Abstract
Wild subspecies of Olea europaea constitute a source of genetic variability with huge potential for olive breeding to face global changes in Mediterranean-climate regions. We intend to identify wild olive genotypes with optimal adaptability to different environmental conditions to serve as a source of rootstocks and resistance genes for olive breeding. The SILVOLIVE collection includes 146 wild genotypes representative of the six O. europaea subspecies and early-generations hybrids. These genotypes came either from olive germplasm collections or from direct prospection in Spain, continental Africa and the Macaronesian archipelago. The collection was genotyped with plastid and nuclear markers, confirming the origin of the genotypes and their high genetic variability. Morphological and architectural parameters were quantified in 103 genotypes allowing the identification of three major groups of correlative traits including vigor, branching habits and the belowground-to-aboveground ratio. The occurrence of strong phenotypic variability in these traits within the germplasm collection has been shown. Furthermore, wild olive relatives are of great significance to be used as rootstocks for olive cultivation. Thus, as a proof of concept, different wild genotypes used as rootstocks were shown to regulate vigor parameters of the grafted cultivar “Picual” scion, which could improve the productivity of high-density hedgerow orchards.
Keywords: Olea europaea, wild germplasm, molecular markers, genetic variability, vigor, branching, rootstock, grafting
Introduction
The wild relatives of domesticated crops possess genetic diversity useful for developing more productive, nutritious and resilient crop varieties (Castaneda-Alvarez et al., 2016), and for preserving global food security against the serious threat of climate change (Vincent et al., 2013). Wild relatives of the domesticated olive tree (Olea europaea L.) are evergreen, drought tolerant, usually multi-stemmed small trees or large shrubs with very good adaptability to different environmental conditions (Médail et al., 2001; Green, 2002; Kassa et al., 2019). Wild olives grow in arid and semiarid regions at different altitudes and soil types, including those exposed to severe water deficit, salinity and low temperatures (Cantos et al., 2002; Baldoni et al., 2006; Klepo et al., 2013; Belaj et al., 2016; Chiappetta et al., 2017). This adaptability to adverse environmental conditions makes wild olive trees suitable to grow in marginal soils (e.g., at risk of desertification), to colonize deforested habitats or to rehabilitate devastated regions (Bekele, 2005; Kassa et al., 2019). Six olive subspecies have been recognized that occur in different natural distribution ranges in Europe, Africa, and Asia (Green, 2002): (1) O. europaea subsp. europaea, which includes wild types or oleasters [var. sylvestris (Mill.) Lehr] and the domesticated olive (var. europaea) that are common in the whole Mediterranean basin; (2) O. e. subsp. cuspidata (Wall. ex G. Don) Cif. distributed from South Africa to south-eastern Egypt and from the Middle East to India and China; (3) O. e. subsp. laperrinei (Batt. & Trab.) Cif. in the central Saharan mountains; (4) O. e. subsp. maroccana (Greut. & Burd.) P. Vargas et al. in south-western Morocco; (5) O. e. subsp. cerasiformis Kunk. & Sund. in Madeira; and (6) and O. e. subsp. guanchica P. Vargas et al. in the Canary Islands.
Besnard et al. (2007) showed through nuclear and plastid DNA data that the main wild progenitor of the cultivated olive (O. e. subsp. europaea var. europaea) is the wild Mediterranean olive, also known as oleaster (O. e. subsp. europaea var. sylvestris). Olive domestication from wild oleaster populations has involved the selection of a small number of desirable genotypes with bigger fruits, which were asexually propagated through cuttings. Such selection and propagation practices may contribute to reduce genetic diversity of the cultivated genepool (Rugini et al., 2011), but continuous hybridization events with local wild populations have, however, occurred during the long and ongoing domestication process (Besnard et al., 2013b, 2007). A higher genetic diversity is still observed in the wild genepool (Lumaret et al., 2004; Baldoni et al., 2009; Belaj et al., 2010; Besnard et al., 2013a; Chiappetta et al., 2017; Kassa et al., 2019). Wild olives therefore represent an important source of genes for crop improvement of resistance to abiotic stresses [e.g., salinity (Cantos et al., 2002), water deficit (Hernández-Santana et al., 2019), soil pollution (Murillo et al., 2005)], vigor (León et al., 2020), crop yield and quality (Hannachi et al., 2008; Baccouri et al., 2011; León et al., 2018), as well as for resistance to biotic factors such as the Verticillium wilt (Colella et al., 2008; Arias-Calderon et al., 2015b; Trapero et al., 2015; Jimenez-Fernandez et al., 2016). Wild olive genotypes have been tested in limited breeding studies, showing potential to shorten the juvenile period or to increase flower production (Klepo et al., 2014), to improve oil composition (Hannachi et al., 2008; León et al., 2018) and to improve resistance to soil-borne diseases (Arias-Calderon et al., 2015a).
An alternative and direct approach to take advantage of the gene-pool of wild germplasm is the use of selected wild genotypes as rootstocks, which greatly increases the efficiency of perennial crops. Rootstocks are commonly chosen for rooting capacity, abiotic and biotic stress resistance, and their ability to beneficially alter scion phenotypes such as precocity (early bearing), production, and fruit quality (Warschefsky et al., 2016). It is interesting to note that wild olive rootstocks were widely used in ancient cultivation systems (Barazani et al., 2014), while modern olive crops, unlike other perennial woody crops, use self-rooted cultivars. Reduction of vigor through the use of dwarf rootstocks is of particular interest in the cultivation of woody fruit trees. The main drawback of super-intensive olive orchards, also known as high-density hedgerow (HDH) system, is the difficulty to control the tree size to allow the movement of the harvesting machines (Tous et al., 2010). Cultivars used for HDH exhibit greater branching associated with smaller vigor parameters (Rosati et al., 2013). These features, which are difficult to gather in the same variety, determine that only a few traditional olive cultivars meet partially the low vigor requirement for HDH system, mostly “Arbequina,” “Arbosana,” and “Koroneiki” (Diez et al., 2016). Even these cultivars require tree size control by means of strict pruning and fertirrigation practices (Fernandez et al., 2013), which are expensive procedures. In addition, the HDH system excludes the possibility of using traditional cultivars of higher vigor, but of outstanding socioeconomic importance. Some studies indicate that certain olive cultivars used as rootstocks can regulate vigor traits like the canopy volume, stem section and production of the grafted scion (Baldoni and Fontanazza, 1990; Pannelli et al., 2002; Del Río and Caballero, 2006; Tous et al., 2012; Romero et al., 2014; Rugini et al., 2016). The use of wild genotypes to control the vigor of the grafted cultivar is also a matter of great interest (León et al., 2020), but no rootstocks of proven quality are currently available at either commercial or experimental levels.
It would therefore be desirable to have a catalog of wild genotypes representing most of the variability of the O. europaea species characterized for agronomical or eco-physiological traits of greatest interest. In the present study, we have characterized a germplasm collection of 146 olive genotypes representative of the six Olea europaea subspecies including hybrids. The collection has been genotyped and phenotyped for a number of morphological and developmental traits of interest. As a proof of concept, the ability of a number of wild genotypes to modify vigor features of the olive cultivar “Picual” has been addressed.
Materials and Methods
Plant Material and Culture Conditions
The wild olive germplasm collection, called SILVOLIVE, includes 146 genotypes obtained from seeds of mother trees prospected in their natural habitats or maintained in different Olive Germplasm Banks (WOGB-IFAPA Córdoba, WOGB-INRA Marrakech, and CEFE Montpellier; Table 1). The genotypes were in-vitro germinated from zygotic embryos of seeds from olive trees belonging to all subspecies of Olea europaea L. including hybrids (see Table 1 for detail): O. e. subsp. guanchica (GUA, ANA, HER, and BAR); O. e. subsp. cerasiformis (CER); O. e. subsp. maroccana (MAR); O. e. subsp. cuspidata (CUS, CEH); O. e. subsp. europaea (ACO, ACZ, AJA, AMK, AMS, AOU, APR, ARC, FRA, and TAM); and O. e. subsp. laperrinei (DHO) consisting of zygotic embryos of “Dhokar,” a Maghreb cultivated hybrid between laperrinei and europaea (Besnard et al., 2013a). The “Frantoio” (FRA) cultivar was the only elite olive variety exceptionally used as mother tree because of its potential interest in transmitting resistance to Verticillium wilt (Lopez-Escudero et al., 2004). The genotypes APR1 and ARC1 were previously obtained as seeds from salt-resistant wild olive trees present in Puerto Real (Cádiz, Spain) and Odiel (Huelva, Spain) salt marshes, respectively (Cantos et al., 2002).
TABLE 1.
Origin and code of the 146 olive genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection.
| Mother tree |
Number of genotypes | |||||
| Subspecies | Lineage | Variety | Natural localization | Prospection | Acronym | |
| europaea | E1-e | “Frantoio”Ω | Tuscany, Italy | WOGB, Córdoba, Spain Acc. Number 80 | FRA | 4 |
| “Acebuche de Puerto Real” oleasterΩ | Puerto Real saline marshes, Cádiz, Spain | In-vitro germplasm collection M. Cantos (IRNAS, CSIC) | APR | 1 | ||
| Unnamed oleasterΩ | Cádiz Mountains, Spain | WOGB, Córdoba, Spain Acc. Number W45 | ACZ | 10 | ||
| Unnamed oleaster× | Coria del Río, Seville, Spain | Coria del Río, Seville, Spain | ACO | 5 | ||
| Unnamed oleaster× | Marrakech Mountains, Morocco | Marrakech, Morocco | AMK | 11 | ||
| Unnamed oleaster× | Amskroud, Morocco | Amskroud, Morocco | AMS | 9 | ||
| E2 | “Raboconejo” oleasterΩ | Saltés Island in Odiel saline marshes, Huelva, Spain | In-vitro germplasm collection M. Cantos (IRNAS, CSIC) | ARC | 1 | |
| Unnamed oleaster× | Tamri, Morocco | Tamri, Morocco | TAM | 5 | ||
| Unnamed oleaster× | Aourir, Morocco | Aourir, Morocco | AOU | 12 | ||
| E3 | Unnamed oleasterΩ | Sierra de Jaén, Spain | WOGB, Córdoba, Spain Acc. Number W69 | AJA | 6 | |
| laperrinei X europaea | E1-/1 | “Dhokar”× | Tataouin zone, Tunisia | WOGB, Marrakech, Morocco Acc. Number Oct413 | DHO | 12 |
| guanchica | M-g1 | guanchicaΩ | Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain | WOGB, Córdoba, Spain Acc. Number W49 | GUA | 9 |
| M-g1 | guanchica× | Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain | Anaga, Tenerife, Spain | ANA | 18 | |
| M-g1 | guanchica× | La Gomera, Canary Islands, Spain | Hermigua, La Gomera, Spain | HER | 6 | |
| M-g2 | guanchica× | Gran Canaria, Canary Islands, Spain | Cañón del Cernícalo, Gran Canarias, Spain | BAR | 9 | |
| cerasiformis | M-c | cerasiformisΩ | Madeira Islands, Portugal | CEFE Montpellier, France Acc. Number Cer3 | CER | 2 |
| maroccana | M-m | maroccana× | Imouzzer, Morocco | Imouzzer, Morocco | MAR | 3 |
| cuspidata X europaea | A | cuspidata× | Grahamstown, South Africa | CEFE Montpellier Acc. Number Gr3 & Gr5 | CUS | 8 |
| cuspidata X europaea | A | cuspidataΩ | Kirstenbosch, South Africa | CEFE Montpellier, France Acc. Kirstenbosch | CEH | 15 |
| Total number of genotypes | 146 | |||||
All mother accessions, except “Frantoio” and “Dhokar,” are wild. ×Seeds obtained from different mother trees. ΩSeeds obtained from the same mother tree.
Seeds were surface-sterilized and germinated in-vitro in a hormone-free medium (Rugini, 1984) incubated in a growth chamber with 16 h light photoperiod (34 μM intensity with 70% red: 30% blue light-emitting diodes, LEDs, at 25 ± 2°C. Seedlings were cut into uninodal segments and micropropagated in the same Rugini medium supplemented with 1 mg/L zeatin in the same growth chamber described before. For whole plant regeneration, grown shoots were transferred to rooting medium (50% strength Rugini medium) supplemented with α-naphthalacetic acid (0.8 mg/L). Rooted seedlings were ex-vitro acclimatized for 3 weeks, transplanted to 2.5 L pots and then grown under greenhouse conditions.
Morphological and Architectural Traits
Different morphological and architectural traits were evaluated on ex-vitro potted plants at different growing stages. In potted plants, 13 months after transplanting ex-vitro acclimatized seedlings, we recorded: primary shoot height; number of secondary stems; number of tertiary stems; number of total nodes; total number of leaves; basal stem diameter (measured at 5 cm above ground with a vernier caliper); and fresh weight (leaf, shoot, and root). The morphological parameters were calculated according to the following equations:
Morphological traits of 103 wild genotypes were measured in three independent experiments, using 7–10 plants per genotype (Supplementary Table S4). In order to compare the results obtained from the different assays, the GUA1 variety was grown in the three different assays to normalize the data. Ratios obtained from two parameters measured in the same plant were calculated from absolute (non-normalized) values. Correlations between vigor parameters measured in grafted plants represent the average value of 8–12 plants per grafted genotype +/− standard errors. Correlation graphics and the respective R2-values were calculated with the Excel software.
Ploidy Level
Polyploids have been described within the O. europaea complex as a consequence of recent neopolyploidization events in Macaronesia (i.e., hexaploid maroccana and tetraploid cerasiformis; Besnard et al., 2008) and in the Hoggar mountains (i.e., presence of a few triploids in subsp. laperrinei; Besnard et al., 2008). It was thus necessary to first determine the ploidy level of each individual of the SILVOLIVE collection. This was determined by flow cytometry according to the methodology described by Aleza et al. (2009). Samples consisted of small pieces of leaves (∼ 0.5 mm2) collected from each genotype, which were directly compared to a well-known diploid cultivar (Córdoba WOGB, acc. number W45) as a control. Samples were chopped together using a razor blade in the presence of a nuclei isolation solution (High Resolution DNA Kit Type P, solution A; Partec ®, Münster, Germany). Nuclei were filtered through a 30 μm nylon filter and stained with a DAPI solution (4,6-diamine-2-phenylindol; High Resolution DNA Kit Type P, solution B; Partec ®). Following a 5 min incubation period, stained samples were run in a CyFlow ®) flow cytometer equipped with optical parameters for the detection of DAPI fluorescence at 365 nm. Histograms were analyzed using the CyView software (Partec ®), which determines peak position, co-efficient of variation (CV), arithmetic mean and median of the samples.
Chloroplastic DNA Polymorphism
Genomic DNA was extracted from leaf disks using the Sigma kit REDExtract-N-AmPlant PCR. We then used plastid markers to discriminate between the different wild olive provenances in our collection [Note that three plastid lineages have been described in the Mediterranean olive (Besnard et al., 2011): lineages E1 from the eastern Mediterranean basin, and lineages E2 and E3, both from the western Mediterranean region (hereafter referred to E1, E2, and E3, respectively)]. Ten chloroplastic DNA (cpDNA) loci previously reported (Weising and Gardner, 1999; Besnard et al., 2003, 2011, 2013a; Baali-Cherif and Besnard, 2005; Besnard, 2008; Garcia-Verdugo et al., 2010) were analyzed in the present study (Supplementary Tables S1, S2).
Primers for PCR-amplification of the cpDNA markers are listed in Supplementary Table S2. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) were performed at a final volume of 20 μL with 10 ng of template DNA, 0.5 μM primer concentration, and 2 units of MyTaqTM Red DNA Polymerase (BIOLINE) through conventional PCR procedures using a BIO-RAD T100 thermal cycler. After amplification, 2 μL of the PCR product was run on a 2% agarose gel to verify amplification product size. PCR products were sequenced and chromatograms were visualized using the “Chromas” software to identify SNPs and indels. For each genotype, a final sequence was obtained through concatenation of the loci following this order: ccmp5, OeR16Qa, matK2-3, QR-1, QR-2, QR-3, trnTD-2, trnTL-1, SSR-31, and SSR-45. For each subspecies and Mediterranean lineage, we also added as a reference the same concatenated sequences extracted from full plastomes available in the NCBI database. A full chloroplastic sequence was, however, not available for subspecies cerasiformis. All sequences were then aligned and analyzed with the “MEGA6” software (Tamura et al., 2013). A phylogenetic analysis was performed by maximum likelihood based on the Tamura 3-parameter model (Tamura, 1992).
Nuclear Microsatellite (SSR) Markers
Leaf samples from in-vitro grown seedlings were used to purify genomic DNA with the Sigma kit RED-Extract-N-AmPlant PCR. Five polymorphic nuclear SSR markers (Sefc et al., 2000) were then used to establish a genetic profile for every individual. The description of the SSR markers, including primer sequences, repetitive motif, allele size, and references are described in Supplementary Table S3. To get reference genotypes, DNA was also obtained from wild and cultivated olives maintained in different germplasm collections: subsp. cerasiformis (CEFE Montpellier, accession Cer3), subsp. guanchica (WOGB Córdoba, accession W49), subsp. europaea E1 (WOGB Córdoba, accession W45), subsp. europaea E3 (WOGB Córdoba, accession W69), as well as the cultivars “Dhokar” (WOGB Marrakech, accession Oct413) and “Frantoio” (WOGB Córdoba, accession 80). PCR reactions were performed as previously explained. SSR fragment analysis was performed with the “Peak Scanner” program (Applied Biosystems). A genotype matrix was built (Supplementary Table S3) and analyzed in R as explained below.
Grafting
To determine grafting compatibility, the olive “Picual” and “Hojiblanca” cultivars were grafted onto 43 wild genotypes using 10 potted plants per genotype. As a control, plants from both cultivars were also grafted onto their own roots. Leaves were removed from semi-hardwood wild genotypes grown for 18 months under greenhouse conditions after ex-vitro acclimatization. Rootstock plantlets were cut 20 cm from the ground level. “Picual” scions with similar stem diameter, or slightly thinner than those of the rootstocks, were cut into sections containing 3–4 nodes and their leaves removed from the base. To avoid tearing the bark, two slanted downward notches were rapidly made in the basal node of the scion (characteristic tip shape). Then, a 2-cm lengthwise incision was made in the cut tip of the rootstock stem using a sharp knife to quickly insert the scion, making sure that the two sets of cambial tissue coincide. A biodegradable synthetic tape was used to seal the graft union in order to stop the entry of microorganisms and to prevent the rootstock and scion tissue cells from drying out. The grafted plant was grown for a year under greenhouse conditions before performing measurements of morphological scion features.
R Functions and Statistical Analyses
The software R was used for different genotyping and phenotyping analyses (R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).1 For the analyses of the morphological traits, a principal component analysis (PCA) based on the correlation data matrix was performed using the package “mice” to interpolate missing values, and “factoextra” to calculate the principal components. For the analysis of nuclear markers, a genotype matrix was built considering allele sizes (Supplementary Table S3) and analyzed with the “POLYSAT” package (Clark and Jasieniuk, 2011). Then, a matrix of genetic distances was created according to Bruvo et al. (2004). The principal coordinate analysis was plotted using the “POLYSAT” package. Morphological parameters of grafted plants were represented as the average values of 8–10 plants +/– standard errors. Asterisks indicate significant differences with the self-grafted Picual plants value. The data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and multiple comparisons of means were analyzed by Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant difference). The multiple range test was calculated using the Statistical Analysis System (STATGRAPHICS Centurion XVI software; http://www.statgraphics.com; StatPoint Technologies, Warrenton, VA, United States).
Results
The wild olive germplasm collection SILVOLIVE includes 146 genotypes obtained from seeds of up to 120 mother trees from 19 different locations, prospected in their natural habitats or from Olive Germplasm Banks (Table 1). After in-vitro germination, the genotypes were micropropagated to ensure the availability of clonal plant material required for subsequent genotyping and phenotyping assays.
Genotyping and Ploidy Level Determination of the SILVOLIVE Collection
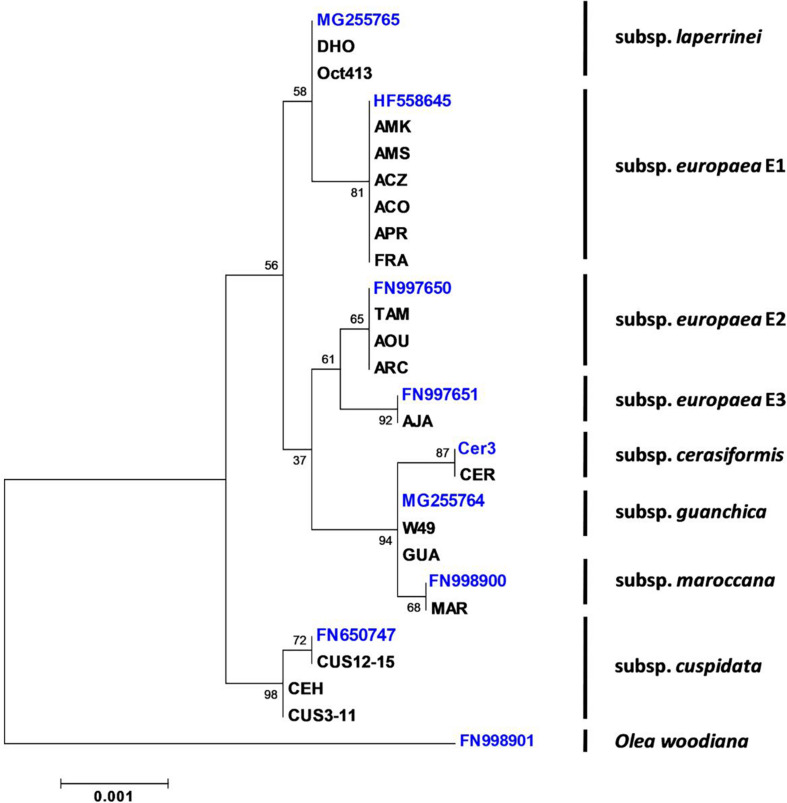
To determine the origin and the degree of genetic variability of the SILVOLIVE genotypes, chloroplastic and nuclear markers have been used. Chloroplastic polymorphisms have been widely used to analyze the phylogeographic history of the olive complex (Besnard et al., 2003, 2007, 2018). According to the cpDNA markers obtained (Supplementary Tables S1, S4), the main maternal lineages of African and Mediterranean wild olives are represented in the SILVOLIVE collection (Figure 1), confirming the wide genetic variability represented in the germplasm collection. The three chloroplastic lineages previously identified in the subsp. europaea – as E1, E2, and E3 (Besnard et al., 2007) – were also sampled. We could also identify differences in the cpDNA of cuspidata genotypes. The previously fully sequenced cuspidata haplotype (NCBI accession number FN650747) includes the genotypes CUS12, CUS13, CUS14, and CUS15. The cuspidata genotypes CUS3, CUS4, CUS6, and CUS11 showed a polymorphism (C to T change) in the trnT-trnL spacer (Besnard et al., 2003). This attests that CUS trees (Table 1) were issued from two mothers (Gr3 and Gr5), not sharing the same chloroplastic haplotype.
FIGURE 1.
Phylogenetic relationships among wild olive genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection according to plastid markers. Sequences of the chloroplast markers were used to determine the phylogenetic relationships through the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Tamura 3-parameter model (Tamura, 1992). Phylogenetic analyses were conducted with MEGA6 (Tamura et al., 2013). The tree with the highest log likelihood (–5551.0632) is shown. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained by applying the Neighbor-Joining method to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the Maximum Composite Likelihood (MCL) approach. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites [5 categories (+G, parameter = 0.05)]. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured as the number of substitutions per site. The total number of positions in the final dataset was 3,818. Support of nodes was estimated with 1,000 bootstraps. NCBI Accession numbers of the plastomes, used here as reference genomes, are the following: Olea europaea subsp. europaea lineage E1 (HF558645); O. e. subsp. europaea lineage E2 (FN997650); Olea europaea subsp. europaea lineage E3 (FN997651); O. e. subsp. laperrinei (MG255765); O. e. subsp. maroccana (FN998900); O. e. subsp. guanchica (MG255764); O. e. subsp. cuspidata (FN650747); O. woodiana (FN998901). For cerasiformis, with no available full plastome sequence, the mother tree from the CEFE Montpellier collection (Cer3) was used to sequence the chloroplast markers. Other mother trees were also verified: W49 = Olea europaea subsp. guanchica from the WOGB Córdoba collection; Oct413 = Olea europaea subsp. laperrinei variety Dhokar from the WOGB Marrakech collection. Olea woodiana (FN998901) served as the outgroup species to root the tree.
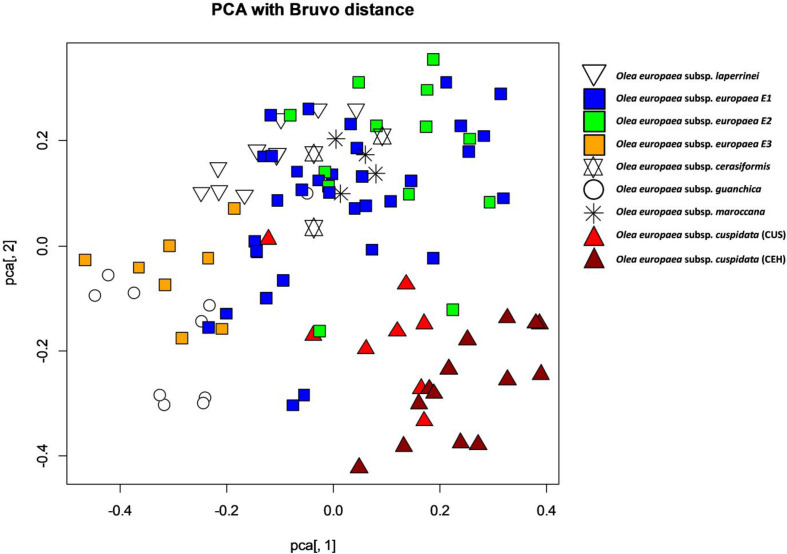
To assess the possible genetic admixture imposed by the open pollination of the trees that gave rise to the genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection, nuclear microsatellite markers, which are co-dominantly inherited, were analyzed. Five SSR markers were sufficient to distinguish all individuals of the SILVOLIVE collection (Supplementary Table S5). While the cpDNA markers allowed distinguishing genotypes according to their maternal origin (following to some extent the taxonomy; Besnard et al., 2018) our SSR dataset did not allow a clear distinction of taxa (Figure 2), with many SSR alleles shared between subspecies (Supplementary Table S5). Thus, individuals belonging to the same chloroplastic lineage (e.g., europaea-E1) exhibited a relatively large nuclear diversity (Figure 2). This may result from the admixture produced by sexual crossings of wild mother trees with pollen of genetically diverse trees present in the prospection sites, mainly in WOGBs.
FIGURE 2.
Genetic dispersion of 105 genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection according to nuclear SSR markers. Genetic distance matrices were calculated according to Bruvo et al. (2004). To represent the distribution of the genotypes according to their genetic distances, Principal Coordinate Analysis and plotting were subsequently performed with the package “POLYSAT” in R (Clark and Jasieniuk, 2011). Plotted symbols represent different subspecies or lineages of Olea europaea, and different colors identified the genotypes according to the classification obtained by chloroplastic markers. To compute allele copy number, POLYSAT uses the combinatorics utilities in R (the “combn” and “permn” functions from the COMBINAT package) to match all possible combinations of alleles and find the smallest sum of geometrically transformed distances between alleles (Equation 2) of Bruvo et al. (2004).
Multiple polyploidy levels were revealed in the SILVOLIVE collection through flow cytometry (Supplementary Figure S1) and nuclear microsatellite analyses (Supplementary Table S5). The results showed the presence of triploids harboring the cpDNA of subsp. europaea-E2 (AOU10), laperrinei (DHO10A, DHO11A) and cerasiformis (CER1 and CER3); and hexaploid genotypes harboring the cpDNA of all genotypes of subsp. maroccana. All genotypes of cuspidata, guanchica, europaea-E1 and europaea-E3, as well as most europaea-E2 genotypes and laperrinei x europaea hybrids were confirmed as diploids. The presence of triploid genotypes suggests the occurrence of hybridization between diploid and polyploid genotypes in the prospecting zones, or spontaneous events of polyploidization.
Morphological Traits of the SILVOLIVE Collection
Growth habits and vigor traits can be quantified in olive seedlings a minimum of 9 months after germination (Hammami et al., 2011). Different morphological features of root and shoot parts have thus been measured to define vigor and branching habits in 103 wild olive genotypes 13 months after ex-vitro acclimatization. In Supplementary Table S6, genotypes have been primarily classified according to their height because it has been described as a good trait to predict the vigor of olive plants grown in pots (De la Rosa et al., 2006). A strong phenotypic variability was observed in the height of the wild genotypes, which displayed differences of up to five times between the maximum and minimum values (Supplementary Figure S1). Among the genotypes analyzed, two hexaploids were included in the group of very reduced vigor; four triploid genotypes were distributed along the low, medium and high vigor groups; and no multiploid genotypes were present in the group of very high vigor genotypes (Supplementary Table S6). Vigor parameters, represented by the plant height showed high and positive correlations with the basal stem diameter, the shoot biomass, the total leaf biomass and the total plant biomass (Supplementary Table S7). Other group of correlated parameters comprises features characteristic of branching habits, including the branching efficiency, the branching frequency and the number of tertiary stems. The total number of nodes (and leaves) and the number of secondary stems correlated with both vigor and branching parameters. Finally, the root-to-shoot ratio showed negative correlations with both vigor and branching parameters. We observed that the high R/S ratio and the low shoot branching are traits highly represented in genotypes of very low and low vigor (Supplementary Table S8). High branching is overrepresented in the group of intermediate-vigor genotypes. Finally, the low R/S ratio is typical of genotypes with high or very high vigor (Supplementary Table S8).
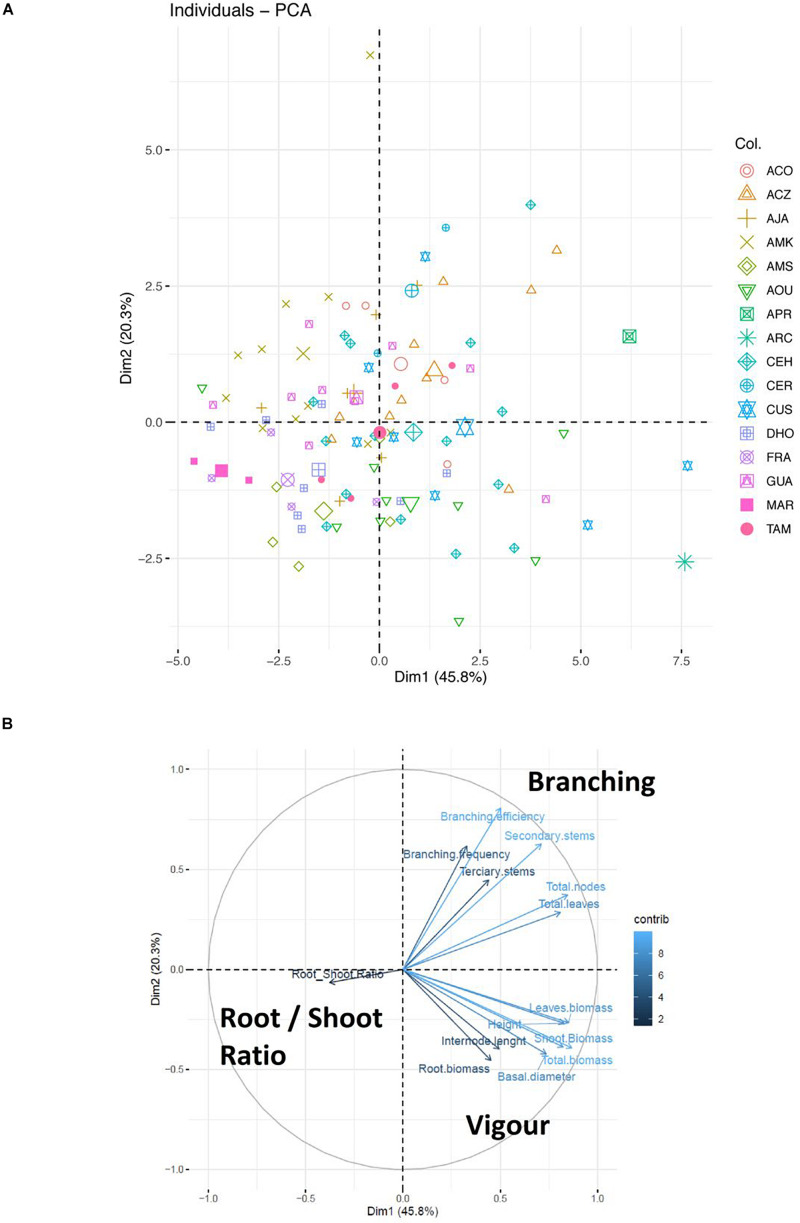
According to a PCA analysis that explains 66.1% of total variability of the morphological traits measured, different groups of genotypes could be distinguished (Figure 3). ARC, AOU, CUS, and CEH genotypes are mainly characterized by high values of vigor traits: plant height, stem basal diameter, plant biomass, shoot biomass, root biomass, total leaf biomass and internode length; APR, ACZ, CER, and CEH are mainly characterized by high values of branching traits: branching efficiency branching frequency, number of secondary and tertiary stems, total number of nodes and total number of leaves; AMK, GUA, AJA, and DHO genotypes are mainly characterized by low vigor traits; MAR and DHO genotypes are mainly characterized by low branching habits and high root-to-shoot ratio. The high variability of genotypes was not only observed at the level of the whole collection, but also within the same subspecies, and even within the offspring of the same tree, as observed for example in ACZ, CUS, AOU, DHO, or CEH genotypes (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of morphological parameters of wild olive subspecies. Data concerning morphological parameters were converted into a matrix of numerical values. The missing data were interpolated using the “Mice” package as a preliminary step to the calculation of the main components using “Prcomp.” In (A) the two main components of variability, explaining here 66.5% of the total variability, were identified using the “Fviz_eig (res.pca)” algorithm and the results were plotted in a graphic. In (B) the contribution of each variable is depicted in the two main components previously represented in (A).
Regulation of Scion Features by Wild Genotypes Used as Rootstocks
Tree grafting on clonal rootstocks is an important practice for morphological uniformity, improvement of environmental adaptability and crop quality of plants. However, it is not a widespread procedure in olive nursery production. In a first attempt to confirm the grafting compatibility of the wild genotypes with commonly used cultivars, the two high-vigor Spanish varieties “Picual” and “Hojiblanca” were grafted on 43 genotypes belonging to subspecies guanchica, cerasiformis, laperrinei, cuspidata, and europaea (lineages E1, E2, and E3) or their hybrids. All the accessions assayed, including the most genetically distant subsp. cuspidata showed grafting compatibility with the cultivated olive varieties used (Supplementary Table S9). Low efficient grafting compatibility was observed only for subsp. europaea lineage E2, for which a single genotype was tested.
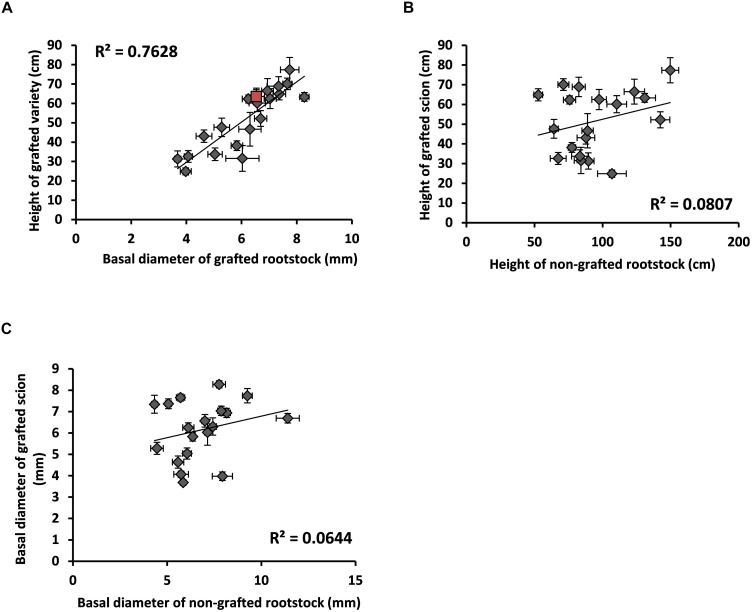
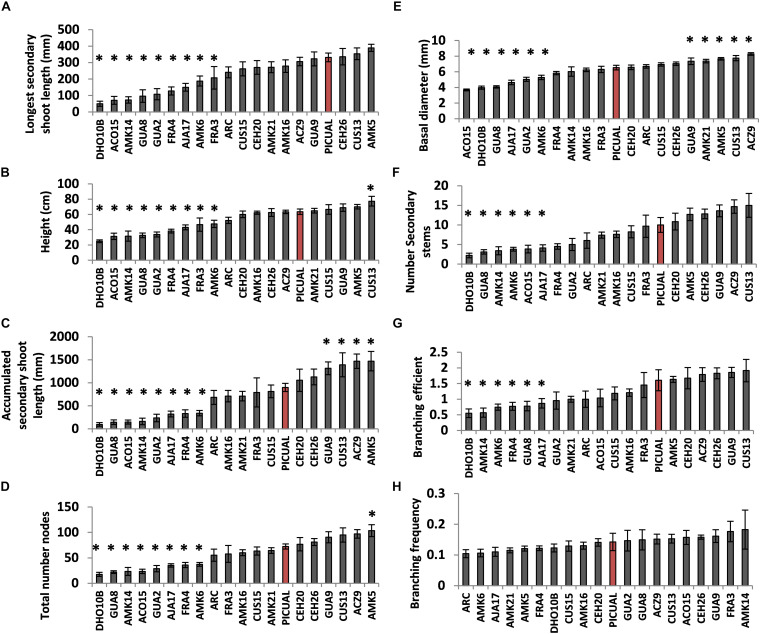
As a proof of concept, morphological traits were examined in the “Picual” scion grafted on 20 different wild olive genotypes. When used as rootstocks, many wild genotypes modified vigor parameters of the “Picual” scion (Figure 4A). As expected, most of the genotypes classified as very-low to intermediate vigor (Supplementary Table S6; DHO10B, ACO15, AMK14, GUA8, GUA2, FRA4, AJA17, AMK6, and FRA3) significantly reduced vigor properties of the grafted scion (Figures 5A–E). Conversely, high vigor genotypes such as ACZ9, CUS13 and CUS15 increased the vigor of the grafted scion (Figures 5A–E). However, some contradictory relationships were also observed. Thus, AMK5, AMK21, and GUA9, classified as very low- and low-vigor genotypes (Supplementary Table S6), significantly increased vigor parameters in the grafted “Picual” variety (Figure 5E). This indicates that not only the rootstock but also some other unknown effects (e.g., the rootstock x scion interaction) determined the scion properties in the grafted plant. As a result, when vigor traits such as basal diameter and height were compared within the same grafted plant, a positively significant correlation was observed (Figure 4A). However, when the vigor trait either height (Figure 4B) or basal diameter (Figure 4C) was compared between the grafted and the non-grafted plant, no clear correlation was observed.
FIGURE 4.
Vigor regulation of the “Picual” scion by wild rootstock genotypes. Wild genotypes grown in pots for 1 year after ex-vitro acclimatization were grafted with the cv. “Picual”. Morphological features were measured 1 year after grafting. (A) Correlation between the rootstock basal diameter and the scion height. Values correspond to the average value of different individuals (N = 8–12), with self-grafted “Picual” labeled in red color. (B) Correlation between height of the non-grafted rootstock and height of the grafted scion. Values correspond to the average value of different individuals (N = 8–12) of each genotype. (C) Correlation between the basal diameter of the non-grafted rootstock and the height of the grafted scion. Values correspond to the average value of different individuals (N = 8–12) of each genotype. Error bars in 2 dimensions (in A–C).
FIGURE 5.
Comparison of morphological parameters measured in the Picual scion grafted on different genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection. Potted plants grown under greenhouse conditions were used 1 year after grafting. The parameters measured were: The longest secondary shoot length (A); the plant height (B); the accumulated secondary shoot length calculated as the sum of all secondary shoots length (C); the total number of nodes (D); the basal stem diameter at 5 cm from ground (E); the total number of secondary stems (F); the branching efficiency (G); and the branching frequency (H). Bars are the average of 7–10 plants. Asterisks indicate significant differences with self-grafted Picual plants labeled as red bar. The data were subject to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and multiple comparisons of means were analyzed by Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant difference). Multiple range test was calculated using the Statistical Analysis System (STATGRAPHICS Centurion XVI software; http://www.statgraphics.com; StatPoint Technologies, Warrenton, VA, United States).
While many of the tested genotypes reduced to some extent vigor parameters of the “Picual” scion (9 out of 20 genotypes showed statistically significant reductions of most vigor traits assayed; Figures 5A–F), modification of branching traits was less evident (Figures 5G,H). Most of the genotypes that reduced vigor also significantly reduced branching efficiency (Figure 5G), although no significant differences in branching frequency were observed (Figure 5F). However, FRA3, which showed significant reductions of some vigor traits, maintained similar branching efficiency, and higher (although not statistically significant) branching frequency, than the self-grafted “Picual.”
Discussion
Ecological and socio-economic issues regarding the future of olive cultivation are essential in the light of present global changes, including agronomic, climatic, economic societal, or political changes (Besnard et al., 2018). Genetic erosion has dangerously shrunk the genetic pool of crop species. In the olive cultivation, the use of a small number of cultivars for “modern” olive orchards (e.g., in the HDH system) may lead to genetic erosion in the near future, which may increase the susceptibility of the crop to abrupt climate changes, and to the emergence of new diseases and pests (Esquinas-Alcázar, 2005). Therefore, identification of unexploited adaptive traits in wild olive genotypes and their subsequent utilization is expected to be a major goal of olive crop breeding and rootstock programmes in the close future.
Genetic Diversity of the SILVOLIVE Collection
Germplasm characterization is a key starting point of the pre-breeding process, and molecular markers are a valuable tool for identifying and characterizing olive genotypes (do Val et al., 2012). The gain of genetic diversity in the SILVOLIVE collection was achieved at two levels: (i) firstly, at the whole collection level, it includes genotypes related to all known subspecies of O. europaea, that were here characterized with both plastid and nuclear markers. Besides the genetically distant subspecies cuspidata (Figure 1), genotypes of subspecies europaea, laperrinei, cerasiformis, guanchica, and maroccana belong to a monophyletic lineage from North Africa and the Mediterranean area, as previously reported (Médail et al., 2001; Rubio de Casas et al., 2006; Besnard et al., 2018); (ii) secondly, at the level of individuals, many accessions of the collection resulted from admixture between genetically distant parents. It is expected that hybrid offspring displays phenotypic performance superior to their parents due to a higher heterozygosity (Shull, 1948). The greatest manifestation of heterosis in the SILVOLIVE collection is expected to occur in genotypes resulting from the cross between cuspidata and europaea (CUS and CEH genotypes) since both parental subspecies present the maximum genetic distance (Figure 1). The admixture produced by sexual crossings of wild mother trees with pollen of diverse origin in collections or natural conditions (Figure 2), has further increased the genetic diversity and heterosis of the SILVOLIVE collection.
Different ploidy levels are also represented in the collection, first with the hexaploid maroccana, and second with triploids of different origins. The triploid genotypes CER1 and CER3 were obtained from a verified 4x cerasiformis mother tree (CEFE Montpellier, accession Cer3) and may thus result from a cross with a diploid father tree of the CEFE collection. The triploid AOU10, harboring the europaea-E2 chloroplast lineage, was prospected in the Southwest Morocco, where the hexaploid maroccana subspecies is endemic. AOU10 could be the product of a sexual crossing between a diploid female parent (europaea) with a hexaploid male parent (maroccana), although a tetraploid genotype should be rather expected. The possibility that AOU10 just resulted from a spontaneous triploidization between two oleasters cannot be ruled out (Besnard and Baali-Cherif, 2009). Similarly, the two triploid progenies issued from “Dhokar” from the WOGB Marrakech are very likely issued from a spontaneous events of polyploidization. A high level of unreduced gametes is indeed expected in “Dhokar” due to its hybrid status (Besnard et al., 2013a) that may lead to abnormalities during the formation of gametes (Mason and Pires, 2015).
Phenotypic Diversity of the SILVOLIVE Collection
The diversity of morphological features in olive trees (shoot growth, root development, root-to-shoot biomass ratio, branching habits, total leaf surface, etc.) can be enormously relevant in terms of plant-soil interaction, plant hydraulic properties, water and nutrient uptake abilities, photosynthetic capacity, abiotic stress resistance, etc., as previously shown for a number of SILVOLIVE genotypes (Hernández-Santana et al., 2019). Illustrating the huge phenotypic variability of the collection, genotypes like DHO6A have a root biomass that approximates that of the aerial part (Supplementary Figure S2), whereas other genotypes like AMK34, AJA7 or CUS14 have a root biomass five times lower than that of their corresponding aerial biomass. Root anatomy can mediate responses to a range of abiotic and biotic stressors. In many soils, a deep-rooting, water-conserving root phenotype is likely to have several advantages (Warschefsky et al., 2016).
Besides the root development, the morphological traits measured have been organized in two groups of correlative traits, which identifies two sets of vigor and branching parameters respectively (Figure 3 and Supplementary Table S7). Particularly plant vigor traits show great variability (e.g., up to 5 times differences in height; Supplementary Figure S2). Highly vigorous phenotypes with high root biomass could be of interest to rehabilitate deforested habitats or at risk of desertification (Bekele, 2005; Kassa et al., 2019), while low-vigor genotypes could be particularly interesting for different reasons. On the one hand, they could reasonably be better suited to reduce vigor of grafted scions, which should be of great relevance for HDH olive plantations. On the other hand, 45% of very low- and low-vigor genotypes present high root-to-shoot ratio (Supplementary Table S8), which may determine a more favorable plant-soil interaction in term of stress resistance, nutrient- and water-use efficiencies. These traits may favor the reduction of irrigation and fertilizers, promoting a more sustainable agriculture. This is particularly true for very low- and low-vigor genotypes like DHO6A, AMK21, DHO12A, AMK9, GUA8, AMK12, CEH2, FRA4, DHO10B, and AMS7 (Supplementary Table S6 and Supplementary Figure S1). Most AMK genotypes (10 out of 11) are classified as low or very low vigor genotypes (Supplementary Figure S2), being a possible source of low-vigor genes. However, genotypes with low vigor are frequently discarded in olive breeding programs because of their long juvenile period (De la Rosa et al., 2006). This wide variability of vigor features was also observed in wild olive genotypes from the SILVOLIVE collection grown in the field for a longer time (León et al., 2020). Thus, similarly to the phenotype observed in potted plants, AMK genotypes showed low vigor when grown in the field, supporting the fact that morphological features observed in young plants grown in pots, like vigor, are still observed in field-grown plants. The possibility that the low-vigor AMK genotypes are inbred individuals should be bear in mind, because they could be more susceptible to adverse situations of biotic or abiotic origin.
Around 3.3 times variability was observed in the basal stem diameter of the wild olives collection. In general, genotypes with greater heights have thicker trunks, showing a positive correlation in potted plants (R2 = 0.7581), as reported also in SILVOLIVE genotypes grown in the field (León et al., 2020). However, some varieties such as FRA1, AMS15, AMK26 and DHO6A, showed thicker primary stems despite having low vigor traits according to other morphological features. The number of secondary stems also showed high variability (Supplementary Figure S1 and Supplementary Table S6), with CEH3, ACZ7, and ACZ8 exhibiting the highest number of lateral branches. The AMK26 genotype is remarkable, with the smallest size and the highest branching frequency (Supplementary Figure S1). Cultivars used for HDH orchards, such as “Arbequina” and “Arbosana,” exhibit greater branching frequency associated with smaller diameters of trunk, branches and shoots. This means low-vigor plants producing a greater number of smaller secondary stems and shoots that reduce permanent structures for a given canopy volume (Rosati et al., 2013). In this study, genotypes with low basal diameter and high branching like AMK26, CUS14, AMK27, AMK5, AJA17, AOU13, AMS12, GUA9, ACO15, ACO14, CER3, GUA4, ACZ4, and CUS3, have been identified. The branching habit is one of the main factors affecting carbon partitioning between wood and leaves. Low-vigor and high-branching genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection have a higher number of nodes and leaves (R2 = 0.7), which means increased canopy density and may determine higher number of potential fruiting sites, becoming an important trait to be used to produce and export more assimilates toward fruits (Rosati et al., 2018). Otherwise, the hexaploid MAR1 and MAR3, together with most FRA and AMS genotypes show high apical growth with a low number of secondary stems.
SILVOLIVE, a Germplasm Collection for the Identification of Rootstocks That Improve Olive Cultivation
Traditional olive plantations are characterized by low tree density and rain fed orchards with low yields. Progressive intensification of olive cultivation, with higher densities, irrigated, and mechanically harvested orchards has significantly increased crop productivity [e.g., higher production at lower costs; Rallo et al. (2013)]. But intensive cultivation has strongly reduced the diversity of cultivars in olive orchards, increased the demand of inputs and the risk of environment unbalances (Rallo et al., 2016) dealing, for example, to higher incidence of soil-borne diseases (Lopez-Escudero and Blanco-Lopez, 2005; Lopez-Escudero and Mercado-Blanco, 2011; Perez-Rodriguez et al., 2015). Given that grafting compatibility can occur across broad phylogenetic distances, crop wild relatives are of great significance to grafted perennial crops. Olive cultivation, specially intensive crops, could benefit from the use of clonal rootstocks, which have been proposed to potentially improve a number of agronomic traits such as: resistance to Verticillium wilt (Porras-Soriano et al., 2003; Bubici and Cirulli, 2012); tolerance to frost injury (Pannelli et al., 2002) and iron chlorosis (Alcantara et al., 2003); and early maturation (Malik and Bradford, 2004). But the main drawback of HDH orchards is the difficulty to control the tree size to allow the movement of the harvesting machines (Tous et al., 2010). Only a few traditional olive cultivars meet partially the low vigor requirement for HDH plantations, mostly “Arbequina,” “Arbosana,” and “Koroneiki” (Diez et al., 2016). Even these cultivars require tree size control by means of strict pruning and fertirrigation practices (Fernandez et al., 2013), which are expensive procedures. In addition, the HDH system excludes the possibility of using traditional cultivars of higher vigor, but outstanding socioeconomic importance. Rootstock-induced reduction in scion vigor, or “dwarfing” causes a decrease in tree size, reducing the need for pruning in commercial orchards. But to our knowledge, no rootstocks of proven quality are presently available at either commercial or experimental levels.
The question arises whether the phenotypic features previously described in genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection can be somehow transmitted to the grafted scion. Plant shoot vigor is affected by numerous root-depending factors including root hydraulic pressure, water uptake efficiency, hormone production, nutrient uptake, and stomatal conductance. Convincing evidence has been provided that these traits are genetically encoded by the root portion of the grafted plant, playing the rootstock genotype essential roles in shaping variation of these traits in the scion (Warschefsky et al., 2016). In addition, rootstocks can also affect the branching pattern of the scion (Costes et al., 2010) and promote early and more abundant bearing in young olive trees (Rosati et al., 2017, 2018). On the one hand, we have verified that all subspecies can be grafted with commercial olive varieties, including cuspidata, which has the maximum genetic distance with europaea (Supplementary Table S9). On the other hand, we have also confirmed that wild genotypes used as rootstocks modify the morphological properties of the grafted scion (Figures 4A, 5). In general, a correspondence is observed between the vigor of the genotype and the vigor transmitted to the grafted scion. However, graft combinations have also been observed in which this correlation does not occur, with low-vigor genotypes increasing the vigor of the grafted scion (e.g., AMK5, AMK21, and GUA9; Figure 5E), strongly suggesting that other factors (e.g., the rootstock x scion interaction) are also relevant to determine the properties of the grafted tree. It is noteworthy that in a first trial with 20 genotypes of variable vigor, 9 genotypes significantly reduced vigor parameters of the grafted “Picual” scion (Figure 5). This represents 45% of the genotypes tested, which indicates that the ability to reduce vigor is a common trait in the collection of wild genotypes. Most of the rootstocks that reduce vigor of the “Picual” scion also significantly reduced the branching efficiency as a consequence of the reduction in the number of secondary stems (Supplementary Figure S2), given the strong correlation between both parameters (R2 = 0.93). However, no significant differences were observed in the branching frequency or average number of secondary stems per bud.
Conclusion
This work has been carried out on plants grown in pots 1 year after grafting. It is therefore necessary to extend this study to field conditions for a greater number of years to obtain more conclusive data. For example, determining the rootstock effect on the branching frequency might require greater root development in the soil and a larger canopy volume. With this aim, field trials are currently being developed under HDH conditions with 35 selected genotypes used as rootstocks of the “Picual” and “Arbequina” scions. In addition, some of the genotypes tested have been proven resistant or extremely resistant to Verticillium wilt (to be published), one of the most threatening disease for olive cultivation due to the severity of damage caused and its rapid extension (Inderbitzin and Subbarao, 2014). The identification of one or several Verticillium-resistant dwarfing rootstocks in the collection of wild genotypes could give an important boost to the high density cultivation of olive grove, opening the possibility of: increasing the sustainability of the crop (e.g., reducing pruning and the use of fungicides); and introducing new oil or table olive cultivars (of higher vigor) into the HDH system.
Therefore, the SILVOLIVE collection, which represents an important part of the genetic variability of the species, has been genotyped and phenotyped. Great variability has been found in the wild genotypes at both genotypic and phenotypic levels. When used as rootstocks, wild genotypes modify growth parameters of the grafted scion. According to their specific characteristics, genotypes of the SILVOLIVE collection have great potential interest to: (i) restore vegetation on degraded soils or at risk of desertification; (ii) provide relevant traits or genes in breeding programs; (iii) be used as rootstocks for olive cultivation, mostly for high-density hedgerow (HDH) orchards.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
PD-R participated in all experimental tasks, as well as in writing the manuscript. JF-N, JE, and CR-N participated in vigor measurement of ungrafted plants in pots. RM and AC participated in genotyping the collection with nuclear SSR markers. NC contributed in the development of the phylogenetic analyses and in the study of the genetic distances. PA contributed in determining the ploidy level of genotypes. MC and JG-F contributed in obtaining plant material and its multiplication in vitro. AB, LL, and GB contributed in obtaining plant material and in writing the manuscript. JC-F conceived research plans, supervised the experiments, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. Abdelmajid Moukhli from INRA, UR Amélioration Génétique des Plantes et de la Qualité, CRRA, Marrakech, Morocco, for providing seeds of the DHO genotypes, prospected in the WOGB-INRA, Marrakech; Prof. Said Wahbi from the Cadi Ayyad University of Marrakesh, Morocco, for providing seeds of the AMK genotypes; Prof Abdelhamid el Mousadik from the Laboratoire Biotechnologies and Valorisation des Ressources Naturelles (LBVRN) of the Faculty of Sciences of Agadir, Morocco, for helping us during the prospection of seeds from the TAM, AMS, AOU genotypes in south-western Morocco; and Dr. Carlos García-Verdugo from Canary botanical garden – CSIC associated unit, Spain, for providing seeds from the ANA, HER, BAR genotypes obtained in Canary Islands, Spain. Technical assistance of Francisco Durán, Miriam Pérez, María del Mar Gamero and Pilar Alcántara is acknowledged. GB is member of the EDB laboratory supported by the excellence projects Labex CEBA (ANR-10-LABX-25-01) and Labex TULIP (ANR-10-LABX-0041), managed by the French ANR. The CEFE olive collection is managed by the Platform “Terrains d’Expériences” of the LabEx CeMEB (ANR-10-LABX-04-01).
Funding. This work was supported by the FEDER-CSIC grant RECUPERA-2020 (Ref. 20134R089), the Grupos Operativos Intra-autonómicos FEDER-MAPAMA grant (Ref. 201600200066 29), and the Spanish National Research Council Proyectos Intramurales CSIC-201640E069, CSIC-201740E041, and CSIC-201940E077.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2020.00629/full#supplementary-material
References
- Alcantara E., Cordeiro A. M., Barranco D. (2003). Selection of olive varieties for tolerance to iron chlorosis. J. Plant Physiol. 160 1467–1472. 10.1078/0176-1617-01013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleza P., Juarez J., Hernandez M., Pina J. A., Ollitrault P., Navarro L. (2009). Recovery and characterization of a Citrus clementina Hort. ex Tan. ‘Clemenules’ haploid plant selected to establish the reference whole Citrus genome sequence. BMC Plant Biol. 9:110 10.1186/1471-2229-9-110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Calderon R., Rodriguez-Jurado D., Bejarano-Alcazar J., Belaj A., de la Rosa R., León L. (2015a). Evaluation of Verticillium wilt resistance in selections from olive breeding crosses. Euphytica 206 619–629. [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Calderon R., Rodriguez-Jurado D., León L., Bejarano-Alcazar J., De la, Rosa R., et al. (2015b). Pre-breeding for resistance to Verticillium wilt in olive: Fishing in the wild relative gene pool. Crop Protect. 75 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Baali-Cherif D., Besnard G. (2005). High genetic diversity and clonal growth in relict populations of Olea europaea subsp laperrinei (Oleaceae) from Hoggar, Algeria. Ann. Bot. 96 823–830. 10.1093/aob/mci232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccouri B., Guerfel M., Zarrouk W., Taamalli W., Daoud D., Zarrouk M. (2011). Wild olive (Olea europaea L.) selection for quality oil production. J. Food Biochem. 35 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Baldoni L., Cultrera N. G., Mariotti R., Ricciolini C., Arcioni S., Vendramin G. G., et al. (2009). A consensus list of microsatellite markers for olive genotyping. Mol. Breed. 24 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Baldoni L., Fontanazza G. (1990). Preliminary-results on olive clonal rootstocks behavior in the field. Acta Horticult. 286 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Baldoni L., Tosti N., Ricciolini C., Belaj A., Arcioni S., Pannelli G., et al. (2006). Genetic structure of wild and cultivated olives in the central Mediterranean basin. Ann. Bot. 98 935–942. 10.1093/aob/mcl178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barazani O., Westberg E., Hanin N., Dag A., Kerem Z., Tugendhaft Y., et al. (2014). A comparative analysis of genetic variation in rootstocks and scions of old olive trees – a window into the history of olive cultivation practices and past genetic variation. BMC Plant Biol. 14:146 10.1186/1471-2229-14-146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekele T. (2005). Recruitment, survival and growth of Olea europaea subsp cuspidata seedlings and juveniles in dry Afromontane forests of northern Ethiopia. Trop. Ecol. 46 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Belaj A., Munoz-Diez C., Baldoni L., Satovic Z., Barranco D. (2010). Genetic diversity and relationships of wild and cultivated olives at regional level in Spain. Sci. Horticult. 124 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Belaj A., Veral M. G., Sikaoui H., Moukhli A., Khadari B., Mariotti R., et al. (2016). “Olive genetic resources,” in The Olive Tree Genome, eds Rugini E., Baldoni L., Muleo R., Sebastiani L. (Berlin: Springer International Publishing AG; ), 27–54. [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G. (2008). Chloroplast DNA variations in Mediterranean olive. J. Horticult. Sci. Biotechnol. 83 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Baali-Cherif D. (2009). Coexistence of diploids and triploids in a Saharan relict olive: evidence from nuclear microsatellite and flow cytometry analyses. C. R. Biol. 332 1115–1120. 10.1016/j.crvi.2009.09.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Rubio de Casas R., Vargas P. (2003). A set of primers for length and nucleotide-substitution polymorphism in chloroplastic DNA of Olea europaea L. (Oleaceae). Mol. Ecol. Notes 3 651–653. [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., El Bakkali A., Haouane H., Baali-Cherif D., Moukhli A., Khadari B. (2013a). Population genetics of Mediterranean and Saharan olives: geographic patterns of differentiation and evidence for early generations of admixture. Ann. Bot. 112 1293–1302. 10.1093/aob/mct196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Khadari B., Navascués M., Fernández-Mazuecos M., El Bakkali A., Arrigo N., et al. (2013b). The complex history of the olive tree: from Late Quaternary diversification of Mediterranean lineages to primary domestication in the northern Levant. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 280 20122833 10.1098/rspb.2012.2833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Garcia-Verdugo C., Rubio de Casas R., Treier U. A., Galland N., Vargas P. (2008). Polyploidy in the olive complex (Olea europaea): evidence from flow cytometry and nuclear microsatellite analyses. Ann. Bot. 101 25–30. 10.1093/aob/mcm275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Hernandez P., Khadari B., Dorado G., Savolainen V. (2011). Genomic profiling of plastid DNA variation in the Mediterranean olive tree. BMC Plant Biol. 11:80 10.1186/1471-2229-11-80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Rubio de Casas R., Vargas P. (2007). Plastid and nuclear DNA polymorphism reveals historical processes of isolation and reticulation in the olive tree complex (Olea europaea). J. Biogeogr. 34 736–752. [Google Scholar]
- Besnard G., Terral J. F., Cornille A. (2018). On the origins and domestication of the olive: a review and perspectives. Ann. Bot. 121 385–403. 10.1093/aob/mcy002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruvo R., Michiels N. K., D’Souza T. G., Schulenburg H. (2004). A simple method for the calculation of microsatellite genotype distances irrespective of ploidy level. Mol. Ecol. 13 2101–2106. 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02209.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubici G., Cirulli M. (2012). Control of Verticillium wilt of olive by resistant rootstocks. Plant Soil 352 363–376. [Google Scholar]
- Cantos M., Troncoso J., Linan J., Troncoso A., Rapaport H. (2002). Obtaining salt (NaCl) tolerant olive plants: 1) some physiological and anatomical characteristics of olive plants growing in harsh saline zones. Acta Horticult. 586 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda-Alvarez N. P., Khoury C. K., Achicanoy H. A., Bernau V., Dempewolf H., Eastwood R. J., et al. (2016). Global conservation priorities for crop wild relatives. Nat. Plants 2:16022 10.1038/nplants.2016.22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiappetta A., Muto A., Muzzalupo R., Muzzalupo I. (2017). New rapid procedure for genetic characterization of Italian wild olive (Olea europaea) and traceability of virgin olive oils by means of SSR markers. Sci. Horticult. 226 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Clark L. V., Jasieniuk M. (2011). POLYSAT: an R package for polyploid microsatellite analysis. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 11 562–566. 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.02985.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colella C., Miacola C., Amenduni M., D’Amico M., Bubici G., Cirulli M. (2008). Sources of verticillium wilt resistance in wild olive germplasm from the Mediterranean region. Plant Pathol. 57 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Costes E., Lauri P. E., Regnard J. L. (2010). Analyzing fruit tree architecture: implications for tree management and fruit production. Horticult. Rev. 32 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- De la Rosa R., Kiran A. I., Barranco D., León L. (2006). Seedling vigour as a preselection criterion for short juvenile period in olive breeding. Aust. J. Agricult. Res. 57 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Del Río C., Caballero J. M. (2006). Resultados preliminares sobre el empleo de patrones para modificar el vigor y/o la producción de la variedad de olivo ‘Picual’. Actas Horticult. (SECH) 45 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Diez C. M., Moral J., Cabello D., Morello P., Rallo L., Barranco D. (2016). Cultivar and tree density as key factors in the long-term performance of super high-density olive orchards. Front. Plant Sci. 7:1226 10.3389/fpls.2016.01226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- do Val A. D. B., Ferreira J. L., Neto J. V., Pasqual M., de Oliveira A. F., Borem A., et al. (2012). Genetic diversity of Brazilian and introduced olive germplasms based on microsatellite markers. Genet. Mol. Res. 11 556–571. 10.4238/2012.March.8.4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquinas-Alcázar J. (2005). Protecting crop genetic diversity for food security: political, ethical and technical challenges. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6 946–953. 10.1038/nrg1729 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. E., Perez-Martin A., Torres-Ruiz J. M., Cuevas M. V., Rodriguez-Dominguez C. M., Elsayed-Farag S., et al. (2013). A regulated deficit irrigation strategy for hedgerow olive orchards with high plant density. Plant Soil 372 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Verdugo C., David Forrest A., Balaguer L., Fay M. F., Vargas P. (2010). Parallel evolution of insular Olea europaea subspecies based on geographical structuring of plastid DNA variation and phenotypic similarity in leaf traits. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 162 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Green P. (2002). A revision of Olea L. (Oleaceae). Kew Bull. 57 91–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hammami S. B. M., León L., Rapoport H. F., De la Rosa R. (2011). Early growth habit and vigour parameters in olive seedlings. Sci. Horticult. 129 761–768. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi H., Breton C., Msallem M., El Hadj S. B., El Gazzah M., Berville A. (2008). Differences between native and introduced olive cultivars as revealed by morphology of drupes, oil composition and SSR polymorphisms: a case study in Tunisia. Sci. Horticult. 116 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Santana V., Diaz-Rueda P., Diaz-Espejo A., Raya-Sereno M. D., Gutierrez-Gordillo S., Montero A., et al. (2019). Hydraulic traits emerge as relevant determinants of growth patterns in wild olive genotypes under water stress. Front. Plant Sci. 10:291 10.3389/fpls.2019.00291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inderbitzin P., Subbarao K. V. (2014). Verticillium systematics and evolution: how confusion impedes verticillium wilt management and how to resolve it. Phytopathology 104 564–574. 10.1094/PHYTO-11-13-0315-IA [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Fernandez D., Trapero-Casas J. L., Landa B. B., Navas-Cortes J. A., Bubici G., Cirulli M., et al. (2016). Characterization of resistance against the olive-defoliating Verticillium dahliae pathotype in selected clones of wild olive. Plant Pathol. 65 1279–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Kassa A., Konrad H., Geburek T. (2019). Molecular diversity and gene flow within and among different subspecies of the wild olive (Olea europaea L.): a review. Flora 250 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Klepo T., De la Rosa R., Satovic Z., León L., Belaj A. (2013). Utility of wild germplasm in olive breeding. Sci. Horticult. 152 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Klepo T., Toumi A., de la Rosa R., Leon L., Belaj A. (2014). Agronomic evaluation of seedlings from crosses between the main Spanish olive cultivar ‘Picual’ and two wild olive trees. J. Horticult. Sci. Biotechnol. 89 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- León L., de la Rosa R., Velasco L., Belaj A. (2018). Using wild olives in breeding programs: implications on oil quality composition. Front. Plant Sci. 9:232 10.3389/fpls.2018.00232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- León L., Díaz-Rueda P., Belaj A., De la Rosa R., Carrascosa C., Colmenero-Flores J. M. (2020). Evaluation of early vigor traits in wild olive germplasm. Sci. Horticult. 264 109–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Escudero F. J., Blanco-Lopez M. A. (2005). Effects of drip irrigation on population of Verticillium dahliae in olive orchards. J. Phytopathol. 153 238–239. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Escudero F. J., del Rio C., Caballero J. M., Blanco-Lopez M. A. (2004). Evaluation of olive cultivars for resistance to Verticillium dahliae. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 110 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Escudero F. J., Mercado-Blanco J. (2011). Verticillium wilt of olive: a case study to implement an integrated strategy to control a soil-borne pathogen. Plant Soil 344 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lumaret R., Ouazzani N., Michaud H., Vivier G., Deguilloux M. F., Di Giusto F. (2004). Allozyme variation of oleaster populations (wild olive tree) (Olea europaea L.) in the Mediterranean Basin. Heredity 92 343–351. 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik N. S. A., Bradford J. M. (2004). Reciprocal grafting between early maturing and normal maturing olive varieties: preliminary effects on the nature of juvenility and flowering. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. S., Pires J. C. (2015). Unreduced gametes: meiotic mishap or evolutionary mechanism? Trends Genet. 31 5–10. 10.1016/j.tig.2014.09.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Médail F., Quézel P., Besnard G., Khadari B. (2001). Systematics, ecology and phylogeographic significance of Olea europaea L. ssp maroccana (Greuter & Burdet) P. Vargas et al., a relictual olive tree in south-west Morocco. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 137 249–266. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo J. M., Madejon E., Madejon P., Cabrera F. (2005). The response of wild olive to the addition of a fulvic acid-rich amendment to soils polluted by trace elements (SW Spain). J. Arid Environ. 63 284–303. [Google Scholar]
- Pannelli G., Rosati S., Rugini E. (2002). The effect of clonal rootstocks on frost tolerance and on some aspects of plant behaviour in Moraiolo and S. Felice olive cultivars. Acta Horticult. 586 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Rodriguez M., Alcantara E., Amaro M., Serrano N., Lorite I. J., Arquero O., et al. (2015). The Influence of Irrigation Frequency on the Onset and Development of Verticillium Wilt of Olive. Plant Dis. 99 488–495. 10.1094/PDIS-06-14-0599-RE [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras-Soriano A., Martin M. L. S., Piedra A. P. (2003). Grafting olive cv. Cornicabra on rootstocks tolerant to Verticillium dahliae reduces their susceptibility. Crop Protect. 22 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Rallo L., Barranco D., Castro-Garcia S., Connor D. J., Gomez, del Campo M., et al. (2013). High-density olive plantations. Horticult. Rev. 41 303–383. [Google Scholar]
- Rallo L., Caruso T., Diez C. M., Campisi G. (2016). “Olive growing in a time of change: from empiricism to genomics,” in The Olive Tree Genome, eds Rugini E., Baldoni L., Muleo R., Sebastiani L. (Berlin: Springer International Publishing AG; ), 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Romero A., Hermoso J. F., Tous J. (2014). Olive rootstocks to control ‘arbequina IRTA-I18’ clone vigour results from a second one comparative trial. Acta Horticult. 1057 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati A., Paoletti A., Al Hariri R., Morelli A., Famiani F. (2018). Partitioning of dry matter into fruit explains cultivar differences in vigor in young olive (Olea europaea L.) trees. HortScience 53 491–495. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati A., Paoletti A., Caporali S., Perri E. (2013). The role of tree architecture in super high density olive orchards. Sci. Horticult. 161 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati A., Paoletti A., Pannelli G., Famiani F. (2017). Growth is inversely correlated with yield efficiency across cultivars in young olive (Olea europaea L.) Trees. HortScience 52 1525–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio de Casas R., Besnard G., Schonswetter P., Balaguer L., Vargas P. (2006). Extensive gene flow blurs phylogeographic but not phylogenetic signal in Olea europaea L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 113 575–583. 10.1055/s-2006-924728 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugini E. (1984). In vitro-propagation of some olive (Olea europaea sativa L.) cultivars with different root-ability, and medium development using analytical data from developing shoots and embryos. Sci. Horticult. 24 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Rugini E., De Pace C., Gutierrez-Pesce P., Muleo R. (2011). “Olea,” in Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources: Temperate Fruits, ed. Kole C. (Berlin: Springer; ), 79–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rugini E., Silvestri C., Ceccarelli M., Muleo R., Cristofori V. (2016). Mutagenesis and biotechnology techniques as tools for selecting new stable diploid and tetraploid olive genotypes and their dwarfing agronomical characterization. HortScience 51 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Sefc K. M., Lopes S., Mendonca D., Dos Santos M. R., Machado M. L. D., Machado A. D. (2000). Identification of microsatellite loci in olive (Olea europaea) and their characterization in Italian and Iberian olive trees. Mol. Ecol. 9 1171–1173. 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.00954.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. H. (1948). What is “Heterosis”? Genetics 33 439–446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K. (1992). Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G+C-content biases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9 678–687. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Stecher G., Peterson D., Filipski A., Kumar S. (2013). MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30 2725–2729. 10.1093/molbev/mst197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tous J., Romero A., Francisco Hermoso J. F. (2010). New trends in olive orchard design for continuous mechanical harvesting. Adv. Horticult. Sci. 24 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tous J., Romero A., Hermoso J. F., Ninot A. (2012). Influence of different olive rootstocks on growth and yield of the ‘arbequina IRTA-i.18 (R)’ clone. Acta Horticult. 924 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Trapero C., Rallo L., Lopez-Escudero F. J., Barranco D., Diez C. M. (2015). Variability and selection of verticillium wilt resistant genotypes in cultivated olive and in the Olea genus. Plant Pathol. 64 890–900. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent H., Wiersema J., Kell S., Fielder H., Dobbie S., Castaneda-Alvarez N. P., et al. (2013). A prioritized crop wild relative inventory to help underpin global food security. Biol. Conserv. 167 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Warschefsky E. J., Klein L. L., Frank M. H., Chitwood D. H., Londo J. P., von Wettberg E. J. B., et al. (2016). Rootstocks: diversity, domestication, and impacts on shoot phenotypes. Trends Plant Sci. 21 418–437. 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weising K., Gardner R. C. (1999). A set of conserved PCR primers for the analysis of simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in chloroplast genomes of dicotyledonous angiosperms. Genome 42 9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.