Abstract
Background
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a life-threatening cerebrovascular disease. Neuroinflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of HIE, in which microglia are key cellular mediators in the regulation of neuroinflammatory processes. Colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), a specific endogenous ligand of CSF1 receptor (CSF1R), is crucial in microglial growth, differentiation, and proliferation. Recent studies showed that the activation of CSF1R with CSF1 exerted anti-inflammatory effects in a variety of nervous system diseases. This study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of recombinant human CSF1 (rh-CSF1) and the underlying mechanisms in a rat model of HIE.
Methods
A total of 202 10-day old Sprague Dawley rat pups were used. HI was induced by the right common carotid artery ligation with subsequent exposure of 2.5-h hypoxia. At 1 h and 24 h after HI induction, exogenous rh-CSF1 was administered intranasally. To explore the underlying mechanism, CSF1R inhibitor, BLZ945, and phospholipase C-gamma 2 (PLCG2) inhibitor, U73122, were injected intraperitoneally at 1 h before HI induction, respectively. Brain infarct area, brain water content, neurobehavioral tests, western blot, and immunofluorescence staining were performed.
Results
The expressions of endogenous CSF1, CSF1R, PLCG2, protein kinase C epsilon type (PKCε), and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) were gradually increased after HIE. Rh-CSF1 significantly improved the neurological deficits at 48 h and 4 weeks after HI, which was accompanied by a reduction in the brain infarct area, brain edema, brain atrophy, and neuroinflammation. Moreover, activation of CSF1R by rh-CSF1 significantly increased the expressions of p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB, but inhibited the activation of neutrophil infiltration, and downregulated the expressions of IL-1β and TNF-α. Inhibition of CSF1R and PLCG2 abolished these neuroprotective effects of rh-CSF1 after HI.
Conclusions
Our findings demonstrated that the activation of CSF1R by rh-CSF1 attenuated neuroinflammation and improved neurological deficits after HI. The anti-inflammatory effects of rh-CSF1 partially acted through activating the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway after HI. These results suggest that rh-CSF1 may serve as a potential therapeutic approach to ameliorate injury in HIE patients.
Keywords: Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, CSF1, CSF1R, PLCG2, Neuroinflammation, Microglia
Introduction
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a life-threatening cerebrovascular disease which is associated with high morbidity and mortality in infants, resulting in life-long neurodevelopmental impairment, such as cerebral palsy, mental retardation, cognitive deficits, epilepsy, and learning and visual impairments [1–3]. The incidence of HIE in live births is 0.1–0.8% in developed countries, but may vary, with rates as high as 2.6% in undeveloped countries [4]. Currently, therapeutic hypothermia, given shortly after birth, can improve functions and minimize symptoms induced by HIE [5]. However, 50% of infants still suffer from severe neurodevelopmental impairment or even death [6]. The cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the pathogenesis of HIE, specifically post-HI neuroinflammation, are complex and remain unclear.
Colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), also known as macrophage-CSF (M-CSF), is a secreted cytokine that is essential to regulate the growth and differentiation of macrophage lineage cells (e.g., macrophages, osteoclasts, and microglia) [7, 8]. In the central nervous system (CNS), CSF1 is primarily expressed on neurons, microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes [7, 9], which can regulate neuroinflammation, reconstruct damaged white matter, and maintain social behavior [10, 11]. The biological effects of CSF1 are mediated by CSF1 receptor (CSF1R), a unique tyrosine kinase transmembrane receptor [12]. CSF1 binding activates CSF1R through a process of oligomerization and trans-phosphorylation [13]. CSF1R is primarily expressed on microglial cells in the brain [14], with a minimal expression on neurons in the hippocampus and cortex [15]. Neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in the brain injury of neonatal HIE [16]. Microglia are the brain-resident macrophages, and their activation is the initial step in the inflammatory responses of the CNS diseases, such as stroke, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) [17–19]. CSF1R is essential for microglia viability [15, 20], which not only regulates the development, proliferation, and maintenance of microglia but also plays a major role in neuroinflammation [21, 22]. Moreover, the expression and activity of CSF1R are increased after brain damage [15, 23]. Wlodarczyk et al. reported that stimulation of CSF1R by recombinant mouse CSF1 could induce the expansion of CD11c positive microglia, leading to improvement of EAE symptoms and less demyelination [24]. In the experimental stroke, microglia play neuroprotective roles by phagocytosing neutrophils and inhibiting reactive astrocyte-induced inflammatory processes [25]. Depletion of microglia by CSF1R inhibitor exacerbated ischemic infarction and neurological deficits following ischemic stroke [26]. However, the effects of CSF1R activation have never been investigated in the setting of HIE.
Phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCG2) belongs to the family of phospholipase C-gamma, which is the downstream molecule of the CSF1R [27]. Previous studies have demonstrated that PLCG2 was required for CSF1-induced differentiation of monocytes, microglia, immune, inflammatory responses [28, 29]. PLCG2 phosphorylation leads to an increase in production of the cellular signaling molecules, diacylglycerol (DAG), and inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate (IP3), which further promotes a wide range of downstream signals, including the phosphorylation of protein kinase C (PKC) family members, such as PKC epsilon (PKCε) [30, 31]. PKCε, a serine/threonine kinase isoform of the PKC family, exerts wide-scale mitochondrial protection and has an essential neuroprotective function against ischemic injury [32, 33]. It has been reported that PKCε has an anti-inflammatory role in the CNS by regulating the functions of microglia and astrocytes [34, 35]. The activation of PKCε influences a number of signaling mechanisms, such as modulating the phosphorylation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (CREB) [36]. CREB has been proved to be a transcription factor that participates in anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammation, and other pathological processes in cerebral ischemia injury, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and HIE [37, 38]. CREB is an important downstream signaling molecule that mediates the biological effects of CSF1 in neurons and macrophages. Recombinant human CSF1 (rh-CSF1) reduced excitotoxin-induced neuronal loss and gliosis via the phosphorylation of CREB, thus attenuating brain injury [15].
In this present study, we explored the role of CSF1 in HIE. We demonstrated, for the first time, that intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 attenuated ischemia-induced neuroinflammation via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway in a rat model of neonatal HIE (shown in Fig. s1).
Methods
Animals
In this study, unsexed Sprague Dawley rat pups were purchased from Envigo Labs (Livermore, CA) with their mothers. Ten-day old rat pups (n = 202, weight = 16–22 g) were used. All animals were kept in a 12 h light/dark cycle, in a controlled room environment, with libitum access to breast milk, water, and food. All experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Loma Linda University, which comply with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of laboratory Animals in Neuroscience Research and ARRIVE guidelines.
HIE model
The animal model of neonatal HIE was performed as previously described [39]. Briefly, rat pups were placed into a temperature-controlled chamber and anesthetized with isoflurane (3% induction, 2.5% maintenance). The temperature was controlled using incubators and a heated blanket during the operative and postoperative period. The rat neck was swabbed with alcohol and draped using standard sterile techniques after anesthesia induction. A small lateral incision (approximately 3–5 mm in length) was made to the right of the midline, across the sagittal plane. Next, the right common carotid artery was isolated and gently separated from its surrounding structures. The right carotid artery was double ligated with 5.0 surgical silk and severed between the ligatures. Gentle pressure was used to control bleeding, and the skin was closed with sutures. All surgeries were completed in 5–9 min. After the surgical procedure, the rats were allowed to recover from anesthesia for 1 h on temperature-controlled heating blankets. Pups were then placed in a 500 ml airtight jar in a 37 °C water bath and were exposed for 2.5 h to a gas mixture of 8% oxygen and 92% nitrogen, which was delivered into the jar via inlet and outlet portals. For the sham animals, the right common carotid artery was subjected to exposure, but without ligation, cutting, or exposure to hypoxic conditions. Thereafter, the animals were returned to their mothers and left in the incubator for 48 h.
Experimental design
Experiment 1
To characterize the time course expressions of endogenous CSF1, CSF1R, PLCG2, PKCε, and CREB after HI, the rats were randomly divided into 7 groups (n = 6/group): Sham, 6 h HI, 12 h HI, 24 h HI, 48 h HI, 72 h HI, and 7 d HI. The right (ipsilateral) brain samples were collected for western blot analysis. The rats in the sham group were sacrificed at 24 h after HI.
Experiment 2
To evaluate the neuroprotective effects of rh-CSF1 treatment in HIE, the optimal dose of rh-CSF1 treatment for HI injury was tested. Rats were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 6/group): Sham, HI + Vehicle, HI + rh-CSF1 (40 μg/kg), HI + rh-CSF1 (80 μg/kg), and HI + rh-CSF1 (160 μg/kg). Rats were administered intranasally with rh-CSF1 or vehicle (double distilled water, DDH2O) at 1 h after HI induction followed by one more injection at 24 h after HI. Infarct volume, brain edema, short-term neurobehavioral tests (negative geotaxis), and body weights were evaluated at 48 h after HI.
Experiment 3
To evaluate CSF1 and CSF1R expressions and characterize the expression of exogenous rh-CSF1 in the rat brain after intranasal administration at 48 h after HI. Rats were randomly divided into 3 groups (n = 4/group): Sham, HI + Vehicle, and HI + rh-CSF1 (optimal dose). Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1), a microglia marker, was co-stained with CSF1 or CSF1R to determine colocalization of microglia with CSF1 or CSF1R. Immunofluorescence staining and western blot were conducted to determine the expression of rh-CSF1 in rat brain tissues.
Experiment 4
To evaluate the long-term effects of exogenous rh-CSF1 treatment, the rats were randomly divided into 3 groups (n = 8/group): Sham, HI + Vehicle, and HI + rh-CSF1 (optimal dose). Neurobehavioral tests including Foot-fault, Rotarod, and Morris water maze were performed at 4 weeks after HI, after which the rats were sacrificed. The brains were removed and cut into ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres, which were then weighed separately, and subsequently prepared for Nissl staining.
Experiment 5
To assess whether CSF1R was involved in the underlying mechanisms of rh-CSF1-mediated neuroprotective effects, the CSF1R inhibitor, BLZ945, was used to inhibit CSF1R. Rats were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 6/group): Sham, HI + vehicle (vehicle of rh-CSF1, DDH2O), HI + rh-CSF1, HI + rh-CSF1 + dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Vehicle of BLZ945), and HI + rh-CSF1 + BLZ945. Rh-CSF1 (optimal dose) or DDH2O were administered intranasally at 1 h and 24 h after HI induction. BLZ945 or DMSO was injected intraperitoneally at 1 h before HI induction. Infarct volume, brain edema, negative geotaxis, body weight, western blot, and immunofluorescence staining were examined at 48 h after HI.
Experiment 6
To assess whether PLCG2 was involved in the underlying mechanisms of rh-CSF1-mediated neuroprotective effects, U73122 was used to inhibit the activity of PLCG2. Rats were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 6/group, shared with Experiment 5 except for the group of HI+rh-CSF1+U73122): Sham, HI + vehicle (vehicle of rh-CSF1, DDH2O), HI + rh-CSF1, HI + rh-CSF1 + DMSO (Vehicle of U73122), and HI + rh-CSF1 + U73122. Rh-CSF1 (optimal dose) or DDH2O was administered intranasally at 1 h and 24 h post-HI induction. U73122 (30 mg/kg) or DMSO was injected intraperitoneally at 1 h before HI. Infarct volume, brain edema, negative geotaxis, body weight, western blot, and immunofluorescence staining were examined at 48 h post-HI.
The rectal temperature, heart rate, and respiration rate of each group were measured in Experiment 2, 5, and 6.
Drug administration
Rh-CSF1 (40, 80, 160 μg/kg, Abcam, USA) or vehicle of rh-CSF1 (DDH2O) was administered intranasally at 1 h and 24 h after HI. A total of 5 μl of rh-CSF1 or DDH2O was given every 2 min in alternating nares. BLZ945 (60 mg/kg, Cayman chemical, USA), U73122 (30 mg/kg, Cayman chemical, USA), or DMSO was injected intraperitoneally at 1 h before HI.
Measurement of infracted area
At 48 h after HI, the rat pups were anesthetized and euthanized, followed by immediate transcardiac perfusion using 20 mL of chilled phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 0.01 M, pH 7.4). The brains were removed, sectioned into slices (2 mm), and stained with 2% solution 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride monohydrate (TTC) (Sigma Aldrich Inc., USA) for 5 min and then washed in PBS [40]. The brain slices were digitally photographed to outline and the total area of contralateral hemispheres and non-infarcted area of ipsilateral hemispheres for each slice was measured using Image J software (NIH, USA). The infarcted areas were calculated using the following formula: [(total area of contralateral hemisphere) − (area of un-infarcted area of ipsilateral hemisphere)] / (total area of contralateral hemisphere × 2). The average value was taken to represent the percentage of infarcted area for that animal.
Brain water content
Brain water content was performed as previously described [41]. The rat pups were anesthetized and euthanized at 48 h after HI, and the brain hemispheres were quickly removed and separated into ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. The right (ipsilateral) cerebral hemispheres were weighed immediately to obtain the wet weight and then dried at 100°C for 48 h. The dried brain was re-weighed. The percentage of brain water content was calculated as (wet weight − dry weight) /wet weight × 100%.
Neurological evaluation
Negative geotaxis test was performed in a blinded setup at 48 h after HI for evaluating short-term neurological function. Foot-fault, Rotarod, and Morris water maze tests were performed in a blinded setup at 4 weeks after HI for evaluating long-term neurological function.
Negative geotaxis test
Negative geotaxis test was performed by placing rat pups on a sloping board (45°) with their head facing downward. Next, the time was recorded to determine the length of time it took for the pups to rotate their body so that they are facing upward. The maximum testing time was 60 s, and any recordings exceeding 60 s were documented as 60 s.
Rotarod test
The Rotarod test was performed by placing the rat pups on a rotating horizontal rod (Columbus Instruments Rotamex, USA), then the times were recorded when the rats fell. The rotation speed started from 5 or 10 rpm separately and accelerated 2 rpm every 5 s. The maximum testing time was 60 s, and any times exceeding 60 s were recorded as 60 s [42].
Foot-fault test
The Foot-fault test was performed by placing the rat pups on a horizontal grid floor (square size 20–40 cm with a mesh size of 4 cm2) elevated 1 m above ground for 1 min. A Foot-fault was defined as when the animal inaccurately placed a forelimb or hindlimb, causing the paw to fall down between the grid bars. The number of foot-faults for each rat was recorded using video equipment and analyzed by an investigator blind to the experimental groups.
Morris water maze test
The Morris water maze test was performed on days 23–27 after HI to evaluate spatial learning capacity and memory, as previously shown [43]. A hidden platform was submerged in a pool of water using visual cues around the room. The rats underwent a 6-day test, consisting of 5 trials in both cued and hidden tests over 5 days, and a probe trial being conducted on the final day. None of the trials lasted more than 60 s, a 10-min interval between consecutive trials was allotted for rest. On day 1, the rats were trained using a visible platform in the cued test (block 1). If the rats had not found the platform in 60 s, they were manually guided to the platform. On days 2–5, the rats were required to find a platform submerged 1 cm below the water in the memory test (blocks 2-5), if the rats had not discovered the platform in 60 s, they were manually guided to the platform. On day 6, the platform was removed in the probe trial, and the time that each rat took in the platform quadrant was measured (block 6). A video recording system-2000 (San Diego Instruments Inc, USA) traced all of the animals’ activities and the swim paths to quantify the total distance of swimming, latency to reach the platform and swimming speed.
Western blotting analysis
Western blot was processed as described previously [44]. After TTC staining and images were recorded at 48 h after HI, the brain slices were divided into ipsilateral and contralateral cerebrums and stored immediately in a −80 °C freezer for future use. The right/ipsilateral hemisphere tissue was homogenized in RIPA lysis buffer (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA) with protease inhibitor cocktail for 15 min and then centrifuged at 14,000g at 4 °C for 30 min. The supernatant was collected, and protein quantification was performed using a detergent compatible assay (Bio-Rad, DC™ Protein Assay). Equal amounts of protein were loaded onto a 10%~12% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel and electrophoresed. Next, they were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, which were blocked with 5% non-fat blocking grade milk (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA) and incubated at 4 °C with the following primary antibodies: anti-CSF1 (reacts with human and rats, 1:1000, Abcam, USA), anti-CSF1 (reacts specifically with human, 1:500, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), anti-CSF1R (1:500, LSBio, USA), anti-p-CSF1R (1:1000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), anti-PLCG2 (1:500, Novus biologicals, USA), anti-p-PLCG2 (1:1000, Abcam, USA), anti-PKCε (1:1000, Abcam, USA), anti-p-PKCε (1:1000, Abcam, USA), anti-CREB (1:1000, Abcam, USA), anti-p-CREB (1:1000, Abcam, USA), anti-interleukin (IL) -1β (1:1000, Abcam, USA), TNF-α (1:1000, Abcam, USA) and Goat anti-β-actin (1:3000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA). Then, the appropriate secondary antibodies (1:3000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA) were incubated at room temperature for 2 h. The membranes were probed with an ECL Plus chemiluminescence reagent kit (Amersham Biosciences, USA). The specific bands were visualized by an ECL Plus chemiluminescence reagent kit (Amersham Biosciences, USA). The relative density of protein was analyzed using Image J software (NIH, USA).
Histological analysis
Rat pups were transcardially perfused under deep anesthesia with cold PBS and 10% formalin at 2 days or 28 days after HI. The brains were removed and fixed in 10% formalin for 24 h, and then stored in a 30% sucrose solution at 4 °C until they sank. After being embedded into OCT compound (Scigen Scientific, USA) and frozen, the coronal sections were cut sequentially at 8–10 μm thickness for immunofluorescence (2 days after HI) and 15–20 μm for Nissl staining (28 days after HI) at −20 °C with a cryostat (LM3050S; Leica Microsystems, Germany).
Immunofluorescence staining
Immunofluorescence staining was performed as described previously [45]. The sections were permeabilized with 0.3% Triton X-100 for 10 min and then blocked with 5% donkey serum for 2 h at room temperature. Subsequently, sections were incubated at 4 °C overnight with primary antibodies: Iba-1 (1:200, Abcam, USA), anti-CSF1 (1:100, Abcam, USA), anti-CSF1R (1:100, LSBio, USA), IL-1β (1:200, Abcam, USA), myeloperoxidase (MPO) (1:200, Abcam, USA). The following day, the sections were incubated with the appropriate fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:150) for 1 h at room temperature and mounted using Vectashield Antifade Mounting Medium with DAPI (Vector Laboratories Inc., USA). The stained sections were then captured under a fluorescence microscope (Leica DMi8, Leica Microsystems, Germany), and the staining positive cells were counted and averaged from the 5 fields of view within peri-lesion area under the microscope.
Nissl staining
Nissl staining was performed to evaluate brain tissue loss. The sections were successively dehydrated in 95% and 70% ethanol for 2 min and then stained with 0.5% cresyl violet (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) for 2 min, followed by dehydration with 100% ethanol and xylene for 2 min twice, respectively, before the sections were mounted with DPX (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). The sections were imaged using a microscope (Olympus-BX51) equipped with MagnaFire SP 2.1B software (Olympus). A total of 3 slices were used from each brain to determine the average percent of tissue loss, which was measured using Image J software (NIH, USA). The percentage of brain tissue loss was calculated using the same equation for the infarct area. Brain weight loss was calculated using the following formula: weight of contralateral hemisphere-weight of the ipsilateral hemisphere.
Statistical analysis
The data were presented as mean ± SD and plotted using Graph Pad Prism 8 (Graph Pad Software, USA). Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS v. 21.0 software (IBM, USA). Single-factor analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA)) was used followed by multiple comparisons among groups using the Tukey post hoc test. Student’s t test was used to compare the differences between the two groups. Differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Expression levels of endogenous p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB were upregulated in a time-dependent manner after HI
As shown in Fig. 1, the endogenous expression levels of p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB were upregulated after HI, and peaked at 24 h when compared with the sham group (P < 0.05).
Fig. 1.
Temporal expression of endogenous p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB in the ipsilateral hemisphere brain after HI. a Representative western blot bands of the time course. b-g Western blot data analysis showed that endogenous expression levels of p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB were upregulated over 7 d after HI, starting at 6 h and peaking at 24 h after HI. *P < 0.05 vs sham; #P < 0.05 vs 6 h HI; @P < 0.05 vs 12 h HI; $P < 0.05 vs 24 h HI. Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 6 in each group
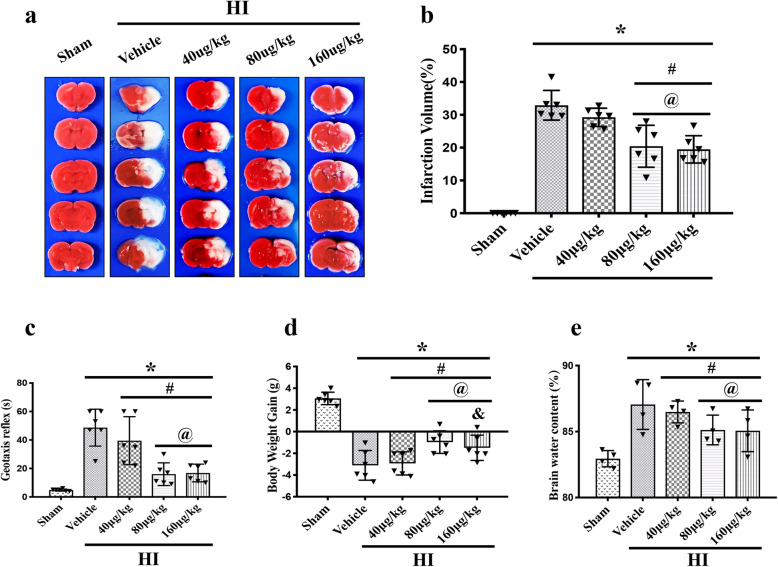
Intranasal administration of exogenous rh-CSF1 reduced infarcted area, brain edema, improved short-term neurological deficits and reduced body weight loss at 48 h after HI
TTC staining (Fig. 2a and b) revealed that no significant differences were found regarding the infarcted area in the low dose group (40 μg/kg) when compared with the vehicle group (P > 0.05). Medium (80 μg/kg) and high (160 μg/kg) doses of rh-CSF1 treatment significantly reduced the percentage of the infarcted area when compared with the low dose and vehicle groups (P < 0.05).
Fig. 2.
Effect of intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 on brain infarcted area, brain edema, short-term neurological function and body weight at 48 h after HI. a–b TTC staining showed that medium (80 μg/kg) and high (160 μg/kg) dose of rh-CSF1 significantly reduced the infarcted area when compared with the low (40 μg/kg) dose and vehicle. c Geotaxis reflex test showed that all HI animals had a significantly longer reflex time than the sham group. All three doses of rh-CSF1 treatments significantly improved geotaxis reflex performance compared with the vehicle-treated HI animals. In addition, the medium (80 μg/kg) and high (160 μg/kg) doses of rh-CSF1 resulted in a significantly shorter reflex time than the low (40 μg/kg) dose. d All HI animals showed significant weight loss compared with the sham group. All three doses of rh-CSF1 treatment significantly reduced the weight loss with the best effects in medium-dose group (80 μg/kg). e All HI animals showed significant brain water content increase compared with the sham group. The medium (80 μg/kg) and high (160 μg/kg) doses of rh-CSF1 treatment significantly reduced brain edema compared with the vehicle and low (40 μg/kg) dose-treated HI animals. *P < 0.05 vs sham; #P < 0.05 vs vehicle; @P < 0.05 vs rh-CSF1 (40 μg/kg); &P < 0.05 vs rh-CSF1 (80 μg/kg); Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 6 in each group
Negative geotaxis tests (Fig. 2c) showed that pups spent more time rotating to the upward head position when compared to the sham group at 48 h after HI (P < 0.05). Rh-CSF1 significantly improved neurological function compared with the vehicle-treated animals. Medium and high doses of rh-CSF1 decreased the reflex time significantly when compared with the low dose and vehicle groups (P < 0.05).
Body weight measurement results (Fig. 2d) showed that three doses of rh-CSF1 dose treatments (40, 80, and 160 μg/kg) significantly decreased body weight loss when compared with the vehicle group at 48 h after HI (P < 0.05), of which the medium dose group (80 μg/kg) showed the best performance when compared to the other two doses groups (P < 0.05). Thus, 80 μg/kg of rh-CSF1 was selected as the optimal dose and used for the remaining experiments.
Brain water content (Fig. 2e) showed that no significant difference was found regarding the brain edema in the low dose group (40 μg/kg) when compared with the vehicle group (P > 0.05). Medium (80 μg/kg) and high (160 μg/kg) doses of rh-CSF1 treatment significantly reduced brain edema when compared with the low dose and vehicle groups (P < 0.05).
Intranasal administration of exogenous rh-CSF1 resulted in the expression of human CSF1 in the rat brain at 48 h after HI
Immunofluorescence staining depicted the fluorescence staining of human CSF1 on the cell after intranasal administration of exogenous rh-CSF1 at 48 h after HI (Fig. 3a), and western blot data showed the bands of human CSF1 in the rat brain (Fig. 3b, c), but not in the sham group or vehicle groups. These results illustrated that exogenous rh-CSF1 could enter the rat brain tissue via the intranasal administration route.
Fig. 3.
Expression of exogenous rh-CSF1 in rat brain after intranasal administration at 48 h after HI. a Representative microphotographs of immunofluorescence staining depicted the human CSF1 expression in the rat brain after the intranasal administration of exogenous rh-CSF1. b Representative western blot bands showed the expression of human CSF1 in the rat brain after intranasal administration of exogenous rh-CSF1. c Quantitative analysis of western blot bands showed that there was a significant amount of human CSF1 in the rat brain after intranasal administration of exogenous rh-CSF1. Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 6 in each group
Double immunofluorescence staining showed the colocalization of CSF1 and CSF1R with microglia at 48 h after HI
Double immunofluorescence staining showed that CSF1 and CSF1R colocalized with the Iba-1 positive microglial at 48 h after HI. The expression of CSF1 and CSF1R on microglia was increased after HI including the vehicle group and rh-CSF1-treated animals when compared with the sham group. Intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 promoted proliferation and activation of microglia and further increased the expression of CSF1 and CSF1R on microglia when compared to the vehicle group (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Double immunofluorescence staining of CSF1 and CSF1R with Iba-1 in rat brain at 48 h after HI. a Representative microphotographs of CSF1 and CSF1R and Iba-1 staining in the ipsilateral cortex of rat brain. CSF1 and CSF1R were colocalized with Iba-1 positive microglia in the sham, vehicle, and rh-CSF1 treatment groups, respectively. b Brain slice of rats at 48 h after HI. The upper right panel of brain slice indicates the location for staining analysis (small blue box). c, d Quantitative analysis of CSF1-positive Iba-1 and CSF1R-positive Iba-1 cells in the ipsilateral cortex at 48 h after HI. Compared with the sham group, immunofluorescence staining showed an increase in expression of CSF1 and CSF1R on microglia in the vehicle group and rh-CSF1-treated animals. Intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 further increased the expression of CSF1 and CSF1R on microglia than that of the vehicle group. Green indicated CSF1 and CSF1R positive staining, red indicated Iba-1 positive microglia staining, and blue indicated DAPI positive nuclear staining. Merge showed the colocalization of CSF1 and CSF1R with microglia. *P < 0.05 vs sham; #P < 0.05 vs vehicle; Scale bar =50 μm; n = 4 in each group
Rh-CSF1 reduced neuroinflammation at 48 h after HI
Immunofluorescence staining of MPO and IL-1β were performed to evaluate the neuroinflammation. As shown in Fig. 5, the number of IL-1β/MPO-positive cells in the vehicle group was higher compared to the sham group at 48 h after HI, while intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 significantly reduced IL-1β/MPO-positive cells when compared to the vehicle group.
Fig. 5.
Effects of BLZ945 and U73122 co-administration with rh-CSF1 on immunofluorescence staining of MPO and IL-1β at 48 h after HI. Representative microphotographs (a-b) and quantification of (c-d) IL-1β and MPO positive cells showed the number of IL-1β/MPO-positive cells was significantly increased in all HI animals compared to shams. Rh-CSF1 treatment or Rh-CSF1 with DMSO significantly reduced the neuroinflammation, but such effects were reversed by either BLZ945 or U73122. *P < 0.05 vs. sham; #P < 0.05 vs. HI+ vehicle; @P < 0.05 vs. HI+ rh-CSF1 + DMSO; Scale bar =100 μm; Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 4 in each group
Rh-CSF1 improved long-term neurological deficits and reduced brain atrophy at 4 weeks after HI
In the rotarod test, animals in the vehicle group had significantly shorter falling latency at both 5 rpm and 10 rpm accelerating velocity tests when compared with the sham group at 4 weeks after HI. However, rh-CSF1 treatment markedly improved the rotarod performance of HIE rats at both 5 rpm and 10 rpm velocities when compared with the vehicle group (P < 0.05, Fig. 6a).
Fig. 6.
Effects of rh-CSF1 on brain atrophy and neurological functions at 4 weeks post-HI. Rh-CSF1 treatment group showed significant improvement in the rotarod test (a), foot fault test (b), and spatial memory loss in terms of swimming less distance to find the platform (c) when compared with the vehicle. Rh-CSF1 treatment group also showed a decrease in escape latency (d), and more time spent in the target quadrant during the probe trial (e-f) when compared with the vehicle. f Representative picture of swim track in Probe Trial. Representative microphotograph of Nissl staining showed brain tissue loss in the ipsilateral hemisphere (g). Rh-CSF1 treatment significantly reduced brain weight loss and the percent of tissue loss (h-i) when compared with the vehicle. *P < 0.05 vs sham; #P < 0.05 vs vehicle. Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 8 in each group
In the foot-fault test, animals in the vehicle group displayed more foot-faults on the contralateral side (left) when compared with the sham group at 4 weeks after HI. However, rh-CSF1 treatment markedly improved the foot-faults performance when compared with the vehicle group (P < 0.05, Fig. 6b).
In the water maze test, animals in the vehicle group swam a significantly greater distance in 1 min (Fig. 6c), had longer escape latency (Fig. 6d), and required more time to find the platform in the target quadrant during the probe trial (Fig. 6e, f) when compared with the sham group (P < 0.05). However, rh-CSF1 treatment improved memory and learning abilities with the decreased total swimming distance (Fig. 6c) and shorter time to find the platform (Fig. 6d), as well as more time spent in the platform quadrant (Fig. 6e, f) when compared with the vehicle group (P < 0.05).
Nissl staining was conducted to assess the brain atrophy at 4 weeks after HI. HI caused severe brain damage, characterized by significant brain tissue loss and brain weight loss of the ipsilateral hemisphere, while intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 significantly attenuated brain tissue loss and brain weight loss when compared with the vehicle group (P < 0.05, Fig. 6 g, h, i).
Inhibition of CSF1R and PLCG2 reversed the neuroprotective effects of rh-CSF1 at 48 h after HI
To evaluate whether CSF1 exerts its neuroprotective effects via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway, we used BLZ945 (the specific CSF1R inhibitor) and U73122 (the specific PLCG2 inhibitor) with intranasal rh-CSF1 treatment. Both inhibitors reversed the neuroprotective effects of rh-CSF1, resulted in an increase in the percentage of the infarcted area and brain edema when compared with the corresponding control groups (P < 0.05, Fig. 7a, b, e). The Negative geotaxis test showed that rats treated with either CSF1R or PLCG2 inhibitors with rh-CSF1 had significantly impaired neurological function when compared with the corresponding rh-CSF1 treatment control groups (P < 0.05, Fig. 7c). Consistently, there was a significant change in body weight in the animals treated by intraperitoneally injected with CSF1R or PLCG2 inhibitor with intranasal rh-CSF1 when compared with corresponding treatment control groups (P < 0.05, Fig. 7d). In addition, the intensity levels of MPO and IL-1β in both inhibitor groups were much higher compared to the corresponding treatment control groups at 48 h after HI (P < 0.05, Fig. 5).
Fig. 7.
Effects of CSF1R inhibitor BLZ945 and PLCG2 inhibitor U73122 co-administration with rh-CSF1 on infarction volume, brain edema, body weight, geotaxis reflex at 48 h after HI. a-b All HI animals have a significantly greater percentage of infarction compare to the sham group. Rh-CSF1 treatment or Rh-CSF1 with DMSO significantly reduced the infarction area, but such effects were reversed by either BLZ945 or U73122. c Geotaxis reflex performance was significantly worse in all HI animals compared to the sham group. Rh-CSF1 treatment or Rh-CSF1 with DMSO treatment groups improved this neurological deficit. However, either BLZ945 or U73122 significantly abolished the neurological benefit of rh-CSF1 treatment. d All of HI animals had significant body weight loss than shams. Rh-CSF1 treatment or Rh-CSF1 with DMSO significantly attenuated HI-induced body weight loss, which were reversed by BLZ945 or U73122. e All HI animals showed significant brain water content increase compared with the sham group. Rh-CSF1 treatment or Rh-CSF1 with DMSO significantly reduced HI-induced brain edema, which were reversed by BLZ945 or U73122. *P < 0.05 vs. sham; #P < 0.05 vs. HI+ vehicle; @P < 0.05 vs. HI+ rh-CSF1+ DMSO. Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 6 in each group
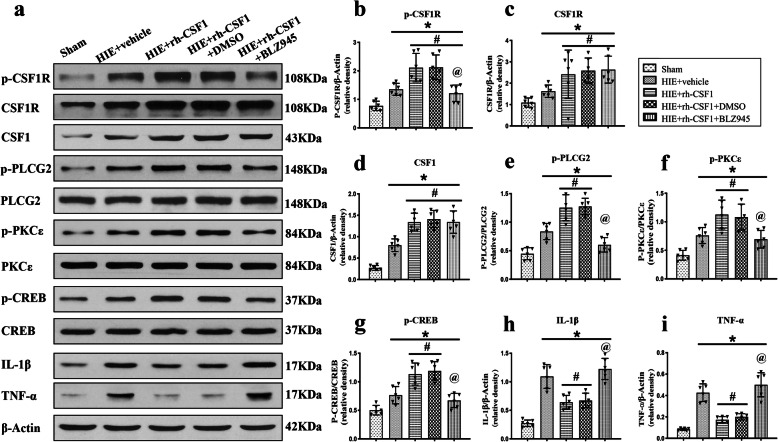
Inhibition of CSF1R and PLCG2 reversed the anti-neuroinflammation effect of rh-CSF1 through the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway at 48 h after HI
Western blot data showed that all target proteins and critical inflammatory cytokines, including CSF1, total-CSF1R, p-CSF1R, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, p-CREB, IL-1β, and TNF-α were upregulated at 48 h after HI when compared with the sham group. However, after rh-CSF1 treatment, the expressions of CSF1, total-CSF1R, p-CSF1R, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB further increased (P < 0.05, Fig. 8a-g), but the expression of pro-inflammatory IL-1β and TNF-α were decreased (P < 0.05, Fig. 8 h-i) when compared with the vehicle group. CSF1R inhibitor significantly decreased p-CSF1R expression, thereby abolishing the effects of rh-CSF1, evidenced by the attenuated levels of p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB, and increased expression levels of IL-1β and TNF-α compared with the DMSO group at 48 h after HI (P < 0.05, Fig. 8a-i).
Fig. 8.
CSF1R inhibitor BLZ945 abolished the anti-inflammatory effects of rh-CSF1 via CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway at 48 h after HI. a Representative western blot bands. b–i Densitometric quantification of p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2/PLCG2, p-PKCε/PKCε, p-CREB/CREB, IL-1β and TNF-α in the ipsilateral hemisphere showed that rh-CSF1 treatment upregulated the levels of p-CSF1R, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB, leading to less pro-inflammatory cytokines of IL-1β and TNF-α. BLZ945 significantly abolished such effects when administered with rh-CSF1. *P < 0.05 vs. sham; #P < 0.05 vs. HI+ Vehicle; @P < 0.05 vs. HI+ rh-CSF1 + DMSO; Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 6 in each group
To further clarify the role of downstream proteins, PLCG2 inhibitor was used. The western blot data showed that the PLCG2 inhibitor significantly decreased p-PLCG2 expression, thereby abolishing the effects of rh-CSF1, as evidenced by the attenuated level of p-PKCε and p-CREB, and increased expression levels of IL-1β and TNF-α compared with DMSO group at 48 h after HI (P < 0.05, Fig. 9a-i).
Fig. 9.
PLCG2 inhibitor U73122 abolished the anti-inflammatory effects of rh-CSF1 via CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway at 48 h after HI. a Representative western blot bands. b–i Densitometric quantification of p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2/PLCG2, p-PKCε/PKCε, p-CREB/CREB, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the ipsilateral hemisphere showed that U73122 significantly abolished the effects of rh-CSF1 treatment on protein levels of p-PLCG2, p-PKCε and p-CREB when administered with rh-CSF1. *P < 0.05 vs. sham; #P < 0.05 vs. HI+ Vehicle; @P < 0.05 vs. HI+ rh-CSF1 + DMSO; Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 6 in each group
The change of pro-inflammatory IL-1β cytokine level in brain tissues (Fig. 8 h and Fig. 9 h) is consistent with the finding of immunofluorescence staining of IL-1β (Fig. 5).
Overall, the intervention of CSF1, CSF1R, and PLCG2 inhibitors did not result in any significant changes in rectal temperature, heart rate, and respiration rate compared to the corresponding treatment control groups at 48 h after HI (data not shown).
Discussion
This study is the first to explore the therapeutic effect of rh-CSF1 against neuroinflammation and the potential underlying mechanisms after experimentally inducing HIE in rats. Our findings showed that (1) The expression levels of endogenous p-CSF1R, CSF1R, CSF1, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB were increased after HI in rats, which peaked at 24 h after HI. CSF1 and CSF1R were expressed on microglia at 48 h after HI. (2) Administration of 80 μg/kg rh-CSF1 remarkably reduced the percentage of the infarcted area, brain edema and body weight loss, improved short- and long-term neurological deficits, accompanied by a decrease in neuroinflammation after HI. (3) Rh-CSF1 treatment significantly upregulated the protein levels of p-CSF1R, CSF1R, p-PLCG2, p-PKCε, and p-CREB but downregulated the protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. (4) CSF1R inhibitor, BLZ945, or PLCG2 inhibitor, U73122, abolished the beneficial effects of rh-CSF1 as seen from our neurological tests and neuroinflammatory markers. Taken together, our findings indicated that CSF1R activation with rh-CSF1 ameliorated neuroinflammation, which leads to the improvement of neurobehavioral impairments after HI. This neuroprotection was, at least partly attributed to the activation of microglial PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway.
CSF1 is a cytokine of the mononuclear phagocytic system that is upregulated in a variety of CNS diseases, such as AD [46], EAE [47], and neuro HIV [23]. The biological effects of CSF1 are mediated by CSF1R, which is crucial in promoting the migration, proliferation, differentiation, survival, and polarization of macrophage-lineage cells. CSF1R signaling appears to be a necessary condition of growth factor receptor for microglia, which blocks microglial cell death [14]. The expressions of CSF1 and CSF1R were upregulated in HIV CNS disease and autoimmune encephalomyelitis [48, 49]. In this study, our results suggested that the expression levels of CSF1, CSF1R, PLCG2, PKCε, and CREB were increased as early as 6 h and peaked at 24 h after HI. Several damaging factors of brain injury have been proposed to be involved in experimental HIE models, such as neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, and mitochondria dysfunction [50]. The increased CSF1, CSF1R, PLCG2, PKCε, and CREB expression levels may indicate that they are involved in the endogenous neuroprotective mechanism following HI.
We then tested the effectiveness of rh-CSF1 in the HI model. Based on the time course results and the half-life of rh-CSF1, we treated the pups at 1 h and 24 h after HI. Intranasal administration is a non-invasive approach. The large surface area of the nasal mucosa was conducive to rapid drug absorption and served as a viable and direct method in transporting the drug into the brain [51]. Due to the advantages of intranasal administration, this method was selected to administer rh-CSF1 to neonatal HI rats in our study. Immunofluorescence staining and western blot results verified the expression of exogenous human CSF1 in the rat brain after HI, demonstrating the effectiveness of intranasal administration route of rh-CSF1 into the brain. Our results showed that the intranasal rh-CSF1 at a dose of 80 μg/kg reduced cerebral infarction area, brain edema, negative geotaxis reflex time, and alleviated body weight loss effectively, accompanied by an increase CSF1 positive microglia, and attenuation of neuroinflammation at 48 h after HI. Hippocampal injury can cause long-term cognitive and memory dysfunction after HI [52]. Previous studies reported that the extent of atrophy in the ipsilateral hemisphere and hippocampus was closely associated with short-term sensorimotor dysfunction and long-term neurological functions closely [53]. Our results consistently showed that intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 significantly improved long-term neurological performances of rotarod test, foot-fault test, and morris water maze test, accompanied by the reduction in the volume of brain tissue loss and percentage of brain weight loss in the ipsilateral hemisphere at 4 weeks after HI.
CSF1 is mainly expressed on microglia, neurons, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes in the CNS [7, 15]. However, CSF1R is primarily localized on microglia [54] and some on neurons in the hippocampus and cortex under physiological conditions [15]. A previous study has been reported that the CSF1R expression was increased in activated microglia after ischemic brain injury in mice [55]. In our study, double immunofluorescence staining indicated that CSF1 and CSF1R were colocalized with microglia at 48 h after HI, which coincided with the previous study. Microglia and/or peripheral infiltration of macrophages play both protective and deleterious roles in the pathology in CNS diseases, which may vary among diseases or may change dynamically as the disease progresses. CSF1 treatment can stimulate the proliferation and activation of microglia, which is protective against neurological dysfunctions and neuroinflammation in a variety of CNS diseases [24, 56–58]. Previous studies have shown that CSF1 improved memory deficits after AD [15], reduced motor behavioral deficits of Parkinson’s disease [59], and ameliorated EAE symptoms [24]. However, microglial depletion by CSF1R inhibitor resulted in dramatically increased the number of neutrophils and augmented the astrocytic production of inflammatory mediators in brain tissues, which eventually exacerbated neurological deficits and brain infarction after ischemic stroke [25, 26]. Furthermore, previous studies have also been reported that CSF1 signaling influenced the phenotype of mononuclear phagocytes, and triggered microglial polarization toward an M2-like phenotype (immunosuppressive), with increased production of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 [60, 61]. All these studies indicated that CSF1 activated proliferation and differentiation of microglia, thus reducing neuroinflammation and playing a neuroprotective role, while the correlation between CSF1 and HIE has not been reported. In the present study, the brain tissue expression levels of CSF1 and CSF1R were increased as well as CSF1/CSF1R positive microglia cells after HI, suggesting an endogenous mechanism of protection. Intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 was able to further enhance the upregulation of CSF/CSF1R signaling. Meanwhile, neuroinflammation is an important component of HIE pathogenesis. We found the significant increases in IL-1β/MPO-positive cells and higher cytokine levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in ipsilateral brain tissues at 48 h after HI. Intranasal rh-CSF1 attenuated the neuroinflammation after HI as well, suggesting that the upregulation of microglia CSF/CSF1R signaling was in favor of suppression of inflammatory responses. Therefore, CSF1R might serve as a novel anti-inflammation target in the setting of HIE.
We further investigated the mechanism underlying the anti-neuroinflammatory effect of CSF1 in HIE. CREB, a transcription factor, responds to a variety of growth factors and inflammatory signals, which mediate the transcription of genes including cAMP-response elements, such as inflammation-related genes of IL-10 and TNF-α [62]. Phosphorylation of CREB protein was activated in the “ischemic penumbra” region in an animal model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion [63]. Ischemia-resistant dentate granulosa cells had higher levels of CREB phosphorylation than that in ischemia-susceptible CA1 neurons, suggesting CREB phosphorylation as a key factor in achieving ischemic tolerance [63]. The increased CREB phosphorylation has also been shown to be neuroprotective after HI [64]. Interestingly, CSF1 reduced excitotoxic neuronal damage by maintaining the phosphorylation of CREB [15]. In our study, the exogenous rh-CSF1 administration reduced the neuroinflammatory response after HI and promoted the up-regulation of the CREB phosphorylation, which was consistent with previous studies. In addition, BLZ-945, a selective inhibitor of CSF1R, reversed the beneficial effects of CSF1 and significantly downregulated the phosphorylation of CREB. These findings implicated that CSF1 could reduce the inflammatory response after HI by activating CREB signaling. However, the exact mechanism between CSF1/ CSF1R and CREB activation has not yet been elucidated.
The PLCG2 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme, known as phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCγ2) that catalyzes 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate to IP3 and DAG using calcium as a cofactor. IP3 and DAG are the second messengers that are important for transmitting signals across cell membranes from growth factor receptors and immune system receptors and are particularly important to immune cells, including B cells, natural killer cells, mast cells, and microglia [29]. Mutations in the gene have been found in spontaneous inflammation, antibody deficiency, neurodegenerative diseases, and dementia [65, 66]. It has been found that CSF1-induced differentiation of human monocytes requires CSF1R activation and downstream PLCG2 phosphorylation [28]. PLCG2 is also involved in regulating microglial function. U73122 is a potent inhibitor of PLCG2, which inhibits the production of IP3 and DAG in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils [67] and affects the cellular viability of microglia [68]. Consistent with these findings, our results showed that intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 increased PLCG2 phosphorylation and reduced neuroinflammation, but these effects were reversed by the co-administration of CSF1R inhibitor U73122. Calcium and DAG can activate the PKC family, including PKCε, which result in the phosphorylation of other molecules and changes in cell activity [69, 70]. PKCε is a protein kinase with a potent anti-inflammatory effect. Waza et al. reported that PKCε regulated the interaction between conexin43 and the ATP sensitive K+ channel subunit in cardiomyocyte mitochondria, which prevented hypoxia-induced cell death [71]. Activation of PKCε reduced neuroinflammation [34] and acute ischemic brain injury [72]. Our results showed that rh-CSF1 increased PKCε phosphorylation, which was reversed by PLCG2 and CSF1R inhibitors, suggesting that the activation of CSF1/PLCG2/PKCε signaling pathway contributed to the beneficial effects following neonatal HI. In addition, CSF1R and PLCG2 inhibitors offset the CSF1-induced upregulation of CREB and phosphorylation. These results implied that PLCG2/PKCε was the upstream signaling of CREB in response to CSF1/CSF1R activation. Collectively, these results suggested that rh-CSF1 reduced neuroinflammatory responses, at least in part via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway.
HIE triggers a robust inflammatory response that exacerbating brain damage post-injury [73]. The acute innate immune response is critical in regulating neonatal HIE injury. Due to gender differences in pro- and anti-inflammatory response, male infants are more susceptible to HI insult and develop severer long-term cognitive deficits than females with comparable brain damage [74]. Microglial activation and accumulation were previously identified as pathological markers for HIE in human infants [75]. However, emerging evidence has shown that microglia play a dual role after brain injury, which can be pro-inflammatory or beneficial depending on its phenotype status [76]. In a rat model of HIE, the microglial depletion aggravated neuronal damage and apoptosis after the HI insult, implicating the early neuroprotection provided by resident microglia [77]. We found that rh-CSF1 promotes the anti-neuroinflammation status of microglia by activation CSF-1R after HI, leading to improved short-term neurological deficits and long-term cognitive function. These results suggest the potential of rh-CSF1 to serve as a new therapeutic approach in HIE patients. The intranasal administration route is invasive and readily clinical translatable. Indeed, recent studies have demonstrated the importance of CSF-1R signaling in microglial and neural development and function in which CSF-1R activations resulted in pleotropic protective effects in multiple neurological diseases [78]. In addition to microglia regulation, rh-CSF-1 may exert directly activating the neuronal CSF-1R and promoting neuronal survival after HI. Neuronal depletion of CSF-1R exacerbated the excitotoxicity injury and subsequent neurodegeneration [15]. Systemic CSF-1 administration increased the neuronal expression of p-CREB, an essential survival signaling, with the resultant improvement of cognitive function in a mouse model of AD [15]. Although our focus is neuroinflammation in the current study, the neuronal effects of rh-CSF1 need to be further explored in the setting of experimental HIE.
There are several limitations to this study. First, previous studies showed that the CSF1 was also expressed in astrocytes and neurons. The anti-apoptotic effects and blood-brain barrier protection of CSF1 after HI requires further investigation. Second, CSF1 could also induce autophagy to regulate human monocyte differentiation through the CAMKK2/PRKAA1/ULK1 signaling pathway [28]. However, we could not exclude the contribution of other signaling pathways to the anti-inflammatory effects of CSF1 in the HI model. Lastly, we did not test the effects of rh-CSF1 on female rat pups. There is increasing evidence suggests that HIE is a sexually dimorphic disease [74]. Future studies are warranted to validate the other neuroprotective functions and potential mechanisms as well as gender differences associated with CSF1 after HI.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the intranasal administration of rh-CSF1 reduced the percentage of infarcted areas, brain edema, and improved neurobehavioral deficits, by attenuating neuroinflammation after HI in rats. The anti-inflammatory effects of CSF1 were, at least in part, mediated through the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway. Thus, rh-CSF1 may serve as a novel therapeutic approach to ameliorate brain injury in patients with HIE.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Recombinant human CSF1 (rh-CSF1) attenuates neuroinflammation via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway in a rat model of neonatal HIE.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Loma Linda University, which comply with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals in Neuroscience Research and ARRIVE guidelines.
Abbreviations
- AD
Alzheimer's disease
- CNS
Central nervous system
- CREB
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding
- CSF1
Colony-stimulating factor 1
- CSF1R
Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor
- DAG
Diacylglycerol
- EAE
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- HIE
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- IACUC
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
- IP3
Inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate
- PKCε
Protein kinase C epsilon
- PLCG2
Phospholipase C-gamma 2
- TTC
Triphenyltetrazolium chloride
Authors’ contributions
This study was designed by XH, SRL, DMD, GZ, and JHZ. The experiments were completed by XH, SRL, RL, JH, SCX, and GZ. XH, LH, and CL performed the statistical analysis. XH, SRL, and CL finished writing the manuscript. GZ and JHZ provided supervision and final check. All the authors read the final version of this paper and approved it.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NS104083) to John H. Zhang, a grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 81601051) to Dr. Xiao Hu, and a grant from Jiangsu provincial medical talents project fund (QNRC2016263) to Dr. Gang Zuo.
Availability of data and materials
The data support the findings of this study and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiao Hu and Shirong Li contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Gang Zuo, Email: neurozg@163.com.
John H. Zhang, Email: jhzhang@llu.edu, Email: johnzhang3910@yahoo.com
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12974-020-01862-w.
References
- 1.McDonald CA, Djuliannisaa Z, Petraki M, Paton MCB, Penny TR, Sutherland AE, et al. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stromal cells protects against neonatal hypoxic(-)ischemic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2449. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abbasi H, Gunn AJ, Bennet L, Unsworth CP. Latent phase identification of high-frequency micro-scale gamma spike transients in the hypoxic ischemic EEG of preterm fetal sheep using spectral analysis and fuzzy classifiers. sensors (Basel) 2020;20(5):1424. doi: 10.3390/s20051424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Li M, Cui MM, Kenechukwu NA, Gu YW, Chen YL, Zhong SJ, et al. Rosmarinic acid ameliorates hypoxia/ischemia induced cognitive deficits and promotes remyelination. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(5):894–902. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.268927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Douglas-Escobar M, Weiss MD. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(4):397–403. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Finder M, Boylan GB, Twomey D, Ahearne C, Murray DM, Hallberg B. Two-year neurodevelopmental outcomes after mild hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in the era of therapeutic hypothermia. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Herrera TI, Edwards L, Malcolm WF, Smith PB, Fisher KA, Pizoli C, et al. Outcomes of preterm infants treated with hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev. 2018;125:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2018.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Easley-Neal C, Foreman O, Sharma N, Zarrin AA, Weimer RM. CSF1R ligands IL-34 and CSF1 are differentially required for microglia development and maintenance in white and gray matter brain regions. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2199. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wu Z, Harne R, Chintoan-Uta C, Hu TJ, Wallace R, MacCallum A, et al. Regulation and function of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF1) in the chicken immune system. Dev Comp Immunol. 2020;105:103586. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.103586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chitu V, Gokhan S, Nandi S, Mehler MF, Stanley ER. Emerging roles for CSF-1 receptor and its ligands in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 2016;39(6):378–393. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kierdorf K, Prinz M. Microglia: same same, but different. J Exp Med. 2019;216(10):2223–2225. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wylot B, Mieczkowski J, Niedziolka S, Kaminska B, Zawadzka M. Csf1 Deficiency dysregulates glial responses to demyelination and disturbs CNS white matter remyelination. Cells. 2019;9(1) 99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Stanley ER, Chitu V. CSF-1 receptor signaling in myeloid cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(6). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Xu Q, Malecka KL, Fink L, Jordan EJ, Duffy E, Kolander S, et al. Identifying three-dimensional structures of autophosphorylation complexes in crystals of protein kinases. Sci Signal. 2015;8(405):rs13. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Elmore MR, Najafi AR, Koike MA, Dagher NN, Spangenberg EE, Rice RA, et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling is necessary for microglia viability, unmasking a microglia progenitor cell in the adult brain. Neuron. 2014;82(2):380–397. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Luo J, Elwood F, Britschgi M, Villeda S, Zhang H, Ding Z, et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling in injured neurons facilitates protection and survival. J Exp Med. 2013;210(1):157–172. doi: 10.1084/jem.20120412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen Z, Hu Y, Lu R, Ge M, Zhang L. MicroRNA-374a-5p inhibits neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome targeted Smad6. Life Sci. 2020;252:117664. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yenari MA, Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA. Microglial activation in stroke: therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics. 2010;7(4):378–391. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2010.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chu F, Shi M, Zheng C, Shen D, Zhu J, Zheng X, et al. The roles of macrophages and microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2018;318:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hansen DV, Hanson JE, Sheng M. Microglia in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol. 2018;217(2):459–472. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201709069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Oosterhof N, Kuil LE, van der Linde HC, Burm SM, Berdowski W, van Ijcken WFJ, et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) regulates microglia density and distribution, but not microglia differentiation in vivo. Cell Rep. 2018;24(5):1203–1217. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lin W, Xu D, Austin CD, Caplazi P, Senger K, Sun Y, et al. Function of CSF1 and IL34 in macrophage homeostasis, inflammation, and cancer. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2019. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Spangenberg E, Severson PL, Hohsfield LA, Crapser J, Zhang J, Burton EA, et al. Sustained microglial depletion with CSF1R inhibitor impairs parenchymal plaque development in an Alzheimer's disease model. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3758. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11674-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Irons DL, Meinhardt T, Allers C, Kuroda MJ, Kim WK. Overexpression and activation of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor in the SIV/macaque model of HIV infection and neuroHIV. Brain Pathol. 2019;29(6):826–836. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wlodarczyk A, Benmamar-Badel A, Cedile O, Jensen KN, Kramer I, Elsborg NB, et al. CSF1R stimulation promotes increased neuroprotection by CD11c + microglia in EAE. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:523. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Otxoa-de-Amezaga A, Miro-Mur F, Pedragosa J, Gallizioli M, Justicia C, Gaja-Capdevila N, et al. Microglial cell loss after ischemic stroke favors brain neutrophil accumulation. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;137(2):321–341. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1954-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jin WN, Shi SX, Li Z, Li M, Wood K, Gonzales RJ, et al. Depletion of microglia exacerbates postischemic inflammation and brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(6):2224–2236. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17694185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barbosa CM, Bincoletto C, Barros CC, Ferreira AT, Paredes-Gamero EJ. PLCgamma2 and PKC are important to myeloid lineage commitment triggered by M-SCF and G-CSF. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(1):42–51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Obba S, Hizir Z, Boyer L, Selimoglu-Buet D, Pfeifer A, Michel G, et al. The PRKAA1/AMPKalpha1 pathway triggers autophagy during CSF1-induced human monocyte differentiation and is a potential target in CMML. Autophagy. 2015;11(7):1114–1129. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Magno L, Lessard CB, Martins M, Lang V, Cruz P, Asi Y, et al. Alzheimer's disease phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) protective variant is a functional hypermorph. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0469-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cheeseman KL, Ueyama T, Michaud TM, Kashiwagi K, Wang D, Flax LA, et al. Targeting of protein kinase C-epsilon during Fcgamma receptor-dependent phagocytosis requires the epsilonC1B domain and phospholipase C-gamma1. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17(2):799–813. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-12-1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nakamura Y, Fukami K. Regulation and physiological functions of mammalian phospholipase C. J Biochem. 2017;161(4):315–321. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvw094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kumar V, Weng YC, Wu YC, Huang YT, Chou WH. PKCepsilon phosphorylation regulates the mitochondrial translocation of ATF2 in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration. BMC Neurosci. 2018;19(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12868-018-0479-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zuo G, Zhang T, Huang L, Araujo C, Peng J, Travis Z, et al. Activation of TGR5 with INT-777 attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via cAMP/PKCepsilon/ALDH2 pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;143:441–453. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gessi S, Borea PA, Bencivenni S, Fazzi D, Varani K, Merighi S. The activation of mu-opioid receptor potentiates LPS-induced NF-kB promoting an inflammatory phenotype in microglia. FEBS Lett. 2016;590(17):2813–2826. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Derouiche A, Geiger KD. Perspectives for Ezrin and radixin in astrocytes: kinases, functions and pathology. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3776. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mylroie H, Dumont O, Bauer A, Thornton CC, Mackey J, Calay D, et al. PKCepsilon-CREB-Nrf2 signalling induces HO-1 in the vascular endothelium and enhances resistance to inflammation and apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;106(3):509–519. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Guan X, Wang Y, Kai G, Zhao S, Huang T, Li Y, et al. Cerebrolysin ameliorates focal cerebral ischemia injury through neuroinflammatory inhibition via CREB/PGC-1alpha pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jaworska J, Zalewska T, Sypecka J, Ziemka-Nalecz M. Effect of the HDAC inhibitor, sodium butyrate, on neurogenesis in a rat model of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia: potential mechanism of action. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(9):6341–6370. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1518-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rice JE, 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1981;9(2):131–141. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dock H, Theodorsson A, Theodorsson E. DNA methylation inhibitor Zebularine confers stroke protection in ischemic rats. Transl Stroke Res. 2015;6(4):296–300. doi: 10.1007/s12975-015-0397-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang Z, Zhou F, Dou Y, Tian X, Liu C, Li H, et al. Melatonin alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced secondary brain injury in rats via suppressing apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and mitochondria injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2018;9(1):74–91. doi: 10.1007/s12975-017-0559-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tanaka M, Ogaeri T, Samsonov M, Sokabe M. The 5alpha-reductase inhibitor finasteride exerts neuroprotection against ischemic brain injury in aged male rats. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(1):67–77. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0624-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Griemert EV, Recarte Pelz K, Engelhard K, Schafer MK, Thal SC. PAI-1 but not PAI-2 gene deficiency attenuates ischemic brain injury after experimental stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(4):372–380. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0644-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liu H, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xi G. Brain ceruloplasmin expression after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage and protection against iron-induced brain injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(1):112–119. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0669-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wei Q, Leng S, Li C, Han B, et al. Activation of sigma-1 receptor enhanced pericyte survival via the interplay between apoptosis and autophagy: implications for blood-brain barrier integrity in stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2019. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Walker DG, Tang TM, Lue LF. Studies on colony stimulating factor receptor-1 and ligands colony stimulating factor-1 and interleukin-34 in Alzheimer's disease brains and human microglia. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:244. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Borjini N, Fernandez M, Giardino L, Calza L. Cytokine and chemokine alterations in tissue, CSF, and plasma in early presymptomatic phase of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE), in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0757-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Knight AC, Brill SA, Queen SE, Tarwater PM, Mankowski JL. Increased microglial CSF1R expression in the SIV/macaque model of HIV CNS disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2018;77(3):199–206. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlx115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nissen JC, Thompson KK, West BL, Tsirka SE. Csf1R inhibition attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and promotes recovery. Exp Neurol. 2018;307:24–36. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.05.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu X, Ma Y, Wei X, Fan T. Neuroprotective effect of licochalcone a against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion in rat primary cortical neurons by attenuating oxidative stress injury and inflammatory response via the SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(4):3210–3219. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chauhan MB, Chauhan NB. Brain uptake of Neurotherapeutics after intranasal versus intraperitoneal delivery in mice. J Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;2(1):009. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Byeon JH, Kim GH, Kim JY, Sun W, Kim H, Eun BL. Cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal damage induced by hypoxic-ischemic brain injury and prolonged febrile convulsions in immature rats. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(1):22–29. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Herold F, Torpel A, Schega L, Muller NG. Functional and/or structural brain changes in response to resistance exercises and resistance training lead to cognitive improvements - a systematic review. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2019;16:10. doi: 10.1186/s11556-019-0217-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Erblich B, Zhu L, Etgen AM, Dobrenis K, Pollard JW. Absence of colony stimulation factor-1 receptor results in loss of microglia, disrupted brain development and olfactory deficits. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Raivich G, Haas S, Werner A, Klein MA, Kloss C, Kreutzberg GW. Regulation of MCSF receptors on microglia in the normal and injured mouse central nervous system: a quantitative immunofluorescence study using confocal laser microscopy. J Comp Neurol. 1998;395(3):342–358. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19980808)395:3<342::aid-cne6>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.De I, Nikodemova M, Steffen MD, Sokn E, Maklakova VI, Watters JJ, et al. CSF1 overexpression has pleiotropic effects on microglia in vivo. Glia. 2014;62(12):1955–1967. doi: 10.1002/glia.22717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chang KH, Wu YR, Chen YC, Wu HC, Chen CM. Association between CSF1 and CSF1R polymorphisms and Parkinson's disease in Taiwan. J Clin Med. 2019;8(10):1529. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Horti AG, Naik R, Foss CA, Minn I, Misheneva V, Du Y, et al. PET imaging of microglia by targeting macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(5):1686–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812155116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Neal ML, Fleming SM, Budge KM, Boyle AM, Kim C, Alam G, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of CSF1R by GW2580 reduces microglial proliferation and is protective against neuroinflammation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. FASEB J. 2020;34(1):1679–1694. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900567RR. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fleetwood AJ, Lawrence T, Hamilton JA, Cook AD. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF) and macrophage CSF-dependent macrophage phenotypes display differences in cytokine profiles and transcription factor activities: implications for CSF blockade in inflammation. J Immunol. 2007;178(8):5245–5252. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.8.5245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pepe G, De Maglie M, Minoli L, Villa A, Maggi A, Vegeto E. Selective proliferative response of microglia to alternative polarization signals. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1011-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Miao Y, He T, Zhu Y, Li W, Wang B, Zhong Y. Activation of hippocampal CREB by rolipram partially recovers balance between TNF-alpha and IL-10 levels and improves cognitive deficits in diabetic rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015;35(8):1157–1164. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0209-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hu BR, Fux CM, Martone ME, Zivin JA, Ellisman MH. Persistent phosphorylation of cyclic AMP responsive element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 transcription factors following transient cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1999;89(2):437–452. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hung PL, Hsu MH, Yu HR, Wu KLH, Wang FS. Thyroxin protects white matter from hypoxic-ischemic insult in the immature Sprague(-)Dawley rat brain by regulating periventricular white matter and cortex BDNF and CREB pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9):2573. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Conway OJ, Carrasquillo MM, Wang X, Bredenberg JM, Reddy JS, Strickland SL, et al. ABI3 and PLCG2 missense variants as risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases in Caucasians and African Americans. Mol Neurodegener. 2018;13(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0289-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.van der Lee SJ, Conway OJ, Jansen I, Carrasquillo MM, Kleineidam L, van den Akker E, et al. A nonsynonymous mutation in PLCG2 reduces the risk of Alzheimer's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and frontotemporal dementia, and increases the likelihood of longevity. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138(2):237–250. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02026-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gotwals P, Cameron S, Cipolletta D, Cremasco V, Crystal A, Hewes B, et al. Prospects for combining targeted and conventional cancer therapy with immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(5):286–301. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gilbert DF, Stebbing MJ, Kuenzel K, Murphy RM, Zacharewicz E, Buttgereit A, et al. Store-operated ca(2+) entry (SOCE) and purinergic receptor-mediated ca(2+) homeostasis in murine bv2 microglia cells: early cellular responses to ATP-mediated microglia activation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016;9:111. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Friedman BA, Srinivasan K, Ayalon G, Meilandt WJ, Lin H, Huntley MA, et al. Diverse brain myeloid expression profiles reveal distinct microglial activation states and aspects of Alzheimer's disease not evident in mouse models. Cell Rep. 2018;22(3):832–847. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhu L, Jones C, Zhang G. The role of phospholipase C signaling in macrophage-mediated inflammatory response. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:5201759. doi: 10.1155/2018/5201759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Waza AA, Andrabi K, Hussain MU. Protein kinase C (PKC) mediated interaction between conexin43 (Cx43) and K(+)(ATP) channel subunit (Kir6.1) in cardiomyocyte mitochondria: implications in cytoprotection against hypoxia induced cell apoptosis. Cell Signal. 2014;26(9):1909–1917. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Surendran D. PKCgamma and PKCepsilon are differentially activated and modulate neurotoxic signaling pathways during oxygen glucose deprivation in rat cortical slices. Neurochem Res. 2019;44(11):2577–2589. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02876-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Liu F, McCullough LD. Inflammatory responses in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(9):1121–1130. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Al Mamun A, Yu H, Mirza MA, Romana S, McCullough LD, Liu F. Myeloid cell IRF4 signaling protects neonatal brains from hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int. 2019;127:148–157. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.12.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Del Bigio MR, Becker LE. Microglial aggregation in the dentate gyrus: a marker of mild hypoxic-ischaemic brain insult in human infants. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1994;20(2):144–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1994.tb01173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Rawlinson C, Jenkins S, Thei L, Dallas ML, Chen R. Post-ischaemic immunological response in the brain: targeting microglia in ischaemic stroke therapy. Brain Sci. 2020;10(3):159. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10030159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tsuji S, Di Martino E, Mukai T, Tsuji S, Murakami T, Harris RA, et al. Aggravated brain injury after neonatal hypoxic ischemia in microglia-depleted mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01792-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chitu V, Stanley ER. Regulation of embryonic and postnatal development by the CSF-1 receptor. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;123:229–275. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Recombinant human CSF1 (rh-CSF1) attenuates neuroinflammation via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε/CREB signaling pathway in a rat model of neonatal HIE.
Data Availability Statement
The data support the findings of this study and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.