Figure 4: CEP85L is required to localize and activate the lissencephaly protein, CDK5.
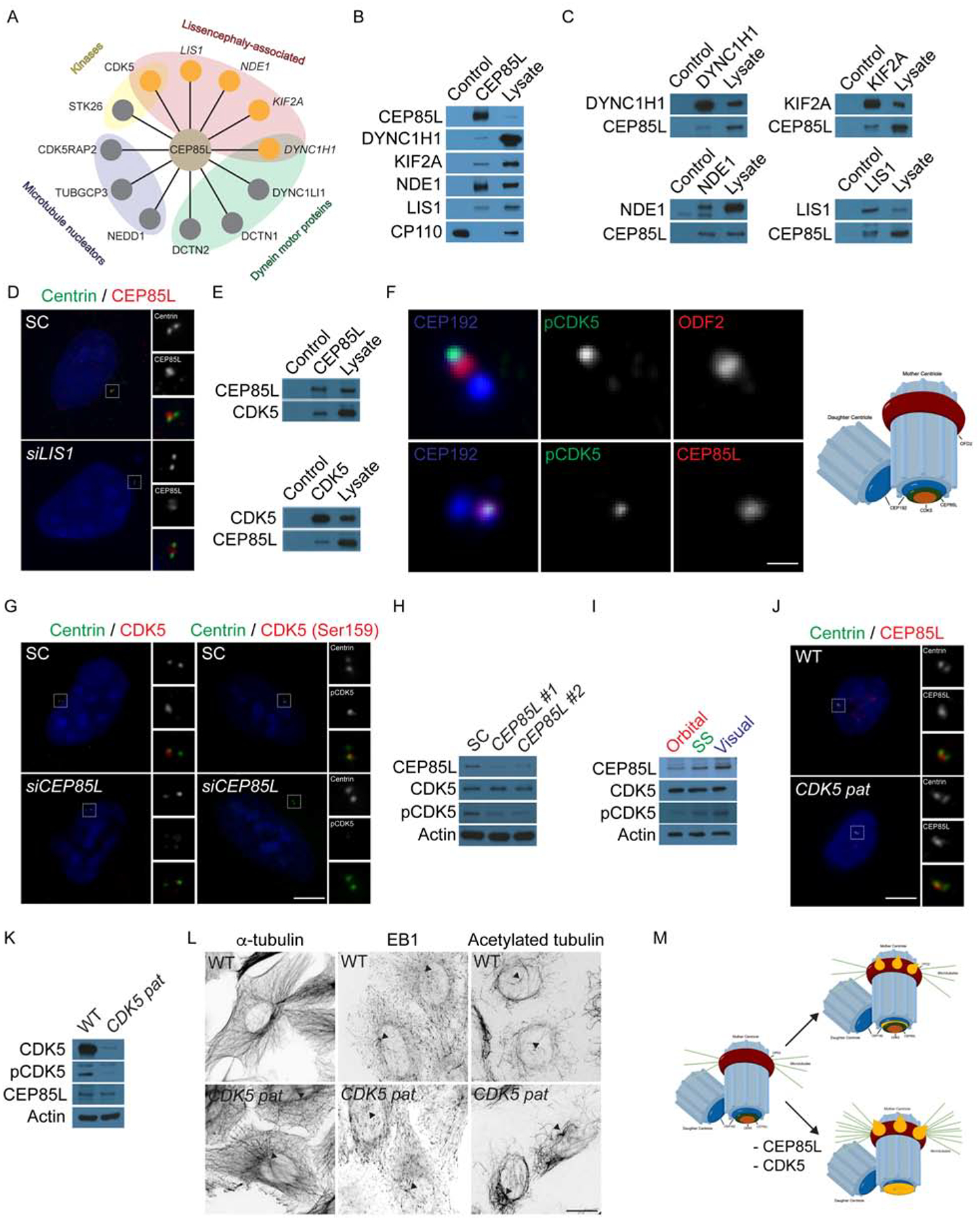
A. Schematic of centrosomal CEP85L interacting proteins identified by endogenous immunoprecipitation of CEP85L followed by LC-MS/MS analysis. Interactors were sorted and prioritized based on centrosomal localization and disease-association. B. Immunoprecipitated endogenous CEP85L and CP110 from HeLa cell lysates was immunoblotted for co-precipitating proteins for CEP85L, DYNC1H1, KIF2A, NDE1 and LIS1. CP110 served as a negative control throughout. Lysate represents 5% of the total cell lysate used in the immunoprecipitation assays. C. HeLa cell lysate was subjected to immunoprecipitation of DYNC1H1, KIF2A, NDE1 and LIS1. Precipitating proteins were immunoblotted for CEP85L, DYNC1H1, KIF2A, NDE1 and LIS1. D. U2-OS cells transfected with siRNA to SC or LIS1 co-stained with Centrin (green) and CEP85L (red). E. HeLa cell lysate was subjected to immunoprecipitation of CEP85L, CDK5, and CP110, which served as a negative control. Precipitating proteins were immunoblotted for CEP85L and CDK5. F. Airyscan maximum projections of U2-OS cells co-stained with antibodies to pCDK5 (green), ODF2 (red, to mark the subdistal appendages of mother centrioles), CEP85L (red), and CEP192 (blue) to mark the proximal domains of the centrioles. Scale bar represents 1μm for Airyscan images. G. Immunofluorescence of SC and CEP85L siRNA-transfected U2-OS cells co-stained for Centrin (green) and CDK5 (red) or pCDK5 (red). Scale bars represent 5mm for all images. H. Total cell lysates from U2-OS cells transfected with SC, CEP85L #1 or #2 probed with antibodies to CEP85L, CDK5, and pCDK5. Actin served as a loading control. I. Whole cell lysate from the posterior frontal, parietal and occipital lobes of a GW 23 human fetus blotted for CEP85L, CDK5 and pCDK5. Actin served as a loading control. J. WT and CDK5 patient fibroblasts (p.V162fsX19, CDK5 pat) co-stained with antibodies to Centrin (green) and pCDK5 (red). K. Whole cell lysate from WT or CDK5 patient fibroblasts probed with antibodies to CDK5, pCDK5, and CEP85L. Actin served as a loading control. L. Inverted images of WT and CDK5 patient cells stained with α-tubulin, EB1 or acetylated tubulin. Triangles denote the centrosome. Scale bars represent 10μm for all images. M. CEP85L (green) localizes CDK5 (beige) to the proximal end of mother centrioles (CEP192, blue) to be activated. At the centrosome CDK5 activity restricts the accumulation of LIS-associated proteins (orange) that localize to the proximal mother centriole and its subdistal appendages. Consequently, loss of CEP85L or CDK5 causes the excessive localization of LIS-proteins resulting in excessive anchoring of microtubules at the mother centriole leading to cells incapable of migrating.
