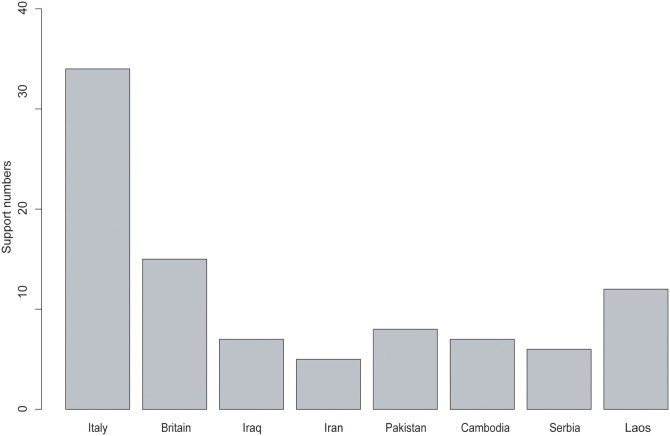
We appreciate the experience and suggestions Ma et al. have shared concerning medical practices for burns during the COVID-19 outbreak [1]. According to the website of the National Health Commission of China, China (refers to the Chinese government and Chinese medical personnel) has shared its anti-epidemic expertise with more than 180 countries and at least ten international organizations.The “China-Central and Eastern European Countries New Crown Pneumonia Epidemic Prevention and Control Expert Video Conference” was held on March 13, 2020 [2]. During this video conference, Chinese experts shared their experience in combating the COVID-19 outbreak with 17 countries in Central and Eastern Europe. In addition, the experience was shared through video communication with Italy, the United Kingdom, Germany, the United States, Latin America, and the Caribbean. These countries need time to accumulate experience. Practical advice on fighting the disease is readily available for these and other nations to gain confidence in their fight. As of May 8, 2020, there were 3,679,499 confirmed cases and 254,199 deaths worldwide, with both metrics exhibiting a rapid increase in many parts of the world [3]. China not only shares its valuable experience but also actively supports the international community. In terms of material help, China has assisted 89 countries and four international organizations. Furthermore, Chinese medical teams have rushed to the front line both in Wuhan, China [4] and in many other countries, supporting local medical professionals in their fight against COVID-19 (Fig. 1 ). We firmly believe that through joint efforts, the people of the world would be able to overcome the COVID-19 epidemic.
Fig. 1.
Chinese medical teams have rushed to the front line in many countries.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Chinese government and Chinese healthcare providers for their selfless dedication to fighting the epidemic!
References
- 1.Ma S., Yuan Z., Peng Y., Chen J., Li H.S., Luo Q.Z. Experience and suggestion of medical practices for burns during the outbreak of COVID-19. Burns. 2020;(April):30236–30239. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2020.03.014. pii: S0305-4179(20)30236-9. (2020-03-27). [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.http://world.people.com.cn/n1/2020/0314/c1002-31631938.html.
- 3.https://www.who.int/redirect-pages/page/novel-coronavirus-(covid-19)-situation-dashboard.
- 4.Feng Z.H., Cheng Y.R., Chen J., Ye L., Zhou M., Wang M.W. Chinese medical personnel against the 2019-nCoV. J Infect. 2020;80(5):578–606. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.011. [2020-02-07]. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]