Summary
Although cellular stress response is important in maintaining function and survival, overactivation of late-stage stress effectors causes dysfunction and death. We show that the Myelin Transcription Factors Myt1 (Nzf2), Myt2 (Myt1l, Nztf1, Png-1), and Myt3 (St18, Nzf3) prevent such overactivation in islet β-cells. Thus, we found that co-inactivating the Myt TFs in mouse pancreatic progenitors compromised postnatal β-cell function, proliferation, and survival, preceded by upregulation of late-stage stress-response genes Activating Transcription Factors (e.g., Atf4) and Heat Shock Proteins (Hsps). Myt1 binds putative enhancers of Atf4 and Hsps, whose overexpression largely recapitulated the Myt mutant phenotypes. Moreover, Myt(MYT)-TF levels were upregulated in mouse and human β-cells during metabolic stress-induced compensation, but downregulated in dysfunctional type 2 diabetic (T2D) human β-cells. Lastly, MYT knockdown caused stress-gene overactivation and death in human EndoC-βH1 cells. These findings suggest that Myt TFs are essential restrictors of stress-response overactivity.
Graphical Abstract
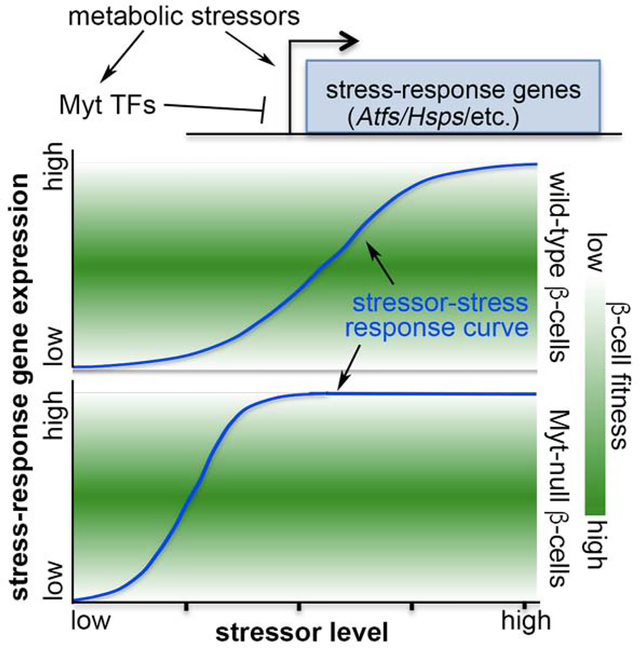
eTOC:
Precisely regulating stress response is necessary for cell function and survival under stressful conditions. In this study, Hu et al. showed that a family of Myelin Transcription Factors, themselves induced by cellular stress, directly repress the transcription of late-stage stress-response genes to facilitate postnatal islet β-cell proliferation, function, and survival.
Introduction
The unfolded-protein response (UPR) and oxidative stress response (OSR) are central protectors of cell function and survival (Hwang and Qi, 2018; Sies et al., 2017). During UPR in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), unfolded proteins sequester resident chaperones such as GRP78/Bip to stimulate early sensor-effectors, including Inositol-Requiring-1 (IRE1), Protein Kinase RNA-like ER Kinase (PERK), and Activating Transcription Factor 6 (ATF6) (Cao and Kaufman, 2014). Activation of these effectors downregulates overall protein production by affecting transcription, splicing, and translation mechanisms. Their activation also preferentially induces translation of several late-acting stress-pathway effectors such as Atf4, heat-shock proteins (Hsps), and Xbp1 – molecules required for nascent peptide folding and ER-associated protein degradation (Hwang and Qi, 2018). In the cytoplasm, conditions that cause protein denaturation, such as heat shock and reactive-oxygen species (ROS), activate heat-shock factors (HSFs) that induce transcription of Hsp and chaperonin (Cct) genes, which aid protein folding (Fulda et al., 2010). Nrf2 is also activated to induce enzymes to remove toxic ROS (Sies et al., 2017) during OSR. Collectively, these responses allow cells to survive in stressful environments. However, chronic activation or acute overactivation causes cell dysfunction and death (Hotamisligil and Davis, 2016). For neuronal and pancreatic islet β-cells, which cannot be readily regenerated, such loss of cells causes neuronal diseases and type 2 diabetes (T2D) (Cao and Kaufman, 2014; Chaari, 2019).
Over their long lifespan, pancreatic β-cells make exceedingly large amounts of insulin. This near-constant process inevitably co-produces mis-folded proinsulin (up to 20% of nascent proinsulin), which accumulates and induces UPR in the ER (Sun et al., 2015; Szabat et al., 2016). Glucose metabolism in β-cells, required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS), also increases ROS production that promotes insulin secretion at low levels, but activates OSR and UPR when level rise above a certain threshold (Guo et al., 2013; Hartl et al., 2011). The UPR and OSR in healthy β-cells facilitate protein homeostasis, insulin secretion, and cell proliferation (Lipson et al., 2006; Sharma et al., 2015; Szabat et al., 2016). However, OSR and UPR overactivation attenuates general protein translation and activates pro-apoptotic genes, such as CHOP, causing β-cell failure, a frequent occurrence under insulin resistance (IR) conditions. In the latter, peripheral tissues need higher insulin output for glucose homeostasis (Iurlaro and Munoz-Pinedo, 2016). β-cells compensate by increasing proliferation and insulin secretion, triggering more insulin biosynthesis and boosting UPR (Regazzi et al., 2014; Swisa et al., 2017b). Additionally, sustained high blood glucose levels causes excessive ROS production, exacerbating the already fully operational stress response and cause β-cell dysfunction/death, leading to T2D (Swisa et al., 2017b). Thus, β-cells are challenged to tune their stress response within a range that allows robust secretory function to be balanced with cell survival (Fonseca et al., 2011; Song et al., 2008).
The Myelin Transcription Factors (Myt TFs) [i.e. Myt1 (Nzf2), Myt2 (Myt1l, Nztf1, Png-1), and Myt3 (St18, Nzf3)] are paralogous zinc-finger proteins expressed in neural and neuro-endocrine cells (Gu et al., 2004; Henry et al., 2014; Kim and Hudson, 1992; Tennant et al., 2012; Vasconcelos et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2007). These TFs are known to promote the differentiation and maintain the function of neuronal cells, which principally occurs by recruiting the coregulator Sin3 to assemble histone deacetylases (HDAC)-containing chromatin modifiers thus repressing transcription (Mall et al., 2017; Romm et al., 2005; Scoville et al., 2015). Intriguingly, hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia potentiate Myt3 expression in β-cells (Henry et al., 2014; Tennant et al., 2012), implying a potential role in the stress response. Unfortunately, studying precisely how Myt TFs function in vivo has been greatly hampered by genetic compensation between the Myt family members (Wang et al., 2007).
We recently reported that early pancreatic removal of Myt1, 2, and 3 using Pdx1-driven Cre in Myt1F/F; Myt2F/F; Myt3F/F mice (termed 6F; Pdx1Cre hereafter) resulted in defective insulin secretion in post-weaning islets. This was thought to be due to precocious activation of Syt4 production, a key regulator of vesicle-plasma membrane fusion and insulin secretion in neonatal β-cells (Huang et al., 2018). Yet overexpression of Syt4 specifically in β-cells did not mimic the overt diabetes observed of 6F; Pdx1Cre mice (Huang et al., 2018), suggesting that other Syt4-independent processes were deregulated upon loss of Myt function. We show here that Myt TFs, themselves regulated by metabolic stressors, regulate the level of the cellular stress response, which is essential in controlling β-cell function, proliferative state, and survival.
Results
Inactivation of Myt TFs compromises β-cell proliferation, function, and survival
The 6F; Pdx1Cre mice were examined in greater detail than previously with the objective of revealing other processes regulated by Myt TFs in β-cells. Myt proteins were efficiently inactivated in 6F; Pdx1Cre pancreatic cells (Figure S1A), and there was no change in hypothalamic Myt levels, where spurious Pdx1Cre activity has been reported (Figure S1B). In addition, there were no obvious defects in the exocrine pancreas of mutant mice (Figure S1C).
6F; Pdx1Cre mice displayed higher fasting blood-glucose levels by postnatal day 14 (P14) in comparison to wild-type, Pdx1Cre, and Myt1F/F; Myt2F/F; Myt3F/F (termed 6F) controls, becoming more pronounced with aging (Figure 1A, Table S1) and correlated with the reductions in both 6F; Pdx1Cre body weight (Figure 1A) and glucose-induced plasma insulin level (Figure 1B). There was no change in the islet α-cell secreted plasma glucagon levels (Figure 1C) or insulin sensitivity (Figure 1D). As expected, glucose induced insulin secretion (GSIS) was compromised in isolated P14 6F; Pdx1Cre islets (Figure 1E).
Figure 1: Loss of Myt TFs reduces functional β-cell mass.
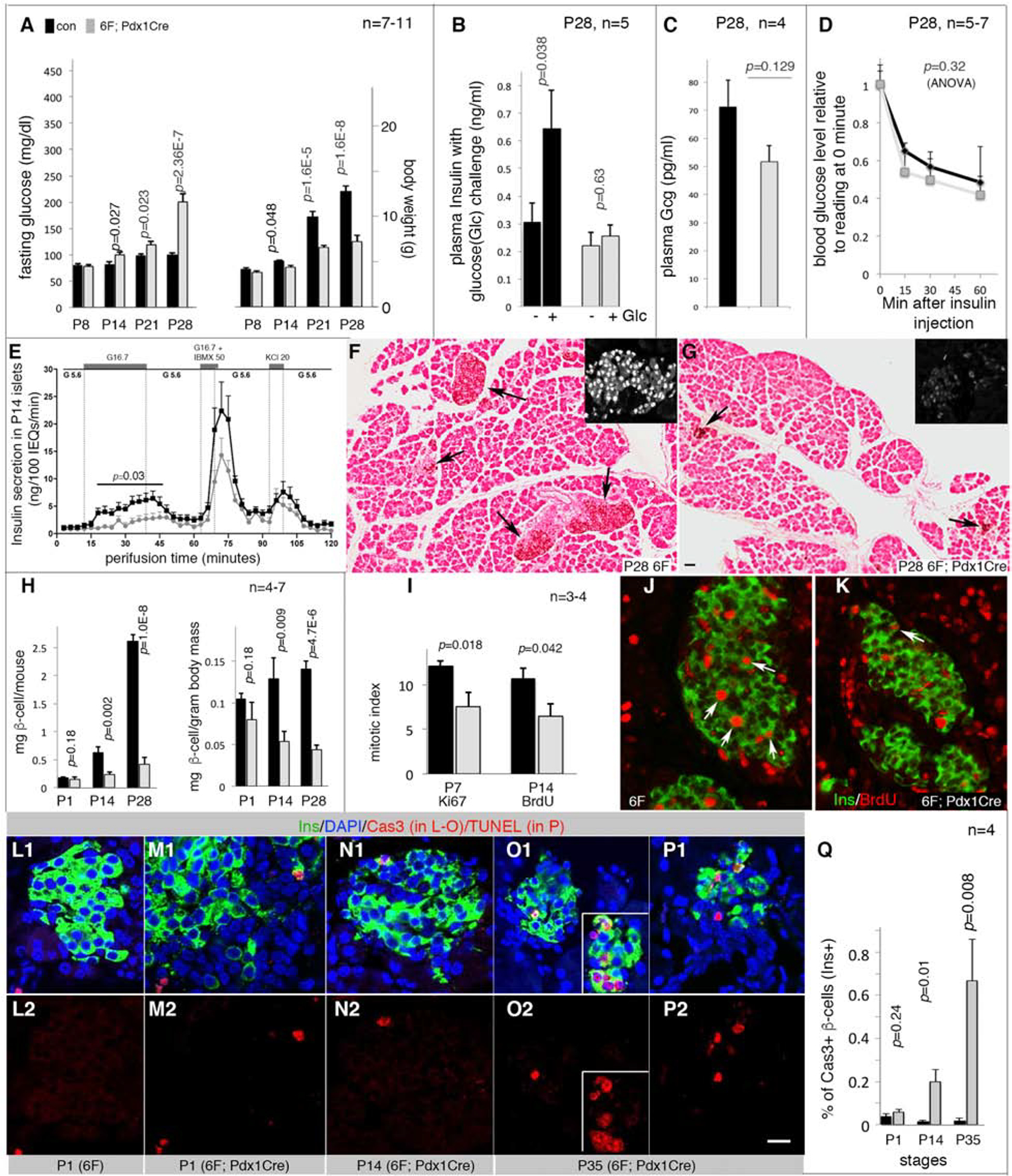
Also see Figure S1 and Table S1. The p-values were type 2, 2-tailed t-test except in D and E (ANOVA). Error bars in all quantification panels, SEM. “n”, the number of mice used. Black bars or lines, controls. Grey bars or lines, mutants.
(A) Glycemic phenotypes (left) and body weight (right). Controls include wild type, Pdx1Cre, and 6F mice.
(B) Plasma insulin before and 30 minutes after glucose challenge.
(C) Plasma glucagon (Gcg) levels in mice fasted overnight.
(D) Insulin tolerance tests. p, one-way ANOVA.
(E) Insulin-secretion assays via perifusion with sequential inductions by: G5.6 (5.6 mM glucose), G16.7, G5.6, G16.7 + 50 μM IBMX (a cyclase inhibitor to increase intracellular cAMP levels), G5.6+KCl (20 mM), and G5.6. p value is from one-way ANOVA, calculated between control/mutant samples stimulated by G16.7.
(F, G) Insulin detection with horse-radish peroxidase (HRP)-staining to visualize insulin+ cells (black arrows). Scale bar = 50 μm. Insets, examples of islet stained for Pdx1, showing islet morphology.
(H) β-cell mass, mg β-cells per mouse or mg β-cells per gram of body weight.
(I-K) Mitotic indices (I) assayed with Ki67 expression (P7. I) or BrdU incorporation (P14, with 2-day BrdU feeding. J, K.). Arrows, mitotic cells.
(L-Q) β-cells with activated Caspase 3 (Cas3, L-O) or TUNEL signals (P). The two rows are merged (top) and single (bottom) channels. Insets in O2 showed a cluster of Cas3+ β-cells. In P2, scale bar = 20 μm, applicable to J-P.
Although 6F; Pdx1Cre islets appeared largely normal in newborn mice, they were smaller than controls later on (Figure 1F, G). A reduced β-cell mass was observed within two weeks of birth (Figure 1H), accompanied by decreased proliferation (Figure 1I–K) and increased apoptosis (Figure 1L–Q).
Inactivating Myt TFs gradually reduces hallmark proteins in postnatal β-cells
Molecular defects in perinatal 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells were initially screened via immunofluorescence (IF) for various proteins important for β-cell development and function, such as the Glut2 glucose transporter and Mafa, Mafb, Pdx1, and Nkx6.1 TFs (Bastidas-Ponce et al., 2017). Both immature (P1 and P7) and mature (P28) islets were examined to define stage specific function of Myt TFs. While no change was observed in any of these β-cell markers at P1, the levels of Glut2, Mafa, and Pdx1 were reduced at P7 and P28 (Figure 2, columns 1–3). In contrast, Nkx6.1 levels were unchanged at all times (Figure 2, Column 4), while Mafb was elevated in β-cells after P7 (Figure 2, column 5). Intriguingly, the reduction in Mafa and Pdx1 in P7 6F; Pdx1Cre islet cells did not coincide with reduced mRNA levels by quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) (Figure S2A), implying that Myt TFs do not directly regulate Mafa and Pdx1 gene transcription at this stage and that the reduction in protein arose post-transcriptionally.
Figure 2. Myt TFs are required for sustained expression of several β-cell markers.
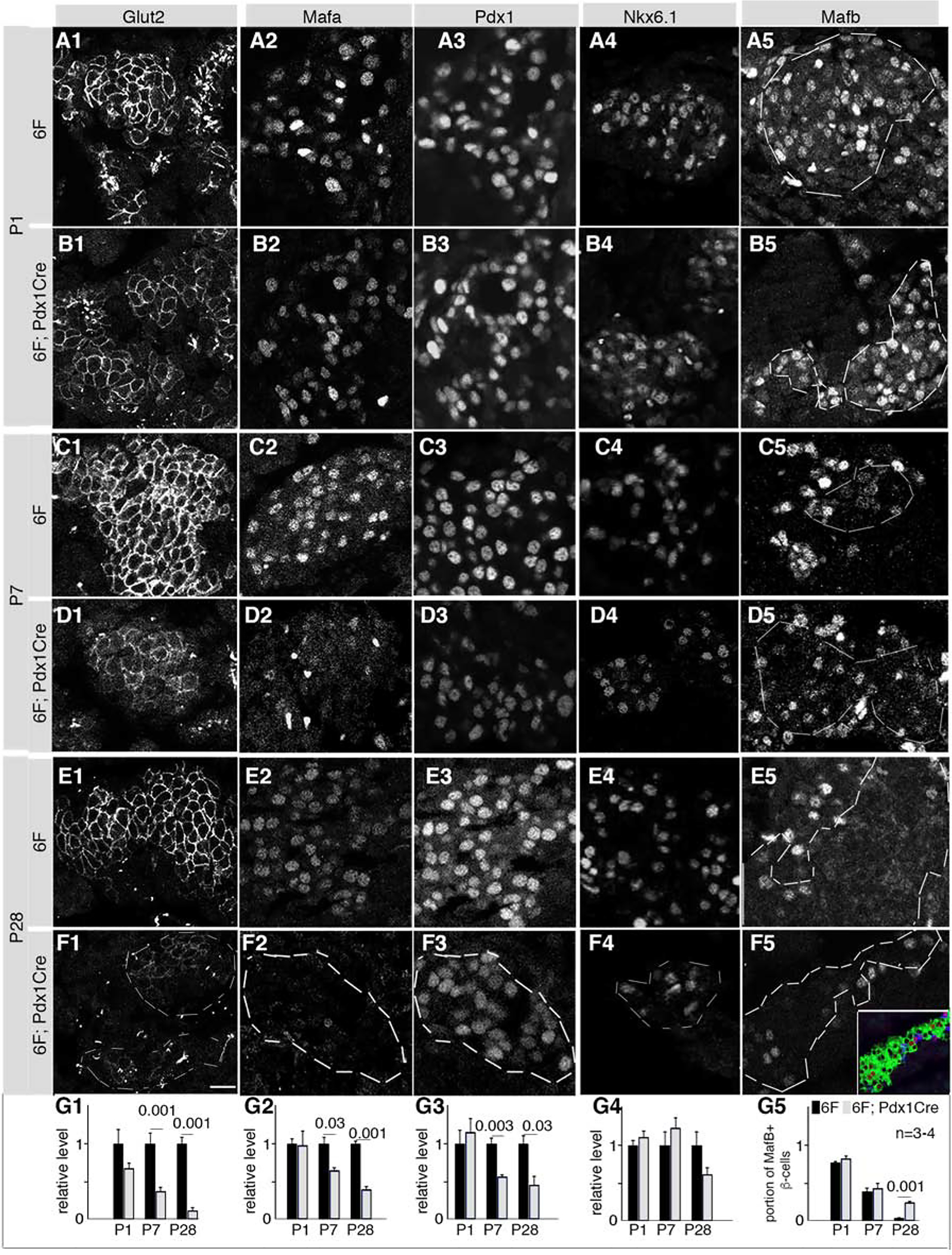
Also see Figure S2 and Table S1. Mice were derived from crosses between 6F and Myt1F/F; Myt2F/+; Myt3F/F; Pdx1Cre mice.
(A-F) Images of each assayed protein in islet cells in various stages and genotypes. Co-expression of insulin and/or Pdx1 located β-cells but are not shown [see inset in F5 (green: insulin, red: Mafb) as example]. Dotted lines in some panels circled β-cell areas (column 5) or islets (F1–F4). Scale bar in F1=20 μm, equal in all panels.
(G1–G5) Quantification of relative IF of corresponding markers (in each column) at various stages, assayed with Image J. Error bars, SEM. Three or four mice (“n”) were used for each assay. The p values (t-test, type 2, 2 tails) lower than 0.05 are indicated.
We extended our qPCR gene expression analysis using P1 and P14 islets to other TFs essential to β-cell function, including Hnf4a, Isl1, Mnx1, Neurod1, Nkx2.2, and Pax6, (Bastidas-Ponce et al., 2017). Mafa, Mafb, Nkx6.1, and Pdx1 were also included to determine if their response to Myt-inactivation changes over perinatal growth. Insm1, Mafb, Neurod1, and Pax6 expression levels were elevated in P1 6F; Pdx1Cre islets, although there was no change in other TFs (Figure S2B). Only Isl1 showed significant upregulation, while Mnx1 was downregulated at P14 (Figure S2C). However, there was no overt activation of Sst in P14 6F; Pdx1Cre islets (Figure S2C), a defining phenotype of Mnx1-null β-cells (Pan et al., 2015). Moreover, because elevated Insm1, Isl1, Mafb, Neurod1, and Pax6 in 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells would be expected to promote β-cell function and survival (Gu et al., 2010; Gutierrez et al., 2017; Swisa et al., 2017a) - opposite to the phenotypes observed - we concluded that these gene products, like Mnx1, are not the major effectors of Myt TF mutant β-cell dysfunction. We therefore turn to RNA-seq to identify bona fide functional Myt-target genes.
Myt TF-inactivation in pancreatic progenitors induces stress-response pathways in postnatal β-cells
RNA-seq analysis of flow-sorted Mip-eGFP transgene (TG)-expressing P1 β-cells revealed 1,432 down- and 1,432 up-regulated genes (Table S2). P1 β-cells were chosen to avoid postnatal confounding physiological abnormalities that can contribute to gene expression changes. This study revealed several β-cell TFs with upregulated expression (Insm1, Mnx1, Neurod1, Nkx2.2, and Pax6) or no change (Table S3), similar to P1 islet-based qPCR assays. The findings for Mnx1, Mafb, and Nkx2.2 are presumably different between islets and β-cells due to multiple islet cell types expressing these gene products (compare Table S3 and Figure S2B).
Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis identified several altered pathways in 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells (Subramanian et al., 2005). Ten of the top 14 (adjusted p<0.02) were upregulated, with seven of the ten associated with viral infection or ER-protein processing (Figure S3A, p<0.02, adjusted), all related to inflammatory or stress responses. The four downregulated pathways were associated with insulin secretion [Rap1 signaling (Kelly et al., 2010)], protein synthesis (ribosome), and/or proliferation (Ras and PI3K-AKT signaling) (Figure S3A). Intriguingly, the stress-response genes in the “protein processing in ER” category were among the most upregulated in 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells, including Atf4, Dnajb1, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, Hsph1, and Hspb1 (Table S2). Each of these stress effectors are associated with post-transcriptional control (Pan, 2013), in line with the reduced Mafa and Pdx1 protein (and not mRNA) production in 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells. We focused on evaluating how the stress-response genes contribute to the Myt-mutant phenotype in the rest of this study.
Myt-deficient β-cells activate late-stage stress effectors without activating early-stage sensor-effectors
Up-regulated mRNA for 12 of the 13 stress genes was verified in P1 and P14 6F; Pdx1Cre islets not subjected to flow sorting (Figure 3A), eliminating the possibility that tissue dissociation and flow sorting influenced their expression state.
Figure 3. Myt1 binds putative enhancers of several stress-response genes.
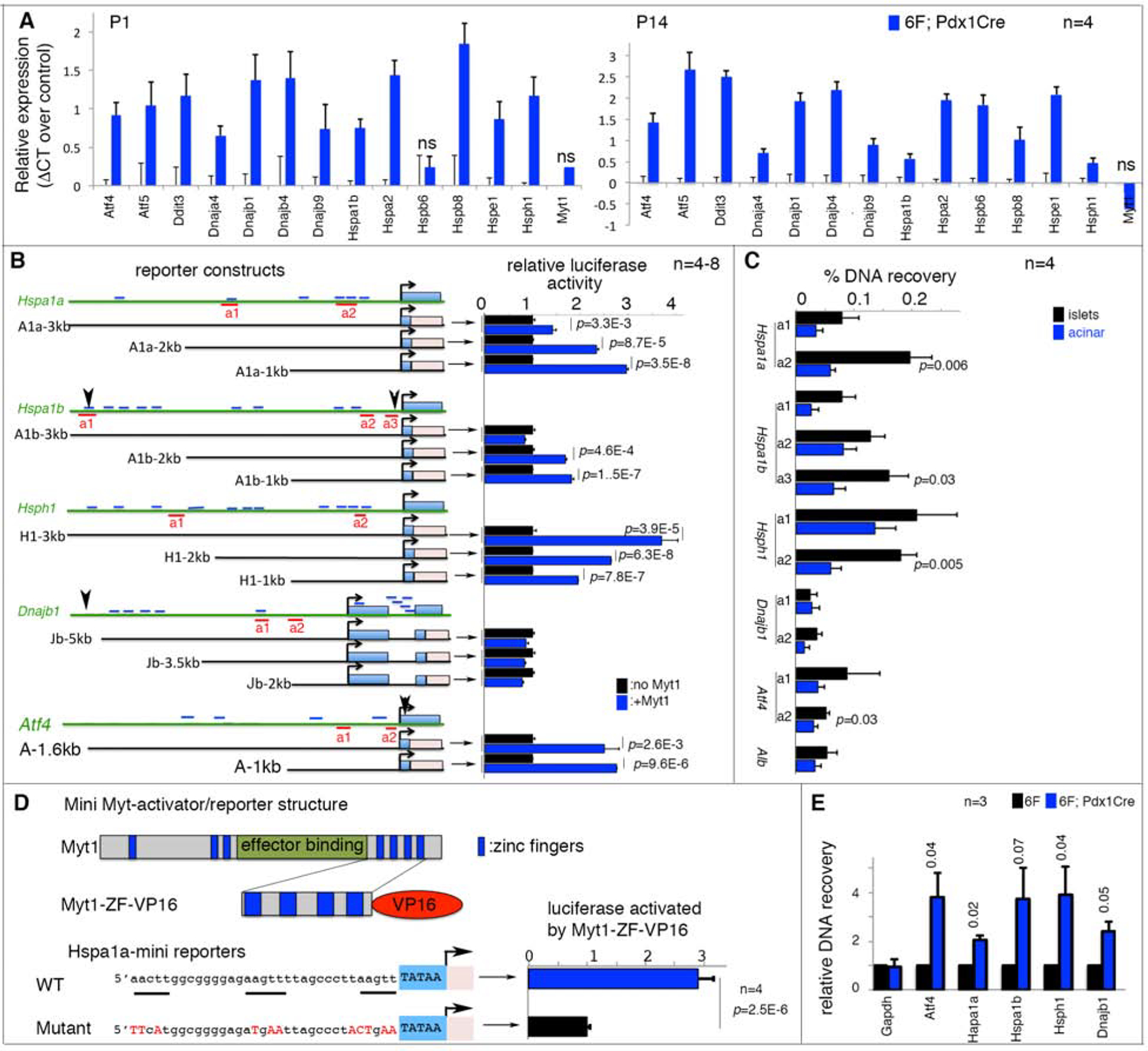
Also see Figure S3, S4, and Table S1. Error bars in all panels, SEM. p values in all quantification panels are from type 2, 2-tailed t-test.
(A) qPCR assays of mRNA levels in 6F and 6F; Pdx1Cre islets. “n”, number of mice, assayed as biological repeats. All expression changes except three marked “ns” are significant, with p<0.05.
(B) Reporter assays of stress-gene control elements. Diagrams on left: 5’ distal regions assayed. The approximate sizes (kb) of used regulatory regions are marked. Light-blue rectangles, stress-gene exons. Pink rectangles, firefly luciferase cDNA. Short blue lines, AAGTT motifs. Red underlines, amplicons for ChIP-PCR in panel C. Arrowheads (Hspa1b, Dnajb1, and Atf4), DNA elements reported to bind with Myt1 and/or Myt2 in heterologous cells. The right side bars in panel B, relative reporter activities assayed in HEK293T cells. p values <0.02 are marked.
(C) ChIP-PCR assays of Myt1 protein enrichment on putative stress-gene enhancers. Locations of PCR amplicons are shown in panel B. “n”, number of immunoprecipitations. p-values smaller than 0.05 are indicated. Acinar cells that do not express Myt1 were negative controls.
(D) Reporter assays using the “a2” Myt1-binding site of Hspa1a enhancers (a2 in panel B). The motif in wild type and mutated form was fused to a minimal CMV TATA box to produce reporters. The activator was a fusion protein between the C-terminal 4 zinc-fingers of Myt1 and a VP-16 activation domain. “n”, number of luciferase assays.
(E) ChIP-PCR assays of H3K27Ac in promoter regions of several stress genes using a rabbit anti-H3K27Ac antibody and chromatin of P14 6F or 6F; Pdx1Cre islets. The recovery was first normalized against DNA input in each sample. Recovery from 6F islets was then nominally set at 1 for group comparisons. “n”, number of chromatin preparations.
Despite elevated stress-gene expression in P1 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells, no stress-associated ER lumen dilation was detected (Figure S3B) nor was there any reduction in PERK-eIF2α-regulated protein translation (Figure S3C). In addition, Ire1α-mediated Xbp1 mRNA splicing was not increased in P1 or P14 6F; Pdx1Cre islets (Figure S3D). Stress-induced nuclear Foxo1 translocation was not obvious until P14, when high blood-glucose levels were observed (Figure S3E). Lastly, the expression of classical Atf6 targets such as Xbp1, Hspa5, Hsp90b1, as well as HSF targets such as Ccts were unchanged in P1 mutant β-cells (Figure S3F). Overall, these data indicate that up-regulation in late-acting stress-response gene in 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells was not mediated by the early-acting UPR sensor-effectors but instead by direct transcriptional repression.
Supporting our hypothesis, data mining of ChIP-seq data derived from fibroblasts and neuronal progenitors (Mall et al., 2017; Vasconcelos et al., 2016) identified putative Myt TF-binding sites in the 5’ cis-regulatory regions of Atf4, Hspa1b, and Dnajb1 (Table S2). In silico analyses also found multiple AAGTT consensus [reported Myt TF binding site (Bellefroid et al., 1996)] within 5’ cis-regulatory regions of Atf4, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, Hsph1, and Dnajb1 (Figure 3B). These bioinformatic results imply that Myt TFs could directly regulate stress-response genes in multiple cell types.
Myt1 binds to cis-regulatory sequences within stress-response mediators
To determine if the Myt TFs can exert regulatory control via the 5’-flanking regions of Atf4, Dnajb1, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, and Hsph1, luciferase-reporter constructs driven by sequences spanning their putative Myt binding elements were analyzed in co-transfection assays with Myt1 in HEK293T cells (Figure 3B). Myt1 significantly activated expression of the Atf4, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, and Hspa1 reporters, but not Dnajb1. The more modest effect on Dnajb1-driven transcription could reflect the absence in our construct of the fibroblast and neuronal Myt-binding site at roughly - 6 kbp (Mall et al., 2017)(Vasconcelos et al., 2016), which were unclonable for unknown reasons.
While expecting transcription repression by Myt TFs on their target genes from our in vivo results, Myt binding site driven reporters were activated in HEK293T cells, an “activity reversals” also reported by other groups. Specifically, the Myt TF AAGTT binding motif mediates transcriptional activation by Myt1 in cell culture (Bellefroid et al., 1996; Manukyan et al., 2018; Yee and Yu, 1998). The endogenous DNA motif, however, was found in repressed genes by ChIP-seq (Mall et al., 2017; Vasconcelos et al., 2016). These findings suggest that the chromatin landscape and likely Myt TF-interacting coregulators determine Myt transcriptional activity - either repression or activation.
Because of technical challenges involved in introducing Myt TF overexpression (OE) in primary β-cells at a physiological level (but see the db/db islet model below, which has Myt3 OE) or deriving transcriptional reporters that mimic endogenous chromatin configurations, we developed three alternative approaches to explore how Myt TFs regulate Atf4, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, Hsph1, and Dnajb1 expression. First, ChIP-PCR tested for Myt1 binding in mouse islets within endogenous gene loci using a highly specific Myt1 antibody (Figure S4A). Significant binding was observed within several Myt1-element-containing regions of the Hspa1a, Hspa1b, Hsph1, and Atf4 genes in islet cells compared to Myt1 non-producing acinar-cell controls (Figure 3C, S4B). Second, we analyzed whether a reporter gene driven by the Myt1-binding elements within the −435 to −402 bp region in Hspa1a was responsive to a fusion transcriptional activator between the Myt1 zinc fingers and the VP16 transactivation domain (Myt1ZF-VP16), which lacks the important protein domains that interact with co-regulators (Romm et al., 2005). Activation by Myt1ZF-VP16 in HEK293T cells was dependent on the presence of the wild-type Hspa1a enhancer (Figure 3D). Finally, the histone modification state near the endogenous promoters of Atf4, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, Hsph1, and Dnajb1 was analyzed in control and 6F; Pdx1Cre islets. Note that Myt TFs were proposed to work by recruiting Sin3/HDAC complexes for histone deacetylation (Mall et al., 2017; Romm et al., 2005), such that if Myt TFs repress these stress genes, we expected increased histone acetylation without Myt TFs. 6F; Pdx1Cre islets have significantly higher H3K27Ac levels near the promoters of these genes (Figure 3E). Collectively, these data suggest that the Myt TFs directly repress Atf4, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, Hsph1, and Dnajb1 transcription in vivo, leading us to test if OE of these stress genes can recapitulate some aspects of the 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cell abnormalities.
Over-expressing Hsps or Atf4 compromises postnatal islet β-cell proliferation, survival, and function
A tetracycline-inducible transgene was used to over-express Hsph1, Hspa1b, Dnajb1, and eGFP (termed TetO3H, Figure S5A), with eGFP identifying the overexpressing cells. The TG driver for Hsp-OE was RiprTTA, producing the reverse tetracycline-controlled transactivator specifically in β-cells under the regulation of a rat Insulin 2 enhancer/promoter (Nir et al., 2007). Continuous doxycycline (Dox) administration from embryonic day 16.5 (E16.5) resulted in ~6-fold Hsp-OE in P2 islets (Figure S5B). As reported by others (Brennand et al., 2007; Cai et al., 2012; Dadi et al., 2014), RiprTTA activates transgene expression in only a portion of the β-cell pool, producing mosaic islets that have eGFP+ and eGFP− β-cells (Figures 4A and S5C).
Figure 4. Hsp-OE compromises β-cell proliferation, identity, and survival.
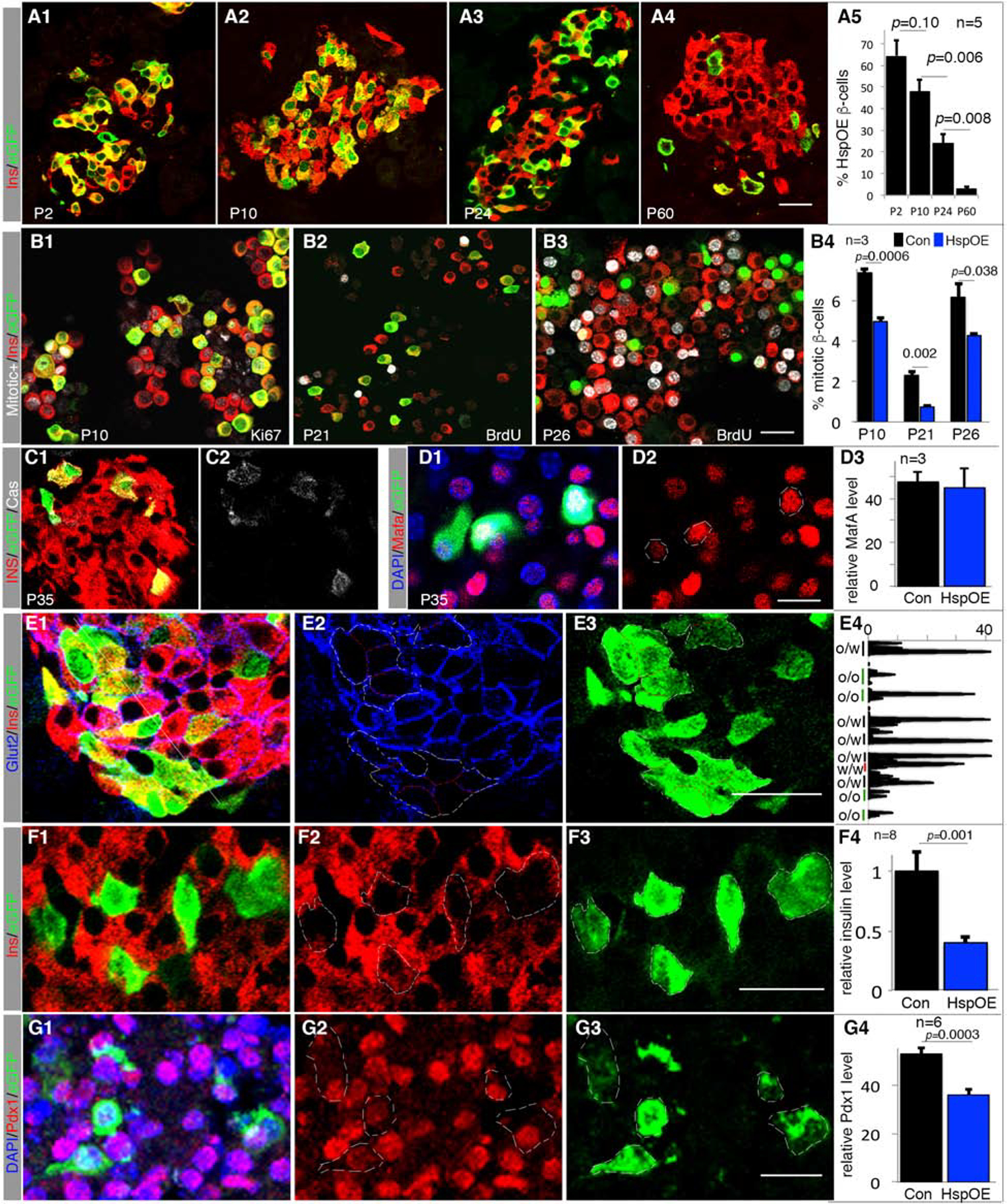
Also see Figure S5 and Table S1. Error bars in all quantification panels, SEM. “n”, number of pancreata examined. “p” values in all quantifications are from type 2, 2-tailed t-test.
(A) Portion of Hsp-OE β-cells at several postnatal stages, monitored via eGFP expression. p-values are indicated.
(B) Mitotic activity of β-cells with (eGFP+ cells) or without Hsp-OE (eGFP− cells). P10 (B1) cells were assayed for Ki67, and P21 (B2) and P26 (B3) via BrdU incorporation (in water supply) between P19-P21 or P21-P26, respectively. Scale bar=20 μm. p-values are indicated.
(C-G) Expression of β-cell markers in P35 islets with Hsp-OE, quantified with ImageJ. E4 is a line scan (yellow thin line in E1, top-left to bottom-right), showing Glut2 intensity along the borders of OE (O) or non-OE (W) cells. p-values smaller than 0.05 are shown. White circles mark outlines of whole β-cells. Scale bars = 20 μm.
The proportion of eGFP+ β-cells in Hsp-OE mice fell from ~64% at P2 to 1–3% at P60 under continuous Hsp-OE (Figure 4A). There was no TG silencing (Figure S5D, E), but lowered proliferation in Hsp-OE cells (Figure 4B). There was also increased apoptosis by P35 (Figure 4C), although not at P10 (Figure S5F). While Mafa and Mafb protein levels were unaffected by Hsp-OE at several stages examined (Figure 4D, S5G, H), the levels of Glut2, insulin, and Pdx1 were reduced in post-weaning Hsp-OE β-cells (Figure 4E–G, S5G–I). These results suggest that Hsp-OE mediates aspects of the proliferative, cell survival, and gene expression responses seen in 6F; Pdx1Cre islets.
To determine how Atf4 upregulation contributed to the 6F; Pdx1Cre phenotypes, ATF4-OE was activated by crossing Ins1Cre (with Cre knocked into the Ins1 locus) with Rosa26-ATF4LoxTG mice. This resulted in ~3-fold OE of ATF4 in P1 islets (Figure S6A–B). While mice with ATF4-OE displayed only slightly higher blood-glucose levels at P8, most developed diabetes by five weeks of age (Figure S6C). These defects were preceded by an increased α- to β-cell ratio and decreased β-cell Glut2, insulin, Mafa, and Pdx1 production (Figure 5A–E). The relative change in the proportion of α- to β-cells coincided with increased α-cell and decreased β-cell proliferation (Figure 5F), without obvious effects on β-cell apoptosis (Figure S6D, E). Additionally, ATF4-OE islets secreted an abnormally high amount of insulin at non-stimulating (basal) glucose concentrations, although substantial glucose-responsiveness was maintained (Figure 5G). These results suggest that upregulation of ATF4 alone has more impact on β-cell protein production than Hsph1, Hspa1b and Dnajb1.
Figure 5. ATF4-OE compromises β-cell gene expression and insulin secretion.
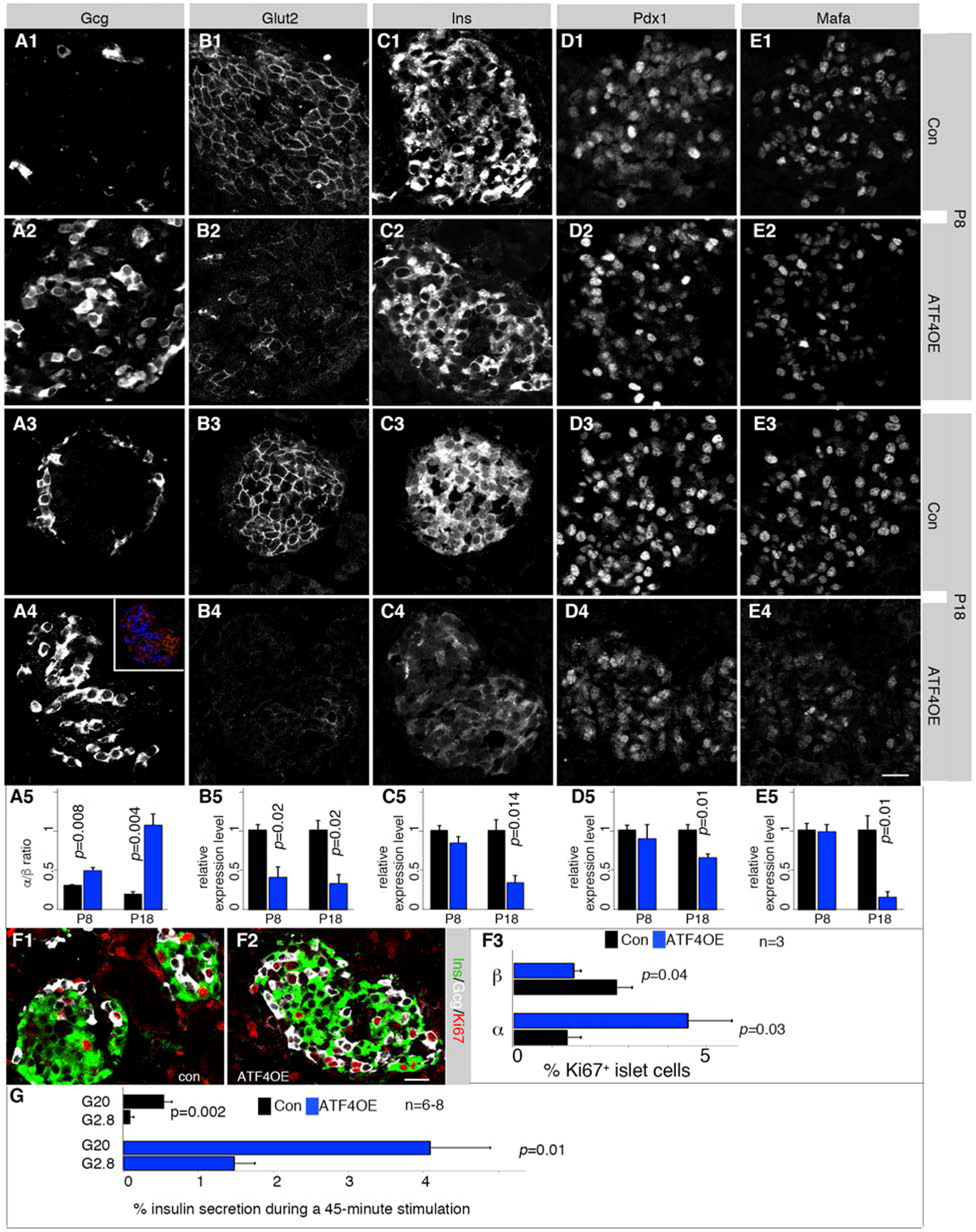
Also see Figure S6 and Table S1. Error bars, SEM. “p” values in all quantification panels are from type 2, 2-tailed t-test.
(A-E) Detection of several β-cell markers. Controls (Con) are Rosa26-ATF4LoxTG pancreata. Inset in A4 is an example of how α (blue) and β (red) cells were identified. Three to four (n=3–4) pancreata were quantified for each marker. p-values <0.05 are marked. Scale bar in E4 = 20 μm, applicable to all panels.
(F) Mitotic assays via Ki67 staining. “n”, number of pancreata quantified. p-values are marked. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(G) GSIS results of P14 control and ATF4-OE islets. “n”, number of secretion assays from 3 mice (each having at least two technical duplicates).
To determine if OE of any protein can lead non-specifically to compromised β-cells, we over-produced tdTomato (tdT) using Pdx1CreER; Ai9 mice. Ai9 is a transgene that allow high tdT production after Cre-mediated recombination. Thus, tamoxifen administration at E15.5 activated tdT expression in ~50% of pancreatic β-cells (Figure S6F) yet had no detectable effect on adult islet insulin or Pdx1 levels (Figure S6F). Collectively, these results suggest that the Myt TFs normally prevent the overactivation of Atf4, Hsph1, Hspa1b, and Dnajb1, which is required for postnatal mouse β-cell proliferation, survival, and function.
Myt3 protein levels are induced by metabolic stress in diabetic db/db mouse β-cells
We next tested if metabolic stress would reciprocally tune Myt TF levels during β-cell compensation in obese, diabetic db/db mice. Comparing islets from 3-month-old db/db mice with db/+ controls, we found that Myt3 but not Myt1 or Myt2 protein levels were significantly up-regulated (Figure 6A–D). Intriguingly, Myt3 transcript levels were not changed (Figure 6E, Table S4), suggesting post-transcriptional regulation of Myt3 production. Notably, isolated db/db islets were still glucose-responsive despite being exposed to the hyperglycemic state of the mice (Figure 6F).
Figure 6. Myt (MYT) TF up-regulation in mouse β-cells during compensation but down-regulation in dysfunctional human β-cells.
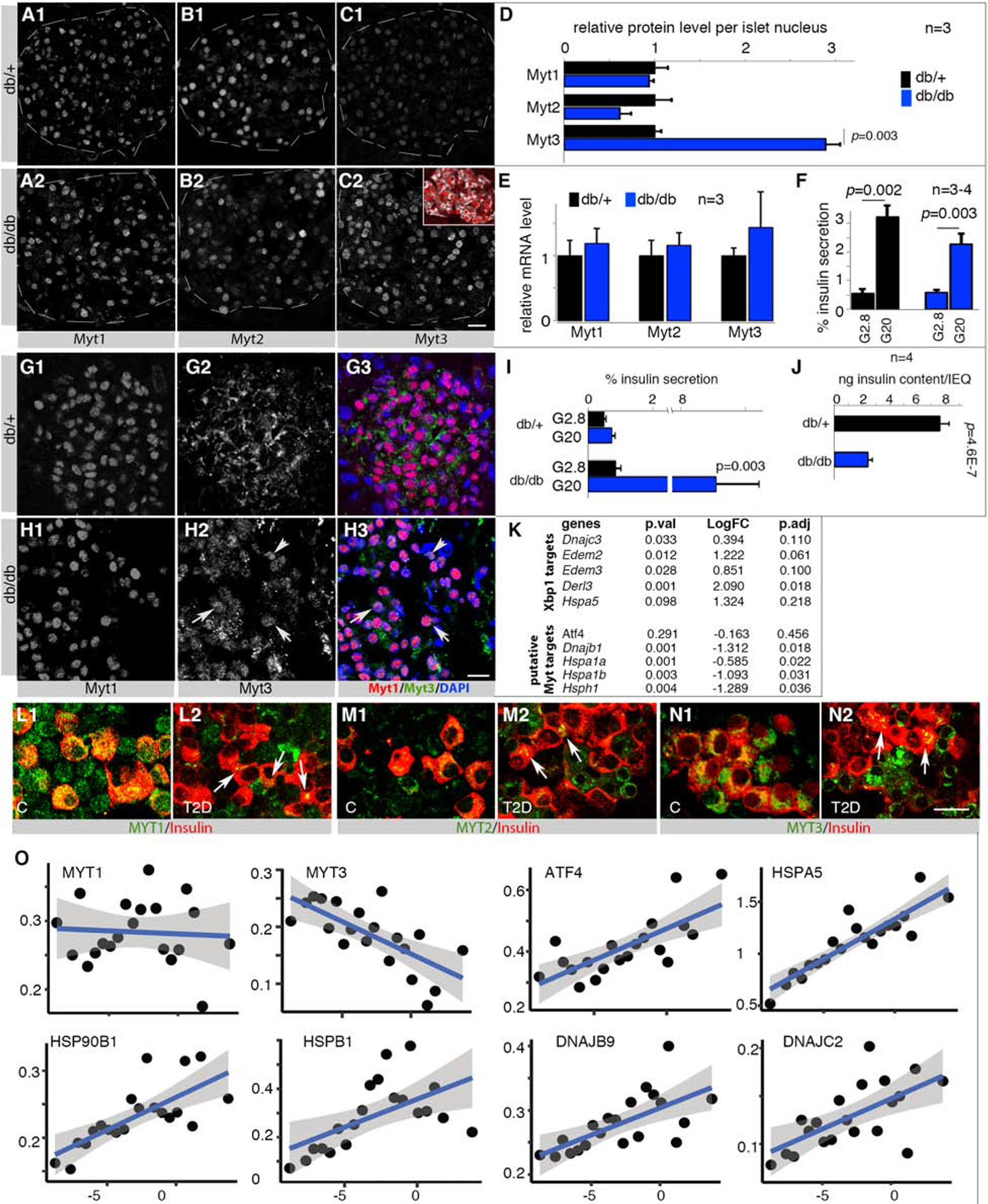
Also see Figure S7 and Table S1, S4, S5. Error bars in all quantification panels, SEM. “p” values in all quantification panels are from type 2, 2-tailed t-test.
(A-F) Myt TF at the protein (A-D) or mRNA (E) level in 3-month-old islet cells of db/+ and db/db mice that maintain GSIS (F). Inset in C2 shows β-cells (Insulin+, white) that express Myt3 (red). “n”, number of mice examined. p-values <0.05 are marked. Scale bar in C2 = 20 μm, applicable from A-C.
(G, H) Myt1/Myt3 detection in 18-month-old db/+ and db/db islets. Arrows in H2 and H3 point to examples with nuclear Myt3. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(I, J) GSIS assays of 18-month old islets, presented as % of insulin secretion within a 45-minutes stimulation window or total insulin content per islet-equivalency (IEQ).
(K) Gene-expression changes (log-fold change or LogFC, detected via RNA-seq) between 3-month-old db/db and db/+ islets; representative examples presented. See Table S4 for more genes.
(L-N) MYT TF expression in normal and T2D donor islets. Arrows in M2, N2, and O2 point to several β-cells with low but detectable MYT TFs. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(O) RePACT-analysis of MYT and stress gene transcription in ~35,000 β-cells of six normal and 3 T2D islet donors. X-axis, pseudo-time trajectory of T2D progression (left to right). Y-axis, relative gene expression. Each dot represents a β-cell subpopulation. The blue line represents average gene-expression trajectory. Blue shades indicate range of gene expression with 95% confidence levels.
We then tested if metabolic stress-regulated Myt TF production in β-cells was maintained over aging. In older db/+ euglycemic mice, a larger fraction of the Myt3 pool was localized to the cytoplasm (e.g., at 8-month-old, Figure S7A), so that it became predominantly cytoplasmic by 18 months (Figure 6G). In contrast, db/db Myt3 was predominantly nuclear in islet cells at all ages tested (Figure 6H, S7B), which displayed high glucose responsiveness despite an overall insulin content reduction in each islet (Figure 6I, J). These findings suggest that the nuclear Myt3, itself modulated by stress, promotes β-cell compensation in response to obesity-induced insulin resistance.
The enhanced Myt3 production in 3-month-old islets allowed us to test if physiological Myt3 upregulation can repress stress-gene transcription. We analyzed the published RNA-seq data in 3-month-old control and db/db islets (Neelankal John et al., 2018), focusing on stress-response genes (Table S4). Consistent with high cellular stress in db/db islet cells (indicated by increased Xbp1 mRNA splicing, Figure S3D), there were significant or trends of increased expression of genes including Dnajc3, Edem2, Edem3, Derl3, and Hspa5 (Figure 6K). These are direct targets of the early stress sensor-effectors, but their expression was unaltered by Myt TF inactivation (Table S2). In contrast, there was trending or significant decrease in expression in Atf4, Dnajb1, Hspa1a, Hspa1b, and Hsph1, the putative Myt TF targets (Figure 6K). These findings further support the idea that Myt TFs selectively repress these late-stage stress-response effectors.
MYT-TF downregulation is associated with stress-gene upregulation in dysfunctional human T2D β-cells
The MYT1, 2, and 3 proteins were present in most functional human β-cells (Figure 6L–N). While MYT1 was mostly nuclear (Figure 6L1), MYT2 and MYT3 were cytoplasmic (Figure 6M1, N1). This pattern is similar to Myt3 in aged mouse islets. Notably, MYT1, 2, and 3 protein levels were downregulated in most non-glucose-responsive T2D islet β-cells (Figure 6L2, M2, N2. Figure S7C). The cytoplasmic localization of MYT3 in human β-cells had also been reported earlier (Henry et al., 2014), which was also observed in human β-cells that were transduced with epitope-tagged MYT3 (Figure S7D), suggesting that the observed MYT3 signals are correct.
MYT TF mRNA expression was next examined in T2D human β-cells. A challenge here is the heterogeneous nature of T2D, between individual patients and even islets from the same patient (Wang and Kaestner, 2019). To avoid this issue, we utilized our recently devised RePACT algorithm to analyze single-cell expression data, which can reveal progressive movement along a pseudotime-trajectory from functional to dysfunctional cell states (Fang et al., 2019). There was a significant anti-correlation (adjusted p=0.0007) between the RePACT-inferred T2D-progression process and MYT3 mRNA levels, but not for MYT1 or MYT2 (Figure 6O and Table S5). A positive correlation was observed between the T2D pseudo-timeline and expression of several ATFs, HSPA5 (BIP), HSP27, 40, and 90 family genes (Figure 6O and Table S5). These findings suggest that MYT3 is transcriptionally downregulated during β-cell failure.
To investigate if acute physiological stressors regulate MYT TF levels, human islets were treated for 40 hours at a supra-physiological 16.7 mM glucose concentration. While these conditions had little effect on GSIS, β-cell MYT1 protein levels were up-regulated in a significant and selective pattern (Figure 7A–D, S7E, F). In contrast, the amount and nuclear localization of MYT3 was rather specifically increased by lipotoxic 0.6 mM palmitate, which compromised but did not eliminate GSIS [Figure 7E–H; compared to MYT1 and MYT2 (Figure S7G, H)]. However, neither MYT1 nor MYT3 transcript levels were changed by these treatments (Figure S7I). Thus, MYT TF levels are also influenced by acute metabolic stress conditions in normal human islets, which is primarily through post-transcriptional effects on MYT1 and/or MYT3. In contrast, MYT TF protein levels were decreased in T2D human β-cells when β-cell failure occurred, presumably at both transcriptional (MYT3) and post-transcriptional (MYT1 and MYT2) levels.
Figure 7. Human MYT TFs are responsive to metabolic stress and required for human β-cell line survival.
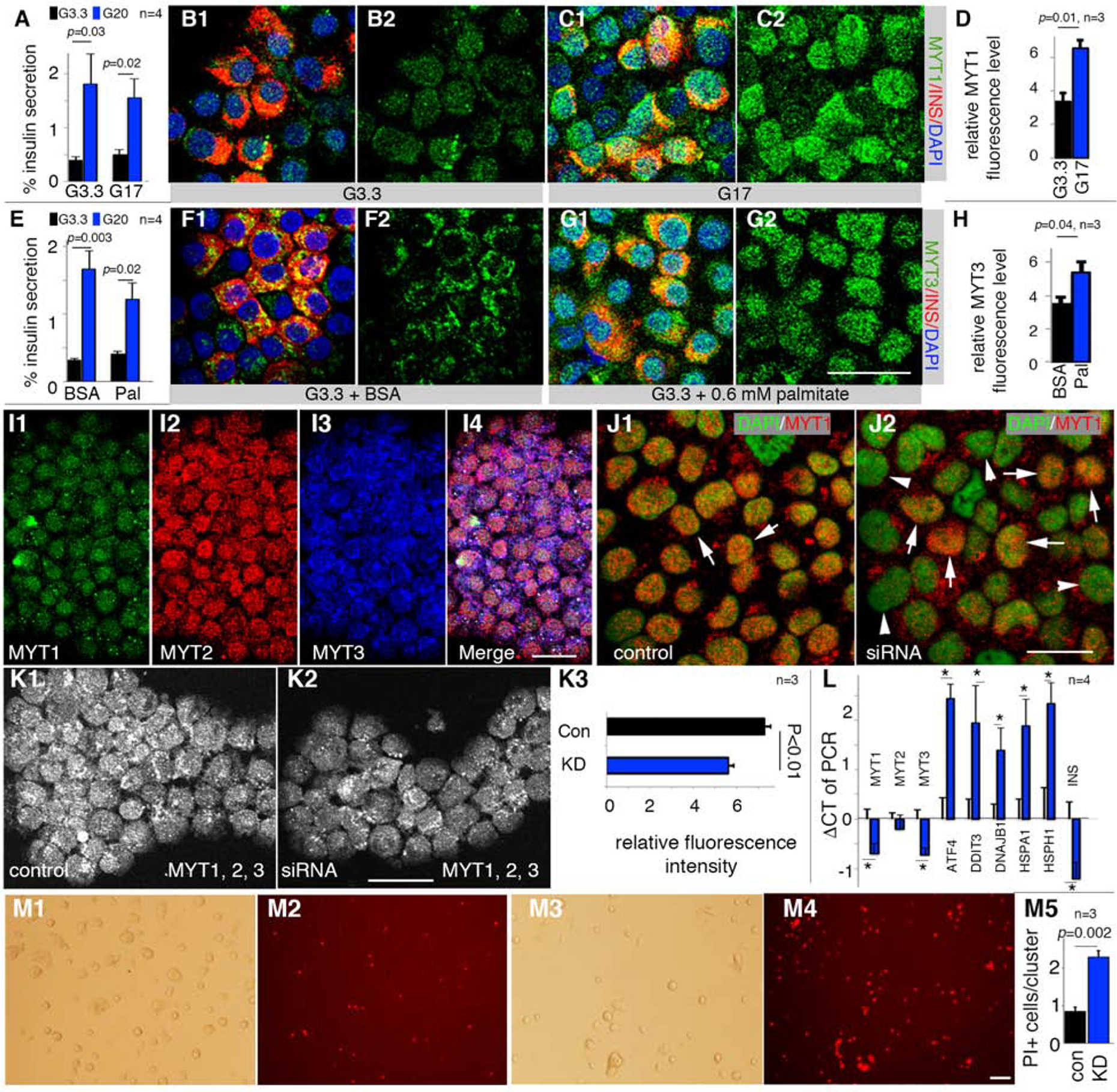
Also see Figure S7 and Table S1. Error bars in all quantification panels, SEM. “p” values in all quantification panels are from type 2, 2-tailed t-test.
(A-D) GSIS [A, under 3.3 mM (G3.3) and 20 mM (G20) glucose] and MYT1 production of human β-cells after 40-hour treatment with 17 mM (G17) glucose. A merged MYT1/Insulin and single MYT1 channel are shown. “n” in panel a, number of GSIS assays. “n” in D, batches of islets used. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(E-H) Same as A-D with 0.6 mM palmitate (Pal) instead of G17.
(I) MYT TF detection in EndoC-βH1 cells. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(J) siRNA-based MYT1 KD three days after siRNA transfection. Arrows, MYT1+ nuclei. Arrowheads, cells with lowered MYT1 signal. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(K) Staining and quantification of MYT TFs in viable EndoC-βH1 cells after MYT KD. MYT1, 2, 3 signals were combined into one single channel (K1, K2) and quantified with Image J (K3). “n”, batches of KDs; 10–15 cell clusters (i.e. island-like cell aggregates wherein cells proliferate) in each sample. Scale bar = 20 μm.
(L) Effect of MYT KD on transcription of several stress genes in EndoC-βH1 cells. “*”, p<0.05. “n”, batches of KDs.
(M) Propidium iodide (PI) assays of cell death three days after MYT TF KD. Bright field and PI fluorescence are shown. M1 and M2, cells transfected with control siRNA. M3 and M4, cells transfected with cocktails of siRNA that target MYT1, 2, and 3. Quantification was number of PI+ cells per cell cluster. Scale bar = 100 μm. “n”, batches of KDs.
MYT TFs are required for human β-cell survival
To provide further support for MYT TF action in stress-pathway gene regulation in human β-cells, siRNA-based MYT knockdown was performed in the human EndoC-βH1 cell line, which displays functional properties similar to primary human β-cells (Tsonkova et al., 2018) and expression of MYT1, 2, and 3 (Figure 7I). MYT siRNA treatment effectively reduced their protein and mRNA levels in a majority of EndoC-βH1 cells (Figure 7J, K). As expected from our earlier findings, these conditions led to elevated ATF4, DNAJB1, HSPA1, and HSPH1 expression (Figure 7L) and increased β-cell death (Figure 7M).
Discussion
Stress-response pathway activation needs to be calibrated so as to allow sufficient proteomic homeostasis but not high enough to induce catastrophic cellular dysfunction and death. We show here that Myt TFs can tune this response in pancreatic β-cells. Because ChIP analysis revealed Myt TF sites within likely cis-regulatory sequences of the Atf and Hsp genes in islet cells (our studies), neuronal progenitors, and fibroblasts (Mall et al., 2017; Vasconcelos et al., 2016), it is plausible that Myt TFs provide a general protective mechanism that allows stress-prone cells to function and survive.
Myt TFs regulate multiple genetic pathways
Previously we reported that Myt-dependent inhibition of precocious Syt4 expression regulates β-cell maturation (Huang et al., 2018). Now we show that Myt TF controls the stress-response as an essential influence in postnatal β-cells. Additionally, loss of Myt function deregulates many other molecular pathways (e.g., infection/inflammatory responses, PI3K-AKT, Rap1, and Ras signaling) that have well-established roles in β-cell proliferation and function (Elghazi et al., 2007; Font de Mora et al., 2003; Kelly et al., 2010). We propose that the Myt family could be considered as a functional nexus that interconnects these intracellular pathways that are essential to physiological homeostasis.
Bidirectional regulation between Myt TFs and stress-response pathways
The findings reported here suggest that Myt TFs directly regulate the late-stage stress-pathway genes (Atf4, Hsps), but not the early-stage stress sensor-effectors (Atf6, IRE1, PERK) (Hetz and Papa, 2018). Such a late-not-early selective mechanism is advantageous, because the Myt TFs do not affect the activation of the early stress effectors, which allows early stress response to reduce unfolded protein levels to maintain proteomic homeostasis, but ensure Atf4/Hsps expression stays at relatively low levels to avoid stress-induced cell death/dysfunction. The observation that Atf4- and Hsph1, Hspa1b and Dnajb1-OE recapitulates a large portion of the 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cell phenotypes further highlights their role as key downstream mediators of the Myt TFs. However, we suggest cautionary interpretation of the Atf4- or Hsp-OE data, because excessive OE can disable β cells via Myt TF-independent pathways, although our inability to effect β-cell identity markers altered in 6F; Pdx1Cre mice by tdT OE in a wildtype context suggests this is not the case (Figure S6F).
In murine and human β-cells, stress conditions that did not eliminate GSIS caused increased nuclear Myt TF levels via post-transcriptional upregulation and/or cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling. For by-far unknown reason, this Myt TF-upregulation appears to be disabled at the transcriptional (MYT3) and/or post-transcriptional (MYT1/MYT2/MYT3) level, especially in failed/dysfunctional human T2D β-cells. These findings buttress the idea that tuning the function of these TFs is required for optimal β-cell compensatory responses.
Exploring how metabolic stress regulates Myt proteins will be interesting. To this end, mouse and human cells produce multiple Myt3 mRNA isoforms (with over 50 human MYT3 mRNA isoforms detected), encoding proteins with different N-termini (Bulfone et al., 2005). It is possible that various stressors alter the relative transcript levels to produce proteins with different stability or subcellular localization. Moreover, the different 5’ mRNA sequences in these transcripts may contain unique reading frames that allow preferential translation of distinct Myt3(MYT3) isoforms under stress (Young and Wek, 2016). Lastly, Myt1/Myt3 could be post-translationally modified to gain different properties. Future studies are essential to unravel these various effectors of Myt TF control.
MYT TFs in islet β-cells are disabled in human T2D donors but not in db/db diabetic mice
MYT TF levels were substantially reduced in dysfunctional human T2D β-cells. Earlier studies had also shown decreased MYT3 expression in T2D β-cells (Axelsson et al., 2017) and up-regulation of ATF1, ATF3, Hsp40, 70, 90, and 105 (Bugliani et al., 2013; Gunton et al., 2005; Hartman et al., 2004; Marselli et al., 2010; Segerstolpe et al., 2016). Notably, however, we did not observe Myt-TF inactivation in diabetic db/db islet cells in mice even at 18 months of age. In contrast, there was increased Myt3 nuclear localization in these islet cells, coinciding with their sustained glucose responsiveness, supporting the roles of Myt3 in β-cell compensation. We do not yet know how to explain this species-based discrepancy, but it may be connected to the distinct sensitivity of human and mouse β-cells to metabolic stress-induced failure.
Myt TFs selectively regulate a subset of stress-response genes
The absence of Myt TFs did not affect expression of superoxide dismutase (Sod) or catalase (Cat), thus distinguishing the Myt TFs from other stress-activated TFs such as Foxo1 and Nrf2. Foxo1 positively potentiates Mafa, Pdx1, and ROS scavenging enzyme genes (i.e. Gpx, Sod, Cat) to improve glucose sensing, insulin production, cell proliferation, and ROS removal (Kitamura et al., 2005; Talchai et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2016). Nrf2 activation elevates the expression of antioxidant proteins for ROS degradation (Ma, 2013). We propose that the partially overlapping responses of Myt, Foxo, and Nrf2 TFs to cell stressors collectively provide multimodal selectivity and robustness amongst the various kinds of cellular stresssurvival machinery.
Myt TFs may have both repressor and activator activities
While Myt TFs were concluded to act predominantly as transcriptional repressors, ChIP-seq identified Myt1 or Myt2 motifs associated with in vivo activation (Mall et al., 2017; Vasconcelos et al., 2016), suggesting a strong locus-dependent ability for Myt TFs to activate or repress. We found equal numbers of up- and down-regulated genes in 6F; Pdx1Cre β-cells from newborn mice (Table S2). Intriguingly, many up-regulated genes fell into the stress-response category, whereas down-regulated genes were generally associated with promoting β-cell proliferation and function (Figure S3A). Thus, we speculate that Myt TFs can both directly activate genes required for β-cell compensation and repress those mediating cell failure to enhance overall β-cell function. Defining how Myt TFs regulate their targets in the future, likely via interactions with Sin3 and/or other co-regulators, will shed light on mechanisms dictating these opposing activities.
In summary, our overall findings revealed the key roles and mechanisms of Myt TFs, themselves regulated by stress response, in tuning stress-gene expression in β-cells. Excessively high or low levels of Myt activity can both cause β-cell failure, by overly repressing or activating stress responses. This model is similar to several other protective mechanisms wherein both lack or overactivation of certain signals can cause disease, including immune responses (Blach-Olszewska and Leszek, 2007) and neural activation (Coyle and Puttfarcken, 1993). Devising methods to tune the Myt activities could potentially prevent/delay β-cell failure and the development of T2D.
STAR Methods:
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead contact:
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Guoqiang.gu@vanderbilt.edu (615-936-3634).
Material Availability:
Plasmids, mouse lines, and antibodies generated in this study will be available through the lead contact upon reasonable request.
Data and Code Availability:
The original data analyzed in this study are in ArrayExpress under ID code E-MTAB-2266 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-2266/), E-MTAB-6615 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-6615/), and in https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE107489.
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
Mouse derivation
Mouse usage followed protocols approved by the Vanderbilt University IACUC for GG, in compliance with regulations of AAALAC. All mice were euthanized by isoflurane inhalation, followed by decapitation or cervical dislocation.
Wild-type CD1 (ICR) mice were from Charles River Laboratories. The C56BL/6J, Ai9 [Gt(ROSA)26Sortm9(CAG-tdTomato)Hze], B6.BKS(D)-Leprdb/J (B6 db), Rip-rTTA [Tg(Ins2-rtTA)2Efr/J], Rosa26-ATF4LoxTG (B6;129X1-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm2(ATF4)Myz/J), and Ins1Cre [B6(Cg)-Ins1tm1.1(cre)Thor/J] mice were from the Jackson Laboratories. The Pdx1Cre and Pdx1CreER mice were described in (Gu et al., 2002). The derivation of Myt1F/+, Myt2F/+, and Myt3F/+ mice were described in (Huang et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2007). The TetO3H mice were derived by pronuclear injection, with a DNA construct made by ligating a bi-directional Tet-ON-3G promoter (Clontech), the coding sequences of Hspa1b, HspH1, Dnajb1, eGFP and SV40 early poly-adenylation signals as indicated in Figure S5A. The entire construct was sequence-verified. Note that H2A peptide-breakers were included so that each mRNA could make two proteins (Figure S5A). Five independent transgenic lines were derived, with founders directly crossing with RiprTTA mice to establish stable lines.
Mouse crossing schemes
For producing the Myt triple mutants, Myt1F/F; Pdx1Cre mice [~50% CD1 background, based on crossing history (Wang et al., 2007)] were crossed with Myt2F/+ mice [~50% CD1 background]. Myt1F/+; Myt2F/+; Pdx1Cre mice were then crossed with Myt3F/+ animals (~50% CD1 background) to obtain Myt1F/+; Myt2F/+; Myt3F/+; Pdx1Cre mice, which were out-crossed twice with CD1 mice in order to ensure a mixed CD1 genetic background. The Myt1F/+; Myt2F/+; Myt3F/+; Pdx1Cre mice were then intercrossed. From ~20 litters of mice, two wild-type (WT), four Pdx1Cre, five Myt1F/F; Myt2F/F; Myt3F/F (denoted as 6F), and four Myt1F/F; Myt2F/F; Myt3F/F; Pdx1Cre (denoted as 6F; Pdx1Cre) mice were obtained. No phenotypic differences were found amongst the WT, Pdx1Cre, and 6F mice (Table S1). Thus, most of the studies use 6F (littermates of 6F; Pdx1Cre mice) as controls, derived from two types of crosses: 1) 6F X Myt1F/+; Myt2F/F; Myt3F/F; Pdx1Cre; 2) 6F X Myt1F/F; Myt2F/+; Myt3F/F; Pdx1Cre. These mice were euglycemic and fertile up to 8-month after birth, allowing the above crossing.
For Hsp OE, TetO3H mice (males and females) were crossed with RiprTTA mice (females and males). The day of vaginal plug appearance was counted as embryonic day 0.5 (E0.5). To induce Hsp OE, pregnant mice were put on water supply with 200 microgram/ml Dox from E16.5 ad lib until the day of tissue collection. For initial Hsp OE characterization, via eGFP expression, all five lines were used. Two were euthanized because of their low (<10%) penetrance of eGFP production in β-cells. Three had similar portions of β-cells expressing eGFP, so that one was randomly chosen for all studies presented here. For testing the potential silencing of Rip-rTTA or TetO3H transgenes in adult ages, isolated islets from Hsp-OE; Rip-rTTA mice were treated with Dox at 2-month of age without prior exposure. For ATF4 OE, a similar crossing scheme was used, except that the Rosa26-ATF4LoxTG and Ins1Cre mouse lines were used and no Dox was introduced. Rosa26-ATF4LoxTG/+ and Ins1Cre littermates were all included as controls.
Cell lines:
HEK293T cells used in transcription assays were from ATCC (CRL-3216™). EndoC-βH1 was from UniverCell-Biosolutions (France). For XL-1 blue and DH5α bacteria strains used for routine plasmid amplification were from the Vanderbilt Molecular Biology Core facility, grown in liquid broth (LB).
METHOD DETAILS
Blood glucose and plasma hormone assays
Fasting glucose levels were read via tail snip after 6-hour (before one month old) or overnight (after one month old) fasting. For plasma insulin assay, retro-orbital blood collection was used.
Insulin tolerance test (ITT)
Mice were fasted for 4 hours. Insulin was injected at 1 unit/kg. Blood glucose was then measured. The blood glucose levels were read with a NovaMaxplus meter using blood from tail tip.
Pancreatic islet isolation
Pancreata were directly digested (for P1, P7, and P14 pancreata) (Huang and Gu, 2017) or perfused (for pancreata older than 2 weeks) with 0.5 mg/ml Type IV collagenase dissolved in Hanks Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) with Ca2+/Mg2+. After digestion at 37 °C, lysates were washed in RPMI 1066 with 5.6 mM glucose and 10% fetal bovine serum (i.e. RPMI-FBS) 4 times. Islets were hand-picked in RPMI-FBS for downstream usage.
Insulin secretion assays
For static insulin secretion, the % of total insulin secreted within a 45-minute window was measured unless noted. Hand-picked islets were allowed to recover in RPMI-FBS for 2 hours or overnight. Islets were washed twice with pre-warmed KRB solution (2.8 mM glucose, 102 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.2 mM MgCl2, 2.7 mM CaCl2, 20 mM HEPES, 5 mM NaHCO3, and 10 mg/ml BSA, pH 7.4) and then incubated in KRB (37 °C) for one hour, washed with pre-warmed KRB once more. 10–15 islets were then transferred into each of the wells of 12-well plates with 1 ml pre-warmed KRB to start the secretion assays. For all assays, four or more mice of each genotype were used for islet isolation, with islets from two or more mice mixed and examined as 2–3 technical replicas. Total insulin was assayed after ethanol-acid extraction as in (Huang et al., 2018). Insulin was measured with an Elisa kit from ALPCO. Assays from human islets use similar method, except the basal glucose was 3.3 mM.
For perifusion assays, hand-picked islets were incubated overnight in RPMI-FBS with 10 mM glucose for recovery. Islets were then placed in a 1-ml perifusion chamber, equilibrated in KRB with 5.6 mM glucose for 30 min and then challenged with 16.7 mM glucose, 5.6 mM glucose + 50 μM IBMX, and 5.6 mM glucose + 20 mM KCl. The perifusion fractions were collected in 3-min intervals at 1 ml/min flow rate and assayed for insulin by radioimmunoassay.
Gene expression assays by qPCR
RNA was prepared from hand-picked islets with TRIzol (Life Technologies) and a DNA free RNA™ kit (Zymo Research). 20–100 ng total RNAs were then used for cDNA preparation and qPCR, utilizing SYBR green master mix of the Bio-Rad system, with oligos listed in reagent table. Note that the human ATF4 and mouse Atf4 coding sequences are conserved, making it possible to assay both cDNAs with a single pair of oligos.
Protein pulse labeling assays
Hand-picked islets were allowed to recover for ~2 hours in RPMI-FBS media. Islets were then transferred to media with 1:4 mix of RPMI-1640: Cys/Met-depleted DMEM with 20 mM glucose and 10% FBS, supplemented with 35S-labeled Cys/Met. After four hours, labeled islets were incubated in RPMI-FBS for 15 minutes, washed in PBS, and lysed for gel-electrophoresis and quantification (aided with Image J). The number of cells from each islet sample was determined via real-time PCR to compare the relative copy number of genomic DNA. Lysates of same numbers of cells were loaded into each lane of the protein gels for comparison.
IF and β-cell mass assays
Antibody staining followed standard procedures. Briefly, pancreatic or other issues were dissected. They would be: 1) directly frozen, sectioned, and then fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes followed by permeabilization and antibody staining with Ki67 or Mafa antibodies; 2) fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4 °C, washed with PBS 3 times, frozen, and sectioned for transcription factor and Glut2 staining; 3) fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4 °C, washed with PBS 3 times, and prepared as paraffin sections. In this case, the tissue will be sequentially dehydrated with 45, 70, 80, 95, and 100% ethanol, and twice with xylene, and embedded in paraffin. For hormone staining, the paraffin block will be sectioned, rehydrated with the above xylene and ethanol solutions in reverse orders, and stained with antibodies. Small tissues (<0.5 mm in each dimension) can be directly fixed. Large pancreata (older than P14) were cut into 5–10 small pieces and fixed. Six and 20 μm thick sections were prepared for paraffin and frozen tissues, respectively. Sections were stained with antibodies diluted in basal solution (1X Phosphate Buffered Saline + 0.1% triton100 + 0.1% Tween-20 + 0.1% BSA + 0.05% donkey serum). Antibodies used were listed in Key Resource Table. For imaging, laser-scanning microscopy (LSM) was used. When expression levels of a protein between samples were compared, slides/cells were processed side-by-side, and images were captured utilizing identical optical/electronic settings. For protein level quantification, LSM images taken under identical parameters were selected for Image J-based particle quantification. Double blind tests were used.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies (with fold of dilution indicted) | ||
| 488-donkey anti Guinea Pig (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 706-545-148 RRID:AB_2340472 |
| 488-donkey anti goat igG (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 705-545-147 RRID:AB_2336933 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Guinea Pig IgG (H+L) (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 706-605-148 RRID:AB_2340476 |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 711-545-152 RRID:AB_2313584 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rabbit (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 711-605-152 RRID:AB_2492288 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 715-605-150 RRID:AB_2340862 |
| Alexa Fluor® 594 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 715-585-150 RRID:AB_2340854 |
| Alexa Fluor® 594 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Goat IgG (H+L) (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 705-585-003 RRID:AB_2340432 |
| Alexa 647 AffiniPure Rabbit Anti-Syrian Hamster IgG (H+L) (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 307-605-003 RRID:AB_2339601 |
| Rat anti-BrdU (1:500) | ABcam | Ab-6326 RRID:AB_305426 |
| biotin anti Rat (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 712-065-151 (RRID: N/A) |
| Cy3-Donkey anti-mouse (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoreserach | 715-165-150 RRID:AB_2340813 |
| Cy3-streptavidin (1:1000) | Vector laboroatories | SA-1300 (RRID: N/A) |
| Cy5- streptavidin (1:1000) | Vector laboroatories | SA-1500 (RRID: N/A) |
| FITC anti Rabbit (1:1000) | Jackson Immunoresearch | 711-095-152 RRID:AB_2315776 |
| Goat anti-Pdx1 (1:2000) | ABcam | AB47383 RRID:AB_2162359 |
| Goat anti-insulin (1:500) | Santa Cruz | sc-7839 RRID:AB_2296108 |
| Guinea pig anti insulin (1:1000) | Dako | A0564 RRID: NA |
| Rabbit anti-Myt1 (1:1000) | This lab. Mech. Dev. 2007. 124, 698–910. | NA |
| Mouse anti-glucagon (1:5000) | Millipore | MabN238 RRID:NA |
| Rabbit anti-Pdx1 (1:5000) | ABcam | AB47267 RRID:AB_777179 |
| Rabbit anti-Nkx6.1 (1:5000) | Gift of P. Serup, Copenhagen, Denmark | NA |
| Rabbit anti-MafB (1:1000) | Bethyl | A700–046 RRID: NA |
| Rabbit anti-Cleaved Caspase 3 (1:500) | SYSY | #105173 RRID:AB_887838 |
| Rabbit anti-glucagon (1:100) | ABcam | AB92517 RRID:AB_10561971 |
| Rabbit anti-Ki67(1:500) | Abcam | Ab 15580 RRID: AB_443209 |
| Rabbit anti-HA (1:500) | Cell Signaling Technology | #3724 RRID: AB_1549585 |
| Guinea pig anti-Myt2 (Myt1L) (1:1000) | This lab. See *M of this paper. | NA |
| Rat anti-Myt3 (1:500) | This lab. See *M of this paper. | NA |
| Normal IgG (1 μg/IP) | Cell Signaling | #2729S RRID: AB_1031062 |
| Rabbit anti-H3K27Ac (1 μg/IP) | Millipore | #07–360 RRID: AB_310550 |
| Bacterial and Virus Strains | ||
| Bl-21 | Vanderbilt MPB Core | NA |
| DH5-alpha | Vanderbilt MPB Core | NA |
| Xl-1 | Vanderbilt MPB Core | NA |
| Biological Samples | ||
| Bovine serum albumin | Sigma | A9418 |
| Donkey Serum | Jackson Immunoresearch | 017-000-121 RRID:AB_2337258 |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Atlanta Biologicals | S10250 |
| Human islet (normal) | IIDP | NA |
| Human islet (normal) | Clinical Islet Transplantation Laboratory, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY | NA |
| Human islet (diabetic) | Clinical Islet Transplantation Laboratory, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY | NA |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and other key reagents | ||
| Collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum | Sigma-Aldrich | C5138 |
| DMSO | Sigma-Aldrich | D2650 |
| Doxycycline | Sigma-Aldrich | D9891 |
| DAPI | Sigma-Aldrich | D9542 |
| paraformaldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich | P6148 |
| Trypsin | Sigma-Aldrich | C5138–5G |
| SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase | ThermoFisher | 18080085 |
| RNaseOUT Recombinant Ribonuclease Inhibitor | ThermoFisher | 10777019 |
| T4 DNA Polymerase | NEB | M0203S |
| paraformaldehyde | Sigma | P6148 |
| HBSS | ThermoFisher | 14025092 |
| High capacity cDNA synthesis | Applied BIosystems | 4368814 |
| RPMI1066 | Sigma-Aldrich | R8758 |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Corning | 35010-cv |
| BSA | Sigma-Aldrich | 9048468 |
| Nano-Glo® Dual-Luciferase® Reporter Assay System | Promega | N1610 |
| CRML-1066 | ThermoFisher | 11530037 |
| Cyclophilin B Control siRNA | Dharmacon | D-001820-01-05 |
| Nontargeting Control siRNA | Dharmacon | D-001810-01-05 |
| Human MYT1 targeting siRNA | Dharmacon | L-005271-00-0005 |
| Human MYT2 (MYT1L) targeting siRNA | Dharmacon | L-022771-00-0005 |
| Human MYT3 (ST18) targeting siRNA | Dharmacon | L-008451-02-0005 |
| SYBER Green qPCR mix | Biorad | 1705060 |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| Serum Glucagon assay | The Vanderbilt Hormone Assays & Analytical Cores | NA |
| Magna ChIP™ HiSens Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit | Millipore | 17–10460 |
| Experimental Models: Cell lines | ||
| HEK293 | ATCC | CRL-11268 |
| EndoC-βH1 | UniverCell-Biosolutions | EndoC-βH1 |
| Experimental Models: Organisms | ||
| Myt1F/F | This lab | NA |
| Myt2F/F | This lab | NA |
| Myt3F/F | This lab | NA |
| Pdx1Cre | Jackson laboratories | Tg(Pdx1-Cre)89.1 |
| InsCre | Jackson laboratories | B6(Cg)-Ins1tm1.1(cre)Thor/J |
| Rosa26-ATF4LoxTG | Jackson laboratories | B6;129X1-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm2(ATF4)Myz/J |
| Db/+ | Jackson laboratories | B6.BKS(D)-Leprdb/J |
| Pdx1CreER | This lab (Gu et al., 2002) | NA |
| Ai9 | Jackson laboratories | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm9(CAG-tdTomato)Hze |
| HspOE | This lab/this work | N/A |
| ICR | Charles Rivers | CD-1 |
| DNA oligos for Genotyping | ||
| TTGAAACAAGTGCAGGTGTTCG | IDT | Pdx1Cre |
| ATGTGGCGTCCACGGGGAGT | IDT | |
| CCCTAGGCTCTCTGTGGTTGCAC | IDT | TetO-Hsp |
| GGTCGCTGAACTCATTGGCGAT | IDT | |
| CCAGAAGCTTGGTGTAGAGCAG | IDT | rTTA |
| GGCTGGCTCTGCACCTTGGTGATC | IDT | |
| TCCACCTGTCCGTTCAGTG | IDT | Myt1F |
| AGATCCTTCCAGGGTGGAGA | IDT | |
| GTATGGGGAAACTGCTGAATGAA | IDT | Myt1LF |
| GCATCCAGACAGACTGCGGTGA | IDT | |
| TGAGACTGAGACTACTTGTTAGC | IDT | Myt3F |
| GCTTTCTGGGTTCATTTCTG | IDT | |
| GGTGTAGCTGATGATCCGAATA | IDT | Ins1Cre |
| CATGATCTCCGGTATTGAAAC | IDT | |
| GGCTCCTCTCTTACATGGATCT | IDT | ATF4OE allele |
| CTTCGACCAGTCGGGTTTG | IDT | |
| DNA oligos for Real-time RT-PCR or mouse tissues | ||
| CCAGTAGCCTGGGAAGACAT | IDT | hspa1b |
| CAGTGCCAAGACGTTTGTTT | IDT | |
| TGAAACCTCTGCAAATTCAAA | IDT | dnajb9 |
| GCTTCAGACATTTAGTAACCCAAG | IDT | |
| CAGAGAGCTGTCTTGGAGCA | IDT | hspb8 |
| TCAAACACACACACAATGCC | IDT | |
| TGACATGGATCAGGTGGAGT | IDT | DNAja4 |
| GGCTCTTCGTCATCTTCCTC | IDT | |
| CAGGGCCAACAGAGGTCACA | IDT | Ddit3 |
| TCCTCTTCCTCCTGGGCCAT | IDT | |
| AGAGTTATTGGATATGGGCTGCCA | IDT | Dnajb4 |
| GGCAGGGAGATGCTTCCTCA | IDT | |
| TCATCGGCGACAAGTCGGAA | IDT | Hspa2 |
| AAGGTCTGCGTCTGCTTGGT | IDT | |
| ACAGCCTCCCTAAGCCCTCT | IDT | Hspb6 |
| GAGGCCTGCGTGGTGATAGA | IDT | |
| AGGAGTGCTGCCGAAACTGT | IDT | Hspe1 |
| ACTCTTTCCTTTCCCTCCTGACC | IDT | |
| ATAAGGCCCGAAGCCAGAGG | IDT | Atf5 |
| TGTGACGCTGGAGACAGACG | IDT | |
| CCCACCAGACAATCTGCCTTCT | IDT | atf4 |
| CCAGGTGGGTCATAAGGTTTGGG | IDT | |
| TGTGTTTAATCCCGAGAGGA | IDT | Hsph1 |
| GGTCAGGTAGCCAAATGCTT | IDT | |
| ACTGGACTCTTGCCCTCTGT | IDT | DNAjb1 |
| CCCACACAGTGGAGACTGAC | IDT | |
| AGTGGGCAGCCATGAGGTTT | IDT | Myt1 |
| GGACATAAAGAAGGAACTTC | IDT | |
| GCTGGTAAGGAACTAGGTCCT | IDT | XBP1 |
| CTCACGGCCTTGTGGTTGAGA | IDT | |
| GGATGCAGGGATGATGTTCT | IDT | GAPDH |
| AACTTTGGCATTGTGGAAGG | IDT | |
| CCGGGTTATGTGAGCCCAA | IDT | Nkx6.1 |
| CTGGACAGCAAATCTTCGCC | IDT | |
| CACCAGTTCAAGCTCAACAAG | IDT | Mnx1 |
| GGTTCTGGAACCAAATCTTCAC | IDT | |
| GTTCTGGGGCTCAAGATCAA | IDT | Insm1 |
| GTCAGCGTACTCCTCCTTGC | IDT | |
| GATCTGAATCCTACAAGCTCCTG | IDT | Hnf4a |
| CCCTCGTGTCACATCTTCTTT | IDT | |
| TGAAGCCTATGCTGCACTTG | IDT | Isl1 |
| ACGTGCTTTGTTAGGGATGG | IDT | |
| CAGACCCATAACACTCAAGAGG | IDT | NeuroD1 |
| GGAGTGTGTGTTGGCATTTATT | IDT | |
| GGTAGTTGCTCGCCATCCA | IDT | Mafb |
| CCCAGCTTCAGTCCGACTGA | IDT | |
| CCAGGTTGTCTAAATTGG | IDT | Pdx1 |
| GTTGGGTATAGCCGGAGAGA | IDT | |
| AAGAACACGTAAGGCCCAAG | IDT | Glut2 |
| AGCAACTGGGTCTGCAATTT | IDT | |
| ACCACGTGCGCTTGGAGGAG | IDT | MafA |
| ACCTCCTCCTTGCTGAA | IDT | |
| GCAGATGCAAAAGTCCAGGTG | IDT | Pax6 |
| CAGGTTGCGAAGAACTCTGTTT | IDT | |
| DNA oligos for ChIP-PCR in regulatory regions | ||
| CAGTTGGGATTAAAGGCTTGAG | IDT | Hspa1a-a1 |
| GAACAGGGCCGAAGATGAGA | IDT | |
| ATCTCCCTGGGTCTCCTAAA | IDT | Hspa1a-a2 |
| GTTGTGTACAGTTTGTTGTGATTTG | IDT | |
| AGCCTAATTCCCGAATGAAA | IDT | Hspa1b-a1 |
| TCCCAGTACCAGTCCTCTCA | IDT | |
| GTGTCAATAGCAGCACCAGCA | IDT | Hspa1b-a2 |
| GGTTCGCTAGAGAGTACGGAT | IDT | |
| TCCTCCGGCTCGCTGATTG | IDT | Hspa1b-a3 |
| GCGCCTTTAAGGAGTCTTCA | IDT | |
| GGAGAGATGGCTCAGTGGTT | IDT | HspH1-a1 |
| TGTTGGGATTTGAACTGAGG | IDT | |
| CTGGAGTCAACTGGAACGAA | IDT | HspH1-a2 |
| GCTAAAACTGACCGAGCTTGC | IDT | |
| AATCATCTCTTTCAAGAACACC | IDT | Dnajb1-a1 |
| TGGTGAAGTTGACATTATTCTG | IDT | |
| CCCAAGGTCACACAGCCAGA | IDT | Dnajb1-a2 |
| CAGGGAATGGGACTGCCTGA | IDT | |
| CAAAGAGAGGACATAGTTACCCT | IDT | Atf4-a1 |
| CCCAAAGAAGTCACAAGTGC | IDT | |
| CCAGGTGCAGAGCCAATAG | IDT | Atf4-a2 |
| GTGGGACACCTAGCCAAAGCT | IDT | |
| TGCTAGGCAGAATGACTCAAA | IDT | Albumin |
| GAGACCGTAATAAATTCAACTGTATCC | IDT | |
| Oligos for MytZf-Vp16 fusion/reporter construction | ||
| CGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGTCGAGTAGGCGTGTACGGTGGGAGGCCTATATAAGCAGAGCTCGTTTAGTGAACCGTCAGATCGCCTGGAGACGCCATCCACGCTGTTTTGACCTCCATAGAAGACACCGGGACCGATCCAGCCTCCGCGGCCCCGAATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGATCCTCTAGTCAGCTGACGC | IDT | CMV minimal promoter |
| GAATTCCACCATGGCGTACCCATACGATGTTCCTGACTATGCTGGCTCTTATCCGTATGACGTCCCTGACTATGCAACTGGAGGGGAAGTCACCCTAACCAACT | IDT | 5’ fusion |
| TCTGGCTGTCCCAGAGCAACCTTTGCTGGAAGTGGGTCCGCGTACAGCCGCGCGCGTACGA | IDT | junction |
| GCGGCCGCTACCCACCGTACTCGTCAATTCCAAGGGCA | IDT | 3’ fusion |
| Oligos for Real-time RT-PCR of human tissues | ||
| GGCCACATCACCGGGAACTA | IDT | MYT1 |
| AGTGGGCAGCCATGAGGTTT | IDT | |
| CTCACACACCGCAGCTTGTC | IDT | MYT2 |
| GCCCGCTGTTTGATGGTCAG | IDT | |
| CTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGGACTC | IDT | GAPDH |
| AGTAGAGGCAGGGATGATGT | IDT | |
| CAGCTGCTGCCATCCTGAAC | IDT | MYT3 |
| GGCATGCAGACTCTGTGGCT | IDT | |
| CATCCACAGCCAGCCATTCG | IDT | ATF4 |
| TTACCTGGAGGTGGCCAAGC | IDT | |
| TGCAGAGATGGCAGCTGAGT | IDT | DDIT3 |
| GCAGGTCCTCATACCAGGCT | IDT | |
| GGGAGGCCTTCTCCAGGAAC | IDT | DNAJB1 |
| GTGGCTGCACAGTGAACGTC | IDT | |
| GGTCAGCACCATGGACGAGA | IDT | HSPA1 |
| AAGCACTGGCCTTTCCAGGT | IDT | |
| GGCTGAGGAAGTGGGACCTC | IDT | HSPH1 |
| GTTGCCTGCCTCACTCTGC | IDT | |
| CTGGAGAACTACTGCAACTAGAC | IDT | INS |
| TGCTGGTTCAAGGGCTTTAT | IDT | |
| GGCTCCTCTCTTACATGGATCT | IDT | ATF4 |
| CTTCGACCAGTCGGGTTTG | IDT | |
| DNA oligos for H3K27Ac ChIP-PCR near promoter regions | ||
| GGCGTCTCGCGTGATAACCT | IDT | Atf4-RTO21 |
| GTGGGACACCTAGCCAAAGCT | IDT | |
| GCTGATTGGCCCAGCGGAGA | IDT | Hspa1a-RTO24 |
| CTGCGCCTTTAAGGAGTCTT | IDT | |
| TCCTCCGGCTCGCTGATTG | IDT | Hspa1b-RTO33 |
| GCGCCTTTAAGGAGTCTTCA | IDT | |
| AGGAAGCGGAAGTGGCACGTG | IDT | Hsph1-RTO49 |
| CTACTGAGGAGAACTTTCCAGA | IDT | |
| GGCGTTGACCAGAGTAGAGA | IDT | Dnajb1-RTO41 |
| CTCCGTGACGCAGCACAT | IDT | |
| GGTCCAAAGAGAGGGAGGAG | IDT | Gapdh |
| GCTACGTGCACCCGTAAAGC | IDT | |
| Software and Algorisms | ||
| ImageJ | Schneider et al., 2012 PMCID: PMC5554542 |
https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ |
| TopHat and Cufflink |
Trapnell et al, 2012 PMCID: PMC3334321 |
https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat/index.shtml |
| Webgestalt | Wang et al., 2017 PMCID: PMC5570149 |
http://www.webgestalt.org/ |
| bumphunter | Jaffe et al., 2012 PMCID: PMC3304533 |
http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/bumphunter.html |
| Aperio ImageScope – Pathology slide viewing Software | NA | https://www.leicabiosystems.com/digital-pathology/manage/aperio-imagescope/ |
| IBM SPSS Statistics software | IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp. |
https://www.ibm.com/analytics/spss-statistics-software |
| Excel | Microsoft Office |
https://office.microsoft.com/excel |
| Deposited data used | ||
| E-MTAB-2266 | ArrayExpress | https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-2266/ |
| E-MTAB-6615 | ArrayExpress | https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-6615/ |
| Db islet expression | GEO | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE107489 |
| Plasmids used | ||
| Firefly luciferase-eGFP fusion | Addgene | #119816 |
| Renila luciferase | Addgene | #118016 |
| A1a-3kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A1a-2kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A1a-1kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A1b-3kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A1b-2kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A1b-1kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| H1–3kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| H1–2kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| H1–1kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| Jb-5kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| Jb-3.5kb -firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| Jb-2kb-firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A-1.6kB-firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| A-1kB-firefly luciferase | This study | NA |
| WT-Mini-Hspa1a-luc | This study | NA |
| Mut-Mini-Hspa1a-luc | This study | NA |
| CMV-Myt1ZF-Vp16 | This study | NA |
For antibodies produced in this lab, the rabbit anti-Myt1 was described previously (Neelankal John et al., 2018). Guinea pig anti-Myt2 and rat anti-Myt3 were produced following similar method. Specifically, a cDNA encoding Myt2 amino acid residues 263–494 (as numbered in AAC53457.1) or that encoding Myt3 amino acid residues 60–298 (as numbered in BAE2409.1) was fused with that encoding a maltose binding protein. The fusion protein was purified and used as an antigen. Antibody production was performed by Strategic Bio-solutions (Newark, DE). The antigens locate 5’ to the floxed exons, so that in theory these antigens should be produced from Myt2− or Myt3− alleles, respectively. To our pleasant surprise, the resulting antibodies detected no signals in 6F; Pdx1Cre islets (Figure S1A) or single gene mutants (not shown) but see (Huang et al., 2018). These findings not only prove the specificity of the antibodies but also showed that the mutant alleles did not produce the expected N-terminal Myt fragments that may act as dominant negative molecules. Moreover, these fragments have no other homologous sequence upon comparison with human sequences except MYT2 or MYT3, respectively.
For quantifications of β-cell mass and replication index throughout the pancreas, the pancreatic block was sectioned at 20 μm intervals. One third to one fifth of all sections were labeled and scanned using Aperio ScanScope or an Olympus X51. Β-cell mass was then calculated based on the total pancreas weight and the percentage of tissues area that labeled for insulin.
Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) followed established procedure. Briefly, islets were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1M cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4) overnight at room temperature. Islets were then washed and treated in 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1M cacodylate buffer for 1 hour. Islets were then washed, embedded, thin-sectioned for imaging. For unbiased ER examination, image capture and quantification were performed under double-blind settings.
β-cell mitosis and apoptosis assays
For mice younger than P10, frozen pancreatic sections were prepared for Ki67 staining and quantification. For older mice, multiple-day BrdU feeding via drinking water (50 ng/ml) were performed. The pancreata were recovered, sectioned, and stained for % of Ins+ cells that incorporated BrdU. Up to 5% of all islet sections were quantified in each mice. Alternatively, hand-picked islets were dissociated into single cells, spun onto glass slides, and stained for marker expression and counting. For apoptotic cell counting, similar scheme was used.
Human islet culture
Hand-picked human islets (>95% purity) were cultured in CRML-1066 media with 10% FBS and 3.3 mM glucose overnight. For high glucose treatment, media were switched to 10% FBS with 3.3 or 20 mM glucose. For palmitate treatment media were switched to that containing 0.5% BSA or 0.6 mM palmitate with 5% FBS. Islets were cultured for ~40 hours and assayed for GSIS and mRNA expression. For immunoassays, islets were washed 2X with PBS and dissociated into small cell clusters (single to ~20-cell) and cytospun onto slides for after-fixation and staining/imaging.
Gene expression in human EndoC-βH1 cells
Human EndoC-βH1 cells were grown in DMEM containing 5.6 mM glucose, 2% BSA, 50 μM 2-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM nicotinamide, 5.5 μg/mL transferrin, 6.7 ng/mL selenite, 100 units/mL penicillin, and 100 units/mL streptomycin (Ravassard et al., 2011). For siRNA transfection [with a mix of three individual siRNAs (20 nM each)], dissociated cells were incubated with siRNA (with RNAiMax) for 5 minutes before plating. Gene expression assays were performed three days after infection or transfection by directly lysing cells on plates for RNA assays or recovered, cyto-spun onto glass slides for protein expression assays. Human islets were purchased from IIDP or obtained from the Clinical Islet Transplantation Laboratory, University of Louisville, KY. Hand-picked islets were dissociated into single cells and Cyto-spun onto glass slides for antibody staining.
Protein abundance assay at per cell levels
Stained cells (with IF, dilution were marked on the key reagent Table) using tissue sections or dissociated islet cells that were cyto-spun onto glass slides. Mutant/OE and control slides were processed side by side. Confocal images were taken under identical parameters using non-saturating conditions. Image J was then used to quantify the fluorescence intensity. For Glut2 and insulin assays, the averaged fluorescence intensity within selected areas was used. For transcription factor assays, nuclei were circled and assayed for intensity. For background subtraction, areas outside the islets and inter-nuclear areas were assayed. Three to four pancreata were assayed, with three to ten representative microscopic areas assayed.
Luciferase assays
The luciferase reporter construction followed routine molecular cloning process. Briefly, BAC clones carrying the Hsp genomic regions were purchased from Oakland Children’s Hospital. PCR were then used to amplify the genomic fragments to drive firefly luciferase-eGFP fusion protein expression. The constructs were then sequenced for verification.
For making firefly luciferase reporters with the 33-bp Myt1-binding sites of Hspa1a, a minimal CMV promoter was synthesized and ligated with the Hspa1a enhancer and the firefly luciferase reporter. The artificial Myt1ZF-VP16 constructs were made by PCR fragment ligation: the 4-zinc finger region was amplified with PCR, using a full length Myt1 cDNA as template; the VP-16 region was PCR-amplified with the rTTA cDNA as template. The oligos used were in reagent table. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myt1 overexpressing or control plasmids, together with firefly luciferase reporters and a Renilla luciferase internal control. Cells were then lysed two days after transfection to assay the firefly and Renilla luciferase activity using a Dual Luciferase Assay kit (Perkin Elmer) following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Putative Myt-binding site identification
The putative Myt1 and Myt2 binding sites were identified by examining the supplementary tables in (Mall et al., 2017; Vasconcelos et al., 2016) based on ChIP-seq data and in silico search of the AAGTT motives recognized by the Myt TFs.
ChIP-PCR assays
ChIP assays used a Magna-CHIP™ HiSens kit from Millipore. Briefly, adult islets and acinar clusters were handpicked, fixed in 1% formaldehyde for 14 minutes and washed 2X with cold PBS. Islets were then frozen for storage. When ~3000 islets were obtained, they were thawed and dounced into single cells in lysis buffer provided in the kit, and sonicated to ~100–400 base pair fragments. Chromatin preparation from acinar cells followed the same process. The immunoprecipitation was done using 1 μg purified antibodies per 0.4 μg chromatin overnight. Oligos were listed in reagent table. H3K27Ac-based ChIP followed similar methods.
Myt TF overexpression in human islet cells
Lentivirus expressing HA-tagged human MYT3, driven by a CMV promoter, was produced as in (Huang et al., 2018). Primary human islet were partially dissociated into cell clusters between 1–5 cells and infected with virus at ~5 MOI per cell overnight. Infected cells were then prepared as pseudo-islets in hanging-drop (~1000 cells per drop of 35 μl of CMRL-1066 with 10 mM glucose) for 3–4 days, which were cultured in 20 mM glucose for ~40 hour before expression assays.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Sample size and statistical analysis
All experiments contained at least two biological replicas and two technical replicas, so that all assays had at least 4 independent experiments. Statistical analyses utilized standard Student’s t-test for pairwise comparisons or one-way ANOVA for comparing multiple groups of data points. A p-value of 0.05 or lower was considered significant.
RNA-seq Data quantification
___Bulk RNA-seq analysis
The original RNA-seq data of Myt mutant/control cells were deposited in ArrayExpress under ID code E-MTAB-2266 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-2266/) and E-MTAB-6615 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-6615/). The data were generated with purified β-cells using Mip-eGFP expression as a surrogate for insulin production (Huang et al., 2018). The RNA-seq data for db/db and control islets were downloaded from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE107489. After downloading the data, raw reads were processed and analyzed with TopHat and Cufflinks to determine the relative abundance of gene expression at each stages, reported as log2 transformed FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads, Table S2)(Trapnell et al., 2012). To avoid excluding false negative genes, we included all genes with adjusted p-value smaller than 0.05. We also included other genes with a difference above 2-fold and a p-value smaller than 0.02.
___Single cell RNA-seq analysis
For a full description of RePACT (regressing principle components for the alignment of continuous trajectory)-based human β-cell analysis, please refer to the star methods of (Fang et al., 2019). Briefly, we used Dropseq• to generate massively parallel single-cell transcriptome data (~39,000 β-cells, from 1,800 human islet). In RePACT, we first performed PCA to reduce the dimension of transcriptome data. Next, we used regression analysis to draw two optimal trajectory lines reflecting the T2D-relevant variation. In this study, we used the top 10 PCs as predictors. The numeric projection of each cell on the T2D trajectory (T2D index) served as a measurement of the degree to which the cell has transformed during disease development. We then binned the cells into a number of pseudo-states according to the index values. By comparing cells from different pseudo-states, RePACT greatly improved the statistical power to identify gene signatures for T2D status in α or β-cell.
Supplementary Material
Table S2: Related to Figures 2 and 3. List of genes differentially expressed between P1 control and 6F; Pdx1Cre Mip-eGFP+ β-cells, assayed via RNAseq. Fold change {LogFC, calculated as log(2) [(average FPKM of mutant) - (average FPKM of control)/(average FPKM of control)], where FPKM is Fragment Per Kilo-base per Million), p-value, adjusted p-value with Benjamini and Hochberg method, and gene expression levels in three controls and three mutants (FPKM, log2 transformed) were listed. Also included are in silico results showing if Myt1 or Myt2 (Myt1L) binds to any of the locus. The original Myt TF-DNA interaction data were from Mall et al., 2017 (Nature 544, 245–249.) and Vasconcelos et al., 2016 (Cell Rep 17, 469–483).
Table S1: Related to all figures. Detailed quantification data used in charts of all figures/supplemental figures.
Highlights:
Myt TFs repress late-stage stress-response genes in mouse and human β-cells.
Atf4 and Hsps are major Myt TF target-genes required for postnatal β-cell fitness.
Metabolic stress induces nuclear Myt TF during mouse/human β-cell compensation.
MYT TFs are inactivated in dysfunctional human T2D β-cells.
Acknowledgements
We thank Chunhua Dai and Alvin C. Powers (Vanderbilt University Medical Center) for assistance with the human islet studies, and William Gu (Montgomery Bell Academy, Nashville) for text editing. This study is supported by grants from NIDDK (DK065949 for GG/RS, DK090570 for RS, DK106228 for GG/IK) and JDRF (1-2009-371 for GG). Confocal and TEM imaging were performed with VUMC Cell Imaging Shared Resource (funded by CA68485, DK20593, DK58404, DK59637 and EY08126). We also thank the Islet Isolation and Procurement Core of Vanderbilt Medical Center for hormone assays (funded by DK20593).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Declaration of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Axelsson AS, Mahdi T, Nenonen HA, Singh T, Hanzelmann S, Wendt A, Bagge A, Reinbothe TM, Millstein J, Yang X, et al. (2017). Sox5 regulates beta-cell phenotype and is reduced in type 2 diabetes. Nat Commun 8, 15652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas-Ponce A, Scheibner K, Lickert H, and Bakhti M (2017). Cellular and molecular mechanisms coordinating pancreas development. Development 144, 2873–2888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellefroid EJ, Bourguignon C, Hollemann T, Ma Q, Anderson DJ, Kintner C, and Pieler T (1996). X-MyT1, a Xenopus C2HC-type zinc finger protein with a regulatory function in neuronal differentiation. Cell 87, 1191–1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blach-Olszewska Z, and Leszek J (2007). Mechanisms of over-activated innate immune system regulation in autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 3, 365–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand K, Huangfu D, and Melton D (2007). All beta cells contribute equally to islet growth and maintenance. PLoS Biol 5, e163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugliani M, Liechti R, Cheon H, Suleiman M, Marselli L, Kirkpatrick C, Filipponi F, Boggi U, Xenarios I, Syed F, et al. (2013). Microarray analysis of isolated human islet transcriptome in type 2 diabetes and the role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in pancreatic beta cell dysfunction. Mol Cell Endocrinol 367, 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfone A, Carotenuto P, Faedo A, Aglio V, Garzia L, Bello AM, Basile A, Andre A, Cocchia M, Guardiola O, et al. (2005). Telencephalic embryonic subtractive sequences: a unique collection of neurodevelopmental genes. J Neurosci 25, 7586–7600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Q, Brissova M, Reinert RB, Pan FC, Brahmachary P, Jeansson M, Shostak A, Radhika A, Poffenberger G, Quaggin SE, et al. (2012). Enhanced expression of VEGF-A in beta cells increases endothelial cell number but impairs islet morphogenesis and beta cell proliferation. Dev Biol 367, 40–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao SS, and Kaufman RJ (2014). Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in cell fate decision and human disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 21, 396–413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaari A (2019). Molecular chaperones biochemistry and role in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Biol Macromol 131, 396–411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle JT, and Puttfarcken P (1993). Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262, 689–695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadi PK, Vierra NC, Ustione A, Piston DW, Colbran RJ, and Jacobson DA (2014). Inhibition of pancreatic beta-cell Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II reduces glucose-stimulated calcium influx and insulin secretion, impairing glucose tolerance. J Biol Chem 289, 12435–12445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elghazi L, Rachdi L, Weiss AJ, Cras-Meneur C, and Bernal-Mizrachi E (2007). Regulation of beta-cell mass and function by the Akt/protein kinase B signalling pathway. Diabetes Obes Metab 9 Suppl 2, 147–157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang Z, Weng C, Li H, Tao R, Mai W, Liu X, Lu L, Lai S, Duan Q, Alvarez C, et al. (2019). Single-Cell Heterogeneity Analysis and CRISPR Screen Identify Key beta-Cell-Specific Disease Genes. Cell Rep 26, 3132–3144 e3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca SG, Gromada J, and Urano F (2011). Endoplasmic reticulum stress and pancreatic beta-cell death. Trends Endocrinol Metab 22, 266–274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Font de Mora J, Esteban LM, Burks DJ, Nunez A, Garces C, Garcia-Barrado MJ, Iglesias-Osma MC, Moratinos J, Ward JM, and Santos E (2003). Ras-GRF1 signaling is required for normal beta-cell development and glucose homeostasis. EMBO J 22, 3039–3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O, and Samali A (2010). Cellular stress responses: cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell Biol 2010, 214074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu C, Stein GH, Pan N, Goebbels S, Hornberg H, Nave KA, Herrera P, White P, Kaestner KH, Sussel L, et al. (2010). Pancreatic beta cells require NeuroD to achieve and maintain functional maturity. Cell Metab 11, 298–310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu G, Dubauskaite J, and Melton DA (2002). Direct evidence for the pancreatic lineage: NGN3+ cells are islet progenitors and are distinct from duct progenitors. Development 129, 2447–2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu G, Wells JM, Dombkowski D, Preffer F, Aronow B, and Melton DA (2004). Global expression analysis of gene regulatory pathways during endocrine pancreatic development. Development 131, 165–179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunton JE, Kulkarni RN, Yim S, Okada T, Hawthorne WJ, Tseng YH, Roberson RS, Ricordi C, O’Connell PJ, Gonzalez FJ, et al. (2005). Loss of ARNT/HIF1beta mediates altered gene expression and pancreatic-islet dysfunction in human type 2 diabetes. Cell 122, 337–349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S, Dai C, Guo M, Taylor B, Harmon JS, Sander M, Robertson RP, Powers AC, and Stein R (2013). Inactivation of specific beta cell transcription factors in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 123, 3305–3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez GD, Bender AS, Cirulli V, Mastracci TL, Kelly SM, Tsirigos A, Kaestner KH, and Sussel L (2017). Pancreatic beta cell identity requires continual repression of non-beta cell programs. J Clin Invest 127, 244–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl FU, Bracher A, and Hayer-Hartl M (2011). Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 475, 324–332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman MG, Lu D, Kim ML, Kociba GJ, Shukri T, Buteau J, Wang X, Frankel WL, Guttridge D, Prentki M, et al. (2004). Role for activating transcription factor 3 in stress-induced beta-cell apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 24, 5721–5732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C, Close AF, and Buteau J (2014). A critical role for the neural zinc factor ST18 in pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem 289, 8413–8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetz C, and Papa FR (2018). The Unfolded Protein Response and Cell Fate Control. Mol Cell 69, 169–181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil GS, and Davis RJ (2016). Cell Signaling and Stress Responses. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C, and Gu G (2017). Effective Isolation of Functional Islets from Neonatal Mouse Pancreas. J Vis Exp. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C, Walker EM, Dadi PK, Hu R, Xu Y, Zhang W, Sanavia T, Mun J, Liu J, Nair GG, et al. (2018). Synaptotagmin 4 Regulates Pancreatic beta Cell Maturation by Modulating the Ca(2+) Sensitivity of Insulin Secretion Vesicles. Dev Cell 45, 347–361 e345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J, and Qi L (2018). Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum: Crosstalk between ERAD and UPR pathways. Trends Biochem Sci 43, 593–605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iurlaro R, and Munoz-Pinedo C (2016). Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J 283, 2640–2652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P, Bailey CL, Fueger PT, Newgard CB, Casey PJ, and Kimple ME (2010). Rap1 promotes multiple pancreatic islet cell functions and signals through mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 to enhance proliferation. J Biol Chem 285, 15777–15785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JG, and Hudson LD (1992). Novel member of the zinc finger superfamily: A C2-HC finger that recognizes a glia-specific gene. Mol Cell Biol 12, 5632–5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura YI, Kitamura T, Kruse JP, Raum JC, Stein R, Gu W, and Accili D (2005). FoxO1 protects against pancreatic beta cell failure through NeuroD and MafA induction. Cell Metab 2, 153–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson KL, Fonseca SG, Ishigaki S, Nguyen LX, Foss E, Bortell R, Rossini AA, and Urano F (2006). Regulation of insulin biosynthesis in pancreatic beta cells by an endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein kinase IRE1. Cell Metab 4, 245–254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Q (2013). Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53, 401–426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mall M, Kareta MS, Chanda S, Ahlenius H, Perotti N, Zhou B, Grieder SD, Ge X, Drake S, Euong Ang C, et al. (2017). Myt1l safeguards neuronal identity by actively repressing many non-neuronal fates. Nature 544, 245–249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manukyan A, Kowalczyk I, Melhuish TA, Lemiesz A, and Wotton D (2018). Analysis of transcriptional activity by the Myt1 and Myt1l transcription factors. J Cell Biochem 119, 4644–4655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marselli L, Thorne J, Dahiya S, Sgroi DC, Sharma A, Bonner-Weir S, Marchetti P, and Weir GC (2010). Gene expression profiles of Beta-cell enriched tissue obtained by laser capture microdissection from subjects with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 5, e11499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neelankal John A, Ram R, and Jiang FX (2018). RNA-Seq Analysis of Islets to Characterise the Dedifferentiation in Type 2 Diabetes Model Mice db/db. Endocr Pathol 29, 207–221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir T, Melton DA, and Dor Y (2007). Recovery from diabetes in mice by beta cell regeneration. J Clin Invest 117, 2553–2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan FC, Brissova M, Powers AC, Pfaff S, and Wright CV (2015). Inactivating the permanent neonatal diabetes gene Mnx1 switches insulin-producing beta-cells to a delta-like fate and reveals a facultative proliferative capacity in aged beta-cells. Development 142, 3637–3648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T (2013). Adaptive translation as a mechanism of stress response and adaptation. Annu Rev Genet 47, 121–137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravassard P, Hazhouz Y, Pechberty S, Bricout-Neveu E, Armanet M, Czernichow P, and Scharfmann R (2011). A genetically engineered human pancreatic beta cell line exhibiting glucose-inducible insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 121, 3589–3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R, Dalle S, and Abderrahmani A (2014). Compensatory mechanisms of pancreatic beta cells: insights into the therapeutic perspectives for diabetes. J Diabetes Res 2014, 217387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romm E, Nielsen JA, Kim JG, and Hudson LD (2005). Myt1 family recruits histone deacetylase to regulate neural transcription. J Neurochem 93, 1444–1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scoville DW, Cyphert HA, Liao L, Xu J, Reynolds A, Guo S, and Stein R (2015). MLL3 and MLL4 Methyltransferases Bind to the MAFA and MAFB Transcription Factors to Regulate Islet beta-Cell Function. Diabetes 64, 3772–3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segerstolpe A, Palasantza A, Eliasson P, Andersson EM, Andreasson AC, Sun X, Picelli S, Sabirsh A, Clausen M, Bjursell MK, et al. (2016). Single-Cell Transcriptome Profiling of Human Pancreatic Islets in Health and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab 24, 593–607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma RB, O’Donnell AC, Stamateris RE, Ha B, McCloskey KM, Reynolds PR, Arvan P, and Alonso LC (2015). Insulin demand regulates beta cell number via the unfolded protein response. J Clin Invest 125, 3831–3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sies H, Berndt C, and Jones DP (2017). Oxidative Stress. Annu Rev Biochem 86, 715–748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B, Scheuner D, Ron D, Pennathur S, and Kaufman RJ (2008). Chop deletion reduces oxidative stress, improves beta cell function, and promotes cell survival in multiple mouse models of diabetes. J Clin Invest 118, 3378–3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, et al. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 15545–15550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J, Cui J, He Q, Chen Z, Arvan P, and Liu M (2015). Proinsulin misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress during the development and progression of diabetes. Mol Aspects Med 42, 105–118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swisa A, Avrahami D, Eden N, Zhang J, Feleke E, Dahan T, Cohen-Tayar Y, Stolovich-Rain M, Kaestner KH, Glaser B, et al. (2017a). PAX6 maintains beta cell identity by repressing genes of alternative islet cell types. J Clin Invest 127, 230–243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swisa A, Glaser B, and Dor Y (2017b). Metabolic Stress and Compromised Identity of Pancreatic Beta Cells. Front Genet 8, 21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabat M, Page MM, Panzhinskiy E, Skovso S, Mojibian M, Fernandez-Tajes J, Bruin JE, Bround MJ, Lee JT, Xu EE, et al. (2016). Reduced Insulin Production Relieves Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Induces beta Cell Proliferation. Cell Metab 23, 179–193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talchai C, Xuan S, Lin HV, Sussel L, and Accili D (2012). Pancreatic beta cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic beta cell failure. Cell 150, 1223–1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant BR, Islam R, Kramer MM, Merkulova Y, Kiang RL, Whiting CJ, and Hoffman BG (2012). The transcription factor Myt3 acts as a pro-survival factor in beta-cells. PLoS One 7, e51501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, and Pachter L (2012). Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7, 562–578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsonkova VG, Sand FW, Wolf XA, Grunnet LG, Kirstine Ringgaard A, Ingvorsen C, Winkel L, Kalisz M, Dalgaard K, Bruun C, et al. (2018). The EndoC-betaH1 cell line is a valid model of human beta cells and applicable for screenings to identify novel drug target candidates. Mol Metab 8, 144–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos FF, Sessa A, Laranjeira C, Raposo A, Teixeira V, Hagey DW, Tomaz DM, Muhr J, Broccoli V, and Castro DS (2016). MyT1 Counteracts the Neural Progenitor Program to Promote Vertebrate Neurogenesis. Cell Rep 17, 469–483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S, Zhang J, Zhao A, Hipkens S, Magnuson MA, and Gu G (2007). Loss of Myt1 function partially compromises endocrine islet cell differentiation and pancreatic physiological function in the mouse. Mech Dev 124, 898–910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang YJ, and Kaestner KH (2019). Single-Cell RNA-Seq of the Pancreatic Islets--a Promise Not yet Fulfilled? Cell Metab 29, 539–544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee KS, and Yu VC (1998). Isolation and characterization of a novel member of the neural zinc finger factor/myelin transcription factor family with transcriptional repression activity. J Biol Chem 273, 5366–5374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young SK, and Wek RC (2016). Upstream Open Reading Frames Differentially Regulate Gene-specific Translation in the Integrated Stress Response. J Biol Chem 291, 16927–16935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang T, Kim DH, Xiao X, Lee S, Gong Z, Muzumdar R, Calabuig-Navarro V, Yamauchi J, Harashima H, Wang R, et al. (2016). FoxO1 Plays an Important Role in Regulating beta-Cell Compensation for Insulin Resistance in Male Mice. Endocrinology 157, 1055–1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S2: Related to Figures 2 and 3. List of genes differentially expressed between P1 control and 6F; Pdx1Cre Mip-eGFP+ β-cells, assayed via RNAseq. Fold change {LogFC, calculated as log(2) [(average FPKM of mutant) - (average FPKM of control)/(average FPKM of control)], where FPKM is Fragment Per Kilo-base per Million), p-value, adjusted p-value with Benjamini and Hochberg method, and gene expression levels in three controls and three mutants (FPKM, log2 transformed) were listed. Also included are in silico results showing if Myt1 or Myt2 (Myt1L) binds to any of the locus. The original Myt TF-DNA interaction data were from Mall et al., 2017 (Nature 544, 245–249.) and Vasconcelos et al., 2016 (Cell Rep 17, 469–483).
Table S1: Related to all figures. Detailed quantification data used in charts of all figures/supplemental figures.
Data Availability Statement
The original data analyzed in this study are in ArrayExpress under ID code E-MTAB-2266 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-2266/), E-MTAB-6615 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-6615/), and in https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE107489.


