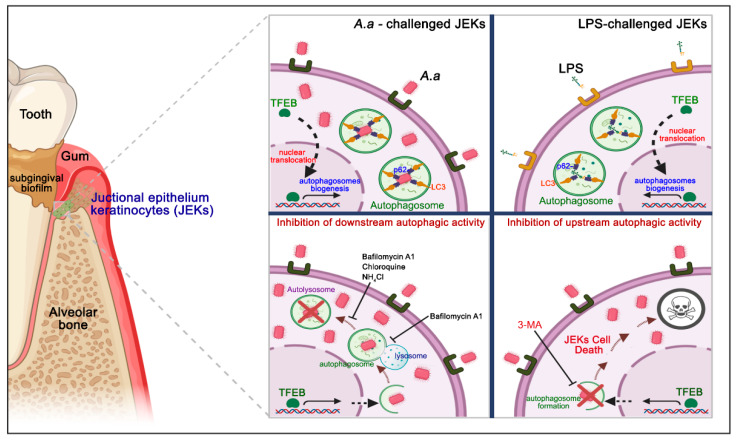
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the junctional epithelium keratinocytes-autophagy induced by A. actinomycetemcomitans infection. The junctional epithelium represents the main site of the initial interaction between the dysbiotic subgingival biofilm and host. The challenge and binding of A. actinomycetemcomitans and its purified LPS on JEKs surface triggers TFEB translocation to the nucleus and autophagosomes biogenesis. Bacteria and LPS internalized are sequestered to the autophagosomes in formation, through recruitment to the p62-cargo adapter protein, and interact with LC3 protein, favoring autophagy activation (upper panel). Treatment with the alkalinizing compounds of lysosomes bafilomycin A1, chloroquine, and NH4Cl, which inhibit the late stages of autophagic flow, induced intracellular bacteria accumulation and significantly increased the infected-JEKs number (lower left panel). Inhibition of autophagosome biogenesis with 3-MA induces cell death in JEKs challenged with A. actinomycetemcomitans or its purified LPS in the initial stage of infection (lower right panel). This figure was designed using BioRender.com.