Abstract
Background
Members of the genus Proteus are mostly opportunistic pathogens that cause a variety of infections in humans. The molecular evolutionary characteristics and genetic relationships among Proteus species have not been elucidated to date. In this study, we developed a multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) approach based on five housekeeping genes (HKGs) to delineate phylogenetic relationships of species within the genus Proteus.
Results
Of all 223 Proteus strains collected in the current study, the phylogenetic tree of five concatenated HKGs (dnaJ, mdh, pyrC, recA and rpoD) divided 223 strains into eleven clusters, which were representative of 11 species of Proteus. Meanwhile, the phylogenetic trees of the five individual HKGs also corresponded to that of the concatenated tree, except for recA, which clustered four strains at an independent cluster. The evaluation of inter- and intraspecies distances of HKG concatenation indicated that all interspecies distances were significantly different from intraspecies distances, which revealed that these HKG concatenations can be used as gene markers to distinguish different Proteus species. Further web-based DNA-DNA hybridization estimated by genome of type strains confirmed the validity of the MLSA, and each of eleven clusters was congruent with the most abundant Proteus species. In addition, we used the established MLSA method to identify the randomly collected Proteus and found that P. mirabilis is the most abundant species. However, the second most abundant species is P. terrae but not P. vulgaris. Combined with the genetic, genomic and phenotypic characteristics, these findings indicate that three species, P. terrae, P. cibarius and Proteus genospecies 5, should be regarded as heterotypic synonyms, and the species should be renamed P. terrae, while Proteus genospecies 5 has not been named to date.
Conclusions
This study suggested that MLSA is a powerful method for the discrimination and classification of Proteus at the species level. The MLSA scheme provides a rapid and inexpensive means of identifying Proteus strains. The identification of Proteus species determined by the MLSA approach plays an important role in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of Proteus infection.
Keywords: Proteus, Multilocus sequence analysis, Taxonomy, Identification
Background
The genus Proteus belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae is a motile gram-negative bacterium that survives in soil, water, and the intestinal tracts of mammals. Most members of the genus Proteus are opportunistic pathogens that cause a variety of infections in humans, including urinary tract infections [1], wounds, and respiratory tract, skin, eye, ear, nose, and throat infections [2].
The genus was first described by Hauser and was successively separated into two species, Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris, on the basis of the ability of these species to ferment maltose [2]. Strains of P. vulgaris comprised three biogroups based on three biochemical reactions, namely, indole production, salicin fermentation and aesculin hydrolysis. Biogroup 1 was characterized by being negative for those three reactions, named P. penneri [3]. By contrast, biogroup 2 was positive for the three reactions and retained the name P. vulgaris. Biogroup 3 was positive for indole production but negative for salicin fermentation and aesculin hydrolysis [4] and further separated into four groups by DNA-DNA hybridization, which were designated Proteus genospecies 3, 4, 5 and 6 [4]. Genospecies 3 can be distinguished from Proteus genospecies 4, 5 and 6 because it is negative for Jordan’s tartrate utilization and was named by the species of P. hauseri, while genospecies 4, 5 and 6 remained unnamed due to their undistinguishable phenotypic differentiation [4]. In addition, six newly defined species, i.e., P. terrae and P. cibarius, P. alimentorum, P. columbae, P. faecis and P. cibi, were proposed recently based on phylogenetic, phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and genotypic analyses [5–9]. Thus, the genus Proteus comprises ten validly published species and three unnamed genospecies to date (4, 5 and 6).
Except for those six newly defined species, the classification of other Proteus species and genospecies was based on the difference in biochemical reactions and DNA-DNA hybridization, which were designed 19 years ago or even further in the past [4, 10]. In particular, the molecular evolutionary characteristics and genetic relationships among those Proteus phenospecies and genospecies have not been elucidated to date due to the absence of a molecular typing method in the Proteus genus. Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) based on several housekeeping genes (HKGs) has previously been successfully employed to delineate boundaries between closely related bacterial species, subspecies and component strains [11–13]. Partial sequences of protein-encoding genes have proven useful for species identification and as phylogenetic markers in the family Enterobacteriaceae [14, 15].
In the present study, we developed a five-gene MLSA approach to delineate genetic similarities and differences among Proteus species. We used this MLSA method to type the genotypic species of 223 Proteus strains that were identified by phenotypes. Our data indicate that MLSA is a powerful method for the discrimination, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Proteus at the species level; meanwhile, we revealed taxonomic relationships between phenotypic and genotypic species, specifically, modifying two phenotypic taxonomy using this MLSA method.
Results
MLSA of the five concatenated HKGs
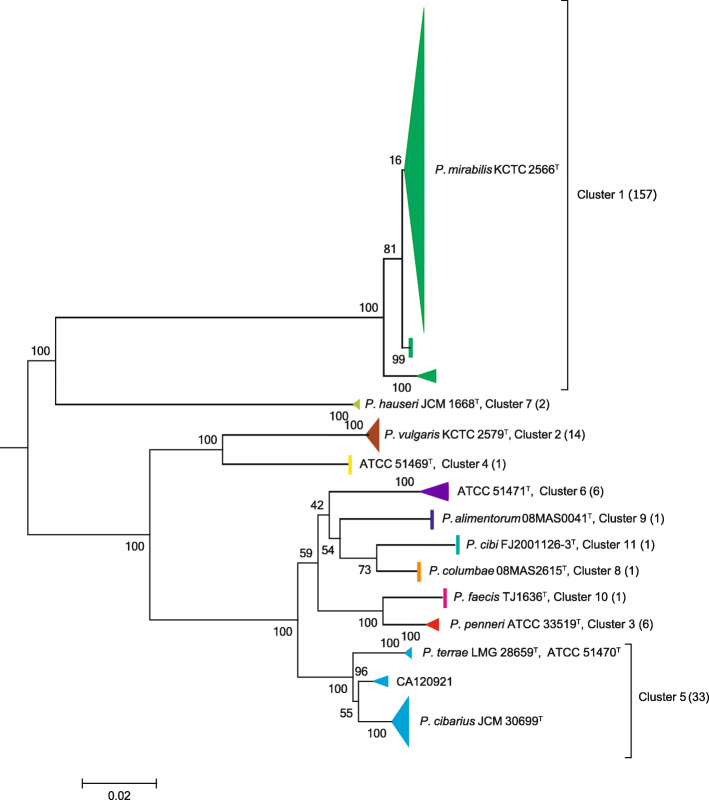
Of all 223 Proteus strains collected in this study, the phylogenetic tree of the concatenated 5 genes divided them into eleven clusters (Fig. 1), representing thirteen species. Among the clusters, ten contained one type strain of each. However, cluster 5 was comprised of three type strains, i.e., Proteus genospecies ATCC 51470T, P. cibarius JCM 30699T and P. terrae LMG 28659T.
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic reconstruction of Proteus strains based on concatenated dnaJ, mdh, pyrC, recA and rpoD gene sequences. The tree is based on 3157 nt of common sequences. Analysis was performed using the maximum-likelihood method. The scale bar indicates substitutions per site. The type strains were indicated in each cluster, if included. The strain number of each species is shown in parentheses
As expected, among the 223 Proteus strains, P. mirabilis (cluster 1) is the largest cluster (n = 157, 70.4%) distinctly separated from the others, and there are three subclusters within this cluster. Cluster 5 is the second largest among Proteus strains (n = 33, 14.8%) followed by P. vulgaris (cluster 2) (n = 14, 6.3%) and P. penneri (cluster 7) (n = 6, 2.7%).
Identification of Proteus species by phylogenetic analysis of five individual genes
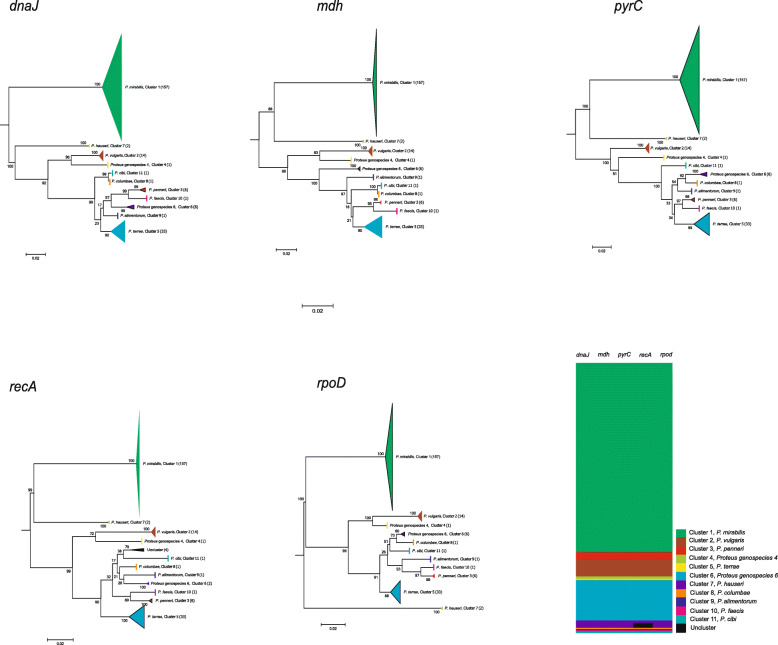
Phylogenetic trees based on five individual HKGs were also constructed (Fig. 2). Phylogenetic trees of the five HKGs (dnaJ, mdh, pyrC, recA and rpoD) can be divided into eleven clusters, representing eleven species and corresponding to that of the concatenated tree. Meanwhile, phylogenetic trees of four individual HKGs (dnaJ, mdh, pyrC and rpoD) were the same as that of the concatenated tree, both in numbers of species (cluster) and strain numbers within each species (cluster). There is one inconsistency between trees of recA and concatenated 5-gene: recA identified four strains as unclusters, whereas the four strains were identified by concatenated 5 genes, and the other four HKGs were identified as genospecies 6 (Fig. 2). The results showed that it is inaccurate to classify the species of Proteus by using a single housekeeping to reflect general gene phylogenetic tree and it only reflects the evolution by itself, which is caused by genetic recombination or specific selection. While the phylogenetic tree constructed by five concatenated HKGs can overcome the basis.
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic reconstructions of Proteus strains based on five individual genes and their identification with five concatenated genes of species. The strain number of each species is shown in parentheses. The scale bar indicates substitutions per site
Inter- and intraspecies distances of HKGs
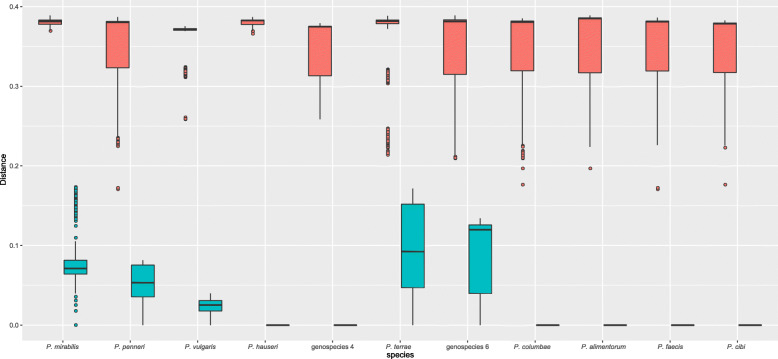
The inter- and intraspecies distances of HKGs were summarized in a boxplot of the concatenated 5 genes (Fig. 3). All interspecies distances were clearly different from intraspecies distances. Among the interspecies boxplots, two species, P. mirabilis, and P. hauseri, indicated compacted distance ranges (both standard deviations, SD = 0.004), whereas the remaining nine species shared dispersive distance ranges (SD ranges from 0.024 to 0.065). On the other hand, among the intraspecies boxplots, P. hauseri possessed a compacted distance range (SD = 0.000) compared to that of five species (SD range from 0.012 to 0.058). Meanwhile, boxplots of the five individual genes (Figure S1) indicated the same trends of intra- and interspecies distance as that of the concatenated 5 genes, although there were small parts overlapping in species 5 and 6 of pyrC. The detailed genetic distance and median values of individual genes and the concatenated 5 genes are summarized in Table S1.
Fig. 3.
Intra- and interspecies distances of eleven species inferred by concatenated 5-gene MLSA. In each boxplot, from bottom to top: minimum, median and maximum. Inter: interspecies standard deviation (SD); Intra: intraspecies SD; Proteus genospecies 4, P. columbae, P. alimentorum, P. faecis, P. cibi including only one value and thus no intraspecies SD
Web-based DNA-DNA hybridizations among species
To confirm the correctness of strains among the eleven species, we used web-based DDH, such as dDDH and ANI, to detect their similarity values. Among the eleven species defined in this study, the dDDH and ANI values of the type/representative strains were 23.5–57.1% and 80.8–94.4% (Table 1), less than the proposed cutoff level for species delineation, i.e., 70 and 95%, respectively. Notably, among the three subclusters within cluster 5 (Fig. 1), either among the three published type strains (Proteus genospecies ATCC 51470T, P. cibarius JCM 30699T and P. terrae LMG 28659T) or representative strain (CA142267) among the three subclusters, their dDDH and ANI values were more than the proposed cutoff level for species delineation. These results indicate that strains within cluster 5 actually belong to the same species.
Table 1.
dDDH relatedness and ANI values among the eleven species
| Strains a | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | P. mirabilis | P. penneri | P. vulgaris | P. hauseri | Proteus genospecies 4 | Proteus genospecies 5 | P. cibarius | P. terrae | CA142267 | Proteus genospecies 6 | P. columbae | P. alimentorum | P. faecis | P. cibi | |||||||||||||||
| DDH/ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | DDH | ANI | |
| Strainsa | a | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b | 24.7 | 82.1 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c | 24.4 | 81.7 | 37.5 | 89.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| d | 23.5 | 80.8 | 25.8 | 83.3 | 25.1 | 82.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| e | 24.6 | 81.8 | 41.5 | 90.9 | 44.5 | 91.6 | 25.8 | 83.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| f | 24.3 | 81.8 | 44.6 | 91.7 | 37.7 | 89.6 | 25.8 | 83.1 | 40.0 | 90.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| g | 25.1 | 82.6 | 44.5 | 91.7 | 37.5 | 89.6 | 25.7 | 83.2 | 39.9 | 90.2 | 72.3 | 96.9 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||
| h | 24.1 | 81.5 | 44.6 | 91.8 | 37.5 | 89.5 | 25.7 | 83.3 | 39.9 | 90.2 | 93.1 | 99.2 | 71.2 | 96.7 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||
| i | 24.4 | 82.0 | 44.9 | 91.8 | 37.6 | 89.7 | 25.8 | 83.1 | 39.8 | 90.3 | 74.4 | 97.1 | 72.3 | 96.8 | 72.6 | 96.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||
| j | 25.0 | 82.4 | 44.8 | 91.7 | 36.0 | 89.0 | 26.1 | 83.4 | 37.8 | 89.5 | 47.3 | 92.3 | 47.1 | 92.5 | 47.3 | 92.4 | 48.3 | 92.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||
| k | 24.8 | 81.9 | 46.3 | 92.1 | 36.8 | 89.1 | 26.0 | 83.4 | 37.9 | 89.6 | 48.9 | 92.7 | 48.3 | 92.6 | 48.8 | 93.0 | 49.8 | 93.0 | 57.1 | 94.4 | 100 | 100 | |||||||
| l | 24.9 | 82.0 | 46.3 | 92.1 | 36.4 | 89.0 | 25.9 | 83.3 | 37.8 | 89.6 | 48.7 | 92.8 | 48.1 | 92.7 | 48.5 | 92.7 | 49.2 | 92.3 | 52.4 | 93.7 | 53.9 | 93.9 | 100 | 100 | |||||
| m | 24.1 | 81.6 | 52.7 | 93.7 | 35.8 | 88.7 | 25.7 | 83.1 | 36.5 | 89.1 | 45.9 | 91.9 | 45.5 | 91.9 | 45.9 | 92.0 | 46.6 | 92.1 | 47.1 | 92.2 | 48.6 | 92.7 | 48.5 | 92.6 | 100 | 100 | |||
| n | 24.6 | 81.9 | 45.3 | 92.0 | 35.5 | 88.3 | 25.8 | 83.0 | 36.5 | 89.0 | 45.8 | 92.0 | 45.5 | 92.0 | 45.9 | 92.0 | 46.6 | 92.3 | 49.2 | 92.0 | 51.4 | 93.3 | 50.5 | 93 | 49.5 | 92.9 | 100 | 100 | |
a Strain: a, P. mirabilis ATCC 29906T(GenBank accession no. ACLE00000000.1); b, P. penneri ATCC 33519T (PHFJ00000000); c, P. vulgaris KCTC 2579T (PHNN000000000); d, P. hauseri JCM 1668T (PGWU00000000); e, Proteus genospecies 4 ATCC 51469T (PENV00000000); f, Proteus genospecies 5 ATCC 51470T (PENU00000000); g, P. cibarius JCM 30699T (PGWT00000000); h, P. terrae LMG 28659T (PENS00000000); i, CA142267; j, Proteus genospecies 6 ATCC 51471T (PENT00000000); k, P. columbae 08MAS2615T (NGVR00000000); l, P. alimentorum 08MAS0041T (NBVR00000000); m, P. faecis TJ1636T (PENZ00000000); n, P. cibi FJ2001126-3T (PENW00000000)
Results were percentages based on Formula 2, calculate distances and DDH estimates with GGDC 2; ANI values were estimated using the web-based service ANI calculator (http://www.ezbiocloud.net/tools/ani)
Reclassification of Proteus genospecies 5 and P. cibarius to P. terrae
Since either MLSA of the five concatenated HKGs or phylogenetic analysis of five individual genes indicated that three type strains, i.e., Proteus genospecies ATCC 51470T, P. cibarius JCM 30699T and P. terrae LMG 28659T, fell into one cluster (cluster 5 in Fig. 1), further web-based DNA-DNA hybridizations, such as dDDH and ANI, confirmed that among the three subclusters within cluster 5, either among the three type strains or representative strain (CA142267) among the three subclusters, their dDDH and ANI values were higher than the proposed cutoff level for species delineation (70% for dDDH and 95% for ANI, Table 1). The genomic analysis provided evidence that strains within cluster 5 actually belonged to the same species.
Further phenotypic characteristics were detected among type strains of Proteus genospecies 5, P. cibarius and P. terrae, and slight distinctive properties were observed (Table 2). Only minor differences were obtained between the type strains of the three species, including growth at the optimum temperature, growth range in NaCl and pH, utilization of DNase, lipase and citric acid, and DNA G + C content. Combined with the genetic, genomic and phenotypic characteristics, three species, P. terrae reported by Behrendt et al. 2015, P. cibarius reported by Hyun et al. 2016 and Proteus genospecies 5 reported by O’Hara et al. 2000, should be regarded as the heterotypic synonyms of Proteus terrae reported by Behrendt et al. 2015.
Table 2.
Distinctive phenotypic characteristics among the type strains P. terrae, P. cibarius and Proteus genospecies 5a
| Characteristic | P. terrae | P. cibarius | Proteus genomospecies 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth in optimum temperature (°C) | 37 | 35 | 37 |
| Growth range in NaCl (%,w/v) | 0–15 | 0–12 | 0–15 |
| Growth range in pH | 4–9 | 4–9 | 4–9 |
| DNase (25 °C) (3 days) | + | + | + |
| Lipase (olive oil) (7 days) | – | + | – |
| CIT | – | – | + |
| DNA G + C content (mol %) | 37.9 | 37.8 | 37.8 |
aSpecies strain: P. terrae LMG 28659T; P. cibarius JCM 30699T; Proteus genospecies 5 ATCC 51470T
Discussion
MLSA has been used for classification at the species level in numerous Enterobacteriaceae [14–21]. MLSA has the advantage of being more convenient and more conducive to popularization in the primary research institution than the whole genome sequencing method. Normally, four to seven HKGs were selected for MLSA to determine phylogenetic relationships. It has been recommended that researchers use sequence data from more than one gene to reduce the possibility of ambiguities caused by genetic recombination or specific selection. MLSA is increasingly applied to obtain a higher resolution power between species within a genus and provides a perspective for the genotypic taxonomic analyses of genus Proteus [22]. In this study, the five housekeeping genes (dnaJ, mdh, pyrC, recA, and rpoD) contain high conservative sequence and high variable sequence, which are considered to have a slow and constant rate of evolution and resolution in the distinction of species level. When amplified by PCR of 223 tested Proteus strains collected, the five HKGs sequence data were deposited to NCBI GenBank and have a good corresponding relationship of consistency among different species. Thus, we established the MLSA method with the five genes for taxonomic analysis of the Proteus genus. Our MLSA-based approach can be used to effectively discriminate Proteus sp. and enable the delineation of species boundaries with high confidence. To the best of our knowledge, this report describes the first MLSA method to classify the genus Proteus at the species level.
Our MLSA method divided all 223 Proteus strains into eleven clusters, representative of eleven species, which is inconsistent with the thirteen Proteus species in the current literature in subsequent studies; we confirmed that there are eleven Proteus species by using MLSA. Among the eleven species, P. mirabilis was the majority species collected in this study, which agrees with numerous reports of the Proteus genus classified by phenotypic methods, and the most common cause of the intentional disease is Proteus mirabilis [2]. However, even all P. mirabilis isolates were phenotypic with the same distinguishing biochemical features, i.e., positive for ornithine decarboxylase but negative for sucrose and maltose only. Species P. mirabilis can be further divided into three dominant subclusters, representing three subtypes that have demonstrated no biochemical difference or genetic difference. In contrast, species P. vulgaris was the most conserved cluster among the eleven species and exhibited one of the minimum intraspecies distances of HKGs (Fig. 2). Traditional biochemical identification P. vulgaris includes biogroup 2 and biogroup 3. By using MLSA, the P. vulgaris includes biogroup 2. Interestingly, P. hauseri was phylogenetically more closely to P. mirabilis than any other species (Fig. 1), although P. hauseri was previously classified to biogroup 3 of P. vulgaris [4]. MLSA as an alternative method for the whole genome sequence analysis is more accurate than biochemical identification of Proteus species. Cluster 5 included three subclusters, and the web-based DDH and ANI values indicated that strains within the cluster (including three type strains, Proteus genospecies ATCC 51470T, P. cibarius JCM 30699T and P. terrae LMG 28659T) actually belong to the same species. P. cibarius and P. terrae were defined as new species of the genus Proteus, possibly because both studies excluded type strain of Proteus genospecies 5 (such as ATCC 51470T) [4]. Meanwhile, papers of the two species were accepted for publication recently (2015 and 2016) at different journals [5, 6] to ensure that they did not cite each other. We also emended three subclusters of cluster 5 into Proteus terrae.
Proteus is the most common opportunistic pathogen, of which P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris have long been considered the two most common species [2, 23, 24]. Clinically, different treatment schemes may be adopted according to the most abundant species of Proteus [25, 26]. In this study, we used the established MLSA method to identify the randomly collected Proteus and found that P. mirabilis is the most common genospecies of Proteus. However, the second most common is P. terrae but not P. vulgaris, and this result is notably different from that of clinical phenotype identification [2]. The reason for this finding is that in the clinic, strains of Proteus genospecies 4, 5 and 6 have long been identified as P. vulgaris by phenotypic biochemical reactions [4]; meanwhile, the result of this study indicates that Proteus genospecies 5 accounts for a large proportion (Fig. 1). Moreover, P. penneri and P. hauseri are initially classified as different biogroups of P. vulgaris [4]. Because accurate identification at the species level is of great significance for the clinical treatment of Proteus infection, MLSA-based identification should be suggested in the classification of the Proteus genus.
Emended description of Proteus terrae Behrendt et al. 2015
Proteus terrae (ter’rae. L. gen. n. terrae of the soil).
Proteus terrae are gram-negative, straight-rod-shaped, motile bacteria that occur singly or in pairs [6]. Cells are facultatively anaerobic and swarm with periodic cycles when cultured on a 1.5% agar nutrient medium. The range of growth temperature is from 10 °C to 45 °C, and the optimum temperature is 37 °C. The range of salt tolerance is from 0 to 15%, and the optimum NaCl is 1%. The API 20E strain is positive for indole production and maltose and negative for ornithine decarboxylase, citrate utilization, and amygdalin. Based on the API, the 50CH strain is positive for L-rhamnose and sucrose and negative for arbutin, aesculin, and salicin. The strain type of Proteus terrae is LMG 28659T (=DSM 29910T = N5/678).
Conclusions
This study suggested that MLSA is a powerful method for the discrimination and classification of Proteus at the species level. The MLSA scheme provides a rapid and inexpensive means of identifying Proteus strains. The identification of Proteus species determined by the MLSA approach plays an important role in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of Proteus infection. First, in comparison with the phenotypic biochemical classification (species) method, all tested strains can be divided into eleven clusters (genospecies) by the MLSA method, representing eleven species of Proteus. Second, our study revealed the phenospecies of strains composed of different genotypes at different phylogenetic scales. Third, our MLSA method proposed the emendation of the description of the genus Proteus: P. terrae, P. cibarius and Proteus genospecies 5, should be regarded as heterotypic synonyms, and the species should be renamed P. terrae.
Methods
Definition of species, phenospecies and genospecies in this study
To classify the biotype and genotype of Proteus isolates, we referred to the literature. We designated “phenospecies” as species identified by phenotypic traits, such as biochemical reactions; “genospecies” refer to genotype identified by MLSA of this study. To maintain consistency, genospecies 3, 4, 5 and 6 are equal to genomospecies 3, 4, 5 and 6 reported by O’Hara [4].
Bacterial isolates and biochemical identification
A total of 223 Proteus strains were analyzed in this study. Among these strains, 210 were collected and isolated from seven provinces in China from 2002 to 2015. Specifically, 181 strains were isolated from clinical samples (feces of diarrhea patients and patients with nosocomial infections, such as blood, urine and wounds), and 29 strains were isolated from food. The 210 strains were identified as Proteus species by biochemical tests (API 20E). Meanwhile, type strains of ten Proteus species and three genospecies were also obtained and used for MLSA and biochemical tests, i.e., P. mirabilis KCTC 2566T, P. vulgaris KCTC 2579T, P. penneri ATCC 33519T, P. hauseri JCM 1668T, P. cibarius JCM 30699T, P. terrae LMG 28659T, P. columbae 08MAS2615T, P. alimentorum 08MAS0041T, P. faecis TJ1636T, P. cibi FJ2001126-3T, genospecies 4 (ATCC 51469T), 5 (ATCC 51470T) and 6 (ATCC 51471T). Separate biochemical tests (salicin fermentation, aesculin hydrolysis, DNase, lipase, acetate utilization and tartrate) were assessed using agents (Guangdong HuanKai Microbial Technology Co., Ltd.) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Experiments that did not yield clear results were performed in triplicate.
DNA extraction, PCR amplification and sequencing
The genomic DNA from Proteus strains was extracted using a genomic DNA purification kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted DNA was dissolved in TE buffer and stored at − 20 °C until use as PCR templates. Five candidate HKGs were used for MLSA analysis, i.e., dnaJ, mdh, pyrC, recA and rpoD. The primer sets were designed and are listed in Table 3. For PCR amplification, each reaction was performed in a final volume of 50 μl containing 25 μl of 2× Taq PCR MasterMix (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China), 1.5 μl 10 μM of each forward and reverse primer, 2 μl DNA template, and 20 μl ddH2O. The reaction mixture was subjected to denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 52 to 55 °C for 30 s and extension at 72 °C for 1 min/kb. An extension step of 10 min at 72 °C was performed following the last cycle to ensure full-length synthesis of the fragment. All PCR products of the five HKGs were commercially directly sequenced in both directions (TsingKe Biological Technology, Beijing, China). The forward and reverse sequences of each housekeeping gene were assembled by using DNASTAR’s lasergene sequence analysis software.
Table 3.
PCR primers used in this study
| Primer | Nucleotide sequence (5′ to 3′) | Amplicon size (bp) | Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| dnaJ-F | CRATGAAATATCACCCAGAYCG | 790 | 55 °C |
| dnaJ-R | ACACGRCCATCMAGWGTT | ||
| mdh-F | GCAAAGAAACGGGCATRTT | 769 | 55 °C |
| mdh-R | CRGGTGGTATTGGTCAGG | ||
| pyrC-F | TGATTGGCATGTTCACTT | 745 | 52 °C |
| pyrC-R | GATTCTTTGCGATGTTGT | ||
| recA-F | CTRTACCAWGCACCMGCTT | 807 | 52 °C |
| recA-R | AGGKTCTATCATGCGTCT | ||
| rpoD-F | CGGGAAGGTGAAATTGAT | 775 | 52 °C |
| rpoD-R | CGATAGACATACGACGGT |
MLSA analysis
Phylogenetic trees were constructed by MLSA of the concatenated sequence of five HKG fragments (dnaJ-mdh-pyrC-recA-rpoD, 3157 bp) and the five individual HKGs. The total lengths of the alignments used were 629 bp (dnaJ), 635 bp (mdh), 647 bp (pyrC), 701 bp (recA) and 545 bp (rpoD). Comparison analyses of the sequences were conducted with BioEdit software (Ibis Biosciences, Carlsbad, CA, USA). ClustalW was used to perform multiple alignments of the nucleotide sequences. The phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA 7.0 for the maximum-likelihood (ML) method. In the ML method, the General Time Reversible model which is very extensive model in constructing the phylogenetic tree was selected, and the rate matrix, the base frequencies, the invariable site proportion and the gamma distribution were determined via likelihood. Phylogenetic tree branch support estimation and 1000 replications were calculated to obtain the bootstrap values.
Intra- and interspecies phylogenetic distance of HKGs
Intraspecies phylogenetic distance was defined as the phylogenetic distance within the strains from the same species, and interspecies phylogenetic distance was defined as the phylogenetic distance of strains from a species with strains from other species. The phylogenetic distance between strains was calculated using MEGA 7.0 with the Kimura 2 parameter model which is the default model to calculate the distance. The minimum, median, and maximum intra- and interspecies values for each species were calculated. Variance of compacted or dispersive distance of species analyzed using Fisher’s exact test.
Genomic relatedness among isolates of different species
The genomic relatedness among isolates of different species was further evaluated by web-based DNA-DNA hybridizations (DDH), such as in silico DDH (dDDH) and average nucleotide identity (ANI) to detect their similarity values [27, 28]. dDDH values were determined using the genome-to-genome distance calculator (GGDC) web server (http://ggdc.dsmz.de/), and ANI values were measured by the EZ BioCloud platform (http://www.ezbiocloud.net/tools/ani), with similarity values of 70 and 95% as the standard threshold for species boundaries, i.e., two isolates represented different species when their dDDH and ANI values were below the 70 and 95% thresholds, respectively [27, 28]. Except for P. mirabilis ATCC 29906T, all of the other test Proteus strains’ whole genome sequences were sequenced by our group, and these data were deposited into the NCBI database. The GenBank accession numbers are listed below in Table 1 [7–9].
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Intra- and inter-species distances of eleven species infer by five individual genes. In each boxplot, from bottom to top: minimum, median and maximum. Table S1. Intra- and inter-species genetic distance median values and ranges of concatenated 5-gene and five individual genes.
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank chief physician Yonglu Wang from Ma’anshan Center for Disease Control and Prevention for help with strains collection.
Abbreviations
- MLSA
Multilocus sequence analysis
- HKGs
Housekeeping genes
- ANI
Average nucleotide identity
- dDDH
Digital DNA-DNA hybridizations
Authors’ contributions
DW and HD conceived and designed the experiments. BL and HD collected strains. HD, ZH, HC and KY performed laboratory experiments. ZL analyzed and interpreted the data. ZL and ZH contributed reagents and materials. DW and HD wrote the manuscript. DW revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570134) and the National Sci-Tech Key Project (2018ZX10102001, 2018ZX10734404) from the National Health Commission, China. These funds were used in study design, strain collection, data analysis and the manuscript publication.
Availability of data and materials
The nucleotide sequences of five HKGs are deposited in the GenBank nucleotide sequence database under the accession numbers dnaJ: MG492023-MG492065, MG492068-MG492222, MG492228, MG492230-MG492232, MG492234-MG492250; mdh: MG492251-MG492295, MG492298-MG492452, MG492458, MG492460, MG492462-MG492478; pyrC: MG492479-MG492515, MG492518-MG492672, MG492678, MG492680, MG492682-MG492706; recA: MG492707-MG492733, MG492735, MG492737-MG492738, MG492743-MG492897, MG492900-MG492934; rpoD: MG492935-MG492959, MG492961, MG492963, MG492969-MG493125, MG493128-MG493162.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12866-020-01844-1.
References
- 1.Li X, Zhao H, Lockatell CV, Drachenberg CB, Johnson DE, Mobley HL. Visualization of Proteus mirabilis within the matrix of urease-induced bladder stones during experimental urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 2002;70(1):389–394. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.389-394.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.O'Hara CM, Brenner FW, Miller JM. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000;13(4):534–546. doi: 10.1128/CMR.13.4.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hickman FW, Steigerwalt AG, Farmer JJ, III, Brenner DJ. Identification of Proteus penneri sp. nov., formerly known as Proteus vulgaris indole negative or as Proteus vulgaris biogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1982;15:1097–1102. doi: 10.1128/JCM.15.6.1097-1102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O'Hara CM, Brenner FW, Steigerwalt AG, Hill BC, Holmes B, Grimont PA, Hawkey PM, Penner JL, Miller JM, Brenner DJ. Classification of Proteus vulgaris biogroup 3 with recognition of Proteus hauseri sp. nov., nom. rev. and unnamed Proteus genomospecies 4, 5 and 6. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50 Pt 5:1869–1875. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-5-1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hyun DW, Jung MJ, Kim MS, Shin NR, Kim PS, Whon TW, Bae JW. Proteus cibarius sp. nov., a swarming bacterium from Jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood, and emended description of the genus Proteus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016;66(6):2158–2164. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Behrendt U, Augustin J, Sproer C, Gelbrecht J, Schumann P, Ulrich A. Taxonomic characterisation of Proteus terrae sp. nov., a N2O-producing, nitrate-ammonifying soil bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015;108(6):1457–1468. doi: 10.1007/s10482-015-0601-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dai H, Wang Y, Fang Y, Xiao T, Huang Z, Kan B, Wang D. Proteus columbae sp. nov., isolated from a pigeon in Ma'anshan, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018;68(2):552–557. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dai H, Wang Y, Fang Y, Huang Z, Kan B, Wang D. Proteus alimentorum sp. nov., isolated from pork and lobster in Ma'anshan city, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018;68(4):1390–1395. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dai H, Chen A, Wang Y, Lu B, Chen J, Huang Y, Li Z, Fang Y, Xiao T, Cai H, et al. Proteus faecis sp. nov., and Proteus cibi sp. nov., two new species isolated from food and clinical samples in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2019;69(3):852–858. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.003248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brenner DJ, Hickman-Brenner FW, Holmes B, Hawkey PM, Penner JL, Grimont PA, O'Hara CM. Replacement of NCTC 4175, the current type strain of Proteus vulgaris, with ATCC 29905. Request for an opinion. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995;45(4):870–871. doi: 10.1099/00207713-45-4-870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Perez-Cataluna A, Lucena T, Tarazona E, Arahal DR, Macian MC, Pujalte MJ. An MLSA approach for the taxonomic update of the Splendidus clade, a lineage containing several fish and shellfish pathogenic Vibrio spp. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2016;39(6):361–369. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2016.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tampakaki AP, Fotiadis CT, Ntatsi G, Savvas D. Phylogenetic multilocus sequence analysis of indigenous slow-growing rhizobia nodulating cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) in Greece. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2017;40(3):179–189. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2017.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yanokura E, Oki K, Makino H, Modesto M, Pot B, Mattarelli P, Biavati B, Watanabe K. Subspeciation of Bifidobacterium longum by multilocus approaches and amplified fragment length polymorphism: description of B. longum subsp. suillum subsp. nov., isolated from the faeces of piglets. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2015;38(5):305–314. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2015.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martinez-Murcia AJ, Monera A, Saavedra MJ, Oncina R, Lopez-Alvarez M, Lara E, Figueras MJ. Multilocus phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2011;34(3):189–199. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2010.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hall M, Chattaway MA, Reuter S, Savin C, Strauch E, Carniel E, Connor T, Van Damme I, Rajakaruna L, Rajendram D, et al. Use of whole-genus genome sequence data to develop a multilocus sequence typing tool that accurately identifies Yersinia isolates to the species and subspecies levels. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02395-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ioannidou V, Ioannidis A, Magiorkinis E, Bagos P, Nicolaou C, Legakis N, Chatzipanagiotou S. Multilocus sequence typing (and phylogenetic analysis) of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli strains isolated from clinical cases in Greece. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6:359. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alvarez-Perez S, de Vega C, Herrera CM. Multilocus sequence analysis of nectar pseudomonads reveals high genetic diversity and contrasting recombination patterns. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Thompson FL, Gevers D, Thompson CC, Dawyndt P, Naser S, Hoste B, Munn CB, Swings J. Phylogeny and molecular identification of vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71(9):5107–5115. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5107-5115.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brady C, Cleenwerck I, Venter S, Coutinho T, De Vos P. Taxonomic evaluation of the genus Enterobacter based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA): proposal to reclassify E. nimipressuralis and E. amnigenus into Lelliottia gen. nov. as Lelliottia nimipressuralis comb. nov. and Lelliottia amnigena comb. nov., respectively, E. gergoviae and E. pyrinus into Pluralibacter gen. nov. as Pluralibacter gergoviae comb. nov. and Pluralibacter pyrinus comb. nov., respectively, E. cowanii, E. radicincitans, E. oryzae and E. arachidis into Kosakonia gen. nov. as Kosakonia cowanii comb. nov., Kosakonia radicincitans comb. nov., Kosakonia oryzae comb. nov. and Kosakonia arachidis comb. nov., respectively, and E. turicensis, E. helveticus and E. pulveris into Cronobacter as Cronobacter zurichensis nom. nov., Cronobacter helveticus comb. nov. and Cronobacter pulveris comb. nov., respectively, and emended description of the genera Enterobacter and Cronobacter. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2013;36(5):309–319. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2013.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dikow RB. Genome-level homology and phylogeny of Shewanella (Gammaproteobacteria: lteromonadales: Shewanellaceae) BMC Genomics. 2011;12:237. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Colston SM, Fullmer MS, Beka L, Lamy B, Gogarten JP, Graf J. Bioinformatic genome comparisons for taxonomic and phylogenetic assignments using Aeromonas as a test case. mBio. 2014;5(6):e02136. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02136-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Glaeser SP, Kampfer P. Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) in prokaryotic taxonomy. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2015;38(4):237–245. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2015.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rozalski A, Sidorczyk Z, Kotelko K. Potential virulence factors of Proteus bacilli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997;61(1):65–89. doi: 10.1128/.61.1.65-89.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Muller HE. Occurrence and pathogenic role of Morganella-Proteus-Providencia group bacteria in human feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1986;23(2):404–405. doi: 10.1128/JCM.23.2.404-405.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cohen MM., Jr Proteus syndrome review: molecular, clinical, and pathologic features. Clin Genet. 2014;85(2):111–119. doi: 10.1111/cge.12266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hamilton AL, Kamm MA, Ng SC, Morrison M. Proteus spp. as Putative Gastrointestinal Pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018;31(3):e00085–e00017. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00085-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goker M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee I, Kim YO, Park SC, Chun J. OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2015;66:1100–1103. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.000760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Intra- and inter-species distances of eleven species infer by five individual genes. In each boxplot, from bottom to top: minimum, median and maximum. Table S1. Intra- and inter-species genetic distance median values and ranges of concatenated 5-gene and five individual genes.
Data Availability Statement
The nucleotide sequences of five HKGs are deposited in the GenBank nucleotide sequence database under the accession numbers dnaJ: MG492023-MG492065, MG492068-MG492222, MG492228, MG492230-MG492232, MG492234-MG492250; mdh: MG492251-MG492295, MG492298-MG492452, MG492458, MG492460, MG492462-MG492478; pyrC: MG492479-MG492515, MG492518-MG492672, MG492678, MG492680, MG492682-MG492706; recA: MG492707-MG492733, MG492735, MG492737-MG492738, MG492743-MG492897, MG492900-MG492934; rpoD: MG492935-MG492959, MG492961, MG492963, MG492969-MG493125, MG493128-MG493162.