Abstract
Stem cell-based regenerative medicine is a promising approach for tissue reconstruction. However, a large number of cells are needed in a typical clinical study, where conventional monolayer cultures might pose a limitation for scale-up. The purpose of this review was to systematically assess the application of microcarriers in Mesenchymal Stem Cell cultures. A comprehensive search was conducted in Medline via Ebscohost, Pubmed, and Scopus, and relevant studies published between 2015 and 2019 were selected. The literature search identified 53 related studies, but only 14 articles met the inclusion criteria. These include 7 utilised commercially available microcarriers, while the rest were formulated based on different surface characteristics, all of which are discussed in this review. Current applications of microcarriers were focused on MSC expansion and induction of MSCs into different lineages. These studies demonstrated that MSCs could proliferate in a microcarrier culture system in-fold compared to monolayer cultures, and the culture system could simulate a three-dimensional environment which induces cell differentiation. However, detailed studies are still required before this system were to be adapted into the scale of GMP manufacturing.
Introduction
Mesenchymal stem cells
Adult mesenchymal stem cells are becoming increasingly popular as a potential cell source in regenerative medicine nowadays. This multipotent CD 34− fibroblast-like stem cell has the ability to differentiate into specialized cells such as adipocytes, osteocytes, chondrocytes, and myocytes [1–3]. It can be isolated from various adult tissue sources such as blood or adipose tissue, dermis, muscle, dental pulp, and Wharton’s jelly [4–7]. In contrast to embryonic pluripotent stem cells, MSC is devoid of ethical, histocompatibility, and teratomas-formation issues. In addition to that, several studies successfully demonstrated the efficacy of MSCs in regenerating new tissues and repair defects [8–11].
Stem cell-based regenerative medicine is an emerging approach for tissue reconstruction. Allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant has the potential to play a significant role in the treatment of autoimmune diseases or hematopoietic disorders. However, the applications of therapy are limited due to morbidity and mortality of graft versus host disease (GVHD). Studies have reported that mesenchymal stem cells could reduce inflammatory cytokines through interplay with several subsets of immune cells; thus the immunoregulatory capacity of MSCs makes them of great interest in clinical studies involving GHVD [12–14].
Anti-inflammatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells
Aside from its regenerative capabilities, MSCs are known for its immunosuppression or anti-inflammatory ability in cell transplantations. The role of MSCs as an anti-inflammatory agent has become more evident with the elucidation of the mechanism of inflammation, which includes the release of intracellular cytokines such as interleukin-1α from injured cells or activation of macrophages by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) interaction with receptors to generate proinflammatory cytokines [15–17].
According to the results reported by [18], administration of MSCs into a mouse model successfully inhibited bleomycin (BLM)-induced elevation of TNF-α, IL-1α, and IL1RN mRNA in the lungs, which protected lung tissues from BLM-induced injury by blocking TNF-α and IL-1α, the main proinflammatory cytokines in the lungs. A similar anti-inflammatory property was reported by Oh et al., where the suppression of IL-2 and IFN-γ, and the reduced infiltration of CD4+ cells by MSCs, showed a reduction in corneal inflammation and neovascularisation [19]. In short, the anti-inflammatory effects of MSCs have been reported in various events such as lung injury, myocardial infarction, corneal injury, sepsis, and diabetic wound healing [20–23].
Cytokines in inflammatory events
Inflammatory mechanisms in GVHD were generally associated with activation of immune cells (T cells, B cells, and macrophages) in the presence of antigen-presenting cells (APC). These immune cells will release substances called cytokines which regulate or facilitate immune responses. For instance, the IL-1 pathway plays a crucial role in generating sterile inflammation, which is similar in effect as that produced by tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in lung injuries [24]. In addition, the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 in serum also contributed to sepsis in a mouse model [25]. In addition to that, the secretion of TNF-α and IL-1α by macrophages also induced peritonitis in a mouse model [26].
TNF-α is a prototypical member of a large superfamily known as TNF/TNFR superfamily, which comprises more than 40 family members. The TNF-α gene is a single-copy gene on human chromosome 6 (murine chromosome 17), which codes for a 27-kDa (233 amino acid) protein that is proteolytically cleaved into a 17-kDa (157 amino acid) molecule [27]. TNF-α is secreted from activated macrophages by induction of Toll-like receptors and other factors, and generally after priming with interferon gamma (IFN-γ). It is rapidly released after trauma, infection, or exposure to bacterial-LPS and was shown to be one of the early abundant mediators in inflamed tissues. Apart from that, the role of TNF-α during inflammation is mostly associated with coordination of the pro-inflammatory cytokine cascade. Therefore, TNF-α is considered as a master regulator of pro-inflammatory cytokines during inflammation [28].
Mesenchymal stem cells expansion
Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells require billions of cells [29] and two-dimensional platforms, which might pose a challenge in scaling-up. In a clinical study of acute ischemic stroke, it was suggested that the number of MSCs required for administration to a single patient ranged from 1–8 × 106 MSCs per kg of body mass, depending on the indication [30]. Innovation of cell culture products aim to address surface limitations imposed by monolayer culture flasks. Multi-layered flasks which could accommodate up to 40 layers of culture chambers is a good example of such innovation. However, difficulty in observing the in-cultured cells could be a potential downside of this innovation. In order to achieve a scalable undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cell number for cell transplantation and tissue engineering applications, 3-dimension culture techniques seem to be a more reliable approach compared to 2D cultures. Mesenchymal stem cell expansion in bioreactors potentially provide ease of scalability, flexible modes of operation, better process monitoring, and control compatibility. For example, Zhou et al. (2013) developed a novel strategy for 3D expansion of bone marrow MSCs, which produced a 10.4 ± 0.8-fold increase compared to 2D cultures on day 5.
3-D cell culture
Various tissue-engineering studies utilising a 3D scaffold system have shown their efficacy in in vitro culture of MSCs. Three-dimensional culture conditions simulates environment of cells in vivo, therefore providing a suitable condition that enhances cellular activities that are not observed in normal monolayer cultures [31].
While 3D scaffold systems propose unique attractive advantages, these also brought about significant challenges for MSC culture including: (i) the use of undefined components from human or animal tissue, which may result in batch-to-batch variation and poses risks for pathogen and immunogen transfer [32, 33], and thus an obstacle for good manufacturing practice (GMP) in cell production [34]; (ii) substantial cell aggregation that could possibly lead to MSC differentiation or senescence [35]; (iv) limited cell expansion rates and yield per volume [36]; and (v) unpredictable consequences of long-term serial expansion.
One way to address a few of the abovementioned challenges is to adapt the use of microcarriers. These micron-sized spherical particles were initially used for the growth of adherent cells for viruses and production of vaccines [37–39]. Over the decades, properties of microcarriers underwent various modification and innovation to meet the need of different cell types. To date, there are numerous manufacturers and multiple microcarrier varieties are commercially available.
Microcarrier in 3-D culture
Microcarriers provide surface matrices that enable attachment of adherent cells to form cell-microcarrier complexes suspended in growth medium [40]. The fundamental structure of microcarriers are tiny beads (size ranging from 100–300 microns) that are able to maintain suspension during stirring. A number of microcarriers have been synthesized and made commercially available, e.g. glass, diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-dextran, acrylamide, polystyrene, collagen, and alginate [41].
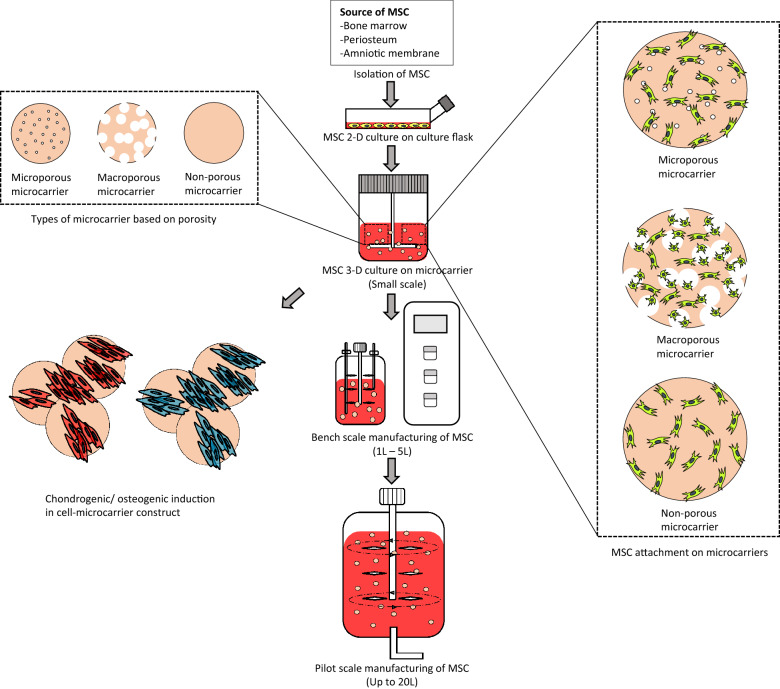
Microcarrier-based cell culture systems are relatively flexible as they promote higher cell yield and can be integrated into existing bioprocess manufacturing systems such as stirred bioreactors and spinner flasks [42]. Such microcarriers have been established for vaccine production or fermentation processes decades ago, however, downstream processes were only focused on metabolites instead of cells. In cell-based therapy, the product of interest are the cells itself, and the main objective of bioprocessing changed from maximising the yield of metabolites to harvesting large quantities of MSCs. Since mesenchymal stem cells required a support surface for cell division, microcarriers are often added into culture media to provide sufficient adherent surface for MSCs in three-dimensional culture. Figure 1 shows the basic approach of up-scaling MSC production in microcarrier-based culture system. Microcarriers provide a large surface area for cell growth during proliferation in suspension cultures, thus allowing scaling-up of cell production in small volumes of medium [43]. In addition to that, the suspended system provides better nutrient intake and gas exchange, and at the same time the adjustable stirring mechanism provides control over shear stress which might facilitate differentiation along certain lineages [44]. This approach could be an ideal model for MSC expansion for its large surface area per unit volume of media compared to T-flask cultures. Hence, the selection of microcarriers are crucial as it would contribute a direct impact on cell expansion.
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustrating the basic flow of up-scaling MSC culture from laboratory scale into manufacturing scale. To date, a “pre-adaptation” period prior microcarrier culture system in MSC is still required, where 2-D culture flasks were used for cell isolation. The up-scale of MSC production can be first optimising culture condition in a small-scale culture system (usually 10–500 mL), followed by up-scaling into bench scale (1–5 L), and finally up to manufacturing scale (up to 20 L). There are 3 major types of microcarrier: non-porous, microporous and macroporous. Cells attach differently based on the porosity of the microcarrier. In general, cells will be attached on the surface of non-porous and microporous microcarrier; while microporous microcarrier provides larger spaces, which allow cells to attach into the inner part of the microcarrier. Due to the similarity towards human body environment, MSCs-microcarriers constructs were found to be able to differentiated into osteo- and chondro-lineage in a specific condition
To date, there are vast reports which suggests extensive choices of suitable microcarriers for mesenchymal stem cell culture. Alginate/PEG-based microcarriers could provide good attachment and proliferation of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells, with well-controlled microcarrier degradation for harvesting [45]. The use of Cytodex type 1 from GE healthcare for porcine bone marrow-derived MSCs could produce cell numbers of approximately 4 × 105 cells/mL [46], while the use of Cytodex type 3 showed similar cell numbers (3.8 × 105 cells/mL) for human placental MSCs [47].
Methods
Search strategy
The review was conducted to systematically assess articles on the application of microcarriers for MSC culture. Three databases were comprehensively used to search for relevant studies; Medline via Ebscohost, Pubmed, and Scopus. The keywords used were the combination of words “Mesenchymal Stem Cell” AND “Microcarriers”.
Selection criteria
The year limit for searches was from 2015 to 2018, and only studies published in English were considered. The search outcomes identified all articles containing the word “mesenchymal stem cell” and “microcarrier”. Databases were searched individually to ensure all relevant studies were considered. The titles and abstract were carefully screened for eligibility related to the topic of interest. Primary studies related to microcarrier application were included. Review articles, news articles, letters, editorials, and case studies were excluded from the search.
Data extraction and management
Data were extracted from each eligible article by two reviewers. The selected papers were screened in several phases prior to inclusion. First, titles that were not relevant to the topic were excluded. Next, abstracts of the papers were screened, and unrelated studies were excluded. All duplicates were removed. The following data were summarized from the selected studies: authors, year, source of MSCs, applications, type of microcarrier used, results, and conclusion.
Results
Search result
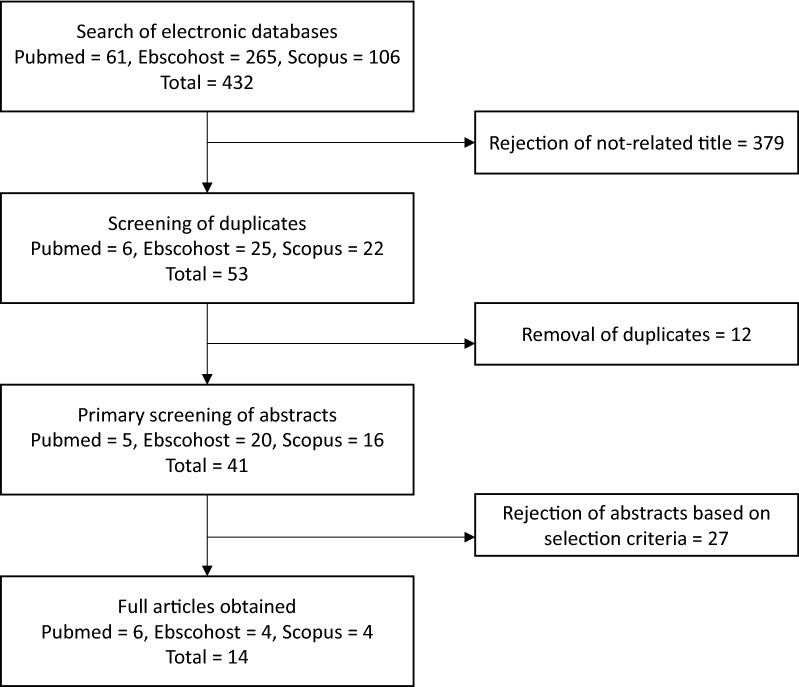
The primary search identified 432 articles: 61 articles were derived from Pubmed, 265 from Ebscohost, and 106 articles from Scopus. To minimize bias and improve the strength of the related articles, two reviewers independently assessed the articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. A total of 379 articles were removed as they were unrelated to either mesenchymal stem cells or microcarriers. A joint discussion was conducted to achieve consensus on differences which emerged during the assessment. From the 53 remaining articles, 12 duplicates were removed before full articles were retrieved. From the remaining 41 articles, 27 articles were rejected based on the inclusion criteria as these articles were not primary studies, were not related to mesenchymal stem cells or microcarriers, or were unavailable as full articles. Finally, a total 14 studies were selected for data extraction in this review. The flow chart of the selection process is shown in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Flow chart of the article selection process from Pubmed, Ebscohost, and Scopus databases
Study characteristics
All studies were published between 2015 and 2019 and reported on in vitro studies. Thirteen studies utilised human mesenchymal stem cells, while only one reported using rat MSCs. Seven out of 14 articles utilised commercially available microcarriers, while the rest were formulated based on different surface characteristics. From the generated data, articles were classified into three aspects: Microcarriers in MSC culture, MSC expansion and MSC differentiation. A summary of the studies is provided in Table 1.
Table 1.
Summary and classification of the 14 articles selected from the database search
| Author | Sample source | Application | Microcarrier used | Culture media used | Result | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chui et al. [51] | Human MSCs-hTERT cell line | MSC expansion |
Electrosprayed genipin cross-linked alginate-chitosan microcarrier Cytodex 1 |
Low glucose DMEM + 10% FBS |
MSCs cultured on fabricated microcarriers had a 26% higher cell attachment and twice the proliferation rate compared to the commercial microcarrier No significant difference in gene expression between the two microcarriers for the positive MSC surface markers as well as showing either low or no signal for negative MSC surface markers |
Genipin cross- linked alginate–chitosan based microcarriers can act as a potential alternative to commercial microcarriers for MSC expansion |
| 2 | Gupta et al. [60] | Human periosteum-derived cells | MSC Bone forming potential | Cultispher S | High glucose DMEM + 10% FBS/HPL |
HPL resulted in faster cell proliferation compared to FBS Cell viability and trilineage differentiation capability were that maintained by HPL, although a suppression of adipogenic differentiation potential was observed HPL supplementation resulting in almost three times more mineralized tissue within calcium phosphate scaffolds |
The use of HPL in bioreactor-based expansion of hPDCs is an optimal solution that increases expansion efficiency along with promoting bone forming capacity of these cells |
| 3 | Krutty et al. [59] | Bone marrow MSC | MSC expansion | PNIPAM grafted microcarriers | MEM α + 10% FBS |
The microcarriers create a reproducible surface that does not rely on the adsorption of xenogenic serum proteins to mediate cell adhesion MSCs cultured on this fabricated microcarriers achieve sixfold expansion and retain their ability to differentiate after harvesting |
PNIPAM grafted microcarriers are a relevant platform for expanding cells while maintaining hMSC functionality |
| 4 | Tanimowo Aiyelabegan et al. [57] | Rat bone marrow MSC | MSC osteogenic differentiation | k-casein conjugated agarose microspheres | DMEM |
The cell viability of the synthesized microspheres significantly different from uncoated microspheres, but similar to the control and commercial microcarriers This microcarrier systems upregulated the expression of osteo- genic differentiation markers on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured on the carrier systems |
k-casein conjugated agarose microspheres culturing environment may assist in reducing the need for expensive hormones and growth factors that directs differentiation, and thus, could reduce the risk of unwanted systemic side effects in vivo and aid the clinical translatability of MSCs that are cultured using this strategy for bone TE |
| 5 | Heathman et al. [63] | Bone marrow MSC | MSC expansion | Plastic P-102L microcarriers | PRIME-XV MSC Expansion SFM |
It was found that growth rate though an intermediate value of ~ 1.3 NJS did not cause sampling difficulties, clumping and poor growth. At this range of agitation intensities, cell quality remained unchanged post-harvest Direct aeration of the culture medium both with and without Pluronic F68 via a sparger at NJS was detrimental to BM-hMSC growth |
Alternative methods of supplying sufficient levels of oxygen to microcarrier bioreactor systems culturing BM-hMSCs may have to be developed as well as establishing the level of pCO2 that they can tolerate as these systems are scaled up to manufacture commercially-viable cell numbers |
| 6 | Yuan et al. [62] | Bone marrow MSC | MSC expansion | PNIPAM grafted microcarriers | MEM α + 10% FBS |
hMSC aggregates generated from the bioreactor maintained comparable immunomodulation and cytokine secretion properties compared to the ones made from the culture plate At room temperature, hMSCs were self-assembled into 3D hMSC aggregates in PBS-VW bioreactor and remain as single cells in bioreactor owing to different hydrodynamic conditions |
Thermal responsive microcarriers could scale-up the production of hMSC aggregates in the suspension bioreactor for integrated cell expansion |
| 7 | Dias et al. [58] | hMSC (Lonza, Walkersville, MD) | Serum-free MSC expansion | PEG-based hydrogel coated Hillex II amine-functionalized microcarriers |
MEM α + 10% FBS Lonza serum-free MSC growth media |
High cell expansion was apparent in serum-free media on coated microcarriers with some aggregation during expansion Osteoblast and adipocytes differentiation apparent in serum-free condition on PEG |
The PEG hydrogel coating reduced microcarrier aggregation during MSC culture |
| 8 | Lin et al. [69] | Fetal bone marrow MSC | hMSC-microcarrier constructs chondrogenic differentiation |
Cytodex 1 Cytodex 3 SphereCol Cultispher-S |
MEM α + 10% FBS | Narrow range of 70% cell confluency, cell number of 10 x 10^3, and microcarrier of 300 per construct generate the optimal microenvironment for efficient chondrogenic differentiation | Scalable microcarrier-spinner cultures enhance the chondrogenic potential of the MSC, supporting their use for large-scale cell expansion in cartilage cell therapy |
| 9 | Rafiq et al. [61] | Bone marrow MSC (Lonza, Walkersville, MD) | Automated hMSC expansion | Plastic P102-L microcarrier |
DMEM + 10% FBS PRIME-XV MSC Expansion SFM |
More than 250% increase in yield compared to the serum-based process The combination of both serum-free and automated processing improved the reproducibility more than tenfold compared to the serum-based, manual spinner flask process |
Ambr15 microbioreactor is an effective tool for bioprocess development of hMSC microcarrier cultures and improves both process yield and consistency. |
| 10 | Takahashi et al. [70] | Bone marrow MSC | MSC expansion | Cytodex 1 | Low glucose DMEM + 10% FCS |
30 rpm was the lowest agitation rate necessary for the suspension of Cytodex 1 microcarriers, and the cells grew fastest at 60 rpm The percentages of CD90- and CD166-positive cells among cells grown on Cytodex 1 at 60 rpm (91.5 and 87.6%) were comparable to those of cells grown in the pre-culture on dishes |
Beads-to-beads subcultivation method maintaining the expressions of the cell surface antigens CD90 and CD166, while adjusting agitation rate could decrease the microcarrier aggregation |
| 11 | Zhang et al. [71] |
Human amniotic MSC HUVEC |
Pre-vascularized modular bone tissue fabrication | CultiSpher S |
DMEM + 10% FBS MEM α + 10% FBS |
Microtissues were formed with high cellularity after 4 weeks culture in spinner flask, evenly distributed cells and tube formation ability Coculture with HUVECs exerted an inhibitory effect on osteogenic differentiation of MSCs |
An effective method to fabricate pre-vascularized bone microtissues was established, which would lay a solid foundation for subsequent development of vascularized tissue grafts for bone regeneration |
| 12 | Nienow et al. [54] | Bone marrow MSC | MSC expansion |
Solohill plastic Solohill collagen |
DMEM + 10% FBS |
hMSCs were successfully cultured using the minimum agitator speed required for complete microcarrier suspension The cells were shown to retain their desired quality attributes and were able to proliferate with the reported cell detachment protocol |
Theagitation strategy with respect to culture and harvest therefore offers a sound basis for a wide range of scales of operation |
| 13 | Song et al.[56] | Bone marrow MSC | MSC expansion | Thermosensitive glass microcarrier | Low glucose DMEM + 10% FBS |
NIPAAm was successfully grafted on to the surface of the microcarriers, providing an excellent biocompatible environment for BMMSC adhesion and growth BMMSCs could be fully removed from the thermosensitive glass microcarriers with remained cell viability |
This new substrate can provide a better 3D environment for cell growth and cell recovery, which is expected to be utilized in vitro for massive cell expansion by combining with the dynamic bioreactor |
| 14 | Lakhkar et al. [55] |
hMSCs MG63 osteoblast-type cells |
MSC Oesteogenic induction | Titanium phosphate glass microcarrier | Low glucose DMEM + 10% FCS |
The microcarrier proliferative capacity is increasing in MG63 cell Expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and osteopontin, significantly greater Scanning electron microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy images reveal favorable MG63 and human mesenchymal stem cell adhesion on the Ti5 microsphere surfaces |
The titanium phosphate glass microcarrier function as platforms for guided osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs. It is expected that these approaches will in future facilitate the development of viable bone tissue in vitro for use in bone replacement therapies |
Discussion
The database search provided 14 articles related to Wharton’s Jelly and microcarrier. From these articles, various sources were examined regarding microcarrier application on MSC culture. This review assessed the application of microcarrier on MSC culture, which may have remarkable potential for different usage in future application.
Microcarrier in MSC culture
Generally, microcarriers can be divided into 3 major types: non-porous, microporous and macroporous (Fig. 1). While non-porous microcarriers are relatively straightforward with limited surface area, the microporous structure of microcarriers allow cells attached on the carrier to undergo material transfer on the basolateral side of the cell; however, the surface area available for cell attachment is also limited on the outer surface of the microcarrier. In contrast, macroporous microcarriers provide a larger pore size that enable cells to enter into the microcarrier. In this case, macroporous microcarriers contributes a larger surface area per millilitre of media compared to microporous microcarriers, hence potentially higher cell yields in large scale cultures [48]. Table 2 shows the summary of the microcarrier used in the 14 studies selected aforementioned, the details were arranged based on the material, surface feature, diameter, porosity, concentration in culture and results of application for each microcarriers.
Table 2.
Summary and classification of the microcarrier used in the 14 studies selected
| Availability | Microcarrier | Material | Surface feature | Diameter (µm) | Porosity | Concentration | Cell yield | Cell differentiation | Manufacturer | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercially available | Cell expansion | |||||||||
| Glass microcarrier (G102-1521) | Cross-linked polystyrene | Silica glass | 125–212 | Non-porous | 35 mg/mL | – | – | Pall corporation | [56] | |
| Hillex II microcarrier | Polystyrene | Positive charge amine | 160–200 | Microporous | 3 cm2 per 24-well | 1.2 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | Pall corporation | [58] | |
| Solohill plastic | Plastic | Plastic surface | 90–150 | Non-porous | 6000 unit/mL | 1–5 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | Pall corporation | [54] | |
| 5 cm/mL | 8.1 × 10^5 cells/mLa | – | [61] | |||||||
| 5 cm/mL | 9.6 × 10^4 cells/mLb | – | [63] | |||||||
| Solohill collagen | Polystyrene | Collagen coated | 125–212 | Non-porous | 6000 unit/mL | 1–5 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | Pall corporation | [54] | |
| Cytopores 1 | Cellulose | Positive charge (0.9–1.20 meq/g) | 230 | Macroporous | 1.2 mg/mL | 1.5 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | GE Healthcare | [70] | |
| Cytopores 2 | Cellulose | Positive charge (1.65–1.95 meq/g) | 230 | Macroporous | 1.2 mg/mL | 1.4 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | GE Healthcare | [70] | |
| Cell expansion & differentiation | ||||||||||
| Cytodex 1 | Cross-linked de × tran | Positive charge | 147–247 | Microporous | 2.7 mg/mL | 5.2 × 10^5 cells/mLb | Chondrogenesis | GE Healthcare | [69] | |
| 3 mg/mL | 4.3 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | [70] | |||||||
| 1.7 mg.mL | 0.86 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | [51] | |||||||
| Cytodex 3 | Cross-linked dextran | Gelatin coated | 141–211 | Microporous | 4 mg/mL | 3.55 × 10^5 cells/mLb | Chondrogenesis | GE Healthcare | [69] | |
| – | – | Osteogenesis | [57] | |||||||
| CultiSpher S | Gelatine | Gelatine | 130–380 | Macroporous | 0.5 mg/mL | 2.46 × 10^5 cells/mLb | Chondrogenesis | Sigma | [69] | |
| 2 mg/mL | – | Vascularise bone-like microtissue | [65] | |||||||
| 1 mg/mL | 1.3 × 10^5 cells/mL | [60] | ||||||||
| SphereCol | – | Collagen | 125–212 | Microporous | 1.2 × 10^3 microcarrier/mL | 3.58 × 10^4 cells/mLb | Chondrogenesis | Sigma | [69] | |
| Silica glass microsphere | Silica | Silica | 0.15–5 | Non-porous | 16 mg/mL | 3.3 × 10^5 cells/mL | Osteogenesis | Polysciences Inc | [55] | |
| In-house fabrication/modification | Cell expansion | |||||||||
| PVG coated microcarrier | Polystyrene | PVG-RGD coated | 125–212 | Non-porous | – | – | – | – | [59] | |
| PNIPAM grafted microcarrier | Polystyrene | PNIPAM coated | 50–100 | 10 mg/mL | 9.4 × 10^4 cells/mL | – | – | [62] | ||
| Alginate-chitosan microcarrier | Genipin cross-linked-alginate | Chitosan | 200–300 | – | 1.72 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | – | [51] | ||
| PNIPAAm-grafted microcarrier | Cross-linked polystyrene | Thermosensitive PNIPAAm grafted surface | 125-212 | Non-porous | 35 mg/mL | – | – | – | [56] | |
| PEG coated hydrogel | Polystyrene | PEG hydrogel surface | 400 | Non-porous | 3 cm2 per 24-well | 1.12 × 10^5 cells/mL | – | – | [58] | |
| Cell expansion & differentiation | ||||||||||
| Ti5 microcarrier | Titanium phosphate glass | Titanium phosphate glass | 50–100 | Non-porous | 16 mg/mL | 4.5 × 10^5 cells/mL | Osteogenesis | – | [55] | |
| Agarose microcarrier | Agarose | Casein | 100–150 | – | – | Osteogenesis | – | [57] | ||
aMicrocarrier added in mid of study
bApproximated value
The fabrication material of microcarriers is also a crucial factor in microcarrier cultures because of its physical and chemical effects towards cells, which include porosity, mechanical strength, permeability of nutrients, size, density, and shape [49]. In order to facilitate adherent cells to attach on the carrier surface, the divalent cations or protein available in culture medium is important so that cell could utilise it for attachment. Polymers such as polystyrene, plastic, or glass are commonly utilised as the basic matrix of microcarriers; these microcarriers are usually positively charged or chemically bounded to facilitate the attachment of adherent cells which possess an uneven distribution of negative surface charge. While microcarriers with higher charge densities were developed to promote cell adhesion for cell lines with weak adhesion (E.g. Cytopore 1 & 2), these microcarriers poses a challenge during cell harvesting due to difficulties with cell detachment at the end of the culture [50].
To overcome this problem, biopolymers (dextran, gelatin, cellulose, agarose, alginate) were introduced as they potentially facilitate cell harvesting while providing a biocompatible environment for cultures [51, 52]. In addition, microcarriers with surface modifications (E.g. protein or collagen coated), could also achieve a similar effect as the microcarriers mentioned above. Fibronectin for example, is commonly used to coat plastic or glass microcarriers to increase cell adhesion in microcarrier cultures, and used in concentrations ranging from 1–50 ug/mL [53–55]. On the other hand, compounds such as casein, chitosan, or even PNIPAAm was grafted on the surface of microcarriers to modify its adhesion properties and to provide an easier solution for cell harvesting [51, 56, 57].
Application of microcarriers in MSC culture
MSC expansion
A study found that PEG coated microcarriers supported the expansion of hMSCs in a serum-free environment, with doubling time under 25 h in the growth phase, as well as preserving its osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation post-harvest [58]. Genipin cross-linked alginate-chitosan microcarriers were demonstrated to provide 26% higher MSC attachment and twice the proliferation rate compared to the commercial microcarrier, Cytodex 1. The cells produced were easily detached without an extended incubation period or intense agitation during harvesting [51]. Whereas Krutty et al. developed a chemically defined PVG microcarrier which achieved a six-fold expansion in MSCs, while retaining their ability to differentiate after harvesting [59].
Under xenogenic-free culture conditions, Gupta et al. reported that HPL resulted in faster cell proliferation by 5.2 ± 0.61-fold in comparison to 2.7 ± 02.22-fold in FBS [60]. In addition, an automated serum-free, microcarrier culture system was established. It was found that such approach can produce more than tenfold MSC expansion compared to serum-based, manual spinner flask methods [61].
Several studies have been conducted on the formation of MSC-microcarrier aggregates and explored possible methods to overcome drawbacks associated with such culture strategies. It was suggested that hMSC aggregates generated from thermal responsive microcarriers in bioreactors maintained comparable immunomodulation and cytokine secretion compared to conventional culture strategies [62]. Heathman and co-workers reported a minimum agitation speed in a bioreactor system to obtain high cell numbers; however, low agitation were still accompanied by cell aggregation, leading to inconsistencies between pre- and post-harvest sampling. Therefore, an alternative oxygen supply method is needed to overcome the current downsides faced by readily available methods, which introduced shear forces to the cells during increased agitation speeds in up-scaling of cultures [63]. On the other hand, a protocol which utilised short periods of intense agitation in the presence of enzymes such that the cells were detached yet remained undamaged and retained post-harvest characteristics, was reported [54].
MSC differentiation
Aside from up-scaling MSC expansion, more researchers were shifting their focus towards inducing cell differentiation in microcarrier cultures simulating a three-dimensional human body environment. Lin et al. showed that chondrogenic pellets generated from microcarrier cultures developed larger pellet diameters, and produced more DNA, GAG and collagen II per pellet with greater GAG/DNA and collagen II/DNA ratios compared with that of tissue culture flasks, while similar result were observed by using another type of microcarrier [64]. An increasing number of studies have highlighted bone formation potential by using microcarrier cultures, for example, a new process developed by Zhang et al. fabricated pre-vascularized bone microtissues by integrating microcarrier culture and co-culture with MS and HUVEC [65]. Aside from that, Tanimowo et al. fabricated a novel agarose-k-casein microsphere which upregulated the expression of osteogenic differentiation markers in bone marrow MSCs [57]. A titanium phosphate glass microcarrier that enhances bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2) and osteopontin (OPN) expression by h-MSC was introduced. BMP-2 is considered an important protein in cell differentiation and tissue regeneration, which is normally associated with osteoinductive growth factors [66]; OPN on the other hand is mainly related to bone metabolism and remodelling [67]. In this case, it was suggested that titanium phosphate glass microcarriers influenced hMSC differentiation and metabolic activity and could contribute in bone tissue engineering [55].
Conclusion
Limitation of cell numbers in MSC-based cell therapy enlightened multiple approaches to increase the cell yield. Three-dimensional microcarrier cultures seems to be a potential candidate in the up-scaling production of MSCs. This review demonstrates that microcarriers, whether commercially available or produced in-house, were capable of enhancing production and inducing chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation in MSCs.
However, several challenges in this system need to be addressed during cell manufacturing. The yields of MSC up-scale activity are still showing inconsistency from one another, even similar culture techniques and consumables were used. This problem could be possibly due to the batch-to-batch variances present in undefined media which relying on animal/human derived serum as main supplement. The variation from each batches of serum further affect the quality of the up-scaled product by different sources of origin, brands, and present of unidentified risk of contamination. In this case, one of the solutions to minimise this variations is the adaptation of serum free media (SFM) in MSC culture as mentioned by Ota et al. [68]. Aside from cell yield variations, the downstream harvesting approaches still require optimisation to improve cell recovery; in fact, MSC differentiation efficiency in 3D system remains uncertain and the mechanism is still not well-studied. Therefore, detailed studies are still required before this system to be adopted into the scale of GMP manufacturing.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- MSC
Mesenchymal stem cell
- GVHD
Graft versus host disease
- PAMPs
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- DAMPs
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- BLM
Bleomycin
- TNF
Tumor necrosis factor
- IL
Interleukin
- IFN
Interferon
- APC
Antigen-presenting cell
- GMP
Good manufacturing practice
- DEAE
Diethylaminoethyl
- PEG
Polyethylene glycol
- HPL
Human platelet lysate
- GAG
Glycosaminoglycan
Authors’ contributions
MDY, RBHI, MHN, JXL and MBF conceived of the presented idea. MDY and BK developed the theory followed by performing the data extractions. MDY and NS verified the data extraction methods and data extracted. MDY supervised the findings of this work. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The research was performed with the financial support of Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (FF-2019-448; FF-2019-448/1).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the Scopus, Ebscohost, and Pubmed repository.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Abomaray FM, Al Jumah MA, Kalionis B, AlAskar AS, Al Harthy S, Jawdat D, et al. Human chorionic villous mesenchymal stem cells modify the functions of human dendritic cells, and induce an anti-inflammatory phenotype in CD1 + dendritic cells. Stem Cell Rev Reports. 2015;11(3):423–441. doi: 10.1007/s12015-014-9562-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen X, Armstrong MA, Li G. Mesenchymal stem cells in immunoregulation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2006;84(5):413–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1711.2006.01458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Keating A. Mesenchymal stromal cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 2006;13:419–425. doi: 10.1097/01.moh.0000245697.54887.6f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Maharlooei MK, Bagheri M, Solhjou Z, Jahromi BM, Akrami M, Rohani L, et al. Adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cell (AD-MSC) promotes skin wound healing in diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;93(2):228–234. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baba K, Yamazaki Y, Ikemoto S, Aoyagi K, Takeda A, Uchinuma E. Osteogenic potential of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells cultured with umbilical cord blood-derived autoserum. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(8):768–772. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2012.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.O’Donoghue K. Identification of fetal mesenchymal stem cells in maternal blood: implications for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 2003;9(8):497–502. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gag063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kerkis I, Ambrosio CE, Kerkis A, Martins DS, Zucconi E, Fonseca SA, et al. Early transplantation of human immature dental pulp stem cells from baby teeth to golden retriever muscular dystrophy (GRMD) dogs: local or systemic? J Transl Med. 2008;6(1):35. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-6-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vojtaššák J, Danišovič L, Kubeš M, Bakoš D, Jarábek L, Uličná M, et al. Autologous biograft and mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of the diabetic foot. Neuroendocrinol Lett. 2006;27:134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Petite H, Viateau V, Bensaïd W, Meunier A, De Pollak C, Bourguignon M, et al. Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18(9):959–963. doi: 10.1038/79449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Takewaki M, Kajiya M, Takeda K, Sasaki S, Motoike S, Komatsu N, et al. MSC/ECM cellular complexes induce periodontal tissue regeneration. J Dent Res. 2017;96(9):984–991. doi: 10.1177/0022034517708770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ren L, Ma D, Liu B, Li J, Chen J, Yang D, et al. Preparation of three-dimensional vascularized MSC cell sheet constructs for tissue regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:301279. doi: 10.1155/2014/301279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lim JY, Ryu DB, Lee SE, Park G, Min CK. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) attenuate cutaneous sclerodermatous graft-versus-host disease (Scl-GVHD) through inhibition of immune cell infiltration in a mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(9):1895–1904. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.02.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang L, Gu Z, Zhao X, Yang N, Wang F, Deng A, et al. Extracellular vesicles released from human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells prevent life-threatening acute graft-versus-host disease in a mouse model of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1874–1883. doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berger M, Mareschi K, Castiglia S, Rustichelli D, Mandese A, Migliore E, et al. In vitro mesenchymal progenitor cell expansion is a predictor of transplant-related mortality and acute GvHD III-IV after bone marrow transplantation in univariate analysis: a large single-center experience. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019;41(1):42–46. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000001281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Prockop DJ, Youn OhJ. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs): role as guardians of inflammation. Mol Ther. 2012;20:14–20. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Soehnlein O, Lindbom L. Phagocyte partnership during the onset and resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:427–439. doi: 10.1038/nri2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rock KL, Latz E, Ontiveros F, Kono H. The Sterile Inflammatory Response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010;28(1):321–342. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ortiz LA, DuTreil M, Fattman C, Pandey AC, Torres G, Go K, et al. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(26):11002–11007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704421104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oh JY, Kim MK, Shin MS, Lee HJ, Ko JH, Wee WR, et al. The anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic role of mesenchymal stem cells in corneal wound healing following chemical injury. Stem Cells. 2008;26(4):1047–1055. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Luo G, Cheng W, He W, Wang X, Tan J, Fitzgerald M, et al. Promotion of cutaneous wound healing by local application of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood. Wound Repair Regen. 2010;18(5):506–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2010.00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jeon YK, Jang YH, Yoo DR, Kim SN, Lee SK, Nam MJ. Mesenchymal stem cells’ interaction with skin: wound-healing effect on fibroblast cells and skin tissue. Wound Repair Regen. 2010;18(6):655–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2010.00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Smith AN, Willis E, Chan VT, Muffley LA, Isik FF, Gibran NS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce dermal fibroblast responses to injury. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rodriguez-Menocal L, Shareef S, Salgado M, Shabbir A, Van Badiavas E. Role of whole bone marrow, whole bone marrow cultured cells, and mesenchymal stem cells in chronic wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0001-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Eigenbrod T, Park J-H, Harder J, Iwakura Y, Núñez G. Cutting edge: critical role for mesothelial cells in necrosis-induced inflammation through the recognition of IL-1α released from dying cells. J Immunol. 2008;181(12):8194–8198. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Németh K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PST, Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E 2-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009;15(1):42–49. doi: 10.1038/nm.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Choi H, Lee RH, Bazhanov N, Oh JY, Prockop DJ. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by activated MSCs attenuates zymosan-induced mouse peritonitis by decreasing TLR2/NF-κB signaling in resident macrophages. Blood. 2011;118(2):330–338. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-327353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Spriggs DR, Deutsch S, Kufe DW. Genomic structure, induction, and production of TNF-alpha. Immunol Ser. 1992;56:3–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Maini RN, Elliott MJ, Brennan FM, Feldmann M. Beneficial effects of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) blockade in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Clin Exp Immunol. 1995;101:207–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb08340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rowley J, Abraham E, Campbell A, Brandwein H, Oh S. Meeting lot-size challenges of manufacturing adherent cells for therapy. Vol. 10, BioProcess International. 2012. www.corning.com/lifesciences/whatsnew. Accessed 2 Jan 2020.
- 30.Díez-Tejedor E, Gutiérrez-Fernández M, Martínez-Sánchez P, Rodríguez-Frutos B, Ruiz-Ares G, Lara ML, et al. Reparative therapy for acute ischemic stroke with allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue: a safety assessment: a phase II randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-center, pilot clinical trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23(10):2694–2700. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Levenberg S, Burdick JA, Kraehenbuehl T, Langer R. Neurotrophin-induced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on three-dimensional polymeric scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(3–4):506–512. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen VC, Couture SM, Ye J, Lin Z, Hua G, Huang HIP, et al. Scalable GMP compliant suspension culture system for human ES cells. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(3):388–402. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2012.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zweigerdt R, Olmer R, Singh H, Haverich A, Martin U. Scalable expansion of human pluripotent stem cells in suspension culture. Nat Protoc. 2011;6(5):689–700. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Halme DG, Kessler DA. FDA regulation of stem-cell–based therapies. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(16):1730–1735. doi: 10.1056/NEJMhpr063086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen AKL, Chen X, Choo ABH, Reuveny S, Oh SKW. Critical microcarrier properties affecting the expansion of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2011;7(2):97–111. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2011.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Serra M, Correia C, Malpique R, Brito C, Jensen J, Bjorquist P, et al. Microencapsulation technology: a powerful tool for integrating expansion and cryopreservation of human embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(8):e23212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Van Hemert P, Kilburn DG, Van Wezel AL. Homogeneous cultivation of animal cells for the production of virus and virus products. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1969;11(5):875–885. doi: 10.1002/bit.260110513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Giard,’ DJ, Thilly WG, Wang DIC, Levine2 DW. Virus Production with a Newly Developed Microcarrier System. Applied and environmental microbiology. 1977. http://aem.asm.org/. Accessed 16 Dec 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Sinskey AJ, Fleischaker RJ, Tyo MA, Giard DJ, Wang DIC. Production of cell-derived products: virus and interferon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;369(1):47–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb14176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.YekrangSafakar A, Acun A, Choi J-W, Song E, Zorlutuna P, Park K. Hollow microcarriers for large-scale expansion of anchorage-dependent cells in a stirred bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018;115(7):1717–1728. doi: 10.1002/bit.26601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tavassoli H, Alhosseini SN, Tay A, Chan PPY, Weng Oh SK, Warkiani ME. Large-scale production of stem cells utilizing microcarriers: a biomaterials engineering perspective from academic research to commercialized products. Biomaterials. 2018;181:333–346. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rafiq QA, Brosnan KM, Coopman K, Nienow AW, Hewitt CJ. Culture of human mesenchymal stem cells on microcarriers in a 5 l stirred-tank bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett. 2013;35(8):1233–45. https://dspace.lboro.ac.uk/2134/14778. Accessed 2 Jan 2020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Malda J, Frondoza CG. Microcarriers in the engineering of cartilage and bone. Trends Biotechnol. 2006;24:299–304. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yourek G, McCormick SM, Mao JJ, Reilly GC. Shear stress induces osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Regen Med. 2010;5(5):713–724. doi: 10.2217/rme.10.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Li C, Qian Y, Zhao S, Yin Y, Li J. Alginate/PEG based microcarriers with cleavable crosslinkage for expansion and non-invasive harvest of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;64:43–53. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092849311630265X?via%3Dihub. Accessed 11 Aug 2019. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Ferrari C, Balandras F, Guedon E, Olmos E, Chevalot I, Marc A. Limiting cell aggregation during mesenchymal stem cell expansion on microcarriers. Biotechnol Prog. 2012;28(3):780–787. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hewitt CJ, Lee K, Nienow AW, Thomas RJ, Smith M, Thomas CR. Expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells on microcarriers. Biotechnol Lett. 2011;33(11):2325–2335. doi: 10.1007/s10529-011-0695-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Eibes G, dos Santos F, Andrade PZ, Boura JS, Abecasis MMA, da Silva CL, et al. Maximizing the ex vivo expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells using a microcarrier-based stirred culture system. J Biotechnol. 2010;146(4):194–197. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Healthcare G. Microcarrier cell culture: Principles and methods. GE Healthcare/Amersham. 2005. http://www.gelifesciences.co.kr/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/023.8_Microcarrier-Cell-Culture.pdf. Accessed 11 Jan 2020.
- 50.Nienow AW, Rafiq QA, Coopman K, Hewitt CJ. A potentially scalable method for the harvesting of hMSCs from microcarriers. Biochem Eng J. 2014;15(85):79–88. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chui CY, Odeleye A, Nguyen L, Kasoju N, Soliman E, Ye H. Electrosprayed genipin cross-linked alginate–chitosan microcarriers for ex vivo expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res - Part A. 2019;107(1):122–133. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gröhn P, Klöck G, Zimmermann U. Collagen-coated Ba2 + -alginate microcarriers for the culture of anchorage-dependent mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1997;22(5):970–975. doi: 10.2144/97225rr06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Heathman TRJ, Stolzing A, Fabian C, Rafiq QA, Coopman K, Nienow AW, et al. Scalability and process transfer of mesenchymal stromal cell production from monolayer to microcarrier culture using human platelet lysate. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(4):523–35. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1465324916000189. Accessed 11 Aug 2019 . [DOI] [PubMed]
- 54.Nienow AW, Hewitt CJ, Heathman TRJ, Glyn VAM, Fonte GN, Hanga MP, et al. Agitation conditions for the culture and detachment of hMSCs from microcarriers in multiple bioreactor platforms. Biochem Eng J. 2016;108:24–9. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1369703X15300309. Accessed 11 Aug 2019.
- 55.Lakhkar NJ, Day R, Kim H-W, Ludka K, Mordan NJ, Salih V, et al. Titanium phosphate glass microcarriers induce enhanced osteogenic cell proliferation and human mesenchymal stem cell protein expression. J Tissue Eng. 2015;6:204173141561774. doi: 10.1177/2041731415617741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Song K, Yang Y, Wu S, Zhang Y, Feng S, Wang H, et al. In vitro culture and harvest of BMMSCs on the surface of a novel thermosensitive glass microcarrier. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;58:324–30. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493115302988?via%3Dihub. Accessed 12 Aug 2019. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 57.Tanimowo Aiyelabegan H, Ebadi M, AliKardar G, Lotfibakhshaiesh N, Abedin Dorkoosh F, EbrahimiBarough S, et al. k-Casein upregulates osteogenic differentiation on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured on agarose microcarriers. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater. 2019;69(6):373–380. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Dias AD, Elicson JM, Murphy WL. Microcarriers with Synthetic Hydrogel Surfaces for Stem Cell Expansion. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(16):1700072. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Krutty JD, Dias AD, Yun J, Murphy WL, Gopalan P. Synthetic, chemically defined polymer-coated microcarriers for the expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells. Macromol Biosci. 2019;19(2):1800299. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201800299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gupta P, Hall GN, Geris L, Luyten FP, Papantoniou I. Human platelet lysate improves bone forming potential of human progenitor cells expanded in microcarrier-based dynamic culture. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(8):810–821. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rafiq QA, Hanga MP, Heathman TRJ, Coopman K, Nienow AW, Williams DJ, et al. Process development of human multipotent stromal cell microcarrier culture using an automated high-throughput microbioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017;114(10):2253–2266. doi: 10.1002/bit.26359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yuan X, Tsai A-C, Farrance I, Rowley J, Ma T. Aggregation of culture expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in microcarrier-based bioreactor. Biochem Eng J. 2018;131:39. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2017.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Heathman TRJ, Nienow AW, Rafiq QA, Coopman K, Kara B, Hewitt CJ. Agitation and aeration of stirred-bioreactors for the microcarrier culture of human mesenchymal stem cells and potential implications for large-scale bioprocess development. Biochem Eng J. 2018;136:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2018.04.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lin YM, Lim JFY, Lee J, Choolani M, Chan JKY, Reuveny S, et al. Expansion in microcarrier-spinner cultures improves the chondrogenic potential of human early mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(6):740–753. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.03.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang S, Zhou M, Ye Z, Zhou Y, Tan W-S. Fabrication of viable and functional pre-vascularized modular bone tissues by coculturing MSCs and HUVECs on microcarriers in spinner flasks. Biotechnol J. 2017;12(8):1700008. doi: 10.1002/biot.201700008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.De Fusco C, Messina A, Monda V, Viggiano E, Moscatelli F, Valenzano A, et al. Osteopontin: relation between adipose tissue and bone homeostasis. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:4045238. doi: 10.1155/2017/4045238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Poon B, Kha T, Tran S, Dass CR. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and bone therapy: successes and pitfalls. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016;68(2):139–147. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ota M, Takagaki K, Takaoka S, Tanemura H, Urushihata N. A new method to confirm the absence of human and animal serum in mesenchymal stem cell culture media. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(8):1102–1106. doi: 10.7150/ijms.32100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lin YM, Lee J, Lim JFY, Choolani M, Chan JKY, Reuveny S, et al. Critical attributes of human early mesenchymal stromal cell-laden microcarrier constructs for improved chondrogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0538-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Takahashi I, Sato K, Mera H, Wakitani S, Takagi M. Effects of agitation rate on aggregation during beads-to-beads subcultivation of microcarrier culture of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology. 2017;69(3):503–509. doi: 10.1007/s10616-016-9999-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zhang S, Zhou M, Ye Z, Zhou Y, Tan WS. Fabrication of viable and functional pre-vascularized modular bone tissues by coculturing MSCs and HUVECs on microcarriers in spinner flasks. Biotechnol J. 2017;12(8):1–28. doi: 10.1002/biot.201700008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the Scopus, Ebscohost, and Pubmed repository.