Abstract
Background
There are high mortality and morbidity rates due to poisonous snakebites globally with sub-Saharan Africa having some of the highest cases. However, traditional medicine practitioners (TMP) have been treating snakebites in Uganda for long despite the fact that few studies have been conducted to document such vital and rich indigenous traditional knowledge before it is lost. This study aimed to document the medicinal plant species used by experienced TMP in treating snakebite envenomation in selected post-conflict parts of Uganda. An ethnopharmacological survey was conducted in Kitgum, Serere, Kaberamaido and Kaabong districts in Uganda. Twenty-seven TMP with expertise in treating snakebites were purposively identified using the snowball technique and interviewed using semi-structured questionnaires. Data were analysed using simple descriptive statistics.
Results
Sixty plant species from 28 families were documented with high consensus among the isolated indigenous Ik tribe of Kaabong district. Most of the plant species used were from the Asteraceae and Fabaceae families with eight species each. The genus Echinops was the most well-represented with three species. The most commonly used plant species were of citation were Steganotaenia araliaceae (16), Microglossa pyrifolia (Lam.), Gladiolus dalenii Van Geel (13), Aframomum mildbraedii Loes. (11), Jasminum schimperi Vatke and Cyathula uncinulata (Schrad) Schinz (10) and Crinum macowanii Baker and Cyphostemma cyphopetalum (Fresen.) Desc. ex Wild & R.B. Drumm (10). S. araliaceae which was mentioned by all the TMP in the Ik community was used for first aid. Most of the plant species were harvested from the wild (68.75%) and were herbs (65.0%) followed by trees (23.3%). The most commonly used plant parts were roots (42.6%) and leaves (25.0%). Thirteen different methods of preparation and administration were used. Most of the medicines were administered orally (61.2%) and topically (37.6%). The commonest methods of oral application were cold water infusions (32.5%) and decoctions (21.7%).
Conclusions
TMP widely use several medicinal plant species for treating snakebite envenomation in the selected post-conflict regions of Uganda
Keywords: Medicinal plants, Envenomation, Snakebite, Traditional medicine practitioners, Post-conflict, Uganda
Background
Worldwide, more than five million people suffer snakebite envenomation leading to 25,000–125,000 deaths, while an estimated 400,000 people are left with permanent disabilities [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified snakebites as one of the most neglected tropical diseases (NTD) in terms of incidence, severity, and clinical characteristics. This has served as a basis for the advocacy for snakebite envenomation [2]. The burden of snakebite envenomation was eventually recognized in June 2017 and then enlisted as a NTD category A by WHO [2, 3].
Snakebite envenoming primarily affects residents of rural communities in Africa, Asia, Latin America and New Guinea and possess a serious health challenge [4]. It is an occupational, environmental and domestic health hazard that exacerbates the already impoverished state of these communities [1]. Venoms consist of mainly toxic modified saliva of poisonous snakes. They are complex mixtures of enzymes, proteins, non-proteins and metalloproteinases [5]. The most important venom components that cause serious clinical effects are pro-coagulant enzymes, cytolytic or necrotic toxins, haemolytic and myolytic phospholipases A2, pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurotoxins and haemorrhagins [6]. Broadly, there are two types of toxins, namely, neurotoxins, which attack the central nervous system, and haemotoxins, which target the circulatory system and kill victims very first. Snakes with neurotoxic venom include cobras, mambas, sea snakes, kraits and coral snakes [5]. Snakes with haemotoxic venom include rattlesnakes, copper head and cottonmouths [7]. Snake venoms can be neutralized by antibodies obtained after immunizing domestic animals with them. This led to the production of anti-venom called antisera. A major drawback of serum therapy is its prohibitive cost and chance that victims are often some distance away from medical care when bitten [8]. The search for novel venom inhibitors from natural products is therefore relevant because of their potential to complement serum therapy in neutralizing mainly the local damages of envenomation. Plant extracts constitute an excellent alternative with a range of anti-venom activities [7].
Africans have traditionally been treating poisonous snakebites using herbs [9–12]. For instance, of the 147 patients bitten by snakes seen between November 1995 and October 1996, 90% of them used herbs in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa [13]. In Kenya, 32 medicinal plants have been documented for the treatment of snakebites [14, 15]. In central Uganda, 36 plant species were documented for treating snakebites [10]. A total of 25 plants were documented for the treatment of snakebites in eastern Uganda, Bulamogi County, Uganda [11]. Five other medicinal plant species were documented for treatment of snakebites in the Northern sector of Kibale National Park in western Uganda [16].
The current population of Uganda is over 45.3 million [17]. More than 80% of Ugandans are involved in agriculture and live in rural areas [18]. This makes them highly vulnerable to snakebite envenomation coupled with lack of access to antisera in health facilities. There is a widespread use of medicinal plants for the treatment of snakebites in Uganda. However, there are no statistics available on snakebite envenomation and treatment. Additionally, ethnopharmacological surveys of plants used for the treatment of snakebites have not been done in many parts of Uganda. This study aimed to document the plant species used in the treatment of snakebite envenomation in the Acholi, Teso and Karamoja sub-regions of Uganda. These are post-conflict regions and were affected during the war led by Joseph Kony’s Lord’s resistance army (LRA) rebel outfit. The LRA war begun in 1986 and lasted over 18 years [19]. Anecdotal evidence points to a high prevalence of snakebite envenomation experienced by returnees during the post-conflict resettlement in northern Uganda. This is because as many as 2 million people who had fled the fighting were forced into internally displaced people’s camps in north of the country [20].
Results
Twenty-seven TMP were purposively selected and interviewed. Twenty-five were women and the rest were men. The average age of the respondents was 54.7 years and ranged from 36 to 95 years. The majority of the respondents (80%) were illiterate, with only 20% having attained primary education and were all peasant farmers (Table 1).
Table 1.
Socio demographic characteristics of the traditional medicine practitioners
| TMPS interviewed | |
|---|---|
| Age range | 36–95 |
| Females | 5 |
| Males | 22 |
| Total | 27 |
| Level of education | |
| Diploma | 0 |
| Advanced level | 0 |
| Ordinary level | 0 |
| Primary | 12 |
| None | 15 |
Sixty plant species from 28 families and fifty-one genera were documented (Table 2). The plant families with most species were Asteraceae (8), Fabaceae (7), Asparagaceae and Amaranthaceae with 4 species each and Euphorbiaceae, Meliaceae and Solanaceae with 3 species each (Fig. 1). The genus with the most plant species was Echinops (3). This was followed by Annona, Chlorophytum spp., Eucalyptus and Solanum with two species each (Table 2).
Table 2.
Medicinal plant species used in the management of snakebites in Acholi, Teso and Karamoja sub-regions of Uganda
| Family/scientific name (voucher number) | Local name (language) | Parts used | Habit | Mode of preparation and administration | Wild/domesticated | Frequency of mention | Documented use in the treatment of snakebite envenomation elsewhere |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amaranthaceae | |||||||
| 1. Cyathula uncinulata (Schrad) Schinz (ODF 001) | Kulabakak (Ik) | R | H | Apply powder to bite area after making small cuts with a razor blade. | W | 10 | No reports |
| Amaryllidiaceae | |||||||
| 2. Allium cepa L. (ODF 019) | Tungulu (Luo) | Blb | H | Decoction and drink | D | 1 | Externally applied for the treatment of snakebite in Salem district of India [21] and Colombia [22]. Bulbs are chewed for snakebite in eastern and central Uganda [10, 11]. |
| 3. Ammocharis tinneana (Kotschy & Peyr.) Milne-Redh. & Schweick (ODF 025) | Joda (Luo) | L | H | Decoction and drink | D | 1 | No reports |
| 4. Crinum macowanii Baker (ODF 20) | (Ateso) | B | H | Powdered and mixed with powder of C. cyphopetalum and applied topically. Powder also dissolved in and drink. | 10 | No reports | |
| Annonaceae | |||||||
| 5. Annona chrysopylla (ODF 023) | Obolo (Luo) | L, R St | Sh | Decoction. Stems and leaves used for repelling snakes | W | 4 | No reports |
| 6. Annona senegalensis Pers. (ODF 002) | Obolo (Luo) | R/L | T |
Pound and mix with water. Drink once/chew root and apply on the bitten area the next day. Stems barks used to repel snakes |
W/D | 9 | Methanolic leaf extracts inhibited Echis ocellatus (Viper) venom activities [23]. Methanol root extract reduced hyperthermia and directly detoxified snake venom by 16–33% in rats against cobra (Naja nigricotlis nigricotlis) venom in rats [24]. |
| Apiaceae | |||||||
| 7. Steganotaenia araliaceae Hochst. (ODF 003) | Segere (Ik) | L | S |
Chew and swallow juice as first aid. Pound leaves, mix with water & wash out the venom from eyes to avert blindness. |
W | 16 | Used in western Kenya for snakebite [14] |
| Asparagaceae | |||||||
| 8. Albuca abyssinica Jacq. (ODF 004) | Amujej (Ateso) | Blb/L | H | Crush leaves/bulbs, mix with water and drink as a purgative/apply on the bitten area/planted as a snake repellent | W | 3 | No reports |
| 9. Chlorophytum spp 1 (ODF 022) | Emutungulu akwangan (Ateso) | Tb | H | Pound and apply on the snake bitten area | D | 2 | No reports |
| 10. Chlorophytum spp 2 (ODF 024) | Eryau (Ateso) | Tb | H | Chew fresh roots | D | 2 | No reports |
| 11. Sansevieria trifasciata Prain (ODF 036) | Tworo (Luo) | L | H | Pound and drink juice. Apply topically | W | 3 | Snake bites and poison antidote in southern Uganda [25] |
| Asteraceae | |||||||
| 12. Echinops longifolius A. Rich. (ODF 011) | Ofilifil (Ik), okeya (Luo) | L | H | Burn to make and apply on bitten site once only/rub directly on bitten part/mix 1 tsp with water. | W | 9 | No reports |
| 13. Echinops amplexicaulis Oliv. (ODF 013) | Lukwang (Luo) | R | H | Pound, mix with water and drink once only/chew and apply on site the next day | W | 3 | Used in northern Uganda [26]. A novel crystalline caffeic acid from roots has anti-venom agents for hemolytic snake venoms [27]. |
| 14. Echinops issphaerocephalus L (ODF 005) | Okeya (Luo) | R | H | Pound, mix with water and drink once only/chew and apply on site the next day | W | 2 | No reports |
| 15. Erigeron floribundus (Kunth) Sch.Bip. (ODF 021) | Ejut dolei (Ateso) | L | H | Squeeze juice and drink 3 times a day for at least 3 days | W | 3 | No reports |
| 16. Lactuca inermis Forssk. (ODF 027) | Ekile (Ateso) | R | H | Mix the powder with cold water & drink 3 times a day for at least 3 days | W | 3 | No reports |
| 17. Microglossa pyrifolia (Lam.) Kuntze (ODF 006) | Ekiya Lo’emun (Ik), Etutum (Ateso) | R | H | Pound and mix with water and drink for 2 days/mix powder with cold water and drink 3 times a day for at least 3 days | W | 13 | Used in Mukono district in central Uganda for snakebite treatment [10, 28]. An infusion is drunk for snakebite [11]. |
| 18. Sigesbeckia orientalis L. (ODF 035) | Yat twol (Luo) | L | H | Squeeze juice and drink/paste apply topically | W | 5 | No reports |
| 19. Vernonia biafrae Oliv. & Heirn (ODF 030) | Ebwolibwol (Ateso) | R | H | Pound and mix with water and drink as a purgative | W | 2 | No reports |
| Colchicaceae | |||||||
| 20. Gloriosa superba L (ODF 007) | Lobon bong (Ik) | R | H | Powder sometimes mixed with the powder of G. dalenii for various snake types, spider and scorpion stings. | W/D | 8 | No reports |
| Convolvulaceae | |||||||
| 21. Astripomoe amalvacea (Klotzsch) A. Meeuse (ODF 008) | Apom (Ateso) | R/St | H | Pound and mix with water and drink once a day for 2–5 day | W | 3 | A paste from the tuber is applied externally on snakebite wounds [21, 29]. |
| Crassulaceae | |||||||
| 22. Kalanchoe sp. (ODF 032) | Ecucuka (Ateso) | L | H | Leaf juice/paste taken orally | W/D | 2 | No reports |
| 23. Bryophyllum delagoense (Eckl. & Zeyh.) Druce (ODF 031) | Omucaga (Ateso) | L | H | Leaf juice/paste taken orally | D | 2 | No reports |
| Cucurbitaceae | |||||||
| 24. Coccinia grandis (L.) Voigt (ODF 033) | Bomo twol (Luo) | R | H | Decoction | W | 2 | No reports |
| Euphorbiaceae | |||||||
| 25. Euphorbia hirta L (ODF 029) | Acakacak (Luo) Orurungo (Ateso) | B | H | Decoction | W | 5 | Roots are eaten for snakebite in central Uganda [10]. |
| 26. Euphorbia hypericifolia L. (ODF 009) | Loje (Ik) | L | H | Pound/squeeze juice and apply directly to bitten part twice a day for 2 days | W | 6 | No reports |
| 27. Euphorbia tirucalli L. (ODF 028) | Kilajok (Luo) | Sp | H | Drink sap and apply topically | D | 2 | Western Uganda [16] |
| Fabaceae | |||||||
| 28. Canavalia ensiformis (L) DC. (ODF 026) | Yat twol (Luo) | Sd | H | Chew seeds | D | 2 | No reports |
| 29. Glycine max(L.) Merr. (ODF 037) | Soya (Luo) | Sd | H | Chew seeds | D | 1 | Seeds used in central Uganda [10]. |
| 30. Indigofera arrecta A.Rich. (ODF 040) | Eragwii (Ateso) | R | Decoction and drink or powder applied topically | W | 5 | Roots used for snakebites as a poultice [11]. A leaf infusion drunk for snakebites [30] | |
| 31. Indigofera spicata Forssk. (ODF 038) | Yat twol (Luo) | R, L and S | H | Pound and drink juice and apply topically | W | 8 | No reports |
| 32. Lonchocarpus laxiflorus Guill. & Perr (ODF 059) | Eputon (Ateso) | R | T | Vomiting | W | 1 | No reports |
| 33. Piliostigma malabaricum (Roxb.) Benth. (ODF 046) | Ogali (Luo) | T | L/B | Decoction | W | 2 | No reports |
| 34. Tamarindus indica L. | Chwaa (Luo) | T | Sd | Chew/apply to the snake-bitten area | W/D | 7 | Seeds are crushed & taken orally as anti-venom [31]. Seeds used for scorpion stings [32] |
| 35. Senna hirsuta (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby (ODF 050) | Elekumare (Ateso) | R | T | Mix the powder with cold water and drink 3 times daily for at least 3 days | W | 3 | No reports |
| Iridaceae | |||||||
| 36. Gladiolus dalenii Van Geel (ODF 014) | Lodokole (Ik) | B | H | Make small cuts around the bitten area & apply powder once/mix powder with water & drink | W | 13 | Venomous stings & bites in Cameroon [33]. |
| Lamiaceae | |||||||
| 37. Hoslundia opposita Vahl (ODF 010) |
Etutu/Tutu (Ateso) Itutu (Kumam) |
R | Sh | Crush in water and drink/rub on bitten part/powder and mix with about ¼ l of warm water and drink twice a day for 3 days | W | 5 | Root chewed and make a poultice for snakebites [11]. |
| Meliaceae | |||||||
| 38. Azadirachta indica A.Juss. (ODF 039) | Neem* (Acholi) | F | T | Decoction | D/W | 6 | A decoction or poultice used in central Uganda [10]. |
| 39. Pseudocedrela kotschyi (Schweinf.) Harms (ODF 041) | Ekaka (Ateso) | R | Sh | Apply powder topically/make decoction and drink | W | 5 | No reports |
| 40. Toona ciliata M. Roem. (ODF 012) | Yat bwoc/Yat luu pa coo (Luo) | R | T | Pound, mix with water and drink only once. | W | 4 | No reports |
| Moringaceae | |||||||
| 41. Moringa oleifera Lam. (ODF 056) | Moringa* | R/B | T | Decoction | D | 2 | Bark and root juice used in central Uganda [10]. |
| Myrtaceae | |||||||
| 42. Eucalyptus viminalis Labill.(ODF 052) | Kalatuc (Luo) | R/L | T | Decoction | D | 1 | No reports |
| 43. Eucalyptus spp. (ODF 053) | Kalatuc (Luo) | L | T | Decoction | D | 2 | No reports |
| Musaceae | |||||||
| 44. Musa spp. (ODF 042) | Amemo (Luo) | L | R | Decoction | D | 2 | Juice from Musa balbisiana and Musa × paradisiaca in central Uganda [10]. |
| Oleaceae | |||||||
| 45. Jasminum schimperi Vatke (ODF 057) | Ederut (Ateso) | R | H | Mix the powder with powder from C. cyphopetalum and dissolve in water and drink/apply powder topically | W | 10 | No reports |
| Opiliaceae | |||||||
| 46. Opilia amentacea Roxb. (ODF 054) | Epolokiliok (Ateso) | R | CSh | Apply powder on cuts & also drink | W | 1 | Root paste is taken internally to cure snakebite by herbalists in India [21]. |
| Pedaliaceae | |||||||
| 47. Sesamum calycinum subsp. angustifolium (Oliv.) Ihlenf. & Seidenst (ODF 015) | Abal/Emelerait (Ateso), Kilode (Luo) | R | H | Crush in water and drink/rub juice on the bitten part | W | 2 | No reports |
| Phyllanthaceae | |||||||
| 48. Phyllanthus ovalifolius Forssk (ODF 043) | Elakas (Ateso) | R | Sh | Powder, mix with cold water and drink 3 times a day for at least 3 days/apply topically | W | 3 | Root chewed, followed by drinking lots of water to induce vomiting in the management of snakebites in Ethiopia [34] |
| Poaceae | |||||||
| 49. Imperata cylindrica (L) Raeusch. (ODF 055) | Obiya (Ateso/Luo) | R | H | Chew | W | 1 | Root chewed for snakebite in eastern Uganda [10, 11]. |
| 50. Sporobolus pyramidalis P.Beauv. (ODF 001) (ODF 044) | Ajiki (Luo) | L | H | Decoction | W | 1 | No reports |
| Rubiaceae | |||||||
| 51. Gardenia ternifolia Schumach. & Thonn. (ODF 045) | Ekoroi (Ateso) Odwong (Luo) | R | T | Powder, mix with cold water and drink 3 times a day for at least 3 days/apply topically | W | 6 | A roots infusion is drunk for snakebite treatment [11]. |
| Rutaceae | |||||||
| 52. Citrus limon (L.) Osbeck (ODF 047) | Lemun (Luo) | Fr | T | Squeeze out juice and drink | D | 1 | The juice is drunk [10]. |
| 53. Zanthoxylum chalybeum Engl. (ODF 048) | Eusuk (Ateso) | S, R | Powder, mix with cold water and drink thrice daily for at least 3 days/apply topically | W | 5 | No reports | |
| Sapindaceae | |||||||
| 54. Zanha golungensis Hiern (ODF 016) | Ekiya Lo’emun (Ateso) | R/St | T | Pound and mix with water and drink twice | W | 4 | No reports |
| Solanaceae | |||||||
| 55. Capsicum annuum L. (ODF 049) | Kamulari (Luo), Emulalu (Ateso) | F | H | Chew/powder, mix with cold water and drink 3 times a day for at least 3 days/apply topically | D | 5 | No reports |
| 56. Solanum giganteum Jacq. (ODF 017) | Ocok (Luo) | R/L | Sh | Drink ½ cup of decoction/Apply powder to small incisions made around the bite area/burn dry leaves and make victim inhale for severe cases and emergencies | W | 2 | No reports |
| 57. Solanum incanum L. (ODF 056) | Ocok (Luo) | S | R | Decoction | W | 3 | Snakebite treatment in Lira district, northern Uganda [35] and Mukono in central Uganda [10]. |
| Vitaceae | |||||||
| 58. Cyphostemma adenocaule (Steud. ex A.Rich.) Desc. ex Wild & R.B.Drumm. (ODF 058) | Anuno (Luo) | R | H | Decoction | W | 5 | No reports |
| 59. Cyphostemma cyphopetalum (Fresen.) Desc. ex Wild & R.B.Drumm (ODF 034) | Anona (Kumam) | R | H | Pound and squeeze out juice and taken orally | W | 10 | No reports |
| Zingiberaceae | |||||||
| 60. Aframomum mildbraedii Loes. (ODF 018) | Acaet/Asawot (Ateso), Oceyo (Kumam), Ocayo (Luo) | Rh | H | Root juice is drink/powdered & mixed with C. cyphopetalum powder & water then drink/applied topically. | W | 11 | No reports |
H herb, Sh shrub, T tree, Csh creeping shrub, Hb habit, PU- parts used, L leaves, R root, B Blb, S stem bark, Sp sap, F fruit, Bb bulb, WD wild/domesticated, FM frequency of mention
*Local name adapted from the English name
Fig. 1.
Families of medicinal plant species used in the management of snakebite envenomation in the Acholi, Teso and Karamoja sub-regions of Uganda
The most commonly mentioned plant species were Steganotaenia araliaceae (16), Microglossa pyrifolia and Gladiolus dalenii both at 13; Aframomum mildbraedii (11); Jasminum schimperi, Cyathula uncinulata, Crinum macowanii and Cyphostemma cyphopetalum (10); Annona senegalensis (9); Echinops longifolius (9); Gloriosa superba and Indigofera spicata (8); and Tamarindus indica (7). S. araliaceae was mentioned by all the TMP in the Ik community. It was used as first aid and is said to cause immediate vomiting only when used by someone bitten by a venomous snake.
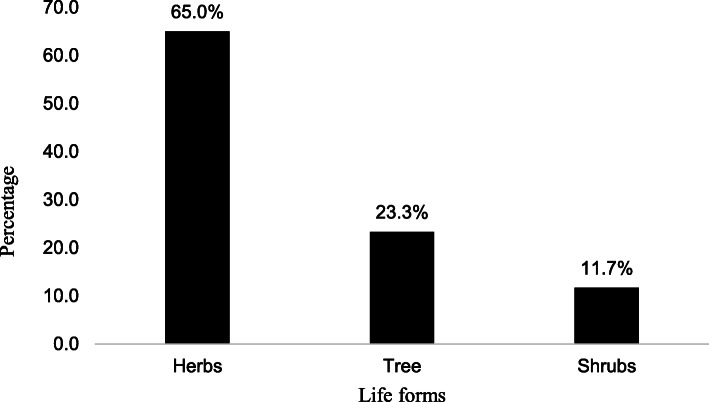
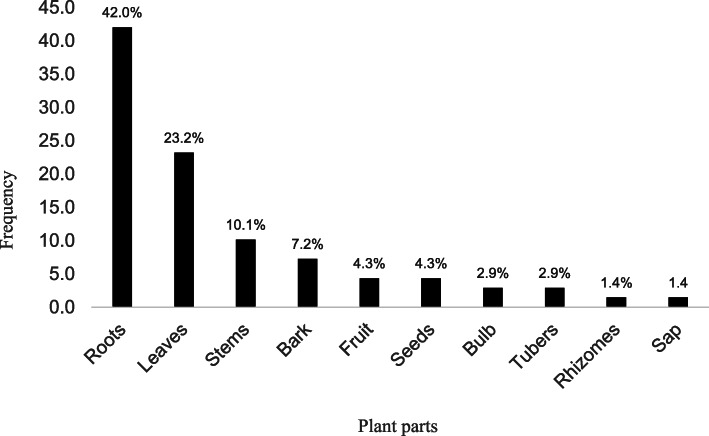
Most of the plant species used were herbs (65.0%), followed by trees (23.3%) and shrubs (11.7%) (Fig. 2). The most commonly used plant parts were roots (42.6%), leaves (25.0%), stems (10.3%) and bark (7.4%). The least used parts were rhizomes and sap both at 1.5% (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2.
Life forms of medicinal plant species used in the management of snakebites envenomation in Acholi, Teso and Karamoja sub-regions of Uganda
Fig. 3.
Plant parts used in the management of snakebites envenomation in Acholi, Teso and Karamoja sub-regions of Uganda
Medicinal plant preparation and administration
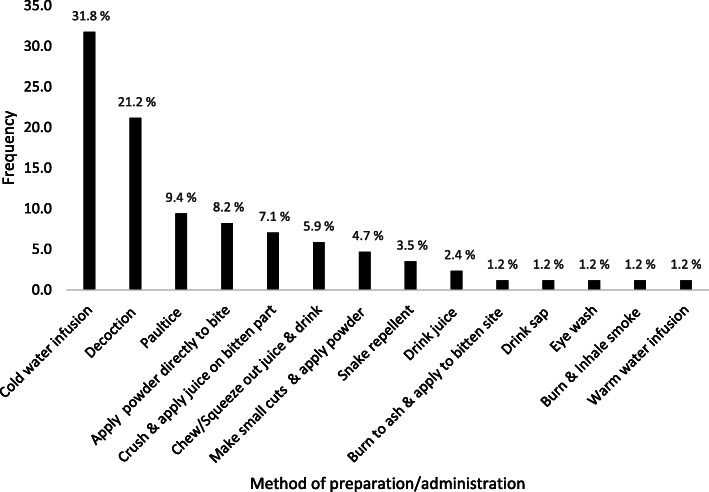
The methods of preparation and administration were grouped into thirteen categories. Most of the herbal medicines were prepared for oral administration (62.5%). The rest were administered topically (32.5%) with the exception of inhalation of smoke from burnt plant material (1.2%). The commonest methods of oral application were cold water infusions (31.8%), decoctions (21.2%) and chewing or squeezing juice from the plant material and drinking it (5.9%) (Fig. 4). The commonest topical methods of application were poultices (9.4%) and direct application of powders to the bitten site or juice (8.2%), followed by the application of powder to bite area after making small cuts with a razor blade (4.7%). Some of the plant species were used as snake repellents (3.6) and one specie was used for making an eyewash (1.2%) for cases of ocular envenomation by spitting cobras. One herbalist reported burning the plant material and making the patient inhale the smoke in cases where they were unconscious (1.2%). However, the herbalists were not aware of any specific modes of action of the medicinal plant species they used with the exception of a few species that acted as emetics (Table 2).
Fig. 4.
Methods of preparation/administration of the herbal medicines in the Acholi, Teso and Karamoja sub regions of Uganda
In the Ik community in Kaabong district, herdsmen, farmers and hunters usually moved with small quantities of G. dalenii powder as a quick remedy in case they were being bitten by a poisonous snake. In case of a snakebite, small cuts are made at the site and the powder applied. Generally, the consensus among the TMP was high in the relatively closed and isolated Ik community. Additionally, the medicinal plant species used by the Ik were generally unique to them and not used by the other communities in Kitgum, Kaberamaido and Serere districts. These included G. dalenii, E. longifolius, Cyathula uncinulata and Steganotaenia araliaceae.
Knowledge acquisition and transfer
Most herbalists acquired their knowledge on the use of medicinal plants for snakebite management from their parents and grandparents (80%) other relatives (12%). Two unique cases (8%) were registered. The first case involved the observation of self-medication in snakes by one herbalist. The said herbalist acquired the knowledge on the use of Microglossa pyrifolia for treatment of snakebites by observing a snake wounded in a fight with another snake. The injured snake reportedly recovered from its injuries after ingesting the leaves of M. pyrifolia. In the second instance, another herbalist who mainly uses the root of Opilia amentacea for all snakebite cases acquired this knowledge from the observation that the stems of O. amentacea had whitish scale-like appearance, akin to the scales of some snakes.
Type of snakebites treated
Cyathula uncinulata, Astripomoe amalvacea, Kalanchoe sp. and Hoslundia opposita were specifically mentioned as being used for treating puff adder bites. Euphorbia hypericifolia was also used for treating scorpion and spider stings. Microglossa pyrifolia was used for treating all types of snakebites except the puff adder bites. Bryophyllum delagoense and Steganotaenia araliaceae were used for treating cobra bites. In addition, S. araliaceae was used as first aid for all snakebites among the Ik only. Most of the plant species used were harvested from the wild (68.75%), whereas 24.24% were domesticated and 6.25% were both domesticated and wild. Thirty-seven (61.6%) of the documented plant species did not have any previous references about use in snakebite treatment literature. However, some of the plant species are from genera with many well-known plant species used for snakebite such as Solanum, Annona, Echinops, Euphorbia and Indigofera
Unidentified medicinal plant species used
An additional nine plant species were mentioned by the herbalists for treating snakebite envenomation in Kitgum district (Table 3). However, we were not able to collect voucher specimen for these species for identification for several reasons including wildfires that had destroyed some of their habitats, drought, insecurity near the Uganda Sudan border and difficulty in locating some of the species because they were naturally rare.
Table 3.
Unidentified plant species used for snakebite treatment
| Local name (Acholi) | Part used | Habit | Mode of preparation and administration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Obokoleb | T | R/B | Decoction |
| 2. Abangabanga | H | Sd | Chew |
| 3. Lalega dyel | S | R | Decoction |
| 4. Acilo | S | R/L | Decoction |
| 5. Amomo | S | R | Decoction |
| 6. Lacer | S | F/L | Decoction/bath |
| 7. Ngili | H | R | Decoction |
| 8. Te-okwero | S | R | Chew |
| 9. Kokobelle mol | S | L/Sp | Decoction |
T tree, H herb, S shrub, R root, B bark, L leaves, F flowers, Sp sap
Discussion
Even though most herbs were used singly, some of the herbalists prepared polyherbal formulations for use. One of the TMP disclosed his formula consisting of Pseudocedrela kotschyi, Gardenia ternifolia, Zanthoxylum chalybeum, Indigofera arrecta and Capsicum frutescens. The herbalists used different herbal formulations to treat their patients. These differences can be attributed to some variations in local flora of the regions, culture, training and the circumstances under which the patients presented. The most frequently cited plant species in this study were selected for farther evaluation of their antivenom potentials in vivo and their phytochemical composition. These experiments are on-going and the findings will be published in due course. The sustainable use of the plant resources raises concerns since most of them are harvested from the wild. To worsen matters, the roots of these plant species are the most widely used parts. Harvesting of roots is destructive to the plant species and is a threat to both the trade of the herbalists and the survival of the plant species. It is encouraging however to note that some herbalists had made attempts to domesticate some of the plant species they used by growing them in their backyards.
Although we reported that most of the plant species recorded in this study do not have any previous documentation for use in snakebite treatment literature, some unique cases stand out. We recorded for the first time the use of Opilia amentacea in the treatment of snakebite envenomation in Uganda. Interestingly, the same species is used in India for treating snakebite envenomation [21]. However, O. amentacea was only reported by a single renowned traditional healer commonly known as “Dr. Snake”. The use of O. amentacea was associated with the doctrine of signatures (DoS) or similarities. The selection of plant species for the treatment of particular conditions because of their resemblance to particular body organs is not a new concept. This DoS or similarities attributes the therapeutic properties of some plants to particular morphological characters or features they possess, i.e. “like treats like” [36]. This particular herbalist began using this plant because of the scale-like and dotted appearance of its bark and its creeping habit. This is the first report on the doctrine of signatures with O. amentacea with reference to snakebite. According to Bennett [37], the doctrine of signatures is found throughout the world and has had a long history of use. He further argues that considering the DoS from the classical morphological perspective has rarely led to the discovery of medicinal plants and the approach is therefore unproductive and largely untestable. The DoS cannot therefore be considered scientific [36, 37], although parts of its utility lie in facilitating the process of understanding the subjective, psychological, and spiritual dimensions of nature [38].
Another interesting observation was the routine use of prayers during healing. One particular healer was observed to always begin his plant collection routine in the bush with prayers. He prayed to God beseeching him to give the plant species their healing power before he begun harvesting. He professed the catholic faith and attributed his success to his God. This particular healer had a medicinal plant garden and a special treatment room/hut in which he treated his patients. He got official recognition with a certificate from the ministry of culture in Uganda as early as 1986. The citation of prayers by herbalists who profess Christianity during healing rituals has previously been reported in parts of Uganda such as the west [39]. Prayers form an integral part of the belief system and are believed to make the treatment successful.
The transfer of traditional knowledge is by word of mouth. The TMP identify and train particular children on the identification, preparation and administration of the herbs. We report a unique case of self-medication in snakes. This provides an insight into the potential antivenom properties of Microglossa pyrifolia. Although previous studies have reported cases of self-medication especially in primates such as chimpanzees [40, 41], we have not come across previous reports of self-medication in snakes. However, according to Shurkin [42], some lizards are believed to survive venomous snake bites by eating roots of particular plants. It is therefore not farfetched to consider self-medication in snakes.
According to the in-charge of Timu health centre II in Kaabong district, there were relatively many reports of snake bites in the Ik community, but there were few cases reporting to the health facility. Even those who reported to the health centre came several days after being bitten by snakes for supportive treatment after initially managing the snakebites with herbs. The health centre also did not have any antisera for treatment of snake bites.
Conclusion
TMP widely use several medicinal plant species for treating snakebite envenomation in the post-conflict sub-regions of Acholi, Teso and Karamoja in Uganda. There is a high consensus by herbalists in the Ik community on different plant species used. Most of the plant species are harvested from the wild, prepared as infusions and used orally. The knowledge of medicinal plant use is transmitted orally.
Methods
Study design and setting
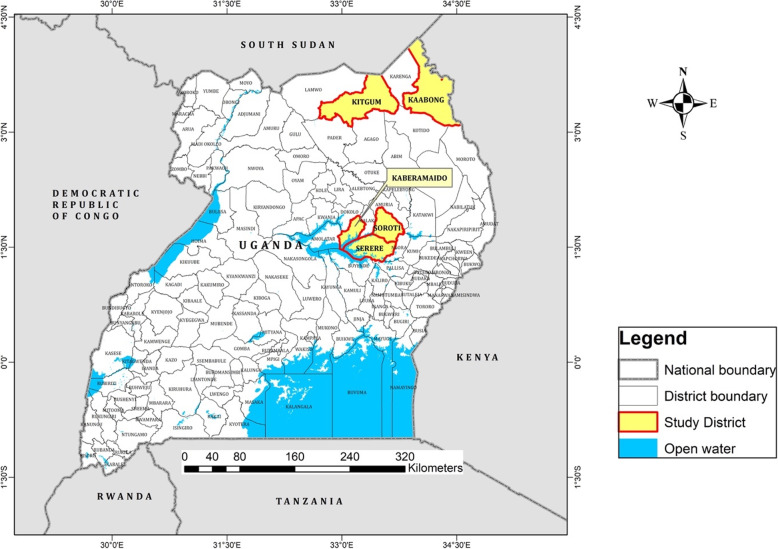
An ethnopharmacological study was conducted in the districts of Soroti in Mukura/Asuret sub-counties (1.7229° N, 33.5280° E), Serere in n Bugondo, Okulonyo & Kyere sub-county (4994° N, 33.5490° E), Kaberamaido, Anyara sub-county (1.6963° N, 33.2139° E) in the Teso sub-region, Kitgum, Namukora and Orom sub-counties (3.3397° N, 33.1689° E, Acholi sub-region) and Kaabong, Timu sub-county (3.5126° N, 33.9750° E, Karamoja sub-region) (Fig. 5). The data were collected between August and October 2017 using interviews with semi-structured questionnaires These areas have tropical and savanna type vegetation [43]. The study areas were selected because they are recovering from protracted LRA war; they are remote. Additionally, these areas have limited access to modern health facilities with antisera and have been reported to have frequent snakebites [44, 45].
Fig. 5.
Map of Uganda showing study sites
Characteristics of participants
Traditional medicine practitioners or herbalists with expertise in treating patients bitten by snakes were purposively selected and identified using the snowball technique [46]. In each of the study areas, there are associations of general traditional healers. Each of these associations has specialists such as traditional birth attendants, bone setters and those that treat snakebites within its ranks. Through these networks, we were able to get referrals to the specific snakebite treatment experts.
Plant collection and identification
Voucher specimens of the plant species mentioned in the study were collected using standard procedures [47] and taken to Makerere University herbarium for identification. The scientific names of the plant species were identified based on the plant list [48]. Plant families were verified using the angiosperm phylogeny group IV [49].
Data analysis
The data were analysed using simple descriptive statistics in Microsoft Excel 2019.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Makerere-Sweden bilateral research fellowship 2015/2020 for funding the study as well as Gulu University for providing an enabling environment for conducting the study. We also acknowledge the traditional medicine practitioners from the Ik community in Kaabong, Kaberamaido, Kitgum and Serere districts; the local leadership of the respective districts for their support in conducting this survey; research assistants Benjamin Okello, Emmanuel Onekanono, Lazarus Aryon, Anthony Oluka Eridu and Ronald Onen; and survey guides and language translators Denis Omongin, Evalyne Auma Opio, Alex Okwel from Timu Health centre II.
Authors’ contributions
OFD conceptualized the study and wrote the protocol under the guidance of BR, NJ and AG. OFD and AG conducted the ethnopharmacological survey, analysed the data and drafted the manuscript under the supervision of BR and NJ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded in part by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency 353 (Sida) and Makerere University under Sida contribution No: 51180060.
Availability of data and materials
Supporting data to this article is publicly available in the Mendeley data repository: Data, V2, 10.17632/g788hgn5t2.2
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from Gulu University research ethic committee (GUREC-003-20) prior to the study and the Uganda National Council of Science & Technology (UNCST, No. SS 5207). Permission was also obtained from the local authorities to conduct the study in the respective sites. Written prior informed consent was obtained from each of the participants before every interview.
Consent for publication
All participants referred to in this study gave their consent for publication
Competing interests
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Gutiérrez JM, Warrell DA, Williams DJ, Jensen S, Brown N, Calvete JJ, Harrison RA, Initiative GS (2013) The need for full integration of snakebite envenoming within a global strategy to combat the neglected tropical diseases: the way forward. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7: e2162–e2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.WHO . WHO guidelines for the production, control and regulation of snake antivenom immunoglobulins. Geneva: Switzerland; 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chippaux J-P. Snakebite envenomation turns again into a neglected tropical disease! J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2017;23:38. doi: 10.1186/s40409-017-0127-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Warrell DA. WHO, Guidelines for the prevention and clinical management of snakebite in Afrika. Africa, Brazzav: Reg. Off; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Warrell DA. Snakebite. Lancet. 2010;375:77–88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61754-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gold BS, Wingert WA. Snake venom poisoning in the United States: a review of therapeutic practice. South Med J. 1994;87:579–589. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199406000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Oliveira CZ, Maiorano VA, Marcussi S, Sant’Ana CD, Januário AH, Lourenço MV, Sampaio SV, França SC, Pereira PS, Soares AM. Anticoagulant and antifibrinogenolytic properties of the aqueous extract from Bauhinia forficata against snake venoms. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;98:213–216. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.12.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shah K, Sherstha J, Thapa C. Snakebite management guideline. Kathmandu: Epidemiology and Disease Control Division, Department of Health Services, Zoonoses Control Sub-section, Government of Nepal; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rajendran K, Shirwaikar A, Mehta M, Bharathi RV. In vitro and in vivo anti-snake venom (Daboia russelli) studies on various leaf extracts of Acalypha indica Linn. Int. J. Phytomedicine. 2010;2.
- 10.Ntume R, Anywar UG. Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used in the treatment of snakebites in Central Uganda. Curr Life Sci. 2015;1:6–14. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tabuti JR, Dhillion SS, Lye KA. Traditional medicine in Bulamogi county, Uganda: its practitioners, users and viability. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;85:119–129. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(02)00378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Das K. Medicinal plants for snake bite treatment-future focus. Ethnobot Leafl. 2009;2009:11. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Newman WJ, Moran NF, Theakston RDG, Warrell DA, Wilkinson D. Traditional treatments for snakebite in a rural African community. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1997;91:967–969. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1997.11813228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Owuor BO, Mulemi BA, Kokwaro JO. Indigenous snake bite remedies of the Luo of western Kenya. J Ethnobiol. 2005;25:129–141. doi: 10.2993/0278-0771(2005)25[129:ISBROT]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Owuor BO, Kisangau DP. Kenyan medicinal plants used as antivenin: a comparison of plant usage. J Ethnobiol Ethnomedicine. 2006; 10.1186/1746-4269-2-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Namukobe J, Kasenene JM, Kiremire BT, Byamukama R, Kamatenesi-Mugisha M, Krief S, Dumontet V, Kabasa JD. Traditional plants used for medicinal purposes by local communities around the Northern sector of Kibale National Park, Uganda. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;136:236–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.World Population Review (2020) No Title. https://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/uganda-population/.
- 18.Anderson J, Learch C, Gardner S. National survey and segmentation of smallholder households in Uganda. Solut: Underst. Their Demand Financ. Agric. Digit; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Van Acker F. Uganda and the Lord’s Resistance Army: the new order no one ordered. Afr Aff (Lond) 2004;103:335–357. doi: 10.1093/afraf/adh044. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ministry of Health Uganda, WHO (2005) Health and mortality survey among internally displaced persons in Gulu, Kitgum and Pader districts, Northern Uganda. Kampala, Uganda.
- 21.Alagesaboopathi C. Ethnomedicinal plants used for the treatment of snake bites by Malayali tribal’s and rural people in Salem district, Tamilnadu, India. Int J Biosci. 2013;3:42–53. doi: 10.12692/ijb/3.2.42-53. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vásquez J, Alarcón JC, Jiménez SL, Jaramillo GI, Gómez-Betancur IC, Rey-Suárez JP, Jaramillo KM, Muñoz DC, Marín DM, Romero JO. Main plants used in traditional medicine for the treatment of snake bites n the regions of the department of Antioquia, Colombia. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;170:158–166. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.04.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Emmanuel A, Ebinbin A, Amlabu W. Detoxification of Echis ocellatus venom-induced toxicity by Annona senegalensis Pers. J Complement Integr Med. 2014;11:93–97. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2012-0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Adzu B, Abubakar MS, Izebe KS, Akumka DD, Gamaniel KS. Effect of Annona senegalensis rootbark extracts on Naja nigricotlis nigricotlis venom in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;96:507–513. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.09.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Okello J, Ssegawa P. Plants used by communities of Ngai sub-county, Apac District, Northern Uganda. Afr J Ecol. 2007;45:76–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2028.2007.00742.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kamatenesi MM, Acipa A, Oryem-Origa H. Medicinal plants of Otwal and Ngai Sub Counties in Oyam District, Northern Uganda. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2011;7:7. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-7-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Agoro JW (1978) Crystalline caffeic acid derivatives and compositions and method for treating snakebite.
- 28.Hamill FA, Apio S, Mubiru NK, Mosango M, Bukenya-Ziraba R, Maganyi OW, Soejarto DD. Traditional herbal drugs of southern Uganda: Part III: Isolation and methods for physical characterization of bioactive alkanols from Rubus apetalus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;87:15–19. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(03)00097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Samy RP, Thwin MM, Gopalakrishnakone P, Ignacimuthu S. Ethnobotanical survey of folk plants for the treatment of snakebites in Southern part of Tamilnadu, India. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;115:302–312. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tugume P, Kakudidi EK, Buyinza M, Namaalwa J, Kamatenesi M, Mucunguzi P, Kalema J. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plant species used by communities around Mabira Central Forest Reserve, Uganda. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2016;12:1–28. doi: 10.1186/s13002-015-0077-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ushanandini S, Nagaraju S, Harish Kumar K, Vedavathi M, Machiah DK, Kemparaju K, Vishwanath BS, Gowda TV, Girish KS. The anti-snake venom properties of Tamarindus indica (leguminosae) seed extract. Phytother Res. 2006;20:851–858. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Anywar G, Oryem-Origa H, Kamatenesi Mugisha M. Wild plants used as nutraceuticals from Nebbi district, Uganda. European J Med Plants. 2014;4:641–660. doi: 10.9734/EJMP/2014/7634. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ngoupaye GT, Bum EN, Ngah E, Talla E, Moto FCO, Taiwe GS, Rakotonirina A, Rakotonirina SV. The anticonvulsant and sedative effects of Gladiolus dalenii extracts in mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2013;28:450–456. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.d’Avigdor E, Wohlmuth H, Asfaw Z, Awas T. The current status of knowledge of herbal medicine and medicinal plants in Fiche, Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2014;10:38. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-10-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Oryema C, Bukenya-Ziraba R, Omagor N, Opio A. Medicinal plants of Erute county, Lira district, Uganda with particular reference to their conservation. Afr J Ecol. 2010;48:285–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2028.2009.01147.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Court WE. The doctrine of signatures or similitudes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1985;6:225–227. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(85)90104-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bennett BC. Doctrine of signatures: an explanation of medicinal plant discovery or Dissemination of knowledge? Econ Bot. 2007;61:246–255. doi: 10.1663/0013-0001(2007)61[246:DOSAEO]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Richardson-Boedler C. The doctrine of signatures: a historical, philosophical, scientific view (II) Br Homeopath J. 2000;89:26–28. doi: 10.1054/homp.1999.0349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kamatenesi Mugisha M, Asiimwe S, Namutebi A, Borg-Karlson A-K, Kakudidi EK. Ethnobotanical study of indigenous knowledge on medicinal and nutritious plants used to manage opportunistic infections associated with HIV/AIDS in western Uganda. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;155:194–202. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huffman MA. Chimpanzee self-medication: a historical perspective of the key findings. In: Hosaka K, Zamma K, Nakamura M, Itoh N, editors. Mahale Chimpanzees 50 Years Res. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2015. pp. 340–353. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Huffman MA. Current evidence for self-medication in primates: A multidisciplinary perspective. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1997;104:171–200. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644(1997)25+<171::AID-AJPA7>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shurkin J. News feature: animals that self-medicate. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:17339–17341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419966111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Thomas AS. The vegetation of the Karamoja district, Uganda: an illustration of biological factors in tropical ecology. J Ecol. 1943:149–77.
- 44.Wangoda R, Watmon B, Kisige M. Snakebite management: experiences from Gulu Regional Hospital Uganda. East Cent. Afr J. Surg. 2004;9(1):82–6.
- 45.Nabatanzi V. Kamuli, Mbende, Gulu top in number of snakebites. New Vis. Uganda’s Lead. Dly: New Vision; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Browne K. Snowball sampling: using social networks to research non-heterosexual women. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:47–60. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000081663. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Martin GJ (1995) Ethnobotany: a methods manual. 10.1007/978-1-4615-2496-0.
- 48.The plant list (2020) The plant list. http://theplantlist.org.
- 49.Angiosperm phylogeny group IV (2020) Angiosperm phylogeny group IV. http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Supporting data to this article is publicly available in the Mendeley data repository: Data, V2, 10.17632/g788hgn5t2.2