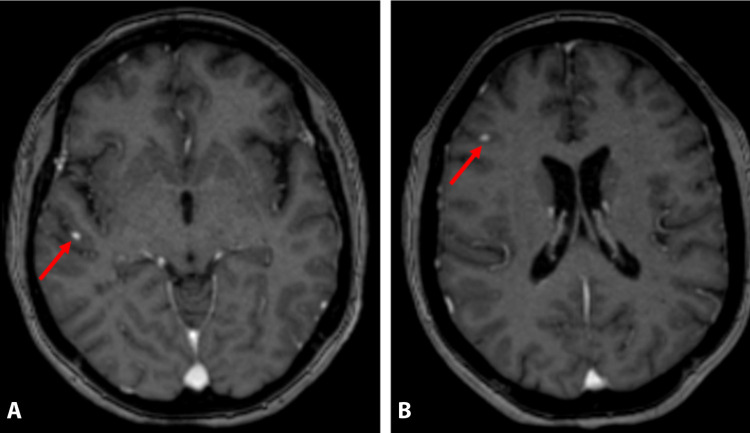
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging showing a few leptomeningeal micronodular lesions (Fig. 1 ). A 43-year-old woman was referred with complaints of severe headache, cough, and fever. The patient had systemic lupus erythematosus disease for ten years. Her body temperature was measured as 38.6 °C. Laboratory findings revealed mild leukocytosis (WBC = 12,450/mm3). Real-time reverse-transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) was positive for COVID-19. Thorax computed tomography (CT) showed common ground glass densities in both lung parenchyma. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging showed a few leptomeningeal micronodular lesions (Fig. 1). The lupus patients may be more susceptible for a more severe COVID-19 disease course [1]. CT scans appear sensitive virus detection [2].
Fig. 1.
References
- 1.Sawalha A.H., Manzi S. Coronavirus disease-2019: implication for the care and management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Rheumatol. 2020 doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2020.20055. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Long C., Xu H., Shen Q., et al. Diagnosis of the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): rRT-PCR or CT? Eur J Radiol. 2020;126:108961. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]