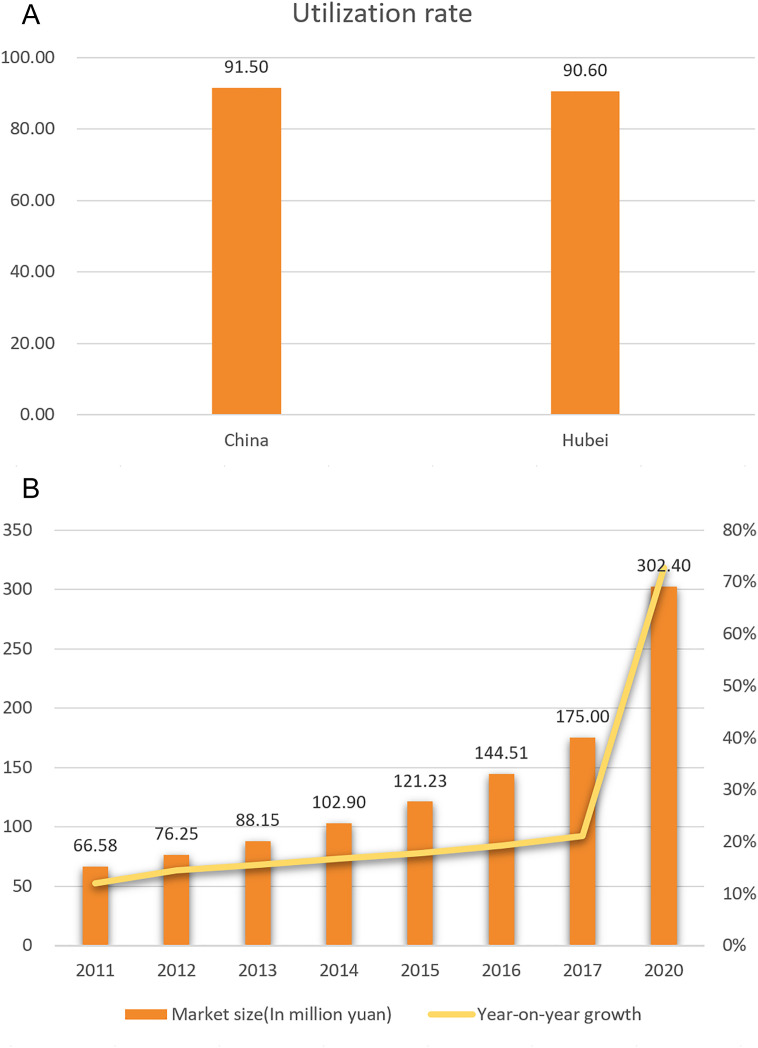
We appreciate the work that Kai Zhang has done to highlight the treatment of COVID-19 in China via the use of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) [1]. COVID-19 initially occurred in China at the end of December 2019 [2]. The Chinese government began to build many shelter hospitals in Hubei Province to treat patients with COVID-19, and medical workers from all over the country rushed to Wuhan to provide assistance [3]. Among the medical staff supporting Hubei Province, there were more than 4500 members of China's TCM system. In addition, TCM has been approved for the treatment of COVID-19 [4]. As of March 23rd, among the patients with COVID-19, 74,187 patients (about 91.5%), had been treated with TCM; of these, 61,449 people were treated in Hubei Province (Fig. 1A). Clinical efficacy data has shown that the overall effective rate of TCM treatment has reached more than 90% [5].
Fig. 1.
A. The patients with COVID-19 had been treated with TCM China and Hubei Province. B. The scale of the TCM market has significantly grown.
TCM is heavily involved in the fight against COVID-19, and has played an important role in the overall prevention of the disease, as well as in the treatment and rehabilitation of infected patients [6]. According to a number of US media reports, with the spread of the epidemic in the United States, the demand for TCM to treat colds and improve immunity has increased significantly. Consequently, the scale of the TCM market has grown significantly (Fig. 1B).
Although TCM treatment has played an important role in this epidemic, it is also important to note that it is relatively difficult for TCM articles to be published in journals around the world. The reasons for this are believed to be as follows. First, the treatment process of TCM is individualized; not everyone's medication is exactly the same, and it is therefore difficult to evaluate the curative effect of TCM via Western medicine assessment methods. Second, there are many classifications of TCM, and the style and manner of each type of medicine are very different. Third, the origins and curative effects of TCM are different, as can be the effects of the same prescription. Fourth, Chinese doctors generally do not accept Western medical treatment processes, and the writing method of TCM practitioners is also different from that of Western medicine practitioners. Finally, TCM practitioners are trained for a long time, and foreigners have some difficulties in understanding TCM.
We believe that TCM can play an important role in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 during this epidemic. However, determining how to improve TCM on the international stage going forward remains unclear. We trust that with the joint efforts of practitioners of TCM, it will surely be highlighted by the world.
Funding
No funding was received.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Acknowledgment
Our team would like to express our sincere gratitude to the medical staff all over the world who are fighting on the front lines against COVID-19.
References
- 1.Zhang K. Is traditional Chinese medicine useful in the treatment of COVID-19? Am J Emerg Med. Mar 25, 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.03.046. [pii: S0735-6757(20)30188-1] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rothan H.A., Byrareddy S.N. The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J Autoimmun. May 2020;109 doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feng Z.H., Cheng Y.R., Chen J., Ye L., Zhou M.Y., Wang M.W. Chinese medical personnel against the 2019-nCoV. J Infect. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.011. [S0163-4453(20)30082-7] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.National Health Commission . 7th ed. March 3, 2020. Diagnosis and treatment protocol of COVID-19.http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19 [in Chinese] [Google Scholar]
- 5.National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine; News report. More than 90% patients accepted the treatment of traditional Chinese medicine. http://www.satcm.gov.cn/xinxifabu/meitibaodao/2020-03-24/14229.html
- 6.Bai Qi-zhou, Wang Bing. In: Da-cheng, Zhang Siyuan, He Xiaoyang, Yang Ning, Yunjiu Gou., editors. Vol. 41. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ; 2020. Progress in the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia by traditional Chinese medicine; pp. 1–18. (Med Ed) [Google Scholar]