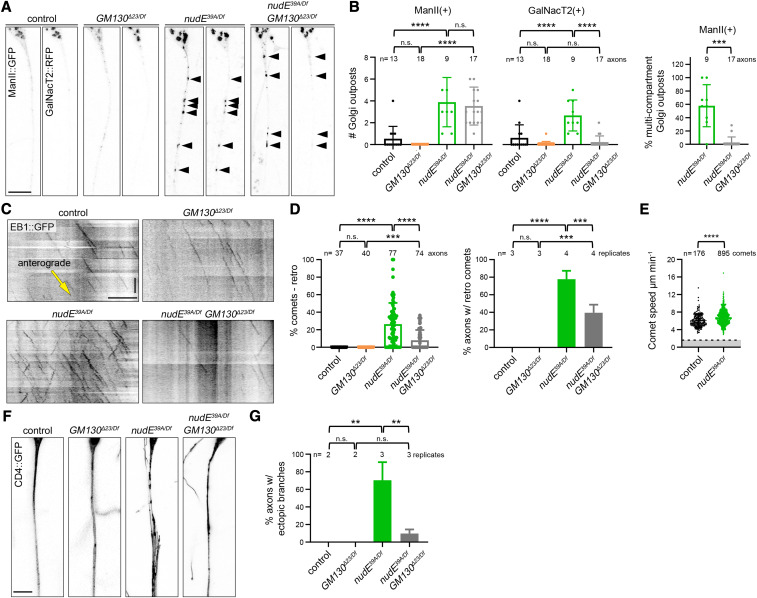
Figure 2.
Misoriented microtubules in nudE mutant axons are significantly reduced when GM130 is eliminated. (A and B) Golgi outposts (marked by ManII::GFP and GalNacT2::RFP; arrowheads) mislocalize to axons in nudE39A/Df mutant neurons. In nudE39A/Df mutant neurons, the loss of GM130 does not affect the mislocalization of ManII-positive Golgi outposts, but suppresses the mislocalization of GalNacT2-positive outposts; as a result, the percentage of multicompartment ManII-positive outposts is dramatically reduced. ***P = 0.001–0.0001 and ****P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Scale bar, 10 µm. (C and D) In the absence of nudE, axonal microtubule polarity is perturbed. Eliminating GM130 reduces the number of misoriented microtubules in nudE39A/Df mutant axons. Cell body is to the left; yellow arrow indicates the direction of anterograde comet movement. ***P = 0.001–0.0001, and ****P < 0.0001; Kruskal–Wallis test with post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison analysis (% retro comets) and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis (% axons). Scale bars, 10 µm (x-axis) and 30 sec (y-axis). (E) The speed of EB1::GFP comets in control and nudE39A/Df mutant axons is consistent with microtubule plus-end growth, indicating nudE39A/Df mutant axons indeed contain microtubules with mixed polarity (comets moving at speeds below the dotted line would be consistent with microtubule minus-end growth). ****P < 0.0001, Mann–Whitney U-test. (F and G) The ectopic branches that sprout from nudE39A/Df mutant axons are suppressed by removing GM130. n = 16 (control), 27 (GM130Δ23/Df), 59 (nudE39A/Df), and 41 (GM130Δ23/Df; nudE39A/Df) axons in replicates as indicated (G). **P = 0.01–0.001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Scale bar, 10 µm. All data are mean ± SD. Antero, anterograde; n.s., not significant; retro, retrograde; RFP, red fluorescent protein.