual method for applying the Hansch approach to drug design. J. Med. Chem 1977, 20, 463–469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Roig AI; Eskiocak U; Hight SK; Kim SB; Delgado O; Souza RF; Spechler SJ; Wright WE; Shay JW Immortalized epithelial cells derived from human colon biopsies express stem cell markers and differentiate in vitro. Gastroenter. 2010, 138, 1012–1021. e1–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.MacIntyre AC; Cutler DJ The potential role of lysosomes in tissue distribution of weak bases. Biopharm. Drug Dispos 1988, 9, 513–526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kazmi F; Hensley T; Pope C; Funk RS; Loewen GJ; Buckley DB; Parkinson A Lysosomal sequestration (trapping) of lipophylic amine (cationic amphiphilic) drugs in immortalized human hepatocytes (Fa2N-4 cells). Drug Metab. Dispos 2013, 41, 897–905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lien EA; Solheim E; Ueland PM Distribution of tamoxifen and its metabolites in rat and human tissues during steady-state treatment. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4837–4844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Reasor MJ, Hastings KL; Ulrich RG Drug-induced phospholipidosis: issues and future directions. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2006, 5, 567–583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McNaney CA; Drexler DM; Hnatyshyn SY; Zvyaga TA; Knipe JO; Belcastro JV; Sanders M An automated liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry process to determine metabolic stability half-life and intrinsic clearance of drug candidates by substrate depletion. Assay Drug Dev. Technol 2008, 6, 121–129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang C; Williams NS A mass balance approach for calculation of recovery and binding enables the use of ultrafiltration as a rapid method for measurement of plasma protein binding for even highly lipophilic compounds. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2013, 75, 112–117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kalvass JC; Maurer TS Influence of nonspecific brain and plasma binding on CNS exposure: Implications for rational drug discovery. Biopharm. Drug Dispos 2002, 23, 327–338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kwon Y (2001). The Handbook of Essential Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Drug Metabolism for Industrial Scientists. Kluwer Academic /Plenum Publishers, New York: pp 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ellis GL; Amewu R; Sabbani S; Stocks PA; Shone A; Stanford D; Gibbons P; Davies J; Vivas L; Charnaud S; Bongard E; Hall C; Rimmer K; Lozanom S; Jesús M; Gargallo D; Ward SA; O’Neill PM Two-step synthesis of achiral dispiro-1,2,4,5-tetraoxanes with outstanding antimalarial activity, low toxicity, and high-stability profiles. J. Med. Chem 2008, 51, 2170–2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chen H; Tsalkova T; Chepurny OG; Mei FC; Holz GG; Cheng X; Zhou J Identification and characterization of small molecules as potent and specific EPAC2 antagonists. J. Med. Chem 2013, 56, 952–962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.