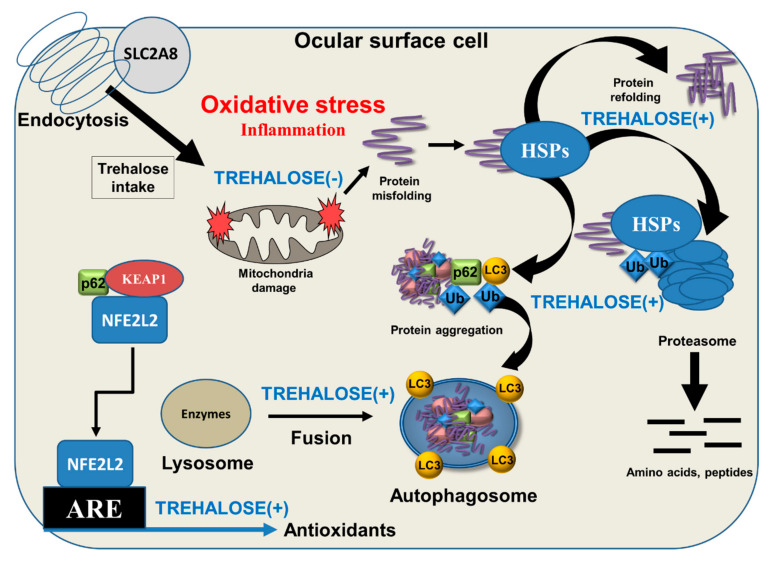
Figure 2.
Schematic presentation of intracellular cytoprotective effects of trehalose. Trehalose intake to cells is via endocytosis and under the control of Solute Carrier Family 2 Member 8 (SLC2A8). Ocular surface cells are constantly exposed to environmental oxidative stress, which may evoke mitochondrial damage, protein misfolding, aggregation, and inflammation. Trehalose helps protein refolding together with heat shock proteins (HSPs) and enhances ubiquitin (Ub)-mediated proteasomal and microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B light chain 3 (LC3)-controlled autophagic clearance. LC3 and p62/SQSTM1 have binding sites to Ub that direct the sealed material to autophagic degradation. Moreover, p62/SQSTM1 regulates antioxidant production via transcription factor NFE2L2 released from NFE2L2-KEAP1 (kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1) and p62/SQSTM1 complex, allowing its binding to the antioxidant response element (ARE) protein and promote the transcription of antioxidative proteins. All beneficial functions of trehalose (TREHALOSE (+)) prevent oxidative-stress-induced inflammation (TREHALOSE (-)).