Abstract
Background
Coronavirus has serially overtaken our metropolitan hospitals. At peak, patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome may outnumber mechanical ventilators. In our Miami Hospital System, COVID‐19 cases have multiplied for 4 weeks and elective surgery has been suspended.
Methods
An Otolaryngologic Triage Committee was created to appropriately allocate resources to patients. Hospital ethicists provided support. Our tumor conference screened patients for nonsurgical options. Patients were tested twice for coronavirus before performing urgent contaminated operations. N95 masks and protective equipment were conserved when possible. Patients with low‐grade cancers were advised to delay surgery, and other difficult decisions were made.
Results
Hundreds of surgeries were canceled. Sixty‐five cases screened over 3 weeks are tabulated. Physicians and patients expressed discomfort regarding perceived deviations from standards, but risk of COVID‐19 exposure tempered these discussions.
Conclusions
We describe the use of actively managed surgical triage to fairly balance our patient's health with public health concerns.
1. INTRODUCTION
Our tradition in medicine, dating back to the Hippocratic oath in the fifth‐centuryBC, 1 has emphasized the importance of putting our patient first, avoiding choices that might harm them, and not considering issues unrelated to that particular patient's health as we make our medical decisions. Public health considerations involving risks to providers and other patients have not normally been factored into the decision. Furthermore, what we have known to be best for the patient in the past, has not involved calculating the risk of contracting a potentially fatal infectious disease while merely walking into the hospital.
Recently, however, the unprecedented and now‐familiar events related to the Coronavirus Two induced pandemic and the illness that the virus causes (COVID‐19) have affected communities all over the globe,2, 3, 4 including South Florida. By the time of this writing, Newsweek reported, based on U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data, that coronavirus had surpassed heart disease and cancer as the number one killer of Americans on a daily basis. 5
On March 14, U.S. Surgeon General Jerome Adams recommended in a tweet that hospitals stop all elective procedures amid the COVID‐19 outbreak. 6 The same day our two hospitals' administrations issued an electronic communication asking surgeons to cancel all elective surgeries at our facilities. On March 20, the Governor of Florida issued a formal ban on elective surgery. 7 Permissible procedures included “removal of cancerous tumors, transplants, limb‐threatening vascular surgeries, trauma‐related procedures, and dental care related to the relief of pain and management of infection.” 7 In practice, in oncologic surgery, it was left to each institution to determine what was urgent, and which patients would be best served by receiving surgery, despite increased risk to the patient, providers, and other patients during the pandemic.
Our approach, as we addressed surgical triage, was to consider each patient's risk of complications related to receiving surgery in the midst of the pandemic and deciding if that risk “tipped the scales” toward delaying care or planning an alternative treatment. Though data were scarce, experience in China and Italy indicated that the risk of either directly developing a coronavirus infection, or of ending up with a complication requiring care in the midst of a situation of inadequate medical resources, might outweigh the benefit of receiving cancer surgery earlier in certain cases.3, 4, 8
The greatest paradigm shift that occurs in times of crisis, however, is the concept that the good of society, and the health of the caregivers and other patients, may have some weight in the equation, even as clinicians continue to make our patients' well‐being our primary goal. Considering these additional factors is the part that we may find most difficult to adjust to. Furthermore, as we approach so called “surge” conditions in any disaster, and resources approach the point of being overwhelmed, these factors may become more important, and even approach or surpass those of the patients themselves.9, 10
In times of crisis, it is clearly recognized that standards of medical care may have to be altered. In an almost clairvoyant publication, intensivist and disaster management expert Michael Christian, MD, published an essay entitled “Triage” in October2019, 9 just before anyone imagined the events that were about to unfold in Wuhan, China. He defines triage as “allocating scarce resources in order to do the greatest good for the greatest number.” He emphasizes that appropriately performed triage, while difficult, can save large numbers of lives, by preserving resources for “salvageable” patients. One must add to this equation the need to protect caregivers so they can attend to other patients. There is an extensive literature on appropriate crisis triage, based on experience during warfare11, 12, 13 and natural disasters.14, 15 This was most recently seen in our own country with the crisis in New Orleans in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, when physicians in hospitals had to triage civilian patients in a manner normally seen only in the midst of battle.14, 15
While we can extrapolate from triage and management models developed for times of war or natural disaster, this global pandemic is a different entity entirely, affecting almost the entire planet at once.2, 3, 4 It involves an ascension to a peak volume and then a descension, rather than a single disaster date as would occur with a natural disaster or act of war, and it is affecting Asia, Europe, Africa, and the Americas within months of each other.2, 3 The Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome‐Coronavirus One (SARS‐CoV‐1) epidemic of 2001‐2004, 16 the hemagglutinin 1 and neuraminidase 1 (H1N1) influenza epidemic of 2009‐2010, 17 the Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome of 2012, 18 and the West African Ebola epidemic 19 of 2013 to 2014, were much more geographically confined. Perhaps for this reason, there are no published reports of a need for triage of patient with cancer during such epidemics. H1N1Influenza, in particular, was known to be virulent in patients with hematological malignancies, 17 especially if undergoing treatment, but we found no reports that access to health care was threatened, requiring triage of solid cancers. There were limited anecdotal reports of health access issues during the Ebola crisis in West Africa; they hinted at some of the issues we currently face.20, 21, 22
The ethics of triage and management in situations of crisis including pandemics have been extensively discussed, modeled and prepared for, and it is widely accepted that the rules need to be adjusted to each new situation. 9 Biddison et al 10 in a consensus statement in the critical care literature, identify 23 ethical guidelines for crisis situations. The importance of communication with patients and families and the possibility of consulting ethicists are emphasized. Moreover, they comment: “We suggest critical care resources be allocated based on specific triage criteria, irrespective of whether the need for resources is related to the current disaster/pandemic or an unrelated critical illness or injury.”
Our purpose here is to provide a practical working example of how one large head and neck oncology group sought to ensure that patients requiring head and neck surgery received appropriate triage during the pandemic, and were neither put at increased risk of a poor outcome from their tumor nor from COVID‐19 infection.
2. PATIENTS AND METHODS
As of this writing, we continue to experience the ascending portion of the COVID‐19 crisis, where resources are being protected but are still available. We have not had to deny access to surgery in a way that would not meet normal standards of care, but we did have to make choices that would not have been made in normal times. We would like to share the process and approach that was used to make these decisions in three example cases, and provide a table listing 65 patients triaged over a 3‐week period with their diagnosis, history, and disposition (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Diagnosis, history, planned procedure, and disposition of 65 triaged patients during the ascending pandemic.
| Anticipated date of surgery | Location | Patient history | Diagnosis | Surgical procedure | Disposition/risk of viral transmission | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | March 23, 2020 | University | A 69‐year‐old male with two masses in the left parotid gland, fine‐needle aspiration (FNA) with “reactive lymphoid hyperplasia” and benign epithelial cells | Neoplasm of unknown behavior of parotid gland | Superficial parotidectomy, sternocleidomastoid muscle flap |
Delayed Low risk |
Rescheduled to June |
| 2 | Mid‐March, date not specified | University | Case 1 in the text | Metastatic papillary cancer of the thyroid to retropharyngeal nodes |
Bilateral parapharyngeal/retropharyngeal Exploration, neck dissections |
Delayed Low risk |
Repeat magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (previous study 3 months ago). Plan surgery for June |
| 3 | Mid‐March, date not specified | University | A 53‐y‐old female with a nonpalpable cytologically proven deep recurrence of parotid cancer after surgical treatment several years ago in another institution. Normal facial nerve function | Intermediate‐grade mucoepidermoid cancer of parotid | Revision parotidectomy |
Delay Low risk |
Repeat MRI (previous study 4 months ago). Plan surgery for late May. Postoperative radation will be needed |
| 4 | March 23, 2020 | University | A 43‐y‐old female with 2 cm left parotid mass growing over the last 10 y, previous FNA showing pleomorphic adenoma, now experiencing discomfort, but not rapid growth | Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland | Superficial parotidectomy, sternocleidomastoid muscle flap |
Delayed Low risk |
Rescheduled to late April |
| 5 | March 24, 2020 | University | A 62‐y‐old male with history of basal cell carcinoma of the left upper lip s/p surgical resection in 2005 now with slow recurrence | Recurrent basal cell carcinoma of the lip | Lip resection, local advancement flap reconstruction |
Delayed Low risk |
Patient moved from 3/24 to 5/1 due to COVID‐19 and patient's wife having compromised immune system. Combined case with facial plastic surgeon |
| 6 | March 30, 2020 | University | A 62‐y‐old female with T4bN0 hypopharyngeal cancer extensively involving supraglottis, who had emergency tracheostomy recently | Malignant neoplasm of larynx | Total laryngectomy, partial pharyngectomy, possible composite glossectomy and tongue base resection, bilateral neck dissection, free flap |
Approved High risk |
Operated the following week |
| 7 | March 30, 2020 | University | Case 3 in the text | Malignant neoplasm of oral cavity | Composite procedure with resection of floor of mouth and mandibular resection, neck dissection, anterolateral thigh free flap vs radial forearm free flap vs scapula free flap |
Approved High risk |
Operated the following week. Had false‐positive postoperative SARS‐CoV‐2 Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT PCR). Otherwise he had an uneventful recovery. |
| 8 | March 30, 2020 | County Hospital | Case 2 in the text | Retrosternal multinodular goiter, severe tracheal compression, hyperparathyroidism | Left hemithyroidectomy for retrosternal goiter, possible sternotomy, possible total thyroidectomy, parathyroid exploration |
Approved Low‐risk surgery High‐risk airway management Change in surgical approach suggested |
Goiter with severe airway impingement and respiratory distress. It was recommended that patient be prepared for standby extracorporeal membrane oxygenation to prior to fiberoptic awake intubation, to reduce likelihood of emergency cricothyroidotomy |
| 9 | March 30, 2020 | County Hospital | A 57‐y‐old female with acoustic neuroma, brainstem compression, and symptomatic | Acoustic neuroma | Right retrosigmoid approach for removal of acoustic neuroma |
Approved Low risk |
Surgery performed |
| 10 | March 31, 2020 | University | A 64‐y‐old female with desmoplastic melanoma, 3.5 mm depth | Lower lip melanoma | Lip resection, sentinel lymph node biopsy, adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement for primary reconstruction |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 11 | March 31, 2020 | County | A 48‐y‐old female with a history of kidney transplant, immunosuppression, had a large scalp cancer resected with negative margins by a surgical oncologist with plan for staged free flap reconstruction by our service | Secondary scalp defect with bone exposure, immunosuppression | Latissimus dorsi muscle free flap, scalp debridement, neck exploration for preparation of vessels |
Delayed Low risk |
It was felt paramount to keep this immunosuppressed transplant patient out of hospital. Wound care with wound‐vac, wound granulating. |
| 12 | March 31, 2020 | County | A 36‐y‐old female with large right parapharyngeal space mass. FNA—salivary neoplasm. Well circumscribed on imaging | Parapharyngeal space mass of uncertain behavior | Transcervical parapharyngeal space resection |
Delayed Low risk |
Repeat imaging 3 months |
| 13 | March 31, 2020 | County Hospital | A 79‐y‐old female from nursing home with sacral ulcer, pneumonia, vent dependence, COVID negative | Ventilator dependence | Tracheostomy |
Approved High risk |
Medical intensive care unit, inpatient, add on, surgery performed |
| 14 | March 31, 2020 | University | A 54‐y‐old male with tongue squamous cell carcinoma (SCCA) | Malignant neoplasm of anterior two‐thirds of tongue | Hemiglossectomy, direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, bronchoscopy, esophagoscopy, possible tracheostomy, possible split thickness skin graft from the thigh |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 15 | March 31, 2020 | University | A 56‐y‐old male with FNA + SCCA cystic left neck mass | Neck mass, progressive, growth, cystic, left tonsil suspicious, but not enough for office biopsy | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, bronchoscopy, esophagoscopy, tonsillectomy, possible neck mass excision, possible neck dissection |
Approved, Reduce extent of surgery. High risk |
Left tonsil removed and positive for Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)‐related SCCA. Did not perform panendosopy and contralateral tonsillectomy as originally planned. Would have been a TORS candidate but will go for radiation therapy (RT). |
| 16 | March 31, 2020 | University | A 64‐y‐old female with asymmetric tonsils, lymphoma suspected | Tonsil neoplasm, suspect lymphoma | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, Bronchoscopy, esophagoscopy, possible bilateral tonsillectomy |
Approved High risk Changed surgical approach suggested |
Recommendation was to remove one tonsil and frozen section. If suspicious for lymphoma can avoid contralateral tonsillectomy and panendoscopy. This is exactly what happened |
| 17 | March 31, 2020 | University | A 86‐y‐old male with growing scalp lesion | Sarcoma of scalp | Radical tumor resection, skin substitute graft to scalp |
Approved Low risk |
Surgery performed. |
| 18 | April 1, 2020 | University | A 67‐y‐old male former smoker | Malignant neoplasm of tonsil and tongue base | Radical resection of tonsil, tonsillar pillars and/or retromolar trigone, limited pharyngectomy, near complete tongue base resection, neck dissection, tracheostomy, radial forearm free flap vs anterolateral thigh free flap, split thickness autograft |
Approved High risk |
Salvage surgery after chemotherapy and radiation. Prior surgery on a different primary years before. Forearm flap used |
| 19 | April 1, 2020 | University | A 34‐y‐old male presented with hoarseness and has a diagnosis of superficially invasive cancer | Malignant neoplasm of glottis | LASER(Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) direct laryngoscopy‐ bilateral lesion excision with microscope direct laryngoscopy‐ bilateral vocal fold injection, therapeutic with microscope |
Approved High risk |
Patient is young and strongly prefers surgical therapy over radiation. Due to his young age and relatively superficial tumor, it was felt appropriate to proceed with surgery. Avoidance of LASER suggested but felt to be difficult. Extra suction at high power and N95 mask as in all surgeries. |
| 20 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 58‐y‐old female with advanced laryngeal cancer. Radiation failure | Malignant neoplasm of larynx | Total Laryngectomy, bilateral neck dissection, radial forearm free flap, split thickness autograft |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 21 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 75‐y‐old male with right‐sided visual loss | Nasal/sinus tumor, suspected malignancy | Nasal/sinus endoscopy with biopsies |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed. Result was inflammatory rather than malignant |
| 22 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 62‐y‐old male smoker with T4 N1 SCCA larynx | Right glottic cancer | Total laryngectomy, bilateral neck dissections |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 23 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 61‐y‐old male smoker, drinker | Tongue Cancer | Hemiglossectomy with composite resection of floor of mouth, partial pharyngectomy, neck dissection possible bilateral, tracheostomy, radial forearm free flap, split thickness skin graft |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 24 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 67‐y‐old male with T2 N2c base of tongue cancer suspected | Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of base of tongue, neck mass | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy |
Approved High risk |
Endoscopy performed. Biopsy revealed HPV‐related base of tongue cancer. Not a good candidate for TransOral Robotic Surgery (TORS), crosses midline, bilateral adenopathy, so chemoradiation regardless of situation. |
| 25 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 22‐y‐old female with growing, massive adenopathy | Castleman's disease, rule out lymphoma | Right Neck Node Excision |
Approved Low risk |
Surgery performed |
| 26 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 46‐y‐old male with high‐grade carcinoma of nasal cavity and ethmoid, presented with eye, sinus pain |
Malignant neoplasm of ethmoidal sinus |
Craniofacial approach to anterior cranial fossa with maxillectomy, anterior skull base resection of bilateral lesion, intradural with dural repair |
Approved High risk Suggested changes in technique |
Surgery performed. Avoid drill and microdebrider. Plastic cover recommended over face and nose with small holes for scope to divert plume from cautery and aerosolized debris |
| 27 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 67‐y‐old male presented with hoarseness | T4aN2 SCCA of larynx | Total Laryngectomy |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 28 | April 2, 2020 | University | A 56‐y‐old female with a midline neck mass consistent with a benign thyroglossal duct cyst | Thyroglossal duct cyst | Sistrunk procedure |
Delayed Low risk |
Patient rescheduled 6/11/20 due to COVID‐19, and her surgery being elective and non‐urgent |
| 29 | April 2, 2020 | County Hospital | A 42‐y‐old female with superficial supraglottic SCCA | Malignant neoplasm of the supraglottis | Microdirect laryngoscopy with LASER |
Approved High risk Suggested changes in technique |
Recommendation to avoid use of LASER. Instead of laser, cold technique used with electrocautery at low setting |
| 30 | April 2, 2020 | County Hospital | A 65‐y‐old male with dysphagia, lesion on fiberoptic examination |
Supraglottic/ hypopharyngeal mass |
Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy |
Approved High risk |
Needs biopsy to proceed with non‐surgical therapy |
| 31 | April 2, 2020 | County Hospital | A 41‐y‐old male with tonsil lesion, throat discomfort | Tonsil lesion | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy |
Approved High risk |
Tonsillar fossa ulcer in patient with history of left tonsil cancer. Soft tissue radionecrosis vs cancer |
| 32 | April 2, 2020 | County Hospital | A 71‐y‐old male with pain in throat, palpable tongue base mass, neck mass | Tongue base mass, neck mass | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy |
Approved High risk |
Rescheduled 2/2 positive COVID test. We will need to wait at least 2 wk and retest COVID‐19 RT‐PCR |
| 33 | April 3, 2020 | County Hospital | A 64‐y‐old male with growing neck mass | Cervical lymphadenopathy, concern for lymphoma |
Neck excisional lymph node biopsy |
Approved Low risk |
Surgery performed |
| 34 | April 3, 200 | University | A 88‐y‐old male with advanced laryngeal cancer | Malignant neoplasm of larynx | Total Laryngectomy, partial pharyngectomy, bilateral neck dissection, adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 35 | April 3, 2020 | University | A 48‐y‐old male smoker with right tail of parotid mass and FNA showing oncocytic neoplasm. Growth of tumor has been slow over 2 y | Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of the parotid gland | Superficial parotidectomy, sternocleidomastoid muscle flap, abdominal fat graft |
Delayed Low risk |
Concern with low‐grade malignancy. Due to COVID‐19 patients elective surgery has been rescheduled for late May 8, 2020 |
| 36 | April 6, 2020 | University | A 76‐y‐old male smoker with T3N1M0 HPV+ SCCA of the left tonsil (just over 4 cm in vertical dimension) TORS candidate | Malignant neoplasm of the tonsil | TORS radical tonsillectomy, neck dissection |
Canceled High risk |
Transfer to radiation. Initially was scheduled for TORS. Due to COVID‐19 situation, as well as presence of a second node on Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET CT), he was strongly advised to proceed with RT. Patient was insistent on surgical therapy, but eventually agreed |
| 37 | April 6, 2020 | University | A 27‐y‐old male with thyroid nodule, positive FNA for papillary cancer | Thyroid cancer | Total thyroidectomy, Central compartment neck dissection |
Delayed, Low risk |
Thyroid Ca with metastases in the neck; plan for repeat FNA to confirm diagnosis in neck; suspected slow growing papillary cancer |
| 38 | April 6, 2020 | University | A 71‐y‐old female with prominent growing lymph nodes |
Lymphadenopathy |
Excisional biopsy of upper neck node |
Approved Very Low risk since intubation avoided |
Likely lymphoma. Excisional biopsy under local anesthesia with sedation |
| 39 | April 6, 2020 | County Hospital | A 58‐y‐old male, smoker with progressive dysphagia | Malignant neoplasm of hypopharynx | Pharyngectomy, total laryngectomy, bilateral neck dissections, radial forearm vs anterolateral thigh free flap reconstruction, split thickness skin graft |
Canceled High risk |
It meets criteria for being considered unresectable. Borderline for surgery, and plan is for chemotherapy/RT based on tumor board presentation |
| 40 | April 6, 2020 | County Hospital | A 31‐y‐old female with cerebrospinal fluid leakage occurring after discharge from craniofacial resection for anterior fossa meningioma | Cerebrospinal fluid leak after craniofacial resection | Bilateral sinus surgery complex/skull base with CSF leak repair |
Approved High risk Suggested changes in technique |
Proceed with surgery. Plastic face cover. Avoid use of microdebrider and drill |
| 41 | April 9, 2020 | University | A 64‐y‐old male with growing neck mass | Neck mass, + FNA for SCCA | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy |
Approved High risk |
Tonsil cancer suspected but not definite. May require tonsillectomy. |
| 42 | April 9, 2020 | University | A 63‐y‐old male, progressive odynophagia | Malignant neoplasm of base of tongue | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy |
Approved High risk |
Submucosal recurrence in BOT; risk of bleeding and airway |
| 43 | April 9, 2020 | University | A 79‐y‐old female with painful growing tongue lesion. Biopsy + SCCA | Tongue SCCA | Partial glossectomy, possible hemiglossectomy, neck dissection, possible split thickness skin graft |
Approved High risk Change in surgical approach suggested |
Surgery performed. Original plan for tracheostomy changed to intubation for one to two nights and avoid tracheostomy if possible. Original indication for tracheostomy felt to be borderline |
| 44 | April 9, 2020 | University | A 64‐y‐old male with painful tongue lesion | Tongue SCCA | Hemiglossectomy, neck dissection, trachesotomy, radial forearm free flap, split thickness skin graft |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 45 | April 9, 2020 | University | A 63‐y‐old male with change in voice and tongue mobility |
Neoplasm of uncertain behavior midline skull base, progressive 10th and 12th nerve weakness |
Endoscopic endonasal clival tumor biopsy, probable subtotal resection or excision of neoplastic, vascular, or infectious lesion of base of anterior cranial fossa, intradural, |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed. Plastic cover used and minimized drill and microdebrider during approach |
| 46 | April 9, 2020 | University | A 20‐y‐old female transferred from a hospital in Tampa with periorbital cellulitis. Eye swollen closed, pain with eye movement, no loss of vision |
Subperiosteal abscess of left orbit with orbital involvement |
Nasal/sinus endoscopy surgical with ethmoidectomy, possible orbitotomy |
Delay or Cancel High risk |
Patient tested Positive for COVID‐19. Delay and temporize with intravenous antibiotics and operate if becomes negative or if vision deteriorates. Watch vision closely and symptoms for signs of COVID‐19 infection. Repeat testing when appropriate. Patient signed out against medical advice and was given oral antibiotics. He will follow‐up with an otolaryngologist in Tampa. |
| 47 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 50‐y‐old male with recurrent laryngeal cancer after RT | Malignant neoplasm of larynx | Total laryngectomy, bilateral neck dissection, left anterolateral thigh free flap, possible pectoralis major muscle flap |
Canceled by patient High risk |
The patient is from our area but opted to drive 7 hours away to Jacksonville for consultation with plan to receive surgery there due to lowerCOVID‐19 prevalence. |
| 48 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 60‐y‐old male, Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)+, diabetic, renal failure on dialysis, with new oral lesion on frenulum, nasal vestibular lesion | Oral mass, Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of base of tongue, cancer vs papilloma, nasal papilloma | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, midline oral vestibule lesion excision with complex repair, left benign lesion excision of the nose |
Delay High risk |
Nasal vestibule and floor of mouth papillomatous lesion; Recommend biopsy in office for now |
| 49 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 73‐y‐old male with hoarseness | Fiberoptic exam and review of outside pathology consistent with severe dysplasia | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy, microdirect laryngoscopy with removal of lesion, tracheoscopy |
Delay High risk |
Tumor board review of pathology confident lesion is “in situ” carcinoma at most. Microlaryngoscopy in 8 wk |
| 50 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 62‐y‐old male with papillary thyroid cancer requesting surgery as soon as possible | Thyroid cancer | Total thyroidectomy, Possible paratracheal lymph node dissection |
Delay Low risk |
Well‐differentiated cancer and no airway issues. Recommend waiting 3 months |
| 51 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 72‐y‐old male painful superficial oral lesion, equivocal biopsy | Tongue cancer | Partial glossectomy, direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 52 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 91‐y‐old male with excellent performance status with growing parotid tumor. History of skin cancer. FNA reveals carcinoma with squamous features | Malignancy of parotid | Parotidectomy, neck dissection, sternocleidomastoid flap, possible pectoralis major muscle flap, cervicofacial advancement, radical resection of tumor neck, auriculectomy |
Cancel Low risk |
Patient presented at Tumor board April 9, 2020. Patient has likely metastases |
| 53 | April 10, 2020 | University | A 77‐y‐old female with dysphagia and history of hypopharyngeal stenosis | Dysphagia, hypopharyngeal stenosis | Pharyngoplasty, dilation, direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy |
Delay High risk |
Attempt at radiologic gastrostomy first to allow delay in procedure. Ultimately this was successful |
| 54 | April 13, 2020 | University | A 38‐y‐old female with tongue lesion | Tongue SCCA | Partial glossectomy, neck dissection |
Approved High risk |
Depth of invasion was 3 mm on biopsy. Clinical examination consistent with a superficial lesion. Surgeon questioned whether there was any benefit to deferring neck dissection and performing watchful waiting. Recommendation per Tumor board was to maintain standard of care and perform the neck dissection, particularly since the neck dissection represented the low‐risk portion of the procedure |
| 55 | April 14, 2020 | University | A 81‐y‐old female with supraclavicular mass, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). |
Metastatic SCCA of skin |
Neck dissection, advancement flap |
Approved Low risk |
Surgery performed |
| 56 | April 15, 2020 | University | A 52‐y‐old male with SCCA floor of mouth |
Oral cancer, Neck mass |
Composite resection of oral cavity cancer, left neck dissection, direct laryngoscopy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy, tracheostomy, radial forearm free flap vs fibula free flap, left split thickness skin graft |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 57 | April 16, 2020 | University | A 63‐y‐old female with recurrent laryngeal SCCA after RT | Malignant neoplasm of larynx | Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy, total laryngectomy, possible flap |
Approved High risk |
Surgery scheduled in the near future |
| 58 | April 16, 2020 | University | A 37‐y‐old male with parotid mass, equivocal FNA. Surgeon concerned regarding risk of malignancy in a young person and wants to proceed | Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of parotid gland | Parotidectomy, sternocleidmastoid flap, possible neck dissection |
Delayed Low risk |
Case was discussed with our ethicist. Low‐grade malignancy is a possibility, but imaging (CT) is stable between December and April and tumor is well encapsulated. Recommend delay for two months. Surgeon and patient are comfortable with the recommendation. |
| 59 | April 16, 2020 | University | A 75‐y‐old female with tongue SCCA |
Malignant neoplasm determined by biopsy of tongue |
Direct laryngoscopy with biopsy, rigid esophagoscopy, partial glossectomy, neck dissection, adjacent tissue transfer of the mouth |
Approved High risk |
Surgery performed |
| 60 | April 17, 2020 | University | A 63‐y‐old female with a large pigmented lesion of face which has undergone recent changes | Invasive Melanoma, at least 0.9 mm depth, occurring withing a larger insitu lentigo maligna | Wide resection of face, cheek, integra graft face, sentinel node biopsy. Secondary reconstruction will occur after final margins available |
Approved Low risk |
Committee suggested consideration for doing only wide local excision and not performing sentinel node biopsy, in order to simplify the procedure and reduce chance of inpatient stay, particularly in a lesion of borderline thickness. However biopsy was felt potentially to underrepresent depth and the surgeon proceeded with sentinel node biopsy. False positive RT PCR led to 4 day delay. |
| 61 | April 16, 2020 | University | A 83‐y‐old female for transfer from another hospital, with respiratory deterioration, chronic aspiration, after previous chemoradiation failure and subsequent pharyngectomy with laryngeal preservation, and free flap by our service. She has a tracheostomy and gastric tube and was just weaned from 5 weeks of mechanical ventilation related to aspiration pneumonia. | Chronic aspiration, recurrent aspiration pneumonia | Total laryngectomy, narrow field, possible regional flap, possible free flap |
Initially delayed Later approved a week later after the patient showed further signs of respiratory deterioration.Visible aspiration reported on fiberoptic examination High risk |
Case was discussed with ethicist. Patient was initially refused with a request that they temporize at her inpatient facility with tracheostomy cuff inflation and increased suctioning and ambulation. The patient continued to deteriorate and we agreed to accept in transfer for urgent laryngectomy to treat aspiration. She has been transferred. Surgery was delayed by a false positive RT PCR. After multiple subsequent negative tests she underwent a successful total laryngectomy and pectoralis major flap. |
| 62 | April 17, 2020 | University | A 46‐y‐old obese male with submandibular mass growing slowly for 2 y | Submandibular gland mass | Submandibular gland excision |
Delay for 3 months Low risk |
FNA suggestive of myoepithelial cell‐rich neoplasm with differential diagnosis of myoepithelial cell‐rich pleomorphic adenoma, basal cell adenoma, and myoepithelioma |
| 63 | April 17, 2020 | University | A 75‐y‐old male with T2N0M0 HPV+ SCCA of the right tonsil. TORS candidate | Malignant neoplasm of the tonsil | TORS radical tonsillectomy, neck dissection | Canceled | TORS canceled, referred for radiation, due to risks associated with COVID‐19 |
| 64 | April 15, 2020 | University | A 42‐y‐old male with history of chemoradiation and 4 wk postoperative from major head and neck surgery, with fistula, suspected late necrosis of radial forearm free flap | Oropharyngeal cancer, fistula, free flap loss | Wound debridement, pectoralis major flap, pharyngeal repair |
Approved High risk |
Surgery pending repeat COVID‐19 PCR testing |
| 65 | April 17, 2020 | University | A 55‐y‐old male with right neck mass and sore throat. No office throat exam done due to COVID and fact that seen only by telemedicine. FNA suspicious for lymphoma | New neck mass | Direct Laryngoscopy, rigid esophagoscopy, rigid bronchoscopy |
Approved. High risk if panendoscopy performed |
May do a simple awake head and neck physical examination and nasopharyngoscopy in the OR after COVID testing and proceed with lymph node biopsy under local anesthesia |
Our system of triage evolved over this period of time, both in terms of the number of negative RT PCR tests for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Coronavirus Two (SARS‐CoV‐2)required to approve patients for surgery, and in terms of the emphasis on avoiding surgery. We sought to maintain previous standards of care, while making adjustments based on the ascending COVID‐19 crisis. The primary goal was always the well‐being of the patient. If any potential harm from not proceeding immediately with surgery was not felt to be outweighed by the benefit of keeping the patient away from the hospital during the pandemic, then the surgery was performed, albeit with technical modifications to increase safety. In cases where delays were believed to have little impact, or where nonsurgical therapies were thought to represent reasonable alternatives, the benefit of keeping the patient safe from viral infection or the risk of unknowingly operating during the prodrome of a COVID‐19infection, 20 might be judged to tip the scales away from surgery. The public health benefits related to other patients and providers were noted but assigned lower weight.
We created a committee of six senior faculty from a department of 32 clinical otolaryngologists. This Surgical Review Committee reviewed all proposed operative cases from our university and county hospitals, nearly all of which involved head and neck tumors.
There were five stages to the triage process:
- The primary surgeons evaluated their preoperative patients and made decisions with each patient regarding treatment adjustment. If a variation occurred relative to the original plan or to our standard practice, it generally was one of the following:
- Delay of surgery for 2 to 3 months.
- Transfer to a nonsurgical treatment, only if that approach met normal standards of care.
- Change in surgical approach (ie, reduction of powered instrumentation during endoscopic transnasal resection of neoplasms).
In all but the most straightforward cases, the surgeon as a next step would consult electronically with a colleague from the Surgical Review Committee. This allowed for an initial review of the case prior to the formal committee discussion.
Multidisciplinary questions were taken to a Head and Neck Tumor Board (conducted virtually), where issues related to triage during the pandemic drove the discussion. Subspecialized medical and radiation oncologists participated and could confirm agreement with the plans and acceptance of patients in those cases where a shift to nonsurgical care was advised.
For those cases in which the surgeon felt surgery was essential, the discussion was taken to the formal Surgical Review Committee again conducted “virtually.” Presentation at the committee could result in suggested alterations of the surgical plan, delay of surgery, or transfer to a nonsurgical approach.
If the surgeon, colleagues, or committee members, felt uncomfortable with the committee recommendations, consultation with our hospital ethicists was an option. Later, if uneasiness was expressed by the patient or family, involvement of the ethicist was again considered. In fact, we consulted with individual ethicists intermittently regarding our processes and approach, but never needed to involve the formal university ethics committee regarding specific patients.
Various new standards evolved during this process. Some of these overlap with those suggested by Day et al in their recent guidelines. 23 Some were uncontroversial, such as a delay of surgery for most benign diagnoses. Yet even a benign diagnosis can entail critical airway obstruction or aspiration, or other acute loss of vital function for which the window of intervention could not be extended. When magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) findings suggested a more aggressive and rapidly evolving process despite a benign biopsy, clinical features, and imaging took precedence. An example of this was an intranasal mass, suspected to be a benign inverted papilloma or juvenile angiofibroma, with progressive optic nerve compression and increasing vision loss.
A second standard was to consider delay of surgery for slow‐growinglow‐grade malignant tumors. Equivocal fine‐needle aspiration (FNA) cytologic results could create uncertainty, but these situations were usually resolved by examining the clinical scenario and comparing serial imaging. In some cases, repeat biopsy or imaging was suggested, but the additional risk of more medical interventions to the patient and staff in the coronavirus setting was always weighed. Delays were justified for these more indolent malignancies, particularly if serial observation confirmed stability on physical examination and/or imaging, and if the patient had risk factors for a worse outcome with COVID‐19 infection. However, given the reports of poor outcomes in healthy patients operated on during the prodrome of a COVID‐19 infection, 8 even healthy patients were considered at risk.
A third standard was the transfer of the patient from a high‐risk surgical procedure to nonsurgical therapy when this represented an equivalent standard of care. The most common type of surgery for which this transition occurred was for T1 and T2 oropharyngeal cancer, with negative or early stage neck disease, where radiation with or without chemotherapy is a standard alternative treatment. Endoscopic LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) resections (transoral LASER microscopic [TLM] surgery), usually performed for supraglottic or glottic cancer at our institution, represented a similar category. The possibility of inhalation of smoke plume and the proximity of the surgeon to the endoscope and the patient's oral cavity make these high‐risk procedures for viral transmission in either direction.
A fourth standard was that if delay or transfer to nonsurgical therapy could not be justified, such as for high‐grade cancers, an unsafe wound needing reconstruction, or respiratory issues, then surgery should proceed as soon as possible, but—with the exception of immediate life or death emergencies—should wait for appropriate COVID‐19 testing.
We quickly realized however, that even with negative testing we still needed to proceed with full personal protective equipment (PPE) especially for high‐risk procedures involving mucosal incisions or use of instrumentation resulting in potential aerosolization of viral particles, as testing could give a false sense of security. Initially one negative SARS‐CoV‐2 test was required, but early on, after case 3 (below), this was converted to two negative test results with the last negative result within 24 hours of surgery. Apparent false negatives and false positives occasionally occurred, disrupting surgical planning and postoperative care. This is consistent with early reports from China, which report false‐negative rates as high as 30% in known COVID‐19 patients. 24 No data are available on sensitivity and specificity of routine testing of asymptomatic preoperative patients. We were greatly assisted by the rapid institution of reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) testing of nasopharyngeal swabs for SARS‐CoV‐2 by our clinical laboratories, progressing within 10 days from a test that took 3 or 4 days to produce results to one that produced results in a few hours. Quigen Rotorgene Platform using U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention primer pairs and the Genmark platform were the two principal types of tests used.25, 26
If proceeding with surgery, suggestions were often given to reduce the scope of surgery or make the surgical technique safer. For example, in one case it was thought unjustified to send an early, relatively superficial T1 supraglottic cancer in a young patient to radiation, but it was excised by cold technique instead of LASER, in order to avoid the aerosolized LASER plume. Another modification was the use of plastic covers for nasal endoscopic skull base surgery (Figure 1) along with additional suctions used to evacuate bone dust and cautery‐induced plumes, similar to smoke evacuators used in LASER surgery.
FIGURE 1.

Plastic cover for nasal endoscopic skull base surgery [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
A fifth standard was that scheduling of tracheostomy required special consideration. Tracheotomy is potentially one of the highest risk operations we perform for possible COVID‐19 transmission due to the possibility of aerosolized secretions. At the same time, tracheostomy on an intubated patient may allow for weaning from the ventilator and exit from the intensive care unit (ICU), freeing the spot for another patient.
Tracheostomy in a COVID‐19 positive patient presents a high risk. The likelihood that tracheostomy would truly facilitate weaning for a particular patient was carefully considered, and several guidelines and publications and recommendations from our recently created departmental COVID‐19 tracheotomy advisory committee were seriously weighed. Our department developed institutional guidelines and protocol for tracheotomy during the pandemic based on available published national and international guidelines, taking into account the specific situation of our institution during the pandemic. Current guidelines recommend delay of tracheostomy when appropriate in the setting of acute SARS‐CoV‐2 infection until the patient becomes less infectious. 27
3. RESULTS
From February 14, 2020, to April 10, 2020, we saw 129 new or suspected head and neck cancers and 83 benign tumors at our National Cancer Institute (NCI) designated cancer center. Suspected benign processes were all rescheduled from clinic after March 9, so the benign tumors were all seen before that. In addition, 13 new cancers were seen at our county hospital over the same period, along with 8 benign tumors. Patients needing surgery from among the patients seen at both institutions would largely have been operated on in March and April.
Between March 15, 2020, and March 20, 2020, when our hospital instituted the policy forbidding “elective” surgery, 281 otolaryngology procedures already on the surgical schedule were canceled at the University Hospital based on the initial determination by the surgeons and their coordinators that they were elective. Another 215 patients had been pending surgical scheduling in our Otolaryngology Department but did not yet have an assigned date. An additional smaller number of scheduled ears, nose, and throat procedures were at some point in scheduling at our county hospital and were also canceled or not scheduled, approximately 50 cases.
One hundred and eleven cases were left on the surgical schedule by otolaryngologists after March 20, for consideration as urgent. In addition, an unquantified and probably larger group of patients were in the process of being prepared for surgery, and soon to be scheduled, and were “self‐triaged” to wait or treat nonsurgically by the surgeons or by patients who were themselves concerned about coronavirus infection despite having another serious diagnosis.
Thus, hundreds of patients were cut off from “normal” head and neck surgical care. Those with urgent, mostly neoplastic diagnoses, were triaged through the processes described under Section 2.
Table 1 lists the first 65 patients that were triaged during the initial 3 weeks after suspension of elective surgery. All patients who made it on to the surgical schedule during these 3 weeks are listed. Diagnosis, patient history, original surgical plan, and committee recommendations and disposition are included. Patients who were transferred to nonsurgical care or delayed at the time of the primary surgeon's clinic evaluation or through our tumor conference are not all included. Benign tumors without airway issues are not included unless the surgeon decided to request approval for surgery. Surgeries presenting through the Emergency Room or Trauma Unit were also not included, but transfers from other hospitals were evaluated just as outpatients would be. Our goal is to provide an overview of the process that occurred. Three unique cases are described below.
4. CASE PRESENTATIONS
4.1. Case 1: Suspected malignancy in retropharyngeal nodes
An asymptomatic 37‐year‐old woman with a history of papillary cancer of the thyroid, presented in December 2019, referred for suspected malignancy involving high retropharyngeal lymph nodes bilaterally, detected on a contrasted CT in October 2019 (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2.

Contrast computed tomography axial and coronal reveal retropharyngeal adenopathy
The patient had four previous surgeries for well‐differentiated papillary thyroid cancer at other institutions. In 2006, she underwent total thyroidectomy, removal of one central compartment node, and nine lateral neck lymph nodes of which six contained malignancy. Based on abnormal ultrasounds and thyroglobulin levels over the years, the patient was taken back to surgery on three subsequent occasions, including a comprehensive procedure in 2018, with revision neck dissection bilaterally including level 6 and left level 5. Seven of 31 lymph nodes were positive.
Her only medication was oral levothyroxine. Head and neck physical examination was notable only for surgical scars.
Due to the unusual location of these lymph nodes, there was concern that these might represent a more aggressive lesion. The CT was indistinct in evaluating the borders of the lesions. There were additional involved lymph nodes more inferiorly in the right neck and some questionable lymph nodes by CT criteria on the left. Review of her surgical pathology from 2018 confirmed classical papillary thyroid cancer. Her thyroglobulin was 6.0, unstimulated. Stimulated thyroglobulin elevated to 29.3.
We advised contrasted MRI, and positron emission tomography/CT (PET‐CT) to further evaluate, along with presentation at our multidisciplinary head and neck tumor conference. The MRI showed the well‐encapsulated cystic retropharyngeal lymph nodes more distinctly (Figure 3), with 2 cm as the largest dimension. The PET‐CT was negative for fluorodeoxyglucose uptake, suggesting low‐grade lesions. The retropharyngeal lesions were felt to be inaccessible for FNA.
FIGURE 3.

Magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium, T2 images reveal cystic abnormal retropharyngeal lymph nodes more distinct
We recommended bilateral revision neck dissection followed by bilateral exploration of the parapharyngeal space, carefully following the carotid upward to excise the retropharyngeal lymph nodes. Laryngeal nerve integrity monitoring would be used. Mobilization of the tail of parotid, ligation of the external carotid artery, and possible identification of the facial nerve in the parotid were felt to be potentially necessary to achieve the exposure of the retropharyngeal nodes. The patient was consented appropriately regarding risks, including cranial neuropathies and first bite syndrome.
The patient obtained second opinion and presented again in early March, and surgery was scheduled 2 weeks later. By March 15, the COVID‐19 pandemic was in ascendance and elective surgery was suspended. The working rule in our Case Review Committee had been to delay surgery for well‐differentiated thyroid cancer. This case was prereviewed by committee members because of the unusual anatomic location of the lesions. The recommendation was to repeat the MRI to confirm stability on two similar studies. Repeat MRI confirmed no changes in the lesions between January and April. Based on this, we recommended not to hospitalize during the pandemic and planned surgery in 3 months.
4.2. Case 2: Massive goiter with severe tracheal compression
A 62‐year‐old woman presented to our County Hospital Emergency Department reporting dyspnea on exertion.
She now was noted to have reduced oxygen saturation after exertion. CT with iodinated contrast at our facility confirmed severe tracheal compression and a 5 mm tracheal width (Figure 4). The compression was positional and on certain axial images the tracheal lumen appeared completely obscured (Figure 5). The patient received intravenous dexamethasone during this admission, respiration improved, and she was discharged and counseled to avoid heavy exertion and avoid laying on the right side.
FIGURE 4.
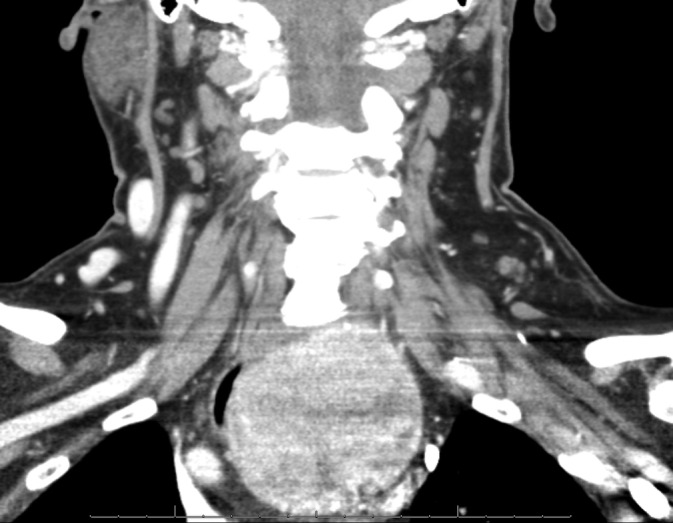
Coronal computed tomography with contrast reveals massive goiter with tracheal compression and 5‐mm tracheal airway
FIGURE 5.
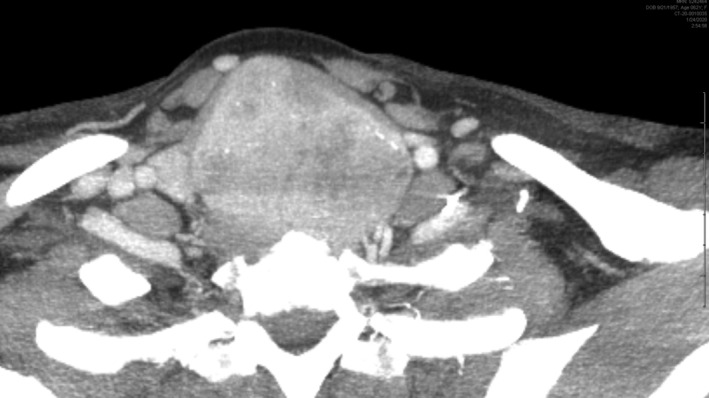
Axial computed tomography with contrast reveals massive goiter. Trachea is almost completely obscured when patient leans slightly to the right
The patient also had several elevated calcium levels and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels, with her highest preoperative PTH at 110 pg/mL and calcium at 11.4 mg/dL. Subsequent ultrasound and “four‐dimensional” CT (respiration correlated/parathyroid protocol CT) did not localize a parathyroid adenoma.
The next week, the patient was back in the emergency room with dyspnea. Due to breathing difficulties, we canceled a planned parathyroid (technetium 99 sestamibi) nuclear scan, and surgery was scheduled urgently. The plan for airway management was awake fiberoptic intubation with the smallest reinforced endotracheal tube that would fit over a flexible bronchoscope and was long enough to reach beyond the narrowing of the trachea, which was estimated to be a size six tube. We would not be able to use the larger diameter tubes with electrodes for nerve integrity monitoring. The emergency backup plan for airway management was a cricothyroidotomy to allow placement of a smaller diameter, shorter, pediatric size tube. At this point the pandemic was in its ascendance. Significant questions were raised regarding the risk of infection of the team during emergency airway management. Therefore, given that she was comfortable on room air at rest, the patient was discharged, and surgery was delayed for a few days so that it could be moved to a cardiac bypass operating room which was set up for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). She also was tested and negative for COVID‐19 by nasopharyngeal swab RT‐PCR assay.
At surgery all staff in the room wore N95 masks and full PPE, including face shields, hats, and gowns. Under local anesthetic, the patient underwent bilateral femoral line placement to allow for more rapid conversion to ECMO if necessary. The nose and throat were topically anesthetized with sparing use of topical lidocaine cream, avoiding aerosolized topical anesthetic. She was successfully intubated awake using a fiberoptic bronchoscope and size 6 reinforced tube, which just reached the distal obstruction. The plan had been to initiate ECMO if fiberoptic intubation failed, in order to reduce risk of aerosolization of viral particles during an awake cricothyroidotomy.
The multinodular goiter was excised with visualization and preservation of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The goiter was bluntly delivered from the mediastinum. Two obviously enlarged parathyroids were encountered, and frozen‐section biopsy suggested parathyroid hyperplasia. We removed both ipsilateral parathyroids and the intraoperative PTH dropped to 48. Representative frozen‐section biopsy confirmed benign colloid nodule. At this point, we elected not to explore contralaterally.
The patient recovered uneventfully with no respiratory issues and was discharged 24 hours after surgery. Final pathology confirmed the intraoperative diagnoses.
4.3. Case 3: Advanced oral cavity cancer with false‐positiveCOVID‐19RT‐PCR
A 60‐year‐old man presented with a 7‐month history of a right‐sided oral lesion, progressive over time, which was increasingly painful.
A biopsy showed invasive moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Past medical history included myocardial infarction and angioplasty 3 years before. His only medication was aspirin. Patient had smoked cigarettes for 25 years, used chewing tobacco, and drank four drinks of liquor daily.
Physical examination revealed a right posterior buccal lesion, bulging into the cheek and extending from inferior alveolar ridge to superior alveolar ridge with trismus.
CT with iodine‐based contrast media and PET‐CT demonstrated the oral lesion with limited bone erosion at the superior alveolar ridge. A 1‐cm round level 1B node was positive on PET‐CT.
The patient was scheduled for tracheostomy, full‐thickness buccal resection, marginal mandibulectomy, partial maxillectomy, right neck dissection, and anterolateral thigh free flap reconstruction. Committee review classified surgery as urgent and without equivalent nonsurgical alternatives. He had one negative COVID‐19RT‐PCR performed 3 days before surgery.
Shortly before surgery our policy changed to require that all urgent mucosal surgeries have two COVID‐19RT‐PCR tests. Since testing had a 3‐day turnaround time, a second test was sent on the morning of surgery, but surgery proceeded. The operation was uncomplicated. Staff wore N95 masks, face shields, and gowns. His postoperative course was typical, but on postoperative day 3, his preoperative COVID‐19RT‐PCR test resulted positive and the patient was moved to a COVID‐19 ward. The patient never had symptoms.
Significant controversy arose because residents and nurses had been caring for his tracheostomy using N95 masks and face shields, but not always with full PPE. The surgeons involved had to defend the ethics of proceeding to surgery with a pending COVID‐19RT‐PCR. All future mucosal cases were subsequently required to have two tests with results completed before surgery. Fortunately, our facility concurrently acquired a rapid test with two‐hour turnaround time, and a third test performed on postoperative day 4 which returned negative. Given the two negative tests, and absence of symptoms, it was decided that the second test was likely a false positive. The patient spent only one night on the designated coronavirus floor.
One member of the operative team, a “scrub” technician who entered the procedure briefly, later became mildly symptomatic and tested positive for coronavirus RT‐PCR. Other members of the surgical team and nurses and house staff performing postoperative care all tested negative. The origin of the exposure of our technician is difficult to determine.
The patient was discharged home on postoperative day 9 with a nasogastric feeding tube and a tracheostomy tube with a plan to remove both soon in the office. Final pathology revealed negative margins, perineural invasion at the primary site, and a 9‐mm lymph node grossly involved by cancer at level 1B with extracapsular extension, leading to a recommendation for chemoradiation postoperatively.
5. DISCUSSION
No randomized trials provide data regarding the appropriate systems and policies for the triage of patients with potentially fatal cancers during a global pandemic. The infrastructure and regulations for appropriate triage of the ill and injured that have been developed for crisis triage during war and natural disaster serve as guides, but these situations are not the same, as they may be more intense, but are more limited in time and area of geographic involvement. What is safe, fair, and appropriate may not always be clear as the availability of medical resources decreases over time, and while these are threatened in the future, they are still selectively available in the present. Our policies must change and evolve depending on the magnitude of the situation.9, 28
In the absence of data to guide us, we involved the most experienced surgeons available, and extensive open discussion in multiple forums was followed by formal committee review in order to make decisions. While in theory the committee chairman had the final word, there was always a consensus regarding the appropriate approach. Even primary surgeons who were advocating for a surgical plan on their specific patient accepted the magnitude of the situation and the reasons for decisions that were made.
In the escalating phase of an epidemic when the hospital is trying to keep beds open in anticipation of patient needs, what is appropriate and ethical may be very different from when the pandemic is at its peak.9, 28 Difficult decisions may seem unjustified at a point where we are preparing for expected volume, but still have unoccupied beds, compared to later when the system enters crisis mode. However it would be a fallacy to think that we can “catch up” later, and modeling studies of pandemic crises generally confirm that proper early triage can save lives dramatically over a “first come first served” approach.9, 28 At the same time others have pointed out that triage poorly done, based on improper clinical parameters, can actually lead to worse outcomes.9, 28, 29, 30 This could occur due to underestimating or overestimating the severity of a patient's condition, and underutilizing or overutilizing resources, and can actually save fewer lives rather than more.28, 29, 30 Thus recommended decisions must be based on appropriate in depth criteria, including understanding and reviewing histology or cytology when possible, and reviewing or repeating imaging when appropriate.
In the absence of exact data, even more problematic is how to factor in the changing level of risk over time of coronavirus infection in these patients with cancer, some of whom fall in high‐risk groups for COVID‐19, while also considering the public health goals of conserving ICU beds, ventilators, and PPE. Furthermore, we must then calculate the risk level and relative importance of protecting providers, not only out of fairness to the provider, but also because the provider is a valuable resource in short supply who will be able to treat other patients during the pandemic.9, 28, 29, 30 At the time of writing this manuscript, our healthcare systems (UHealth and Jackson Memorial Hospital) have so far reported the death of one nurse, one MRI technician, one physician faculty member, and one radiology technician as a result of COVID‐19.
We emphasize the importance of communicating well with patients and surgeons throughout the process, and reminding them to consider all risks, including risk of COVID‐19, emphasizing the Surgeon General recommendations regarding elective surgery, and providing data as needed regarding alternatives for cancer treatment.
Several specialty societies have published guidelines regarding cancer management during the pandemic. These do not specify at what point they should be instituted, and how severe the situation should be. Some of the recommendations allow potential misinterpretation. For example, the Society of Surgical Oncology has suggested delay of treatment for thin invasive melanomas, and prioritization of surgery only for thicker melanomas. 31 While the reasons for this recommendation are understood, and there are many details to consider, the approach seems debatable in a situation where resources are being protected, but some are still available, as this early group of invasive melanomas are those most likely to be cured by surgery.
The American Head and Neck Society has not published specific guidelines. We have referred here to the publication by Day et al 23 that provides some reasonable guidelines and we add our suggestions here. Our recommendations, in the absence of randomized data, come from practical work triaging surgeries during this process:
All head and neck cases for which a change in plan is under consideration should be reviewed by a multidisciplinary tumor conference to provide care recommendations specifically in the context of COVID‐19 with appropriate documentation of how the pandemic has impacted treatment recommendations.
A departmental surgical review committee should be established to evaluate all cases proposed for surgical care to provide independent review of appropriate urgency for surgical scheduling. This committee provides a second level of review that is guided by the primary physician's assessment and recommendations, multidisciplinary recommendations from tumor conference, as well as the important independent perspective of non‐head and neck surgeons with regard to resource utilization and patient and staff safety concerns. The surgical review committee should have real‐time access to hospital ethics committee consultation when necessary.
We suggest delay for 2 to 3 months of surgery for low‐grade malignancies, including well differentiated thyroid cancers and low‐grade parotid cancers, and skin cancers not threatening vital functions.
We recommend that these patients be followed closely with consideration for repeat imaging during this period to allow for correction of the approach if the tumor is progressing.
When surgery is clearly the superior option for a high‐grade mucosal cancer, such as for oral cavity cancer, we would recommend proceeding to surgical treatment. At the height of the pandemic surge this may to be interrupted, but when capacity is still available, these patients' survival is at stake and they should have a fair claim to available resources.
The importance of available rapid accurate testing for active SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in order to allow surgical care to be offered cannot be overstated. Naturally, given the novelty of this virus, current testing technology is in its early stages. We eagerly await more accurate and reliable testing, including well‐validated data for false negatives and false positives in the setting of preoperative patients without symptoms of COVID‐19.
During this brief point in time, mucosal cancers for which nonsurgical options are considered appropriate should be considered for nonsurgical treatment. Specifically, transoral robotic surgery (TORS) and transoral laser microsurgery are often used in clinical scenarios where nonsurgical options offer equivalent survival, and both represent high‐risk procedures for SARS‐CoV‐2 transmission.
During endoscopic surgery the surgeon's face is sometimes in close proximity to the rigid laryngoscope during parts of the procedure. Even when behind the microscope, they could, in theory, inhale SARS‐CoV‐2 particles in smoke plume. Given the significant false‐negative rate 24 of available tests for COVID‐19, even with two negative tests, there is still some risk to the surgeon and staff. We do have information reporting that the rate of acquiring COVID‐19 is higher for head and neck surgeons, ophthalmologists, and oral surgeons than it is for radiation oncologists, presumably due to the greater risk of exposure to aerosolized or touched secretions. 32
It should be acknowledged, in terms of ethics, that the decision to irradiate patients instead of operating endoscopically is one of those situations where we are weighing the public health risk, including the risk to the surgical team, and transferring risk to another setting with limited data to support it. The risk to the patient, in particular, of 6 weeks of radiation with multiple trips to the facility has not been proven to be less than a single endoscopic intervention. Since there are risks associated with an inpatient stay and possible lack of access to medical resources during a surge, in addition to risk of viral exposure, it is very hard to quantify this “moving target” relative to 30 to 35 visits to radiation oncology. Some have pointed out that for immunocompromised patients in particular, multiple trips to the hospital also represent a significant risk, 33 but the answer is just not known.
Currently at our institution, all patients undergoing radiation and chemotherapy are being tested for COVID‐19 prior to start of treatment, but not repeatedly. Patients testing positive on that first test get treated separately at the end of the day. There is a risk that a patient could have a true‐negative test at the outset, only to develop COVID infection later and then unknowingly expose other patients or radiation oncology staff during any period in which the infection was not clinically evident.
The most significant concern in the definitive radiation setting is the risk, not to the staff, but to the patient. In our institution, there is no routine testing of unexposed faculty or staff for COVID‐19 infection. The use of PPE by staff varies by role, with many staff members wearing simple masks only. Radiation therapy technologists wear N95 masks, face shields, and gloves while treating patients with head/neck cancer, but the nursing staff and some physicians wear only gloves and simple masks. Fundamentally, the difference in testing policy regarding patients (mandatory testing) and staff (no routine testing) has the potential for significant risk to patients over the extended timeframe of radiation treatment.
As we move from a complete ban on elective surgery, toward reincorporating some relatively important cases that have been awaiting institutional clearance for surgery, significant stress will likely occur as we try to determine to which of these patient's medical resources should be allocated first. This will create new conversations and may lead to tension between services as debates develop about the relative value of investing resources in “sicker” patients vs “more salvageable patients.”
The head and neck patients triaged to delay in surgical care, primarily the low‐grade malignancies, will be the first group for reconsideration by the surgical review committee. These patients will now face perhaps an even more complex path on their journey to finally achieving the surgical care they need in this unprecedented time. They will now be evaluated alongside nonmalignant cases with the potential for serious complications with ongoing delay. Such cases might include erosive cholesteatomas with bone loss and risk of cerebrospinal fluid leak, or similar patients with aggressive but benign paranasal sinus disease. In our system these will compete for operative time that has been assigned to the Otolaryngology Department. Such comparisons are likely to be much more nuanced than the decisions the surgical review committee has faced to this point and may present even greater challenges to decision making.
Prachand et al, in a general surgical setting, recently published online regarding this dilemma and their own “Cumulative Medically Necessary Time‐Sensitive(MeNTS) Score,” which attempts to introduce objectivity into this process. While we have not attempted to use this tool, such efforts at maintaining objectivity may help introduce greater fairness into this process. 34
6. CONCLUSIONS
The coronavirus pandemic has forced us to rethink our usual paradigms in head and neck surgery. We describe our department's choice to use a “top down” approach, with supervision and control of the operating rooms at an administrative level. We recommend that triage be conducted with the patient's personal health interests as the guiding principle, and that public health concerns be weighed as a strong secondary consideration.
Civantos FJ, Leibowitz JM, Arnold DJ, et al. Ethical surgical triage of patients with head and neck cancer during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Head & Neck. 2020;42:1423–1447. 10.1002/hed.26229
REFERENCES
- 1. Miles S, ed. Oath of Hippocrates. The Hippocratic Oath and the Ethics of Medicine. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2004:1‐208. [Google Scholar]
- 2. Deng S‐Q, Peng H‐J. Characteristics of and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):575‐585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Gabutti G, d'Anchera E, Sandri F, Savio M, Stefanati A. Coronavirus: update related to the current outbreak of COVID‐19. Infect Dis Ther. 2020. 10.1007/s40121-020-00295-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ahn DG, Shin HJ, Kim MH, et al. Current status of epidemiology, diagnosis, therapeutics, and vaccines for novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19). J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;30(3):313‐324. 10.4014/jmb.2003.03011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Impelli M.. Coronavirus becomes number one cause of death per day in U.S., surpassing heart disease and cancer. Newseek (online). April 9, 2020 (based on CDC statistics).
- 6.U.S. Surgeon General @ Surgeon_General, Hospital & Healthcare Systems, Please Consider Stopping Elective Procedures until we can #FlattenTheCurve, Twitter. 8:07 A.M 14 March, 2020. https://twitter.com/surgeon_general/status/1238798972501852160?lang=en
- 7. State of Florida, Office of the Governor, Executive Order EO . Emergency Management—COVID‐19—Nonessential Elective Medical Procedures. Tallahassee, FL. Accessed March 20, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lei S. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients undergoing surgeries during the incubation period of COVID‐19 infection. EClin Med. 2020;21: 10.1016/jeclinm.2020.200331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Christian MD. Triage. Crit Care Clin. 2019;35(4):575‐589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Biddison LD, Berkowitz KA, Courtney B, et al. Ethical considerations: care of the critically ill and injured during pandemics and disasters: CHEST consensus statement. Task force for mass critical care. Chest. 2014;146(4 suppl):e145S‐e155S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Mansky R, Scher C. Thoracic trauma in military settings: a review of current practices and recommendations. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2019;32(2):227‐233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Strous RD, Gold A. Ethical lessions learned and to be learned from mass casualty events by terrorism. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2019;32(2):174‐178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Falzone E, Pasquier P, Hoffmann C, et al. Triage in military settings. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2017;36(1):43‐51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Pou AM. Ethical and legal challenges in disaster medicine: are you ready? South Med J. 2013;106(1):27‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Pou AM. Hurricane Katrina and disaster preparedness. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(14):1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Demmler GJ, Ligon BL. Severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (SARS): a review of the history, epidemiology, prevention, and concerns for the future. Semin Pediatr Infect Dis. 2003;14(3):240‐244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Vilar‐Compte D, Shah DP, Vanichanan J, et al. Influenza in patients with hematological malignancies: experience at two comprehensive cancer centers. J Med Virol. 2018;90(1):50‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Azhar EI, Hui DSC, Memish ZA, Drosten C, Zumla A. The Middle East respiratory syndrome. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019;33(4):891‐905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Hasan S, Ahmad SA, Masood R, Saeed S. Ebola virus: a global public health menace: a narrative review. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019;8(7):2189‐2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Pottie K. Cancer in a time of Ebola. Can Med Assoc J. 2016;188(10):759‐760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Wang S, Lifson MA, Inci F, Liang LG, Sheng YF, Demirci U. Advances in addressing technical challenges of point of care diagnostics in resource‐limited settings. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2016;16(4):449‐459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Bolkan HA, Bash‐Taqi DA, Samai M, Gerdin M, von Schreeb J. Ebola and indirect effects on health service function in sierra leone. PLoS Curr. 2014;6. 10.1371/currents.outbreaks.0307d588df619f9c9447f8ead5b72b2d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Day AT, Sher DJ, Lee RC, et al. Head and neck oncology during the COVID‐19 pandemic: reconsidering traditional treatment paradigms in light of new surgical and other multilevel risks. Oral Oncol. 2020;6:104684. 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yang Y, Yang M, Shen C, et al Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019‐nCoV infections 10.1101/2020.02.11.20021493 [DOI]
- 25. Schmitz JE, Tang YW. The GenMark ePlex®: another weapon in the syndromic arsenal for infection diagnosis. Future Microbiol. 2018;13: 1697‐1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Adams JA, Post KM, Bilbo SA, et al. Performance evaluation comparison of 3 commercially available PCR based KRAS mutation testing platforms. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2014;22(3):231‐235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Kowalski LP, Sanabria A, Ridge JA, et al COVID‐19 pandemic: effects and evidence‐based recommendations for otolaryngology and head and neck surgery practice. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28. Ross SW, Lauer CW, Miles WS, et al. Maximizing the calm before the storm: tiered surgical response plan for novel coronavirus (COVID‐19). J Am Coll Surg. 2020. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2020.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Gall C, Wetzel R, Kolker A, Kanter RK, Toltzis P. Pediatric triage in a severe pandemic: maximizing survival by establishing triage thresholds. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(9):1762‐1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Kanter RK. Would triage predictors perform better than first come first served in pandemic ventilator allocation? Chest. 2015;147(1):102‐108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Society of Surgical Oncology Resource for Management Options of Melanoma During COVID‐19, 2020. https://www.surgonc.or/wp‐content/uploads/2020/03/Melanoma‐Resourc‐during‐COVID‐19‐3.30.20.pdf. Accessed April 19, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 32. Givi G, Schiff BA, Chinn SB, et al. Safety recommendations for evaluation and surgery of the head and neck during the COVID‐19 pandemic. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.0780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Civantos AM, Carey RM, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Care of immunocompromised patients with head and neck cancer during the COVID‐19 pandemic: two challenging and informative clinical cases. Head Neck. 2020. 10.1002/hed.26165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Prachand VN, Milner R, Angelos P, et al. Medically‐necessary, time‐sensitive procedures: a scoring system to ethically and efficiently manage resource Scarcity and provider risk during the COVID‐19 pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2020.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


