Abstract
Previously documented arguments, in favor of the suspected impact of a seed and soil mechanism, in the development and progression of isolated pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinomas (isPM) are: (1) uniform and independent from the side of the primary tumor distribution of isPM within the pancreas and, (2) the similar survival rates for singular and multiple isPM. In addition, the present study adds new arguments that further confirm the importance of an seed and soil mechanism in isPM: (1) Within the singular isPM, the size of the metastasis does not affect the overall survival; (2) Within the group of multiple isPMs, the overall survival does not depend on the number of metastases; (3) For synchronous and metachronous isPM, survival rates are also not different, and (4) Within the group of metachronous isPM there is also no correlation between the overall survival and interval until metastases occurs. This unusual ineffectiveness of otherwise known risk factors of solid cancers can be explained plausibly by the hypothesis of a very selective seed and soil mechanism in isPM. It only allows embolized renal carcinoma cells in the pancreas to complete all steps required to grow into clinically manifest metastases. In all other organs, on the other hand, the body is able to eliminate the embolized tumor cells or at least put them into a dormant state for many years. This minimizes the risk of occult micrometastases in distant organs, which could later—after isPM treatment—grow into clinically manifest metastases, so that the prognosis of the isPM is only determined by an adequate therapy of the pancreatic foci, and prognostic factors, such as total tumor burden or interval until the occurrence of the isPM remain ineffective.
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma metastasis, isolated pancreatic metastases, seed and soil mechanism, treatment results
Introduction
The term “seed and soil mechanism” (SSM) coined by Paget back in 1882 (1) concisely describes the particular interaction between embolized tumor cells and potential host organs. After a diffuse, systemic tumor cell dissemination emanating from a primary carcinoma, not all of these cells necessarily mature into manifest metastases. Instead, metastasised tumor cells can only develop into clinically manifest metastases, if the metastasised tumor cells (seed) and cells of the host organ (soil) possess distinct biological properties that exactly match each other. If this is not the case, the metastasised cells will be destroyed. The occurrence of clinically manifest metastases is thus preceded by tumor cell selection.
In human medicine, there are essentially three observations supporting this theory: (1) Paget's main argument came from the clinical observation that individual primary carcinomas—though diffusely spreading their tumor cells through the blood stream—did not metastasise diffusely in all host organs, but apparently had predisposition sites (e.g., breast carcinoma and metastases to the bone). (2) A further support of an SSM theory is the relative resistance of certain individual organs or organ systems, such as muscle or spleen, to metastases. This behavior suggests that local factors that can impede the development of metastases are effective in these organs. (3) Decades later, with the absence of otherwise expected countless lung metastases after peritoneo-venous shunt (2, 3) that was used to treat malignant ascites, the first clinical argument was added.
It was, therefore, surprising to discover (4, 5), that a clearly defined, albeit extremely rare tumor entity exists, whose development and progress can be largely attributed to the hypothesis of an exquisite SSM: isolated pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma (isPM).
Another peculiarity of the isPM, which was already shown in 2006 (6) is that neither singular or multiple occurrence of the isPM, nor a synchronous or a metachronous occurrence of the metastases influenced the treatment outcome. Therefore, the aim of the literature analysis in this study was to investigate further and more extensively this unexpected behavior with regards to a possible involvement of SSM and discuss it in the context of known arguments on the impact of a SSM on isPM.
Material and Methodology
In the present investigation the term isPM was applied to designate those very rare cases of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in which singular or multiple metastases occurred in the pancreas exclusively, both synchronously or metachronously to the primary RCC and definitively or at least over a longer period (>0.5 year).
When presenting previously published arguments (5, 6), the outcomes of previous calculations are reproduced. A literature compilation was prepared for the current investigations on the significance of the time of occurrence and the number and size of isPMs. The observations of synchronous metastases were then compared with metachronous metastases and the singular ones were compared with multiple isPMs. The literature search (Figure 1) was based on the MEDLINE Registry using the key words “renal cell carcinoma and pancreatic metastasis” and covered the period of 67 years, i.e., from 1952 [first description of an isPM (7)] until the end of 2019.
Figure 1.
Search and selection strategy.
From these publications, only patients with isPMs without metastases in other organs at the time or within 6 months before or after isPM diagnosis were selected provided that these were confirmed by tissue diagnosis. These observations were separated in those with and without individual patient data. For calculations of the influence of solitary vs. multiple metastases only those isPMs were considered in which: (1) the exact number of lesions were specified or (2) those that used wording which was clearly indicative of singularity or multiplicity. In order to separate synchronous and metachronous isPM, analogous selection criteria were applied. Only observations containing unambiguous numerical data were used to investigate the influence of the number and size of metastases. For defining the site of the metastatic lesions, only solitary isPMs that were unequivocally assignable to one specific anatomical part of pancreas (by preoperative imaging, the surgeons report, or the resected specimen) were considered. In the few cases of one single institution repeatedly reporting their isPM observations only, the most detailed report was selected for the analysis. In a retrospective literature review, not every report contained data on all variables evaluated. As a result, the number of calculable observations for subset analyses was reduced. Therefore, the actual number of reports and the references providing information on a given variable are specified.
The literature search revealed a total of 1,034 isPM observations (7–223): 527 casuistic notes were juxtaposed with 507 observations from single center and multicentre studies summaries. All continuous data are presented as means and standard deviations. To determine the influence of RCC side on the site of the metastases within the pancreas—a categorical variable—Fisher's exact test was applied; to determine an equally/unequally distribution of isPM in right side (head) or left side (corpus and cauda) of the pancreas—a dichotomous variable—a non-parametric binominal distribution test was carried out. The differences in survival among subgroups were compared by the log-rank test. A Cox regression analysis was applied to determine the influence of possible risk factors on survival, such as number and diameter of metastasis and the time interval until the occurrence of isPM. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Arguments for a “seed and soil” mechanism.
The Metastatic Pathway of isPM
Since the first casuistic notes on isPM, it has been discussed which metastatic mechanism (MM) could lead to the unusual metastatic behavior, with local MM being discussed first. On one hand, a local lymphogenic metastatic MM (28, 72, 85, 90, 143, 165, 177) with a retrograde lymph drainage (158) toward the pancreas as a consequence of a tumorous blockade of retroperitoneal lymph nodes (28, 85, 120, 143, 165) and on the other hand a local venous MM toward the pancreas (28, 72, 85, 90, 165, 177), which is supposed to take place via draining collateral veins of hyper-vascularised tumors (28, 85, 90, 120, 158), or via pre-existing porto-renal anastomoses (90, 158, 224), irrespective of whether renal vein thrombosis was present (28).
The second possible MM is the systemic haematogenic one after intravasation of tumor cells into the circulatory system, which is the case for the majority of organ metastases of solid tumors. The relative importance of the two possible MMs—local or systemic—in the development of isPM can be determined by epidemiological studies. In a systemic haematogenic pathway, the metastases must be diffusely distributed in the pancreas following a uniform distribution with the blood flow, whereas in the local venous/lymphatic pathway, a dependence of the metastasis localization in the pancreas on the side of the primary RCC will occur. Considering that, the left-sided RCC should metastasise more frequently into the nearer corpus and cauda area and right-sided RCC into the nearer caput. Our working group carried out such an epidemiological study for the first time in 2006 on the 236 reported isPM observations (6). Two repeat studies have been subsequently conducted, one on the larger collective of reported isPM observations (N = 814) until 2018 (5) and the current study on the 1,034 isPM observations until the end of 2019. Based on the latest research, Table 1 shows the distribution of the reported isPMs between caput pancreatis (48.4%) and corpus and cauda (51.6%), respectively. When this distribution pattern is compared with the volume distribution of the pancreas, 46% in the caput and 54% in the corpus and cauda (225), determined from anatomical studies, no preference for one pancreatic side can be demonstrated (P = 0.236). The distribution of isPM in the pancreas is completely uniform and correlates only with the volume distribution, and therefore with the blood flow. Table 2 summarizes the results of the analysis regarding the relationship between the side of the RCC and the distribution of metastases within the pancreas, with the result that the distribution of isPM in the pancreas was independent of the side of the former RCC (P = 0.863).
Table 1.
Distribution of isPM within the pancreas (right side = pancreas head; left side = corpus and cauda pancreatic) (N = 256).
| Side | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Right side | 124 | 48.4 |
| Left side | 132 | 51.6 |
Table 2.
Correlation between the side of the primary renal cell carcinoma and the location of metastases within the pancreas (N = 162).
| Localization of the isPM in the pancreas | Side of the renal cell carcinoma | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Both sides | |
| Caput | 47 | 38 | 2 |
| Corpus | 19 | 20 | 1 |
| Cauda | 21 | 13 | 1 |
| Total | 87 | 71 | 4 |
Summing up, these results proved that isPM were evenly distributed over the pancreas and, above all, that there was no dependence on the side of the primary RCC. In the meantime, the latter result was confirmed by a large single institution publications (N > 15) (148, 186, 209, 226), which also highlighted the independence of metastasis localization in the pancreas from the primary RCC side. The analysis of the reported isPM thus provided a result that speaks for the dominant importance of a systemic MM. Following the uniform distribution of tumor cells with the blood stream only, this MM will create a uniform distribution of metastasis within the pancreas and also a distribution which is independently from the side of the RCC.
In addition, the mode of distribution of the few metastases recorded (and successfully treated) between primary renal cancer surgery and subsequent pancreatic surgery (25, 27, 61, 68, 69, 72, 87, 105, 129, 136, 139, 140, 150, 160, 166–168, 173, 175, 189, 193, 204, 211, 223) also shed light on the impact of a systemic hematogenous metastatic pathway in isPM. The 78.0% of these 41 metastases were unequivocally of systemic hematogenous origin. Metastases which might have reflected a local tumor cell spread (e.g., retroperitoneal lymph node metastases, recurrent growths in the former surgical field and contralateral kidney or adrenal metastases), by contrast, carried little significance as they were reported only nine (41) times (22.0%) (27, 105, 136, 140, 166, 175, 211). A comparable dominance of the systemic hematogenous pathway was also documented in the reports detailing the fate of patients after successful isPM surgery. Of 116 metachronous metastases (6, 16, 28, 35, 47, 57, 58, 69, 70, 72, 74, 82, 84–86, 90, 94, 108, 112, 118, 123, 126, 128, 136, 139–141, 149, 159, 160, 166, 168, 173, 175, 176, 178, 180, 181, 183, 187, 198, 203, 204, 218) 76.7% were undoubtedly of systemic hematogenous origin and in no more than 23.3% of the cases, a local pathway had to be taken into consideration (72, 84, 108, 139, 140, 160, 166, 175, 180, 181, 183, 187, 198). In sum, for metastases that occurred both before and after pancreatic surgery those attributable to a systemic hematogenous spread predominated. This corroborates with the idea that systemic hematogenous spread plays a considerable role in isPM (4).
However, the established high significance of a systemic haematogenic MP in the occurrence of isPM raises a fundamental question. Why did a systemic MP lead exclusively to metastases in the pancreas, while all other organs remained free of metastases? Considering the small amount of blood flowing through the 120–180 g of pancreatic tissue, it was very unlikely that all embolized tumor cells are transported exclusively into the pancreas by a pure chance. This is even more true if the multiple metastases observed in about 40% of the patients are taken into account (4), which required repeated synchronous or metachronous tumor cell embolisms. The only known mechanism that can explain this, plausibly at present, is the effect of a pronounced SSM, which permits the colonization of metastasised tumor cells and their growth into manifest metastases exclusively in the pancreas, and either definitively prevents them from settling in all other organs or at least causes years of tumor dormancy (227, 228).
Singular and Multiple isPM, Number and Size of Metastases
Already in 2006, in an analysis of 236 isPM observations, our working group assumed (6) that overall survival (OS) of singular and multiple pancreatic metastases in radically operated isPMs were not divergent and, contradicting individual casuistic publications (96, 99, 165, 176), derived from this fact that not only singular but also multiple isPMs had to be radically treated (139). This result was confirmed in the analysis performed in 2018 (5). On the basis of this result, the 1,034 isPM reported so far were analyzed again to investigate whether this unusual result was related to the postulated SSM. The analysis revealed 406 observations in which singular (N = 244) or multiple (N = 162) occurrences of isPM were undoubtedly mentioned [singular isPMs: (6–8, 10–16, 18, 20–23, 27–30, 32, 38, 39, 41, 43, 44, 46, 47, 49, 51, 52, 54–56, 58, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68–75, 78–80, 82, 85–90, 92, 93, 98, 101, 102, 104, 106–112, 115, 118, 120– 124, 127, 129, 134–137, 140, 141, 146, 149–151, 153, 156, 158–161, 163, 165, 167, 168, 172, 178, 181, 183, 188, 193, 194, 197, 198, 201–204, 206, 208, 210, 212, 214, 216–223); multiple isPMs: (6, 16, 17, 19, 24, 25, 31, 33, 35–37, 40, 42, 45, 48, 53, 57, 63, 65, 67, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 77, 80, 81, 83, 85, 86, 88–91, 95, 97, 99, 102–104, 108, 112, 114, 117, 119, 121, 123, 131, 133, 136, 138–140, 145, 147, 149, 150, 152, 160–162, 166, 169, 170, 173, 174, 180, 181, 189, 194, 196, 203–205, 211, 212, 215, 216, 218, 220)]. The comparison of the two groups (Figure 2) further confirmed the similar survival times observed in singular and multiple metastases (P = 0.350). This result was confirmed by four single institutions (148, 177, 184, 186), one multicentre report (182), and a literature covering the last 10 years (194) which found that the presence of singular or multiple pancreatic metastases had no significant influence on survival.
Figure 2.
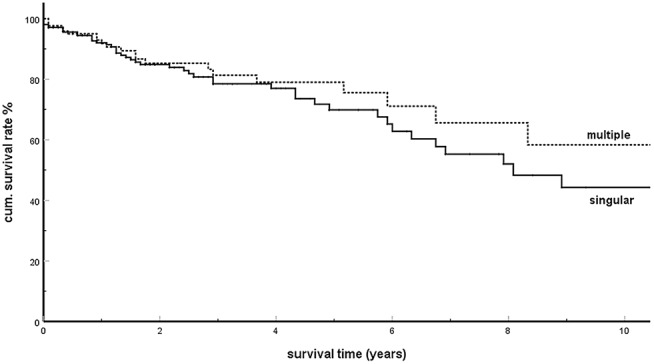
Solitary vs. multiple isPM: Kaplan Meier survival curves (p = 0.350).
In order to further clarify the relationship between tumor volume and survival in isPM, the direct correlation of OS and tumor diameters within the subgroup of singular isPM (N = 244) and the correlation of OS and the number of pancreatic metastases within the group of multiple isPM (N = 162) was investigated (Table 3). Neither the diameter of the singular nor the number of multiple isPMs proved to be relevant prognostic factors (p = 0.423 or 0.754). For “size” of isPM this result is confirmed by two single institution (148, 184) and one multicentre report (182) and a literature review of the last 10 years (194). In summary, as size and number of metastases define the tumor burden both investigations again show that in case of the isPMs the outcome does not depend on the overall tumor burden at the start of therapy.
Table 3.
Univariate Cox proportional hazards model for overall survival.
| Variable | N | Mean | SD | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size of metastasis (mm) | 125 | 35.9 | 20.9 | 1.009 | 0.988–1.030 | 0.423 |
| Number of metastases | 83 | 3.2 | 1.7 | 0.944 | 0.661–1.350 | 0.754 |
| Time interval (years) | 363 | 10.1 | 6.3 | 1.005 | 0.971–1.040 | 0.788 |
N, number of cases with adequate data; SD, standard deviation of mean.
To the best of our knowledge, the only explanation for this unusual behavior of isPM with an outcome independent of tumor volume at the start of therapy is a selective SSM, which only allows the growth of metastasised tumor cells to manifest metastasis in the pancreas and completely prevents it in all other organs or at least blocks it for years. So regardless of whether the overall tumor burden and dependent number of metastasized tumor cells are small or great, in case of isPM, the human body can render harmless or eliminate these cells in all organs with the exception of the pancreas. So, the prognosis of the isPM is only determined by adequate therapy of the only remaining pancreatic foci, and the factor “total tumor burden” remains ineffective.
Synchronous and Metachronous Metastases in isPM
In 2006, our working group pointed out another special feature of isPM (6): the OS was identical for synchronous and metachronous isPM after adequate therapy. This behavior then led to the conclusion that synchronous isPM should also be treated radically. Therefore, for the first time, the striking result of not differing outcomes following treatment for synchronous and metachronous metastases will be analyzed with regards to the effectiveness of an SSM.
Among the 1,034 isPM observations, there were 446 in which a synchronous or metachronous occurrence was undoubtedly mentioned. Of these, 30 isPMs were synchronous compared with 416 metachronous ones [synchronous isPMs: (8, 10, 14, 15, 19, 20, 23, 35, 48, 50, 57, 65, 82, 86, 88, 94, 101, 102, 108, 112, 118, 121, 137, 156, 173, 178, 181, 204, 221); metachronous isPMs: (6, 7, 9, 11–13, 16–18, 21, 22, 25–34, 36–47, 49–59, 61, 62, 64, 66–80, 83–93, 95, 97–99, 102–108, 111–115, 117, 119–124, 126–129, 131–136, 138, 140, 141, 143, 145–147, 149–153, 155, 158–162, 165, 167– 170, 172–176, 180, 181, 183, 187–189, 193, 194, 196–198, 201–206, 208, 210–212, 214–218, 220, 222, 223)]. Figure 3 shows the result of the comparison of the cumulative survival rates (SR) between synchronous and metachronous isPMs: with cumulative 5-years SR of 0.741 and 0.740, respectively, the SRs between these two groups do not differ significantly (P = 0.790).
Figure 3.
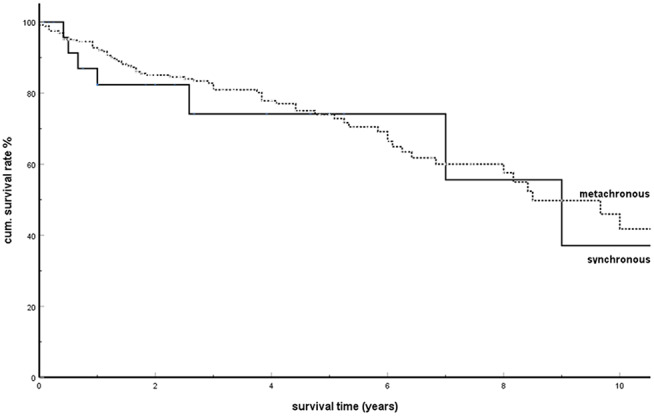
Synchronous vs. metachronous isPM: Kaplan-Meier survival curves (p = 0.790).
In a further study, the SRs were calculated and compared in four subgroups determined by the interval until the occurrence of pancreatic metastases (1. metastases within 2 years; 2. between 3 and 5 years; 3. between 6 and 10 years; and 4. metastases >10 years after the tumor nephrectomy). Figure 4 shows these results. There was no significant difference between the SRs among these groups (P = 0.339). The analysis of the influence of the time interval from tumor nephrectomy to the occurrence of metastases in metachronous isPMs on the survival (Table 3) finally provided a consistent supplementary result. The time interval was not detected as a parameter relevant for the prognosis (P = 0.788).
Figure 4.
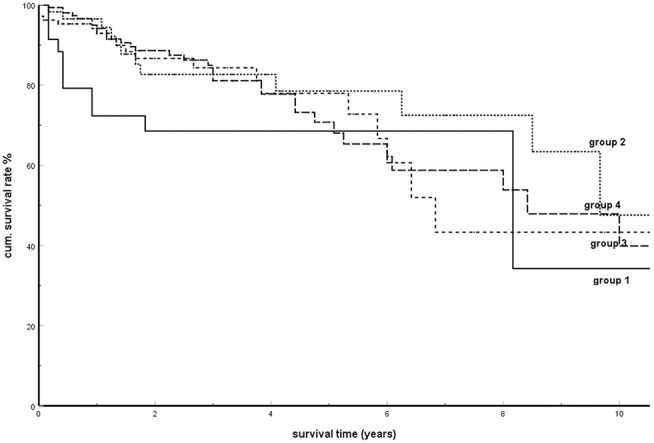
Kaplan-Meier survival curves for metachronous isPM according to interval between tumor nephrectomy and isPM detection (Group 1: <2a; group 2: 3–5a, group 3: 6–10a; group 4: >10a; p = 0.339).
In summary, this analysis showed that the factor “time of occurrence of metastases” had no influence on OS both when comparing synchronous with metachronous metastases and within the group of metachronous isPM. Comparable results were reported in single institution (177, 184) and multicentre reports (182), as well as in two literature reviews (142, 194) and in a review of total pancreatectomies in isPM patients (229), which registered no dependence of the results on the interval after a nephrectomy.
According to current knowledge, the unusual behavior of isPM can be indeed explained by an SSM. Regardless of when, depending on the aggressiveness of primary tumor growth, systemic tumor cell dissemination occurs, the organism is able to eliminate these cells in all organs except the pancreas or at least put them into a dormant state for many years, so that the prognosis of isPM is only determined by adequate therapy of the pancreatic foci, and the “interval” factor remains ineffective too.
Discussion
Clinical Presentation
The RCC is the ninth most common malignant tumor, with over 330,000 new cases each year (230). At the time of diagnosis, 20–30% of those affected already were in the generalization stage (181, 182, 195), and 15–25% of the curatively operated patients will subsequently develop metastases (136, 158, 182, 190, 231) in lung, bone, liver and brain (139, 157, 158, 176, 190, 195, 200, 232). A special feature of RCC, occurring in about 20%, is a protracted course with long-term phases of low tumor progression or even stability for many years (136, 157, 176, 181, 193, 231, 233). The risk of developing metastases more than 10 years after RCC surgery has been reported to be 6.4 (157) to 11% (232). This group with protracted course also includes the exquisitely rare entity of isPM.
Treatment Results
In addition to the exclusive occurrence of pancreatic metastases over many years, other distinctive features of isPMs are (5, 184, 220) (Table 4) late occurrence of metastases [about 10 years after the operation of the RCC (105, 120, 139, 180, 190)], frequent multiple occurrence (40%), and an unusually favorable prognosis for metastatic surgery with a 5-years survival rate of 73%. Reported 5-years SRs vary from 43 to 100% [Thompson 43% (88), Madkhali 50% (209), Tosoian 52% (184), Bassi 53% (105), Konstandinidis 61% (148), Schwarz 63% (182), Sweeney 65% (234), Strobl 67% (235), Ito 70% (207), Fikatas 71% (195), Chatzizacharias 71% (200), Hung 73% (164), Law 75% (108), Sohn 75% (95), Kimura 77% (177), Yuasa 79% (192), Grippa 80% (122), Zerbi 88% (139), Bahra 100% (132)]. A possible explanation for the unusual favorable treatment results could provide the postulated effect of a specific SSM which is effective in isPM. As this SSM absolutely prevents the settlement of embolized tumor cells in all extrapancreatic sites (or at least forces them into a dormant state), this implicates that the successful resection of isPM constitutes the radical elimination of all active tumor tissue and thus inevitably leads to favorable results (in context with the favorable prognosis of treated isPM, those studies (192, 236, 237) are noteworthy that showed that in diffuse metastasing RCC the concomitant presence of pancreatic metastases generally had a positive prognostic relevance). Depending on the site of isPM in head, body or tail or diffuse distribution, and on the number of metastasis within the pancreas standardized surgical techniques are recommended in form of duodeno-pancreatectomies, distal pancreatectomies, and total pancreatectomies. It is, however, remarkable that the 50 atypical local resections performed, provided a correct R0 resection was performed (51, 70, 72, 105, 109, 113, 121, 139, 140, 143, 147, 160, 166, 177, 181, 182, 186, 194, 209, 222), brought forth survival results which did not differ from standard operative procedures (Figure 5, P = 0.368). These results were confirmed by two institutional reports (166, 177) and one literature review of the last decade (194). As standard operative procedures differ from atypical local resections particularly in the greater extent of lymphatic dissection in the former, the identical outcome again demonstrates a minor impact of a lymphogenous tumor cell propagation in isPM. These treatment results emphatically prove that isPM is not a random, first manifestation of a just beginning generalization stage, but an independent, special course of the metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) caused by an SSM.
Table 4.
Analysis of literature review of 1,034 isolated pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma (7–223).
| Variable | Data | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years; N = 765) | 63.2 (9.7) | |
| Sex (m:f) | 423:359 | 54:46 |
| Synchronous:metachronous | 30:416 | 7:93 |
| Time to onset (years; N = 446) | 9.6 (6.7) | |
| Multiple (N = 406) | 162 | 40 |
| Localization (head, body, tail) | 124:55:77 | 48:21:30 |
| Size (mm; N = 245) | 37.5 (20.8) | |
| Peripancreat. lymphnodes (N = 378) | 19 | 5 |
| Surgery:DP:dP:tP:loc Res* (N = 651) | 248:244:109:50 | 38:37:17:8 |
| Histology (clear cell:non-clear cell) | 252:5 | 98:2 |
| Actuarial 5-years survival (N = 409) | 73 |
DP = duodenopancreatectomy; dp = distal pancreatectomy; tp = total pancreatectomy; loc Res = enucleation and segmentresection. N = number of observations with adequate data (standard deviation of mean).
Figure 5.
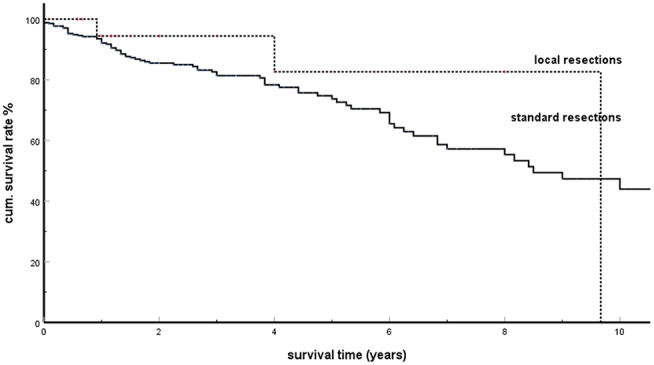
Local resections vs. standard resections in isPM: Kaplan-Meier survival curves (p = 0.368).
For many years, surgical removal was the only therapeutic option for isPM (6). In the recent decades however, dramatic and encouraging changes have been made regarding the medical treatment of mRCC. Targeted therapies with multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors, MTOR inhibitors, VEGF inhibitors and immunotherapies proved to be highly effective in mRCC (238–243). The improvement also concerned the results of medical treatment of the few isPM patients reported so far (163, 178, 190, 244–247). Future prospective studies will have to show the significance of surgical or drug therapy, or combinations of both, for respectable isPM (166, 182, 186, 191).
Metastases Recurrence (Table 5)
Table 5.
Number of recurrence (N) following treatment of isPM and number of affected organs (cases at risk).
| Recurrence organ sites | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| All sites | 116 (265) | 43.7 |
| One organ metastasis | 79 (116) | 68.1 |
| Pancreas | 17 | 21.5 |
| Non-pancreas | 62 | 78.5 |
| Multiple organs metastases | 37 (116) | 31.9 |
| 2-organs | 19 | |
| 3-organs | 6 | |
| Multiple | 12 |
Out of 265 patients with detailed follow up information in a total of 116 (43.7%) (6, 16, 28, 35, 47, 57, 58, 69, 70, 72, 74, 82, 84–86, 90, 95, 96, 104, 108, 112, 118, 123, 126, 128, 136, 139–141, 149, 159, 160, 166, 168, 173, 175, 176, 178, 180, 181, 183, 187, 198, 203, 204, 218), tumor progression with new distant metastases was observed after a mean disease free interval of 29.3 months (SD 28.1; min 3 max 120 months). The high recurrence rate is confirmed in single- and multicentre reports, reporting on rates of 39–100% [Fikatas 39% (195), Crippa 40% (122), Zerbi 43% (139), Anderson 53% (213), Benhaim 55% (186), Schwarz 60% (182), Santoni 67% (190), and Madkhali 100% (209)]. In no <68.1% of cases, the further recurrence occurred in just one single organ and 21.5% of these were observed as anew isPM in the pancreatic remnant. This result reveals a special feature of isPM: a biological stability of the tumor cells lasting for years and leading, in case of recurrence, to the persistence of the oligometastatic course in a high percentage of cases and even to the occurrence of anew isPM with still favorable prognosis (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
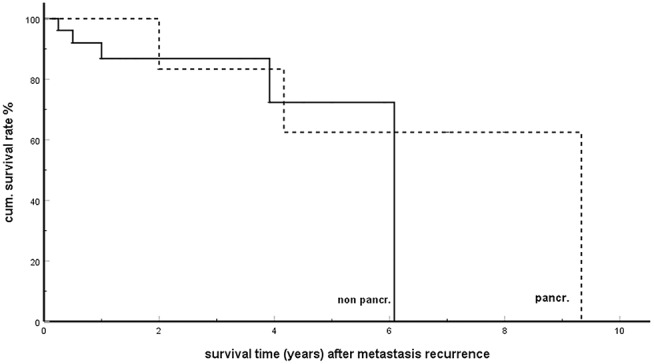
Single organ metastasis recurrence in pancreas (pancr) and in non-pancreatic organs (non-pancr); Kaplan-Meier survival curves (p = 0.423).
The distribution pattern of the subsequently formed distant metastases in different host organ demonstrated a further unusual behavior of the isPM. Though endocrine organs comprise <2% of the volume of the great metastatic organs (liver, bone marrow and brain; Table 6) no <10.3% of the later metastasis (16, 27, 35, 84, 97, 118, 140, 160, 173, 180, 181) were localized in the endocrine system (thyroid 7, adrenal 3 and pituitary gland 2 cases, each). This data suggests a particular preference for endocrine organs as later distant metastases sites in these isPM patients.
Table 6.
Approximate volumes of different metastatic host organs (ml).
| Endocrine organs | Non-endocrine organs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyreoidea | 50 | Liver | 1,200 |
| Adrenal gland | 15 | Brain | 1,400 |
| Pituitary | 2 | Bone marrow | 2,600 |
| Total | 67 (1.2%) | 5,200 | |
Metastatic Mechanism and SSM
Although extensive literature on isPM exists, to our best knowledge, no other investigation has been published which explicitly explores the importance of a possible underlying SSM in this entity.
Our working group hypothesized in 2006 that in isPM “the tumor cells have a high affinity for the pancreas parenchyma” (6). We have since conducted the only known studies in 2018 (4) and 2019 (5) which demonstrated that the pattern of distribution appears to support our hypothesis of a high impact of an SSM in isPM. The more extensive analysis now presented confirms these results and provides additional evidence that there are at least two chains of arguments, which may indicate a high impact of an SSM in isPM: (a) the already suspected mode of distribution of isPM in the pancreas, and (b) newly added the ineffectiveness of risk factors known to influence the prognosis of metastatic solid tumors.
Mode of Distribution of isPM and SSM
First of all, the results as stated in section “The metastatic pathway of isPM" once more proved the even distribution of isPM in the pancreas, and in particular, the independence of the metastatic site within the pancreas from the side of the primary RCC. This suggests a high significance of the systemically haematogenic MM in isPM, as the only mechanism that can bring about an even distribution of metastasis in the pancreas and a pattern of distribution which is independent from the side of the RCC. However, if metastases occur exclusively in the pancreas despite systemic cell dissemination, while all other organs remain free of metastases, this can only be explained by a selection process triggered by an SSM. This allows embolized tumor cells to mature into manifest metastases only in the pancreas, while they are not capable of metastasis formation in all other organs. The observed results thus provided a clue for both: a dominant role of a systemic haematogenic MM and a subsequent very effective SSM (4). This only leaves a subordinate significance, if any, for the local lymphatic or venous pathway, which is further underlined by the rare involvement of the lymphatic system in isPM (177). Only in 4.0% of isPM specimen lymph node metastases were present at the time of tumor nephrectomy (57, 143, 163, 186, 187). More importantly, in the rare lymphatic pathway the isolated occurrence of pancreatic metastases also requires an SSM, which allows the settlement of tumor cells and their growth to metastasis exclusively in the pancreas. Only such an elective acting SSM can explain the complete absence of soft tissue metastases in the entire area between the former renal bed and the pancreas and the rare (5.0%) occurrence of peripancreatic lymph node metastases in isPM (105, 108, 116, 139, 148, 166, 177, 182, 184, 186, 188, 189, 209).
The equally low significance of a local venous MM in isPM is supported by the seldom occurrence (10.3%) of a tumorous infiltration of renal veins [Category IIIb; (27, 57, 68, 73, 90, 118, 141, 143)], a prerequisite for a venous flow reversal toward the pancreas. In general, in the case of locally venous MMs, when renal-portal anastomoses lead to the dissemination and colonization of tumor cells into the pancreas, the hepatopedal flow in the portal vein system should transport the blood and the tumor cells it carries in the liver too, with a subsequent increased risk of occurrence of liver metastases. But this was not the case as only in 8.7% of the casuistic reports later on hepatic metastasis were reported (6, 16, 70, 74, 85, 86, 90, 123, 139, 140, 159, 160, 173, 181). The successful colonization in the pancreas with simultaneous absence of liver metastases can again only be explained by an SSM which prevents the settlement of embolized tumor cells in the liver.
In connection with the organotropy in metastatic formation in isPM, it is worth recalling that the pancreas itself is composed of two organ components: a large exocrine and a small endocrine one. At the moment, it remains unknown whether metastatic settlement in isPM starts in the exocrine or endocrine tissue or in both. In this context the above-mentioned observation is at least remarkable, that in instances of single organ metastatic recurrence an increased number of metastasis in endocrine organs was demonstrated (10.3%).
Ineffectiveness of Risk Factors
Secondly, an equally important result, the analysis showed that isPMs, too, were characterized by the peculiarity that the risk factors, such as singular/multiple metastases, number of metastases, metastasis size, and synchronous/metachronous metastases and interval from RCC surgery to isPM occurrence remained ineffective. This behavior is surprising, since it is generally applicable in metastatic surgery of solid tumors that the treatment result is influenced by the initial tumor burden (248–250). For mRCC, such studies have also been presented (though without mentioning if isPM observations were included), which unanimously confirmed that the initial total tumor burden was a negative prognostic factor (231, 251–253). Metastases surgery also proved that the time of occurrence of metastases was a prognostic factor, e.g., in liver metastases surgery of colorectal cancer (248, 254, 255), gastric cancer (256), and breast cancer (257). After all, these parameters were also risk factors proven in RCC surgery (232, 233, 258–261), as well as in RCC metastases surgery (262–268), although the significance of these factors varied greatly depending on individual properties of primary RCC and metastasis localization and not all factors were equally effective for every metastatic localization. It should be noted, however, that generally these risk factors are only an expression of the magnitude of the risk that after pancreatic metastasis treatment from occult micro metastases in other organs, a generalization stage will result. It is therefore more remarkable that, as a special feature of isPM, the above-mentioned volume and interval dependent risk factors had no influence on the prognosis of isPM. To the best of our knowledge, this feature of isPM can currently only be explained by an SSM which permitted the growth of metastasised tumor cells to manifest metastasis exclusively in the pancreas and definitely, prevented it in all other organs or at least blocks it for years. The effect of such an SSM causes, that in isPM (almost) all extra pancreatic tumor cells were successfully eliminated or at least kept in a dormant state for years by the host organism. So, regardless of whether a singular or multiple systemic tumor cell dissemination occurs from the primary tumor, regardless of whether a further tumor cell dissemination occurs from singular or multiple metastases, from synchronous or metachronous metastases, or from large or small metastases, the human body is able to eliminate—or at least render harmless—these cells in all organs with the exception of the pancreas. This minimizes the risk of extra pancreatic-located distant metastases so that risk factors reflecting the probability of the later occurrence of distant metastases must remain without influence on survival. Thus, the prognosis of isPM is in an unusual way determined only by adequate therapy of the pancreatic foci and the otherwise effective risk factors “tumor burden” and “interval” must remain ineffective.
So, summing up these results, the mode of distribution and the ineffectiveness of risk factors reveal two argumentations but also the unexpected positive survival rates and the high percentage of single organ metastases or even anew isPM in recurrent disease are observations that can be best explained and made plausible by the effect of an SSM. Together these findings therefore support the hypothesis of a high impact of an SSM in isPM. They further provide evidence that in isPMs, for the first time in human medicine, a clearly defined tumor entity is identified the occurrence and course of which, is exclusively triggered by an SSM making isPM to a paradigm of an SSM.
Pathomechanisms Leading to isPM
The biochemical mechanism which causes the only occurrence of pancreatic metastases in isPM is unknown as no such studies have been carried out due to the exquisite rarity of isPM (4). However, the RCC as such has been the subject of biochemical investigations that allow conclusions to be drawn by analogy. The effect of an SSM suggests that primary carcinomas which generate a large number of differently equipped tumor cells will gain an advantage in metastasis settlement, as this increases the probability that a cell capable of metastasis in the respective target organ will reach it. The RCC is characterized by a large heterogeneity (238, 269, 270), for which also the variety of miRNA with altered expression behaviors is responsible, which becomes effective in the RCC. miRNAs control the metastasis behavior through their ability to inhibit numerous target genes involved in different steps of the metastatic cascade, e.g., epithelial-mesenchymal transition (271–274), migration (271, 275–279), and metastasis settlement (280–284). Variable interactions of all these miRNAs in various tumor cells bring about manifold different capabilities for metastasis which increases the odds that one of the embolized tumor cell exactly “fits” the properties of the target organ (5). Studies have also shown that the miRNA profile of the metastatic RRC differed from the profile of the non-metastatic RRC (285, 286), and the miRNA profile in metastases also differed depending on the location of the metastases in the lungs, bones or brain (287). These observations suggested that cell selection influenced by the mRNA profile during metastasis formation was involved.
In general, organotropy can always be expected if the early metastasis phase involved steps that require the successful interaction of tumor cell and host organ properties. In literature, mechanisms have already been identified that can generally be held responsible for organotropy in metastasis formation, and whose involvement in isPM seems at least possible: (a) the interaction of a chemokine receptor on the tumor cell surface and a suitable ligand in the host organ (5). This interaction is a necessary prerequisite for the activation of numerous signal transducing pathways, which are critical in tumor cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, invasion and proliferation (288, 289). As the chemokine receptor equipment is tumor cell specific and the type and level of the ligand is organ-specific, successful interaction will only take place in those tissues where receptors and ligands fit exactly together (288, 290, 291). Breast cancer e.g., was found to express the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7 at high levels. The corresponding ligands CXCL12 and CCL21 are present at elevated levels in lymph nodes, lung, liver and bone marrow—preferred distant metastatic sites of breast cancer (288, 290). (b) The formation of a pre-metastatic niche (PMN) (290–296). It is the result of the ability of respective solid tumors, already before tumor cell embolization occurs, to weaken defense mechanisms which are directed against tumor cells in potential host organs. By disturbing humoral and cellular defense mechanisms in host organs, the subsequent tumor cell embolization and colonization can take place successfully and metastases can form in this organ. The formation of a PMN requires the interaction of three components: primary tumor derived components (273, 296, 297), tumor mobilized bone marrow derived cells (298) and organ components of the future host organ (292, 294, 299, 300). In pre-metastatic niche formation, the capabilities of tumor cells and host organs are involved, this causes organotropy in niche formation (294). The fundamental ability of the RCC to form a PMN is documented by proof of a PMN in the lung (299). The ability to form a PMN in the pancreas, however, is so far not documented for RCC. (c) A different immunoediting in various host organs. First, evidence of the importance of immune defense in RCC was provided by observations of spontaneous regression in metastatic RCC, which were interpreted as a result of enhanced immune defense (69, 301, 302). The recent, successful introduction of immune modulating treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as Anti PD-1 (Nivolumab) or Anti CTLA-4 (Ipilimumab) has impressively demonstrated the high importance of immunoediting in mRCC (239, 241, 301, 303, 304). However, since there are currently no detailed studies of the rare isPM, all considerations regarding the significance of immunoediting (228) in isPM that is either generally altered or only disturbed in the pancreas must remain speculative at present. Although this is quite conceivable, if one regards the aforementioned differentiated miRNA profile in different metastatic organs as a consequence of an immune-dependent selection process. The peculiarity of isPM would then be that in all host organs, except the pancreas, immune-surveillance detects and correctly eliminates the metastasised tumor cells by natural tumor specific T-cell mediated immune response or keeps them in a dormant “equilibrium” state (228). In the pancreas, however, an immunosuppression is present which enables the carcinomas cells to evade immune control and to mature to manifest metastasis. IsPM would thus represent a “single organ deficiency of immune response.”
Limitations of the Study
Potential weaknesses of the presented literature analysis were related to the retrospective character of casuistic reports and a bias in the published casuistic reports cannot be excluded on principle. This methodical limitation is however, at least in part compensated by the confirmation of some results by large single and multicenter reports in the last years.
Conclusion
The hypothesis of a strongly and selectively acting “seed and soil” mechanism can not only be explained by the analysis of the pattern of distribution of isPM, but also by studies on the significance of risk factors after therapy, revealing the peculiarities of isPM. This enables embolized renal carcinoma cells exclusively in the pancreas to complete all the steps that are required for growth to manifest metastases without disturbances, while in all other organs the metastasised carcinoma cells are prevented from colonization (290). According to this hypothesis, isPM is a tumor entity with model character that suggests that the occurrence of manifest metastases is preceded by several multi-step, cascade-like biological processes, which require the exact matching of properties of the tumor cell with those of the host organ (287, 290, 291, 305). Even the interruption of one single step can irreversibly disrupt this “colonization” process (3, 306). This susceptibility (291) of the early metastasis process to disruption opens up the chance for the host organism to prevent embolized tumor cells from growing into metastases. With the isPM, this blockade obviously works successfully in all organs except the pancreas. Therefore, with the isPM, a clearly defined tumor entity is given in human medicine, which is characterized to a large extent by an SSM. The uniform and stable clinical course of the isPM also suggests that the isPM is based on uniform pathogenic mechanisms that remain constant for years. This indicates that biochemical investigations would be meaningful to examine the mechanism leading to the exclusive occurrence of metastases in the pancreas and their absence in all other organs. This could help to shed further light upon the complex metastasis process, which is a prerequisite for the development of therapeutics that once might help to hamper the metastasis process (307).
Author Contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and has approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet. (1889) 1:99–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tarin D, Price JE, Kettlewell MG, Souter RG, Vass AC, Crossley B. Mechanisms of human tumor metastasis studied in patients with peritoneovenous shunt. Cancer Res. (1984) 44:3584–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gassmann P, Haier J. The tumor cell-host interface in the early onset of metastatic organ colonisation. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2008) 25:171–81. 10.1007/s10585-007-9130-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sellner F. Isolated pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: an outcome of a special metastatic pathway or of a specific tumor cell selection? Clin Exp Metastasis. (2018) 35:91–102. 10.1007/s10585-018-9910-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sellner F. Observations on solitary versus multiple isolated pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma: another indication of a seed and soil mechanism? Cancers. (2019) 11:1379. 10.3390/cancers11091379 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sellner F, Tykalsky N, De Santis M, Pont J, Klimpfinger M. Solitary and multiple isolated metastases of clear cell renal carcinoma to the pancreas: an indication for pancreatic surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. (2006) 13:75–85. 10.1245/ASO.2006.03.064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jenssen E A metastatic hypernephroma to the pancreas. Acta Chir Scand. (1952) 104:177–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lawson L, Holt L, Rooke H. Recurrent duodenal haemorrhage from renal carcinoma. Brit J Urol. (1966) 38:133–7. 10.1111/j.1464-410X.1966.tb09690.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Franciosi RA, Russo J. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas thirteen years following nephrectomy. Mil Med. (1969) 134:200–3. 10.1093/milmed/134.3.200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marquand J, Giraud B, Maliakas S. Pancreatic metastasis revealing a kidney neoplasm. J Urol Nephrol. (1971) 77:595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guttman F, Ross M, Lachance C. Pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma treated by total pancreatectomy. Arch Surg. (1972) 105:782–4. 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180110099026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gillet M, Camelit G, Runser G, Clement D. Duodenopancreatic metastasis of kidney cancer revealed by digestive hemorrhage treated by cephalic duodeno-pancreatectomy. Chirurgie. (1974) 100:226–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hermanutz KD, Sonnenberg GE. Late metastasis of a hypernephroid kidney carcinoma to the pancreas with tumor invasion to the duodenum. Fortschr Röntgenstr. (1977) 127:595–7. 10.1055/s-0029-1230774 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Saxon A, Gottesman J, Doolas A. Bilateral hypernephroma with solitary pancreatic metastasis. J Surg Oncol. (1980) 13:317–22. 10.1002/jso.2930130406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yazaki T, Ishikawa S, Ogawa Y, Takahashi S, Nemoto S, Rinsho K, et al. Silent pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma diagnosed at arteriography. Acta Urol Jpn. (1981) 27:1517–22. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Py J, Arnaud J, Cinqualbre J, Adloff M, Bollack C. Pancreatic metastases of nephro-epitheliomas. Acta chir Belg. (1984) 84:117–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Skaarup P, Jorgensen T, Larsen S. Asynchronous metastasizing renal cell carcinoma associated with progressive immune complex glomerulonephritis and proteinuria. Scand J Urol Nephrol. (1984) 18:351–56. 10.3109/00365598409180210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Audisio RA, La Monica G. Solitary pancreatic metastasis occurring 20 years after nephrectomy for carcinoma of the kidney. Tumori. (1985) 71:197–200. 10.1177/030089168507100217 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kishimoto H, Niumra Y, Okamoto K, Tsuchie K, Yamase H, Maeda S, et al. A case of resected renal cell carcinoma with massive pancreatic metastasis. Jap J Cancer Clin. (1985) 31:91–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Amamiya H, Iizumi T, Yazaki T, Waku M, Yasuda H, Takada T, et al. A solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Hinyouki Geka. (1988) 2:167–70. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Carini M, Selli C, Barbanti G, Bianchi S, Muraro G. Pancreatic late recurrence of bilateral renal cell carcinoma after conservative surgery. Eur Urol. (1988) 14:258–260. 10.1159/000472953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hirano M, Douden K, Bantou H, Sakatoku M, Saitoh H, Tachikawa H, et al. Solitary pancreatic metastasis occuring 10 years after nephrectomy for carcinoma of the kidney. Tan to Sui. (1988) 9:233–7. 4002351 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sharma SK, Kumar A, Madhusoodnan P, Banerjee C, Suri S, Dhar M. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. A rare metastatic site. Indian J Cancer. (1988) 25:29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guyenne C, Rat P, Haas O, Baudet JG, Favre JP. Triple metastase pancreatique d'un cancer du rein traitee par duodenopancreatectomie subtotale. Presse Med. (1989) 18:231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Iwanami M, Nakayoshi A, Yagi H, Shimizu K, Kimura K, Suzuki K, et al. A resected case of the asymptomatic pancreatic metastasis in the body and tail of the pancreas from renal cell carcinoma. J Jpn Panc Soc. (1989) 4:100–6. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Roland C, van Heerden J. Nonpancreatic primary tumors with metastasis to the pancreas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. (1989) 168:345–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Simpson NS, Mulholland C, Lioe T, Spence R. Late solitary metastatic renal carcinoma in the pancreas. Ulster Med J. (1989) 58:198–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Strijk SP. Pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma: report of two cases. Gastrointest Radiol. (1989) 14:123–6. 10.1007/BF01889175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Temellini F, Bavosi M, Lamarra M, Quagliarini P, Giuliani F. Pancreatic metastasis 25 years after nephrectomy for renal cancer. Tumori. (1989) 75:503–4. 10.1177/030089168907500522 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gohji K, Matsumoto O, Kamidono S. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Hinyokika Kiyo. (1990) 36:677–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Terashima M, Abe H, Suga K, Matsuya F, Kobayashi K, Itoh S, et al. Two cases of renal cell carcinoma metastasized to the pancreas and to the gallbladder. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. (1990) 23:1952–6. 10.5833/jjgs.23.1952 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Furukawa T, Hattori R, Ohtake H, Souma T, Kinukawa T, Hirai K, et al. A resectable case of pancreatic head metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Hinyouki Geka. (1991) 4:111–4. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kubo K, Morita J, Mizoe J, Ogawa H, Irie G. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas 8 years following nephrectomy. Jpn J Clin Radiol. (1991) 36:509–12. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nishida O, Matsunaga Y, Dekigai H, Um S, Hsieh C, Kimura F. Three elderly cases of renal cell carcinoma with pancreatic metastasis. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. (1991) 28:392–6. 10.3143/geriatrics.28.392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Oka H, Hatayama T, Taki Y, Ueyama H, Hida S, Noguchi M. A resected case of renal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the pancreas. Hinyokika Kiyo. (1991) 37:1531–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tabata T, Kuroda Y, Nishimatsu S, Satoh Y. A resected case of pancreatic tumor metastasized from renal cell carcinoma. J Jpn Panc Soc. (1991) 6:245–50. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yamamoto S, Tobinaga K, Taketomi K, Kimino K, Ashizuka S, Kishikawa M. Pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma occurring 17 years after nephrectomy. J Jpn Soc Clin Surg. (1991) 52:3006–11. 10.3919/ringe1963.52.3006 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fujii M, Kogawa T, Matsuyama K, Yamamoto H, Kaawahito Y, Iinuma S, et al. A case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma to pancreas ten years after nephrectomy. J Kyoto Pref Univ Med. (1992) 101:589–96. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Melo CR, Melo IS, Monteiro AZ, de Mello ES. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Arq Gastroenterol. (1992) 29:110–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nakagawa K, Tsuchiya T, Momono S, Sasaki Y, Sato T. A case of pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. (1992) 25:2200–4. 10.5833/jjgs.25.2200 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rypens F, Van Gansbeke V, Lambilliotte J, Regemorter V, Verhest A, Struyven J. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Br J Radiol. (1992) 65:547–8. 10.1259/0007-1285-65-774-547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Stankard C, Karl RC. The treatment of isolated pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: a surgical review. Am J Gastroenterol. (1992) 87:1658–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Aikou S, Tokura Y, Yamafuji K, Takahashi T, Yoshibide O, Kishii K, et al. A resected case of pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma presenting with acute duodenal bleeding. J Jpn Soc Clin Surg. (1993) 54:2666–72. 10.3919/ringe1963.54.2666 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Calmes JM, Meyer A. Pancreatic hypernephroma manifested by a duodenal hemorrhage. Rev Med Suisse Romande. (1993) 113:629–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ishikawa T, Horimi T, Majima K. A resected case of pancreatic tumor metastasized from renal cell carcinoma. A review of 11 cases in the Japanese and 13 cases in the foreign literature. J Jpn Soc Clin Surg. (1993) 51:1642–7. 10.3919/ringe1963.54.1642 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Tanaka Y, Saika Y, Ohiani H, Fujii R, et al. A case of resection of a solitary pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma occuring 5 years after nephrectomy. J Jpn Panc Soc. (1993) 8:189–95. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Marcote-Valdivieso E, Arlandis F, Baltasar A, Martinez C, Vierna G. Synchronous pancreatic metastasis of renal carcinoma. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. (1993) 83:471–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nan Y, Kuno N, Kurimoto K, Nakamura T, Kobayashi S. A resected case of pancreatic tumor metastasized from renal cell carcinoma diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy through the main pancreatic duct. Gastroenterol Endosc. (1993) 35:1380–1385. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Oda K, Itoh J, Hachisuka K, Yamaguchi A, Isogai M, Utsunomiya H, et al. Value of computer image analysis in improving ERCP images in metastatic tumor of the pancreas. AJR. (1993) 161:885–6. 10.2214/ajr.161.4.8372781 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Reale D, Squillaci S, Guarino M, Milesi F, Forloni B, Vezzini V, et al. Late pancreatic metastasis of renal carcinoma. Description of 2 cases and review of literature. Minerva Urol Nefrol. (1993) 45:183–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sauvanet A, Barthes T, Levy P, Flejou JF. Late pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Pancreas. (1993) 8:742–6. 10.1097/00006676-199311000-00014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Takeuchi H, Konaga E, Harano M, Watanabe K, Takeuchi Y, Hara M, et al. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Acta Med Okayama. (1993) 47:63–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Vergara V, Marucci M, Marcarino C, Brunello F, Capussotti L. Metastatic involvement of the pancreas from renal cell carcinoma treated by surgery. Ital J Gastroenterol. (1993) 25:388–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yanagisawa T, Nakayama K, Kashiwagi M, Tanaka J, Kashiwagi T, Mizusaki K, et al. Three cases of resectable pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Geka Shinryo. (1993) 35:651–5. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zugel N, Leipprand F, Weckermann D, Witte J. Solitäre Pankreaskopfmetastase bei hypernephroidem Carcinom. Fortschr Med. (1994) 112:388–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Dousset B, Andant C, Guimbaud R, Roseau G, Tulliez M, Gaudric M, et al. Late pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasonography. Surgery. (1995) 117:591–4. 10.1016/S0039-6060(05)80261-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fabre JM, Rounanet P, Dagues F, Blanc F, Baumel H, Domergue J. Various features and surgical approach of solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. (1995) 21:683–6. 10.1016/S0748-7983(95)96079-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Onishi T, Ohishi Y, Iizuka N, Suzuki Y, Shirakawa H, Hatano T, et al. Clinical characteristics of 7 renal cell carcinoma patients developing a solitary pancreatic metastasis after nephrectomy. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. (1995) 86:1538–42. 10.5980/jpnjurol1989.86.1538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Orita M, Morita N, Hiraoka H, Noshima S, Takaimashi T, Esato K. A case of resected pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma 14 years after radical nephrectomy. J Jpn Panc Soc. (1995) 10:63–8. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Takashi M, Takagi Y, Sakata T, Shimoji T, Miyake K. Surgical treatment of renal cell carcinoma metastases: prognostic significance. Int Urol Nephrol. (1995) 27:1–8. 10.1007/BF02575213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Barras JP, Baer H, Stenzl A, Czerniak A. Isolated late metastasis of a renal cell cancer treated by radical distal pancreatectomy. HPB Surg. (1996) 10:51–3. 10.1155/1996/56065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hirota T, Tomida T, Iwasa M, Takahashi K, Kaneda M, Tamaki H. Solitary pancreatic metastasis occuring eight years after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. A case report and surgical review. Int J Pancreatol. (1996) 19:145–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Palazzo L, Borotto E, Cellier C, Roseau G, Chaussade S, Couturier D, et al. Endosonographic features of pancreatic metastases. Gastrointest Endosc. (1996) 44:433–6. 10.1016/S0016-5107(96)70095-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Paz A, Koren R, Gal R, Wolloch Y. Late solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Isr J Med Sci. (1996) 32:1319–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Chambers T, Fishman E, Hruban R. Pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Clin Imaging. (1997) 21:40–2. 10.1016/0899-7071(95)00066-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Harrison LE, Merchant N, Cohen AM, Brennan MF. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for nonperiampullary primary tumors. Am J Surg. (1997) 174:393–5. 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)00121-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Robbins EG, Franceschi D, Barkin J. Solitary metastatic tumors to the pancreas: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol. (1997) 92:914–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Adem C, Chetritt J, Guymar S, Bellil K, Ladouch-Badre A, Benlagha N, Bedossa P. Pancreatic metastasis of a renal adenocarcinoma. Apropos on 2 cases. Ann Pathol. (1998) 18:481–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Altschuler E, Ray A. Spontaneous regression of a pancreatic metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma. Arch Fam Med. (1998) 7:516–7. 10.1001/archfami.7.6.516 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Butturini G, Bassi C, Falconi M, Salvia R, Caldiron E, Ianucci A, et al. Surgical treatment of pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinomas. Dig Surg. (1998) 15:241–6. 10.1159/000018621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gupta R, Lallu S, Delahunt B. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of metastatic clear-cell renal carcinoma presenting as a solitary mass in the head of the pancreas. Diagn Cytopathol. (1998) 19:194–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hashimoto M, Watanabe G, Matsuda M, Dohi T, Tsurumaru M. Management of pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: report of four resected cases. Hepatogastroenterology. (1998) 45:1150–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jingu K, Watanabe K, Yamamoto H, Fujita Y, Honda I, Watanabe S, et al. Surgical treatment of a solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: report of a case. Surg Today. (1998) 28:91–4. 10.1007/BF02483616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Merkle E, Boaz T, Kolokythas O, Haaga J, Lewin J, Brambs H. Metastases to the pancreas. Br J Radiol. (1998) 71:1208–14. 10.1259/bjr.71.851.10434919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Sahin M, Foulis AA, Poon FW, Imrie CW. Late focal pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Dig Surg. (1998) 15:72–4. 10.1159/000018591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Z'graggen K, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Rattner D, Sigala H, Warshaw A. Metastases to the pancreas and their surgical extirpation. Arch Surg. (1998) 133:413–7. 10.1001/archsurg.133.4.413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Augustin H, Bacher H, Uggowitzer M, Ott A, Hubmer G, Mischinger H. Pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma mimicking insulinomas. BJU Int. (1999) 83:140–1. 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00855.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Carucci L, Siegelman E, Feldman M. Pancreatic metastasis from clear cell renal carcinoma: diagnosis with chemical shift MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr. (1999) 23:934–6. 10.1097/00004728-199911000-00018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Eriguchi N, Aoyagi S, Hara M, Miyazaki T, Hashino K, Imamura I, et al. A resected case of pancreatic metastasis from primary renal cell carcinoma. Kurume Med J. (1999) 46:119–22. 10.2739/kurumemedj.46.119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ng CS, Loyer EM, Iyer RB, David CL, DuBrow RA, Charnsangavej C. Metastases to the pancreas from renal cell carcinoma: findings on three-phase contrast-enhanced helical CT. AJR. (1999) 172:1555–9. 10.2214/ajr.172.6.10350288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sugiyama M, Katsura M, Yamamoto K, Nouchi W, Abe N, Hatano N, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma causing massive gastrointestinal bleeding in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Hepatogastroenterology. (1999) 46:1199–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yavascaoglu I, Korun N, Oktay B, Simsek U, Ozyurt M. Renal cell carcinoma with solitary synchronous pancreaticoduodenal and metachronous periprostatic metastases: report of a case. Surg Today. (1999) 29:364–6. 10.1007/BF02483065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Fricke P, Schulz HU, Buhtz B, Lippert H. Multiple metachrone Metastasen eines Nierenzellkarzinoms im Pankreas. Fallbeschreibung und Literaturübersicht. Chirurg. (2000) 71:575–9. 10.1007/s001040050860 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ghavamian R, Klein KA, Stephens DH, Welch TJ, LeRoy AJ, Richardson RL, et al. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas: clinical and radiological features. Mayo Clin Proc. (2000) 75:581–5. 10.4065/75.6.581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kassabian A, Stein J, Jabbour N, Parsa K, Skinner B, Parekh D, et al. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas: a single institution series and review of the literature. Urology. (2000) 56:211–5. 10.1016/S0090-4295(00)00639-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Le Borgne J, Partensky C, Glemain P, Dupas B, de Kerviller B. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for metastatic ampullary and pancreatic tumors. Hepatogastroenterology. (2000) 47:540–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mehta N, Volpe C, Haley T, Balos l, Bradley E, Doerr R. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: report of a case. Surg Today. (2000) 30:94–7. 10.1007/PL00010057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Thompson LD, Heffess CS. Renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas in surgical pathology material. Cancer. (2000) 89:1076–89. 10.1002/1097-0142(20000901)89:5 <1076::AID-CNCR17>3.0.CO;2-M [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Espinoza R, Rossi R, Rossi R, Rosenberg H. Metachronous pancreatic metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: 3 new cases. Rev Med Chil. (2001) 129:86–90. 10.4067/S0034-98872001000100012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Faure JP, Tuech JJ, Richer JP, Pessaux P, Arnaud JP, Carretier M. Pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma: presentation treatment and survival. J Urol. (2001) 165:20–2. 10.1097/00005392-200101000-00005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Marusch F, Koch A, Dietrich F, Hoschke B, Gastinger I. A singular late metastasis of renal cell carcinoma inside the pancreas. An uncommon pancreatic tumor. Zentralbl Chir. (2001) 126:391–5. 10.1055/s-2001-14748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ruibal Moldes M, Quintana de la Rosa J, Farina Perez L, Tardaguila F, Ortiz Rey J, Zungri Telo E. Late pancreatic metastasis from renal carcinoma. Actas Urol Esp. (2001) 25:122–4. 10.1016/S0210-4806(01)72585-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Scatarige J, Horton K, Sheth S, Fishman E. Pancreatic parenchymal metastases: observations on helical CT. Am J Roentenol. (2001) 176:695–9. 10.2214/ajr.176.3.1760695 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sohn T, Yeo C, Cameron J, Nakeeb A, Lillemoe K. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas: results of surgical management. J Gastrointest Surg. (2001) 5:346–51. 10.1016/S1091-255X(01)80060-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tada T, Kobayashi G, Noda Y, Kimura K, Ito K, Fujita N. A resected case with multiple pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. (2001) 98:1368–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bechade D, Palazzo I, Desrame J, Duvic C, Herody M, Didelot F, et al. Pancreatic metastasis of renal carcinoma: report of three cases. Rev Med Interne. (2002) 23:862–6. 10.1016/S0248-8663(02)00693-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Chao K, Hurley J, Neerhut G, Kiroff G. Multiple pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma. ANZ J Surg. (2002) 72:310–2. 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2002.02384.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Chou YH, Chiou HJ, Hong TM, Tiu C, Chiou SY, Su CH, et al. Solitary metastasis from renal cell carcinoma presenting as diffuse pancreatic enlargement. J Clin Ultrasound. (2002) 30:499–502. 10.1002/jcu.10104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Eloubeidi MA, Jhala D, Chhieng D, Jhala N, Eltoum I, Wilcox C. Multiple late asymptomatic pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy with immunocytochemical correlation. Dig Dis Sci. (2002) 47:1839–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Hiotis S, Klimstra D, Conlon K, Brennan M. Results after pancreatic resection for metastatic lesions. Ann Surg Oncol. (2002) 9:675–9. 10.1007/BF02574484 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Lisii D, Gaimant A, Sautereau D, Paraf F, Maubon A. Duodenal bleeding revealing a renal cell carcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. (2002) 26:1044–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Peschaud F, Cheynel N, Hagry O, Tremeaux J, Rat P, Favre JP. Surgical treatment of pancreatic metastases from renal carcinoma. Ann Chir. (2002) 127:656–7. 10.1016/S0003-3944(02)00839-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Roviello F, Nastri G, Hako L, Marrelli D, De Stefano A, Cioppa T, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from clear renal cell carcinoma: a clinical case. Chir Ital. (2002) 54:873–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Yachida S, Fukushima N, Kanai Y, Nimura S, Shimada K, Yamamoto J, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma extending into the main pancreatic duct: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2002) 32:315–7. 10.1093/jjco/hyf066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Bassi C, Butturini G, Falconi M, Sargenti W, Mantovavi W, Pederzoli P. High recurrence rate after atypical resection for pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Br J Surg. (2003) 90:555–9. 10.1002/bjs.4072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Giulini S, Portolani N, Bonardelli S, Baiocchi G, Zampatti N, Coniglio A, et al. Distal pancreatic resection with splenic preservation for metastasis of renal carcinoma diagnosed 24 years later from the nephrectomy. Ann Ital Chir. (2003) 74:93–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Hernandez DJ, Kavoussi LR, Ellison L. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urology. (2003) 62:551. 10.1016/S0090-4295(03)00403-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Law CH, Wei AC, Hanna SS, Al-Zahrani M, Taylor BR, Greig B, et al. Pancreatic resection for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: presentation, treatment and outcome. Ann Surg Oncol. (2003) 10:922–6. 10.1245/ASO.2003.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Nakagohri T, Konishi M, Inoue K, Nakamura T, Kinoshita T. Partial pancreatic head resection for pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. (2003) 50:2236–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Pecchi A, Cesinaro A, Torricelli P. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. A case report. Radiol Med. (2003) 105:386–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Uemura T, Kurita A, Nishimura R, Ishizaki M, Takashima S. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma concomitant with early gastric cancer 17 years after nephrectomy. Report of a case. Surg Today. (2003) 33:395–8. 10.1007/s005950300090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Zacharoulis D, Asopa V, Karvounis E, Williamson RC. Resection of renal metastases to the pancreas: a surgical challenge. HPB. (2003) 5:137–41. 10.1080/13651820310000677 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kijvikai K, Ratana-olarn K. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma 14 years after nephrectomy: a case report. J Med Assoc Thai. (2004) 87:1123–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kobayashi A, Yamaguchi T, Ishihara T, Tadenuma H, Nakamura K, Ohshimi T, et al. Spontaneous rupture of pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2004) 34:696–9. 10.1093/jjco/hyh127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Kornprat P, Bacher H, Hauser H, Cerwenka H, El-Shabrawi A, Lackner C, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the pancreas: a case report and literature review. Eur Surg. (2004) 36:381–4. 10.1007/s10353-004-0112-5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Moussa A, Mitry E, Hammel P, Sauvanet A, Nassif T, Palazzo L. Pancreatic metastasis: a multicentric study of 22 patients. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. (2004) 28:872–6. 10.1016/S0399-8320(04)95151-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Paparel P, Cotton F, Voiglio E, Decaussin M, Isaac S, Caillot Jl. A case of late pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Prog Urol. (2004) 14:403–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ninan S, Jain P, Paul A, Menon K. Synchronous pancreatic metastases from asymptomatic renal cell carcinoma. JOP. (2005) 6:26–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Pekmezci S, Saribeyoglu K, Kahya AS, Kapan M, Durgun V. Pancreatic renal cell carcinoma metastasis presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Surgery. (2005) 137:386–7. 10.1016/j.surg.2003.10.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Sotiropoulos G, Lang H, Liu C, Brokalaki E, Molmenti E, Broelsch C. Surgical treatment of pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma. JOP. (2005) 6:339–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Wente MN, Kleef J, Esposito I, Hartel M, Müller MW, Fröhlich E, et al. Renal cancer cell metastasis into the pancreas. Pancreas. (2005) 30:218–22. 10.1097/01.mpa.0000153337.58105.47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Crippa S, Angelini C, Mussi C, Bonardi C, Romano F, Sartori P, et al. Surgical treatment of metastatic tumors to the pancreas: a single center experience and review of the literature. World J Surg. (2006) 30:1536–42. 10.1007/s00268-005-0464-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Köhler K, Haroske G, Ludwig K. Therapie von Pankreasmetastasen beim Nierenzellkarzinom–eine Fallbeschreibung von 5 Patienten. Zentralbl Chir. (2006) 131:425–8. 10.1055/s-2006-949531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Shrikhande SV, Büchler P, Esposito I, Loos M, Büchler MW, Friess H. Splenic and portal vein thrombosis in pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. (2006) 4:25. 10.1186/1477-7819-4-25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Akatsu T, Shimazu M, Aiura K, Ito Y, Shinoda M, Kawachi S, et al. Clinicopathological features and surgical outcome of isolated metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. (2007) 54:1836–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Eidt S, Jergas M, Schmidt R, Siedek M. Metastasis to the pancreas–an indication for pancreatic resection? Langenbecks Arch Surg. (2007) 392:539–42. 10.1007/s00423-007-0148-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Goto T, Dohmen T, Yoneyama K. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2007) 5:A26. 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.04.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Karimi KM, McFadden D. Pancreatic resection for metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas. Am Surg. (2007) 73:58–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Maeda H, Okabayashi T, Nishimori I, Kobayashi M, Sugimoto T, Kohsaki T, et al. Duodenum-preserving pancreatic head resection for pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Langenbecks Arch Surg. (2007) 392:649–52. 10.1007/s00423-007-0204-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Varker KA, Muscarella P, Wall K, Ellison C, Bloomston M. Pancreatectomy for non-pancreatic malignancies results in improved survival after R0 resection. World J Surg Oncol. (2007) 5:145. 10.1186/1477-7819-5-145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Aimoto T, Uchida E, Yamahatsu K, Yoshida H, Hiroi M, Tajiri T. Surgical treatment for isolated multiple pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: report of a case. J Nippon Med Sch. (2008) 75:221–4. 10.1272/jnms.75.221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Bahra M, Jacob D, Langrehr JM, Glanemann M, Schumacher G, Lopez-Hänninen E, et al. Metastasen im Pankreas. Wann ist eine Resektion sinnvoll? Chirurg. (2008) 79:241–8. 10.1007/s00104-007-1390-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kawakami H, Kuwatani M, Yamato H, Shinada K, Hirano S, Kondo S, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma with intraportal tumor thrombus. Inter Med. (2008) 47:1967–70. 10.2169/internalmedicine.47.1418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Matsutani T, Sasajima K, Miyamoto M, Yokoyama T, Maruyama H, Yanagi K, et al. Resection of pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma and an early gastric cancer. J Nippon Med Sch. (2008) 75:41–5. 10.1272/jnms.75.41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Koide N, Yokoyama Y, Oda K, Nishio H, Ebata T, Abe T, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Results of the surgical management and pathologic findings. Pancreas. (2008) 37:104–7. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181619a2f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Schauer M, Vogelsang H, Siewert JR. Pancreatic resection for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a single center experience and review of the literature. Anticancer Res. (2008) 28:361–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Shukla RC, Pathak R, Senthil S. Pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma – case report. Nepal Med Coll J. (2008) 10:275–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Tuech J, Lefebure R, Bridoux V, Albouy B, Lermite E, Le Pessot F, et al. Combined resection of the pancreas and inferior vena cava for pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. (2008) 12:612–5. 10.1007/s11605-007-0295-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Zerbi A, Ortolano E, Balzano G, Borri A, Beneduce AA, Di Carlo V. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: which patients benefit from surgical resection? Ann Surg Oncol. (2008) 15:1161–8. 10.1245/s10434-007-9782-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Deguchi Y, Shimada K, Nara S, Esaki M, Sakamoto Y, Kosuge T, et al. Pancreaticojejunostomy with invagination of the punched pancreatic remnant after medial pancreatectomy and enucleation for multiple metastases of renal cell carcinoma: report of a case. Surg Today. (2009) 39:1086–90. 10.1007/s00595-008-3998-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Machado NO, Chopra P. Pancreatic metastasis from renal carcinoma managed by Whipple resection. A case report and literature review of metastatic pattern, surgical management and outcome. J Pancreas. (2009) 10:413–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Tanis PJ, van der Gaag NA, Busch OR, van Gulik TM, Gouma DJ. Systematic review of pancreatic surgery for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Surg. (2009) 96:579–92. 10.1002/bjs.6606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Volk A, Kersting S, Konopke R, Dobrowolski F, Franzen S, Ockert D, et al. Surgical therapy of intrapancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Pancreatology. (2009) 9:392–7. 10.1159/000181174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Akashi Y, Saiura A, Kishi Y, Koga R, Morimura R, Yoshioka R, et al. Outcome after surgical resection of isolated metastases to the pancreas. Hepatogastroenterology. (2010) 57:1549–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Barbaros U, Sümer A, Demirel T, Karakullukçu N, Batman B, Içsan Y, et al. Single incision laparoscopic pancreas resection for pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. JSLS. (2010) 14:566–70. 10.4293/108680810X12924466008448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Hijioka S, Hifumi M, Mekky M, Takekuma Y, Kawaguchi T, Yokomizo H, et al. Total pancreatectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma with marked extension into the main pancreatic duct. Inter Med. (2010) 49:557–62. 10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2943 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Kitasato A, Tajima Y, Kuroki T, Tsutsumi R, Tsuneoka N, Adachi T, et al. Limited pancreatectomy for metastatic pancreatic tumors from renal cell carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. (2010) 57:354–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Konstantinidis IT, Dursun A, Zheng H, Wargo J, Thayer S, Fernandez-del Castillo C, et al. Metastatic tumors in the pancreas in the modern era. J Am Coll Surg. (2010) 211:749–53. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.08.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Masetti M, Zanini N, Martuzzi F, Fabbri C, Mastrangelo L, Landolfo G, et al. Analysis of prognostic factors in metastatic tumors of the pancreas: a single-center experience and review of the literature. Pancreas. (2010) 39:135–43. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181bae9b3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Mourra N, Arrive L, Balladur P, Flejou JF, Tiret E, Paye F. Isolated metastatic tumors to the pancras. Hôpital St-Antoine experience. Pancreas. (2010) 39:577–80. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181c75f74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Szabó KG, Szentkereszty Z, Tóth LA, Damjanovich L, Sápy P. Distal pancreas resection for metastasis of clear cell renal cancer. Magy Seb. (2010) 63:161–3. 10.1556/maseb.63.2010.4.3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Vujcic T, Brahm J, Buckel E, Ibarra A, Vial MT, Fernández M. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Rev Med Chile. (2010) 138:738–41. 10.4067/S0034-98872010000600011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Yokonishi T, Ito Y, Osaka K, Komiya A, Kobayashi K, Sakai N, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma 25 years after radical nephrectomy. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2010) 56:629–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.D'Ambra M, Ricci C, Casadei R, Minni F. Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Urologia. (2011) 78:5–8. 10.5301/RU.2011.8834 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Irigoin RR, Entrenas AO, Urbano VA, Marin JG, Salgado TP, Zabal JM, et al. Solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2011) 34:624–8. 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2011.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Masago T, Watanabe T, Nemoto R. Small renal cell carcinoma with pancreas metastasis: a case report. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2011) 57:607–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Miyao M, Naito S, Ozono S, Shinohara N, Masumori N, Igarashi T, et al. Late recurrence of renal carcinoma: retrospective and collaborative study of the japanese society of renal cancer. Urology. (2011) 77:379–84. 10.1016/j.urology.2010.07.462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Thadani A, Pais S, Savino J. Metastasis of renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas 13 years postnephrectomy. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2011) 7:697–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Watanabe T, Morinaga S, Numata M, Mikayama Y, Tamura S, Tamagawa H, et al. Pancreatic resection for metastatic tumors to the pancreas. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2011) 38:2068–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.You DD, Choi DW, Choi SH, Heo JS, Kim WS, Ho CY, et al. Surgical resection of metastasis to the pancreas. J Korean Surg Soc. (2011) 80:278–82. 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.4.278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Alzahrani M, Schmulewitz N, Grewal S, Lucas F, Turner K, McKenzie J, et al. Metastases to the pancreas: the experience of a high volume center and a review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. (2012) 105:156–61. 10.1002/jso.22009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Çomunoglu C, Altaca G, Demiralay E, Moray G. Multiple metastatic renal cell carcinoma isolated to pancreas. Malaysian J Pathol. (2012) 34:63–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Firek P, Richter S, Jaekel J, Brehmer B, Heidenreich A. Metastasenresektion nach neoadjuvanter Systemtherapie mit Multityrosinkinaseinhibitoren beim metastasierten Nierenzellkarzinom. Urologe. (2012) 51:398–402. 10.1007/s00120-011-2762-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Hung JH, Wang SE, Shyr YM, Su CH, Chen TH, Wu CW. Resection for secondary malignancy of the pancreas. Pancreas. (2012) 41:121–9. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31821fc8f2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Katsourakis A, Noussios G, Hadjis I, Alatsakis M, Chatzitheoklitos E. Late solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Case Rep Med. (2012) 2012:464808. 10.1155/2012/464808 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Yazbek T, Gayet B. The place of enucleation and enucleo-resection in the treatment of pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. JOP. (2012) 13:433–8. 10.6092/1590-8577/863 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Zygulska AL, Wójcik A, Richter P, Krzesiwo K. Renal carcinoma metachronous metastases to the gall-bladder and pancreas–case report. Pol Przegl Chir. (2012) 84:313–6. 10.2478/v10035-012-0052-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Hata T, Sakata N, Aoki T, Yoshida H, Kanno A, Fujishima F, et al. Repeated pancreatectomy for metachronous duodenal and pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma. Case Rep Gastroenterol. (2013) 7:442–8. 10.1159/000355884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Hoshino Y, Shinozaki H, Kimura Y, Masugi Y, Ito H, Terauchi T, et al. Pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: a case report and literature review of the clinical and radiological characteristics. World J Surg Oncol. (2013) 11:289. 10.1186/1477-7819-11-289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Kapoor R, Kumar R, Dey P, Mittal BR. A late recurrence of renal cell carcinoma as pancreatic metastases: a rare disease. BMJ Case Rep. (2013) 2013:bcr2013009314. 10.1136/bcr-2013-009314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Markinez I, Jiménez R, Ruiz I, Villarreal E, Lizarazu A, Borda N, et al. Pancreatic metastases due to renal carcinoma. Our cases and a literature review. Cir Esp. (2013) 91:90–5. 10.1016/j.cireng.2012.07.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Mqirage M, Zabala Egurrola J, Rodríguez J, Pertusa Peña C. Métastase pancréatique métachrone du cancer du rein: À propos d'un cas. Can Urol Assoc J. (2013) 7:e460–1. 10.5489/cuaj.1388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Niess H, Conrad C, Kleespies A, Haas F, Bao Q, Jauch KW, et al. Surgery for metastasis to the pancreas: is it safe and effective? J Surg Oncol. (2013) 107:859–64. 10.1002/jso.23333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Yabe N, Murai S, Shimizu H, Kitasato K, Yoshikawa T, Oto I, et al. A case of pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma 27 years after nephrectomy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2013) 40:1897–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Yoshikawa Y, Murakami M, Shimizu J, Yasuyama A, Watase C, Kubota M, et al. A case of partial pancreatectomy for recurrent metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the remnant pancreas after subtotal stomach-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2013) 40:1900–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Espinoza E, Hassani A, Vaishampayan U, Shi D, Pontes JE, Weaver DW. Surgical excision of duodenal/pancreatic metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2014) 4:218. 10.3389/fonc.2014.00218 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Kimura Y, Keira Y, Imamura M, Ito T, Nobuoka T, Mizuguchi T, et al. Histopathological aspects of pancreatic metastases in renal cell carcinoma: does the mode of invasion permit limited resections? Pancreat Disord Ther. (2014) 4:2. [Google Scholar]
- 178.Lauro S, Onesti EC, Righini R, Carbonetti F, Cremona A, Marchetti P. A synchronous pancreatic metastasis from renal clear cell carcinoma, with unusual CT characteristics, completely regressed after therapy with sunitinib. Case Rep Med. (2014) 2014:473431. 10.1155/2014/473431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Matsuki M, Ichihara K, Matsuda Y, Taguchi K. Clinical features of six patients with pancreas metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Hinyokika Kiyo. (2014) 60:105–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Minni F, Casadei R, Perence B, Greco VM, Marrano N, Margiotta A, et al. Pancreatic metastases: observations of three cases and review of the literature. Pancreatology. (2014) 4:509–20. 10.1159/000080248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Moletta L, Milanetto AC, Vincenzi V, Alaggio R, Pedrazzoli S, Pasquali C. Pancreatic secondary lesions from renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg. (2014) 38:3002–6. 10.1007/s00268-014-2672-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Schwarz L, Sauvanet A, Regenet N, Mabrut JY, Gigot JF, Housseau E, et al. Long-term survival after pancreatic resection for renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol. (2014) 21:4007–13. 10.1245/s10434-014-3821-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Takeshi A, Mitsuhiro I, Hiromitsu A, Naoyuki Y, Taiichiro S, Hiroki S, et al. Middle segment-preserving pancreatectomy for recurrent metastasis of renal cell carcinoma after pancreatoduodenenctomy: a case report. Case Rep Surg. (2014) 2014:648678. 10.1155/2014/648678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Tosoian JJ, Cameron JL, Allaf ME, Hruban RH, Nahime CB, Pawlik TM, et al. Resection of isolated renal cell carcinoma metastases of the pancreas: outcomes from the Johns Hopkins Hospital. J Gastrointest Surg. (2014) 18:542–8. 10.1007/s11605-013-2278-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Untsch BR, Allen PF. Pancreatic metastasectomy: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering experience and a review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. (2014) 109:28–30. 10.1002/jso.23460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Benhaim R, Oussoultzoglou E, Saeedi Y, Mouracade P, Bachellier P, Lang H. Pancreatic metastasis from clear cell renal cell carcinoma: outcome of an aggressive approach. Urology. (2015) 85:135–40. 10.1016/j.urology.2014.09.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Chang Y, Liaw C, Chuang C. The role of surgery in renal cell carcinoma with pancreatic metastasis. Biomed J. (2015) 38:173–6. 10.4103/2319-4170.137771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Gajendra S, Sachdev R, Mohapatra I, Goel R, Goel S. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an unusual cause of bleeding pancreatic mass. J Clin Diagn Res. (2015) 9:15–7. 10.7860/JCDR/2015/14350.6519 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Kitade H, Yanagida H, Yamada M, Matsuura T, Yoshioka K, Satoi S, et al. Pylorus-preserving total pancreatectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2015) 9:212. 10.1186/s13256-015-0654-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Santoni M, Conti A, Partelli S, Porta C, Sternberg CN, Procopio G, et al. Surgical resection does not improve survival in patients with renal metastases to the pancreas in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Surg Oncol. (2015) 22:2094–100. 10.1245/s10434-014-4256-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Wiltberger G, Bucher JN, Krenzien F, Benzing C, Atanasov G, Schmelzle M, et al. Extended resection in pancreatic metastases: feasibility, frequency, and long-term-outcome: a retrospective analysis. BMC Surgery. (2015) 15:126. 10.1186/s12893-015-0114-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Yuasa T, Inoshita N, Saiura A, Yamamoto S, Urakami S, Masusa H, et al. Clinical outcome of patients with pancreatic metastases from renal cell cancer. BMC Cancer. (2015) 15:46. 10.1186/s12885-015-1050-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Boussios S, Zerdes J, Batsi O, Papakostas P, Seraj E, Pentheroudakis G, et al. Pancreatic resection for renal cell carcinoma: an exceptionally rare coexistence. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2016) 27:198–201. 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.08.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Dong J, Cong L, Zhang TP, Zhao YP. Pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. (2016) 15:30–8. 10.1016/S1499-3872(16)60052-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Fikatas P, Klein F, Andreou A, Schmuck RB, Pratschke J, Bahra M. Long-term survival after surgical treatment of renal cell carcinoma metastasis within the pancreas. Anticancer Res. (2016) 36:4273–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Koga C, Murakami M, Shimizu J, Matsumara T, Kameda C, Kawabata R, et al. A case of multiple pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma diagnosed using EUS-FNA. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2016) 43:2356–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Miura T, Nakamura N, Ogawa K, Watanabe Y, Yonekura K, Sanada T, et al. Resection of pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma 21 years after nephrectomy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2016) 43:2187–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Nihei K, Sakamoto K, Suzuki S, Mishina T, Otaki M. A case of pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2016) 43:2274–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Rückert F, Distler M, Ollmann D, Lietzmann A, Birgin E, Teoule P, et al. Retrospective analysis of survival after resection of pancreatic renal cell carcinoma metastases. Int J Surg. (2016) 26:64–8. 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Chatzizacharias NA, Rosich-Medina A, Dajani K, Harper S, Huguet E, Liau SS, et al. Surgical management of hepato-pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. World J Gastrontest Oncol. (2017) 15:70–7. 10.4251/wjgo.v9.i2.70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Garcia-Major Fernandez RL, Fernandez-Gonzales M. Diagnosis and treatment of isolated metastases from renal clear cell carcinoma: report of a case and review of literature. Cir Cir. (2017) 85:436–9. 10.1016/j.circen.2017.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Ko S, Yun S, Kim S, Kim T, Seo H. Pancreatic resection for renal cell carcinoma metastasis: a case review. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2017) 21:176–9. 10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.3.176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Shatveryan GA, Chardarov NK, Bagmet NN, Ratnikova NP, Bedzhanyan AL, Petrenko KN, et al. Isolated pancreatic metastases of renal cell carcinoma. Khirurgiia (Mosk). (2017) 12:36–40. 10.17116/hirurgia20171236-40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Yagi T, Hashimoto D, Taki K, Yamamura K, Chikamoto A, Ohmuraya M, et al. Surgery for metastatic tumors to the pancreas. Surg Case Rep. (2017) 3:31. 10.1186/s40792-017-0308-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Zianne M, Takahashi N, Tsujibata A, Miwa K, Goto Y, Matano Y. Asymptomatic pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma diagnosed 21 years after nephrectomy. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. (2017) 2017:8765264. 10.1155/2017/8765264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Boni A, Cochetti G, Ascani S, Del Zingaro M, Quadrini F, Paladini A, et al. Robotic treatment of oligometastatic kidney tumor with synchronous pancreatic metastasis: case report and review of the literature. BMC Surg. (2018) 18:40. 10.1186/s12893-018-0371-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Ito T, Takada R, Omoto S, Tsuda M, Masuda D, Kato H, et al. Analysis of prognostic factors in pancreatic metastasis: a multicentre retrospective analysis. Pancreas. (2018) 47:1033–9. 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Limaiem F, Bouraoui S. Metastasis of renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas 11 years postnephrectomy. Pan Afr Med J. (2018) 30:53. 10.11604/pamj.2018.30.53.15355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Madkhali AA, Shin S, Song KB, Lee JH, Hwang DW, Park KM, et al. Pancreatectomy for secondary metastasis of the pancreas: a single-institution experience. Medicine. (2018) 97:e12653. 10.1097/MD.0000000000012653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Nogueira M, Dias SC, Silva AC, Pintob J, Machado J. Solitary pancreatic renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Autops Case Rep. (2018) 23:8. 10.4322/acr.2018.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Yamashita H, Toyama H, Terai S, Mukubou H, Shirakawa S, Ishida J, et al. A patient with multiple pancreatic metastases undergoing total pancreatectomy 18 years after renal cell carcinoma resection. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2018) 45:2214–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Yu Q, Kan F, Ma Z, Wang T, Lin G, Chen B, et al. CT Diagnosis for metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas: three case reports. Medicine. (2018) 97:e13200. 10.1097/MD.0000000000013200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Anderson B, Williams GA, Sanford DE, Lu J, Dageforde LA, Hammill CW, et al. A 22-year experience with pancreatic resection for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). (2019). 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.05.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Ayari Y, Ben Rhouma S, Boussaffa H, Chelly B, Hamza K, Sellami A, et al. Metachronous isolated locally advanced pancreatic metastasis from chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2019) 60:196–9. 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.05.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Brozetti S, Sterpetti AV. Unexpected prolonged survival after extended and emergent resection of pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer. (2019) 50:1055–8. 10.1007/s12029-019-00209-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Endo Y, Noda H, Watanabe F, Kato T, Kakizawa N, Ichida K, et al. A retrospective analysis of preoperative evaluation and surgical resection for metastatic tumors of the pancreas. Indian J Surg Oncol. (2019) 10:251–7. 10.1007/s13193-019-00905-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Geramizadeh B, Kashkooe A, Nikeghbalian S, Malek-Hosseini S. Metastatic tumors to the pancreas, a single center study. Arch Iran Med. (2019) 22:50–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Glinka J, Sanchez Claria R, Ardiles V, de Santibañes E, Pekolj J, de Santibañes M, et al. The pancreas as a target of metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: Results of surgical treatment in a single institution. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2019) 23:240–4. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.3.240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Jo S, Yang IS, Song S. Surgery for metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the pancreatic head: a case report and literature review. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2019) 23:91–5. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.1.91 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Ma Y, Yang J, Qin K, Zhou Y, Ying X, Yuan F, et al. Resection of pancreatic metastatic renal cell carcinoma: experience and long-term survival outcome from a large center in China. Int J Clin Oncol. (2019) 24:686–93. 10.1007/s10147-019-01399-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Teranishi R, Hatanaka N, Hara S, Takayama K, Shimura Y, Ohashi T, et al. Two cases of pancreatectomy for pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2019) 46:561–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Yamaguchi H, Kimura Y, Nagayama M, Imamura M, Tanaka S, Yoshida E, et al. Central pancreatectomy in portal annular pancreas for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case report. World J Surg Oncol. (2019) 17:76. 10.1186/s12957-019-1622-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Wakabayashi T, Uchida T, Oyama H, Tanaka K. A case of laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for metachronous pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi. (2019) 80:983–9. 10.3919/jjsa.80.983 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Saitoh H, Kobayashi N, Yoshida K, Suwata J, Uchijima Y, Nakame Y. Possible metastatic routes via portocaval shunts in renal adenocarcinoma with liver metastasis. Urology. (1991) 37:598–601. 10.1016/0090-4295(91)80336-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Allen-Mersh T. Significance of the site of origin of pancreatic exocrine adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol. (1982) 35:544–6. 10.1136/jcp.35.5.544 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Reddy S, Edil BH, Cameron JL, Pawlik TM, Herman JM, Gilson MM, et al. Pancreatic resection of isolated metastases from nonpancreatic primary cancers. Ann Surg Oncol. (2008) 15:3199–206. 10.1245/s10434-008-0140-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Hedley BD, Chambers AF. Tumor dormancy and metastasis. Cancer Res. (2009) 102:67–101. 10.1016/S0065-230X(09)02003-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Muenst S, Läubli H, Soysal SD, Zippelius A, Tzankov A, Hoeller S. The immune system and cancer evasion strategies: therapeutic concepts. J Intern Med. (2016) 279:541–62. 10.1111/joim.12470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Choi Y, Lee J, Lee C, Han W, Kang C, Lee W. Laparoscopic total pancreatectomy for multiple metastasis of renal cell carcinoma of the pancreas: a case report and literature review. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2017) 21:96–100. 10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.2.96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Jonasch E, Gao J, Rathmell KW. Renal cell carcinoma. BMJ. (2014) 349:g4797. 10.1136/bmj.g4797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Iacovelli R, Lanoy E, Albiges L, Escudier B. Tumour burden is an independent prognosic factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. (2012) 110:1747–54. 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11518.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.McNichols DW, Segura JW, DeWeerd JH. Renal cell carcinoma: long-term survival and late recurrence. J Urol. (1981) 126:17–23. 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)54359-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Dekernion JB, Ramming KP, Smith RB. The natural history of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a computer analysis. J Urol. (1978) 120:148–52. 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)57082-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Sweeney AD, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Brunicardi C, Fisher WE. Value of pancreatic resection for cancer metastatic to the pancreas. J Surg Res. (2009) 156:189–98. 10.1016/j.jss.2009.01.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Strobel O, Hackert T, Hartwig W, Bergmann F, Hinz U, Wente MN, et al. Survival data justifies resection for pancreatic metastases. Ann Sug Oncol. (2009) 16:3340–9. 10.1245/s10434-009-0682-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Kalra S, Atkinson BJ, Matrana MR, Matin SF, Wood CG, Karam JA, et al. Prognosis of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and pancreatic metastases. BJU Int. (2016) 117:761–5. 10.1111/bju.13185 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Grassi P, Verzoni E, Mariani L, De Braud F, Coppa J, Mazzaferro V, et al. Prognostic role of pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: results from an Italian center. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2013) 11:484–8. 10.1016/j.clgc.2013.04.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Jonasch E. Updates to the management of kidney cancers. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2018) 16:639–41. 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Flippot R, Escudier B, Albiges L. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: toward new paradigms in renal cell carcinoma. Drugs. (2018) 78:1443–57. 10.1007/s40265-018-0970-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Chang A, Zhao L, Zhu Z, Boulanger K, Xiao H, Wakefield MR, Bai Q, Fang Y. The past, present and future of immunotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39:2683–7. 10.21873/anticanres.13393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Da Silva JL, Dos Santos A, Nunes N, Lino da Silva F, Ferreira C, de Melo AC. Cancer immunotherapy: the art of targeting the tumor immune microenvironment. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2019) 84:227–40. 10.1007/s00280-019-03894-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Sönmez MG, Sönmez LÖ. New treament modalities with vaccine therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Ann. (2019) 11:119–25. 10.4103/UA.UA_166_17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Adashek JJ, Genovese G, Tannir NM, Msaouel P. Recent advancements in the treatment of metastatic clear cell renal carcinoma: a review of the evidence using second-generation p-values. Cancer Treat Res Commun. (2020) 23:100166. 10.1016/j.ctarc.2020.100166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Chara L, Rodríguez B, Holgado E, Ramírez N, Fernández-Rañada I, Mohedano N, et al. An unusual metastatic renal cell carcinoma with maintained complete response to sunitinib treatment. Case Rep Oncol. (2011) 4:583–6. 10.1159/000335016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Beck J, Bellmunt J, Escudier B. Long-term stable disease in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: sorafenib sequenced to sunitinib and everolimus: a case study. Med Oncol. (2011) 28:1379–83. 10.1007/s12032-010-9589-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Medioni J, Choueiri TK, Zinzindohoue F, Cho D, Fournier L, Oudard S. Response of renal cell carcinoma pancreatic metastasis to Sunitinib treatment: a retrospective analysis. J Urol. (2009) 181:2470–5. 10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Sbitti Y, Debbagh A, Slimani K, Mahi M, Errihani H, Ichou M. When tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib can be discontinued in metastatic renal cell carcinoma to pancreas: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2018) 12:80. 10.1186/s13256-018-1597-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Akgül Ö, Çetinkaya E, Ersöz S, Tez M. Role of surgery in colorectal cancer liver metastases. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:6113–22. 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Taniai N, Akimaru K, Yoshida H, Tajiri T. Surgical treatment for better prognosis of patients with liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. (2007) 54:1805–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Markar SR, Mikhail S, Malietzis G, Athanasiou T, Mariette C, Sasako M, et al. Influence of surgical resection of hepatic metastases from gastric adenocarcinoma on long-term survival: systematic review and pooled analysis. Ann Surg. (2016) 263:1092–101. 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Ishihara H, Kondo T, Yoshida K, Omae K, Takagi T, Iizuka J, Kobayashi H, et al. Evaluation of tumor burden after sequential molecular-targeted therapy in patients with metastatic renal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2017) 47:226–32. 10.1093/jjco/hyw196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Basappa NS, Elson P, Golshayan AR, Wood L, Garcia JA, Dreicer R, et al. The impact of tumor burden characteristics in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Cancer. (2011) 117:1183–9. 10.1002/cncr.25713 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Stein WD, Huang H, Menefee M, Edgerly M, Kotz H, Dwyer A, et al. Other paradigms: growth rate constants and tumor burden determinated using computed tomography data correlate strongly with the overall survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J. (2009) 15:441–7. 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181be1b90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Nakamura S, Suzuki S, Baba S. Resection of liver metastases of colorectal carcinoma. World J Surg. (1997) 21:741–7. 10.1007/s002689900300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Ren L, Lv SX, Zhong YS, Xu JM, Wei Y, Fan J, et al. Prognostic analysis of 669 liver metastasis of colorectal cancer cases. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2009) 12:337–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Ministrini S, Solaini L, Cipollari C, Sofia S, Marino E, D'Ignazio A, et al. Surgical treatment of hepatic metastases from gastric cancer. Updat Surg. (2018) 70:273–8. 10.1007/s13304-018-0536-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Selzner M, Morse MA, Vredenburgh JJ, Meyers WC, Clavien PA. Liver metastases from breast cancer: long-term survival after curative resection. Surgery. (2000) 127:383–9. 10.1067/msy.2000.103883 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Thompson RH, Hill JR, Babayev Y, Cronin A, Kaag M, Kundu S, et al. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma risk according to tumor size. J Urol. (2009) 182:41–5. 10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Doehn C, Siebels M, Steiner T. Nachsorge beim Nierenzellkarzinom in Abhängigkeit des Stadiums und der erfolgten Therapie. Urologe. (2020) 59:162–8. 10.1007/s00120-020-01126-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Shao Y, Xiong S, Sun G, Dou W, Hu X, Yang W, et al. Prognostic analysis of postoperative clinically nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2020) 9:959–70. 10.1002/cam4.2775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Tosco L, Van Poppel H, Frea B, Gregoraci G, Joniau S. Survival and impact of clinical prognostic factors in surgically treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. (2013) 63:646–52. 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.09.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Macherey S, Kauffmann C, Heidenreich A, Doerr F, Wahlers T, Hekmat K. Lungenmetastasenchirurgie beim Nierenzellkarzinom. Urologe. (2017) 56:1025–30. 10.1007/s00120-017-0353-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Assouad J, Petkova B, Berna P, Dujon A, Foucault C, Riquet M. Renal cell carcinoma lung metastases surgery: pathologic findings and prognostic factors. Ann Thorac Surg. (2007) 84:1114–20. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.04.118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Pfannschmidt J, Hoffmann H, Muley T, Krysa S, Trainer C, Dienemann H. Prognostic factors for survival after pulmonary resection of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. (2002) 74:1653–7. 10.1016/S0003-4975(02)03803-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Piltz S, Meimarakis G, Wichmann MW, Hatz R, Schildberg FW, Fuerst H. Long-term results after pulmonary resection of renal cell carcinoma metastases. Ann Thorac Surg. (2002) 73:1082–7. 10.1016/S0003-4975(01)03602-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Ruys AT, Tanis PJ, Iris N, van Duijvendijk P, Verhoef C, Porte RJ, et al. Surgical treatment of renal cell cancer liver metastases: a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol. (2011) 18:1932–8. 10.1245/s10434-010-1526-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Adam R, Chiche L, Aloia T, Elias D, Salmon R, Rivoire M, et al. Hepatic resection for noncolorectal nonendocrine liver metastasis. Analysis of 1452 patients and development of a prognostic model. Ann Surg. (2006) 244:524–35. 10.1097/01.sla.0000239036.46827.5f [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Thelen A, Jonas S, Benckert C, Lopez-Hänninen E, Rudolph B, Neumann U, et al. Liver resection for metastases from renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg. (2007) 31:802–7. 10.1007/s00268-007-0685-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear renal cell carcinoma. Nature. (2013) 499:43–9. 10.1038/nature12222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Mitchell TJ, Rossi SH, Klatte T, Stewart GD. Genomics and clinical correlates of renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol. (2018) 36:1899–911. 10.1007/s00345-018-2429-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Majid S, Varahram S, Hashimoto Y, Bhat NS, et al. MicroRNA-203 inhibits long noncoding RNA HOTAIR and regulates tumorigenesis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2018) 17:1061–9. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Ji S, Zhang X, Han Z, Zhao Y, Lu Q. MicroRNA-372 functions as a tumor suppressor in cell invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ATAD2 in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Let. (2019) 17:2400–8. 10.3892/ol.2018.9871 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Wang L, Yang G, Zhao D, Wang D, Bai Y, Peng Q, et al. CD103-positive CSC exosomes promotes EMT of clear cell renal carcinoma: role of remote MiR-19b-3p. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:86. 10.1186/s12943-019-0997-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Ding X. MicroRNAs: regulators of cancer metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Chin J Cancer. (2014) 33:140–6. 10.5732/cjc.013.10094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Li Y, Chen D, Su Z, Li Y, Liu J, Jin L, et al. MicroRNA-106b functions as an oncogene in renal cell carcinoma by affecting cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 13:1420–6. 10.3892/mmr.2015.4656 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Su Z, Chen D, Zhang E, Li Y, Yu Z, Shi M, et al. MicroRNA-509-3p inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 12:1535–43. 10.3892/mmr.2015.3498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Gu C, Wang Z, Jin Z, Li G, Kou Y, Jia Z, et al. MicroRNA-212 inhibits the proliferation, migration ad invasion of renal cell carcinoma by targeting X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). Oncotarget. (2017) 8:92119–33. 10.18632/oncotarget.20786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Yamasaki T, Seki N, Yoshino H, Itesako T, Hidaka H, Yamada Y, et al. MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell migration and invasion in renal cell carcinoma through targeting caveolin-2 involved in focal adhesion pathway. J. Urol. (2013) 190:1059–68. 10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Wei R, Ye X, Zhao Y, Jia N, Liu T, Lian W, et al. MicroRNA-218 inhibits the cell proliferation and migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through targeting cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A. Oncol Lett. (2019) 17:3211–8. 10.3892/ol.2019.9986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Shiomi E, Sugai T, Ishida K, Osakabe M, Tsuyukubo T, Kato Y, et al. Analysis of expression patterns of microRNAs that are closely associated with renal carcinogenesis. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:431. 10.3389/fonc.2019.00431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Xiao W, Wang X, Wang T, Xing J. MIR-223–3p promotes cell proliferation and metastasis by downregulating SLC4A4 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging. (2019) 11:615–31. 10.18632/aging.101763 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.He C, Chen ZY, Li Y, Yang ZQ, Zeng F, Cui Y, et al. miR-10b suppresses cell invasion and metastasis through targeting HOXA3 regulated by FAK/YAP signalling pathway in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Nephrol. (2019) 20:127. 10.1186/s12882-019-1322-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Li Y, Guan B, Liu J, Zhang Z, He S, Zhan Y, et al. MicroRNA-200b is downregulated and suppresses metastasis by targeting LAMA4 in renal cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine. (2019) 44:439–51. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Zhou H, Tang K, Liu H, Zeng J, Li H, Yan L, et al. Regulatory network of two tumor-suppressive noncoding RNAs interferes with the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2019) 16:554–65. 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Wu X, Weng L, Li X, Guo C, Pal SK, Jin JM, et al. Identification of a 4-microRNA signature for clear cell renal carcinoma metastasis and prognosis. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e35661. 10.1371/journal.pone.0035661 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Yu L, Xiang L, Feng J, Li B, Zhou Z, Li J, et al. miRNA-21 and miRNA-223 expression signature as a predictor for lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and survival in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. J Cancer. (2018) 9:3651–9. 10.7150/jca.27117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Heinzelmann J, Unrein A, Wickmann U, Baumgart S, Stapf M, Szendroi A, et al. MicroRNAs with prognostic potential for metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a comparison of primary tumors and distant metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. (2014) 21:1046–54. 10.1245/s10434-013-3361-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Metastasis: dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. (2002) 2:563–72. 10.1038/nrc865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Walenkamp AM, Lapa C, Herrmann K, Wester HJ. CXCR4 ligands: the next big hit? J Nucl Med. (2017) 58:77S−82S. 10.2967/jnumed.116.186874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Shibue T, Weinberg RA. Metastatic colonization: settlement, adaptation and propagation of tumor cells in a foreign tissue environment. Semin Cancer Biol. (2011) 21:99–106. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Talmadge JE, Fidler IJ. AACR centennial series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:5649–69. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Sceneay J, Smyth M, Möller A. The pre-metastatic niche: finding common ground. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2013) 32:449–64. 10.1007/s10555-013-9420-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 293.Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley AH, Vincent L, Costa C, et al. VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature. (2005) 438:820–7. 10.1038/nature04186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 294.Liu Y, Cao X. Characteristics and significance of the pre-metastatic niche. Cancer Cell. (2016) 30:668–81. 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.09.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 295.Peinado H, Zhang H, Matei IR, Costa-Silva B, Hoshino G, Rodrigues G, et al. Pre-metastatic niches: organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. (2017) 17:302–17. 10.1038/nrc.2017.6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 296.Grange C, Brossa A, Bussolati B. Extracellular vesicles and carried miRNAs in the progression of renal cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:E1832 10.3390/ijms20081832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 297.Liu Q, Zhang H, Jiang X, Qian C, Liu Z, Luo D. Factors involved in cancer metastasis: a better understanding to “seed and soil” hypothesis. Mol Cancer. (2017) 16:176. 10.1186/s12943-017-0742-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 298.Wang Y, Ding Y, Guo N, Wang S. MDSCs: Key criminals of tumor pre-metastatic niche formation. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:172. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00172 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 299.Grange C, Tapparo M, Collino F, Vitillo L, Damasco C, Deregibus MC, et al. Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:5346–56. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 300.Gai C, Pomatto MA, Grange C, Deregibus MC, Camussi G. Extracellular vesicles in onco-nephrology. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:29. 10.1038/s12276-019-0213-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 301.Raman R, Vaena D. Immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a comprehensive review. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 2015:367354. 10.1155/2015/367354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 302.Elhilali M, Gleave M, Fradet Y, Venner D, Saad F, Klotz L, et al. Placebo-associated remissions in a multicentre, randomized, double-blind trial of interferon γ-1b for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. (2000) 86:613–8. 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00880.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 303.Mazza C, Escudier B, Albiges L. Nivolumab in renal cell carcinoma: latest evidence and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2017) 9:171–81. 10.1177/1758834016679942 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 304.Koshkin VS, Barata P, Zhang T, George DJ, Atkins MB, Kelly WJ, et al. Clinical activity of nivolumab in patients with non-clear renal cell carcinoma. J Immunother. (2018) 6:9. 10.1186/s40425-018-0319-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 305.Wang K, Li J, Li S, Bolund L, Wiuf C. Estimation of tumor heterogenity using CGH array data. BMC Bioinformatics. (2009) 10:12. 10.1186/1471-2105-10-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 306.Hunter KW. Host genetics and tumour metastasis. Br J Cancer. (2004) 90:752–5. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 307.Gandalovičová A, Rosel D, Fernandes M, Veselý P, Heneberg P, Cermák V, et al. Migrastatics-antimetastatic and anti-invasion drugs: promises and challenges. Trends Cancer. (2017) 3:391–406. 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.04.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]