Correction to: BMC Immunol 21, 18 (2020)
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12865-020-00349-w
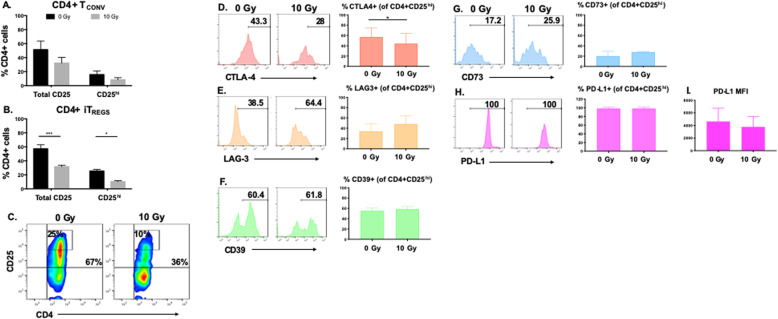
It was highlighted that in the original article [1] some of the bar graphs of Fig. 4 were blank. This Correction article shows the correct Fig. 4. The original article has been updated. The Publisher would like to apologize to the authors and readers for the inconvenience.
Fig. 4.
Phenotypic modulation of CD4 + CD25hi iTREGS by radiation. a CD4+ TCONV cells or b iTREG cells were mock irradiated or exposed to 10 Gy of radiation. Forty-eight hours post treatment CD4+ cells were analyzed for expression of CD25 by flow cytometry. c Representative plots of CD4 + CD25+ total (quadrant) or CD4 + CD25hi cells (box with numbers inset in plot). The expression of (d) CTLA-4, (e) LAG-3, (f) CD39, (g) CD73, (h) PD-L1, and (i) PD-L1 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) were evaluated within the CD4 + CD25hi population 48 h after radiation. Experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Error bars represent SEM. *P ≤ 0.05; ** P ≤ 0.01; *** P ≤ 0.001 by paired, two-tailed Student t test
Reference
- 1.Beauford, et al. Ionizing radiation modulates the phenotype and function of human CD4+ induced regulatory T cells. BMC Immunol. 2020;21:18. doi: 10.1186/s12865-020-00349-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]