Abstract
BACKGROUND
Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide. There is a real need to develop treatment strategies for reducing neurological deficits in stroke survivors, and stem cell (SC) therapeutics appear to be a promising alternative for stroke therapy that can be used in combination with approved thrombolytic or thrombectomy approaches. However, the efficacy of SC therapy depends on the SC homing ability and engraftment into the injury site over a long period of time. Nonetheless, tracking SCs from their niche to the target tissues is a complex process.
AIM
To evaluate SC migration homing, tracking and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of stroke using nanoparticles
METHODS
A systematic literature search was performed to identify articles published prior to November 2019 that were indexed in PubMed and Scopus. The following inclusion criteria were used: (1) Studies that used in vivo models of stroke or ischemic brain lesions; (2) Studies of SCs labeled with some type of contrast agent for cell migration detection; and (3) Studies that involved in vivo cellular homing and tracking analysis.
RESULTS
A total of 82 articles were identified by indexing in Scopus and PubMed. After the inclusion criteria were applied, 35 studies were selected, and the articles were assessed for eligibility; ultimately, only 25 studies were included. Most of the selected studies used SCs from human and mouse bone marrow labeled with magnetic nanoparticles alone or combined with fluorophore dyes. These cells were administered in the stroke model (to treat middle cerebral artery occlusion in 74% of studies and for photothrombotic induction in 26% of studies). Fifty-three percent of studies used xenogeneic grafts for cell therapy, and the migration homing and tracking evaluation was performed by magnetic resonance imaging as well as other techniques, such as near-infrared fluorescence imaging (12%) or bioluminescence assays (12%).
CONCLUSION
Our systematic review provided an up-to-date evaluation of SC migration homing and the efficacy of cellular therapy for stroke treatment in terms of functional and structural improvements in the late stage.
Keywords: Stem cell, Nanoparticles, Homing, Tracking, Near-infrared fluorescence image, Cellular therapy, Magnetic resonance image, Bioluminescence, Stroke
Core tip: The systematic review provided an up-to-date evaluation of stem cell (SC) migration homing, using nanoparticles based on the technical and scientific aspects and combined molecular images. Thus, the efficacy of SC therapy depends on the SC homing ability and engraftment into the injury site over a long period of time, providing functional and structural outcomes in preclinical studies, but limited evidence of outcomes in clinical studies.
INTRODUCTION
Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Because of the increase in life expectancy and population growth, the total number of stroke cases was 104.2 million (UI 98.5-110.1) with considerably increased 3.1% worldwide in the last two decades. Furthermore, stroke patients may suffer from disabilities or incapacities requiring temporary or lifelong assistance, resulting in a substantial economic burden for poststroke care[1,2].
Thus, there is a real need to develop alternative treatment strategies for decreasing neurological deficits, and stem cell (SC) therapeutics appear to be an emerging paradigm in stroke therapy that represents a promising alternative for intervention[3,4].
SCs have the remarkable capability to differentiate into any cell of an organism while retaining the ability to self-replicate and keep the characteristics of their parental cells[5]. Preclinical research has already demonstrated the survival, functional integration, and behavioral effects of SC therapy in experimental stroke models[6-10], which provides a wide scientific basis for beginning small clinical trials of SC therapy in stroke patients. However, efforts to test the safety and efficacy of SCs and their derivatives [primarily mesenchymal SCs (MSCs) and mononuclear cells], not just as a stand-alone therapy but preferably in association with approved thrombolytic treatments or thrombectomy, may further increase the likelihood of the successful translation of SC therapy for stroke treatment clinical applications[11-16].
The efficacy of SC therapy depends on the SC homing ability and engraftment into the injury site over a long period of time, and tracking cells from their niche to the target tissues is a complex process[17,18]. The delivery process is affected by both chemical factors (such as chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors) and mechanical factors (for instance hemodynamic forces applied to the vessel walls in the form of shear stress, vascular cyclic stretching, and extracellular matrix stiffness)[18]. Nevertheless, the monitoring of transplanted SC migration in vivo is usually achieved by labeling cells with a contrast agent and then scanning them in vivo through using molecular imaging[18].
Among the noninvasive molecular imaging modalities used for cell migration analysis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) imaging, and bioluminescence imaging (BLI) show specific characteristics with strengths and weaknesses of each imaging modalities regarding their technical peculiarities, tracking evaluation, translational stage, suitability to monitor SC transplantation[19-24], as shown in Table 1. MRI has a high spatial resolution between 0.02-0.1 mm and a temporal resolution on the order of minutes to hours. The advantages of MRI include a lack of a tissue penetration limit and the fact that it does not use radiation, but the disadvantages include the relatively low sensitivity, low contrast, high cost and long scanning time. As an alternative to improve sensitivity in the CTM traceability process, magnetic nanoparticles (such as magnetite and maghemite) are used, which exhibit biocompatibility, biodegradability, surface-to-volume ratio, and greater surface area. In addition, when its surface is modified with polymeric stabilizers and inorganic molecules (for example, silica, gold, gadolinium, fluorescent dyes) it not only increases sensitivity but also its specificity[25,26]. PET has a low spatial resolution between 1-2 mm and a temporal resolution on the order of seconds to minutes. The advantages include high sensitivity, excellent penetration depth, capability for whole-body imaging, while the disadvantages include the high cost of the cyclotron that is needed and radiation exposure. The SPECT spatial resolution is similar to that of PET, but the temporal resolution is on the order of minutes; the advantages include a high sensitivity and the lack of a tissue penetrating limit or a need for a cyclotron, and the disadvantages are due to radiation exposure and difficulties in quantifying the results. NIRF imaging and BLI have a low spatial resolution between 2-3 mm and 3-5 mm, respectively. The temporal resolution of both techniques is on the order of seconds to minutes; the advantages of NIRF imaging and BLI include high sensitivity, the lack of radiation exposure, low cost, and the fact that they are activatable. In addition, BLI has the advantages of simple equipment operation and non-damaging imaging; the disadvantages of both optical imaging techniques are the attenuation of sensitivity by overlying tissues and poor penetration depth. In addition, molecular imaging modalities shows a wide potentiality not only for in vitro studies and pre-clinical applications but also in the translation of some techniques in clinical studies, such as nuclear images (PET and SPECT) and MRI[19-24].
Table 1.
Molecular imaging modalities
| Image type | Technique | Physical principle | Tracrer | In vitro imaging | Preclincal imaging | Clinical Imaging | Spatial Resolution | Temporal resolution | Penetration depth | Sensitivity | Strengths | Limitations |
| Optical imaging | BLI | Visible light | Luminescent proteins | Yes | Yes | No | 3-5 mm | Seconds to minutes | 1-2 cm | High (+++) | High sensitivity, non-radioactive, cell expansion | Low penetration depth, non-translational |
| FLI | Visible or NIRF light | Proteins or fluorescent dyes | Yes | Yes | No | 2-3 mm | Seconds to minutes | < 1 cm | High (++) | High sensitivity, non-radioactive | Low penetration depth, autofluorescence | |
| Nuclear imaging | PET | High-energy γ-rays | Radioisotopes [89 Zr (78.4 h), 18 F (1.83 h), 11 C (0.34 h), 64 Cu (12.7 h), 68 GA (1.13 h)] | No | Yes | Yes | 1-2 mm | Seconds to minutes | Limitless | High (++) | High penetration depth, high sensitivity | Radiation exposure, high cost |
| SPECT | Low-energy γ-rays | Radioisotopes [99 mTc (6.03 h), 123 I (13.2 h), 111 In (67.4 h)] | No | Yes | Yes | 1-2 mm | Minutes | Limitless | High (++) | High penetration depth, high sensitivity | Radiation exposure, high cost | |
| Magnetic imaging | MRI | Radio waves | Contrast agents | No | Yes | Yes | 0.02-0.1 mm | Minutes to hours | Limitless | Low | High penetration depth, non-radioactive, high spatial resolution | High cost, low sensitivity and contrast |
PET: Positron emission tomography; SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography; BLI: Bioluminescence; FLI: Fluorescence; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; NIRF: Near-infrared fluorescence.
However, technological advances have led to the development of hybrid equipment that allows the use of different imaging modalities at the same time as well as the development of multifunctional probes that can be detected by different molecular imaging modalities, thus providing more information and the complementary evaluation of SC migration homing and tracking after implantation[20-22,25,26]. In addition, other techniques, such as BLI, that require the genetic modification of cells to express the signal, such as the luciferase enzyme signal, allow the evaluation of not only migration but also cellular viability after implantation[27-31].
Therefore, through a systematic review, the present study discusses studies of homing SC migration, tracking and therapy efficacy for stroke treatment using nanoparticles based on the technical and scientific aspects of (1) The characteristics of the SCs used in cell therapy; (2) The characteristics of the contrast agents used; (3) The processes of labeling SCs with nanoparticle-based contrast agents; (4) Preclinical models of stroke induction; and (5) Strategies for the administration of nanoparticle-labeled SCs and their use for studies of their subsequent homing, tracking and therapeutic efficacy for future clinical approaches.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Search strategy
We searched publications published prior to November 2019 indexed in PubMed and Scopus. All procedures were performed according to the PRISMA guidelines[32]. The following selected criteria of interest, boolean operators (DecS/MeSH), and keyword sequences were used: (1) PubMed: (((((((“Cellular Therapy”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Stem cell”[Title/Abstract]) OR “stem cells”[Title/Abstract])) AND ((nanoparticle) OR nanoparticles)) AND (((“cerebral ischemia”[Title/Abstract]) OR “ischemic cerebrovascular accident”[Title/Abstract]) OR stroke[Title/Abstract]))) AND ((Homing) OR tracking); and (2) Scopus: ((TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Stem cell”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Cellular Therapy”))) AND ((TITLE-ABS-KEY (nanoparticle) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (nanoparticles))) AND ((TITLE-ABS-KEY (“cerebral ischemia”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“ischemic cerebrovascular accident”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (stroke))) AND ((TITLE-ABS-KEY (homing) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (tracking))) AND (LIMIT-TO(DOCTYPE, “ar”)) and (LIMIT-TO(LANGUAGE, “English”)).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Only original articles written in the English language were considered for inclusion. The following inclusion criteria were used: (1) Studies that used in vivo models of stroke or ischemic brain lesions; (2) Studies that used SCs labeled with some type of contrast agent for cell migration detection; and (3) Studies that involved in vivo cellular homing and tracking analysis. Articles that were indexed in more than one database (duplicates), incomplete articles, abstracts, reviews, letters, communications, conference presentations, book chapters, editorials and expert opinions, as well as studies involving ex vivo analyses of cellular homing, were excluded.
Data compilation and review
In this review, five of the authors (Nucci MP, Filgueiras IS, Ferreira JM, Oliveira FA, Mamani JB, Rego GNA and Gamarra LF) (in pairs) independently and randomly selected data using the search strategy cited and verified the eligibility of the references. Discrepancies in study selection and data extraction between the two reviewers were discussed with a third reviewer and resolved. The reviewed papers were divided into four categories that addressed the following topics: (1) The characteristics of the nanoparticles used in the experiments and their interactions with cells (Nucci MP, Filgueiras IS, Rego GNA and Mamani JB); (2) The characteristics of cells (type/source) and route of administration (Nucci MP, Filgueiras IS and Ferreira JM); (3) Stroke models (Nucci MP, Ferreira JM and Oliveira FA); and (4) The imaging techniques used for the evaluation of cell homing and tracking (Nucci MP, Oliveira FA and Gamarra LF).
Data analysis
All results were described and presented using the percentage distribution for all variables analyzed in the tables.
RESULTS
Overview of the reviewed literature
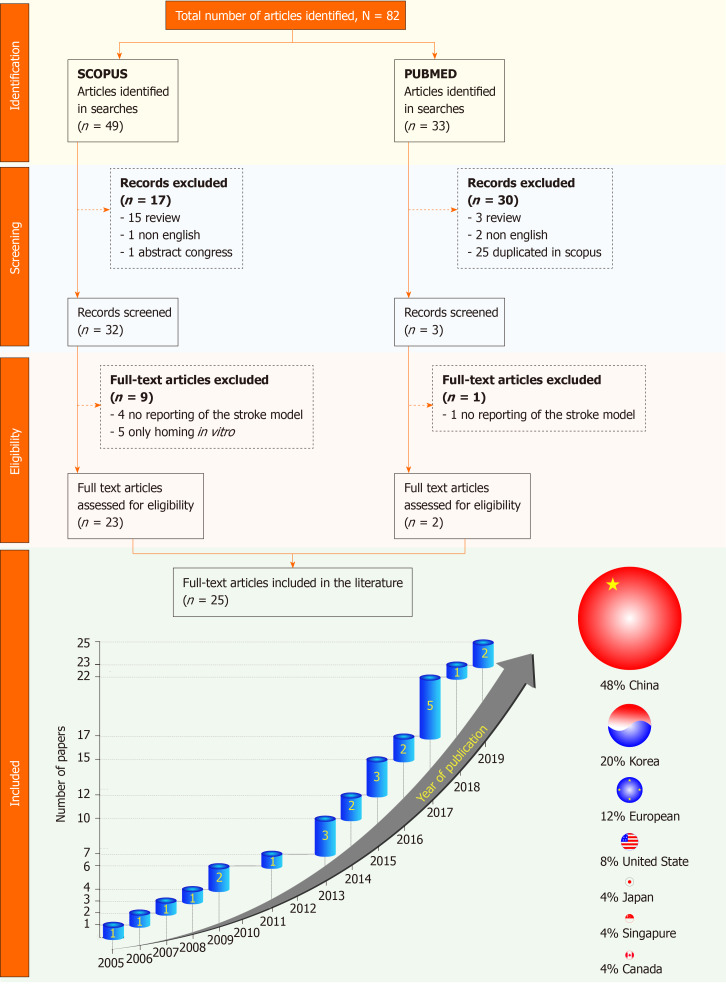
A total of 82 articles were identified by indexing in Scopus and PubMed. After the inclusion criteria were applied, 35 studies were selected, the articles were assessed for eligibility, and only 25 studies were included[28-30,33-54] (Figure 1). Of these, 22 articles (88%) had been published within the past 15 years (2009 to 2019). Most of the studies (76%) were conducted in Asia, mainly in China (48% of all articles), followed by South Korea (20% of all articles), the United States (8%), Canada (4%), and European countries (12%) (Table 2, Figure 1).
Figure 1.
The PRISMA flow diagram provides more detailed information regarding the process of study selection. After the inclusion of studies, the first analysis focused on the publication year distribution; the graphic shows the number of studies per year and the distribution of the studies by the country in which the research was conducted.
Table 2.
Characteristics of the studies and the stem cells used
| Ref. | Yr | Country | Cell type | Source of cells | Medium culture - %FBS |
| Lim et al[33] | 2019 | South Korea | MSC | Human (adipose tissue) | DMEM - 10%FBS |
| Wang et al[29] | 2019 | China | MSC | Human (umbilical cord) | EBM-2 - 0%FBS |
| Yun et al[30] | 2018 | South Korea | NSC | Human (telencephalon) | NR |
| Argibay et al[38] | 2017 | Spain | MSC | Rat (bone marrow) | IMDM - 10%FBS |
| Duan et al[37] | 2017 | China | MSC | Rat (bone marrow) | DMEM - 10%FBS |
| Lu et al[35] | 2017 | China | NPC-Imm | Mice (C17.2) | DMEM - 10%FBS |
| Zhang et al[34] | 2017 | China | NSC | Rat (lateral ventricles) | StemPro NSC - 0%FBS |
| Lin et al[36] | 2017 | China | MSC | Rat (bone marrow) | DMEM -10%FBS |
| Zhang et al[39] | 2016 | China | NSC | Human (bone marrow) | NR |
| Duan et al[40] | 2016 | China | MSC | Rat (bone marrow) | DMEM - 10%FBS |
| Bai et al[42] | 2015 | China | MSC | Mice (bone marrow) | EBM-2 |
| Chen et al[28] | 2015 | China | MSC | Human (umbilical cord) | DMEM-HG |
| Tan et al[41] | 2015 | Japan | MSC | Rat(bone marrow) | DMEM - 10%FBS, |
| Janowski et al[44] | 2014 | Poland | NSC | Human (umbilical cord) | DMEM-F12 - 2%FBS |
| Park et al[43] | 2014 | South Korea | MSC | Rat | DMEM - 0%FBS |
| Zhang et al[45] | 2013 | China | NPC-Imm | Mice (neonatal cerebellum) | DMEM - 10%FBS |
| Tarulli et al[46] | 2013 | Canada | MSC | Rat (bone marrow) | αMEM - 20%FBS |
| Liu et al[47] | 2013 | China | NSC | Rat (neonate) | DMEM-F12 |
| Wang et al[48] | 2011 | China | MSC | Mice (bone marrow) | DMEM |
| Lee et al[50] | 2009 | Singapore | MSC | Human (fetal bone marrow) | DMEM - 10%FBS |
| Song et al[49] | 2009 | South Korea | NPC-Imm | Human (HB1.F3) | DMEM - 5%FBS |
| Kim et al[51] | 2008 | South Korea | MSC | Human | DMEM - 0%FBS |
| Guzman et al[52] | 2007 | United States | NSC | Human | HNCM |
| Syková et al[53] | 2006 | Czech Republic | MSC, rOEC | Mice; Human; Rat | NR |
| Zhu et al[54] | 2005 | United States | NSC | Human | NR |
MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; NSC: Neural stem cells; NPC-Imm: Neural progenitor cell - immortalised; ESC: Embryonic stem cell; rOEC: Rat olfactory ensheathing cells; C17.2: An immortalised mouse neural progenitor cell line; HB1.F3: An immortalized, clonal human NSC line; DMEM: Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium; DMEM-HG: Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium high glucose; DMEM-F12: 50:50 mixture of DMEM and Ham's F12 medium; αMEM: Minimum essential medium Eagle: Alpha modification; EBM-2: Endothelial cell growth basal medium; IMDM: Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; StemPro NSC: Human neural stem cell culture medium; HNCN: Human neurosphere culture medium; NR: No reported.
SC characteristics
The main characteristics of the SCs used in the studies (cell type, source and culture medium) are shown in Table 2. Regarding the type of SC, eleven[28-30,33,39,44,49-52,54,55] (44%) studies used SCs sourced from humans, nine[34,36-38,40,41,43,46,47,56] (36%) used SCs from rats (SCs from humans and rats were used most often), and only five[35,42,45,48,53] (20%) studies used SCs from mice. In terms of the cell source, ten[36-42,46,48,50] (40%) studies used SCs from bone marrow, four[30,34,45,47] (16%) studies used SCs from neonatal brain, three[28,29,44] (12%) studies used SCs from umbilical cord, the study by Lim et al[33] used SCs from adipose tissue, and three[35,45,49] (12%) studies used brain immortal lineage cells. Most of the studies [fifteen of 25 (60%)] used Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with fetal bovine serum during SC culture prior to cell application; two[29,42] (8%) studies used endothelial cell growth basal medium, the study by Argibay et al[38] used Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium, and the study by Zhang et al[57] used StemPro NSCs. The major source of SCs is the bone marrow of rodents (rats and mice), followed by human neonatal brain, which is also widely used.
Contrast agent characteristics used in the SC labeling, homing and tracking analysis
Consecutively, the SCs were submitted to the labeling process with contrast agents for the evaluation of the SC homing and tracking process and the contrast agent physical-chemical properties were described in Table 3. In all studies, magnetic nanoparticles were used as the main contrast agent. Most studies (64%) used synthesized magnetic nanoparticles for the labeling process, and the other 7 (28%) studies used commercial nanoparticles and reported the companies supplying these nanoparticles as Feridex® (or Endorem®) by Advanced Magnetic, United States[49,51,52,54], and Guerbet, France[53]; the study by Janowski et al[44] used ferrite by BioPAL Inc., United States, and the study by Tan et al[41] used Resovist® by Fujifilm RI Pharma Co., Japan. In terms of the physical-chemical characteristics of the contrast agents, the concentration range was between 0.12 mg/mL[40] and 27.9 mg/mL[41], and the concentration of the contrast agent most commonly used was 11.2 mg/mL[49,51-54]. The nanoparticles had core sizes between 3.7 nm[38] and 30 nm[34,39] and hydrodynamic sizes ranging from 10.8 nm[40] to 900 nm[46]. In regard to the analysis of the process of cell labeling, the majority of studies have used nanoparticles coated with dextran[30,38,39,44,49,51-54]; the studies by Zhang et al[45], Wang et al[48] and Chen et al[28] used silica for coating, the study by Lim et al[33] used chitosan, the study by Duan et al[37,40] used poly(D, L-lactide), and the study by Tarulli et al[46] used divinyl benzene polymer. The zeta potential varied between -38 mV[39] and +32.8 mV[40]; eight studies[29,38,39,43,51-54,57] used nanoparticles with a negative zeta potential, and eight studies[29,33,35-37,40,43,44] used nanoparticles with a positive zeta potential. Of the studies, four[29,42-44] used rhodamine as the conjugated agent, the studies by Bai et al[42] and Lim et al[33] used Cy5.5, the study by Lu et al[35] used Nile red, the study by Zhang et al[45] used fluorescein isothiocyanate and the study by Tarulli et al[46] used Dragon green fluorophore. In the studies reporting R2 values, the nanoparticles exhibited the characteristics of a negative contrast agent, with R2 values ranging from 75.8 mmol-1s-1 (lower contrast power by T2) to 701 mmol-1s-1 (high contrast by T2).
Table 3.
Characteristics of the contrast agents used in the stem cell labeling, homing and tracking analysis by molecular imaging modalities
| Ref. | Contrast agent | Concentration (mg/mL) | Core/Hydrodynamic size (nm) | Coating agent | Zeta Potential (mV) | Conjugated agent (Ex/Em: nm) | Image detection mode | R1/R2 (mmol-1. Sec-1) | Developer |
| Lim et al[33] | NP (BCN-Fe3O4) | NR | 20/238.9 | BCN, chitosan | +12.6 | Cy5.5 (675/695) | Dual (Mgt, NIRF) | NR/526.1 | Synthesized |
| Wang et al[29] | Alkyl-SPIO | NR | NR/80-120 | Alkyl-PEI | Approximately +21.0 | NA | Dual (Mgt, BLI) | NR/549.7 | Synthesized |
| Yun et al[30] | Zn0.4Fe2.6O4 (ZnMNP)12 | NR | NR | Dextran | NR | NA | Dual (Mgt, BLI) | NR | Synthesized |
| Argibay et al[38] | Fe3O41 | NR | 3.7/94 | Dextran | -11.0 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR/701 | Synthesized |
| Duan et al[37] | Fe3O4-LCP | 0.12 | 6/136 | PDLLA | +18.0 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR/500.2 | Synthesized |
| Lu et al[35] | PAsp(DMA)-Lys-CA2 (C-NP)2 | NR | NR/64.1 | NR | +15.32 | Nile red (552/636) | Dual (Mgt, VFL) | NR/460.5 | Synthesized |
| PEG-Lys-CA2 (N-NP)2 | NR/69.4 | +0.10 | NR/462.9 | ||||||
| Zhang et al[34] | Ferritin2 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Dual (Mgt, NIRF) | NR | Synthesized |
| Lin et al[36] | SPION | 0.25 | NR/128 | ASP | +21.6 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR/296 | Synthesized |
| Zhang et al[39] | SPION | NR | 30/50 | Dextran | NR | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR/300 | Synthesized |
| Duan et al[40] | Fe3O4-LCP2 | 0.12 | 6/136 | PDLLA | +18.0 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR/500.2 | Synthesized |
| Fe3O42 | 1.00 | 6/10.8 | PLL | +32.8 | NR/457.2 | ||||
| Bai et al[42] | bCD-Gd | NR | NA/24.4 | NA | NR | Cy5.5 (675/695) Rhod (565/620) | Tri (Mgt, NIRF, VFL) | 8.6/NR | Synthesized |
| Chen et al[28] | GRMNB1 | NR | NA/130 | Silica | NR | NA | Dual (Mgt, BLI) | 1.21/127.89 | Synthesized |
| Tan et al[41] | γ-Fe2O3 (ferucarbotran) | 27.90 | 4/60 | Carboxydextran | NR | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR | Resovist®, Fujifilm RI Pharma Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Janowski et al[44] | Fe3O4 | 2.00 | 8/35 | Dextran | +31.0 | Rhod (565/620) | Dual (Mgt, VFL) | 30.4/75.8 | BioPAL Inc, Worcester, MA, USA |
| Park et al[43] | PCION | NR | 11/371.6 | PEG | +28.6 | Rhod (565/620) | Dual (Mgt, VFL) | NR | Synthesized |
| Zhang et al[45] | fmSiO4@SPIONs | NR | 30/151 30/148 | Silica | -22.5 | FITC (490/525) | Dual (Mgt, VFL) | NR/309.53 | Synthesized |
| NR/231.74 | |||||||||
| fdSiO4@SPIONs | -38.0 | ||||||||
| Tarulli et al[46] | Fe3O4 (MPIO) | NR | NR/900 | DBP | < 0 | DGF (480/520) | Dual (Mgt, VFL) | NR | NR |
| Liu et al[47] | SPION | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | Mono (Mgt) | NR | NR |
| Wang et al[48] | Fe3O4 (PMNC) | NR | 8/120 | Silica | -38.0 | Rhod (565/620) | Dual (Mgt, VFL) | 3.81/435 | Synthesized |
| Lee et al[50] | MGIO | NR | 5/602 | PMG | NR | NA | Mono (Mgt) | NR | Synthesized |
| Song et al[49] | FeO1.44 (Feridex) | 11.20 | 5-6/50-180 | Dextran | -12.0 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | 23.9/98.3 | Advanced Magnetic, Cambridge, MA, United States |
| Kim et al[51] | FeO1.44 (Feridex) | 11.2 | 5-6/50-180 | Dextran | -12 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | 23.9/98.3 | Advanced Magnetic, Cambridge, MA, United States |
| Guzman et al[52] | FeO1.44 (Feridex) | 11.2 | 5-6/50-180 | Dextran | -12 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | 23.9/98.3 | Berlex Laboratories, Wayne, NJ, United States |
| Syková et al[53] | Fe3O4 (Endorem) | 15.8 | 4.3-5.6/150 | Dextran | -12 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | 40/160 | Guerbet, Roissy, France |
| Zhu et al[54] | FeO1.44 (Feridex) | 11.2 | 5-6/50-180 | Dextran | -12 | NA | Mono (Mgt) | 23.9/98.3 | Advanced Magnetic, Cambridge, MA, United States |
transduced with the luciferase protein (Vector Type - Lentiviral FUGW-Luc2).
transduced with the GFP protein (Vector type - eGPF/FTH). Ex/Em: Excitation/Emission; NP: Nanoparticle; BCN: Bicyclo[6.1.0]nonyne; Fe3O4: Iron oxide; SPIO: Superparamagnetic iron oxide; LCP: Loaded cationic polymersomes; ZnMNP: Zinc-doped ferrite magnetic nanoparticle; PAsp(DMA): Poly(aspartic acid-dimethylethanediamine); Lys-CA: Lysine-cholic acid; C-NP: Cationic nanoparticle; PEG: Polyethylene glycol; N-NP: Neutral nanoparticle; SPION: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; bCD-Gd: Bacterial cytosine deaminase-gadolinium; GRMNBs: Gold nanorods crystal-seeded magnetic mesoporous silica nanobeads; PCION: Poly-(ethylene glycol)-coated cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles; fmSiO4@SPIONs: Fluorescent mesoporous silica-coated SPIONs; fdSiO4@SPIONs: Fluorescent dense silica-coated SPIONs; PMNC: Polystyrene magnetite nanocluster; MGIO: Microgel iron oxide; MPIO: Micron-sized superparamagnetic iron oxide particles; NR: Not reported; NA: Not applicable; Alkyl-PEI: Amphiphilic low molecular weight polyethylenimine; PDLLA: Poly(D,L-lactide); PEI: Polyetherimide; ASP: Spermine-modified amylose; PLL: Poly-L-lysine; DBP: Divinyl benzene polymer; PMG: Precursor microgel; Cy5.5: Cyanine5.5; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; Rhod: Rhodamine B; pDNA: Plasmid DNA; FTH: Ferritin heavy chain; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; DGF: Dragon green fluorophore; Mgt: Magnetic; NIRF: Near infrared fluorescence; BLI: Bioluminescence imaging; VFL: Visible field fluorescence.
The characteristics of the contrast agents allowed the detection of cells during homing by MRI in all studies, but 11 of the studies also used another agent contrast conjugated to iron oxide, allowing the bimodal detection of SCs; six (24%) studies[35,43-46,48] used visible field fluorescence, three (12%) studies[28-30] used BLI, three (12%) studies[33,34,42] used NIRF imaging and only one study[28] used photoacoustic imaging. Only one study[42] reported trimodal image detection using MRI, visible field fluorescence and NIRF technical assessments.
SC labeling process with the contrast agent
The cell labeling process is an important step where we have to balance two important aspects, high internalization of contrast agents so that it has good detection sensitivity by molecular imaging techniques, but at the same time high cell viability after labeling, so it is necessary, the use of an adequate concentration of contrast agents, for a sufficient incubation time and choice of strategies that increase the internalization efficiency without causing damage to the cell.
By using the SC labeling process with SPION (Table 4), 32% of the selected studies showed that the cells used were from between passage 0 and 17[38], with the majority studies[33,36,40,50] using cells from the fifth passage. As described in the previous paragraph, magnetic nanoparticles were used as contrast agents for all studies, and 5 studies[49,51-54] used Feridex® (or Endorem®), a commercial nanoparticle manufactured by Advanced Magnetic, USA. In most studies[28-30,33-40,42,43,49,50], the iron oxide nanoparticles used were synthetized in-house by the labs. The concentration of contrast agent used during SC labeling ranged between 0.5[45] and 300 μg/mL[33], and the majority of studies (60%) used a concentration between 5 and 33 μg/mL. An incubation time of 24 h for the labeling process was the most frequent (36%) amount of time reported by the studies[38-42,46,47,50,52] and ranged between 0.5[45] and 72 h[49,53]. The main reagent used to induce internalization in 32% of the selected studies was poly L-lysine, which was combined with lipofectamine in the Lu study[35] and with an external magnetic field in the Park et al[43]’s study. Other studies[29,37,40] used poly-etherimide and protamine sulfate[51,52], and the Lim et al[33]’s study used tetraacetylated N-azidoacetyl-D-mannosamine. In fifteen of the 25 selected studies (60%), the efficiency of cell labeling was greater than 95%[28,29,33,35-38,41,46,48-50,52,54]; five of these studies used the ICP technique to quantify the iron load internalized into the cells[33,38,45,48,50,51], and five other studies[28,34,36,37,40,49] used the AAS technique for quantification, while the Guzman et al[52]’s study used semiquantitative analysis by MRI. The range for SPION quantification was between 0.2 pgFe/cell[49] and 33.3 pgFe/cell[50], and 40% of the selected studies did not mention this information. In terms of cellular viability analysis after the labeling process, 56% of studies reported this analysis, of which 36% of studies[29,33-37,40,45,48] used the CCK-8 assay to reveal that more than 90% of cells were viable; the other 10% of studies used different techniques for the cellular viability analysis, such as LDH assays[38], MTT assays[28], flow cytometry[46], and cell counting[52], and these studies also reported high cellular viability. Other in vitro analyses of the labeling process were used in the selected studies, such as confocal imaging[33,46], MRI[29,33-37,40,43,48,49], BLI[28-30], electron microscopy[29,30,34,36-38,40,43,48,50,53] and microarrays[50].
Table 4.
Stem cell labeling process
| Ref. | Cells | Passage | Contrast agent | Concen-tration μg/mL) | Incu-bation time (h) | Strategy of interna-lization | Effici-ency |
Quantification |
Cellular viability |
Others analysis | |||
| (pgFe/cell) | Technique | Method | Results | ||||||||||
| Lim et al[33] | MSC | P5-P7 | NP(BCN-Fe3O4) | 300 | 2 | Ac4ManNAz | 98.7% | 15.3 | ICP-MS | CCK-8 assay | > 95% | CF, SEM, CEM, MRI | |
| Wang et al[29] | MSC | P2-P7 | Alkyl-SPIO | an appropriate amount of Alkyl-PEI/SPIO (N/P = 20) | 6 | PEI | High Eff. | NA | NA | CCK-8 assay | > 90% | BLI, MRI | |
| Yun et al[30] | NSC | NR | ZnMNP | 50 | NR | PLL: 1.5 g/mL | NR | 4.6 | NR | NA | NA | TEM, BLI | |
| Argibay et al[38] | MSC | P0-P2, P9, P17 | Fe3O4 | 100 | 24 | PLL: 1.5 μg/mL | High Eff. | 0.9-7.7 | ICP-OES | LDH assay | NSD | TEM | |
| Duan et al[37] | MSC | P3-P5 | Fe3O4-LCP | 15 | 1.5 | PEI | Approximately 100% | Approximately 9 | AAS | CCK-8 assay | > 90% | TEM, MRI | |
| Lu et al[35] | NPC | NR | C-NP | 10 | 4 | PLL and Lipofectamin | Approximately 99.3% | NA | NA | CCK-8 assay | > 95% | MRI, VFL | |
| N-NP | Approximately 8.7% | ||||||||||||
| Zhang et al[34] | NSC | P2-P3 | Ferritin | MOI: 10 | 24 | PLL | Approximately 63% | 3.5 | AAS | CCK-8 assay | NSD | TEM, MRI, PB | |
| Lin et al[36] | MSC | P5-P9 | ASP-SPION | 30 | 1 | NA | Approximately 100% | 2.68 | AAS | CCK-8 assay | > 90% | MRI, TEM | |
| Zhang et al[39] | NSC | NR | Anti-CD15-SPION | NR | NR | NA | NR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Duan et al[40] | MSC | P3-P5 | Fe3O4-LCP | 15 | 1.5 | PEI | LCP > PLL | 8.373 | AAS | CCK-8 assay | > 90% | TEM, in vitro MRI | |
| Fe3O4 | 25 | 24 | PLL | 9.214 | |||||||||
| Bai et al[42] | MSC | NR | bCD-Gd | 2 μmol | 24 | PLL | NR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Chen et al[28] | MSC | NR | GRMNB | 10 | 2 | NR | High Eff. | 33.62 | AAS | MTT | 87.6 | BLI | |
| Tan et al[41] | MSC | NR | Ferucarbotran | NR | 24 | NA | Approximately 95% | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Janowski et al[44] | NSC | NR | Fe3O4 | 25 | 48 | PLL: 375 ng/mL | NR | NA | NA | NI | NI | NA | |
| Park et al[43] | MSC | NR | PCION | 1 | 0.25 | PLL, EMF | NR | NA | NA | NA | NA | TEM, MRI | |
| Zhang et al[45] | NPC | NA | fmNP | 5, 10, 20, 33 | 0.5, 1, 2, 3 | NA | fmNP > fdNP | 5-30 | ICP-AES | CCK-8 assay | 90%-98% | TB | |
| fdNP | 1-2.5 | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||
| Tarulli et al[46] | MSC | NR | MPIO | 18.8 | 24 | NA | 95% | 54 | Flow cytometry | Flow cytometry | Approximately 94% | CF | |
| Liu et al[47] | NSC | NR | SPION | 14 | 24 | NA | NR | NR | NR | NI | NI | NA | |
| Wang et al[48] | MSC | NR | PMNC | 0.5 mmol | 1 | NA | Approximately 100% | 16-20 | ICP-OES | CCK-8 assay | > 95% | TEM, CF, MRI | |
| Lee et al[50] | MSC | P5, P6 | MGIO | 50 | 24 | NA | Approximately 97% | 33.3 | ICP-OES | NI | > 95% | TEM, microarray | |
| Song et al[49] | NPC | NR | Feridex | 112.4 | 72 | NA | Approximately 100% | 0.2 | AAS | TB | Unaffected | MRI | |
| Kim et al[51] | MSC | NR | Feridex | 1 | 12-16 | PS | NR | 2.6 | ICP/MS | NI | NI | NA | |
| Guzman et al[52] | NSC | NR | Feridex | 5 | 24 | PS: 2.5 μg/mL | 98% | Halved every 3 d (%) | Semiquantitative (MRI) | Cell counting | Approximately 92% | NA | |
| Syková et al[53] | MSC, rOEC | NR | Endorem | 112.4 | 48-72 | NA | NR | NA | NA | NA | NA | TEM | |
| Zhu et al[54] | NSC | NR | Feridex | NR | 1 | Effectene | High Eff. | NA | NA | NR | NI | NA | |
MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; NSC: Neural stem cells; ESC: Embryonic stem cell; rOEC: Rat olfactory ensheathing cells; P: Passage; NR: No reported; NA: Not applicable; NP: Nanoparticle; BCN: Bicyclo[6.1.0]nonyne; Fe3O4: Magnetite; SPIO: Superparamagnetic iron oxide; ZnMNPs: Zinc-doped ferrite magnetic nanoparticles; LCP: Loaded cationic polymersomes; C-NP: Cationic nanoparticle; N-NP: Neutral nanoparticle; ASP: Spermine-modified amylose; SPION: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle; bCD-Gd: Bacterial cytosine deaminase-gadolinium; GRMNB: Gold nanorods crystal-seeded magnetic mesoporous silica nanobeads; MOI: Multiplicities of infection; PCION: Poly-(ethylene glycol)-coated cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles; fmNP: FmSiO4@SPIONs; fdNP: FdSiO4@SPIONs; MPIO: Micron-sized superparamagnetic iron oxide particles; PMNC: Polystyrene magnetite nanocluster; MGIO: Microgel iron oxide; Alkyl-PEI: Amphiphilic low molecular weight polyethylenimine; MOI: Multiplicities of infection; Ac4ManNAz: Tetraacetylated N-azidoacetyl-D-mannosamine; PEI: Polyethylenimine; PLL: Poly-L-Lysine; EMF: External magnetic field; PS: Protamine sulfate; High Eff.: Hight efficiency; LCP: Loaded cationic polymersomes; AAS: Atomic absorption spectrophotometer; CCK-8: Cell counting kit-8; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; MTT: 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide; TB: Turnbull blue; NSD: No significant differences; CF: Confocal fluorescence; SEM: Scanning electron microscope; CEM: Cryoelectron microscope; MRI: Magnetic resonance image; BLI: Bioluminescence image; TEM: Transmission electron microscopy; VFL: Visible field fluorescence; PB: Prussian blue.
Stroke model and brain injury evaluation, the target of SC migration
Stroke was studied mainly with two models, which used either an intraluminal filament to occlude the passage of blood flow to the brain or the photothrombosis technique. Brain damage caused by stroke induction attracts SCs to the target region due to chemotactic signals released by compromised tissue. The first model was reported in 68% of the selected studies (Table 5), and stroke was modeled via middle cerebral artery occlusion[28,30,34-40,43,45,47-49,51,52], with the exception of the Tan et al[41]’s study, which used lacunar infarction. This model was performed in rodents (72% rats), and when rats were used, the majority of studies used Sprague-Dawley males (85%)[30,34-37,40,43,47,49,51,52], followed by Wistar male rats[38,41]. Mice were used in 5 studies: Two of the 5 studies[28,39] used C57 black male mice, two studies[45,48] used CD1 female mice, and only the Guzman et al[52]’s study used nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency male mice. In terms of the weights and ages of the animals used in the studies, the rats used were adults[28,30,34,36,37,40,52] that weighed 250 g in the majority of studies[30,36,37,41,43,49,51] the weights ranged from 240 g[30,41] to 300 g[38,49,51], with the exception of the Liu et al[47]’s study, in which the rats weighed between 160 and 180 g. Mice had a weight ranging from 20[39] to 30 g[28]. The total number of animals used in the studies ranged from 6[49] to 133[38]. The type of ischemia used in the stroke models was transient in most studies, with an average of 120 minutes of ischemia time[28,34,36,43,49]; the ischemia time ranged from 10[52] to 180 min[48]. Most studies used inhaled anesthetics, such as sevoflurane[38], halothane[35], and isoflurane[41,49,52], followed by injected anesthetics, such as pentobarbital[34,39] and chloral hydrate[28,47], and agent anesthetics were also used[43,51]. In all animals, a midline neck incision was performed to access the medial cerebral artery, and only two studies[38,51] controlled blood flow during the procedure. Brain injury was detected by MRI in all studies.
Table 5.
Stroke models induced by filament intraluminal middle cerebral artery, brain injury evaluation and animal features
| Ref. | Ischemia mechanism |
Animals |
n / N | Ischemia type | Ischemia time (min) | Filament type | Anesthesia | Brain induction area (AP; ML to bregma in mm) | Blood flow analysis | Injury evaluation | ||||
| Specie | Type | Sex | Weight (g) | Age (wk) | ||||||||||
| Yun et al[30] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | 240-260 | Adult1 | 3-8/50 | T | 30 | 3-0 nylon suture | NR | MNI | NI | TTC, MRI |
| Argibay et al[38] | MCAo | Rat | Wistar | M | 280-300 | NR | 6/133 | T | 45 | silicon rubber- | 3%-4% sevoflurane | MNI | Laser-Doppler | MRI |
| Duan et al[37] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | 250-280 | Adult1 | 6/54 | NR | NR | NR | NR | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Lu et al[35] | MCAo | Rat | SD | NR | NR | NR | 6/12 | T | 90 | 4-0 nylon suture, silicone coated tip | 1% halothane | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Zhang et al[34] | MCAo | Rat | SD | NR | 250-280 | Adult1 | NR/30 | T | 120 | NR | PB (40 mg/kg) | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Lin et al[36] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | 250-280 | Adult1 | 6/18 | T | 120 | NR | NR | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Zhang et al[39] | MCAo | Mice | C57BL/6J | NR | 20-25 | 8 | NR/45 | T | 20 | Nylon poly-1-lysinecoated | PB (6 mL/kg) | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Duan et al[40] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | NR | Adult1 | NR/24 | NR | NR | NR | NR | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Chen et al[28] | MCAo | Mice | C57BL/6J | M | 25-30 | Adult1 | NR/NR | T | 120 | square knot using a 10 suture | CH (0.4 g/kg) | zygoma/squamosal bone | NI | MRI |
| Tan et al[41] | Lacunar infarction | Rat | Wistar | M | 240-260 | NR | NR/22 | P | NA | NA | 2%-4% ISO | 0; 3 | NI | MRI |
| Zhang et al[45] | MCAo | Mice | CD1 | F | NR | 4 | NR/NR | P | NA | 6-0 rounded tip nylon | NR | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Park et al[43] | MCAo | Rat | SD | NR | 250-280 | NR | 8/16 | T | 120 | Micro clip 24 mm | Rompum (10 mg/kg) + Zoletil (30 mg/kg) | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Liu et al[47] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | 160-180 | NR | 6-8/48 | NR | NR | Nylon | 10% CH (300 mg/kg) | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Wang et al[48] | MCAo | Mice | CD1 | F | NR | 4 | 7/21 | T | 180 | 6-0 rounded tip nylon | NR | NI | NI | MRI |
| Song et al[49] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | 250-300 | NR | 3/6 | T | 120 | NR | 4% ISO | MNI | NI | MRI |
| Kim et al[51] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | 250-300 | NR | 2-6/13 | P | NA | NR | ket. (80-100 mg/kg) + AM (5 mg/kg) | MNI | EEG | MRI |
| Guzman et al[52] | MCAo | Rat | SD | M | NR | Adult1 | 5/10 | P | NA | NA | ISO | MNI + rhinal fissure | NI | MRI |
| Global | Mice | NOD-SCID | NR | NR | 0-1PN | 12-16/28 | T | 5-10 | NA | Cryoanestrhetized | NA | NI | MRI | |
Adult: Rat with 8-16 wk and mice with 6 to 20 wk. MCAo: Middle cerebral artery occlusion; SD: Sprague-Dawley; CD1: An outbred mice derived from a group of outbred Swiss mice; NOD/SCID: Nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency; M: Male; F: Female; NR: No reported; n/N: Number of animals per group/total number of animals; T: Transient; P: Permanent; PN: Postnatal; NA: Not applicable; Ket: Ketamine; Xyl.: Xylamine; ISO: Isoflurane; AM: Aceprozazine maleate; CH: Chloral hydrate; PB: Pentobarbital; MNI: Midline neck incision; EEG: Electroencephalogram; TTC: Triphenyltetrazolium chloride; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
The photothrombotic stroke model (Table 6) was performed more often in mice (approximately 67%) than in rats; the mouse strain used in two studies was Balb/c nude (male/female), and the Bai study used a diabetic mouse model and wildtype mice (male). The rat strain used in two studies was Wistar (male/female), and the Tarulli et al[46]’s study used Long Evans (male). The animal ages ranged from 8 to 12 wk, and the mouse weight was between 20 and 25 g in two studies. The number of animals used in the selected studies ranged from 8 to 39. This stroke model used Rose Bengal administered at a dosage of 100 mg/kg for intraperitoneal administration and at a lower dosage intravenously. The photosensitizer most commonly used was Rose Bengal, which was administered at a dosage of 100 mg/kg intraperitoneally, but the Lee et al[50]’s study used 7.5 mg/kg administered by the tail vein; the Lim et al[33]’s study used 10 mg/kg given by the penile vein, and most studies[29,33,42] performed 15 min of laser application after the administration of the photosensitizer. The Lee et al[50]’s study performed 10 min of laser application, and the laser parameters used in the Lee et al[50]’s study were 60 W (power), 603 nm (wavelength) and 3 mm (diameter). The selected studies do not have a similar laser incidence (brain induction) area, and most studies[29,33,42] used the left temporal region (+2.0 ML to Bregma point). All the selected studies used MRI for injury (ischemia) evaluation, 2 studies[33,42] used NIRF, and the other 2 studies[33,50] used histological analysis with triphenyltetrazolium chloride.
Table 6.
Stroke models induced by the photothrombosis of middle cerebral artery, brain injury evaluation and animal features
| Ref. | Ischemia mechanism |
Animals |
n / N | Photosensitizer - rose bengal (dose; via) |
Laser application parameters |
Anesthesia | Brain induction area (AP; ML to Bregma in mm) | Injury evaluation | |||||||
| Specie | Type | Sex | Weight (g) | Age (wk) | Time (min) | Diameter (mm) | Wavelengh (nm) | Power (W) | |||||||
| Lim et al[33] | PT | Mice | Balb/c nude | M | 20-25 | 10 | 3-5/19 | 10 mg/mL; penile vein | 16 | NR | 561 | NR | Zoletil (50-30 mg/kg i.p.) | 0.5; 2.5 | MRI, NIRF, TTC |
| Wang et al[29] | PT | Mice | Balb/c nude | F | 20-23 | 8 | 4-6/39 | 100 mg/kg | 15 | 4 | NR | NR | PB (50 mg/kg i.p) | -2.0; 2.0 | MRI |
| Bai et al[42] | PT | Mice | Db/Db | M | NR | 8 | 4/8 | 100 mg/kg; i.p. | 15 | NR | NR | NR | 1% ISO | 0.0; 2.0 | MRI, NIRF |
| Mice | Wild type | M | NR | 8 | 10/20 | 100 mg/kg; i.p. | 15 | NR | NR | NR | 1% ISO | 0.0; 2.0 | MRI, NIRF | ||
| Tarulli et al[46] | Focal devascularization | Rat | Long Evans | M | NR | 8-12 | 3/9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | ISO + Ketoprofen | 3.0/-4.0; 1.5/4.5 | MRI |
| Lee et al[50] | PT | Rat | Wistar | F | NR | NR | NR/22 | 7.5 mg/mL; tail vein | 10 | 3 | 603 | 60 | Ket. (7.5 mg/100 g) + Xyl. (1 mg/100 g) | -2.0; -3.0 | MRI, TTC |
| Syková et al[53] | Photochemical | Rat | Wistar | M | NR | 8-12 | NR/NR | NR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NR | NI | MRI |
Blood flow analysis was not reported in any of the selected studies that used stroke models induced by photothrombosis; due to the model induction, all studies showed permanent ischemia after occlusion induction in the specific brain region. n/N: Number of animals per group/total number of animals; W: Watts; AP: Anterior-posterior; ML: Medial-lateral; PT: Photothrombosis; Db/Db: Diabetic mice model; M: Male; F: Female; NR: No reported; i.p.: Intraperitoneal; NA: Not applicable; ISO: Isoflurane; PB: Pentobarbital; Ket: Ketamine; Xyl.: Xylamine; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; NIRF: Near-infrared fluorescence; TTC: Triphenyltetrazolium chloride.
Two studies of clinical evaluation were included in the systematic review; one involved case reports of global cerebral ischemia in children at 18 mo, in which the injury evaluation was performed by MRI[44], while the other involved approximately 16 cases of open brain trauma caused by a mixture of focal and global ischemic processes, which were evaluated by comparing the cellular therapy effect vs that of the control group using fMRI and PET[54].
Imaging techniques used to detect SC migration
The main imaging technique used by all the selected studies for the tracking and homing analysis of SCs labeled with SPIONs was magnetic resonance (Table 7). The maximum time of the homing evaluation used by the selected studies was 160 d or 4 mo (Janowski et al[44]’s study). All selected studies used acute tracking analysis (first 48 h after cell implantation); 3 studies[35,38,43] analyzed immediate homing (less than 24 h), while the other 22 of the 25 (88%) selected studies used a homing evaluation time between 3 and 7 d. Thirteen studies[30,34,36,37,40,41,44,47-49,51-53] used a maximum time of 14 d. Ten of 25 (40%) studies[28-30,33,38,39,41,42,52,56,58] used a MR preclinical equipment system, and of these, seven of 10 studies[28,29,38,39,42,51,56] used MR equipment obtained from the Bruker Company. Regarding the MR clinical equipment used by 60% of all the selected studies, this equipment was most often obtained from General Electric (50%) and the Phillips Medical System (45%); four studies[35,37,43,47] used an animal coil, and three studies[44,45,50] used a human coil. Most studies used ImageJ with MRI software. The largest magnetic field used by the selected studies was 9.4 T[33,38]; the magnetic field ranged between 1.5[44,45,50] to 9.4 T[33,38], and most studies used 3.0 T[30,34-37,39,40,43,46,47]. The main weighted image type used by the selected studies was T2, and only the Bai et al[42] and Kim et al[58] studies also used T1 images. The most used sequence (mode) was Fast Spin Echo - FSE[30,35,37,39,40,42,45,46,48], the other MRI parameters are given in Table 7.
Table 7.
Magnetic resonance imaging features for stem cell homing evaluation
| Ref. | Equipment system | Analysis software | MF (Tesla) | Sequence | Weighted images (TR/TE; ms) | FOV; MT; ST (mm) | Homing evaluation time |
| Lim et al[33] | PC - Agilent Technologies | ImageJ (NIH) | 9.4 | T2 | T2: 4000/32.5 | NA; NA; 1.0 | 1, 3, 7, 10, 14 d |
| Wang et al[29] | PC - PharmaScan - Bruker | ImageJ (NIH) | 7.0 | TSE FLASH GRE | T2: 3000/NA | 20 × 20; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 1, 3, 7 d |
| ParaVision (Bruker) | T2*: 159.4/5 | 55 × 55; 256 × 256; 1.0 | |||||
| Yun et al[30] | Philips Medical Systems; an animal coil | NA | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 4000/80 | 50; 256 × 256; 0.5 | 1 d, 3 w |
| Argibay et al[38] | PC - Bio Spec - Bruker; surface coil array | ImageJ (NIH) | 9.4 | MGE | T2*: 2.9/1.5 | 19.2 × 19.2; 192 × 192; 1.0 | 4 h |
| Duan et al[37] | Achieva - Philips Medical Systems; 4-channel rat coil | ImageJ (NIH) | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 800/60 | 60; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 1-4, 6-8 wk |
| FFE | T2*: 500/18 | ||||||
| Lu et al[35] | Achieva - Philips Medical Systems; 4-channel rat coil | NA | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 200/31 | 60 × 60; 267 × 268; 1.0 | 1, 3, 7, 14 d |
| FFE | T2*: 500/18 | ||||||
| Zhang et al[34] | Achieva - Philips Medical Systems | ImageJ (NIH) | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 800/60 | 60 × 60; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 1-6 wk |
| PDW | PDW: 3000/20 | ||||||
| FFE | T2*: 500/18 | ||||||
| Lin et al[36] | Intera - Philips Medical Systems | ImageJ (NIH) | 3.0 | Multi SE | T2: 2000/20-80 | 80 × 80; 160 × 266; 2.0 | 1-6 wk |
| Zhang et al[39] | PC - PharmaScan - Bruker | ImageJ (NIH) | 7.0 | Turbo RARE | T2: 6000/ 60 | 30; 256 × 256; 0.5 | 2 d, 8 d |
| FLASH GRE | T2*: 400/3.5 | ||||||
| Duan et al[40] | Achieva - Philips Medical Systems | ImageJ (NIH) | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 800/60 | 60; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 wk |
| PDW | PDW: 3000/20 | ||||||
| FFE | T2*: 500/18 | ||||||
| Bai et al[42] | PC - PharmaScan - Bruker | ImageJ (NIH) | 7.0 | SE | T1: 500/15 | 20 × 20; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14 d |
| FSE | T2: 2000/50 | ||||||
| Chen et al[28] | PC - Bio Spec - Bruker | ImageJ (NIH) | 7.0 | RARE SE | T2: 3000/50 | 25.6; 256 × 256; 0.7 | 3 d, 7 d, 14 d |
| Tan et al[41] | PC - Unity INOVA, Varian | NR | 7.0 | SE | T2: 2500/60 | 30 × 30; 512 × 512; NR | 1-42 d |
| Janowski et al[44] | Sonata Maestro Class - Siemens; 8-channel head coil | Osirix (Pixmeo) Amira (Visage Imaging) | 1.5 | SWI | T2*: 49/40 | 230; 168 × 256; 1.6 | 1 d, 1 wk, 1 mo, 2 mo, 4 mo |
| Park et al[43] | Achieva - Philips Medical Systems; animal coil | NA | 3.0 | SE | T2: 11000/125 | NA; 284 × 286; 0.7 | 0 h, 2 d |
| Zhang et al[45] | Sigma - GE Healthcare; a human head coil | NA | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 5840/104 | 45 × 45; 256 × 256; 1.5-2.0 | 1 d, 3 d |
| Map MSME SE | T2: 3500/20-160 | ||||||
| Tarulli et al[46] | Sigma - GE Healthcare | NA | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 4500/35-75 | 40 × 40 × 17; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 1 d, 7 d, 14 d |
| 3D-SPGR | T2*: 25/7 | 40 × 40 × 20; 256 × 256; 1.0 | |||||
| Liu et al[47] | Sigma - GE Healthcare; a rat coil | 3.0 | T2* | T2*: 2560/6.8 | 6.0; NR; 1.6 | 1, 7, 21 d | |
| Wang et al[48] | Sigma - GE Healthcare | NA | 3.0 | FSE | T2: 5840/104 | 45 × 45; 256 × 256; 1.5 | 1, 7, 30 d |
| Lee et al[50] | Sigma - GE Healthcare; a clinical coil | NA | 1.5 | TSE | T2: 2000/81 | 90; 192 × 192; 1.5 | 0, 1, 5, 12 d |
| GRE | 280/20 | 20; 160 × 160; 1.5 | |||||
| Song et al[49] | Sigma - GE Healthcare | NA | 1.5 | T2 | T2: 3500/80 | 60 × 60; 256 × 160; 2.0 | 1d, 3d, 1-4 wk |
| 3D GRE | T2*: 50/20 | 80 × 80; 256 × 160; 2.0 | |||||
| Kim et al[51] | PC - Bio Spec - Bruker | NA | 4.7 | SE | T1: 600/14 | 40 × 30; 256 × 192; 1.0 | 2 d, 1 w, 2 w...10 wk |
| RARE | T2: 5000/90 | ||||||
| FLASH | T2*: 758 × 30 | ||||||
| Guzman et al[52] | PC - Varian Medical Systems | NA | 4.7 | SE | T2: 2500/45 | 40; 256 × 256; 1.0 | 2 d, 7 d, 35 d |
| 3D GRE | T2*: 600/5 | 30 × 30 × 30; 128× 128 × 128 | |||||
| Syková et al[53] | PC - Bio Spec-Bruker | NA | 4.7 | FGE | T2: NA | NA | 1 d, 1-7 wk |
| Zhu et al[54] | Sigma - GE Healthcare | NA | 3.0 | SE | T2: 200/20 | NA | 1 d, 7 d |
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; PC: Preclinical MRI scanner; NIH: National Institutes of Health; NA: Not applicable; MF: Magnetic field; T2: Transverse relaxation time; FSE/TSE: Fast or turbo spin echo; FFE: Fast field echo; PDW: Proton density-weighted; GRE: Gradient echo; MGE: Multiple gradient echo; SPGR: Spoiled gradient recalled echo; SE: Spin echo; FGE: Fast gradient echo; FLASH: Fast low angle shot; PDW: Proton density-weighted; RARE: Rapid acquisition with refocused echoes; SWI: Susceptibility weighted imaging; MSME: Multi-spin-multi-echo; SPGR: Spoiled gradient recalled echo; TR: Time repetition ; TE: Echo time ; FOV: Field-of-view; MT: Matrix; ST: Slice thickness.
The NIRF imaging technique was also used by three of the selected studies[33,34,42] for the tracking and homing analysis of SCs (Table 8); these studies analyzed immediate (less than 24 h) and acute homing (first 48 h), and the maximal time of the homing evaluation used by the selected FT studies was 42 d or 6 wk (Zhang et al[34]’s study); 2 studies[33,34,42] used Cy5.5 as the fluorescence agent, and the other parameters are given in Table 8. The BLI technique was used by 3 of the selected studies[28-30] for the tracking and homing analysis of SCs (Table 9), and all studies analyzed immediate (less than 24 h) and acute homing (first 48 h). The maximal time of the homing evaluation used by the selected BLI studies was 21 d or 3 wk (Yun et al[30]’s study). All studies used luciferase with eGFP as a lentiviral vector and D-luciferin as a fluorescence agent. The dose, time of acquisition and other parameters are given in Table 9.
Table 8.
Near-infrared fluorescence imaging features for stem cell homing evaluation
| Ref. | Agent | Equipment | Software | Excitation / Emission wavelength (nm) | Time of exposition | Follow-up |
| Lim et al[33] | DBCO-Cy5.5 | IVIS Lumina Series III (PerkinElmer) | Living Image (PerkinElmer) | 670/NA | 1 min | In vivo at 1, 3, 7, 10, 14 d; ex vivo at 2, 27, 30, 33, 36 h |
| Zhang et al[34] | LV-FTH-EGFP | small animal in vivo FLI system (in vivo FxPro; Carestream) | MI (Carestream) | 487/509 | NA | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 wk |
| Bai et al[42] | Cy5-5 | Maestro in vivo imaging system (CRi, Woburn) | Maestro v. 2.10.0 | 675/695 | NA | 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14 d |
DBCO: Dibenzylcyclooctyne; Cy5.5: Cyanine 5.5; LV-FTH-EGFP: Lentiviral vector-encoding ferritin heavy chain and enhanced green fluorescent protein; NA: Not applicable; MI: Molecular imaging software; Cri: Cambridge research and instrumentation.
Table 9.
Bioluminescence imaging features for stem cell homing evaluation
| Ref. | Lentiviral vector | Equipment | Software | Substrate | Dose | Image acquisition | Follow-up |
| Wang et al[29] | Luc2/eGFP | IVIS Lumina Series III (Perkin-Elmer) | NR | D-luciferin (Promega, United States) | 100 mL (30 mg/mL) | 10 min after injection | 1 d, 3 d, 7 d |
| Yun et al[30] | Fluc/eGFP | IVIS® Spectrum imaging system (Perkin Elmer) | NR | D-luciferin (Promega, United States) | 150 mg/kg | NR | 1 d, 1 wk, 3 wk |
| Chen et al[28] | Luc/GFP | IVIS Imaging System 200 Series (Caliper) | Living Image 3.0 (Xenogen Corp.) | D-luciferin (Caliper) | 270 mg/g | 15 min after injection | 0, 14 d |
All substrates were administered intraperitoneally. Luc: Luciferase; Fluc: Firefly luciferase; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; eGFP: Enhanced GRP; NR: Not reported.
SC administration strategies after stroke induction, their migration analysis, and the therapeutic effect
After the brain injury induction, SCs are administered by different routes, systemic or local, with their particularities as to the time after stroke induction, number and volume of cells administered. The parameters adopted in the administration of the cells can interfere with the successful migration and the therapeutic effect. The main characteristics of SCs and SC tracking, homing and therapeutic efficacy in the selected studies are described in Table 10. Fifteen (60%) studies[28,29,33,34,36-38,40-43,46,48,50,51] used mesenchymal SCs as the cell type, and the main source was human bone marrow (Table 2) via a xenogeneic graft in 53% of the studies[28,29,33,42,43,46,48,50], via an allogeneic graft in 33% of the studies and via an autologous graft in one study[51]; of the 40% studies that used neural SCs, 60% used a xenogeneic graft, 30% used an allogeneic graft and 10% used an autologous graft. Only the Sykova et al[55]’s study used both xenogeneic and allogeneic grafting. The time of SC implantation after stroke was commonly reported by the selected studies[29,30,37,39,42,49]; the time of implantation after the acute stage of stroke (24 h) ranged from 30 min[28] to 14 d[43]. Regarding cell administration, the main route used by the selected studies was intracerebral (64%), in which 13 (81%) studies administered the cells in the contralateral side of the stroke injury (IC-CTL), one (6%) study administered the cells in the ipsilateral side of the injury, and one study (6%) did not report the specific area of the brain in which the cells were implanted; via this route, the maximum volume of implanted cells was 10 μL, which commonly contained 5 × 105 cells. Another cell administration route reported in six (24%) studies[28,38,45,47,49,53] was the intravenous route (tail and jugular), and the intraarterial (intracarotid) route was used in three (12%) studies[30,38,42]; the intracardial route was used by the Wang et al[29]’s study. These systemic routes allowed the administration of a greater volume, ranging from 100 to 700μL, with a similar quantity of cells (approximately 5 × 105 cells). The range in the number of cells used in the selected studies was between 2.0 × 104 (Janowski et al[44], 2014; Lee et al[50], 2009) and 4.0 × 106 (Song et al[49], 2009); most studies[28,29,35-37,40,41,45] used 5.0 × 105, since the most commonly used SC implantation volume used by the selected studies[36,43,45,47-50] was 5 μL, which ranged between 2[58] and 700 μL[46]. All of the selected studies observed the positive presence of SCs labeled with SPION in the ischemic area. After the homing analysis, these cells were monitored for 21 d by different imaging techniques. The outcome of cellular therapy was analyzed by different approaches, including functional behavioral assessment, structural morphometric analysis of the decrease in the ischemic lesion volume and the evaluation of cellular differentiation using various types of immunohistochemical analysis. To assess the functional outcome of cellular therapy, 8 studies reported behavioral assessment by different tools, for which 6 studies showed positive improvement in the functional analysis mainly after 14 d of cell implantation (ranging from 7 to 21 d). The structural outcome of the infarct volume was reported in 14 studies, in which 11 showed effective improvements as a decrease in the infarct volume in the late stage (14 d after cells implantation). Cellular differentiation was analyzed by measuring different molecular proteins such as Ki67, NeuN, GFAP, TuJ1, MAP2, BrdU, Nestin, TUNNEL, CD31, CD11, CD15, GFP, and MAPK, as well as by using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and tyrosine hydroxylase assays, which reveal positive markers of cellular differentiation mainly 7 d after cell implantation.
Table 10.
Stem cell administration, homing and cellular therapeutic efficiency
| Ref. | Cell Type | Immuno-genicity | Time from stroke (h) |
Cell administration |
Groups | Follow-up |
Outcome |
|||||
| Route | Number | Volume (µL) | Behavior | Infarct volume | Mole-cular proteins/others | Cells mi-gration | ||||||
| Lim et al[33] | MSC | XNG | NR | IC-CTL | 1 × 106 | 5 | Stroke + cells vs Stroke-cells | 1, 3, 7, 10, 14 d | NR | (+) | NR | (+) |
| Wang et al[29] | MSC | XNG | 24 | ITC1 | 5 × 105 | 100 | Alkyl-SPIO/siPHD2 > Alkyl-SPIO/si | 1, 3, 7 d | (+) mNSS; FFT at 14 d | (+) 7 d | (+) Ki67; CD31 -7 d; (+) NeuN -14 d | (+) |
| MSC | XNG | 24 | ITC1 | 5 × 105 | 100 | Alkyl-SPIO/si vs saline | 1, 3, 7 d | (+) mNSS; FFT at 14 d | (-) 7 d | (+) Ki67; CD31 -7 d; (+) NeuN -14 d | (+) | |
| Yun et al[30] | NSC | XNG | 24 | IA-IC | 3 × 106 | 100 | Mag-Cells > UL-Cells/sa-line | 0, 3, 5, 7, 21 d | (+) Cilinder at 21d | NR | (+) MAP2; Nestin; GFAP; TuJ1 -7d | (+) |
| Argibay et al[38] | MSC | ALG | 8 | IA; IV-jugular | 2 × 105; 1 × 106 | 300 | D-MNP-labeled MSC (IA × IV) | 4, 24, 72 h | (-) Cilinder | (-) at 14d | (-) CD31; Ki67; DCX | (+) |
| Duan et al[37] | MSC | ALG | 48 | IC-CTL | 5 × 105 | 3 | Labeled cell > UL-cells | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 wk | (-) mNSS | (-) | (-) TUNNEL (-) GFP | (+) |
| Labeled/UL vs control | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 wk | (+) mNSS at 3, 4, 6, 8 wk | (+) at 4, 6, 8 wk | (+) TUNNEL 7-21 d, (+) GFP 7-21 d | (+) | |||||||
| Lu et al[35] | NPC | ALG | NR | IC-IPS | 5 × 105 | 2.5 | labeling with N-NPS | 0, 3, 7, 14 d | NR | (+) | (+) Nestin | (+) low |
| labeling with C-NP | 0, 3, 7, 14 d | NR | (+) | (+) Nestin | (+) | |||||||
| Zhang et al[34] | NSC | XNG | 48 | IC-CTL | 5 × 105 | 3 | FTH-EGFP-NSC > non trans-ducec NSC | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 wk | (+) mNSS at 1-6 wk | (+) at 1-6 wk | (+) GFAP; Nestin; CD11b at 6 wk | (+) |
| Lin et al[36] | MSC | ALG | 48 | IC-CTL | 5 × 105 | NR | ASP-SPION vs UL vs PBS | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 wk | (-) mNSS | (-) | (-) GFAP; NeuN; CD11 | (+) |
| Zhang et al[39] | NSC | XNG | 7d | IC-CTL | NR | 7 | Stroke pure > Stroke + Ara-C | 0, 2, 8 d | NR | (+) at 8 d | (+) CD15+; Nestin at 8 d | (+) |
| Duan et al[40] | MSC | ALG | 48 | IC-CTL | 5 × 105 | 3 | PLL-SPION or PM > UL | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 wk | NR | (+) at 4, 6 wk | (-) GFP | (+) |
| Bai et al[42] | MSC | XNG | 24 | IA - IC | 1 × 106 | 100 | DM + RWJ + cell > DM + cells | 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14 d | NR | (+) | (+) p38 MAPK at 7 d | (+)2 |
| Chen et al[28] | MSC | XNG | 30 min | IV-femoral | 5 × 105 | Mag-cells > UL-cells | 0, 3, 7, 14 d | (+) VM at 14, 28 d | (+) at 14 d | (+) TuJ1; NeuN; GFAP at 28 d; (+) RT-PCR1 at 28 d | (+) | |
| Tan et al[41] | MSC | ALG | 7 d | IC-CTL | 5 × 105 | 10 | Stroke + cells over time | 0, 1, 7, 14, 21, 42 d | NR | NR | (-) GFP and NeuN at 7 d; (+) GFP and NeuN at 6 wk | (+) |
| Janowski et al[44] | NSC | AuTL | NR | IC | 2 × 104 | 10 | Case over time | 0, 1, 7, 60, 120 d, 33 mo | NR | NR | NR | (+) |
| Park et al[43] | MSC | XNG | 14d | IC-CTL | 6 × 105 | 5 | Pcion/pDNA MSC vs control | 1, 2 d | NR | (-) | NR | (+) |
| Zhang et al[45] | NPC | ALG | 24 | IC-CTL | 5 × 105 | 5 | fsiSPION-NPC vs control | 1, 3 d | NR | (+) | (+) Nestin | (+)2 |
| NPC | ALG | 24 | IV-tail | 1 × 106 | 300 | fsiSPION-NPC vs control | 1, 3 d | NR | NR | (+) Nestin | (+) | |
| Tarulli et al[46] | MSC | XNG | 72 | IV-tail | 3 × 106 | 700 | MPIO-BMSC vs UL-BMSC | 1, 7, 14 d | NR | NR | NR | (+) |
| Liu et al[47] | NSC | XNG | NR | IC-CTL | 3 × 104 | 5 | Stroke + NSC_FA > Stroke + NSC | 1, 7 d | NR | NR | (+) Sox-2 BrdU at 21 d | (+) |
| Wang et al[48] | MSC | XNG | 7d | IC-CTL | 1 × 105 | 5 | FMNC-MSC > UL-MSC vs control (FMNC) | 0, 1, 7, 30 d | NR | NR | (+) TuJ1 | (+) |
| Lee et al[50] | MSC | XNG | 48 | IC-CTL | 2 × 104 | 5 | M600-MSC vs FC-MSC | 1, 5, 12 d | NR | NR | NR | (+) |
| MSC | XNG | 48 | IV-tail | 2 × 106 | 500 | M600-MSC vs control | 5, 12 d | NR | NR | NR | (+) | |
| Song et al[49] | NPC | XNG | 24 | IC-IPS | 4 × 105 | 5 | FO-NPC vs control | 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, 28 d | NR | NR | (+) BrdU; GFAP at 28 d | (+) |
| NPC | XNG | 24 | IV-tail | 4 × 106 | 500 | FO-NPC vs control | 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, 28 d | NR | NR | (+) BrdU; GFAP at 28 d | (+) | |
| Kim et al[51] | MSC | AuTL | 7d | IC-IPS/CTL | 1 × 105 | 2 | Feridex®-labeled hMSC over time for both vias | 2d, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 wk | NR | NR | (-) GFAP; TH; MAP2; TuJ1; Nestin at 10 wk | (+) |
| Guzman et al[52] | NSC | XNG | 7d | IC-CTL | 3 × 105/5 × 104 | NSC-SCns-SPION | 3, 9, 12,18 wk | NR | NR | (+) SC121 or SC101; TuJ1; GFAP; MAP2 at 18 wk | (+) | |
| Syková et al[53] | rOEC | ALG | NR | IC-CTL | NR | NR | OEC-SPION over time | 3-7 wk | NR | NR | (+) NeuN; GFAP at 28 d | (+) |
| MSC | XNG | NR | IV-femoral | NR | NR | MSC over time | 6-30 d | NR | NR | (+) NeuN; GFAP at 28 d | (+) | |
| Zhu et al[54] | NSC | AuTL | NR | IC | NR | NR | Patients treat with NSC and no treat | 2 yr | (+) SEP and DRS at 6, 9 mo | (+) cells uptake by PET at 3, 6 mo | NI | (+) |
left ventricle.
In addition to cell migration analysis, studies reported biodistribution analysis after stem cell administration. The Bay study[42] reported biodistribution in the liver, spleen, heart, lungs, and kidneys; Zhang et al[45] reported that the SPION-labelled cells IV > IA at 3 d after injection were detected in spleen, liver, heart, kidney, and lung. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; NSC: Neural stem cells; ESC: Embryonic stem cell; rOEC: Rat olfactory ensheathing cells; NR: No reported; XNG: Xenogeneic; ALG: Allogeneic; AuTL: Autologous; IC: Intracerebral; IC-CTL: IC contralateral; ITC: Intracardially; IC-IPS: IC ipsilateral; IV: intravenous; IA-IC: Intraarterial through internal carotid artery; Alkyl-SPIO: Amphiphilic low molecular weight superparamagnetic iron oxide; Mag: External magnet; UL: Unlabeled; siPHD2: siRNA against PHD2; C-NP: Cationic nanoparticle; N-NP: Neutral nanoparticle; FTH-eGFP: ferritin heavy chain: Enhanced green fluorescent protein; ASP-SPION: Spermine-modified amylose superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; Ara-C: Cytosine arabinosine; PLL: Poly-L-Lysine; PM: Polymersone; PCION: Poly-(ethylene glycol)-coated cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles; MPIO: Micron-sized superparamagnetic iron oxide particles; DM: Diabetes mellitus; RWJ: RWJ67657; fsiSPION: fmSiO4@SPION; FC: Ferucarbotran; FA: Folic acid; FO: Ferumoxide; FMNC: Fluorescent-magnetite-nanocluster; mNSS: Modified neurological severity score; FFT: Foot-faults test; VM: Vertical movement; SEP: Somatosensory evoked potential; DRS: Disability rating scale; MAP2: Microtubule-associated protein 2; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; TuJ1: Neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; RT-PCR: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; BrdU: 5′-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine; TH: Tyrosine hydroxylase.
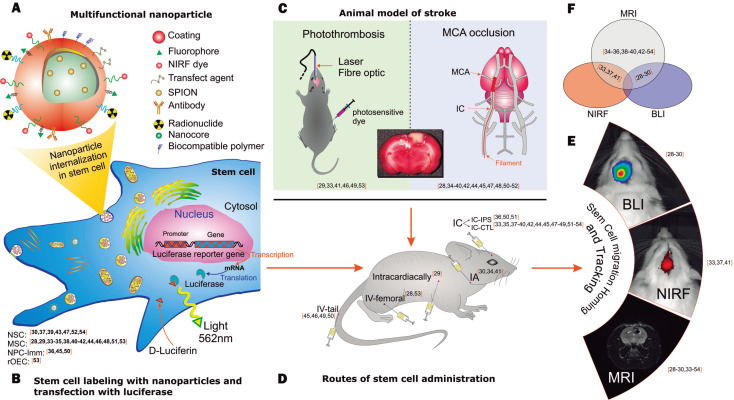
The systematic review outcomes are schematically illustrated in Figure 2, which shows each aspect analyzed for the SC homing, tracking and therapeutic efficacy evaluation for stroke treatment using nanoparticles.
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the aspects of stem cell homing, tracking and therapeutic efficacy evaluated in stroke using nanoparticles in the selected studies included in this review. A: The multifunctional nanoparticle characteristics; B: Characteristics of stem cells labeled with nanoparticles/contrast agents transfected with luciferase; C: Characteristics of the induction of the animal models of stroke; D: Routes of stem cell administration; E: Molecular imaging techniques of stem cell migration homing and tracking; F: The combined imaging techniques used in the stem cell homing analysis. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; NSC: Neural stem cells; NPC-Imm: Neural progenitor cell - immortalized; ESC: Embryonic stem cell; rOEC: Rat olfactory ensheathing cells; IV: Intravenous by tail and femoral veins; IA: Intra-arterial by intracarotid; IC: Intracerebral; CTL/IPS: Contralateral or ipsilateral of brain injury; BLI: Bioluminescence; NIRF: Near-infrared fluorescence; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; MCA: Middle cerebral artery.
DISCUSSION
The current systematic review examined preclinical studies of the homing and tracking of MSCs with SPION used for the treatment of ischemic stroke and found that this cellular therapy improves outcomes overall. The effects were robust regardless of the species, delivery route, time of administration in relation to stroke, MSC immunogenicity, and MSC dose. These results support further translational studies of MSCs in the treatment of ischemic stroke in humans.
The results described above corroborate the recent systematic review of Boncoraglio[59], which reported the exponential growth of the use of this therapeutic method in Eastern countries, mainly in China (Figure 1), by utilizing human cells extracted from bone marrow. It was observed that 15 studies (60%) used mesenchymal cells and 10 (40%) used neural cells, this characteristic or cellular pattern, evidenced by the studies selected in this review, corroborates the current literature and the review[59] cited. The MSC have strong immunomodulatory potential into ischemic or damage area[60], mainly autologous and allogeneic source. The most selected studies used bone marrow as source of SCs, but the human (40%), the review cited[59], showed in these studies, stronger functional effects in the meta-analysis, the most studies of this study used too human SCs of bone marrow.
The selected studies have demonstrated the presence of SCs labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the ischemia area from a few minutes to several days after preclinical stroke induction. However, during the last 15 years, the understanding of the mechanisms of action has significantly advanced; rather than cell replacement, the benefit of SC treatments in stroke seems to result from indirect mechanisms, such as immunomodulation, which are intended to suppress the postischemic inflammatory response and enhance endogenous repair[60].
The meta-analysis study[61] examined the quality of the preclinical MSC studies, given the important bearing this has on translation potential. Over the past 10 years, our group has been improving the evidence finding process for developing treatments for neurological recovery through SCs labeled with iron oxide nanoparticles; in this study, we used the PRISM method, and the median quality score was the same as that in the Boncoraglio et al[59]’s study, which is the most recent and comprehensive meta-analysis of studies of SC transplantation for ischemic stroke. The quality of the twenty-five selected studies in this review was also found to be poor, and the majority of studies reported by Boncoraglio et al[59] showed an unclear risk of bias due to poor methodological reporting. This recent review showed that there are two major trial paradigms or approaches reflected in the translated results that were used to improve bedside stroke care: Neuroprotection in the acute phase and neurorestoration in the chronic phase[59]. The massive, early and fast delivery of SCs into the ischemic area reduces acute tissue injury and benefits from the paracrine effect of SCs, suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment to suppress the apoptosis process[62,63]. During late SC delivery (more than 36 h after ischemic damage), the same studies[62,63] suggest that the chemokine signaling of SCs near the damaged/ischemic areas has already waned, and engraftment is intended to initiate brain remodeling by stimulating quiescent SCs to begin reparative processes, as long as they remain in damaged areas. Even so, SC administration results in enhanced recovery of sensorimotor function, promotion of synaptogenesis, stimulation of nerve regeneration, and suppression of tissue plasminogen activator-induced brain damage[64]. Therefore, the analysis of the homing and tracking SC processes is a pivotal strategy for utilizing preclinical results to increase translational knowledge to improve stroke care at the bedside.
In addition, Sohni et al[65]’s review suggests that MSC homing is inefficient and that many MSCs are trapped in the lungs following systemic administration. Therefore, it is imperative to trace the fate of the injected cells to truly achieve clinical translation aims. The same study cited several molecular imaging techniques to track the injected cells in vivo, such as BLI, SPECT, PET, and MRI. In this review, the maximum time of the homing evaluation used by all selected studies was 160 d or 4 mo (Janowski et al[44]’s study) by MRI; two studies[43,50] reported an immediate homing analysis after SC implantation at 0 h by MRI, 3 studies[35,38,43] analyzed homing fairly quickly (less than 24 h), and most of the selected studies (88%) used homing evaluation times ranging from 1 to 7 d. Late homing evaluation occurred in 13 studies[30,34,36,37,40,41,44,47-49,51-53] at least 14 d after implantation, and this was the most common scenario in the recent literature. Only 3 of the 25 selected studies[33,34,42] performed tracking and homing analysis of SCs by using retroviral vectors to express fluorescent proteins, and the maximum time of homing measured by NIRF was 6 wk, which is nearly 1.5 mo[34]. The maximum time of the BLI homing analysis was reported as three weeks[30]. Sohni et al[65]’s review proposed that the use of multifunctional (dual-labeled cells) nanoparticles or molecular imaging techniques increased the efficacy of determining the SC dose and route of inoculation owing to the time window after stroke and phase effects (early or late) in SCs in the damaged area. Many important aspects were not addressed in most selected studies included in this review.
However, our group showed in a previous study the first standardized methodological approach for triple modal imaging of SCs after stroke in a rodent model, demonstrating SC homing, tracking and therapeutic efficiency using a low dose and a systemic route[25]. In this review, only 6 of the 25 selected studies used bimodal imaging, while three used NIRF[33,34,42] and three used BLI[28-30] combined with MRI. In our previous study, in which fluorescence was combined with resonance imaging techniques, our results showed that correlation analysis of the MNP load internalized into MSCLuc determined via MRI, ICP-MS and NIRF techniques resulted in the same correlation coefficient of 0.99. Evaluation of the BLI, NIRF, and MRI signals in vivo and ex vivo after labeled MSCLuc were implanted into animals showed differences in the contrast images according to the different MNP concentrations, and the physical signals were associated with different techniques (MRI and NIRF; 5 and 20 µg Fe/mL, respectively). Therefore, the temporal analysis showed the acute and late effects of SCs implanted in the sham groups (at 4 h and 6 d) and in the lesion due to the chemical receptors involved in brain damage by comparing the sham group and stroke group, improving the imaging techniques that assist systemic SC administration/dose assessment.
Furthermore, other questions (limitations) are also relevant regarding clinical translation of the results, such as culture conditions, the number of passages, donor age, the toxicity of the contrast agent used in the SC labeling process, and host factors (aging), among others, due to the absence of a reasonable understanding of the pharmacokinetics of the administered cells, which in itself would be an overall nonnegligible adverse effect. In this review, most of the selected studies reported a low cell passage (no later than the fifth passage), and the literature highlighted that a higher passage was associated with decreased telomerase activity, paracrine function, and renewal potential, which reduced cell differentiation and the immunomodulatory impact[66-68]. In terms of the toxicity of the contrast agent used in the SC labeling process, which was usually iron[69], all selected studies used iron oxide nanoparticles as the contrast agent, and the highest SPION concentration was 300 µg/mL[33]; however, the cell viability after the labeling process remained high (more than 95%) according to the CCK-8 assay, and the other selected studies also showed high cell viability when using low SPION concentrations. In our previous study[70], we showed that a high SPION concentration (100 µg/mL) maintained cell differentiation and the absence of cytotoxicity. The most recent selected studies used equipment that generated a high magnetic field (9.4 T), which was developed for preclinical imaging with rodent-specific coils, such as that used in the Lim et al[33] and Argibay et al[38] studies; this increased the detection sensitivity of the nanoparticles and generated greater opportunities for broader temporal analyses as well as the use of labeled SCs with lower SPION concentrations.
Although there were limitations/biases in all the selected studies included in this review, the studies that used behavioral or structural analysis/outcomes showed success in terms of neurological improvement using some sensitive motor tests as well as the reduction of the penumbra or ischemic brain area. Four decades of preclinical research demonstrating the survival, functional integration, and behavioral effects of transplanted SCs in experimental/preclinical stroke models have provided an ample scientific basis to facilitate the translation of clinical trials of SC therapy into treatments for stroke patients[62]. Although therapeutic efficacy has been demonstrated by the functional and structural outcomes of preclinical studies, there have been no relevant outcomes in clinical studies[11]. The best time window for cellular therapy for ischemic stroke has not yet been defined, and a recent clinical trial[71] and Cochrane review[59] suggested a time window between 24 and 36 h after the stroke event. However, a long clinical follow-up is necessary in combination with the use of the homing imaging technique as the gold standard to address the gap between the clinical application and the preclinical cellular therapy outcome. Thus, the prescription of SCs labeled with SPION according to this review may help improve future clinical trials.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Stroke survivors commonly suffer from disabilities requiring temporary or lifelong assistance, resulting in a substantial economic burden for poststroke care and stem cell (SC) therapeutics appear to be a promising alternative for intervention in stroke therapy. However, the efficacy of SC therapy depends on the SC homing ability and engraftment into the injury site over a long period of time.
Research motivation
The analysis of the homing and tracking SC processes is a pivotal strategy for utilizing preclinical results to increase translational knowledge to improve stroke care at the bedside.
Research objectives
In this systematic review, we aim to evaluate SC migration homing, tracking and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of stroke using nanoparticles.
Research methods
A systematic literature search was performed to identify articles published prior to November 2019 that were indexed in PubMed and Scopus. The following inclusion criteria were used: (1) Studies that used in vivo models of stroke or ischemic brain lesions; (2) Studies of SCs labeled with some type of contrast agent for cell migration detection; and (3) Studies that involved in vivo cellular homing and tracking analysis.
Research results
A total of 82 articles were identified by indexing in Scopus and PubMed. After the inclusion criteria were applied, 35 studies were selected, and the articles were assessed for eligibility; ultimately, only 25 studies were included. Most of the selected studies used SCs from human and mouse bone marrow labeled with magnetic nanoparticles alone or combined with fluorophore dyes. These cells were administered in the stroke model (to treat middle cerebral artery occlusion in 74% of studies and for photothrombotic induction in 26% of studies). Fifty-three percent of studies used xenogeneic grafts for cell therapy, and the migration homing and tracking evaluation was performed by magnetic resonance imaging as well as other techniques, such as near-infrared fluorescence imaging (12%) or bioluminescence assays (12%).
Research conclusions
Our systematic review provides a comprehensive, up-to-date evaluation of the SC migration and efficacy of cellular therapy for brain injury. Cellular therapy demonstrated considerable efficacy with regard to the functional and structural evaluation, as well as the differentiation of the cells in the late stage of evaluation (after 7 d of cell implantation), using protein molecular and other tests.
Research perspectives
In summary, a long clinical follow-up is necessary in combination with the use of the homing imaging technique as the gold standard to address the gap between the clinical application and the preclinical cellular therapy outcome. Thus, the prescription of SCs labeled with SPION according to this review may help improve future clinical trials.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
PRISMA 2009 Checklist statement: The authors have read the PRISMA guidelines and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Peer-review started: January 23, 2020
First decision: April 1, 2020
Article in press: April 23, 2020
Specialty type: Cell and tissue engineering
Country/Territory of origin: Brazil
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kim BS, Liu L, Pérez-Campo F, Tanabe S S-Editor: Dou Y L-Editor: A E-Editor: Xing YX
Contributor Information
Mariana Penteado Nucci, LIM44, Hospital das Clinicas HCFMUSP, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil.
Igor Salerno Filgueiras, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil.
João Matias Ferreira, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil.
Fernando Anselmo de Oliveira, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil.
Leopoldo Penteado Nucci, Centro Universitário do Planalto Central, Brasília, DF, Brazil.
Javier Bustamante Mamani, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil.
Gabriel Nery Albuquerque Rego, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil.
Lionel Fernel Gamarra, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo 05529-060, Brazil. lgamarra@einstein.br.
References
- 1.Avan A, Digaleh H, Di Napoli M, Stranges S, Behrouz R, Shojaeianbabaei G, Amiri A, Tabrizi R, Mokhber N, Spence JD, Azarpazhooh MR. Socioeconomic status and stroke incidence, prevalence, mortality, and worldwide burden: an ecological analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMC Med. 2019;17:191. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1397-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:439–458. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30034-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boltze J, Modo MM, Mays RW, Taguchi A, Jolkkonen J, Savitz SI STEPS 4 Consortium. Stem Cells as an Emerging Paradigm in Stroke 4: Advancing and Accelerating Preclinical Research. Stroke. 2019;50:3299–3306. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meamar R, Dehghani L, Ghasemi M, Khorvash F, Shaygannejad V. Stem cell therapy in stroke: a review literature. Int J Prev Med. 2013;4:S139–S146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nawab K, Bhere D, Bommarito A, Mufti M, Naeem A. Stem Cell Therapies: A Way to Promising Cures. Cureus. 2019;11:e5712. doi: 10.7759/cureus.5712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Surugiu R, Olaru A, Hermann DM, Glavan D, Catalin B, Popa-Wagner A. Recent Advances in Mono- and Combined Stem Cell Therapies of Stroke in Animal Models and Humans. Int J Mol Sci. 2019:20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nguyen H, Zarriello S, Coats A, Nelson C, Kingsbury C, Gorsky A, Rajani M, Neal EG, Borlongan CV. Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders: A focus on aging. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;126:85–104. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.09.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang F, Tang H, Zhu J, Zhang JH. Transplanting Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Cell Transplant. 2018;27:1825–1834. doi: 10.1177/0963689718795424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kwak KA, Kwon HB, Lee JW, Park YS. Current Perspectives Regarding Stem Cell-based Therapy for Ischemic Stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:3332–3340. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180604111806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cunningham CJ, Redondo-Castro E, Allan SM. The therapeutic potential of the mesenchymal stem cell secretome in ischaemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38:1276–1292. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18776802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Borlongan CV. Concise Review: Stem Cell Therapy for Stroke Patients: Are We There Yet? Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8:983–988. doi: 10.1002/sctm.19-0076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bhatia V, Gupta V, Khurana D, Sharma RR, Khandelwal N. Randomized Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of Intra-Arterial Infusion of Autologous Stem Cells in Subacute Ischemic Stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39:899–904. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sprigg N, O'Connor R, Woodhouse L, Krishnan K, England TJ, Connell LA, Walker MF, Bath PM. Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor and Physiotherapy after Stroke: Results of a Feasibility Randomised Controlled Trial: Stem Cell Trial of Recovery EnhanceMent after Stroke-3 (STEMS-3 ISRCTN16714730) PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kalladka D, Sinden J, Pollock K, Haig C, McLean J, Smith W, McConnachie A, Santosh C, Bath PM, Dunn L, Muir KW. Human neural stem cells in patients with chronic ischaemic stroke (PISCES): a phase 1, first-in-man study. Lancet. 2016;388:787–796. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30513-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Qiao LY, Huang FJ, Zhao M, Xie JH, Shi J, Wang J, Lin XZ, Zuo H, Wang YL, Geng TC. A two-year follow-up study of cotransplantation with neural stem/progenitor cells and mesenchymal stromal cells in ischemic stroke patients. Cell Transplant. 2014;23 Suppl 1:S65–S72. doi: 10.3727/096368914X684961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Prasad K, Sharma A, Garg A, Mohanty S, Bhatnagar S, Johri S, Singh KK, Nair V, Sarkar RS, Gorthi SP, Hassan KM, Prabhakar S, Marwaha N, Khandelwal N, Misra UK, Kalita J, Nityanand S InveST Study Group. Intravenous autologous bone marrow mononuclear stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke: a multicentric, randomized trial. Stroke. 2014;45:3618–3624. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lin W, Xu L, Zwingenberger S, Gibon E, Goodman SB, Li G. Mesenchymal stem cells homing to improve bone healing. J Orthop Translat. 2017;9:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2017.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fu X, Liu G, Halim A, Ju Y, Luo Q, Song AG. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2019:8. doi: 10.3390/cells8080784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rizzo S, Petrella F, Politi LS, Wang P. Molecular Imaging of Stems Cells: In Vivo Tracking and Clinical Translation. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:1783841. doi: 10.1155/2017/1783841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bose RJC, Mattrey RF. Accomplishments and challenges in stem cell imaging in vivo. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24:492–504. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yahyapour R, Farhood B, Graily G, Rezaeyan A, Rezapoor S, Abdollahi H, Cheki M, Amini P, Fallah H, Najafi M, Motevaseli E. Stem Cell Tracing Through MR Molecular Imaging. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;15:249–261. doi: 10.1007/s13770-017-0112-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang P, Petrella F, Nicosia L, Bellomi M, Rizzo S. Molecular Imaging of Stem Cell Transplantation for Liver Diseases: Monitoring, Clinical Translation, and Theranostics. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4058656. doi: 10.1155/2016/4058656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cassidy PJ, Radda GK. Molecular imaging perspectives. J R Soc Interface. 2005;2:133–144. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2005.0040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lu FM, Yuan Z. PET/SPECT molecular imaging in clinical neuroscience: recent advances in the investigation of CNS diseases. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015;5:433–447. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.03.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.da Silva HR, Mamani JB, Nucci MP, Nucci LP, Kondo AT, Fantacini DMC, de Souza LEB, Picanço-Castro V, Covas DT, Kutner JM, de Oliveira FA, Hamerschlak N, Gamarra LF. Triple-modal imaging of stem-cells labeled with multimodal nanoparticles, applied in a stroke model. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11:100–123. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Maxwell DJ, Bonde J, Hess DA, Hohm SA, Lahey R, Zhou P, Creer MH, Piwnica-Worms D, Nolta JA. Fluorophore-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticle labeling and analysis of engrafting human hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26:517–524. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen G, Lin S, Huang D, Zhang Y, Li C, Wang M, Wang Q. Revealing the Fate of Transplanted Stem Cells In Vivo with a Novel Optical Imaging Strategy. Small. 2018;14 doi: 10.1002/smll.201702679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chen PJ, Kang YD, Lin CH, Chen SY, Hsieh CH, Chen YY, Chiang CW, Lee W, Hsu CY, Liao LD, Fan CT, Li ML, Shyu WC. Multitheragnostic Multi-GNRs Crystal-Seeded Magnetic Nanoseaurchin for Enhanced In Vivo Mesenchymal-Stem-Cell Homing, Multimodal Imaging, and Stroke Therapy. Adv Mater. 2015;27:6488–6495. doi: 10.1002/adma.201502784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang C, Lin G, Luan Y, Ding J, Li PC, Zhao Z, Qian C, Liu G, Ju S, Teng GJ. HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 2 silencing using siRNA delivered by MRI-visible nanoparticles improves therapy efficacy of transplanted EPCs for ischemic stroke. Biomaterials. 2019;197:229–243. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.05.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yun S, Shin TH, Lee JH, Cho MH, Kim IS, Kim JW, Jung K, Lee IS, Cheon J, Park KI. Design of Magnetically Labeled Cells (Mag-Cells) for in Vivo Control of Stem Cell Migration and Differentiation. Nano Lett. 2018;18:838–845. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b04089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Strohschein K, Radojewski P, Winkler T, Duda GN, Perka C, von Roth P. In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging - A Suitable Method to Track Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in a Skeletal Muscle Trauma. Open Orthop J. 2015;9:262–269. doi: 10.2174/1874325001509010262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lim S, Yoon HY, Jang HJ, Song S, Kim W, Park J, Lee KE, Jeon S, Lee S, Lim DK, Kim BS, Kim DE, Kim K. Dual-Modal Imaging-Guided Precise Tracking of Bioorthogonally Labeled Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Mouse Brain Stroke. ACS Nano. 2019;13:10991–11007. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b02173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang F, Duan X, Lu L, Zhang X, Chen M, Mao J, Cao M, Shen J. In Vivo Long-Term Tracking of Neural Stem Cells Transplanted into an Acute Ischemic Stroke model with Reporter Gene-Based Bimodal MR and Optical Imaging. Cell Transplant. 2017;26:1648–1662. doi: 10.1177/0963689717722560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lu L, Wang Y, Cao M, Chen M, Lin B, Duan X, Zhang F, Mao J, Shuai X, Shen J. A novel polymeric micelle used for in vivo MR imaging tracking of neural stem cells in acute ischemic stroke. RSC Adv. 2017;7:15041–15052. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lin BL, Zhang JZ, Lu LJ, Mao JJ, Cao MH, Mao XH, Zhang F, Duan XH, Zheng CS, Zhang LM, Shen J. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Complexed Cationic Amylose for In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging Tracking of Transplanted Stem Cells in Stroke. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2017:7. doi: 10.3390/nano7050107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Duan X, Lu L, Wang Y, Zhang F, Mao J, Cao M, Lin B, Zhang X, Shuai X, Shen J. The long-term fate of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with magnetic resonance imaging-visible polymersomes in cerebral ischemia. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:6705–6719. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S146742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Argibay B, Trekker J, Himmelreich U, Beiras A, Topete A, Taboada P, Pérez-Mato M, Vieites-Prado A, Iglesias-Rey R, Rivas J, Planas AM, Sobrino T, Castillo J, Campos F. Intraarterial route increases the risk of cerebral lesions after mesenchymal cell administration in animal model of ischemia. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40758. doi: 10.1038/srep40758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang F, Duan X, Lu L, Zhang X, Zhong X, Mao J, Chen M, Shen J. In Vivo Targeted MR Imaging of Endogenous Neural Stem Cells in Ischemic Stroke. Molecules. 2016;21 doi: 10.3390/molecules21091143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Duan X, Wang Y, Zhang F, Lu L, Cao M, Lin B, Zhang X, Mao J, Shuai X, Shen J. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide-Loaded Cationic Polymersomes for Cellular MR Imaging of Therapeutic Stem Cells in Stroke. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2016;12:2112–2124. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2016.2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tan C, Shichinohe H, Abumiya T, Nakayama N, Kazumata K, Hokari M, Hamauchi S, Houkin K. Short-, middle- and long-term safety of superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled allogeneic bone marrow stromal cell transplantation in rat model of lacunar infarction. Neuropathology. 2015;35:197–208. doi: 10.1111/neup.12180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bai YY, Wang L, Peng XG, Wang YC, Chang D, Zheng S, Ding J, Li C, Ju S. Non-invasive monitoring of transplanted endothelial progenitor cells in diabetic ischemic stroke models. Biomaterials. 2015;40:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Park JW, Ku SH, Moon HH, Lee M, Choi D, Yang J, Huh YM, Jeong JH, Park TG, Mok H, Kim SH. Cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles for therapeutic engineering and in vivo monitoring of mesenchymal stem cells in cerebral ischemia model. Macromol Biosci. 2014;14:380–389. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201300340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Janowski M, Walczak P, Kropiwnicki T, Jurkiewicz E, Domanska-Janik K, Bulte JW, Lukomska B, Roszkowski M. Long-term MRI cell tracking after intraventricular delivery in a patient with global cerebral ischemia and prospects for magnetic navigation of stem cells within the CSF. PLoS One. 2014;9:e97631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang L, Wang Y, Tang Y, Jiao Z, Xie C, Zhang H, Gu P, Wei X, Yang GY, Gu H, Zhang C. High MRI performance fluorescent mesoporous silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for tracking neural progenitor cells in an ischemic mouse model. Nanoscale. 2013;5:4506–4516. doi: 10.1039/c3nr00119a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tarulli E, Chaudhuri JD, Gretka V, Hoyles A, Morshead CM, Stanisz GJ. Effectiveness of micron-sized superparamagnetic iron oxide particles as markers for detection of migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a stroke model. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37:1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Liu H, Cao J, Zhang H, Qin S, Yu M, Zhang X, Wang X, Gao Y, Wilson JX, Huang G. Folic acid stimulates proliferation of transplanted neural stem cells after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24:1817–1822. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang Y, Xu F, Zhang C, Lei D, Tang Y, Xu H, Zhang Z, Lu H, Du X, Yang GY. High MR sensitive fluorescent magnetite nanocluster for stem cell tracking in ischemic mouse brain. Nanomedicine. 2011;7:1009–1019. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2011.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Song M, Kim Y, Kim Y, Ryu S, Song I, Kim SU, Yoon BW. MRI tracking of intravenously transplanted human neural stem cells in rat focal ischemia model. Neurosci Res. 2009;64:235–239. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lee ES, Chan J, Shuter B, Tan LG, Chong MS, Ramachandra DL, Dawe GS, Ding J, Teoh SH, Beuf O, Briguet A, Tam KC, Choolani M, Wang SC. Microgel iron oxide nanoparticles for tracking human fetal mesenchymal stem cells through magnetic resonance imaging. Stem Cells. 2009;27:1921–1931. doi: 10.1002/stem.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kim D, Chun BG, Kim YK, Lee YH, Park CS, Jeon I, Cheong C, Hwang TS, Chung H, Gwag BJ, Hong KS, Song J. In vivo tracking of human mesenchymal stem cells in experimental stroke. Cell transplant. 2008;16:1007–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Guzman R, Uchida N, Bliss TM, He D, Christopherson KK, Stellwagen D, Capela A, Greve J, Malenka RC, Moseley ME, Palmer TD, Steinberg GK. Long-term monitoring of transplanted human neural stem cells in developmental and pathological contexts with MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:10211–10216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608519104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Syková E, Jendelová P. Magnetic resonance tracking of transplanted stem cells in rat brain and spinal cord. Neurodegener Dis. 2006;3:62–67. doi: 10.1159/000092095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhu J, Wu X, Zhang HL. Adult neural stem cell therapy: expansion in vitro, tracking in vivo and clinical transplantation. Curr Drug Targets. 2005;6:97–110. doi: 10.2174/1389450053345055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sykova E, Jendelova P. In vivo tracking of stem cells in brain and spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res. 2007;161:367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)61026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Syková E, Jendelová P, Herynek V. MR tracking of stem cells in living recipients. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;549:197–215. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-931-4_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang G, Khan AA, Wu H, Chen L, Gu Y, Gu N. The Application of Nanomaterials in Stem Cell Therapy for Some Neurological Diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19:279–298. doi: 10.2174/1389450118666170328115801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kim DH, Seo YK, Thambi T, Moon GJ, Son JP, Li G, Park JH, Lee JH, Kim HH, Lee DS, Bang OY. Enhancing neurogenesis and angiogenesis with target delivery of stromal cell derived factor-1α using a dual ionic pH-sensitive copolymer. Biomaterials. 2015;61:115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Boncoraglio GB, Ranieri M, Bersano A, Parati EA, Del Giovane C. Stem cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;5:CD007231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007231.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Goldman SA. Stem and Progenitor Cell-Based Therapy of the Central Nervous System: Hopes, Hype, and Wishful Thinking. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18:174–188. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Vu Q, Xie K, Eckert M, Zhao W, Cramer SC. Meta-analysis of preclinical studies of mesenchymal stromal cells for ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2014;82:1277–1286. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Borlongan CV. Age of PISCES: stem-cell clinical trials in stroke. Lancet. 2016;388:736–738. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Muir KW. Clinical trial design for stem cell therapies in stroke: What have we learned? Neurochem Int. 2017;106:108–113. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yoo KH, Jang IK, Lee MW, Kim HE, Yang MS, Eom Y, Lee JE, Kim YJ, Yang SK, Jung HL, Sung KW, Kim CW, Koo HH. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human tissues. Cell Immunol. 2009;259:150–156. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2009.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sohni A, Verfaillie CM. Mesenchymal stem cells migration homing and tracking. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:130763. doi: 10.1155/2013/130763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Musiał-Wysocka A, Kot M, Majka M. The Pros and Cons of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Transplant. 2019;28:801–812. doi: 10.1177/0963689719837897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kassem M. Mesenchymal stem cells: biological characteristics and potential clinical applications. Cloning Stem Cells. 2004;6:369–374. doi: 10.1089/clo.2004.6.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sibov TT, Pavon LF, Oliveira DM, Marti LC, Guilhen DD, Amaro E, Jr, Gamarra LF. Characterization of adherent umbilical cord blood stromal cells regarding passage, cell number, and nano-biomarking utilization. Cell Reprogram. 2010;12:391–403. doi: 10.1089/cell.2009.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Alvarim LT, Nucci LP, Mamani JB, Marti LC, Aguiar MF, Silva HR, Silva GS, Nucci-da-Silva MP, DelBel EA, Gamarra LF. Therapeutics with SPION-labeled stem cells for the main diseases related to brain aging: a systematic review. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:3749–3770. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S65616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sibov TT, Pavon LF, Miyaki LA, Mamani JB, Nucci LP, Alvarim LT, Silveira PH, Marti LC, Gamarra L. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells labeled with multimodal iron oxide nanoparticles with fluorescent and magnetic properties: application for in vivo cell tracking. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:337–350. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S53299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hess DC, Wechsler LR, Clark WM, Savitz SI, Ford GA, Chiu D, Yavagal DR, Uchino K, Liebeskind DS, Auchus AP, Sen S, Sila CA, Vest JD, Mays RW. Safety and efficacy of multipotent adult progenitor cells in acute ischaemic stroke (MASTERS): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:360–368. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]