Abstract
The larva of Allomyrina dichotoma (family Scarabaeidae) is an edible insect that is registered in the Korean Food Standards Codex as a food resource. The chemical study on the larvae of A. dichotoma resulted in the isolation of three new tetrahydroquinolines, allomyrinaines A–C (1–3), one new dopamine derivative, allomyrinamide A (4), and four known compounds (5–8). The structures were elucidated on the basis of 1D and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and MS spectroscopic data analysis. Allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) possessed three stereogenic centers at C-2, C-3, and C-4, whose relative configurations were determined by analyses of the coupling constants and the nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy (NOESY) data, as well as DP4+ calculation. The anti-inflammatory effects of compounds 1–4 were evaluated in human endothelial cells. Allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) could stabilize vascular barrier integrity on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced vascular inflammation via inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway. The physiologically relevant concentration was confirmed by Q-TOF-MS-based quantitative analysis on allomyrinaines A–C in crude extract. This study suggests that allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) are bioactive constituents of A. dichotoma to treat vascular inflammatory disorder.
Keywords: Allomyrina dichotoma, anti-inflammatory effect, dopamine derivative, NF-κB, tetrahydroquinoline
1. Introduction
Globally, the most commonly consumed insects are beetles (Coleoptera) [1]. Allomyrina dichotoma L. (family Scarabaeidae, order Coleoptera), a rhinoceros beetle, is mainly distributed in Korea, Japan, China, and Taiwan. Recently, the larva of A. dichotoma has been registered in the Korean Food Standards Codex as a new food resource. Researches have focused on this insect resource for the development of functional food and medicinal material. Chemical investigations of A. dichotoma reported that it contains general nutrients such as fatty acids and nucleosides [2,3]. A biological study of the larvae extract revealed hepatoprotective [4], anticancer [4], antidementia [5], antiobesity [6], and antioxidant [7] activities. Despite the potential application of A. dichotoma in the development of food and medicinal resource, there are few studies on the bioactive small molecules originating from this insect. The objective of this study was thus to explore the bioactive constituents from A. dichotoma larvae.
The presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a bacterial endotoxin, ranks the highest among the risk factors that contribute to lethal endotoxemia [8]. The integrity of vascular endothelium is essential for controlling the flux of proteins, fluids, and immune cells across vessels into tissues, and vascular endothelial dysfunction is a critical event in acute inflammation [9,10]. The systemic accumulation of LPS triggers leukocyte infiltration within the vascular wall and promotes vascular permeability [11]. Therefore, the maintenance of vascular integrity is crucial for vascular and tissue homeostasis.
Previous studies have shown that antidesmone (tetrahydroquinoline alkaloid) derived from Antidesma membranaceum (Euphorbiaceae) has an anti-inflammatory effect on LPS-induced RAW264.7 mouse macrophage cells [12]. The anti-inflammatory effects were regulated through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)–nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathways. Herein, we report on the details of the isolation, structure elucidation of new tetrahydroquinolines (1–3), and a new dopamine derivative (4) as well as their vascular barrier protective effects on LPS-mediated vascular inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Isolated Compounds
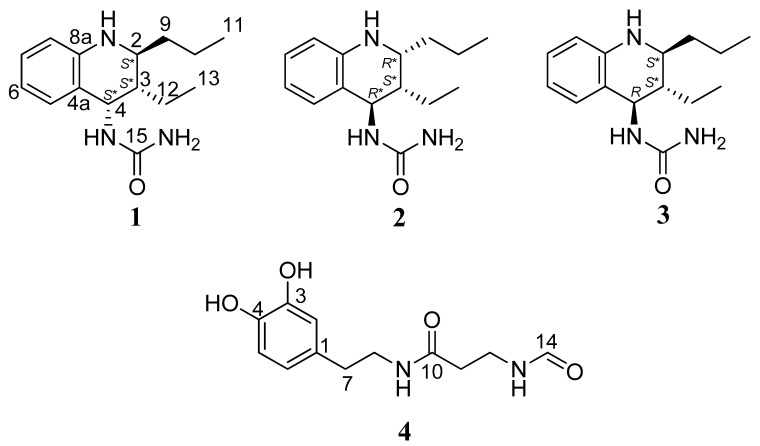
Three new tetrahydroquinolines (1–3) and one new dopamine derivative (4) were isolated from A. dichotoma larvae, and their structures were established by spectroscopic techniques, especially detailed analyses of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra (Figure 1). Compounds 1–3, structurally based on diastereomeric tetrahydroquinolines, were obtained as colorless oil. Their molecular formulas were as C15H23N3O based on observed high resolution electrospray ionization mass (HRESIMS) ions (m/z 262.19 [M + H]+, 284.17 [M + Na]+) and their NMR information.
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of tetrahydroquinolines (1–3) and a dopamine derivative (4).
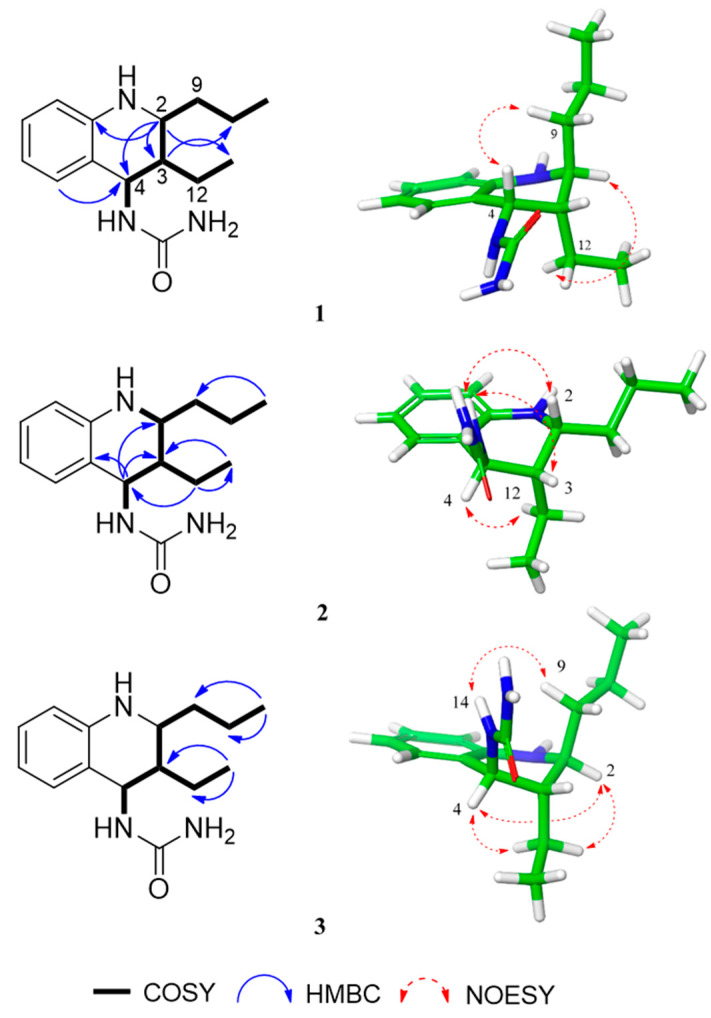
The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 measured in methanol-d4 showed the diagnostic signals of one ortho-disubstituted benzene (δH 7.08, 1H, d, J = 7.47 Hz, H-5; δH 6.92, 1H, m, H-7; δH 6.50, 2H, overlap, H-8 and H-6), three methine (δH 4.99, 1H, d, J = 4.24 Hz, H-4; δH 3.14, 1H, dd, J = 6.54, 11.87 Hz, H-2; δH 1.63, 1H, qd, J = 4.24, 6.54 Hz, H-3), and three methylene (δH 1.55, 1H, m, H2-9; δH 1.46, 1H, m, H2-10; δH 1.32, 2H, m, H2-12) (Table 1). The proton signals at δH 1.00 (3H, t, J = 6.61 Hz, H3-13) and 0.97 (3H, t, J = 6.40 Hz, H3-11) indicated the presence of two terminal methyl groups. A urea and two nitrogen-linked methine carbons were observed at δC 161.8, 52.5, and 47.8. Analysis of the 1H-1H correlation spectroscopy (COSY) data for 1 revealed two individual spin systems: one propyl (H-2–H2-9–H2-10–H3-11) group and one ethyl (H-3–H2-12–H3-13) group (Figure 2). Urea, propyl, and ethyl moieties were connected to C-4, C-3, and C-2, respectively, based on the heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) cross-peaks (Figure 2). According to the NMR and MS spectroscopic data, the planar structure was defined to be a N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-propyl-3-ethyl-4-quinolinyl)-urea. Compound 1 possessed three stereogenic centers at C-2, C-3, and C-4 comprising the piperidine core. The relative configureuration of the piperidine ring in 1 could be established from 1H–1H coupling constants and nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy (NOESY) data analysis (Figure 2). The small coupling constants between H-4 (J = 4.24 Hz) and H-3 indicated a gauche conformation with a torsion angle of approximately 60°. Having established the orientations of H-3 and H-4, there are four possible configurations that are feasible for C-2 to C-4, i.e., axial–equatorial–axial, equatorial–equatorial–axial, axial–equatorial–equatorial, and equatorial–equatorial–equatorial. In the NOESY spectrum, the nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) correlations, H-4/H2-9 and H-2/H2-12, indicated that H-2, H-3, and H-4 were equatorial–equatorial–axial orientations (Figure 2). To clarify the structure, aprotic solvent was employed. A set of additional NOE correlations between NH-14 and H2-12 are present in the acetone-d6 (Table 2) Thus, compound 1 was assigned as N-[(2S*,3S*,4S*)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-propyl-3-ethyl-4-quinolinyl]-urea, namely, allomyrinaine A.
Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic data for compounds 1–3 (600 MHz, methanol-d4).
| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, mult (J in Hz) | δ C | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δ C | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δ C | |
| 2 | 3.14, dd (6.54, 11.87) | 52.5 | 3.28, m | 51.1 | 3.21, td (4.14, 7.43) | 54.2 |
| 3 | 1.63, qd (4.24, 6.54) | 42.7 | 1.68, m | 44.2 | 1.67, qd (5.46, 7.43) | 44.3 |
| 4 | 4.99, d, (4.24) | 47.8 | 4.66, d (3.55) | 50.7 | 4.70, d (5.46) | 50.8 |
| 4a | - | 122.5 | - | 121.2 | - | 123.3 |
| 5 | 7.08, d (7.47) | 128.6 | 7.08, dd (1.02, 7.82) | 131.7 | 7.04, d (7.51) | 129.5 |
| 6 | 6.50, m, overlap | 117.0 | 6.56, m, overlap | 117.8 | 6.56, m, overlap | 117.8 |
| 7 | 6.92, m | 128.9 | 6.96, m | 129.1 | 6.93, m | 128.8 |
| 8 | 6.50, m, overlap | 114.7 | 6.56, m, overlap | 115.6 | 6.56, m, overlap | 115.4 |
| 8a | - | 145.5 | - | 146.3 | - | 145.9 |
| 9 | 1.55, m | 38.3 | 1.53, m | 34.8 | 1.62/1.56, m | 37.4 |
| 10 | 1.46, m | 19.4 | 1.49/1.40, m | 20.4 | 1.52, m | 23.4 |
| 11 | 0.97, t (6.40) | 14.6 | 0.99, m, overlap | 14.5 | 0.97, t (7.55), overlap | 14.6 |
| 12 | 1.32, m | 20.7 | 1.44/0.99, m | 19.4 | 1.50/1.43, m | 19.6 |
| 13 | 1.00, t (6.61) | 12.2 | 0.99, m, overlap | 12.4 | 0.97, t (7.55), overlap | 10.5 |
| 15 | - | 161.8 | - | 161.0 | - | 162.2 |
Figure 2.
The 1H-1H correlation spectroscopy (COSY), heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC), and selected key nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy (NOESY) correlations of 1–3.
Table 2.
1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic data for compounds 1–3 (600 MHz, acetone-d6).
| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, mult (J in Hz) | δ C | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δ C | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δ C | |
| 2 | 3.15, q (6.10, 11.31) | 52.1 | 3.31, brs | 50.6 | 3.24, m | 53.7 |
| 3 | 1.61, qd (4.57, 6.10) | 42.3 | 1.69, td (3.74, 7.87) | 43.8 | 1.66, qd (4.17, 6.72) | 43.7 |
| 4 | 5.08, overlap | 46.9 | 4.71, dd (3.74) | 49.9 | 4.78, t (7.82) | 49.9 |
| 4a | - | 123.1 | - | 121.3 | - | 123.6 |
| 5 | 7.13, d (7.50) | 128.8 | 7.10, d (1.39) | 131.7 | 7.07, d, (7.60) | 129.4 |
| 6 | 6.47, td (1.02, 7.43) | 116.4 | 6.52, td (1.39, 7.78) | 117.1 | 6.50, m | 117.0 |
| 7 | 6.89, m | 128.3 | 6.92, m | 128.5 | 6.89, m | 128.2 |
| 8 | 6.52, d (7.43) | 114.2 | 6.54, d (7.78) | 114.8 | 6.53, d (8.12) | 114.6 |
| 8a | - | 145.1 | - | 146.0 | - | 145.7 |
| 9 | 1.54, m | 37.8 | 1.51, m | 34.8 | 1.62/1.55, m | 37.0 |
| 10 | 1.54/1.45, m | 18.9 | 1.43, m | 18.9 | 1.43, m | 19.2 |
| 11 | 0.93, t (7.18) | 14.5 | 0.94, m, overlap | 14.5 | 0.92, m, overlap | 14.5 |
| 12 | 1.32, m | 20.3 | 1.51/1.38, m | 20.1 | 1.50, m | 23.0 |
| 13 | 0.98, t (7.42) | 12.2 | 0.96, m, overlap | 12.4 | 0.95, m, overlap | 10.4 |
| 15 | - | 159.1 | - | 158.2 | - | 159.5 |
| NH-1 | 5.08, m, overlap | - | 4.96, s | - | 4.88, s | - |
| NH-14 | 5.64, d (9.74) | - | 5.74, d (6.69) | - | 5.59, d (7.78) | - |
| NH2-16 | 5.08, m, overlap | - | 5.01, s | - | 5.09, s | - |
The 1H NMR spectroscopic data of 2 were similar to those of 1. The significant difference was the 13C chemical shift of the C-4 stereogenic center (δC 50.7) deshielded 2.9 ppm compared to that of 1 (δC 47.8), indicating that 2 would be a diastereomer of 1. The JH-3/H-4 value of 3.55 Hz also shows that these two protons are a gauche conformation. NOESY correlations are observed for NH-14/H-2 and H-4/H2-12, implying that H-3/H-4, and H-2/H-4 were oriented as shown in Figure 2. Finally, the structure of 2 was determined as N-[(2R*,3S*,4R*)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-propyl-3-ethyl-4-quinolinyl]-urea, and it was named allomyrinaine B.
The 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic data of 3 were similar to those of 2, except for the deshielded signal at δC 54.2. The NOE correlations between H-4 and H-2 proved that these protons were cofacial (axial–axial or equatorial–equatorial). Additionally, the NOE correlations of H-2 and H-4 to H2-12 suggested that the cyclohexane ring occupied either 2S*,3S*,4R* (3a) or 2S*,3R*,4R* (3b) (Figure S31). The relative configuration at C-3 was conducted by applying computational NMR chemical shift calculations supported by DP4+ analysis [13]. The 1H and 13C NMR chemical shift values of the diastereomers 3a and 3b were compared with those of the experimental NMR data of 3 using the improved probability DP4+ method. The statistical analyses revealed that the probability of diastereomer 3a (2S*,3S*,4R*) is 100.0% in the consideration of both 1H and 13C NMR chemical shift values. Collectively, the structure of 3 was established as N-[(2S*,3S*,4R*)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-propyl-3-ethyl-4-quinolinyl]-urea and assigned the preliminary name of allomyrinaine C. Their electronic circular dichroism (ECD) data did not exhibit significant Cotton effects and specific rotation values were small, indicating that they were presumably scalemic mixtures.
Compound 4 was obtained as brown oil. The molecular formula was determined to be C12H16N2O4 by HRESIMS (m/z 275.1003 [M + Na]+, calcd 275.1008) combined with the 1H and 13C NMR spectra. 1H and HSQC data of 4 disclosed the presence of two OH groups (δH 8.74, 1H, brs, 3-OH; 8.65, 1H, brs, 4-OH), one trisubstituted benzene (δH 6.62, 1H, d, J = 7.96 Hz, H-5; δH 6.56, 1H, d, J = 1.93 Hz, H-2; δH 6.42, 1H, dd, J = 7.96, 1.93 Hz, H-6), and four methylene groups (δH 3.26, q, J = 6.86 Hz, H-12; δH 3.17, q, J = 6.09 Hz, H-8; δH 2.51, m, H-7; δH 2.23, t, J = 6.86 Hz, H-11). The 13C NMR spectrum displayed 12 carbon signals allocated to a nitrogenated tertiary sp2 carbon (δC 170.0), a nitrogenated terminal aldehyde carbon (δC 161.1), six benzene carbons (δC 145.0, 143.5, 130.2, 119.2, 115.9, 115.5), and four methylene carbons (δC 40.6, 35.2, 34.6, 33.9). The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were similar to those of N-acetyldopamine, except for the N-ethylformamide group [14]. Key HMBC correlations from H-7 to C-2/C6, from H-8/H-11 to C-10, and from H-12 to C-14 supported the presence of a formylamino-N-prophyl-propanamide moiety, as well as its connection to C-1. Thus, the structure of 4 was defined as N-(3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl)-1-formamidopropanamide, and it was named allomyrinamide A. The four known analogues were identified as arbutin (5) [15], cyclo(L-Val-L-Pro) (6) [16], inosine (7) [2], and 1,2-benzenediol (8) [17], respectively, by extensive spectroscopic analysis and by comparing their NMR data with those reported in the literature.
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.2.1. Effect of New Compounds (1–4) on Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated Vascular Inflammatory Responses
Vascular inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of multiple organ damage due to septic shock. Gram-negative LPS is one of the major inflammatory pathogens of sepsis [18]. LPS directly activates the vascular endothelium and monocyte/macrophage to induce inflammation [19]. Endothelial cells elicit a series of specific cellular responses, including increased cell adhesion molecule and inflammatory cytokine/chemokine expression [20]. This leads to vascular disruption and the recruitment of leukocytes to enhance the excess inflammatory responses [19].
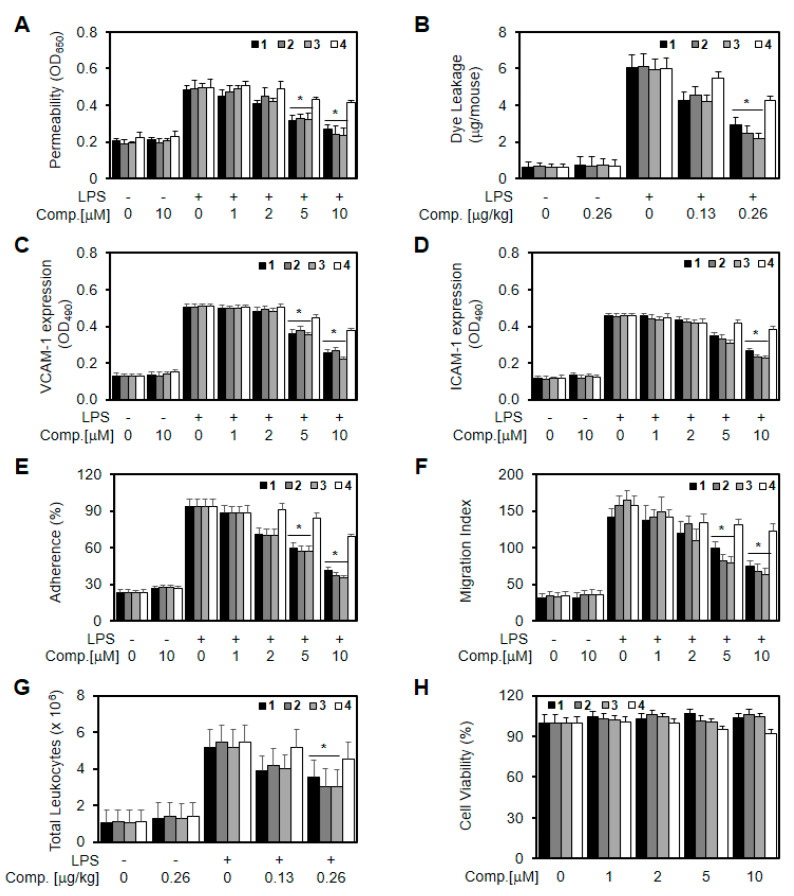
A permeability assay was used to determine the effects of each compound on the barrier integrity of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with each compound (10 µM) alone did not result in an alteration of barrier integrity (Figure 3a). On the other hand, LPS is known to cleave and disrupt endothelial barrier integrity [21]. Thus, HUVECs were treated with various concentrations of each compound for 6 h after the addition of LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4 h. The results shown in Figure 3a indicate that new tetrahydroquinolines (1–3) inhibit the LPS-mediated hyperpermeability in endothelial cells, with the optimal effect occurring at a concentration above 5 µM. To confirm this effect in vivo, the LPS-induced vascular permeability in mice was assessed. As shown in Figure 3B, the new tetrahydroquinolines (1–3) induced a marked inhibition of the peritoneal leakage of dye induced by LPS. Assuming that the average weight of a mouse is 20 g and the average blood volume is 2 mL, then the amount of each compound injected (0.13, 0.26 mg/kg) was equivalent to 5 or 10 µM in peripheral blood.
Figure 3.
Effects of compounds (1–4) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated vascular inflammatory responses. (A) Effect of various concentrations of compounds (1–4) on LPS-induced (100 ng/mL, 4 h) barrier disruption was monitored by the flux of Evans blue bound albumin across human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs); (B) Effect of compounds (1–4) on LPS (15 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced vascular permeability in mice was examined by the flux of Evans blue in mice (expressed μg/mouse, n = 5); LPS-mediated (100 ng/mL) expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) (C) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (D) in HUVECs was analyzed after treating monolayers with each compound (10 μM each) by whole cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); (E) LPS-mediated (100 ng/mL) adherence of monocytes to HUVEC monolayers was analyzed after treating cells with each compound; (F) LPS-mediated (100 ng/mL) migration of human neutrophils through HUVEC monolayers was analyzed after treating cells with each compound; (G) The effects of each compound on LPS (15 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced leukocyte migration in mice (expressed ×106, n = 5); (H) The effects of each compound on cell viability were evaluated using CCK8 assays. The results are expressed as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 vs. LPS.
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) play a pivotal role in the process of vascular inflammatory processes [21]. The adhesion of circulating leukocytes to the vascular endothelium is a fundamental step in leukocyte extravasation during inflammation, and CAMs mediate this process [21]. Therefore, inhibiting the expression of CAMs in vascular endothelial cells is considered to be a promising therapeutic approach for treating vascular inflammatory diseases. We found that LPS induced the upregulation of the surface protein expressions of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 (Figure 3C,D) and that each compound inhibited this effect, suggesting that the inhibitory effects of each compound on the expression of CAMs are mediated via the attenuation of the LPS signaling pathway by each compound. Experiments on CAMs are widely used in vitro for studying the regulation of the interactions between leukocytes and endothelial cells [22]. In addition, an elevated expression of CAMs was found to correspond well with the enhanced binding of leukocytes cells to LPS-activated endothelial cells, followed by their migration. Moreover, treatment with compounds 1–3 resulted in the downregulation of neutrophils adherence and their subsequent migration across activated endothelial cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 3e,f). These results suggest that compounds 1–3 downregulate the pro-inflammatory signaling effect of released LPS, thereby inhibiting the amplification of inflammatory pathways by nuclear cytokines. To confirm this effect in vivo, we examined LPS-induced leukocyte migration in mice. LPS was found to stimulate leukocyte migration into the peritoneal cavities of mice, and treatment with each compound resulted in a significant reduction of peritoneal leukocyte counts (Figure 3g). Therefore, in the current study, treatment with compounds 1–3 resulted in the downregulation of LPS-induced levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, suggesting that compounds 1–3 inhibit the adhesion and migration of leukocytes to an inflamed endothelium. To test the cytotoxicity of each compound, cellular viability assays were performed in HUVECs treated with each compound for 48 h. At concentrations up to 10 µM, each compound did not affect cell viability (Figure 3h). Therefore, the results obtained in this study suggest that the new tetrahydroquinolines (1–3) have potential as therapeutic agents against vascular inflammatory diseases.
2.2.2. Effect of New Compounds (1–3) on the LPS-stimulated Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB), Production of Interleukin-1β (IL-1β)/Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α), and Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK
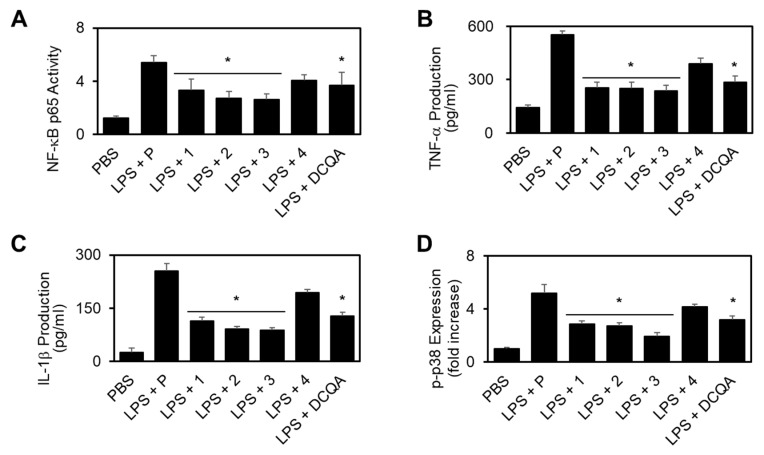
NF-κB activation is required for pro-inflammatory responses, and the 3 most important providers of inflammatory signals in endothelial cells are nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) [21]. Therefore, we tested the effects of each compound on the activation of NF-κB by LPS. As shown in Figure 4a, the activation of NF-κB was increased by LPS, and these increases were significantly reduced by each compound. Therefore, these results indicate that compounds 1–3 can regulate important signals that induce pro-inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells. As a positive control, 3-5-di-O-dihydrocaffeoylquinic acid (DCQA), a compound previously identified to be effective in vascular inflammation, was used [23]. The suppression of vascular inflammation inducing NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, and p-p38 expression with 20 µM of compound was confirmed through previous studies [23].
Figure 4.
Effect of new compounds (1–4) on the LPS-stimulated activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)/ interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). First, 20 μM of 3-5-di-O-dihydrocaffeoylquinic acid (DCQA) was used as positive control. (A) LPS (100 ng/mL)-mediated activation of NF-κB p65 in HUVECs was analyzed after the treatment of cells with 10 μM of each compound for 6 h; LPS (100 ng/mL)-mediated production of TNF-α (B) or IL-6 (C) in HUVECs was analyzed after the treatment of cells with the indicated concentrations of each compound for 6 h; (D) HUVECs were activated with LPS (100 ng/mL), followed by treatment with each compound at different concentrations for 6 h. The effects of each compound on the LPS-mediated expression of phospho-p38 were determined by ELISA. * p < 0.05 vs. LPS.
Based on these results, we hypothesized that each compound might inhibit the expression or activity of these pro-inflammatory molecules. To investigate the potential effects of compounds 1–3 on the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1β, HUVECs were incubated with each compound for 6 h after LPS activation, and then TNF-α and IL-1β levels in the culture media were measured via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Levels of TNF-α and IL-1β showed an increase in LPS-stimulated endothelial cells; these increases were significantly reduced by compounds 1–3 (Figure 4b,c), indicating that compounds 1–3 can regulate the most important signals that induce pro-inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells.
LPS is known to induce pro-inflammatory responses by promoting the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [24]. To determine whether each compound inhibits p38 MAPK in LPS-activated HUVECs, HUVECs were pre-incubated with each compound and then activated with LPS, followed by the examination of phosphor p38 MAPK levels by ELISA. As shown in Figure 4D, LPS induced an upregulated expression of phosphorylated p38, and the significant inhibition of this upregulation was observed by treatment with compounds 1–3.
2.2.3. Protective Effect of Each Compound in Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Septic Mice
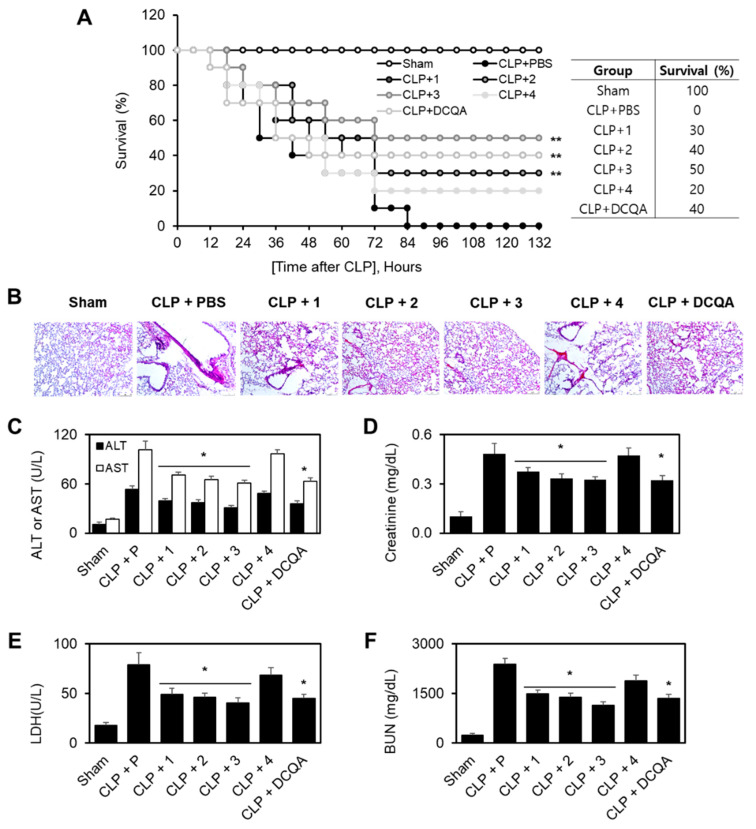
Sepsis is a systemic response to serious infections, and it has a poor prognosis when it is associated with organ dysfunction, hypoperfusion, or hypotension [22]. Based on our previous findings, it was hypothesized that each compound may reduce the mortality in a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis mouse model. To test this hypothesis, each compound was administered to mice after a CLP procedure. Twenty-four h after the operation, the mice showed signs of sepsis, such as shivering, bristled hair, and weakness. The administration of each compound (0.26 mg/kg) 12 h after CLP did not prevent CLP-induced death, so each compound (0.26 mg/kg) was administered twice (12 and 50 h after CLP). Administration of two doses of compounds 1–3 resulted in an increase in the survival rate from 40% to 60%, based on Kaplan–Meier survival analysis (p < 0.0001; Figure 5a). This marked survival benefit that was achieved after the administration of two doses of compounds 1–3 suggested that the protection of LPS-mediated vascular inflammatory responses could be a therapeutic strategy for the management of sepsis and septic shock. We compared DCQA with improved survival in CLP-induced septic mice as a positive control [23].
Figure 5.
Effects of each compound on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced mortality and pulmonary injury. (A) Male C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) were intravenously treated with each compound (0.26 mg/kg) or DCQA (1 mg/kg, positive control at 12 and 50 h after CLP. Animal survival was monitored every 6 h after CLP for 132 h. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was performed for evaluating of the overall survival rates; (B) Male C57BL/6 mice underwent CLP and were administered each compound (0.26 mg/kg) intravenously at 12 and 50 h after CLP (n = 5). Mice were killed 96 h after CLP. Photomicrographs of lung tissues (H&E staining, 200×, White scale bar = 50 µm). The illustrations show representative images from three independent experiments; (C–F) The same as (B,C) except that mice were bled to death. Aspartate transaminase (AST) (C), alanine transaminase (ALT) (C), creatinine (D), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (E), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (F) levels in the plasma were measured. The results are expressed as the means ± SD of five independent experiments (n = 5). * p < 0.05 vs. the CLP group.
To confirm the protective effects of compounds 1–3 against CLP-induced death, its effects were examined upon CLP-induced pulmonary injury. In the sham treatment group, there were no significant differences between the lungs of the treated and untreated mice under the light microscope. In the untreated CLP group, interstitial edema with massive infiltration of inflammatory cells into the interstitium and alveolar spaces was observed, and the pulmonary architecture was severely damaged (Figure 5B). Systemic inflammation during sepsis commonly causes multiple organ failure, and the liver and kidneys are the major target organs [25]. CLP resulted in a significant increase in the plasma levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) (markers of hepatic injury; Figure 5C), as well as creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (markers of renal injury; Figure 5D,E). Compounds 1–3 were able to reverse all of these abnormalities. The levels of another important marker of tissue injury, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), were also reduced by compounds 1–3 in CLP-operated mice (Figure 5F).
2.2.4. Quantitative Analysis of 1–3
The physiologically relevant concentration was confirmed by quadruple time-of-flight mass (Q-TOF-MS)-based quantitative analysis on allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) in crude extract. Based on the calibration curves, the concentrations of allomyrinaines A, B, and C in the extract were estimated to be 12, 15, and 16 μM, respectively (Figure S44). The micromolar range contents of allomyrinaines A–C in the extract represent the biological activity of the edible insect A. dichotoma.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured on a JASCO DIP-370 (Tokyo, Japan) automatic digital polarimeter. UV spectra were recorded on a Shimadazu SPD-M20A PDA detector, and IR spectra were obtained on a Bruker ALPHA FT-IR spectrometer. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments were conducted using Bruker DMX 300 (1H-300 MHz, 13C-75 MHz) and Bruker DMX 600 (1H-600 MHz, 13C-150 MHz) spectrometers. Mass spectral data were obtained on a SYNAPT G2 Waters mass spectrometer (Manchester, UK). Thin layer chromatography (TLC) was executed on glass plates precoated with silica gel 60 F254 and RP-18 F254 (20 × 20 cm, 200 μm, 60 Å, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) was implemented on silica gel (70–230 mesh, Merck), and medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC) was performed utilizing a Biotage IsoleraTM apparatus equipped with a reversed phase C18 SNAP Cartridge KP-C18-HS (120 g and 400 g, Biotage AB, Uppsala, Sweden). Preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was performed using a Gilson system with a UV detector and a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 column (250 × 21.2 mm, 5 μm), a Phenomenex Kinetex Biphenyl column (250 × 21.2 mm, 5 μm), or a Hector column (250 × 21.2 mm, 5 μm). Concentrations of compounds 1–3 in the crude extract were deduced using Q-TOF-MS analysis (Agilent iFunnel 6550 quadrupole time of-flight MS instrument fitted with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source coupled to an Agilent 1290 Infinity HPLC system). Protonated ions of title compounds were extracted in the crude sample, and their areas under curves were plotted with respect to calibration curves with different concentrations of pure compounds 1–3 (Figure S44).
3.2. Insect Material
The larvae of A. dichotoma were collected from the National Academy of Agricultural Science, RDA, Korea and were identified by M-A. Kim (National Academy of Agricultural Science). A voucher specimen (CNU-INS201603) was deposited at the Laboratory of Pharmacognosy of the College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The dried larvae of the A. dichotoma (4.5 kg) were refluxed with 1% acetic acid in EtOH (35 L) for 16 h. The concentrated extract (672.0 g) was subjected to silica gel vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) and was eluted with n-hexane/EtOAc (10:0, 8:2, 6:4, 2:8) and CH2Cl2/MeOH (10:0, 8:2, 6:4, 2:8, 0:10) to yield 9 fractions (AD1 to AD9). AD7 (16.0 g) was fractionated by VLC over silica gel using a stepwise gradient elution (n-hexane/EtOAc/MeOH) to obtain 6 fractions (AD7-1 to AD7-6). Compound 8 (38.0 mg) was separated from fraction AD7-3 (1.3 g) using medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC) with a gradient solvent system MeOH/H2O (1:9 → 8:2). AD7-4 (5.7 g) was subjected to C18 MPLC using a gradient of MeOH/H2O (1:9 → 6:4; 5.5 L, 6:4 → 10:0; 1 L) to obtain 8 subfractions (AD7-4-1 to AD7-4-8). AD7-4-5 (288.7 mg) was purified by employing preparative HPLC with a gradient elution of MeOH/H2O (1:9 → 2:8; 10 min, 2:8 → 2:8; 20 min, 2:8 → 3:7; 25 min, 3:7 → 3:7; 60 min) to produce 6 (43.1 mg, tR = 38 min). Among the remaining fractions, AD9 (103.7 g) exhibited aromatic resonances (δH 6.5-8.0) in its 1H NMR spectrum. Therefore, AD9 was subjected to VLC on silica gel by gradient elution using EtOAc/MeOH (10:0, 8:2, 6:4, 4:6, 2:8, 0:10) as solvents to acquire 6 fractions (AD9-1 to AD9-6). AD9-3 (12.0 g) was divided into 8 subfractions (AD9-3-1 to AD9-3-8) by using C18 MPLC eluted with a gradient of MeOH/H2O (10:90 → 100:0). AD9-3-2 (494.0 mg) was further separated by using HPLC (MeOH/H2O, 10:90) to produce 5 (36.1 mg, tR = 19.8 min). Compound 7 (26.4 mg, tR = 36.2 min) was isolated from AD9-3-3 (584.2 mg) by employing HPLC elution with MeOH/H2O (5:95 → 10:90). AD9-3-4 (1.0 g) was separated by biphenyl column HPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90 → 30:70, 20 min; 30:90 → 30:90, 60 min) gradient eluted to give 11 subfractions (AD9-3-4-1 to AD9-3-4-11). Compound 4 (6.2 mg, tR = 38.9 min) was purified from AD9-3-4-8 (40.1 mg) by utilizing HPLC elution with an isocratic condition (MeOH/H2O, 2:8). AD9-3-6 (159.4 mg) was purified by reversed-phase preparative HPLC with a gradient elution of MeCN/H2O (2:8 → 4:6; 30 min, 4:6 → 5:5; 60 min, 9:1 → 9:1; 75 min) to produce 3 (2.0 mg, tR = 62.0 min), 2 (4.6 mg, tR = 64.5 min), and 1 (3.4 mg, tR = 68.2 min).
3.3.1. Allomyrinaine A (1)
Colorless oil; −44.0 (c 0.05, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 250 (2.94) nm; FT-IR (ATR) νmax 3320, 2942, 2831, 1449, 1115, 1021 cm–1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 284.1737 [M + Na]+, (calcd for C15H23N3ONa, 284.1739).
3.3.2. Allomyrinaine B (2)
Colorless oil; 14.4 (c 0.05, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 246 (2.64) nm; FT-IR (ATR) νmax 3320, 2942, 2831, 1449, 1114, 1021 cm–1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 262.1919 [M + H]+, 284.1740 [M + Na]+, (calcd for C15H24N3O, 262.1919, C15H23N3ONa, 284.1739).
3.3.3. Allomyrinaine C (3)
Colorless oil; −16.5 (c 0.04, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 247 (2.94) nm; FT-IR (ATR) νmax 3321, 2942, 2831, 1450, 1114, 1020 cm–1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 262.1915 [M + H]+, 284.1736 [M + Na]+, (calcd for C15H24N3O, 262.1919, C15H23N3ONa, 284.1739).
3.3.4. Allomyrinamide A (4)
Brown oil; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 280 (3.62) nm; FT-IR (ATR) νmax 3316, 2942, 2831, 1660, 1448, 1415, 1115, 1020 cm–1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δH 8.74 (1H, brs, 3-OH), 8.65 (1H, brs, 4-OH), 7.96 (1H, s, H-14), 7.90 (1H, m, NH-9), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 7.96 Hz, H-5), 6.56 (1H, d, J = 1.93 Hz, H-2), 6.42 (1H, dd, J = 1.93, 7.96 Hz, H-6), 3.26 (2H, q, J = 6.86 Hz, H-12), 3.17 (2H, q, J = 6.09 Hz, H-8), 2.51 (1H, m, H-7, overlapped), 2.23 (2H, t, J = 6.86 Hz, H-11); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δc 170.0 (C-10), 161.1 (C-14), 145.0 (C-3), 143.5 (C-4), 130.2 (C-1), 119.2 (C-6), 115.9 (C-2), 115.5 (C-5), 40.6 (C-8), 35.2 (C-11), 34.6 (C-7), 33.9 (C-12); HRESIMS m/z 253.1185 [M + H]+, 275.1003 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C12H17N2O4, 253.1188, C12H16N2O4Na, 275.1008).
3.4. Computational NMR Chemical Shift Calculations
Conformational searches were carried out using the MacroModel (Version 9.9, Schrödinger LLC, New York, NY, USA) program interfaced in Maestro (Version 11.8, Schrödinger LLC) with a mixed torsional/low-mode sampling method. Advanced conformational searches were performed in the MMFF force field, in the gas phase with a 50 kJ/mol energy window and 10,000 maximum iterations based on the original authors’ recommendations [13]. NMR chemical shift calculations of all conformers within 10 kJ/mol of the relative energy were implemented in the Gaussian 09 package (Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, USA) without geometry optimization in the B3LYP functional at the 6-31G(d,p) level. Chemical shift values were determined according to the equations. The calculated NMR properties were averaged according to the Boltzmann populations, and the conformers with more than 1% population were used for calculations of DP4+ probability analysis facilitated by the Excel sheet provided by Grimblat et al. [13,26].
3.5. Biological Activities
Detailed methods for the biological evaluation in this study are provided in Supplementary data.
4. Conclusions
The larvae of A. dichotoma have attracted attention in the development of food and medicinal materials because of various biological activities that include hepatoprotective [4], anticancer [4], antidementia [5], antiobesity [6], and antioxidant [7] activities. However, there are few chemical studies or bioactive constituents on this insect material. In this study, we have isolated three new tetrahydroquinolines (allomyrinaines A–C), one dopamine derivative (allomyrinamide A), and four known compounds [arbutin, cyclo(L-Val-L-Pro), inosine, 1,2-benzenediol] from the larvae of A. dichotoma. Their structures were elucidated by analyses of spectroscopic data, including 1D and 2D NMR and MS spectra. The stereogenic centers of allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) at C-2, C-3, and C-4 were determined by analyses of the coupling constants and the NOESY data, as well as DP4+ calculation. Recently, tetrahydroquinoline have been reported to have anti-inflammatory activity modulating inflammatory mediators [12,27]. We have investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of new compounds 1–4 in LPS-mediated human endothelial cells. Allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) inhibited LPS-mediated barrier disruption by increasing barrier integrity and inhibiting the expression of CAMs; compounds 1–3 also reduced neutrophils adhesion and migration toward HUVECs. These barrier protective effects of allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) were confirmed in a mouse model, in which treatment with compounds 1–3 resulted in the reduction of CLP-induced mortality and lung damage. This is the first report on the discovery of new tetrahydroquinolines (allomyrinaines A–C) and a dopamine derivative from A. dichotoma larvae. The biological effects of allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) on LPS-induced vascular inflammatory responses have been demonstrated, in which compounds 1–3 inhibit adhesion and the migration of leukocytes to an inflamed endothelium. In association with the protective effects of allomyrinaines A–C (1–3) on LPS-mediated vascular barrier disruption, intravenous administration of compounds 1–3 resulted in an increase in the survival rate from 40% to 60% (p < 0.0001; Figure 5A). Our findings suggest that allomyrinaines A–C are the bioactive constituents of A. dichotoma that are capable of modulating vascular inflammatory diseases, which may warrant the development of this edible insect as a functional food/supplementary resource.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI) in Daejeon, Korea, for supercomputing access.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/10/3406/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-S.B. and M.N.; Acquisition of data, I.P., W.L., Y.Y., H.S., J.O., H.K., M.-A.K., and J.S.H.; Interpretation of data, I.P., W.L., J.-S.B., and M.N.; writing—original draft preparation, I.P., W.L., J.-S.B., and M.N.; writing—review and editing, J.O., J.-S.B., and M.N.; Supervision, J.-S.B. and M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program (NRF-2020R1A2B5B01002415 and NRF-2020R1A2C1004131) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Huis A.V., Itterbeeck J.V., Klunder H., Mertens E., Halloran A., Muir G., Vantomme P. Edible Insects. Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security. Volume 171 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Song M.C., Yang H.J., Bang M.H., Kim Y.C., Kim S.Y., Rho Y.D., Chung S.H., Baek N.I. Isolation and quantitative analysis of inosine as an index component from larva of Allomirina dichotoma. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2006;49:334–338. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Youn K., Kim J.Y., Yeo H., Yun E.Y., Hwang J.S., Jun M. Fatty acid and volatile oil compositions of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012;17:310–314. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2012.17.4.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee J.E., Jo D.E., Lee A.J., Park H.K., Youn K., Yun E.Y., Hwang J.S., Jun M., Kang B.H. Hepatoprotective and anticancer activities of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae. J. Life Sci. 2015;25:307–316. doi: 10.5352/JLS.2015.25.3.307. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim M., Youn K., Yun E.-Y., Hwang J.S., Ahn M.R., Jeong W.S., Jun M. Effects of solvent fractions of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae through the inhibition of in vitro BACE1 and β-amyloid(25-35)-induced toxicity in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Entomol. Res. 2014;44:23–30. doi: 10.1111/1748-5967.12046. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim J., Yun E.Y., Park S.W., Goo T.-W., Seo M. Allomyrina dichotoma larvae regulate food intake and body weight in high fat diet-induced obese mice through mTOR and Mapk signaling pathways. Nutrients. 2016;8:100. doi: 10.3390/nu8020100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Suh H.J., Kim S.R., Lee K.S., Park S., Kang S.C. Antioxidant activity of various solvent extracts from Allomyrina dichotoma (Arthropoda: Insecta) larvae. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2010;99:67–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goldblum S.E., Brann T.W., Ding X., Pugin J., Tobias P.S. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein and soluble CD14 function as accessory molecules for LPS-induced changes in endothelial barrier function, in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1994;93:692–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI117022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Varani J., Ward P.A. Mechanisms of endothelial cell injury in acute inflammation. Shock. 1994;2:311–319. doi: 10.1097/00024382-199411000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aird W.C. Endothelium as a therapeutic target in sepsis. Curr. Drug Targets. 2007;8:501–507. doi: 10.2174/138945007780362782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Czermak B.J., Breckwoldt M., Ravage Z.B., Huber-Lang M., Schmal H., Bless N.M., Friedl H.P., Ward P.A. Mechanisms of enhanced lung injury during sepsis. Am. J. Pathol. 1999;154:1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65358-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lu X., Pu Y., Kong W., Tang X., Zhou J., Gou H., Song X., Zhou H., Gao N., Shen J. Antidesmone, a unique tetrahydroquinoline alkaloid, prevents acute lung injury via regulating MAPK and NF-κB activities. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017;45:34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tuan N.Q., Oh J., Park H.B., Ferreira D., Choe S., Lee J., Na M. A grayanotox-9(11)-ene derivative from Rhododendron brachycarpum and its structural assignment via a protocol combining NMR and DP4 plus application. Phytochemistry. 2017;133:45–50. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee W., Lee H., Kim M.A., Choi J., Kim K.M., Hwang J.S., Na M., Bae J.S. Evaluation of novel factor Xa inhibitors from Oxya chinensis sinuosa with anti-platelet aggregation activity. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:7934–7946. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08330-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Erenler R., Sen O., Aksit H., Demirtas I., Yaglioglu A.S., Elmastas M., Telci I. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from Origanum majorana and investigation of antiproliferative and antioxidant activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016;96:822–836. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee W., Kim M.A., Park I., Hwang J.S., Na M., Bae J.S. Novel direct factor Xa inhibitory compounds from Tenebrio molitor with anti-platelet aggregation activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017;109:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee J., Hwang I.H., Kim J.H., Kim M.A., Hwang J.S., Kim Y.H., Na M. Quinoxaline-, dopamine-, and amino acid-derived metabolites from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017;40:1064–1070. doi: 10.1007/s12272-017-0942-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Riedemann N.C., Guo R.-F., Ward P.A. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat. Med. 2003;9:517–524. doi: 10.1038/nm0503-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jonathan C. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002;420:885–891. doi: 10.1038/nature01326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bierhaus A., Chen J., Liliensiek B., Nawroth P.P. LPS and cytokine-activated endothelium. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2000;26:571–587. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-13214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee W., Park S.Y., Yoo Y., Kim S.Y., Kim J.E., Kim S.W., Seo Y.K., Park E.K., Kim I.S., Bae J.S. Macrophagic stabilin-1 restored disruption of vascular integrity caused by sepsis. Thromb. Haemost. 2018;118:1776–1789. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1669477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bae J.S. Role of high mobility group box 1 in inflammatory disease: Focus on sepsis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012;35:1511–1523. doi: 10.1007/s12272-012-0901-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tuan N.Q., Lee W., Oh J., Kwak S., Lee H.G., Ferreira D., Bae J.S., Na M. Quinic acid derivatives from Salicornia herbacea alleviate HMGB1-mediated endothelial dysfunction. J. Funct. Foods. 2015;15:326–338. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.03.044. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Walton K.L., Holt L., Sartor R.B. Lipopolysaccharide activates innate immune responses in murine intestinal myofibroblasts through multiple signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009;296:G601–G611. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00022.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Astiz M.E., Rackow E.C. Septic shock. Lancet. 1998;351:1501–1505. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)01134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Grimblat N., Zanardi M.M., Sarotti A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015;80:12526–12534. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bui B.P., Oh Y., Lee H., Cho J. Inhibition of inflammatory mediators and cell migration by 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline derivatives in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells via suppression of NF-κB and JNK pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106231–106241. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.