Key Points
Question
What is the genetic architecture of opioid use disorder, and how is it associated with other traits?
Findings
In this genome-wide association study, meta-analysis of 10 544 individuals of European ancestry with opioid use disorder and 72 163 opioid-exposed control individuals identified OPRM1 functional variant rs1799971 as associated with opioid use disorder, with replication in 2 independent samples; no significant associations were detected for individuals of African ancestry (n = 32 088). Opioid use disorder was genetically correlated with 83 traits, including risk of tobacco smoking, depression, neuroticism, worry neuroticism subcluster, and cognitive performance.
Meaning
This genome-wide association study identified a significant genetic variant as associated with opioid use disorder, with replication.
Abstract
Importance
With the current opioid crisis, it is important to improve understanding of the biological mechanisms of opioid use disorder (OUD).
Objectives
To detect genetic risk variants for OUD and determine genetic correlations and causal association with OUD and other traits.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A genome-wide association study of electronic health record–defined OUD in the Million Veteran Program sample was conducted, comprising 8529 affected European American individuals and 71 200 opioid-exposed European American controls (defined by electronic health record trajectory analysis) and 4032 affected African American individuals and 26 029 opioid-exposed African American controls. Participants were enrolled from January 10, 2011, to May 21, 2018, with electronic health record data for OUD diagnosis from October 1, 1999, to February 7, 2018. Million Veteran Program results and additional OUD case-control genome-wide association study results from the Yale-Penn and Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment samples were meta-analyzed (total numbers: European American individuals, 10 544 OUD cases and 72 163 opioid-exposed controls; African American individuals, 5212 cases and 26 876 controls). Data on Yale-Penn participants were collected from February 14, 1999, to April 1, 2017, and data on Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment participants were collected from 1990 to 2007. The key result was replicated in 2 independent cohorts: proxy-phenotype buprenorphine treatment in the UK Biobank and newly genotyped Yale-Penn participants. Genetic correlations between OUD and other traits were tested, and mendelian randomization analysis was conducted to identify potential causal associations.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Main outcomes were International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision–diagnosed OUD or International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision–diagnosed OUD (Million Veteran Program), and DSM-IV–defined opioid dependence (Yale-Penn and Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment).
Results
A total of 114 759 individuals (101 016 men [88%]; mean [SD] age, 60.1 [12.8] years) were included. In 82 707 European American individuals, a functional coding variant (rs1799971, encoding Asn40Asp) in OPRM1 (μ-opioid receptor gene, the main biological target for opioid drugs; OMIM 600018) reached genome-wide significance (G allele: β = −0.066 [SE = 0.012]; P = 1.51 × 10−8). The finding was replicated in 2 independent samples. Single-nucleotide polymorphism–based heritability of OUD was 11.3% (SE = 1.8%). Opioid use disorder was genetically correlated with 83 traits, including multiple substance use traits, psychiatric illnesses, cognitive performance, and others. Mendelian randomization analysis revealed the following associations with OUD: risk of tobacco smoking, depression, neuroticism, worry neuroticism subcluster, and cognitive performance. No genome-wide significant association was detected for African American individuals or in transpopulation meta-analysis.
Conclusions and Relevance
This genome-wide meta-analysis identified a significant association of OUD with an OPRM1 variant, which was replicated in 2 independent samples. Post–genome-wide association study analysis revealed associated pleiotropic characteristics. Recruitment of additional individuals with OUD for future studies—especially those of non-European ancestry—is a crucial next step in identifying additional significant risk loci.
This genome-wide association study examines genetic risk variants for opioid use disorder and determines genetic correlations and causal association with opioid use disorder and other traits.
Introduction
Opioid abuse, addiction, and overdose are at epidemic levels in the United States. Opioids are the leading cause of overdose deaths, and their use has increased dramatically in recent decades.1 A multifaceted approach is needed to address the opioid crisis, including improving our understanding of the biological mechanisms of opioid addiction. Opioids exert their biological effects primarily by binding (mainly in brain and peripheral nervous tissues) to the opioid receptors μ, encoded by OPRM1 (OMIM 600018); κ, encoded by OPRK1 (OMIM 165196); and δ, encoded by OPRD1 (OMIM 165195).2 Numerous candidate-gene association studies of these genes (especially OPRM1) and those encoding-related proteins have been conducted in the past 2 decades,3,4 but prior studies have failed to consistently demonstrate an association (eg, studies on OPRM1*rs1799971).5
rs1799971 (A118G, encoding Asn40Asp),5,6 a functional variant, is one of the most studied candidate variants for substance use traits. Several kinds of evidence support possible functional effects of this single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP): rs1799971 reportedly alters β-endorphin binding and activity,6 may be associated with cortisol response to naloxone blockade,7 may be associated with neurobehavioral functions in a mouse model,8,9 and modulates synaptic function in human-induced pluripotent stem cell lines; alternate-allele protein products show differential N-linked glycosylation.10
Several genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of DSM-IV–defined opioid dependence (OD) yielded significant findings11,12,13,14; 1 GWAS included internal replication13 but none reported clear external replication, probably owing to the limited sample sizes available (the largest study so far included 2015 individuals with OD13). The risk variants identified map to APBB2 (OMIM 602710), PARVA (OMIM 608120), KCNC1 (OMIM 176258), and KCNC2 (OMIM 176256)11 in African American (AA) samples, and CNIH3 (GenBank 149111)12 and RGMA (OMIM 607362)13 in European-ancestry samples. There have also been GWAS of related traits including therapeutic opioid dose (that identified a genome-wide significant [GWS] variant upstream of the OPRM1 locus in AA individuals)15 and opioid overdose (which identified 1 variant near MCOLN1 [OMIM 605248] in AA individuals).16 Of these, only the study on opioid dosing15 included external validation. To our knowledge, no GWAS yet has been sufficiently powered to estimate the SNP-based heritability (h2) of OD.
We conducted GWAS on individuals with International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9)–diagnosed opioid use disorder (OUD) or International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision (ICD-10)–diagnosed OUD and opioid-exposed controls in 79 729 European American (EA) individuals and 30 061 AA individuals from the Million Veteran Program (MVP). Then we meta-analyzed for OUD combining data from the MVP, Yale-Penn, and the Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment (SAGE) samples.17 The latter 2 EA samples were included in a previous publication,13 but were reanalyzed here as a binary diagnostic trait rather than a criterion count for better congruence with available MVP information. rs1799971 was the only variant that was GWS (P = 1.51 × 10−8) in the meta-analysis of EA individuals. We then replicated the result in 2 independent samples.
Methods
MVP Data Sets
The MVP is a cross-sectional mega-biobank supported by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). Enrollment in MVP began January 10, 2011, and is ongoing. Phenotypic data were collected using the VA electronic health record and blood samples were obtained for genetic studies.18 Two phases of genotypic data have been released according to their genotyping epochs and were included in this study. Million Veteran Program phase 1 contains 353 948 individuals, of whom 209 020 were defined previously as unrelated EA individuals, and 57 340 unrelated AA individuals.19 Million Veteran Program phase 2 contains 108 416 individuals. We used the same process as in MVP phase 1 for quality control and to define EA individuals and AA individuals (eAppendix in the Supplement)19; this process yielded 67 268 unrelated EA individuals and 18 214 unrelated AA individuals. The Central VA Institutional Review Board and site-specific institutional review boards approved the MVP study. All relevant ethical regulations for work with human participants were followed in the conduct of the study, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Cases were participants with at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes for OUD (eTable 1 in the Supplement) between 1999 and 2018. In MVP phase 1, there were 6367 EA individuals with OUD (3.0% prevalence, among unrelated participants) and 3151 AA individuals with OUD (5.5% prevalence), and in MVP phase 2, there were 2162 EA individuals with OUD (3.2% prevalence) and 881 AA individuals with OUD (4.8% prevalence). Stringent criteria were applied to define incident opioid-exposed controls.20 In short, we started with all MVP participants and excluded those with exposure to a prescription opioid for less than 7 consecutive days, with VA follow-up less than 6 months after baseline, with cancer diagnosed before or after baseline, with a baseline opioid dosage of more than 90 mg morphine equivalent daily dose, or with OUD diagnosis or OUD treatment at baseline. For the remaining participants, a latent growth mixture model was applied to identify the major classes of opioid dose (measured by morphine equivalent daily dose) trajectories that assigned each individual to the trajectory with the highest probability of membership. Four resultant morphine equivalent daily dose trajectories were designated as low, moderate, escalating, and rapidly escalating. To minimize the potential rate of false negatives in the control group (eTable 2 in the Supplement), participants assigned to the low-dose trajectory without an incident OUD diagnosis during follow-up were defined as controls, yielding 55 429 EA controls and 20 254 AA controls in MVP phase 1 and 15 771 EA controls and 5775 AA controls in MVP phase 2.
Genotyping in MVP was performed using a customized Affymetrix Biobank Array. Imputation and quality control metrics for MVP phase 1 were as described previously.19 Similar processes were used for MVP phase 2 (eAppendix in the Supplement). Genome-wide association study was then performed on the MVP data sets. We used logistic regression implemented in PLINK, version 1.90b4.421 (https://www.cog-genomics.org/plink2) for the OUD GWAS, correcting for age, sex, and the first 10 principal components.
Yale-Penn and SAGE Data Sets
Genome-wide association study for DSM-IV OD criterion counts in EA individuals were performed previously, including 3 phases of Yale-Penn data, and the SAGE cohort (The Database of Genotypes and Phenotypes [dbGaP] study id phs000092.v1.p1).13 We reanalyzed these data using OUD diagnosis. For AA individuals, the first 2 phases of Yale-Penn data were included (because Yale-Penn 3 has only 7 cases and SAGE has only 105 cases and 158 exposed controls, they were not included) (eAppendix in the Supplement).
Meta-analyses
Sample-size–weighted meta-analyses were performed using METAL considering the differences of race/ethnicity, phenotype distribution, association model (linear vs linear mixed), or other sample characteristics.22 Given the unbalanced ratios of cases to controls in MVP samples, effective sample sizes were calculated as neffective = 4/[(1/ncase) + (1/ncontrol)].
The calculated effective sample sizes in MVP were used in meta-analyses and all downstream analyses. Only variants present at least in MVP phase 1, which is the largest sample (approximately 75% of the total EA individuals and approximately 78% of the total AA individuals), and with heterogeneity test P > 5 × 10−8 were retained, leaving 6.91 million variants for AA individuals, 5.07 million variants for EA individuals, and 9.42 million variants for transpopulation meta-analyses.
Replication in Independent EA Samples
We genotyped 4817 recently added Yale-Penn participants who were not included in any prior analysis. We used the Illumina Multi-Ethnic Genotyping Array (Illumina Inc), which includes approximately 1.7 million SNPs. Individuals with mismatched genotypic and phenotypic sex were removed, as were those with excessive heterozygosity. Duplicate individuals with respect to the Yale-Penn discovery samples were removed. The remaining individuals were classified into population groups as for MVP. Among the 2041 genetically classified EA individuals, 508 received a diagnosis of DSM-IV OD, and 206 were opioid-exposed controls. GEMMA (Genome-wide Efficient Mixed-Model Analysis)23 was used for an association test only for rs1799971 (ie, no other markers were evaluated) and corrected for age, sex, and the first 10 principal components.
In the UK Biobank (UKB), we looked up the association between rs1799971 (only this marker, as for the other replication sample) and buprenorphine treatment (mostly used to treat OUD; treatment or medication code: 20003_1140871732). We examined GWAS summary data released by the Neale lab (information available at http://www.nealelab.is/uk-biobank) for 240 cases and 360 901 controls differentiated based on buprenorphine treatment.
SNP-Based h2
Linkage Disequilibrium Score Regression (LDSC)24 was used to estimate the SNP-based h2 using 1000 Genomes Project Europeans or Africans25 as the linkage disequilibrium (LD) reference panel. The major histocompatibility complex region (chr6: 26-34 Mb [mega base pairs]) was excluded. Effective sample size was used in LDSC.
Genetic Correlation
We estimated the genetic correlation (rg) between OUD and 715 publicly available traits from LD Hub26 or other resources using LDSC (eTable 3 in the Supplement).27 Among the tested traits, 232 were published previously (including recent non–LD Hub studies) and 483 from the UKB were unpublished but integrated in LD Hub. Bonferroni correction was applied and correlation was considered significant at a P value threshold of 6.99 × 10−5.
Mendelian Randomization
We used mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to investigate whether exposures (based on 18 published traits that were significantly correlated with OUD [rg: P < 6.99 × 10−5]) have a potential causal association with the liability to OUD (unidirectional). After variant harmonization and filtering, 12 exposures were analyzed. Weighted median,28 inverse-variance weighted (random-effects model),29 and MR-Egger30 were used for MR inference. Evidence of pleiotropic effects was examined by the MR-Egger intercept test30 (eAppendix in the Supplement).
Results
Association Results for OUD in EA Individuals
In this meta-analysis of 8529 individuals with OUD and 71 200 control individuals within the MVP (totaling 79 729 individuals; Table), no variant reached GWS (P < 5 × 10−8; eFigure 1 in the Supplement). The variant with the smallest P value was rs1799971 in OPRM1 (P = 5.90 × 10−8; neffective = 30 443; the minor G allele is protective with a β = −0.142 [SE = 0.026]).
Table. Demographic Characteristics: Discovery Sample.
| Sample | European American individuals | African American individuals | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of cases | No. of controls | Age, mean (SD), y | Female, No. (%) | No. of cases | No. of controls | Age, mean (SD), y | Female, No. (%) | |
| MVP phase 1 | 6367 | 55 429 | 61.2 (13.0) | 5775 (9.3) | 3151 | 20 254 | 57.0 (11.1) | 3400 (14.5) |
| MVP phase 2 | 2162 | 15 771 | 61.2 (13.7) | 1739 (9.7) | 881 | 5775 | 58.0 (11.2) | 1029 (15.5) |
| Subtotal | 8529 | 71 200 | 61.2 (13.2) | 7514 (9.4) | 4032 | 26 029 | 57.2 (11.1) | 4429 (14.7) |
| Yale-Penn 1 | 1043 | 294 | 36.9 (10.3) | 542 (40.5) | 831 | 573 | 42.2 (7.9) | 533 (38.0) |
| Yale-Penn 2 | 724 | 243 | 36.4 (11.4) | 319 (33.0) | 349 | 274 | 42.3 (10.2) | 170 (27.3) |
| Yale-Penn 3 | 54 | 44 | 33.6 (11.6) | 41 (41.8) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| SAGE | 194 | 382 | 35.8 (9.1) | 195 (33.9) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Subtotal | 2015 | 963 | 36.4 (10.5) | 1097 (36.8) | 1180 | 847 | 42.3 (8.6) | 703 (34.7) |
| Total | 10 544 | 72 163 | NA | NA | 5212 | 26 876 | NA | NA |
Abbreviations: MVP, Million Veteran Program; SAGE, Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment.
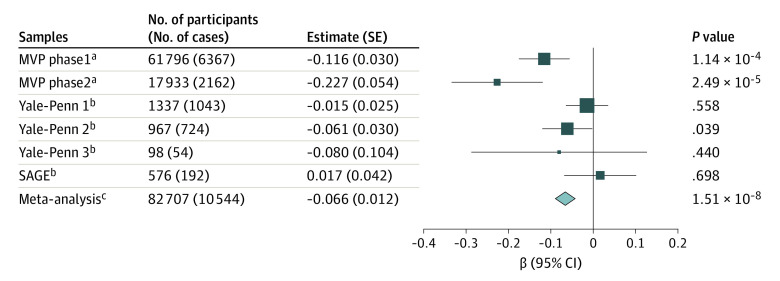
We then meta-analyzed the MVP samples with Yale-Penn (3 tranches) and SAGE samples, bringing the total sample size to 82 707 (10 544 cases and 72 163 opioid-exposed controls; Table). This represents a 23.6% increase in the number of cases. From the meta-analysis, the SNP-based h2 was 0.113 (SE = 0.018), estimated by LDSC. The association of rs1799971 with OUD was GWS (β = −0.066 [SE = 0.012]; P = 1.51 × 10−8; neffective = 33 421) (Figure 1; eFigures 2 and 3 in the Supplement). The LD structure around rs1799971 is complex31 (eFigure 3 in the Supplement). The associations were all in the same direction except for the SAGE sample, which might be owing to its limited sample size. There were no significant results from gene-based association and gene-set analyses.
Figure 1. Associations Between rs1799971*G and Opioid Use Disorder in European American Individuals.
The sizes of the data markers are related to the SE of the estimate. MVP indicates Million Veteran Program; OR, odds ratio; and SAGE, Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment.
aLogistic regression was applied based on unrelated case and control samples in MVP; log (OR) is presented.
bA linear mixed model was applied on complex family-based samples; β is presented.
cEffective sample size weighted meta-analysis was applied; β is presented.
Replication in Independent EA Samples
In total, we analyzed 714 EA individuals (508 individuals with OD and 206 opioid-exposed controls) from the new Yale-Penn samples, and rs1799971*G was associated with reduced OD risk (ie, in the same direction as the discovery meta-analysis; β = −0.074 [SE = 0.038]; P = .049). In the UKB, rs1799971*G was negatively associated with buprenorphine treatment status (240 cases and 360 901 controls; β = −1.90 × 10−4 [SE = 9.13 × 10−5]; P = .04), also consistent with the direction of effect in the discovery sample. A meta-analysis of discovery and replication cohorts for this variant yielded P = 7.81 × 10−10 (β = −0.070 [SE = 0.011]).
Genetic Correlations With Other Traits in EA Individuals
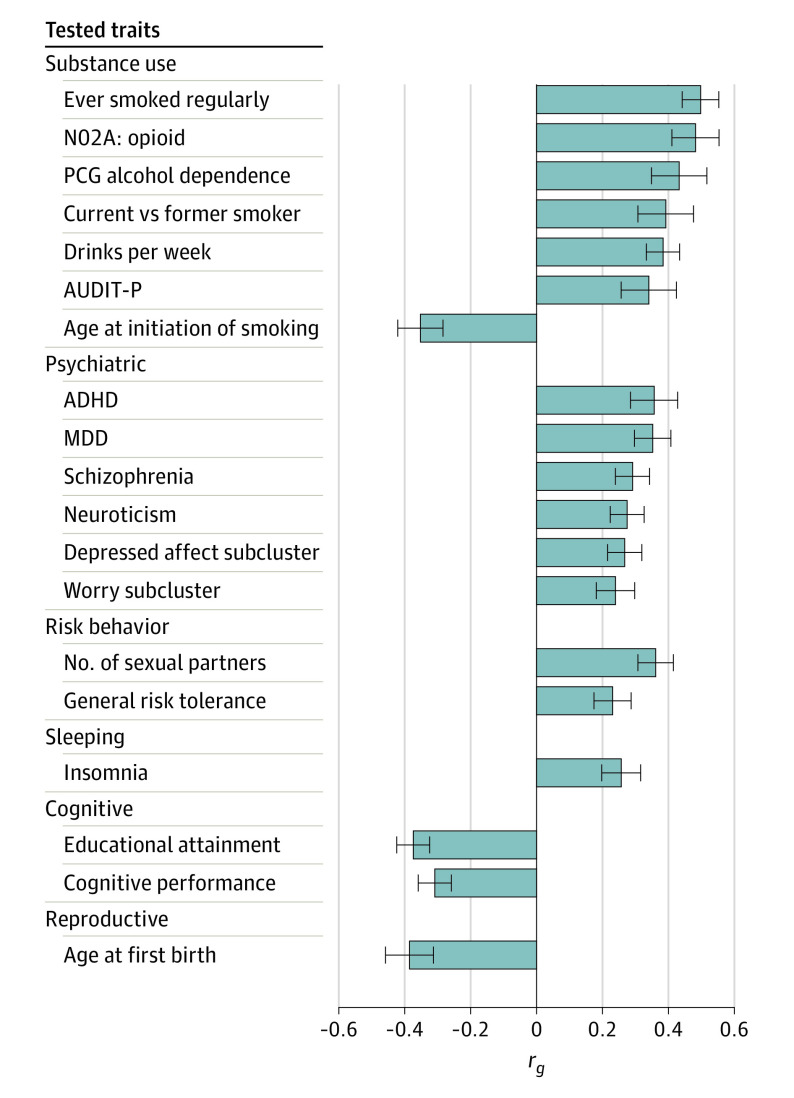
Opioid use disorder was significantly correlated with 83 of the 715 traits tested (eTable 3 in the Supplement). Figure 2 depicts 18 correlated traits from the published literature (eAppendix in the Supplement). Among the correlated substance use–related traits, ever smoked regularly showed the highest correlation with OUD (rg = 0.51 [SE = 0.06]; P = 3.37 × 10−19), followed by opioid medication use in UKB (rg = 0.48 [SE = 0.07]; P = 1.61 × 10−11). Both alcohol dependence and alcohol use quantity (measured by drinks per week) showed high genetic correlations with OUD. Unable to stop smoking (current vs former smoker), and earlier age at smoking initiation were also correlated with OUD. However, correlations with AUDIT-C score (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test–Consumption), total AUDIT score, cigarettes per day, and lifetime cannabis use were not significant after Bonferroni correction. Several psychiatric traits were correlated with OUD, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (rg = 0.36 [SE = 0.07]; P = 6.78 × 10−7), major depressive disorder (rg = 0.35 [SE = 0.06]; P = 1.62 × 10−10), schizophrenia (rg = 0.29 [SE = 0.05]; P = 1.93 × 10−8), neuroticism (rg = 0.27 [SE = 0.05]; P = 8.65 × 10−8), and neuroticism subclusters. Opioid use disorder was positively correlated with risk-taking behavior and insomnia, and negatively correlated with cognitive traits and age of first birth. These findings are consistent with the known adverse medical, psychiatric, and social consequences of OUD.
Figure 2. Genetic Correlations Between Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) and Published Traits.
Listed are the 18 published traits significantly correlated with OUD. ADHD indicates attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; AUDIT-P, Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test–Problems; Depressed affect subcluster, depressed affect neuroticism subcluster; MDD, major depressive disorder; N02A, opioid, self-reported medication-use of opioid drugs (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical classification code, N02A) in UK Biobank; PGC, Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; rg, genetic correlation; and Worry subcluster, worry neuroticism subcluster.
Mendelian Randomization for EA Individuals
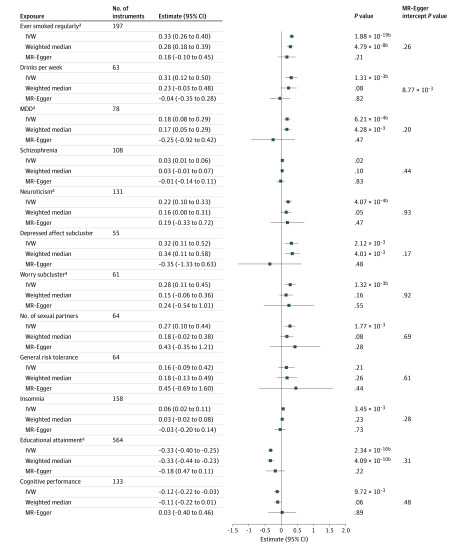
Using MR, we explored possible causal associations of exposures with OUD (Figure 3). Among the 12 tested exposures, 5 supported a possible causal association with liability to OUD by at least 1 method and were without evidence of horizontal pleiotropy (MR-Egger intercept, P > .05): positively with ever smoked regularly, major depressive disorder, neuroticism, and worry neuroticism subcluster, and negatively with educational attainment. There was no significant association between drinks per week and OUD risk by the inverse-variance weighted method, but the estimate could be biased owing to horizontal pleiotropy.
Figure 3. Causal Association With Opioid Use Disorder by Mendelian Randomization (MR).
IVW indicates inverse-variance weighted linear regression; and MDD, major depressive disorder.
aTraits having a causal association with OUD by at least 1 method without evidence of horizontal pleiotropy (MR-Egger intercept P > .05).
bSignificant after multiple testing correction (significance threshold, .05/36 = 1.39 × 10−3).
Association Results for OUD in AA Individuals and Transpopulation Meta-analysis
For AA individuals, 4032 participants with OUD and 26 029 controls within the MVP were meta-analyzed; no variant reached GWS (Table; eFigure 4 in the Supplement). We then meta-analyzed the MVP samples with the Yale-Penn sample (2 tranches), bringing the total sample size to 32 088 (5212 cases and 26 876 opioid-exposed controls); no association was detected (eFigure 5 in the Supplement). There was insufficient power for a robust estimate for SNP-based h2 (0.065 [SE = 0.052]).
Transpopulation meta-analysis combining all data sets was conducted in 114 795 individuals. No significant association was detected (eFigure 6 in the Supplement).
Discussion
Opioid use is at epidemic levels in the United States and is a major cause of death and disability worldwide. Understanding the genetic architecture of OUD might provide clinically useful clues about its biology. However, to our knowledge, only a few risk variants have been identified by GWAS so far, and none has had clear external replication. Several factors contribute to this situation: (1) OUD is a complex psychiatric disease with relatively low heritability, and there is no single variant with a large effect size that can be detected in small cohorts (eg, contrary to alcohol dependence32 with ADH1B (OMIM 103720), and nicotine dependence with the chromosome 15 nicotine receptor cluster33); (2) previous OUD GWAS were relatively small compared with those for legal substance use disorders (eg, the number of alcohol use disorder cases reached 57 564 in a large meta-analysis34); and (3) in published work relevant to opioid use, there was considerable phenotypic heterogeneity across samples. The ascertainment of OUD cases (eg, ICD-diagnosed OUD in the electronic health record, DSM-IV–assessed OD, patients receiving opioid substitution therapy, and daily injectors of illicit opioids) and controls (eg, opioid-exposed individuals or random population with unknown opioid exposure status) differ by study. One way to reach a better understanding of OUD genetics is to increase the sample size in a homogeneous cohort.
For EA individuals, we conducted a GWAS of OUD in a large cohort, the MVP, comprising 8529 cases and 71 200 opioid-exposed controls. Most previously reported variants associated with a wide range of opioid-related traits were not significant in MVP. For some, this reflects a lack of marker information or LD proxies in the MVP; some associations were previously reported in African ancestry populations only11; others were reported in EA individuals, but relevant variants are missing in the MVP data (eg, rs12442183 near RGMA reported by Cheng et al13 was filtered by a low genotype call rate in imputation). No variant reached GWS in this largest-ever cohort individually; OPRM1*rs1799971 was nominally significantly associated with OUD (P = 5.90 × 10−8). We meta-analyzed MVP samples with Yale-Penn and SAGE samples (reanalyzed to match the available phenotype from the MVP more closely), increasing the total sample size to 82 707 (10 544 cases and 72 163 opioid-exposed controls). By adding 4 samples from Yale-Penn and SAGE, rs1799971 reached GWS. The final meta-analyzed P value for this marker is 1.51 × 10−8 (excluding independent replications). rs1799971 was genotyped directly (not imputed) in all samples, discovery, and replication. No association was detected in AA individuals or in transpopulation meta-analyses.
rs1799971 (A118G) maps to exon 1 of the μ-opioid receptor (OPRM1) gene, causing an amino acid change (Asn40Asp). Extensive candidate studies of this variant with a wide range of addictive and other behavioral traits have been conducted over 2 decades.5,35,36 Associations between rs1799971 and opioid-related traits have been inconsistent.5 We conducted hypothesis-free, genome-wide analyses for OUD and detected association at rs1799971 by almost quintupling the number of cases compared with any previous study.5,13 Our increment in exposed controls, often even more limiting than affected individuals with OUD in previous studies, is even greater. Because many individuals exposed to opioids become dependent, an unassessed control group is not an ideal alternative to an opioid-exposed control group even if greater numbers of participants can be achieved, because the former group is more correctly considered “diagnosis unknown,” including many individuals genetically predisposed to OUD who would express that phenotype had they been exposed. We sought replication in 2 independent EA samples. One included newly genotyped individuals in the Yale-Penn sample, and the other was a proxy-phenotype buprenorphine treatment sample from the UKB. The association was replicated in both of these samples.
Multiple substance use–related traits including smoking, alcohol, and opioid use and psychiatric traits were among the top correlates. Several smoking traits were positively correlated with OUD, consistent with the strong correlation between nicotine use and OUD.37,38 Mendelian randomization analysis provided evidence (weak, since it was not supported by all 3 tested methods) that the genetic liability to substance use–related traits has a potential causal association with susceptibility to OUD. Medical opioid use was correlated with OUD, as expected. Alcohol dependence and quantity of alcohol consumed were also genetically correlated with OUD. Thus, it may be feasible for prevention or treatment efforts directed at legal substance use to reduce the burden of consequent OD. Psychiatric traits including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and neuroticism are genetically correlated with OUD, consistent with phenotypic evidence.39,40 Weak evidence from MR analyses also indicated possible causal association with OUD risk of major depressive disorder and neuroticism.
Limitations
This study has some limitations. The sample size, although a major improvement from prior studies, is still not as large as what can be obtained for legal substance use–related traits, and this limited power to detect more GWS signals and to obtain insight into OUD biological mechanisms. Legal substance use traits are more common, and data pertinent to these traits are collected more commonly than for illegal traits in biobanks and electronic health records. Second, the phenotypes in the samples we studied were not identical. The MVP used ICD-9– and ICD-10–diagnosed OUD. There may be false negatives in a sample such as the MVP, owing to stigma and OUD diagnoses not recorded by treatment teams concentrating mostly on medical illness, but few false positives. Third, the replication samples are small (508 individuals with OD in the new Yale-Penn sample and 240 individuals receiving buprenorphine treatment in the UKB), and the associations were only nominally significant; only a single variant was tested in the replication samples. The phenotype in the UKB is a proxy phenotype—buprenorphine treatment. Buprenorphine is a first-line drug for OUD treatment, but it could have been used for other purposes in the UKB population, including pain management; however, if this is true to any considerable extent, it should reduce our power to detect an association, rather than lead to a false-positive finding. Fourth, there has been a lack of recruitment for non-European populations globally (eg, only a few GWASs have been conducted in AA individuals11,15 in smaller cohorts). Meta-analysis of AA individuals combining MVP and Yale-Penn data was underpowered to detect significant signals.
Conclusions
We report here the largest GWAS and the largest meta-analysis for OUD, to our knowledge. This finding may not have direct implications for personalized medicine because the relevant gene is already the main physiological target of all opioids, illegal and therapeutic, which provides, at least, a “proof of principle” of relevance of the finding. Opioid use disorder was genetically correlated with substance use traits, other psychiatric traits, insomnia, and cognitive performance. Among these, ever smoking regularly, major depressive disorder, neuroticism, and cognitive performance were associated with OUD, which provides clues for future prevention efforts. Recruitment of additional individuals with OUD—especially those of non-European ancestry—is a crucial next step.
eAppendix. Methods
eReferences
eFigure 1. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD Meta-Analysis in MVP EAs (Without Yale-Penn or SAGE)
eFigure 2. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD in the Meta-Analysis of EAs Including All Cohorts
eFigure 3. Regional Manhattan Plot for the OPRM1 Region Including rs1799971, and LD Matrix in 1000 Genome European Reference
eFigure 4. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD Meta-Analysis in MVP AAs (Without Yale-Penn)
eFigure 5. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD in the Meta-Analysis of AAs Including All Cohorts
eFigure 6. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD in the Trans-Population Meta-Analysis
eTable 1. ICD-9/10 Codes for OUD in MVP
eTable 2. OUD Cases by Opioid Use Trajectory in MVP
eTable 3. Genetic Correlations Between OUD and 715 Traits Using LDSC
References
- 1.Jalal H, Buchanich JM, Roberts MS, Balmert LC, Zhang K, Burke DS. Changing dynamics of the drug overdose epidemic in the United States from 1979 through 2016. Science. 2018;361(6408):eaau1184. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Darcq E, Kieffer BL. Opioid receptors: drivers to addiction? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19(8):499-514. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0028-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Reed B, Butelman ER, Yuferov V, Randesi M, Kreek MJ. Genetics of opiate addiction. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014;16(11):504. doi: 10.1007/s11920-014-0504-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mistry CJ, Bawor M, Desai D, Marsh DC, Samaan Z. Genetics of opioid dependence: a review of the genetic contribution to opioid dependence. Curr Psychiatry Rev. 2014;10(2):156-167. doi: 10.2174/1573400510666140320000928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schwantes-An TH, Zhang J, Chen LS, et al. Association of the OPRM1 variant rs1799971 (A118G) with non-specific liability to substance dependence in a collaborative de novo meta-analysis of European-ancestry cohorts. Behav Genet. 2016;46(2):151-169. doi: 10.1007/s10519-015-9737-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bond C, LaForge KS, Tian M, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human mu opioid receptor gene alters β-endorphin binding and activity: possible implications for opiate addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(16):9608-9613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chong RY, Oswald L, Yang X, Uhart M, Lin PI, Wand GS. The mu-opioid receptor polymorphism A118G predicts cortisol responses to naloxone and stress. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(1):204-211. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300856 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang Y, Picetti R, Butelman ER, Ho A, Blendy JA, Kreek MJ. Mouse model of the OPRM1 (A118G) polymorphism: differential heroin self-administration behavior compared with wild-type mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(5):1091-1100. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.286 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Robinson JE, Vardy E, DiBerto JF, et al. Receptor reserve moderates mesolimbic responses to opioids in a humanized mouse model of the OPRM1 A118G polymorphism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(11):2614-2622. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Halikere A, Popova D, Scarnati MS, et al. Addiction associated N40D mu-opioid receptor variant modulates synaptic function in human neurons. Mol Psychiatry. Published online September 3, 2019. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0507-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, et al. Genome-wide association study of opioid dependence: multiple associations mapped to calcium and potassium pathways. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;76(1):66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.08.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nelson EC, Agrawal A, Heath AC, et al. Evidence of CNIH3 involvement in opioid dependence. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(5):608-614. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cheng Z, Zhou H, Sherva R, Farrer LA, Kranzler HR, Gelernter J. Genome-wide association study identifies a regulatory variant of RGMA associated with opioid dependence in European Americans. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84(10):762-770. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.12.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Crist RC, Reiner BC, Berrettini WH. A review of opioid addiction genetics. Curr Opin Psychol. 2019;27:31-35. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2018.07.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smith AH, Jensen KP, Li J, et al. Genome-wide association study of therapeutic opioid dosing identifies a novel locus upstream of OPRM1. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(3):346-352. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cheng Z, Yang BZ, Zhou H, Nunez Y, Kranzler HR, Gelernter J. Genome-wide scan identifies opioid overdose risk locus close to MCOLN1. Addict Biol. 2020;25(2):e12811. doi: 10.1111/adb.12811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Edenberg HJ. The collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism: an update. Alcohol Res Health. 2002;26(3):214-218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gaziano JM, Concato J, Brophy M, et al. Million Veteran Program: a mega-biobank to study genetic influences on health and disease. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;70:214-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.09.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kranzler HR, Zhou H, Kember RL, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and use disorder in 274,424 individuals from multiple populations. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1499. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09480-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rentsch CT, Edelman EJ, Justice AC, et al. ; VACS Project Team . Patterns and correlates of prescription opioid receipt among US Veterans: a national, 18-year observational cohort study. AIDS Behav. 2019;23(12):3340-3349. doi: 10.1007/s10461-019-02608-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chang CC, Chow CC, Tellier LC, Vattikuti S, Purcell SM, Lee JJ. Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience. 2015;4:7. doi: 10.1186/s13742-015-0047-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Willer CJ, Li Y, Abecasis GR. METAL: fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(17):2190-2191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhou X, Stephens M. Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat Genet. 2012;44(7):821-824. doi: 10.1038/ng.2310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bulik-Sullivan BK, Loh PR, Finucane HK, et al. ; Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium . LD score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2015;47(3):291-295. doi: 10.1038/ng.3211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, et al. ; 1000 Genomes Project Consortium . A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526(7571):68-74. doi: 10.1038/nature15393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zheng J, Erzurumluoglu AM, Elsworth BL, et al. ; Early Genetics and Lifecourse Epidemiology (EAGLE) Eczema Consortium . LD Hub: a centralized database and web interface to perform LD score regression that maximizes the potential of summary level GWAS data for SNP heritability and genetic correlation analysis. Bioinformatics. 2017;33(2):272-279. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bulik-Sullivan B, Finucane HK, Anttila V, et al. ; ReproGen Consortium; Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Genetic Consortium for Anorexia Nervosa of the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 3 . An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat Genet. 2015;47(11):1236-1241. doi: 10.1038/ng.3406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304-314. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21965 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, Davey Smith G, Sheehan N, Thompson J. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat Med. 2017;36(11):1783-1802. doi: 10.1002/sim.7221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyv080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Levran O, Awolesi O, Linzy S, Adelson M, Kreek MJ. Haplotype block structure of the genomic region of the mu opioid receptor gene. J Hum Genet. 2011;56(2):147-155. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2010.150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence: significant findings in African- and European-Americans including novel risk loci. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19(1):41-49. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tobacco and Genetics Consortium Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat Genet. 2010;42(5):441-447. doi: 10.1038/ng.571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhou H, Sealock JM, Sanchez-Roige S, et al. Meta-analysis of problematic alcohol use in 435,563 individuals identifies 29 risk variants and yields biological insights, pervasive pleiotropy and evidence of causality. Preprint. Posted online August 16, 2019. bioRxiv 738088. doi: 10.1101/738088 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gelernter J, Kranzler H, Cubells J. Genetics of two μ opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) exon I polymorphisms: population studies, and allele frequencies in alcohol- and drug-dependent subjects. Mol Psychiatry. 1999;4(5):476-483. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ray R, Ruparel K, Newberg A, et al. Human mu opioid receptor (OPRM1 A118G) polymorphism is associated with brain mu-opioid receptor binding potential in smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(22):9268-9273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018699108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Clemmey P, Brooner R, Chutuape MA, Kidorf M, Stitzer M. Smoking habits and attitudes in a methadone maintenance treatment population. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1997;44(2-3):123-132. doi: 10.1016/S0376-8716(96)01331-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Richter KP, Gibson CA, Ahluwalia JS, Schmelzle KH. Tobacco use and quit attempts among methadone maintenance clients. Am J Public Health. 2001;91(2):296-299. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.91.2.296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Zhang L, Unützer J, Wells KB. Association between mental health disorders, problem drug use, and regular prescription opioid use. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(19):2087-2093. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.19.2087 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Seal KH, Shi Y, Cohen G, et al. Association of mental health disorders with prescription opioids and high-risk opioid use in US veterans of Iraq and Afghanistan. JAMA. 2012;307(9):940-947. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eAppendix. Methods
eReferences
eFigure 1. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD Meta-Analysis in MVP EAs (Without Yale-Penn or SAGE)
eFigure 2. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD in the Meta-Analysis of EAs Including All Cohorts
eFigure 3. Regional Manhattan Plot for the OPRM1 Region Including rs1799971, and LD Matrix in 1000 Genome European Reference
eFigure 4. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD Meta-Analysis in MVP AAs (Without Yale-Penn)
eFigure 5. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD in the Meta-Analysis of AAs Including All Cohorts
eFigure 6. Manhattan and QQ Plots for OUD in the Trans-Population Meta-Analysis
eTable 1. ICD-9/10 Codes for OUD in MVP
eTable 2. OUD Cases by Opioid Use Trajectory in MVP
eTable 3. Genetic Correlations Between OUD and 715 Traits Using LDSC