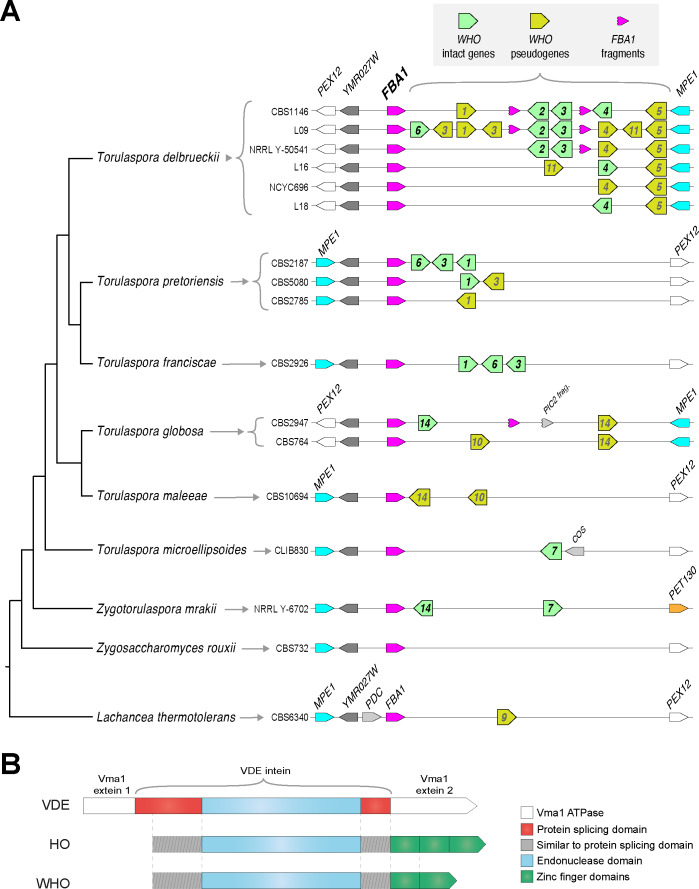
Figure 1. Genomic organization and domain structure of WHO genes.
(A) Polymorphic clusters of WHO genes and pseudogenes downstream of FBA1 in Torulaspora species. Multiple alleles are shown for T. delbrueckii, T. pretoriensis, and T. globosa. WHO genes are indicated by their family number. Fragments of the 3’ end of the FBA1 gene are marked. Genomic views are schematic and not drawn to scale. The phylogenetic tree is based on Shen et al. (2018). (B) Domain structure of HO, VDE and WHO proteins. The protein splicing domain is formed from two regions of the protein that flank the endonuclease domain (Moure et al., 2002).