Figure 1.
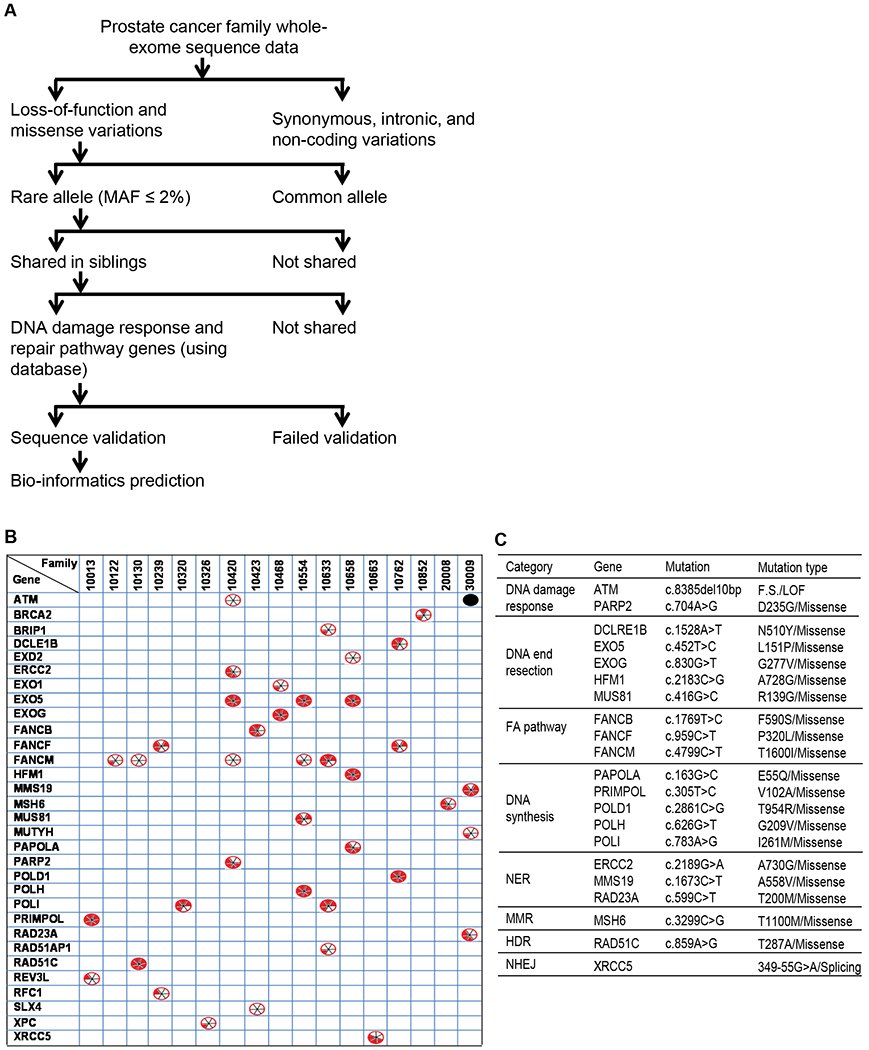
DNA damage response and repair gene mutations shared among members of PCa families and their predicted risk effects. (A) Flow chart showing the various criteria used to narrow down the mutations of interest and identify rare mutations likely to be pathogenic. (B) List of 31 DNA repair genes that are mutated in all PCa patients in one or more families (among 17 of the 20 PCa families studied). The black dot ( ) indicates an insertion-deletion mutation. The divided circles (
) indicates an insertion-deletion mutation. The divided circles ( ) indicate missense mutations. Red sectors indicate that the mutations were predicted to have deleterious effects on gene function according to in silico analyses using one of six programs: 1. SIFT; 2. PolyPhen-2; 3. LRT; 4. MutationTaster; 5.MutationAssessor; 6. CADD. For details see the Materials and Methods section. (C) Functional categorization of the genes mutated in PCa families into eight major groups.
) indicate missense mutations. Red sectors indicate that the mutations were predicted to have deleterious effects on gene function according to in silico analyses using one of six programs: 1. SIFT; 2. PolyPhen-2; 3. LRT; 4. MutationTaster; 5.MutationAssessor; 6. CADD. For details see the Materials and Methods section. (C) Functional categorization of the genes mutated in PCa families into eight major groups.
