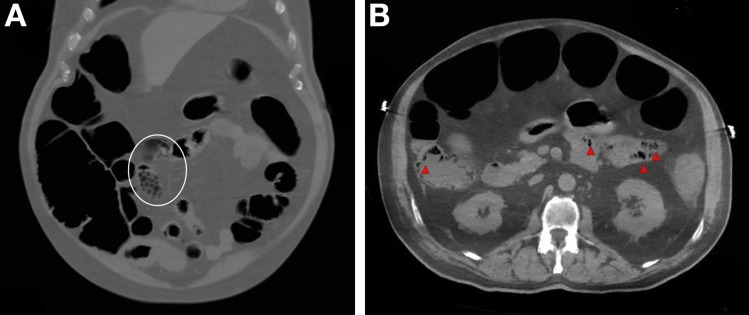
A 72-year-old man with multiple comorbidities presented with diffuse abdominal pain and bleeding per rectum for 1 day. He denied any respiratory symptoms; however, he did test positive for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during screening in his nursing home recently. On arrival, he was febrile (104℉) but hemodynamically stable. Physical examination revealed a distended and diffusely tender abdomen without guarding. Computed tomography of abdomen showed descending and sigmoid colon wall thickening and mid-ascending colon pneumatosis without portal venous gas. This was suggestive of COVID-19–induced ischemic colitis with partial bowel obstruction in the absence of other provoking factors. Patient was treated conservatively with bowel rest, adequate hydration, and intravenous antibiotics. Although his gastrointestinal symptoms improved, his condition was subsequently complicated by sepsis, cardiac ischemia, renal insufficiency, and respiratory failure related to severe COVID-19 infection.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is an uncommon condition identified by multiple gas-filled cysts in the intestinal submucosa/serosa on imaging. Rupture of these cysts causes pneumoperitoneum, which mandates emergent surgical intervention. The pathophysiology of this condition is still under speculation; however, it has been associated with many gastrointestinal and pulmonary conditions. Because of this patient’s absence of initial respiratory symptoms, the hypercoagulability and thromboinflammation associated with COVID-19 may be the culprit leading to bowel ischemia.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest The authors disclose no conflicts.