Abstract
Major phenotypic innovations in social amoeba evolution occurred at the transition between the Polysphondylia and group 4 Dictyostelia, which comprise the model organism Dictyostelium discoideum, such as the formation of a new structure, the basal disk. Basal disk differentiation and robust stalk formation require the morphogen DIF-1, synthesized by the polyketide synthase StlB, the des-methyl-DIF-1 methyltransferase DmtA, and the chlorinase ChlA, which are conserved throughout Dictyostelia. To understand how the basal disk and other innovations evolved in group 4, we sequenced and annotated the Polysphondylium violaceum (Pvio) genome, performed cell type-specific transcriptomics to identify cell-type marker genes, and developed transformation and gene knock-out procedures for Pvio. We used the novel methods to delete the Pvio stlB gene. The Pvio stlB− mutants formed misshapen curly sorogens with thick and irregular stalks. As fruiting body formation continued, the upper stalks became more regular, but structures contained 40% less spores. The stlB− sorogens overexpressed a stalk gene and underexpressed a (pre)spore gene. Normal fruiting body formation and sporulation were restored in Pvio stlB− by including DIF-1 in the supporting agar. These data indicate that, although conserved, stlB and its product(s) acquired both a novel role in the group 4 Dictyostelia and a role opposite to that in its sister group.
Keywords: Polysphondylium violaceum genome, cell type-specific transcriptome, evolution of novel cell types, genetic transformation, DIF-1, polyketide synthase
Introduction
Multicellularity allowed cells to specialize into roles that support the propagation of others within the organism. Modern plants and animals owe their extensive morphological complexity to the progressive specialization of such somatic cells. Unraveling how this occurred is crucial to understand the mechanistic foundation of all extant developmental programs. Dictyostelia represent a group of multicellular organisms, which, depending on the species, contain only spores to propagate the species, or additionally contain cells that form a stalk and other cell types to support the spore mass. Dictyostelia can be subdivided into four major and some minor groupings, with a minor group containing Polysphondylium violaceum (Pvio) as sister clade to major group 4, which contains Dictyostelium discoideum (Ddis) and all other species that use cAMP as chemoattractant (Schaap et al. 2006; Romeralo et al. 2013; Schilde et al. 2019). Apart from the use of cAMP, group 4 shows other innovations, such as proportion regulation of prespore and prestalk cells and acquisition of three new cell types, which form a basal disk that supports the stalk and upper- and lower cups that cradle the spore mass (Schilde et al. 2014). DIF-1 was identified >30 years ago as a secreted factor that induces stalk cell differentiation in Ddis in vitro (Morris et al. 1987). Its biosynthetic enzymes were identified more recently and are the polyketide synthase StlB (Saito et al. 2008), the des-methyl-DIF-1 methyltransferase, DmtA (Thompson and Kay 2000), and the flavin-dependent halogenase, ChlA (Neumann et al. 2010). Null mutants in either of these mutants form weaker migrating slugs with a reduced number of prestalk cells and fruiting bodies that lack the basal disk, which consists of stalk-like cells. Because the stalk is still formed in all null mutants in DIF-1 synthetic enzymes, it was concluded that DIF-1 is mainly required for basal disk, rather than for stalk cell differentiation (Saito et al. 2008). A DIF-1 dechlorinase, DrcA, which deactivates DIF, was also identified, but drcA− mutants showed no developmental defects (Velazquez et al. 2011). Recent studies showed that polyketides produced by another polyketide synthase, StlA, may cooperate with DIF-1 in inducing prestalk differentiation, because a stlB−/stlA− mutant showed reduced expression from the pstA region of the ecmA prestalk promoter (Sato et al. 2013, 2016).
Except for one clade, the Acytostelids, all Dictyostelids form a cellular stalk, but the basal disk appears to be restricted to group 4 and one species, Dictyostelium mexicanum, in group 1 (Romeralo et al. 2013). Nevertheless, the three DIF-1 biosynthetic enzymes StlB, DmtA, and ChlA are present in all four Dictyostelium taxon groups (Gloeckner et al. 2016). Interestingly, in the Acytostelid Acytostelium subglobosum, the function of at least one of the enzymes, DmtA, is not conserved, because A. subglobosum dmtA cannot restore the disk-less phenotype of a Ddis dmtA− mutant (Mohri et al. 2014). Biochemical analysis of DIF-1 metabolism in other species than Ddis suggests that another group 4 species, Dictyostelium mucoroides, as well as Pvio could synthesize DIF-1, but this was not the case for Dictyostelium vinaceo-fuscum in group 3, although this species also produces chlorinated compounds (Kay et al. 1992). Pvio is not reported to form a basal disk, but owes its name to the fact that apart from the main stalk, its fruiting bodies have regular whorls of side branches, each consisting of a stalk and spore head.
We investigate the molecular changes that caused the emergence of novel cell types in the course of evolution. Investigation of Pvio is critical to understand this process in the group 4 Dictyostelia, but thus far there were no protocols to genetically transform this Pvio. We therefore developed protocols for transformation, gene knock-out, and overexpression for this species, analyzed the transcriptomes of its individual cell types and performed transcriptome-guided gene model prediction of an existing Pvio draft genome. To investigate a possible role for DIF-1 in Pvio, we deleted its stlB gene, which is required for the first step in DIF-1 biosynthesis. Surprisingly, the Pvio stlB− mutant showed an increase rather than a decrease in stalk-like cells, suggesting that the role of DIF-1 as inducer of this cell type emerged relatively recently in group 4.
Materials and Methods
Pvio Genome Sequencing and Transcriptomics
The genome of Pvio QSvi11 was sequenced using the 454 sequencing technology (Voelkerding et al. 2009). Sequencing libraries were prepared, sequenced, and assembled as described previously (Ostrowski et al. 2015). Data from the genome sequence are available under BioProject PRJNA45881 in the ENA and NCBI.
Pvio Cell Type-Specific Transcriptomes and Genome Annotation
Total RNA was prepared from purified Pvio QSvi11 spore and stalk cells as well as vegetative cells from Pvio, obtained from three separate experiments, following the cell isolation protocol previously described (Kin et al. 2018). The qualities of the RNAs isolated in three independent experiments were assessed with TapeStation (Agilent) to be excellent (RIN > 8.5) and cDNA libraries were prepared using the Truseq Stranded mRNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina). About 75-bp paired-end reads were sequenced with Illumina NextSeq 500 at the Tayside Centre for Genomic Analysis (https://tcga.org.uk; last accessed April 21, 2020) in two independent runs and were archived in ENA as Bioproject PRJEB34080. The RNA-Seq data were used to annotate the Pvio QSvi11 genome (NCBI Bioproject PRJNA45881) using the pipeline BRAKER1 (Hoff et al. 2016). BRAKER1 utilizes two separate programs, GeneMark-ET (Lomsadze et al. 2014) and AUGUSTUS (Stanke et al. 2008), to create gene models. More specifically, GeneMark-ET incorporates unassembled RNA-Seq reads and generates ab initio gene predications. A subset of GeneMark-ET predicted genes was then used to train AUGUSTUS, which generated the final gene models.
To obtain cell type-specific gene expression profiles, a software package RSEM (Li and Dewey 2011) was used to estimate transcript abundances, with the Bowtie2 aligner for mapping RNA-Seq reads to gene features. We used the “-estimate-rspd” option in RSEM to estimate read start position distributions, which is expected to facilitate more accurate abundance estimates for 3′ biased reads produced from oligo-dT primed libraries (Li and Dewey 2011). The expression data in transcripts per million are listed in supplementary file Pvio_Celltype_TPM.xlsx, Supplementary Material online.
Pvio Transformation
Pvio QSvi11 was cultured on 1/5th SM agar (Formedium, United Kingdom) in association with Escherichia coli 281. When plates started to clear, cells were harvested, washed with KK2 (20 mM K-phosphate, pH 6.2), and incubated in culture dishes at 2×105 cells/ml in HL5 overnight. Cells were harvested and washed with H-50 buffer (Pang et al. 1999) and resuspended in H-50 buffer at 5×107 cells/ml. An aliquot of 0.1 ml of the cell suspension was mixed with 10 µg of plasmid vector DNA, transferred to a 1-mm gap electroporation cuvette, and electroporated by Gene Pulser II (BIORAD) at 0.65 kV and 25 µF with two pulses. The cells were immediately transferred to a dish containing 10 ml HL5 medium and allowed to recover at 21 °C for 5–6 h. The cells were resuspended in 10 ml KK2, containing autoclaved Klebsiella aerogenes (K.aer) (final OD600=8.5), 10% HL5, and 20 µg/ml of G418, shaken for 48 h at 150 rpm, and distributed with G418-resistant E. coli over 1/5th SM agar, containing 50 µg/ml of G418. G418-resistant E. coli were obtained by transforming E. coli B/r with pUC4K (Addgene), which harbors a kanamycin/neomycin selection gene. Transformants were picked up after 4 days and were further grown and developed on 1/5th SM agar with E. coli.
Plasmid Constructs and Knock-Out Diagnosis
The Pvio ortholog of Ddis stlB was identified by BlastP search of the assembled and translated Pvio QSvi11 transcripts with the Ddis StlB sequence, whereas the genome sequence was retrieved by TBlastN search of the Pvio QSvi11 whole-genome shotgun sequence (Bioproject PRJNA45881) with Ddis StlB. Two stlB fragments of 1,606 bp (fragment 1) and 1,339 bp (fragment 2) were amplified from Pvio QSvi11 genomic DNA, using primer combinations Pv_stlB_Frag1F/Pv_stlB_Frag1R and Pv_stlB_Frag2F/Pv_stlB_Frag2R (supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online), respectively, and cloned into vector pLoxP-NeoIII (Kawabe et al. 2012) to flank the loxP-Neo selection cassette. The resulting pPvStlB-KO construct was excised with NotI/XhoI and transformed into Pvio QSvi11. Genomic DNAs were isolated from G418-resistant clones and probed by PCR with primer pairs Pv_stlB_NegF/Pv_stlB_NegR and Pv_stlB_Pos5′/cas1 for stlB gene disruption by homologous recombination (supplementary fig. S2, Supplementary Material online). From 27 investigated clones, 19 clones showed insertion of the LoxP-Neo cassette in stlB. To remove the Neo cassette from the Pvio stlB− cells, cells were transformed with pA15NLS.Cre (Faix et al. 2004) for transient expression of Cre recombinase. Transformed clones were replica-plated with G418-resistant E. coli on lactose/peptone agar supplemented with 50 µg/ml G418 for negative selection.
To generate a fusion of the LacZ reporter with (pre)stalk gene promoters, putative orthologs of the Ddis (pre)stalk genes ecmA or ecmB were identified by BlastP of the translated Pvio QSvi11 transcriptome. Phylogenetic inference of the retrieved sequences revealed that ecmA and ecmB are group 4-specific gene duplicates and that their common ancestor was duplicated in Pvio (supplementary fig. S3, Supplementary Material online). The Pvio genes were named ecmAB1 and ecmAB2. The 868-bp 5′ region of ecmAB1, which includes the start codon, was amplified from Pvio gDNA using primer pair Pv_ecmAB1_P F/Pv_ecmAB1_P R (supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online) and, after XbaI/BglII digestion, cloned into the XbaI and BglII sites of pDdGal-17(H-) (Harwood and Drury 1990) to yield Pv_ecmAB1-lacZ. Both plasmids were transformed into Pvio wild-type cells or G418 sensitive stlB− cells (see above) and after recovery in HL5, transformants were clonally selected during coculture with G418-resistant E. coli on 1/5th SM agar, containing 50 µg/ml of G418.
B-Galactosidase Histochemistry
Pvio cells transformed with Pv-ecmAB1-gal were harvested from growth plates, distributed at 106 cells/cm2 on nitrocellulose filters supported by nonnutrient (NN) agar (1.5% agar in 8.8 mM KH2PO4 and 2.7 mM Na2HPO4) and incubated at 22 °C until the desired developmental stages had been reached. Filters with developing structures were next fixed in glutaraldehyde and stained with X-gal as previously described (Dingermann et al. 1989).
Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
Wild-type and stlB− cells were distributed over NN agar at 105 cells/cm2 and incubated at 4 °C overnight. Cells were next incubated at 22 °C and RNA was isolated from the cells at 3 h intervals. cDNAs were synthesized from 1 µg RNA with the SensiFAST cDNA synthesis kit (Bioline, United Kingdom), which generates 20 µl aliquots of cDNA. cDNA samples of 1 μl were used for quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) with PerfeCTa SYBR Green SuperMix (QuantaBio) and analyzed by LightCycler 96 System (Roche, Germany). The Pvio stalk gene ecmAB1, the (pre)spore gene g1612, and the constitutively expressed gene rpb5 were amplified with primer pairs Pv-ecmAB1-51/Pv-ecmAB1-31, Pv-g1612-51/Pv-g1612-31, and Pv-rpb5-51/Pv-rpb5-31 (supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online). The PCR program consisted of 45 cycles, with 30 s at 95, 55, and 72 °C each.
Results
Polysphondylium violaceum Genome Sequencing and Gene Model Annotation
The genome of Pvio Qsvi11 was sequenced using the Roche 454 sequencing platform, assembled, and archived in NCBI by some of us (J.E.S., A.K., R.S., D.M.M., S.R., K.C.W., and R.A.G.) in 2012. The others collected RNA-Seq data of spore, stalk, and vegetative cells from Pvio QSvi11 to identify conserved cell type-specific genes and used the data to perform gene model prediction of the archived genome. The RNA-Seq reads and the whole-genome assembly were processed with the pipeline BRAKER1 (Hoff et al. 2016), which combines two genome annotations tools, GeneMark-ET and AUGUSTUS. The final gene models generated by AUGUSTUS yielded a total of 10,597 coding sequences (table 1). The Pvio genome is at 25.7 Mb only somewhat larger than that of Dictyostelium lacteum (Dlac), thus far the smallest published dictyostelid genome. This is reflected in the number of coding sequences also being relatively small. With a 68.2% A/T content, the codon bias of Pvio is more similar to that of the groups 1, 2, and 3 representative species Dictyostelium fasciculatum (Dfas), Polysphondylium pallidum (Ppal), and Dlac than to that of Dictyostelium purpureum (Dpur) and Ddis in its sister group 4.
Table 1.
Features of Published Dictyostelid Genomes
| Ddis | Dpur | Pvio | Dlac | Ppal | Dfas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contigs/supercontigs | 226/6 | 1,213/799 | 1,228 | 54/54 | 52/41 | 33/25 |
| Total nucleotides (Mb) | 33.9 | 33.0 | 25.7 | 23.4 | 32.9 | 31.0 |
| Average contig length (kb) | 155 | 27 | 21 | 432 | 320 | 1,064 |
| A/T content (%) overall/in CDS | 77.6/72.6 | 75.5/ND | 68.2/65.5 | 70.2/67.8 | 68/63.8 | 66.2/63.2 |
| Coding sequences (CDS) | 13,258 | 12,410 | 10,597 | 10,232 | 11,694 | 12,007 |
| Average gene length | 1,604 | 1,760 | 1,624 | 1,712 | 1,634 | 1,696 |
| Gene density (CDS per Mb) | 396 | 376 | 412 | 437 | 375 | 392 |
| DNA in CDS (Mb) | 21.3 | 21.8 | 17.3 | 17.5 | 18.7 | 20.2 |
| Intergenic DNA (Mb) | 12.6 | 11.2 | 8.4 | 5.8 | 14.2 | 10.8 |
Note.—Genome statistics for Ddis, Dpur, Dlac, Ppal, and Dfas were retrieved from Eichinger et al. (2005), Gloeckner et al. (2016), Sucgang et al. (2011), and Heidel et al. (2011), respectively. ND, not determined. Dlac, Ppal, and Dfas were renamed as Tieghemostelium lacteum, Heterostelium album, and Cavenderia fasciculata in a new classification of Dictyostelia (Sheikh et al. 2018), which may need revision in the near future (Schilde et al. 2019) and is therefore not used here.
Transformation of Pvio
To establish genetic transformation of Pvio, we first tested resistance to the antibiotics G418, hygromycin, and blasticidin that are routinely used to select Ddis transformants. Many other Dictyostelium species show high general resistance to antibiotics, rendering selection of transformed wild-type cells problematic. Proliferation of Pvio QSvi11 grown in suspension with heat-killed K.aer was suppressed by 20 µg/ml G418 or 30 µg/ml hygromycin, indicating that G418 and hygromycin can potentially be used for selection of transformed cells. To test plasmid entry into the cells, we electroporated Pvio with the LacZ expression vector pA15-Gal (Harwood and Drury 1990) using a protocol developed for Ppal (Kawabe et al. 1999), then incubated cells for 5 h in HL5 and measured β-galactosidase activity in freeze-thawed lysates. The extracts from plasmid-treated cells showed 4.9-fold higher β-galactosidase activity than mock-electroporated cells, indicating that the pA15-Gal had entered Pvio. We also examined the transient expression of LacZ from pA15-Gal after electroporation of other species, such as D. mucoroides S28b, Dictyostelium aureo-stipes YA6, D. fasciculatum SH3, and Dlac TK, but did not detect any increased β-galactosidase activity.
After transformation, Pvio cells were incubated with heat-killed K.aer in suspension culture with 20 µg/ml G418 for 1 week and then distributed with heat-killed K.aer over NN agar plates containing 20 µg/ml G418. After several days, a few clones developed. PCR analysis showed that one of six tested clones contained the NeoR cassette from pA15-Gal, indicating that stable transformation is possible in Pvio (supplementary fig. S1A, Supplementary Material online). Southern-blot analysis showed that only a single copy of the vector was inserted in the genome (supplementary fig. S1B, Supplementary Material online). When needed, this facilitates recycling of the G418-resistance cassette using the cre-loxP system (see below). Although many nontransformed cells were also recovered after selection, we improved the procedure by prolonged selection with higher G418 concentrations and other incremental changes, and our current standard selection procedure (see Materials and Methods) now mostly yields transformed cells. Pvio transformation was also achieved by using vectors which contain the hygromycin-resistance cassette (unpublished results).
Knock-Out of stlB in Pvio
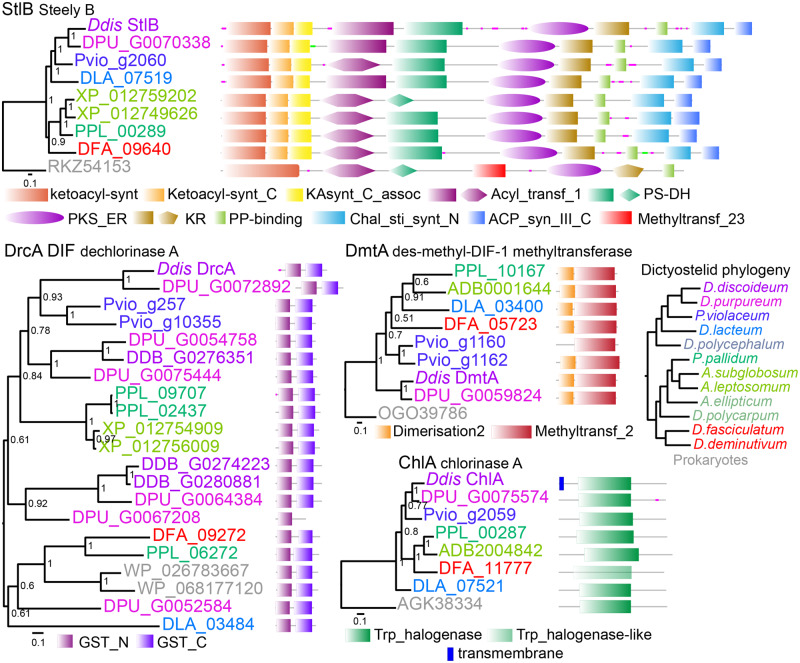
We are interested in the emergence of novel somatic cells during the evolution of multicellularity. In Dictyostelia, this occurs particularly in group 4 with its unique basal disk cells to support the stalk and upper and lower cup cells to anchor the spore mass to the stalk. Basal disk differentiation is induced by the chlorinated polyketide DIF-1 (Saito et al. 2008), which is synthesized by the polyketide synthaste StlB and further modified by DmtA and ChlA (Thompson and Kay 2000; Saito et al. 2008; Neumann et al. 2010), enzymes that are conserved throughout Dictyostelia (Gloeckner et al. 2016). To investigate the ancestral role of DIF-1 signaling, we attempted to delete the Pvio stlB gene. DNA sequences for stlB and the other DIF-1 metabolizing enzymes were retrieved from Pvio QSvi11 transcriptome and genome sequences as highest scoring bidirectional BLAST hits. Gene orthology was further confirmed by phylogenetic inference (fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
—Conservation of DIF-1 metabolic enzymes across Dictyostelia. Putative orthologs of the DIF-1 metabolic enzymes StlB, DmtA, ChlA and DrcA were retrieved by BlastP search of social ameba genomes and GenBank. Sequences were aligned using Clustal Omega (Sievers and Higgins 2014) with five combined iterations and phylogenetic trees were inferred with MrBayes (Ronquist and Huelsenbeck 2003) using a mixed amino acid substitution model with rate variation between sites estimated by a gamma distribution. Bayesian posterior probabilities of the tree nodes are indicated and trees are annotated with the functional domain architecture of the proteins as analyzed by SMART (Schultz et al. 1998). Domains present at E-values above threshold are shown in wash-out color. Gene IDs and locus tags are color coded to reflect the host species as indicated in the dictyostelid core phylogeny (top left), retrieved from Singh et al. (2016). Note that single-gene phylogenies may not strictly follow the species phylogeny, which is based on 47 genes, due to limited phylogenetic signal or clade-specific gene gain and loss.
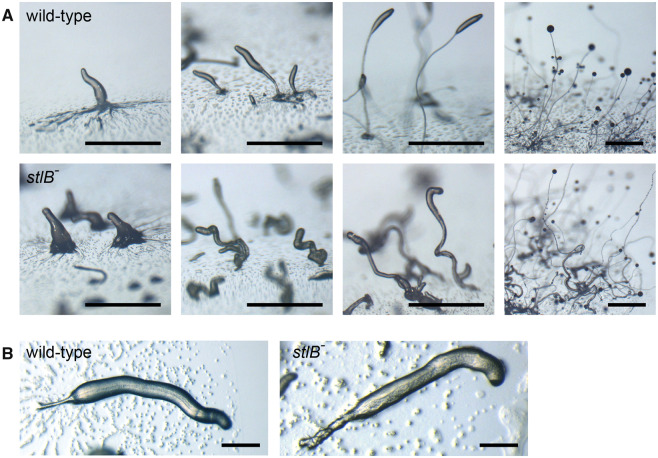
A stlB knock-out construct was designed to replace the essential phospho-pantetheine binding domain of polyketide synthases like stlB (Moretto et al. 2017) with the G418-resistance cassette and stop codons in all reading frames. Homologous recombination was extremely efficient, because 70% of the G418-resistant clones proved to be knock-outs (supplementary fig. S2, Supplementary Material online). The knock-out clones aggregated normally, but formed abnormal primary sorogens, which were overall thicker than those of wild-type and had a curly appearance (fig. 2A).
Fig. 2.
—Phenotype of the Pvio stlB− mutant. Pvio wild-type and stlB− cells were incubated overnight at 4 °C on NN agar at 106 cells/cm2 and then transferred to 22 °C. (A) Developmental morphologies were sequentially photographed at 5, 8, 10, and 30 h at 22 °C. Bars: 1 mm. (B) Stalk formation after 5–8 h at 22 °C, imaged at higher magnification. Bars: 0.2 mm.
Pvio cell masses are normally lifted up rapidly after aggregation by the newly formed stalk, which penetrates the cell mass. This process was delayed in the stlB− mutants and the early stalk was irregularly shaped and several cells thick (fig. 2B), compared to the mostly single cell width of Pvio wild-type stalks. As fruiting body formation progressed, stalks became thinner and looked more regular. The stlB− fruiting bodies also appeared to form fewer side branches, and those that formed often lacked stalks. However, compared with other wild-type Pvio strains, which robustly form many regular whorls of side branches, strain QSvi11, which was chosen here because of its sensitivity to antibiotics, shows rather variable branching, with many fruiting bodies showing no branches at all.
Stalk Gene Expression in Pvio stlB− Mutants
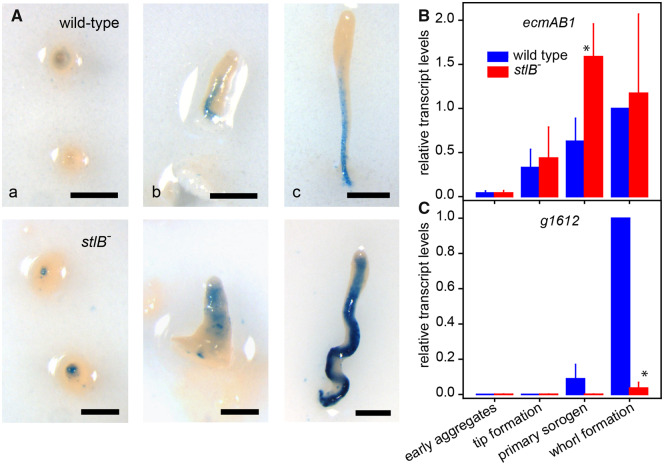
To investigate whether the Pvio stlB− mutant expressed known DIF-regulated stalk genes, we searched for ecmA and ecmB orthologs in the Pvio genome. Two close Pvio relatives to ecmA and/or ecmB were detected, which form a sister clade to Ddis ecmA and ecmB (supplementary fig. S3, Supplementary Material online). They are therefore not true orthologs of either, but the result of an independent gene duplication of the ancestor to Ddis ecmA and ecmB. We therefore named the Pvio genes ecmAB1 and ecmAB2. We prepared fusion constructs of the LacZ reporter gene and the available 868-bp promoter region of the ecmAB1 gene. The loxP neomycin cassette was excised with cre-recombinase from the disrupted stlB gene by transformation of the stlB− mutant with pA15NLS.Cre (Faix et al. 2004), and a G418 sensitive stlB− clone as well as wild-type Pvio were transformed with the Pv_ecmAB1-lacZ construct. Figure 3A shows that in wild-type structures Pvio ecmAB1 is weakly expressed in aggregate tips and more strongly in the stalk of early and later sorogens at some distance from the tip. In the stlB− mutant, aggregate tips express ecmAB1 more strongly than is the case in wild-type, whereas both early and late sorogens express ecmAB1 in the stalk starting from just below the tip. Particularly, in the later sorogens, ecmAB1 was expressed very strongly and conform to the appearance of the sorogens under transillumination (fig. 2B), the ecmAB1-stained stalk was thicker than that of wild-type as well as curly.
Fig. 3.
—Stalk and spore gene expression in Pvio stlB−. (A) EcmAB1 expression pattern. Pvio wild-type and stlB− cells, transformed with the Pv_ecmAB1-lacZ vector, were incubated on nitrocellulose filters supported by NN agar until they had reached the tipped mound (a) and early (b) and late (c) primary sorogen stage. Structures were then fixed and stained with X-gal. Bars: 0.2 mm. (B) Stalk and spore transcript levels. Pvio wild-type and stlB− cells were incubated on NN agar at 4 °C overnight and then at 22 °C for 3, 6, 9, and 12 h, when they had reached the indicated stages. Total RNA was isolated and levels of ecmAB1 stalk-specific transcripts, g1612 (pre)spore-specific transcripts, and rpb5 constitutively expressed transcripts were determined by RT-qPCR. Data for ecmAB1 and g1612 were normalized to rpb5 transcript levels and expressed relative to transcript levels at 12 h for wild-type cells. Means and SD of three experiments, assayed with three technical replicates each, are presented. Asterisks indicate significant differences between wild-type and stlB− transcript levels (t-test, P<0.05).
The intensity of LacZ staining in transformed cells may reflect plasmid copy number rather than the level of promoter activity. We therefore also measured ecmAB1 transcript levels in the developing sorogens directly by RT-qPCR. Figure 3B shows that ecmAB1 transcripts are significantly higher in stlB− mutants than in wild-type cells. To investigate whether the increase in stalk gene expression is accompanied by a loss in prespore gene expression, we also sought for homologs of Ddis spore coat genes in Pvio. Twelve homologs were detected (supplementary fig. S4, Supplementary Material online), but orthology with Ddis spore coat genes could not be unequivocally established.
We used RNA-Seq data of purified Pvio spores, stalks, and vegetative cells (supplementary file Pvio_Celltype_TPM.xlsx, Supplementary Material online) to assess which genes were specifically expressed in spores (supplementary table S2, Supplementary Material online). This only appeared to be the case for g1612 and its close homolog g7962. We therefore used g1612 as a (pre)spore marker. RT-qPCR with g1612-specific primers showed that in wild-type g1612 transcript levels first appeared in primary sorogens and strongly increased when sorogens formed the first whorls of side branches with mature spores. Expression of g1612 was much reduced in stlB− cells (fig. 3B), which could result from overproduction of stalk cells at the expense of prespore cells or from the lack of side branch formation in the stlB− sorogens.
In conclusion, unlike Ddis, where deletion of stlB results in fruiting bodies with thinner stalks and lacking the basal disk with its stalk-like cells, the Pvio stlB− mutant actually overproduces stalk cells, accompanied by overexpression of at least one stalk gene and underexpression of a (pre)spore gene.
Effects of DIF-1 on the Pvio stlB− Mutant
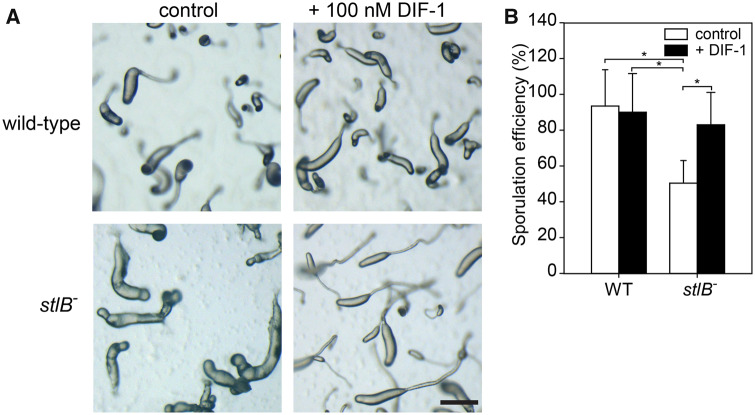
Normal slug and fruiting body formation are restored when the Ddis stlB− mutant is allowed to develop on agar that contains 100 nM DIF-1. We examined whether this is also the case for the Pvio stlB− mutant. Figure 4A shows that 100 nM DIF-1 has no effect on sorogen formation by wild-type Pvio. However, the abnormal sorogens of Pvio stlB− are fully restored to normality in the presence of 100 nM DIF-1. We also tested whether DIF-1 affects sporulation in Pvio stlB−. Figure 4B shows that ∼90% of wild-type cells develop into spores both in the absence and in the presence of DIF-1. For the stlB− mutant, this is only 50% in the absence of DIF-1 and 80% in its presence. These experiments show that DIF-1 restores normal stalk formation and morphogenesis as well as sporulation in the stlB− mutant, demonstrating that the developmental defect caused by the stlB lesion is likely due to defective polyketide synthesis.
Fig. 4.
—Effects of DIF-1 on the stlB− phenotype. (A) Development. Pvio wild-type and stlB− cells were plated on NN agar with or without 100 nM DIF-1, incubated at 4 °C overnight, and then for 6 h at 22 °C. Bar: 0.2 mm. (B) Sporulation efficiency. Cells were developed on 1 cm2 pieces of filter paper supported by NN agar with or without 100 nM DIF-1. After 2 days, filters with mature fruiting bodies were vortexed vigorously in 1 ml of KK2 and spores were counted. Sporulation efficiency was calculated by dividing the number of spores counted by the total number of cells plated initially. Mean and SD of three experiments performed in duplicate are shown. Significant differences are indicated by asterisks (t-test, P<0.02).
Discussion
Polysphondylium violaceum Can Be Genetically Transformed
In the course of our evolutionary comparative studies, we have attempted to make a range of species amenable to genetic transformation. The major obstruction for doing so is the extreme resistance of many species to antibiotics like G418, blasticidin, hygromycin, and nourseothricin that are used for transformation of the model species Ddis. Even Ppal, which we have transformed routinely for many years, is completely resistant to blasticidin and hygromycin and is only effectively killed by 300 µg/ml G418 as opposed to 10 µg/ml for Ddis. In addition, species that are sensitive to antibiotics can resist uptake of plasmid DNA by electroporation or by transfection with calcium phosphate-based transformation protocols. Pvio QSvi11 is sensitive to G418 and hygromycin, but the developmentally more robust strain Pvio P6 is again highly resistant.
We here show that Pvio QSvi11 can be transformed and that by using the cre-lox system the selectable marker can be recycled. An added bonus of this strain is that homologous recombination is extremely efficient. Including stlB, we have at present deleted four genes in Pvio, with all attempts yielding at least 70% positive clones. The position of Pvio as sister clade to group 4 makes it particularly suitable for investigating the genetic change that caused the immense phenotypic innovations of group 4.
Conservation of DIF-1 Metabolizing Enzymes
The polyketide synthase StlB is well conserved throughout the dictyostelid phylogeny, inclusive of its elaborate domain architecture (fig. 1), suggesting that synthesis of the polyketide backbone of DIF-1 should be possible for all species. The des-methyl-DIF-1 methyltransferase DmtA and single chlorinating enzyme ChlA are also conserved as orthologs, albeit that in the group 1 species Dfas the halogenase domain of ChlA is no longer recognized by the domain Markov model, and the DmtA of the group 2 species A. subglobosum is not functionally equivalent to Ddis DmtA (Mohri et al. 2014). Chlorinated compounds are made by all tested species, but only those in group 4 and probably Pvio synthesize DIF-1 (Kay et al. 1992). The dechlorinating enzyme DrcA is one of many gluthatione-S-transferases and is the major enzyme that inactivates DIF-1 in group 4 (Velazquez et al. 2011). The DrcAs from group 4 species cluster in a separate clade (fig. 1), whereas the closest nongroup 4 homologs are about equidistant between DrcA and other group 4 gluthatione-S-transferases. Combined with observations that Pvio cannot dechlorinate DIF-1 (Van Es et al. 1995), this suggests that the ability to dechlorinate DIF-1 evolved only in group 4.
Loss of StlB in Pvio Results in Excessive Stalk Cell Differentiation
In Ddis, deletion of stlB results in longer weaker slugs and fruiting bodies with thinner stalks that lack the basal disk (Saito et al. 2008). The basal disk is a group 4 innovation and is not present in its sister species Pvio (Schilde et al. 2014). To investigate what might be an ancestral role for StlB and DIF-1, we deleted the Pvio stlB gene. The Pvio stlB− mutant differed considerably from the Ddis stlB− mutant. Instead of thinner stalks, Pvio stlB− fruiting bodies had thicker stalks and overexpressed the stalk gene ecmAB1. The stalks were also irregularly shaped and stlB− fruiting bodies showed reduced formation of whorls of side branches and a reduced number of spores. Expression of a (pre)spore gene was also reduced in stlB− sorogens. However, it is not clear whether this is due to the StlB product being directly required for spore gene expression, or to the defective formation of secondary branches, where spore maturation normally initiates during Pvio fruiting body formation. The overproduction of stalk cells in stlB− will additionally reduce the number of cells available for spore formation.
All defects of the Pvio stlB− mutant could be restored by including DIF-1 in the supporting agar, which supports the earlier findings that Pvio probably synthesizes DIF-1 (Kay et al. 1992). However, while required for proper stalk morphology, here DIF-1 is not required for actual stalk cell differentiation.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank the Human Genome Sequencing Center (HSGC) production team, consisting of A. Kurien, P. Aqrawi, F. Arias, R. Awwad, P. Battles, A. Bell, C. Bess, C. Bickham, K. Blankenburg, W. Cai, D. Chau, M. Coyle, S. Denson, L. Forbes, L. Francisco, Q. Fu, R. Goodspeed, S. Gross, S. Gubbala, K. Hirani, M. Hogues, L. Jackson, M. Javaid, J. Jayaseelan, V. Korchina, C. Kovar, F. Lara, S. Lee, M. Li, S. Macmil, C. Mandapat, C. R. Mata, T. Mathew, T. Matskevitch, K. Morales, M. Munidasa, R. Najjar, D. Ngo, L. Nguyen, N. Nguyen, G. Okwuonu, F. Ongeri, T. Palculict, S. Patil, L. Perales, C. Pham, L.-L. Pu, M. Puazo, S. Qi, J. Rouhana, N. Saada, J. Shafer, D. Simmons, L.-Y. Tang, M. Taylor, R. Thornton, S. Vattathil, V. Velamala, M. Wang, C. Kovar, and Y. Han. for Pvio genome sequencing and C. Qu, S. Scherer, and M. Batterton and E. Skinner for genome assembly and annotation, project coordination, and database submissions, respectively. This work was supported by National Science Foundation (EF 0626963 to R.A.G.), the National Institutes of Health (U54 HG003273 to R.A.G.), the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (26-5247 and H28-1002 to T.B.N. and K.K., respectively), European Molecular Biology Organisation (ALTF 295-2015 to K.K.), the Wellcome Trust (100293/Z/12/Z to P.S.), and European Research Council (742288 to P.S.).
Author Contributions
J.E.S. collected the genome reference sample. J.E.S., A.K., R.S., S.R., and R.A.G. designed the genome sequencing project. J.E.S., A.K., and R.S. identified the strain for strategic representation of the major evolutionary branches of the dictyostelids and cultured the strain for genome sequencing. R.A.G. directs the HSGC, D.M.M. directs the HSGC production activities, S.R. coordinated the genome project, K.C.W. directed the genome assembly and annotation, and R.S. and A.K. evaluated the genome assemblies and analyzed the gene content. T.B.N. deleted stlB and examined the stlB− phenotype, Y.K. developed Pvio transformation, K.K. performed Pvio transcriptomics and gene model prediction. T.B.N. and P.S. designed the stlB study and P.S. wrote the article.
Data deposition: The raw RNA-sequencing reads generated during this study are available in the European Nucleotide Archive under study number PRJEB34080. The processed RNA-Seq data set is listed as supplementary data Pvio_Celltype_TPM.xlxs, Supplementary Material online. The Polysphondylium violaceum Whole Genome Shotgun project has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession AJWJ00000000. The version described in this article is version AJWJ01000000.
Literature Cited
- Dingermann T, et al. 1989. Optimization and in situ detection of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene 85(2):353–362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger L, et al. 2005. The genome of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 435(7038):43–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faix J, Kreppel L, Shaulsky G, Schleicher M, Kimmel AR.. 2004. A rapid and efficient method to generate multiple gene disruptions in Dictyostelium discoideum using a single selectable marker and the Cre-loxP system. Nucleic Acids Res. 32(19):e143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloeckner G, et al. 2016. The multicellularity genes of dictyostelid social amoebas. Nat Commun. 7:12085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood AJ, Drury L.. 1990. New vectors for expression of the E. coli lacZ gene in Dictyostelium. Nucleic Acids Res. 18(14):4292–4292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidel A, et al. 2011. Phylogeny-wide analysis of social amoeba genomes highlights ancient origins for complex intercellular communication. Genome Res. 21(11):1882–1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff KJ, Lange S, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M, Stanke M.. 2016. BRAKER1: unsupervised RNA-Seq-based genome annotation with GeneMark-ET and AUGUSTUS. Bioinformatics 32(5):767–769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y, Enomoto T, Morio T, Urushihara H, Tanaka Y.. 1999. LbrA, a protein predicted to have a role in vesicle trafficking, is necessary for normal morphogenesis in Polysphondylium pallidum. Gene 239(1):75–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y, Weening KE, Marquay-Markiewicz J, Schaap P.. 2012. Evolution of self-organisation in Dictyostelia by adaptation of a non-selective phosphodiesterase and a matrix component for regulated cAMP degradation. Development 139(7):1336–1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay RR, Taylor GW, Jermyn KA, Traynor D.. 1992. Chlorine-containing compounds produced during Dictyostelium development. Biochem J. 281(1):155–161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kin K, Forbes G, Cassidy A, Schaap P.. 2018. Cell-type specific RNA-Seq reveals novel roles and regulatory programs for terminally differentiated Dictyostelium cells. BMC Genomics 19(1):764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B, Dewey CN.. 2011. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12(1):323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomsadze A, Burns PD, Borodovsky M.. 2014. Integration of mapped RNA-Seq reads into automatic training of eukaryotic gene finding algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(15):e119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri K, Hata T, Kikuchi H, Oshima Y, Urushihara H.. 2014. Defects in the synthetic pathway prevent DIF-1 mediated stalk lineage specification cascade in the non-differentiating social amoeba, Acytostelium subglobosum. Biol Open. 3(6):553–560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretto L, Vance S, Heames B, Broadhurst RW.. 2017. Dissecting how modular polyketide synthase ketoreductases interact with acyl carrier protein-attached substrates. Chem Commun. 53(83):11457–11460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris HR, Taylor GW, Masento MS, Jermyn KA, Kay RR.. 1987. Chemical structure of the morphogen differentiation inducing factor from Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 328(6133):811–814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann CS, Walsh CT, Kay RR.. 2010. A flavin-dependent halogenase catalyzes the chlorination step in the biosynthesis of Dictyostelium differentiation-inducing factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107(13):5798–5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski EA, et al. 2015. Genomic signatures of cooperation and conflict in the social amoeba. Curr Biol. 25(12):1661–1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang KM, Lynes MA, Knecht DA.. 1999. Variables controlling the expression level of exogenous genes in Dictyostelium. Plasmid 41(3):187–197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeralo M, et al. 2013. Analysis of phenotypic evolution in Dictyostelia highlights developmental plasticity as a likely consequence of colonial multicellularity. Proc R Soc B. 280(1764):20130976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP.. 2003. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19(12):1572–1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T, Kato A, Kay RR.. 2008. DIF-1 induces the basal disc of the Dictyostelium fruiting body. Dev Biol. 317(2):444–453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato YG, Kagami HN, Narita TB, Fukuzawa M, Saito T.. 2013. Steely enzymes are involved in prestalk and prespore pattern formation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 77(10):2008–2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato YG, Suarez T, Saito T.. 2016. Stalk cell differentiation without polyketides in the cellular slime mold. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 80(7):1368–1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P, et al. 2006. Molecular phylogeny and evolution of morphology in the social amoebas. Science 314(5799):661–663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilde C, et al. 2019. A well supported multi gene phylogeny of 52 dictyostelia. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 134:66–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilde C, Skiba A, Schaap P.. 2014. Evolutionary reconstruction of pattern formation in 98 Dictyostelium species reveals that cell-type specialization by lateral inhibition is a derived trait. EvoDevo. 5(1):34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP.. 1998. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95(11):5857–5864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh S, et al. 2018. A new classification of the Dictyostelids. Protist 169(1):1–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sievers F, Higgins DG.. 2014. Clustal omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol Biol. 1079:105–116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R, Schilde C, Schaap P.. 2016. A core phylogeny of Dictyostelia inferred from genomes representative of the eight major and minor taxonomic divisions of the group. BMC Evol Biol. 16(1):251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanke M, Diekhans M, Baertsch R, Haussler D.. 2008. Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding. Bioinformatics 24(5):637–644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucgang R, et al. 2011. Comparative genomics of the social amoebae Dictyostelium discoideum and Dictyostelium purpureum. Genome Biol. 12(2):R20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson CR, Kay RR.. 2000. The role of DIF-1 signaling in Dictyostelium development. Mol Cell. 6(6):1509–1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Es S, Hodgkinson S, Schaap P, Kay RR.. 1995. Metabolic pathways for differentiation-inducing factor-1 and their regulation are conserved between closely related Dictyostelium species, but not between distant members of the family. Differentiation 58(2):95–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez F, Peak-Chew SY, Fernández IS, Neumann CS, Kay RR.. 2011. Identification of a eukaryotic reductive dechlorinase and characterization of its mechanism of action on its natural substrate. Chem Biol. 18(10):1252–1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkerding KV, Dames SA, Durtschi JD.. 2009. Next-generation sequencing: from basic research to diagnostics. Clin Chem. 55(4):641–658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.