Abstract
Background
The average age of the global population is rising at an increasing rate. There is a disproportional increase in Emergency Department (ED) visits by older people worldwide. In the Brazilian health system, complex and severely ill patients and those requiring specialized urgent procedures are referred to tertiary level care. As far as we know, no other study in Latin America has analyzed the impact of demographic changes in tertiary ED attendance. Aim: To describe the sociodemographic characteristics and outcomes of tertiary Brazilian ED users.
Methods
Design: Observational cross-sectional analytic study. Setting: Emergency Department, tertiary university hospital, São Paulo, Brazil. Participants: patients aged 18 years or older attending a tertiary ED (2009–2013). The primary outcomes were hospitalization and mortality; the secondary outcome was ICU admission. Age was categorized as ‘young adults’ (18-39y), ‘adults’ (40-59y), ‘young-older adults’ (60-79y), and ‘old-older adults’ (80-109y). Other variables included sex, reason for attendance, time of ED visit, mode of presentation, type of hospitalization, main procedure, length of hospital stay (LOS) and length of ICU stay (ICU-LOS). We calculated descriptive statistics, built generalized linear mixed models for each outcome and estimated Odds Ratios (95% CI) for the independent categorical variables. The significance level was 5% with Bonferroni correction.
Results
Older age-groups represented 26.6% of 333,028 ED visits, 40.7% of admissions, 42.7% of ICU admissions and 58% of all deaths. Old-older patients accounted for 5.1% of ED visits, 9.5% of admissions and 10.1% of ICU admissions. Hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality rates increased with older age in both sexes. LOS and ICU-LOS were similar across age-groups. The proportions of visits and admissions attributed to young adults decreased annually, while those of people aged 60 or over increased. The ORs for hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality associated with the old-older group were 3.49 (95% CI = 3.15–3.87), 1.27 (1.15–1.39) and 5.93 (5.29–6.66) respectively, with young adults as the reference.
Conclusions
In tertiary ED, age is an important risk factor for hospitalization and mortality, but not for ICU admission. Old-older people are at the greatest risk and demand further subgroup stratification.
Keywords: Aged demography, Emergency department, Older, Outcome, Routinely collected data
Background
The average age of the global population is rising at an increasing rate. People aged 60 and over accounted for 13% of the global population in 2017. While this age group is likely to double by 2050, the population younger than 15 is expected to remain stable [1].
Although older people are a heterogenous group in terms of physiological reserve and rate of functional decline, multimorbidity and use of health services tend to increase as age rises [2–4]. The increase in emergency department (ED) visits by older individuals is greater than the rate of growth of this population in North America, Europe, Asia and Oceania [5–8]. Furthermore, compared to younger adults, older ED patients on average have earlier ED returns, longer hospital stays, greater resource use, and higher rates of hospitalization and adverse outcomes [9, 10].
In the Brazilian health system, complex and severely ill patients and those requiring specialized urgent procedures are referred to tertiary level care [11]. As far as we know, no other study in Latin America has analyzed the impact of demographic changes in tertiary ED attendance.
Aim
To describe the demographic profile of ED users in a tertiary hospital over a 5-year period and to investigate differences in outcomes by sex and age.
Methods
Design
Observational cross-sectional analytic study.
Study period
1st January 2009 to 31st December 2013.
Setting
São Paulo, capital of São Paulo State is the largest city in Brazil, with an estimated population of 12 millions of people. Hospital das Clínicas (HC) is a teaching hospital complex with 2200 beds of University of São Paulo Medical School, serving as the referral center for the whole state. The Central Institute, a tertiary university hospital, is the main unit within the Hospital das Clínicas complex.
Participants
Eligibility criteria
We considered for inclusion all patients aged 18 years or older attending the ED associated with the Hospital das Clínicas Central Institute (ED-HC). Those with obstetric, ophthalmological or otolaryngological problems were not eligible, since they were treated in the adjacent unit. We excluded records if they were incomplete or inconsistent, or if there were duplicates of the unique hospital attendance number or admission authorization form number. Furthermore, we excluded cases that resulted in hospital transfers; outcomes other than discharge or admission and patients that left without a medical consultation (LWBS) or against medical advice (LAMA).
To be eligible for inclusion, a medical evaluation had to be completed during the visit, and its outcome recorded as either admission or discharge. In addition, when the ED visit resulted in admission, we only included those with a final outcome coded as discharge or death. We excluded all other types of ED attendance and admission.
Participant selection
On arrival at ED-HC, the patient (or those accompanying them) provides their personal data and reason for attendance which are recorded in the electronic registration. The system generates a unique number for each separate ED-HC attendance. We considered an ED visit to be complete if a medical evaluation was finished and an outcome recorded electronically (discharge, admission, hospital transfer or other). Patients requiring more than 12 h of observation were admitted.
For each admission, the responsible doctor fills out an admission authorization form with the patient’s data; this generates a new admission authorization form number for the billing system [12, 13]. To conclude the admission, the doctor has to select the main ICD-10 code as well as the outcome (discharge, death, hospital transfer, self-discharge or other). If the patient dies in ED, it is standard practice to admit them on the system with the outcome coded as death.
Variables
We analyzed eligible ED-HC visits with respect to the following variables: age and sex of the patient; year of attendance; mode of presentation to ED-HC being either ‘spontaneous’ (without prior evaluation by another service) or ‘referred’ (having already accessed a different health service, and arriving by ambulance or helicopter); time of ED visit (day shift 7 AM-7 PM or night shift 7 PM-7 AM); and ED outcome (admission or discharge). In cases resulting in admission we analyzed additional factors. These were type of hospitalization (surgical, clinical or other); main procedure (surgical, clinical or transplant-related); length of hospital stay (LOS); use or not of the ICU; length of ICU stay (ICU-LOS); and final admission\ outcome (discharge or death).
The categorical variables were the following: age-group, year of presentation, mode of presentation, reason for attendance, time of ED visit, type of hospitalization, main procedure, and ICU admission. We stratified age into the following groups: young adults (18–39 years), adults (40–59), young-older adults (60–79) and old-older adults (80–109). We categorized the reasons for attendance as either ‘external causes’ (injuries or health conditions related to accidents, trauma, burns, poisoning, environmental events and others, either unintentional or intentional), ‘general and localized symptoms’, ‘evaluation requested by another service’, ‘scheduled attendances’, or ‘other’. The continuous variables were age, LOS (the interval between the admission and discharge billing dates), and ICU-LOS (ICU days billed). Furthermore, we stratified LOS into six categories: 0–1, 2, 3, 4–7, 8–20, > = 21 days of hospitalization. Hospital admissions lasting one day or less were grouped as one category (0–1).
The primary dichotomous outcomes were hospitalization (admission vs ED discharge), and mortality (death vs hospital discharge). The secondary dichotomous outcome was ICU admission (or not). The primary aim was to investigate associations between demographic characteristics (age and sex) and the outcome variables.
Data source
We retrieved routinely collected data from administrative electronic registers maintained by HC, then consolidated them to produce a single dataset. ED attendance data are recorded in the hospital information system, and admissions data in the hospital billing system. In some cases, it was necessary to recode entries, depending on how they were recorded in the electronic system. Otherwise, we obtained data directly from the hospital databases.
Potential biases and analytic issues
This is an observational analytic study of electronic health data collected routinely for administrative purposes and for documentation of clinical care. Routinely collected health data are defined as those collected without a pre-existing research question [14]. Guidelines such as STROBE and its extension, RECORD (REporting of studies Conducted using Observational Routinely-collected health Data), were developed to enhance the quality of observational research and the transparency of results [15, 16]. We used the STROBE and RECORD statements as reporting guidelines.
The study covers a five-year period, and some patients had multiple ED visits and admissions. We identified individuals with more than one ED visit, ranking them by total number of attendances over the 5-year period. As such, we determined an upper-limit for inclusion in the study.
The reasons for attendance were varied and numerous; 72 were recorded in the hospital information system. To facilitate the analysis, we assigned broader categories (‘external causes’, ‘general and localized symptoms’, ‘evaluation requested by another service’, ‘scheduled attendances’, or ‘other’). The category of ‘scheduled attendance’, which describes non-emergency visits (e.g. returning for test results), represents neither ‘spontaneous’ nor ‘referred’ modes of ED presentation (see Variables in the main text), and was therefore defined as missing data.
During the study period, there were changes in the triage processes at ED-HC. Manchester Triage System version II, a new triage system based on individual clinical risk was implemented [17]. We analyzed year of attendance and mode of presentation in order to identify any effect due to these changes.
The high number of study subjects (ED visits) demands a measure of effect size, such as an Odds Ratio (OR) (or log OR), to estimate the magnitude of effect or association between two or more variables [18–20]. The effect size together with its confidence interval provides an estimate of the magnitude of an effect of interest and the precision of that estimate [21, 22]. Generalized linear mixed models (GLMM) for a given dichotomous outcome (dependent variable), using binomial probability distribution and logit link function, allow an estimate of ORs (with 95% confidence intervals) for independent variable categories in relation to respective reference categories.
Statistical analysis
We calculated summary statistics for ED-HC visits and admissions. Categorical variables are presented as total count (n) and percentage. Continuous variables are presented as mean (standard deviation) or median (maximum and minimum values). Descriptive statistics were further stratified according to year, sex and age-group. For the multivariate analysis, generalized linear mixed models were built in order to investigate variables associated with the primary and secondary dichotomous outcomes. All three models had binomial probability distribution and logit link function Results are presented as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). The significance level was set at 5% with Bonferroni correction. All analyses were conducted using SPSS Statistics version 25.0 (IBM, Corp., Armonk, NY).
Results
Participants
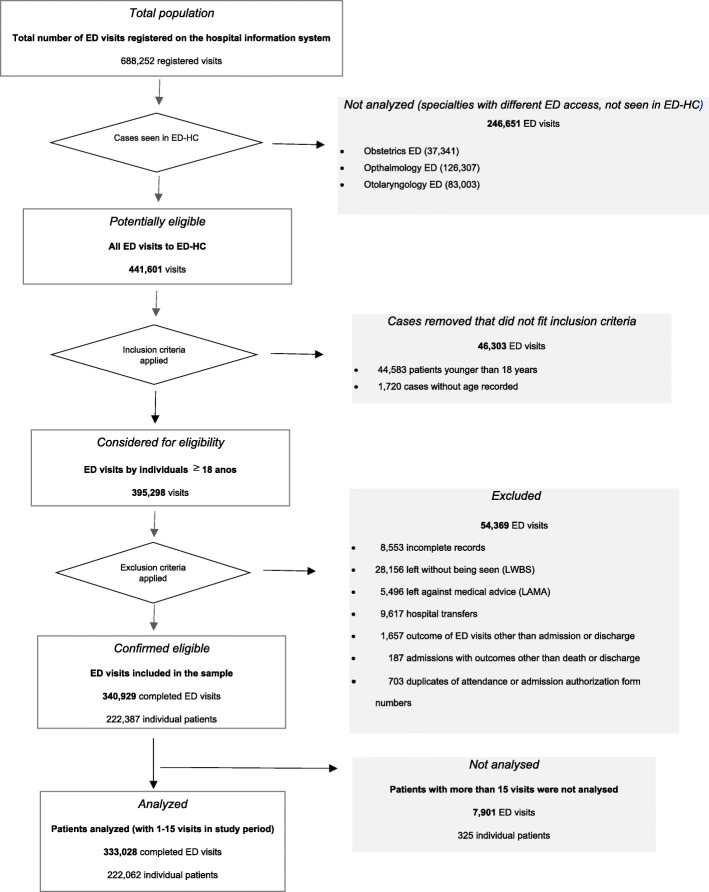
Figure 1 shows the selection process for the study population. After exclusions, the eligible sample was made up of 340,929 consecutive attendances, associated with 222,387 individual patients. The mean (SD) number of visits per person over the 5-year period was 1.53 (1.60) with a range of 1 to 136. The 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles were 1.00, 1.00 and 2.00 respectively. We set a cut-off point for inclusion in the analysis at 15 ED visits per person. Applying this value, there were 222,060 patients (99.99% of the sample) with between 1 and 15 visits, resulting in 333,028 complete attendances (97.68% of the sample). The mean (SD) age was 46.7 (18.6) and the median was 45, with a range of 18 to 108 years (See Table 1).
Fig. 1.
Flow-diagram of case selection process
Table 1.
Sample selection for analysis
| ED visits/patient | ED visits, N | (%) | patients, N | (%) | mean | (SD) | median | (min-max) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eligible sample | 1 to 15 | 333,028 | (97.68) | 222,062 | (99.999) | 46.7 | (18.6) | 45.0 | (18–108) |
| 1 | 166,364 | (48.80) | 166,364 | (74.92) | 44.1 | (18.2) | 41.0 | (18–108) | |
| 2 to 15 | 166,664 | (48.88) | 55,698 | (25.08) | 49.2 | (18.7) | 48.0 | (18–103) | |
| > 15 | 7901 | (2.32) | 325 | (0.001) | 54.9 | (18.3) | 55.0 | (20–99) |
SD Standard Deviation, min-max minimum-maximum. Mean, SD, median and min-max refer to age in years
Characteristics of study subjects
Women made up over half the ED visits (54.6%). Young adults accounted for the majority of attendances (40.8%), followed by adults (32.7%), young-older adults (21.5%) and old-older adults (5.1%). Between 2009 and 2013, the mean and median ages increased by 3.2 and 4 years, respectively (Table 2). There were 52,592 admissions (15.8% of ED attendances), with 13,615 requiring an ICU stay (25,9% of admissions). Of 52,592 hospitalizations, 6674 resulted in death, giving a mortality rate of 12.7% (Table 3).
Table 2.
ED visit demographic data
| ED visits N | (%) | mean age | (SD) | median age | (min-max) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 71,833 | (21.6) | 45.2 | (18.5) | 43 | (18–103) |
| 2010 | 68,386 | (20.5) | 46.1 | (18.3) | 44 | (18–104) |
| 2011 | 70,715 | (21.2) | 46.8 | (18.3) | 46 | (18–101) |
| 2012 | 76,224 | (22.9) | 47.4 | (18.6) | 47 | (18–108) |
| 2013 | 45,870 | (13.8) | 48.4 | (19.4) | 47 | (18–107) |
| Total | 333,028 | (100.0) | 467 | (186) | 45 | (18–108) |
| Women | 181,884 | (54.6) | 46.5 | (18.6) | 45 | (18–108) |
| Men | 151,144 | (45.4) | 46.9 | (18.5) | 46 | (18–102) |
| young adults | 135,763 | (40.8) | 28.4 | (6.1) | 28 | (18–39) |
| adults | 108,830 | (32.7) | 49.5 | (5.7) | 50 | (40–59) |
| young-older adults | 71,602 | (21.5) | 68.2 | (5.6) | 68 | (60–79) |
| old-older adults | 16,833 | (5.1) | 84.7 | (4.1) | 84 | (80–108) |
Percentages are out of the total number of eligible ED visits, or total number of admissions, after exclusions. SD Standard Deviation, min-max minimum-maximum. Mean, SD, median and min-max refer to age in years
Table 3.
ED visit characteristics and missing data
| ED visit Variables | categories | N | (% ED visits) | % Valid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode of presentation | Spontaneous | 316,153 | (94.9) | 94.9 |
| Referred | 16,875 | (5.1) | 5.1 | |
| Valid | 333,028 | (100.0) | 100.0 | |
| Missing | 0 | |||
| Time of ED visit | Day shift (7 AM-7 PM) | 246,520 | (74.0) | 74.0 |
| Night shift (7 PM-7 AM) | 86,508 | (26.0) | 26.0 | |
| Valid | 333,028 | (100.0) | 100.0 | |
| Missing | 0 | |||
| Reason for attendance | Local symptoms | 106,831 | (32.1) | 32.8 |
| General symptoms | 150,423 | (45.2) | 46.2 | |
| External causes | 30,323 | (9.1) | 9.3 | |
| Evaluation | 37,780 | (11.3) | 11.6 | |
| Valid | 325,357 | (97.7) | 100.0 | |
| Missing (scheduled visits) | 7671 | (2.3) | ||
| ED outcome | Admission | 52,592 | (15.8) | 15.8 |
| Discharge | 280,436 | (84.2) | 84.2 | |
| Valid | 333,028 | (100.0) | 100.0 | |
| Missing | 0 | |||
| Admission Variables | ||||
| Type of hospitalization | Surgical | 26,091 | (7.8) | 50.5 |
| Clinical | 25,537 | (7.7) | 49.5 | |
| Valid | 51,628 | (15.5) | 100.0 | |
| Missing (other specialties) | 964 | (0.3) | ||
| Missing (discharged from ED) | 280,436 | (84.2) | ||
| Main Procedure | Clinical | 36,376 | (10.9) | 69.4 |
| Surgical | 14,564 | (4.4) | 27.8 | |
| Transplant-related | 1493 | (0.4) | 2.8 | |
| Valid | 52,433 | (15.7) | 100.0 | |
| Missing (diagnostic testing) | 146 | (0.0) | ||
| Missing (discharged from ED) | 280,449 | (84.2) | ||
| Use of ICU | No | 38,977 | (11.7) | 74.1 |
| Yes | 13,615 | (4.1) | 25.9 | |
| Valid | 52,592 | (15.8) | 100.0 | |
| Missing (discharged from ED) | 280,436 | (84.2) | ||
| Final admission outcome | Death | 6674 | (2.0) | 12.7 |
| Discharge | 45,918 | (13.8) | 87.3 | |
| Valid | 52,592 | (15.8) | 100.0 | |
| Missing (discharged from ED) | 280,436 | (84.2) | ||
| Categorized LOS | 0–1 | 11,252 | (3.4) | 21.4 |
| 2–2 | 6455 | (1.9) | 12.3 | |
| 3–3 | 4612 | (1.4) | 8.8 | |
| 4–7 | 11,158 | (3.4) | 21.2 | |
| 8–20 | 13,462 | (4.0) | 25.6 | |
| 21+ | 5640 | (1.7) | 10.7 | |
| Valid | 52,579 | (15.8) | 100.0 | |
| Missing (discharged from ED) | 280,449 | (84.2) | ||
Missing data: 7671 (2.3%) due to ‘scheduled attendances’, 964 (0.3%) due to admissions to other specialties and 146 (0.0%) due to diagnostic testing. Valid percentages are out of the total number of eligible ED visits, or total number of admissions, after exclusions and without missing data
Table 4 presents ED visit and admission data stratified by age-group and sex. Older age-groups were responsible for 26.6% of ED visits, 37% of referred presentations, 40.8% of all admissions, 42.7% of ICU admissions and 58.1% of all deaths. There were a greater number of men that attended with a referred presentation. Proportionally more men than women were admitted (18.6% vs 13.4%), and they carried a higher in-patient mortality rate (13.4% vs 11.9%). The number of referred presentations, admissions, and in-patient deaths increased proportionally with advancing age from young to old-older adults.
Table 4.
ED visit and admission data categorized by sex and age-group
| Women | (%) | Men | (%) | Total (100%) | young-adult | (%) | adult | (%) | young-older adult | (%) | old-older adult | (%) | Total (100%) | |
| ED visits N (%) | 181,884 | (54.6) | 151,144 | (45.4) | 333,028 | 135,763 | (40.8) | 108,830 | (32.7) | 71,602 | (21.5) | 16,833 | (5.1) | 333,028 |
| Referred presentation N (%) | 6808 | (40.3) | 10,067 | (59.7) | 16,875 | 5473 | (32.4) | 5144 | (30.5) | 4428 | (26.2) | 1830 | (10.8) | 16,875 |
| Admissions N (%) | 24,429 | (46.5) | 28,163 | (53.5) | 52,592 | 13,708 | (26.1) | 17,448 | (33.2) | 16,464 | (31.3) | 4972 | (9.5) | 52,592 |
| ICU admissions N (%) | 6194 | (45.5) | 7421 | (54.5) | 13,615 | 3343 | (24.6) | 4455 | (32.7) | 4441 | (32.6) | 1376 | (10.1) | 13,615 |
| Deaths N (%) | 2914 | (43.7) | 3760 | (56.3) | 6674 | 914 | (13.7) | 1884 | (28.2) | 2630 | (39.4) | 1246 | (18.7) | 6674 |
| Women | (%) | Men | (%) | p-value | young-adult | (%) | adult | (%) | young-older adult | (%) | old-older adult | (%) | p-value | |
| ED visit characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| Referred presentation N (%) | 6808 | (3.7) | 10,067 | (6.7) | < .001 | 5473 | (4.0) | 5144 | (4.7) | 4428 | (6.2) | 1830 | (10.9) | < .001 |
| Admission N (%) | 24,429 | (13.4) | 28,163 | (18.6) | < .001 | 13,708 | (10.1) | 17,448 | (16.0) | 16,464 | (23.0) | 4972 | (29.5) | < .001 |
| Total ED visits N (%) | 181,884 | (1000) | 151,144 | (100.0) | 135,763 | (100.0) | 108,830 | (100.0) | 71,602 | (100.0) | 16,833 | (100.0) | ||
| Admission characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| Surgical hospitalization N (%) | 11,969 | (50.1) | 14,122 | (50.9) | .052 | 7147 | (53.2) | 8665 | (50.6) | 8043 | (49.7) | 2236 | (45.6) | < .001 |
| Surgical main procedure N (%) | 6683 | (27.4) | 7881 | (28.1) | .104 | 3963 | (29.0) | 4809 | (27.7) | 4536 | (27.6) | 1256 | (25.3) | .014 |
| ICU admissions N (%) | 6194 | (25.4) | 7421 | (26.4) | .009 | 3343 | (24.4) | 4455 | (25.5) | 4441 | (27.0) | 1376 | (27.7) | < .001 |
| Deaths N (%) | 2914 | (11.9) | 3760 | (13.4) | < .001 | 914 | (6.7) | 1884 | (10.8) | 2630 | (16.0) | 1246 | (25.1) | < .001 |
| Total hospital admissions | 24,429 | (100.0) | 28,163 | (100.0) | 13,708 | (100.0) | 17,448 | (100.0) | 16,464 | (100.0) | 4972 | (100.0) | ||
| Length of stay | ||||||||||||||
| ICU-LOS mean (SD) | 6.6 (8.0) | 6.7 (8.0) | 6.3 (7.7) | 6.7 (7.9) | 6.9 (8.3) | 6.8 (8.1) | ||||||||
| ICU-LOS median (max-min) | 4.0 (1–74) | 4.0 (1–90) | 3.0 (1–71) | 4.0 (1–90) | 4.0 (1–68) | 4.0 (1–74) | ||||||||
| LOS mean (SD) | 8.6 (11.5) | 8.6 (10.9) | 8.3 (10.7) | 8.7 (11.0) | 8.7 (11.8) | 8.7 (11.1) | ||||||||
| LOS median (max-min) | 5.0 (0–490) | 5.0 (0–178) | 4.0 (0–125) | 5.0 (0–184) | 5.0 (0–490) | 5.0 (0–193) | ||||||||
LOS length of hospital stay, ICU-LOS length of ICU stay, SD Standard Deviation, min-max minimum-maximum. Mean, SD, median and min-max refer to LOS and ICU-LOS in days. Percentages are out of the total number of eligible ED visits, or total number of admissions
Amongst old-older adults, the rates of admission (29.5%) and of in-hospital mortality (25.2%) were three and four times that of young adults (10.1 and 6.7%, respectively). Old-older adults had proportionally fewer surgical hospitalizations and surgical procedures than other age-groups. The proportion of admitted patients requiring an ICU stay was similar for the young and adult groups, and again between young-older and old-older groups. LOS and ICU-LOS differed minimally according to age and sex (Table 4).
Table 5 presents the same data, stratified by sex and age-group combined. There were more female ED attendees in every age bracket. Admission and mortality rates increased with age across both sexes. In all age-groups except old-older adults, there were more men than women with referred presentations, with more men requiring hospital admission, surgical hospitalization, surgical procedures and ICU stays. Mortality was also higher amongst men.
Table 5.
ED visit and admission data by sex and age-group combined
| Sex | Women | Men | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age-group | young adult | adult | young-older adult | old-older adult | young adult | adult | young-older adult | old-older adult | |
| Age-group/sex | N | 74,658 | 60,590 | 36,886 | 9750 | 61,105 | 48,240 | 34,716 | 7083 |
| (%) | (41.0) | (33.3) | (20.3) | (5.4) | (40.4) | (31.9) | (23.0) | (4.7) | |
| ED visit characteristics | |||||||||
| Referred presentations | N | 1819 | 1955 | 1979 | 1055 | 3654 | 3189 | 2449 | 775 |
| (%) | (2.4) | (3.2) | (5.4) | (10.8) | (6.0) | (6.9) | (7.1) | (10.9) | |
| Admissions | N | 6217 | 7711 | 7631 | 2870 | 7491 | 9737 | 8833 | 2102 |
| (%) | (8.3) | (12.7) | (20.7) | (29.4) | (12.3) | (20.2) | (25.4) | (29.7) | |
| Total ED visits | N | 74,658 | 60,590 | 36,886 | 9750 | 61,105 | 48,240 | 34,716 | 7083 |
| (%) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | |
| Admission characteristics | |||||||||
| Surgical hospitalization | N | 3169 | 3778 | 3731 | 1291 | 3978 | 4887 | 4312 | 945 |
| (%) | (52.4) | (50.1) | (49.9) | (45.6) | (53.9) | (51.0) | (49.6) | (45.6) | |
| Surgical main procedure | N | 1726 | 2151 | 2095 | 711 | 2237 | 2658 | 2441 | 545 |
| (%) | (27.8) | (28.0) | (27.5) | (24.9) | (29.9) | (27.4) | (27.7) | (26.0) | |
| ICU admissions | N | 1426 | 1926 | 2064 | 778 | 1917 | 2529 | 2377 | 598 |
| (%) | (22.9) | (25.0) | (27.0) | (27.1) | (25.6) | (26.0) | (26.9) | (28.4) | |
| Deaths | N | 288 | 715 | 1190 | 721 | 626 | 1169 | 1440 | 525 |
| (%) | (4.6) | (9.3) | (15.6) | (25.1) | (8.4) | (12.0) | (16.3) | (25.0) | |
| Total admissions | N | 6217 | 7711 | 7631 | 2870 | 7491 | 9737 | 8833 | 2102 |
| (%) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | |
| Continuous variables | |||||||||
| Age (years) | mean (SD) | 28.3 (6.1) | 49.4 (5.6) | 68.2 (5.7) | 84.9 (4.3) | 28.5 (6.0) | 49.6 (5.8) | 68.2 (5.6) | 84.3 (3.9) |
| median (min-max) | 28 (18–39) | 49 (40–59) | 68 (60–79) | 84 (80–108) | 28 (18–39) | 50 (40–59) | 68 (60–79) | 83 (80–102) | |
| ICU-LOS (days) | mean (SD) | 6.2 (7.8) | 6.6 (7.8) | 6.9 (8.4) | 6.8 (7.9) | 6.3 (7.7) | 6.7 (8.0) | 6.8 (8.2) | 6.9 (8.5) |
| median (min-max) | 3 (1–71) | 4 (1–60) | 4 (1–67) | 4 (1–74) | 3 (1–59) | 4 (1–90) | 4 (1–68) | 4 (1–63) | |
| LOS (days) | mean (SD) | 8.3 (10.6) | 8.7 (10.9) | 8.8 (12.9) | 8.5 (11.1) | 8.3 (10.8) | 8.6 (11.1) | 8.7 (10.8) | 9.0 (11.0) |
| median (min-max) | 4 (0–125) | 5 (0–184) | 5 (0–490) | 5 (0–193) | 4 (0–115) | 5 (0–178) | 5 (0–106) | 5 (0–87) | |
LOS length of hospital stay, ICU-LOS length of ICU stay, SD Standard Deviation; min-max: minimum-maximum. Mean, SD, median and min-max refer to age in years and to LOS and ICU-LOS in days. Percentages are out of the total number of eligible ED visits, or total number of admissions
Table 6 presents data categorized by year of attendance. The proportion of ED-HC visits by young adults decreased annually, falling from 44.4 to 38.2% between 2009 and 2013. In contrast, people over 60 years accounted for proportionally more attendances, rising from 24.1 to 29.9%. Similar trends were observed for admissions and ICU admissions. In 2013, the number of ED visits fell significantly in all age groups, except amongst the old-older adult group. However, the total number of hospital and ICU admissions remained relatively stable. There was little variation in LOS during the 5-year period, but there was a reduction in the mean ICU-LOS.
Table 6.
ED demographic, visit and admission data categorized by year of attendance
| Year | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | (%) | N | (%) | N | (%) | N | (%) | N | (%) | |
| ED visits demographic characteristics | ||||||||||
| Women | 38,530 | (53.6) | 37,410 | (54.7) | 38,816 | (54.9) | 42,612 | (55.9) | 24,516 | (53.4) |
| young adults | 31,918 | (44.4) | 28,581 | (41.8) | 27,980 | (39.6) | 29,753 | (39.0) | 17,531 | (38.2) |
| adults | 22,583 | (31.4) | 22,520 | (32.9) | 24,387 | (34.5) | 24,724 | (32.4) | 14,616 | (31.9) |
| young-older adult | 14,236 | (19.8) | 14,115 | (20.6) | 14,922 | (21.1) | 17,997 | (23.6) | 10,332 | (22.5) |
| old-older adults | 3096 | (4.3) | 3170 | (4.6) | 3426 | (4.8) | 3750 | (4.9) | 3391 | (7.4) |
| ED visits characteristics | ||||||||||
| Referred visits | 2995 | (4.2) | 3142 | (4.6) | 3696 | (5.2) | 3623 | (4.8) | 3419 | (7.5) |
| Admissions | 11,064 | (15.4) | 10,872 | (15.9) | 10,961 | (15.5) | 10,340 | (13.6) | 9355 | (20.4) |
| Total ED visits | 71,833 | (100.0) | 68,386 | (100.0) | 70,715 | (100.0) | 76,224 | (100.0) | 45,870 | (100.0) |
| Admissions demographic characteristics | ||||||||||
| Women | 5043 | (45.6) | 5041 | (46.4) | 5102 | (46.5) | 4854 | (46.9) | 4389 | (46.9) |
| young adults | 3049 | (27.6) | 2945 | (27.1) | 2773 | (25.3) | 2606 | (25.2) | 2335 | (24.9) |
| adults | 3679 | (33.2) | 3647 | (33.5) | 3812 | (34.7) | 3327 | (32.2) | 2983 | (31.9) |
| young-older adult | 3401 | (30.7) | 3275 | (30.1) | 3328 | (30.4) | 3479 | (33.6) | 2981 | (31.9) |
| old-older adults | 935 | (8.4) | 1005 | (9.2) | 1048 | (9.6) | 928 | (9.0) | 1056 | (11.2) |
| Admissions characteristics | ||||||||||
| Surgical hospitalization | 5052 | (46.6) | 5184 | (48.6) | 5274 | (49.0) | 5551 | (54.7) | 5030 | (54.5) |
| Surgical main procedure | 3074 | (27.9) | 2968 | (27.4) | 2871 | (26.3) | 2947 | (28.6) | 2704 | (29.0) |
| ICU admissions | 2479 | (22.4) | 2856 | (26.3) | 2782 | (25.4) | 2847 | (27.5) | 2651 | (28.3) |
| Deaths | 1240 | (11.2) | 1379 | (12.7) | 1407 | (12.8) | 1378 | (13.3) | 1270 | (13.6) |
| Total hospital admissions | 11,064 | (100.0) | 10,872 | (100.0) | 10,961 | (100.0) | 10,340 | (100.0) | 9355 | (100.0) |
| ICU admissions demographic characteristics | ||||||||||
| Women | 1078 | (43.5) | 1300 | (45.5) | 1246 | (44.8) | 1305 | (45.8) | 1265 | (47.7) |
| young adults | 686 | (27.7) | 710 | (24.9) | 659 | (23.7) | 690 | (24.2) | 598 | (22.6) |
| adults | 815 | (32.9) | 923 | (32.3) | 996 | (35.8) | 895 | (31.4) | 826 | (31.2) |
| young-older adult | 770 | (31.0) | 912 | (31.9) | 863 | (31.0) | 987 | (34.7) | 909 | (34.2) |
| old-older adults | 208 | (8.4) | 311 | (10.9) | 264 | (9.5) | 275 | (9.7) | 318 | (12.0) |
| Total ICU admissions | 2479 | (100.0) | 2856 | (100.0) | 2782 | (100.0) | 2847 | (100.0) | 2651 | (100.0) |
| Length of stay | ||||||||||
| ICU-LOS mean (SD) | 7.6 (9.4) | 7.2 (8.6) | 6.8 (8.2) | 6.1 (7.2) | 5.7 (6.3) | |||||
| ICU-LOS median (max-min) | 4.0 (1–77) | 4.0 (1–90) | 4.0 (1–74) | 4.0 (1–71) | 4.0 (1–68) | |||||
| LOS mean (SD) | 8.6 (11.3) | 8.6 (11.1) | 8.6 (10.9) | 8.4 (11.4) | 8.9 (11.4) | |||||
| LOS median (max-min) | 4.0 (0–125) | 4.0 (0–109) | 5.0 (0–193) | 5.0 (0–490) | 5.0 (0–368) | |||||
LOS length of hospital stay, ICU-LOS length of ICU stay, SD Standard Deviation, min-max minimum-maximum. Mean, SD, median and min-max refer to LOS and ICU-LOS in days. Percentages are out of the total number of eligible ED visits, or total number of admissions
Main results
The main factors associated with hospital admission were referred presentation (OR 6.34); belonging to the old-older (3.49), young-older (2.70) and adult (1.75) age-groups; and male sex (1.37).
Admission to ICU was more frequent amongst patients with referred presentations (OR 1.36), and those with a surgical main procedure (OR 5.28). It was also more frequent among old-older (1.27), young-older (1.19) and adult (1.08) age-groups. The OR associated with the adult age-group (compared to young adults) did not reach significance of p < 0.007 with Bonferroni correction (p = 0.014). In a post-hoc analysis young-older and old-older adults also had a similar risk of ICU admission (p = 0.17). There was no association between sex and admission to ICU (p = 0.09).
The main risk factors associated with mortality were ICU admission (OR 7.34) and older age: old-older adults (5.93), young-older adults (3.41), and adults (2.04). External causes (2.26), presentation following referral (1.89) and male sex (1.14) also carried increased OR for mortality. There was no difference in mortality between the years analyzed (p = 0.59). Table 7 summarizes the multivariate analysis results.
Table 7.
Generalized Linear Mixed Models main results
| Hospitalization | Admission to ICU | Mortality | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed effect | p-value | Categories | OR | (CI 95%) | p-value | Categories | OR | (CI 95%) | p-value | Categories | OR | (CI 95%) |
| Year | < .001 | 2013 | 1.21 | (1.12–1.32) | < .001 | 2013 | 1.31 | (1.22–1.42) | .599 | 2013 | 1.03 | (0.93–1.14) |
| 2012 | 0.80 | (0.74–0.86) | 2012 | 1.34 | (1.24–1.44) | 2012 | 1.07 | (0.97–1.18) | ||||
| 2011 | 0.94 | (0.87–1.02) | 2011 | 1.21 | (1.12–1.31) | 2011 | 1.05 | (0.95–1.16) | ||||
| 2010 | 1.01 | (0.94–1.09) | 2010 | 1.32 | (1.22–1.42) | 2010 | 1.08 | (0.97–1.19) | ||||
| 2009 | ref | 2009 | ref | 2009 | ref | |||||||
| Sex | < .001 | men | 1.37 | (1.30–1.44) | .096 | men | 1.04 | (0.99–1.09) | < .001 | men | 1.14 | (1.07–1.21) |
| women | ref | women | ref | women | ref | |||||||
| Age-groups | < .001 | old-older | 3.49 | (3.15–3.87) | < .001 | old-older | 1.27 | (1.15–1.39) | < .001 | old-older | 5.93 | (5.29–6.66) |
| young-older | 2.7 | (2.52–2.88) | young-older | 1.19 | (1.11–1.27) | young-older | 3.41 | (3.09–3.76) | ||||
| adult | 1.75 | (1.64–1.86) | adult | 1.08 | (1.02–1.16) | adult | 2.04 | (1.84–2.25) | ||||
| young adult | ref | young adult | ref | young adult | ref | |||||||
| Mode of presentation | < .001 | referred | 6.34 | (5.81–6.91) | < .001 | referred | 1.36 | (1.27–1.46) | < .001 | referred | 1.83 | (1.71–2.01) |
| self-initiated | ref | self-initiated | ref | self-initiated | ref | |||||||
| Time of ED visit | <.001 | Night shift | 1.34 | (1.27–1.42) | .031 | Night shift | 1.06 | (1.01–1.12) | .004 | Night shift | 1.10 | (1.03–1.17) |
| Day shift | ref | Day shift | ref | Day shift | ref | |||||||
| Type of hospitalization | <.001 | Surgical | 0.87 | (0.81–0.92) | <.001 | Surgical | 0.64 | (0.59–0.69) | ||||
| Clinical | ref | Clinical | ref | |||||||||
| Main procedure | <.001 | Transplant | 0.51 | (0.43–0.61) | <.001 | Transplant | 0.59 | (0.50–0.78) | ||||
| Surgical | 5.28 | (4.97–5.61) | Surgical | 0.79 | (0.73–0.86) | |||||||
| Clinical | ref | Clinical | ref | |||||||||
| ICU admission | < .001 | Yes | 7.34 | (6.75–7.97) | ||||||||
| No | ref | |||||||||||
OR Odds Ratio, CI 95% confidence interval 95%, ref. reference
Discussion
In this cross-sectional observational study of secondary data, we demonstrate an association between older age and higher rates of referred presentation, hospital admission and mortality in a tertiary Brazilian ED. These results are consistent with existing literature. Older adults presenting to ED are often acutely ill and more likely to require higher-level care [23, 24]. A review of 11 international studies reported that one-third to one-half of all ED attendances by older adults resulted in hospital admission, with rates of hospitalization between 2.5 and 4.6 times higher than the youngest patients [25]. However, none of these studies included Latin America data.
Our results may indicate a shift towards an older demographic in the Brazilian ED population. There was an annual fall in the proportion of ED visits by young adults, with those over 60 accounting for proportionally more attendances each year. Recent national data corroborated this trend in the use of hospital resources [26].
Women account for the majority of people visiting ED. [27] Even in countries with greater healthcare utilization amongst men, there is a marked female predominance in the oldest ED patients [28–30]. In this study there were more women in all age-groups, with the exception of young-older adults. There was an increased chance of admission for men in all age categories, except in the old-older group, where the probability of admission was similar to women. Male sex was a minor risk factor for hospitalization (OR 1.37) and mortality (1.14).
ED overcrowding is a problem worldwide. In many countries the number of ED visits is growing faster than the population [31, 32]. In 2012, the ED-HC began implementing a clinical-risk based triage system (Manchester Triage System version II) that assigns categories according to the urgency of the presentation [17]. Cases considered to be non-urgent by the multi-professional team were directed to appropriate alternative primary and secondary care services [33]. The number of cases seen in 2013 decreased significantly in all age-groups except old-older adults. However, the number of admissions, ICU stays and deaths remained stable, as did the number of cases being referred to ED-HC. This indicates that the new triage system was functioning appropriately.
It is important to highlight the growing importance of the oldest patients attending ED. [34–37] In the present study, people aged 80 or over represented 5.1% of ED visits, 9.5% of admissions and 10.1% of ICU admissions. They carried increased ORs for hospital admission (3.49, 95% CI 3.15–3.87), ICU admission (1.27, 1.15–1.39) and in-hospital death (5.93, 5.29–6.66). Between 2009 and 2013, while the three younger age groups selected by the triage system decreased, we observed a stable number of ED visits and increasing ICU admissions by old-older patients. This finding supports the existence of greater risks in this group.
We observed that older patients and those presenting to ED with a referral were more likely to require ICU admission, although the effect size was small in both cases. There were small positive ORs in the two older age-groups (1.19 and 1.27) compared to the reference class of young adults. This finding suggests that differences among age-groups might be mitigated by a judicious selection of patients admitted to ICU. The decision to admit to ICU must weigh up the acuity of illness, existing comorbidities, pre-hospital functional status and the patient’s wishes in relation to resuscitation and ceiling-of-care [38]. In the Netherlands, the number of very elderly patients attending ED has increased, but the number of ICU admissions has remained stable. This is mostly explained by more careful case selection [39]. In Scotland, patients admitted to ICU aged 80–89 had fewer comorbidities than their younger counterparts and underwent a greater proportion of emergency surgeries, but spent less time in ICU than patients under 65 [40]. In the present study, the mean ICU-LOS did not vary significantly between age-groups or sexes, but fell in nearly all the age-groups over the course of the five years studied, suggesting an increased turnover of beds.
This study demonstrates the importance of old-older adults in ED. It highlights the need to identify subgroups that carry greater risk of functional decline and adverse events, such as frail older people, some of whom may be candidates for palliative care. Indeed, subgroups of functional older people at lower risk must also be identified.
Limitations
We studied a large dataset from a single tertiary Brazilian ED covering a 5-year period. It is important to note that, the care of high-complexity patients is centered in tertiary level hospitals and, when acutely ill, such patients present or are referred to tertiary EDs with profiles similar to ED-HC. To our knowledge, this is the first Latin American comprehensive study to analyze associations between aging and tertiary ED attendance.
Five years is a short period to identify the impact of demographic change in the ED population. Moreover, 7901 ED visits due to 325 individuals were excluded because the cut-off for inclusion was set at 15 ED attendances. The mean age in this group was older (see Table 1). Even with this exclusion, we found an annual increase in the mean and median age, as well as in the proportion of patients aged over 60. We also observed a decrease in the proportion of young adults presenting to the ED.
Changes to the triage system altered the sample composition over the study period. The number of visits fell significantly in 2013, however the number of urgent and complex cases remained stable. Comparing each year to 2009, the effect size was minimal for hospitalization and for ICU admission, and there was no difference in mortality.
The definition of age-groups and classification of reasons for attendance could have introduced misclassification bias. The proportion of younger adults visiting ED-HC decreased annually, whereas those aged over 60 increased. We did not find this pattern when analyzing young-older and old-older groups (see Table 6).
The reasons for attendance were not assigned according to defined criteria and were not recorded by healthcare professionals. However, their inclusion in the study allowed ‘scheduled attendances’ to be identified and excluded. We were also able to differentiate ‘external causes’ (trauma, accidents, poisoning, falls, and so on), ‘general and localized symptoms’, and ‘evaluation requested by another service’ as grouped reported reasons for ED visit.
Conclusions
Between 2009 and 2013 the proportion of ED visits and admissions by adults aged 60 or over increased in the largest Brazilian tertiary hospital, meanwhile those by young adults fell. Hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality rates increased with older age in both men and women. However, we found similar LOS and ICU-LOS across age-groups, and small effect sizes associated with ICU admission in older patients. Among tertiary ED patients, age is an important risk factor for hospitalization and mortality, but not for ICU admission. Old-older people are at the greatest risk and demand further subgroup stratification.
Acknowledgements
Part of the content of this manuscript was recently presented in Brazil as an academic thesis (doi: 10.11606/T.5.2019.tde-28022019-100750).
The authors thank Paulo Silveira, Koichi Sameshima and Claudia Szlejf for their suggestions and support.
Abbreviations
- CI
Confidence interval
- ED
Emergency Department
- GLMM
Generalized Linear Mixed Models
- HC
Hospital das Clínicas
- ED-HC
Emergency Department associated with the Hospital das Clínicas Central Institute
- ICU
Intensive Care Unit
- ICU-LOS
length of Intensive Care Unit stay
- LAMA
Leave Against Medical Advice
- LOS
length of in-hospital stay
- LWBS
Leave Without Being Seen
- Min-max
minimum-maximum
- OR
Odds Ratio
- SD
Standard Deviation
- SPSS
Statistical Package for Social Sciences
Authors’ contributions
IV, JG and WF conceived the idea and supervised the study. JG, RD and JB designed the study. JB acquired the data. JG, RD and WF analyzed and interpreted data. JG and WF drafted the manuscript, with critical revisions for important intellectual content from all authors. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare they did not have a specific support, grant or other financial support for this study from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. As such there was no role of a funder in the design of the study; collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; or in the writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo (Comissão de Ética para Análise de Projetos de Pesquisa do HCFMUSP-CAPPesq), CAAE:20619513.3.0000.0068. The institutional Ethics and Research Committee waived the requirement for consent because the project is a retrospective analysis of routinely collected administrative data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. ESA/P/WP/248. New York: United Nations; 2017. https://population.un.org/wpp/Publications/Files/WPP2017_KeyFindings.pdf.
- 2.Wolff JL, Starfield B, Anderson G. Prevalence, expenditures, and complications of multiple chronic conditions in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(20):2269–2276. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.20.2269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gray LC, Peel NM, Costa AP, Burkett E, Dey AB, Jonsson PV, et al. Profiles of older patients in the emergency department: findings from the interRAI multinational emergency department study. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;62(5):467–474. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.dos Reis CS, Noronha K, Wajnman S. Envelhecimento populacional e gastos com internação do SUS: uma análise realizada para o Brasil entre 2000 e 2010. Revista Brasileira de Estudos de População. 2016;33(3):591–612. doi: 10.20947/s0102-30982016c0007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lowthian JA, Curtis AJ, Cameron PA, Stoelwinder JU, Cooke MW, McNeil JJ. Systematic review of trends in emergency department attendances: an Australian perspective. Emerg Med J. 2011;28(5):373–377. doi: 10.1136/emj.2010.099226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McCaig LF, Burt CW. National hospital ambulatory medical care survey: 2003 emergency department summary. Adv Data. 2005;358:1–38. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ad/ad358.pdf.. [PubMed]
- 7.Gabayan GZ, Sarkisian CA, Liang LJ, Sun BC. Predictors of admission after emergency department discharge in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(1):39–45. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li G, Lau JT, McCarthy ML, Schull MJ, Vermeulen M, Kelen GD. Emergency department utilization in the United States and Ontario, Canada. Acad Emerg Med. 2007;14(6):582–584. doi: 10.1197/j.aem.2007.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Samaras N, Chevalley T, Samaras D, Gold G. Older patients in the emergency department: a review. Ann Emerg Med. 2010;56(3):261–269. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2010.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pines JM, Mullins PM, Cooper JK, Feng LB, Roth KE. National trends in emergency department use, care patterns, and quality of care of older adults in the United States. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61(1):12–17. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Paim J, Travassos C, Almeida C, Bahia L, Macinko J. The Brazilian health system: history, advances, and challenges. Lancet. 2011;377(9779):1778–1797. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Carvalho DMT. Sistema de Informações Hospitalares do SUS – SIH-SUS. In: Ministério da Saúde, Organização Pan-Americana da SaúdeCruz FO, editor. A experiência brasileira em sistemas de informação em saúde. Volume1. Brasília: Editora do Ministério da Saúde; 2009. pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pepe VE: Sistema de Informações Hospitalares do Sistema Único de Saúde (SIH-SUS). In A experiência brasileira em sistemas de informação em saúde. Volume 2. Edited by: Ministério da Saúde, Organização Pan-Americana da Saúde, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz. Brasília: Editora do Ministério da Saúde; 2009;2:65–85. ISBN 978-85-334-1545-4.
- 14.Spasoff RA. Epidemiologic methods for health policy. NewYork: Oxford University Press, Inc.; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 15.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, STROBE Initiative The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007;370(9596):1453–1457. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Benchimol EI, Smeeth L, Guttmann A, Harron K, Moher D, Petersen I, et al. The REporting of studies conducted using observational routinely-collected health data (RECORD) statement. PLoS Med. 2015;12(10):e1001885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Santos AP, Freitas P, Martins HMG. Manchester triage system version II and resource utilisation in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2014;31(2):148–152. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2012-201782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Breaugh JA. Effect size estimation: factors to consider and mistakes to avoid. J Manage. 2003;29(1):79–97. doi: 10.1016/S0149-2063(02)00221-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ferguson CJ. An effect size primer: a guide for clinicians and researchers. Prof Psychol Res Pract. 2009;40(5):532–538. doi: 10.1037/a0015808. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sharpe D. Your Chi-Square test is statistically significant: now what? Pract Assess Res Eval. 2015;20(8):1–10. 10.7275/tbfa-x148. Available at: https://scholarworks.umass.edu/pare/vol20/iss1/8.
- 21.Nakagawa S, Cuthill IC. Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biol Rev. 2007;82:591–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maher JM, Markey JC, Ebert-May D. The other half of the story: effect size analysis in quantitative research. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2013;12(3):345–351. doi: 10.1187/cbe.13-04-0082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gruneir A, Silver MJ, Rochon PA. Review: emergency department use by older adults: a literature review on trends, appropriateness, and consequences of unmet health care needs. Med Care Res Rev. 2011;68(2):131–155. doi: 10.1177/1077558710379422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fayyaz J, Khursheed M, Mir MU, Khan UR. Pattern of emergency department visits by elderly patients: study from a tertiary care hospital, Karachi. BMC Geriatr. 2013;13:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-13-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Aminzadeh F, Dalziel WB. Older adults in the emergency department: a systematic review of patterns of use, adverse outcomes, and effectiveness of interventions. Ann Emerg Med. 2002;39(3):238–247. doi: 10.1067/mem.2002.121523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dias RD, Barros JVD. Burden of hospitalisation among older people in the Brazilian public health system: a big data analysis from 2009 to 2015. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2019;73(6):537–543. doi: 10.1136/jech-2018-210783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Roberts DC, McKay MP, Shaffer A. Increasing rates of emergency department visits for elderly patients in the United States, 1993 to 2003. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;51(6):769–774. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Freund Y, Vincent-Cassy C, Bloom B, Riou B, Ray P. Association between age older than 75 years and exceeded target waiting times in the emergency department: a multicenter cross-sectional survey in the Paris metropolitan area, France. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;62(5):449–456. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lowthian JA, Curtis AJ, Jolley DJ, Stoelwinder JU, McNeil JJ, Cameron PA. Demand at the emergency department front door: 10-year trends in presentations. Med J Aust. 2012;196(2):128–132. doi: 10.5694/mja11.10955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Salvi F, Mattioli A, Giannini E, Vita D, Morichi V, Fallani M, et al. Pattern of use and presenting complaints of older patients visiting an emergency Department in Italy. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013;25(5):583–590. doi: 10.1007/s40520-013-0112-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tang N, Stein J, Hsia RY, Maselli JH, Gonzales R. Trends and characteristics of US emergency department visits, 1997-2007. JAMA. 2010;304(6):664–670. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pines JM, Hilton JA, Weber EJ, Alkemade AJ, Al Shabanah H, Anderson PD, et al. International perspectives on emergency department crowding. Acad Emerg Med. 2011;18(12):1358–1370. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2011.01235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Daglius Dias R, Rios IC, Canhada CLB, Fernandes MD, Letaif LS, Bonfá E, Perondi MB. Using the Manchester triage system for refusing nonurgent patients in the emergency department: a 30-day outcome study. J Emerg Manag. 2016;14(5):365. doi: 10.5055/jem.2016.0300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Melzer D, Tavakoly B, Winder RE, Masoli JA, Henley WE, Bie A, Richards SH. Much more medicine for the oldest old: trends in UK electronic clinical records. Age Ageing. 2015;44(1):46–53. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afu113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lowthian JA, Stoelwinder JU, Mcneil JJ, Cameron PA. Is the increase in emergency short-stay admissions sustainable? Trends across Melbourne, 2000 to 2009. EMA - Emerg Med Australas. 2012;24(6):610–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-6723.2012.01609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Leonard C, Bein KJ, Latt M, Muscatello D, Veillard AS, Dinh MM. Demand for emergency department services in the elderly: an 11 year analysis of the greater Sydney area. EMA - Emerg Med Australas. 2014;26(4):356–360. doi: 10.1111/1742-6723.12250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vilpert S, Ruedin HJ, Trueb L, Monod-Zorzi S, Yersin B, Büla C. Emergency department use by oldest-old patients from 2005 to 2010 in a Swiss university hospital. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(1). 10.1186/1472-6963-13-344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Marik PE. Should age limit admission to the intensive care unit? Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2007;24(1):63–66. doi: 10.1177/1049909106295385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Haas LEM, Karakus A, Holman R, Cihangir S, Reidinga AC, de Keizer NF. Trends in hospital and intensive care admissions in the Netherlands attributable to the very elderly in an ageing population. Crit Care. 2015;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1061-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Docherty AB, Anderson NH, Walsh TS, Lone NI. Equity of access to critical care among elderly patients in Scotland: a national cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(1):3–13. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.