Abstract
Introduction
Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus is a β-haemolytic group C streptococcus that is a highly contagious infection in horses and other equines. Streptococcus equi infection of the native human aorta is a rare form of aortitis that has a high mortality owing to rupture. Surgical intervention with debridement and broad spectrum intravenous antibiotics are essential to improve the patient's status.
Report
In this case study, a 71 year old man with horse contact presented with left groin pain related to S. equi aortitis and mycotic aneurysm. He was successfully treated by excision of the infected abdominal aorta and iliac vessels with a biological graft reconstruction, debridement of the retroperitoneum, and application of antibiotic beads.
Discussion
Biological grafts have never been reportedly used in group C streptococcus infection of the native aorta, and the patient recovered without sequelae. The promising outcome of this case may provide a framework for future similar cases.
Keywords: Aortitis, Biologic graft, Group C streptococcus, Streptococcus equi, Vascular allograft
Highlights
-
•
A 71 year old farmer presented with S. equi aortitis and mycotic aneurysm.
-
•
Streptococcus equi infections are rare and are reported after contact with infected horses.
-
•
A human cadaveric aortic bypass graft was used for vascular reconstruction.
-
•
Biological grafts have never been used in S. equi aortitis repair.
-
•
The promising outcomes of this case may provide a framework for future cases.
Introduction
Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus is a β-haemolytic group C streptococcus that commonly infects animals.1 Streptococcus zooepidemicus is an opportunistic pathogen found to colonise in horse nostrils and can cause strangles, which is a highly contagious horse infection and is characterised by abscessation of the lymphoid tissue of the upper respiratory tract.2 Infections in humans are rare and are mostly reported after contact with infected horses. Infectious from S. equi may present as meningitis, endocarditis, bacteraemia, pneumonia, septic arthritis, cellulitis, and glomerulonephritis.2,3 The incidence of aortic infection with S. equi is extremely rare, and only five cases have been reported.4,5 Optimal management includes early diagnosis, rapid surgical intervention, and appropriate antibiotic treatment.3 In this case report, a patient with a S. equi infection of the abdominal aorta and mycotic aneurysm is reported, which was successfully treated using a human cadaveric aorta. Biological grafts have never been used in group C streptococcus infection of the native aorta, and the patient recovered without sequelae. Patient consent for publication was obtained before the submission of this case report.
Case report
A 71 year old man was admitted to the hospital because of left groin pain. He was initially seen in the emergency room of a local hospital; general surgical referral was made for possible left inguinal hernia. Subsequently, he underwent a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis because the general surgeon could not confirm a hernia in the left groin. The CT scan showed an abnormal density in the peri-aortic region with extension into the left iliac artery and vein.
The patient denied any history of systemic illnesses such as diabetes or hypertension. There was a history of past tobacco use. There was a history of pelvic fracture: three years before this admission the patient fell off a horse, which required fixation of the pelvic fracture with a plate and coil embolisation of the right internal iliac artery. He had never undergone any aortic intervention or aortic surgery.
His white cell count on admission was 15 × 109 cells/L and his haemoglobin was 14.6 g/dL. He had no history of high grade fever or chills, but felt ill, with reduced appetite and constipation. Because of the suspected aortic infection, he was started on broad spec spectrum antibiotics, and vascular surgery was consulted.
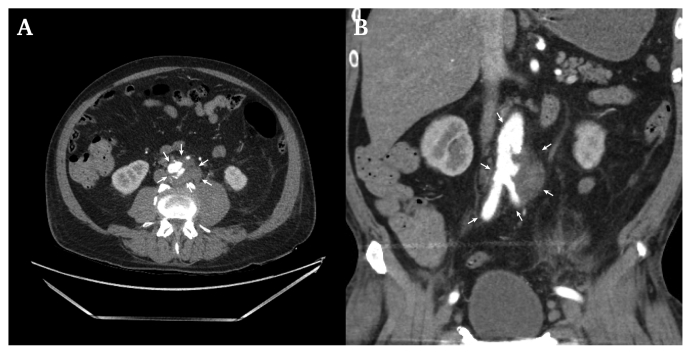
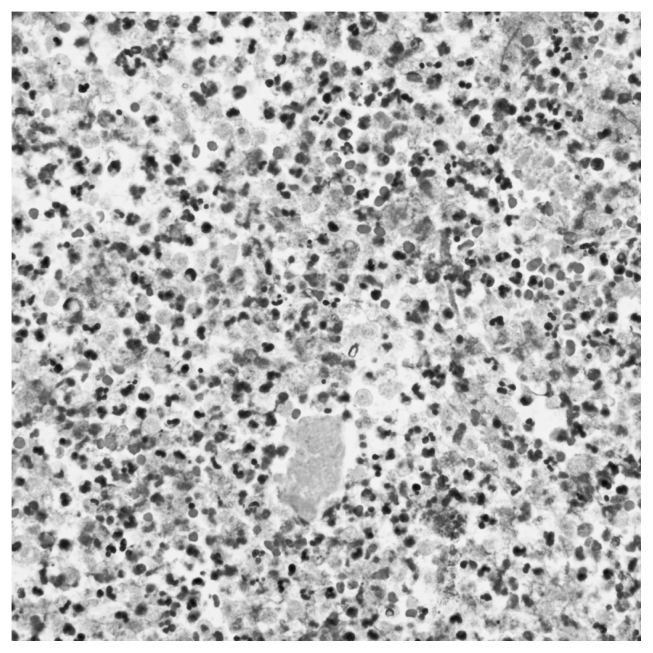
A CT angiogram was obtained, which showed an abnormal appearance of the abdominal aorta, with markedly luminal irregularities with fluid and soft tissue density around the aorta; no obvious rupture was identified (Fig. 1A, B). A single photon emission CT scan was also obtained to evaluate the abdominal aorta and iliac arteries further. Radiopharmaceutical uptake was seen at the level of the distal aorta, consistent with an infectious or inflammatory aetiology. CT guided aspiration of the fluid and subsequent culture were performed. The cultures were positive for the Gram positive coccus S. equi, which was sensitive to multiple antibiotics. It was decided to treat the patient aggressively with intravenous (IV) antibiotics, and resection and reconstruction of the abdominal aorta and iliac arteries with a biological graft (a cryopreserved aorto-iliac allograft provided by CryoLife, Kennesaw, GA, USA) were planned. The patient was treated with ceftriaxone and gentamicin. After antibiotic administration, the white cell count responded. A few days after the admission, he developed sudden onset severe abdominal pain, and an emergency CT scan showed continued aortic inflammation without any rupture or pseudo-aneurysm formation. He subsequently underwent urgent excision of the infected abdominal aorta and iliac vessels and aorto-iliac bypass with a biological graft. Debridement of the retroperitoneum and placement of absorbable vancomycin beads in the retroperitoneum were performed. It was noted that there was a contained rupture and complete loss of integrity of the posterior wall of the aortic bifurcation. Multiple biopsies were obtained from the soft tissue around the aorta. The distal inferior vena cava and left iliac vein were densely adherent to the infected aorta. The infected aorta was removed in pieces to decrease the risk of venous injury. Histological evaluation of the explanted aorta demonstrated acute inflammation with neutrophil infiltration (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
Pre-operative computed tomography angiography (CTA). (A) Transverse CTA scan revealing infrarenal mycotic abdominal aortic aneurysm. (B) Sagittal CTA of infrarenal mycotic abdominal aortic aneurysm and haematoma to the left of the distal aorta.
Fig. 2.
Histological examination of the explanted aorta This histological section of the surgical specimen taking from the explanted aorta demonstrated acute inflammation with neutrophil infiltration.
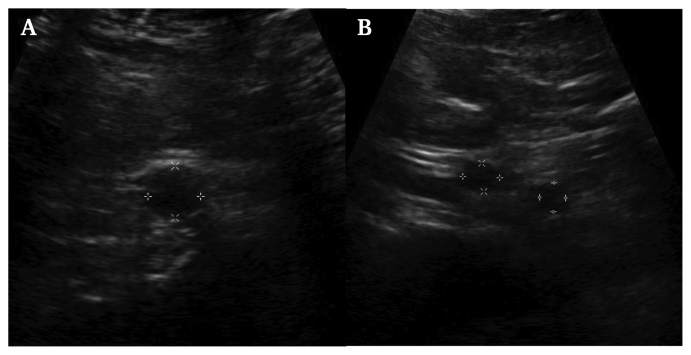
The post-operative course was essentially unremarkable, antibiotics were continued post-operatively, and he was discharged home on IV antibiotics for a total duration of four weeks. The aortic graft was scanned by ultrasound one year after initial surgery, and he is doing well without any recurrence of symptoms (Fig. 3A, B). The biological graft will be monitored for long term recurrence of infection with ultrasonography at annual follow up appointments.
Fig. 3.
One year post-operative ultrasound. (A) An ultrasound image of the transverse distal aortic allograft that shows no recurrent infection or aneurysm. (B) An ultrasound image of the transverse aortic bifurcation with no infection or aneurysm.
Discussion
Infections of the native abdominal aorta are extremely rare. Abdominal aortic infections are most frequently caused by Salmonella and Staphylococcus, whereas streptococcal infections of the aorta are rarely reported.4,6 It is estimated that 0.25%–10% of all streptococcal infectious aortitis are due to group C streptococcus.6 An uncommon variety of group C streptococcus is S. zooepidemicus, with approximately five reported cases.5 Mycotic infections of the aorta (aortitis or aneurysm) are associated with high mortality secondary to rupture.2
Streptococcus zooepidemicus infection is common in animals but very rare in humans and is usually associated with contact with horses, consumption of unpasteurised milk or dairy products, and typically has a similar presentation to other infectious aetiologies. Horse owners often have considerable close contact with their animals, including their mucous secretions. In this case, the patient had raised horses for many years. He was taking care of a horse that was suffering from strangles and did not use a protective barrier.
In most cases of bacterial aortitis, a pre-existing pathology, such as an atherosclerotic plaque or aneurysm sac, is present in the aortic wall and bacteria invade via the vasa vasorum.7 The pathology of aortitis caused by S. equi is currently unknown but could present similarly. When compared with the pathophysiology of other common infections of the aorta, there is a high risk of rupture and subsequent mortality if left untreated.5, 6, 7 If a rupture occurs, the condition is generally fatal, despite emergency surgical intervention.3
The standard treatment of S. equi aortitis is surgical resection and replacement with a prosthetic Dacron or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) graft.4,5 Another surgical treatment option is an extra-anatomical bypass. Extra-anatomical bypass is a good additional option for patients with limited life expectancy. It is typically saved for revascularisation in high risk patients who cannot tolerate aortic cross clamping or in those with a hostile abdomen. This was not the case in the present patient because he had limited comorbidities and was considered low risk. Sometimes prosthetic graft treatments include an omental wrap with preserved blood supply to reduce complications caused by residual infection. The omentum has a rich blood circulation and an abundance of lymphoid tissues, which promotes the clearance of bacteria.5 Lifelong or long term antibiotics are typically mandatory because recurrent infections are common.8
In this case study, a vascular allograft prosthesis was used for aortic graft repair, along with absorbable vancomycin beads. Vascular allograft, which is processed human vascular tissue, has clear advantages over traditional methods. Allografts have displayed the lowest levels of recurrent infection.9 Many studies emphasise the low complication rates of allografts with graft occlusion in 4% of cases, graft infection in 4% of cases, and graft degeneration in 7% of cases. The high efficacy of cryopreserved allografts stems from preserving the integrity of the collagen matrix, smooth muscle, and endothelial layer. The inherent nature of using an allograft helps maintain both vascular tone and antithrombotic properties of the aorta, which results in improved patency and resistance to infection.8 Vancomycin impregnated calcium sulphate beads in the retroperitoneum have been shown to decrease the rate of infection and were used in this case as a preventative measure.10 Omental wraps that are classically used with Dacron or PTFE grafts are not necessary with this technique. The advantages are that the omentum may be missing from previous abdominal surgery, and the additional operating room time for the procedure. This technique allows the closure of retroperitoneum and isolation of the graft from the abdominal cavity, which is not possible with omental wrap.
Conclusion
This is a case report of aortitis caused by S. equi where surgical intervention was completed with a biological aorto-iliac bypass graft. The promising outcomes of this case may provide a framework for future similar cases.
Funding
None.
Declaration of Competing Interest
None.
References
- 1.Altreuther M., Lange C., Myhre H.O., Hannula R. Aortic graft infection and mycotic aneurysm with Streptococcus equi zooepidemicus: two cases with favorable outcome of antibiotic treatment. Vascular. 2013;21:6–9. doi: 10.1258/vasc.2011.cr0299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kittang B.R., Pettersen V.K., Oppegaard O., Skutlaberg D.H., Dale H., Wiker H.G. Zoonotic necrotizing myositis caused by Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus in a farmer. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17:147. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2262-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bronze M.S., Shirwany A., Corbett C., Schaberg D.R. Infectious aortitis: an uncommon manifestation of infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Am J Med. 1999;107:627–630. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.García F., Volo G., Cabrera V. Aortic aneurysm secondary to Streptococcus zooepidemicus. EJVES Extra. 2006;11:91–93. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gonzales A.J., Hughes J.D., Leon L.R., Jr. Probable zoonotic aortitis due to group C streptococcal infection. J Vasc Surg. 2007;46:1039–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.05.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wong J., Chau P.Y., Wei W.I., Ong G.B. Abdominal aortic infection by a group C Streptococcus (S zooepidemicus) Aust N Z J Surg. 1982;52:576–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1982.tb06115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gornik H.L., Creager M.A. Aortitis. Circulation. 2008;117:3039–3051. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.760686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Harlander-Locke M.P., Harmon L.K., Lawrence P.F., Oderich G.S., McCready R.A., Morasch M.D. The use of cryopreserved aortoiliac allograft for aortic reconstruction in the United States. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59:669–674. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bozbuga N., Erentug V., Erdogan H.B., Kirali K., Ardal H., Tas S. Surgical treatment of aortic abscess and fistula. Tex Heart Inst J. 2004;31:382–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Healy A.H., Reid B.B., Allred B.D., Doty J.R. Antibiotic-impregnated beads for the treatment of aortic graft infection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:984–985. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.07.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]