Abstract
Wildland fires have a multitude of ecological effects in forests, woodlands, and savannas across the globe. A major focus of past research has been on tree mortality from fire, as trees provide a vast range of biological services. We assembled a database of individual-tree records from prescribed fires and wildfires in the United States. The Fire and Tree Mortality (FTM) database includes records from 164,293 individual trees with records of fire injury (crown scorch, bole char, etc.), tree diameter, and either mortality or top-kill up to ten years post-fire. Data span 142 species and 62 genera, from 409 fires occurring from 1981-2016. Additional variables such as insect attack are included when available. The FTM database can be used to evaluate individual fire-caused mortality models for pre-fire planning and post-fire decision support, to develop improved models, and to explore general patterns of individual fire-induced tree death. The database can also be used to identify knowledge gaps that could be addressed in future research.
Subject terms: Fire ecology, Ecological modelling
| Measurement(s) | plant morphology trait • tree mortality • fire • tree fire injury • wildfire |
| Technology Type(s) | digital curation |
| Factor Type(s) | year of data collection • geographic location of fire • tree fire injury |
| Sample Characteristic - Organism | trees |
| Sample Characteristic - Environment | forest ecosystem |
| Sample Characteristic - Location | Cascades Region • Blue Mountains • Far Northern Rockies • Sierra Nevada • Piedmont Province • Region of Piedmont • Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain Floristic Province • Northern Rocky Mountains Provincial Park |
Machine-accessible metadata file describing the reported data: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12369293
Background & Summary
Wildfires burn millions of forested hectares annually, influencing regional and global carbon storage, wildlife habitat, hydrology, species diversity, and forest structure, along with human society and economy. Wildland fires directly kill trees, but also interact with other stressors and disturbances to cause additional delayed tree mortality1. The impact of a fire on a forest ecosystem (i.e., fire severity) is often quantified by the proportion of fire-caused tree mortality. Likewise, the severity of a fire regime—the aggregated impact of many fires over time—is often described by the range of variability in proportion of trees killed by fire2,3. Because of the economic and ecological importance of fire-caused tree mortality, a great deal of work has gone into developing predictive models of mortality and integrating those models into decision support systems for management4,5. The most commonly utilized models are based on empirical data: field observations of fire injury and subsequent individual tree mortality in the years following fire. Sometimes injury from fire is measured directly (e.g., crown scorch), while other measurements may be a proxy for injury that can be quickly assessed (e.g., char on bark as a proxy for cambium injury). Measurements of fire-caused injuries used in many individual tree mortality models include percentage crown volume scorched, percentage crown length scorched, percentage crown volume killed, bark char height, and cambium kill rating5–8. Many models also use measurements of tree resistance to fire, particularly bark thickness, which scales positively with tree diameter but at different rates among species4,5.
The most commonly implemented empirical model predicting post-fire tree mortality was developed by Ryan and Reinhardt9 and amended by Ryan and Amman10. This model relies on three parameters to predict probability of mortality within three years of a fire: tree species, injury to the tree crown (in the form of percentage volume of crown scorched by fire), and tree diameter (used to calculate bark thickness). This model has been implemented in many decision support systems predicting post-fire tree mortality, including the First Order Fire Effects Model (FOFEM)11,12, the Fire and Fuels Extension to the Forest Vegetation Simulator (FFE-FVS)13, and BehavePlus14. Within these decision support systems, the model predicts probability of tree mortality. No differentiation is made between obligate seeders and species capable of resprouting; therefore, mortality predictions are more accurately top-kill predictions for resprouting species. Additional models have been developed that account for species’ unique fire resistance traits (e.g., protected buds15,16), biotic consumers7,17,18, and abiotic stress19–21. Models of post-fire tree mortality and top-kill in landscape-scale models and Dynamic Global Vegetation Models (DGVMs) generally employ simplified approaches to modeling fire injury, but still rely on plant functional traits, such as bark thickness, to make mortality predictions for species’ groups22–24.
There have been numerous studies conducted to improve ecological understanding of the many factors that contribute to post-fire tree mortality, and to build predictive models with greater accuracy4,5. In an effort to capture the data from these individual studies to facilitate more expansive analyses and to identify knowledge gaps, we assembled the largest and most comprehensive collection of observations of fire-caused individual tree mortality and top-kill in the United States, the Fire and Tree Mortality (FTM) database (10.2737/RDS-2020-0001)25 (Fig. 1). The purpose of the FTM database is to provide access to data on individual tree mortality or top-kill from wildland and prescribed fire. The FTM database allows for large-scale evaluation of existing post-fire-mortality models over large geographic and climatic ranges for numerous species. Observational data cover the full range of fire injuries and a large proportion of tree sizes for many species, but they also reveal where data are scant or non-existent. By pooling individual datasets and ensuring comparability among variables, it becomes feasible to explore general patterns of fire-induced tree death and top-kill, to develop improved models, and to identify data gaps to inform future research.
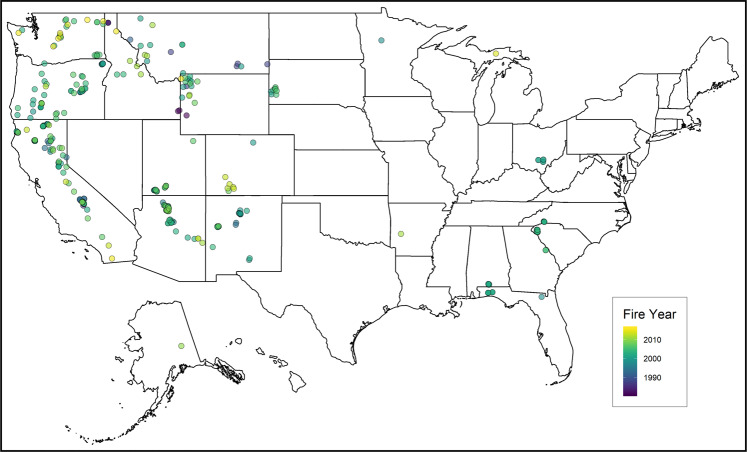
Fig. 1.
Map of fire locations by year of occurrence in the Fire and Tree Mortality (FTM) database. If a site burned twice, only the most recent fire is shown.
Methods
Soliciting data contributions
To construct our FTM database, authors Cansler, Hood, Varner, and van Mantgem conducted a literature search for publications reporting on post-fire tree mortality and contacted corresponding authors, related investigators, and managers to inquire if they were willing to contribute data. We also posted data requests on electronic mailing lists, professional management and science exchange networks, and with technical working groups. We identified and obtained archived datasets or entered them manually from archived copies. Lastly, we coordinated with the National Park Service fire ecology program to include the agency’s Fire Effects Monitoring data26.
Data aggregation and standardization
We developed the FTM database with standardized field observations from 41 contributed databases from researchers, managers, and archived datasets. Some datasets already contained aggregated data from more than one previous study27,28. At a minimum, datasets had to contain measurements of individual trees, stem diameter, fire injury, and post-fire status of above-ground stems (i.e., alive or dead). Post-fire injury measurements were collected either in the same season of the fire, or one to two years after fire. Tree diameter and height measurements were recorded either before the fire, or one to two years after fire. For the majority of cases, status of aboveground stems was recorded one to three years after fire; for some trees, status was re-evaluated in the years following fire. A tree or stem was considered dead when no green foliage remained in the crown. For obligate-seeding species, tree status almost always represents the true status of the individual: when the main stem dies, the tree dies. The exception is where the stem splits at or below breast height (BH, 1.37 m); in this situation, stems are considered separate trees, each with its own status. For species that resprout from the base or root structures, tree status in the FTM database represents survival of the main stem (i.e., top-kill). Resprouting from below-ground structures or above-ground epicormic buds are not captured in the database. We included any tree where post-fire status was measured within 10 years of the fire, noting the post-fire year(s) of status assessment. Only trees that were recorded as alive before the fire were included in the database. Many datasets included variables beyond the required minimum; we retained many variables on fire-caused injuries and biotic agents from the original datasets.
For all contributed datasets, we verified and changed all variable names and units for consistency and labelled the levels of categorical variables. We used summary tables and data visualization to identify outliers, impossible values, and duplicate records. We corresponded with data contributors when additional clarification was needed (Fig. 2). Because many of the contributed datasets were used previously for research, error checking and quality control procedures (QA/QC) had been conducted on much of the data prior to transfer to this project. For most datasets, few errors were found during the QA/QC process. Two large datasets from the National Park Service Fire Effects Monitoring Program26 and the Fire and Fire Surrogate Study28 contained longitudinal data from many sites. In these datasets, we corrected more errors after extensive checking. In the NPS dataset, we identified and removed individual tree records that were likely duplicates. For example, where two records in the same plot shared the same tag number and species, and a similar tree diameter at breast height ("DBH"; 1.37 m above ground), one record was dropped. Likewise, in the Fire and Fire Surrogate dataset (particularly from sites in the Southern USA), some tagged trees were identified as different species in sequential measurements. In these instances we retained the most recent species code, assuming that identities were corrected over time. For all datasets, we enforced consistency in coding of status (live/dead). If a tree was alive in the final assessment year, it was coded as live in previous years. If a tree was dead, it was coded as dead in subsequent years. If a tree re-burned in a second fire and post-fire injury and status information were available following the fire, a new record (row) was made for the tree after the second fire. Database contributors were able to check and offer corrections following the data standardization procedures.
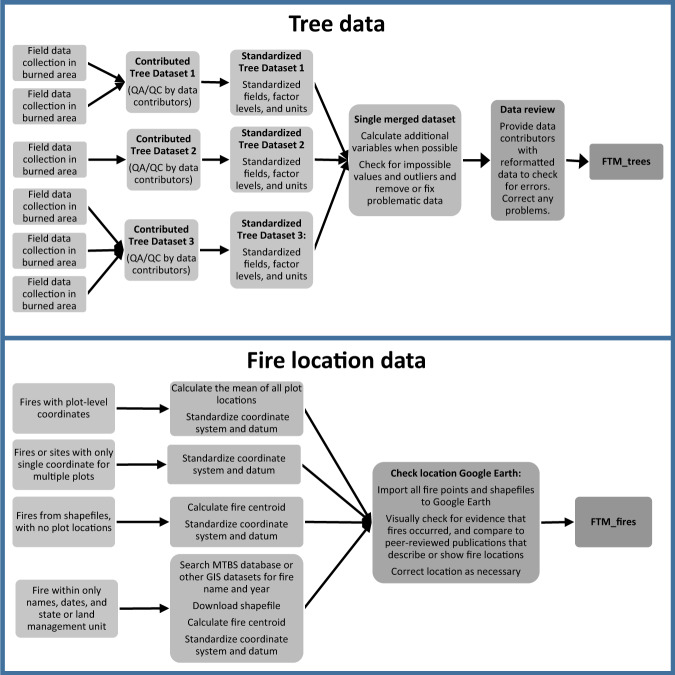
Fig. 2.
Data collection and processing workflows for individual-tree data and fire-location data used to generate the data outputs. For individual-tree data, we performed quality control measures and developed standardized fields and data from 41 contributed datasets (i.e., datasets 1 through 41). At a minimum, contributed datasets had to contain measurements of individual trees, stem diameter, fire injury, and post-fire status of above-ground stems (i.e., alive or dead). Contributed datasets sometimes contained observations from multiple fires, sites, or studies. Contributed datasets contained post-fire injury measurements and tree status collected either in the same season of the fire, or one to two years after fire. In some datasets tree status was re-evaluated in multiple years following fire. We then combined tree data into a single file. Because locations in contributed datasets were provided at different scales (e.g., tree, plot, research site, and fire) we standardized all location data in the FTM database to the scale of a fire event. QA/QC = Quality assurance and quality control. MTBS = Monitoring Trends in Burn Severity https://www.mtbs.gov.
Standardization of taxa
We standardized all scientific nomenclature and species acronyms to follow the PLANTS Database http://plants.usda.gov. Data represent 142 species and 62 genera (Online-only Table 1). Some trees were unidentified or identified only to genus (14 genera; Online-only Table 1). In some instances, trees were identified to genus, but data contributors noted that the tree could be only one of two species. In total, there are three such identifiers: Abies grandis or A. lasiocarpa, Pinus jeffreyi or P. ponderosa, and Picea pungens or P. engelmannii (Online-only Table 1). Finally, some contributed datasets contained unidentified trees that were alive before the fire. We retained those records and with them, a code for “unknown tree”, but we caution that unidentified trees may have been removed from other datasets during earlier quality control steps. In total, the FTM database has 161 unique tree identifier codes.
Online-only Table 1.
Species represented in the FTM database, including number of records (with separate records for trees burned in two fires), individual trees, fire observations, and unique years in which fires occurred. In some instances, trees were identified to genus, but data contributors noted that the tree could be only one of two species.
| Species | Records | Trees | Fires | Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abies amabilis | 111 | 111 | 1 | 1 |
| Abies concolor | 14,389 | 14,175 | 109 | 28 |
| Abies grandis | 2,168 | 2,167 | 19 | 11 |
| Abies grandis or A. lasiocarpa | 453 | 453 | 1 | 1 |
| Abies lasiocarpa | 5,070 | 4,441 | 40 | 14 |
| Abies magnifica | 552 | 552 | 13 | 10 |
| Abies species | 581 | 532 | 1 | 1 |
| Acer floridanum | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Acer grandidentatum | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Acer macrophyllum | 7 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| Acer rubrum | 1,275 | 1,275 | 23 | 5 |
| Acer saccharum | 185 | 185 | 5 | 1 |
| Aesculus glabra | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Ailanthus species | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Albizia julibrissin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Alnus incana | 60 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| Alnus rubra | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| Amelanchier arborea | 34 | 34 | 2 | 2 |
| Aralia spinosa | 9 | 9 | 1 | 1 |
| Arbutus menziesii | 19 | 19 | 4 | 2 |
| Asimina triloba | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Betula lenta | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Calocedrus decurrens | 3,654 | 3,483 | 43 | 17 |
| Carpinus caroliniana | 13 | 13 | 4 | 2 |
| Carya glabra | 20 | 20 | 9 | 5 |
| Carya pallida | 17 | 17 | 5 | 2 |
| Carya species | 127 | 127 | 8 | 2 |
| Carya texana | 89 | 89 | 1 | 1 |
| Carya tomentosa | 151 | 151 | 16 | 5 |
| Castanea dentata | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Castanea pumila | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Celtis laevigata | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Celtis occidentalis | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Cercis canadensis | 10 | 10 | 3 | 2 |
| Chamaecyparis lawsoniana | 69 | 69 | 2 | 2 |
| Chamaecyparis nootkatensis | 26 | 26 | 1 | 1 |
| Chrysolepis chrysophylla | 7 | 7 | 2 | 1 |
| Cornus florida | 357 | 357 | 27 | 5 |
| Cornus nuttallii | 119 | 119 | 5 | 3 |
| Crataegus marshallii | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Crataegus species | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Diospyros virginiana | 94 | 94 | 10 | 3 |
| Fagus grandifolia | 22 | 22 | 7 | 2 |
| Frangula caroliniana | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| Fraxinus americana | 37 | 37 | 1 | 1 |
| Fraxinus pennsylvanica | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fraxinus species | 14 | 14 | 4 | 1 |
| Gleditsia triacanthos | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Hamamelis virginiana | 15 | 15 | 1 | 1 |
| Holodiscus discolor | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Ilex opaca | 40 | 40 | 8 | 3 |
| Juglans nigra | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 |
| Juniperus deppeana | 142 | 141 | 10 | 6 |
| Juniperus monosperma | 21 | 21 | 7 | 5 |
| Juniperus occidentalis | 72 | 72 | 5 | 4 |
| Juniperus osteosperma | 225 | 225 | 20 | 12 |
| Juniperus scopulorum | 807 | 499 | 21 | 11 |
| Juniperus virginiana | 61 | 61 | 9 | 4 |
| Larix occidentalis | 1,189 | 1,189 | 19 | 12 |
| Liquidambar styraciflua | 533 | 533 | 10 | 4 |
| Liriodendron species | 92 | 92 | 6 | 1 |
| Liriodendron tulipifera | 151 | 151 | 15 | 4 |
| Magnolia fraseri | 14 | 14 | 4 | 1 |
| Magnolia grandiflora | 37 | 37 | 2 | 1 |
| Magnolia tripetala | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| Magnolia virginiana | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Morus rubra | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Morus species | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Notholithocarpus densiflorus | 127 | 127 | 4 | 2 |
| Nyssa sylvatica | 516 | 516 | 26 | 5 |
| Ostrya virginiana | 131 | 131 | 1 | 1 |
| Oxydendrum arboreum | 628 | 628 | 20 | 4 |
| Persea borbonia | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Picea engelmannii | 2,996 | 2,876 | 45 | 18 |
| Picea glauca | 46 | 46 | 1 | 1 |
| Picea mariana | 760 | 760 | 1 | 1 |
| Picea pungens | 142 | 142 | 2 | 1 |
| Picea pungens or P. engelmannii | 9 | 9 | 1 | 1 |
| Picea sitchensis | 22 | 21 | 1 | 1 |
| Pinus albicaulis | 1,297 | 834 | 15 | 8 |
| Pinus arizonica | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Pinus attenuata | 268 | 268 | 7 | 5 |
| Pinus banksiana | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Pinus contorta | 18,298 | 11,615 | 46 | 18 |
| Pinus coulteri | 182 | 182 | 1 | 1 |
| Pinus echinata | 748 | 748 | 16 | 5 |
| Pinus edulis | 292 | 292 | 28 | 15 |
| Pinus elliottii | 634 | 634 | 5 | 3 |
| Pinus flexilis | 373 | 353 | 11 | 7 |
| Pinus glabra | 17 | 17 | 5 | 1 |
| Pinus jeffreyi | 1,068 | 1,068 | 26 | 14 |
| Pinus jeffreyi or P. ponderosa | 2,720 | 2,720 | 7 | 5 |
| Pinus lambertiana | 2,592 | 2,549 | 54 | 21 |
| Pinus monophylla | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Pinus monticola | 214 | 214 | 11 | 8 |
| Pinus palustris | 1,957 | 1,957 | 18 | 3 |
| Pinus ponderosa | 64,825 | 61,097 | 260 | 27 |
| Pinus resinosa | 254 | 254 | 2 | 2 |
| Pinus rigida | 35 | 35 | 6 | 1 |
| Pinus sabiniana | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Pinus species | 35 | 35 | 11 | 5 |
| Pinus strobiformis | 283 | 283 | 5 | 5 |
| Pinus strobus | 44 | 44 | 9 | 4 |
| Pinus taeda | 2,236 | 2,236 | 16 | 4 |
| Pinus virginiana | 370 | 370 | 13 | 4 |
| Platanus occidentalis | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Platanus species | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Populus deltoides | 185 | 185 | 2 | 1 |
| Populus grandidentata | 10 | 10 | 4 | 1 |
| Populus tremuloides | 2,648 | 2,647 | 41 | 19 |
| Prunus americana | 21 | 21 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus emarginata | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus mexicana | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus serotina | 334 | 334 | 15 | 4 |
| Prunus species | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus umbellata | 6 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
| Pseudotsuga macrocarpa | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Pseudotsuga menziesii | 21,027 | 20,157 | 111 | 25 |
| Quercus alba | 710 | 710 | 23 | 5 |
| Quercus chrysolepis | 45 | 45 | 10 | 8 |
| Quercus coccinea | 371 | 371 | 20 | 4 |
| Quercus falcata | 448 | 448 | 14 | 4 |
| Quercus gambelii | 496 | 493 | 24 | 13 |
| Quercus garryana | 333 | 333 | 5 | 4 |
| Quercus incana | 7 | 7 | 3 | 1 |
| Quercus kelloggii | 550 | 538 | 29 | 13 |
| Quercus laevis | 61 | 61 | 3 | 1 |
| Quercus laurifolia | 638 | 638 | 6 | 1 |
| Quercus marilandica | 11 | 11 | 3 | 2 |
| Quercus muehlenbergii | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Quercus nigra | 266 | 266 | 12 | 3 |
| Quercus phellos | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Quercus prinus | 731 | 731 | 15 | 3 |
| Quercus rubra | 162 | 162 | 16 | 5 |
| Quercus species | 59 | 59 | 8 | 3 |
| Quercus stellata | 237 | 237 | 14 | 5 |
| Quercus velutina | 230 | 230 | 19 | 5 |
| Quercus wislizeni | 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 |
| Rhus copallinum | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Robinia pseudoacacia | 17 | 17 | 7 | 3 |
| Salix scouleriana | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Salix species | 10 | 9 | 3 | 3 |
| Sassafras albidum | 174 | 174 | 8 | 3 |
| Sassafras species | 65 | 65 | 5 | 1 |
| Sequoia sempervirens | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Sequoiadendron giganteum | 134 | 134 | 16 | 10 |
| Taxus brevifolia | 6 | 6 | 2 | 1 |
| Thuja plicata | 477 | 477 | 5 | 3 |
| Tilia americana | 25 | 25 | 4 | 3 |
| Torreya californica | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Tsuga canadensis | 21 | 21 | 4 | 1 |
| Tsuga heterophylla | 1,674 | 1,673 | 14 | 7 |
| Tsuga mertensiana | 735 | 687 | 2 | 2 |
| Ulmus alata | 108 | 108 | 4 | 3 |
| Ulmus americana | 9 | 9 | 2 | 2 |
| Ulmus rubra | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Unknown species | 500 | 405 | 21 | 9 |
| Vaccinium arboreum | 25 | 25 | 1 | 1 |
| Viburnum rufidulum | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
Calculating injury variables
The FTM database includes several tree injury variables (Table 1). If variables were measured or visually estimated in the field, then we used field-based observations rather than calculated values. When these variables were not measured in the field, if possible, we calculated derived variables from those measured in the field. Specifically, we calculated:
| 1 |
where is pre-fire crown length (m), is tree height (m), and is the pre-fire height of the base of the crown. If or HCB were measured before the fire, we used pre-fire height and crown base height. Otherwise, and were measured post-fire, either the season after the fire or within two years. measurements taken more than two years after the fire were coded as “NA” (not available) and were not used. Studies have established the validity of reconstructing the pre-fire living portion of the crown after fire to estimate pre-fire height and crown base height29,30.
Table 1.
FTM_trees injury-variable names and descriptions.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| CL_m | Pre-fire live crown length rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. |
| HT_m | Either the pre-fire tree height, or if pre-fire height is not measured, the post-fire tree height taken at that same time that fire-injury variables were measured; values are rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. |
| HCB_post | Post-fire height to live crown base rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. |
| CR_post | Post-fire live crown ratio. Crown length divided by tree height (proportion rounded to the nearest 0.01). |
| CSH_m | Height of crown scorch, assessed as the highest visible heat injury to leaves from ground level, rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. Includes scorched and consumed portions of the crown. |
| CLS_m | Length of the pre-fire crown that was scorched or consumed by fire rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. |
| CLK_m | Length of the pre-fire crown for which fire killed tree buds by scorch or consumption, rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. |
| CLS_percent | Percentage of the pre-fire crown length that was scorched or consumed by fire rounded to the nearest 1.0 percent (ranges from 0 to 100). |
| CLK_percent | Percentage of the pre-fire crown that was scorched, resulting in bud kill or consumption by fire, rounded to the nearest 1% (ranges from 0 to 100). |
| CVS_percent | Percentage of the pre-fire crown volume that was scorched or consumed by fire (ranges from 0 to 100). |
| CVS_percent_source | Denotes whether directly assessed in the field or derived as described in FOFEM help document. F = field; C = calculated. |
| CVK_percent | Percentage of pre-fire crown volume killed by fire (range of 0 to 100). |
| CVK_percent_source | Denotes whether directly assessed in the field or derived as described in FOFEM help document. F = field; C = calculated. |
| CVC_percent | Percentage crown volume consumed or blackened by the fire (range of 0 to 100). |
| CBS | Percentage of the circumference of the bole that was scorch (ranges from 0 to 100). |
| BCHA_m | Average bark char vertical height from the ground on a tree bole, rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. Heights were visually estimated or computed as the mean of the maximum and minimum bark char height. |
| BCHM_m | Maximum bark char height from the ground on a tree bole, rounded to the nearest 0.01 meter. |
| BCH_percent | Percentage of tree height blackened or charred, based on the maximum bark char height (values 0 to 100). |
| BCA | Average bark char rating. A bark char rank value (numerical code) was given to each of four quadrants at the base of the tree, then values were averaged. If fewer than four quadrents were measured, this is the average of measered sections. Codes: 0 = unburned, 1 = light, 2 = moderate, and 3 = deep32. |
| CKR | Cambium kill rating. Cambium status (live or dead) was assessed in four quadrants of each tree. If fewer than four quadrants were measured, this is the average of measured sections. CKR is the number of quadrants with dead cambium at the ground line (ranges from 0 to 4)32. |
| GCA | Average ground char rating. Severity of soil heating (based on ground char) was assessed in four quadrants around each tree (1 = light, 2 = moderate, and 3 = heavy [or deep]). The four ratings were then averaged100. If fewer than four quadrants were measured, this is the average of measured sections. |
Also included are variables used to calculate fire-injury variables. Most fire-injury variables were measured in the field the season or year after fire. Fire-injury variables that were derived from field-measured variables are described in the text. Full descriptions are documented in the metadata in Cansler et al.25.
Likewise:
| 2 |
where is post-fire crown length (m), is tree height (m), and is the post-fire height of the base of the crown.
Using the pre- and post-fire crown length, we could calculate the length and percentage of crown length scorched:
| 3 |
and
| 4 |
where CLSmeters = crown length scorched measured in meters, CLSpercent = percentage crown length scorched, CLpre = pre-fire crown length (m), and CLpost = post-fire crown length (m). If CLSmeters was measured in the field, we used that measurement of injury, instead of the change from pre-fire to post-fire crown base height for subsequent calculations.
For studies that separated crown injury as scorch, kill, or consumed, we included the amount of crown consumed in all calculations of crown scorch or crown kill.
For trees without observed crown volume scorched values, we followed the equation in the FOFEM Help manual12 (derived from Peterson and Ryan)31.
| 5 |
where CVSpercent = percentage crown volume scorched, = crown length scorched, and = pre-fire crown length. Because this calculation includes assumptions about tree crown architecture, it may introduce error. Thus in a separate column we coded whether the value was based on field observation or derived from the canopy volume equation.
Likewise, for trees with observations of crown length killed (), but not percentage crown volume killed (), we calculated using the same equation form as in Eq. 5, above:
| 6 |
Where calculations produced an impossible value (<0 or >100) we assigned the value a code of “NA” (see “Usage Notes” below).
Damage to tree stems was measured in several ways. The most common method measured the amount (e.g., height, circumference, or percentage) of char on the tree’s bark (Table 1). Char is blackened residue of bark resulting from incomplete combustion and is a coarse indicator of the duration of bole exposure to flames and heat from the fire. Cambium kill rating (CKR) is an estimate of the amount of cambium kill and stem injury from fire15,32. Measurements of CKR require removing a small sample of bark at four locations at a tree’s base to determine if the underlying vascular meristematic tissue was killed by the fire. CKR is the number of quadrants (0-4) with dead cambium.
Presence or absence of beetles that are primary mortality agents on a given tree species are used in some species-specific post-fire mortality models5,27. These beetle species include Dendroctonus ponderosae (mountain pine beetle) on Pinus spp.; D. valens (red turpentine beetle), D. ponderosae, D. brevicomis (western pine beetle) or Ips spp. (engraver beetles) on Pinus ponderosa; and D. pseudotsugae (Douglas-fir beetle) on Pseudotsuga menziesii. Individual studies may have collected more detailed beetle-attack data, but for the FTM database, we simplified all attack data as presence or absence. Some studies noted presence or absence of primary bark beetles without identifying the species: thus, we combined all presence/absence information for identified and unidentified primary bark beetles into a single “beetle” variable. When studies identified beetles to species, we included species-level presence/absence information. We also included presence/absence information for a few beetle species that are not primary agents of mortality, but have been used as predictors in some models27, such as ambrosia beetle (subfamilies Scolytinae and Platypodinae) and D. valens.
Tree identification, plot design, and study purpose
This database was developed for modeling tree mortality and top-kill at the individual-tree scale. In the FTM_trees.csv file we provide plot and tree number identification information to maintain consistency between the FTM database and the original contributed dataset. This ensures that each tree in the FTM database can be connected to its original record. Additionally, plot numbers and fire names can be used to track how observations are spatially grouped. We also provide study design information, including whether sampling was conducted at the individual-tree scale or if fixed-area or variable-radius plots were used. For fixed-area plots we define plot size and the minimum DBH sampled. For variable-radius plots, we provide the BA factor used. Finally, we provide standardized descriptions of the purpose(s) of the original studies.
Fire locations
We standardized the fire location and year-of-fire data for all observations to a consistent datum and geographic coordinate system (GCS WGS84; Fig. 2). Because locations in contributed datasets were provided at different scales (e.g., tree, plot, research site, and fire) we standardized all location data in the FTM database to the scale of a fire event. If tree or plot coordinates were provided, we took the average of those coordinates to provide a centroid for the fire event. If only research site coordinates were provided, but multiple fires occurred with different start dates, we replicated those coordinates for each fire event. If a fire name and year were provided without associated geographic coordinates, we searched the Monitoring Trends in Burn Severity database https://www.mtbs.gov for the fire, downloaded the fire geospatial data, and used the coordinates of the centroid of the fire perimeter. In instances where fires were not large enough to be in the MTBS database and we lacked coordinates, we used fire perimeter data from the local land management agency to identify fire locations. All fire-location data were uploaded to Google Earth Pro33, and the available high-resolution pre-fire and post-fire imagery and Google Earth database of place names were used to verify the fire occurrence and location. Errors or discrepancies in fire locations and dates were corrected through correspondence with data contributors.
Bark thickness coefficients
We provide data to calculate bark thickness for most of the species in the FTM database, following the method used in FOFEM 6.4. Specifically, bark thickness is estimated from a linear relationship with DBH and a species-specific barkthickness coefficient. FOFEM provides bark thickness coefficients for 192 tree species. If a species is absent, FOFEM users can substitute a species with similar bark thickness for modeling, or use one of the 24 bark-thickness relationships provided at the genus level. For species lacking a species-level bark thickness coefficient in FOFEM, we provide a coefficient from a morphologically similar species or the genus (if available). Of 159 taxa identifiers in the database, we include bark thickness coefficients for 148.
Data Records
The FTM database is available for download from the USDA Forest Service Research Data Archive25. The FTM database includes standardized field observations of fire injury and survival from 164,293 individual trees. Of these, 6,670 trees have records relating to two separate fires, resulting in a total of 170,963 observations. The data span 21 states and include 409 prescribed fires and wildfires from 1981 to 2016 (Fig. 1). The data represent 142 species and 62 genera; 97.3% of the trees are identified to species and 99.7%, to genus.The archived data product consists of a metafile in both HTML and XML formats, a TIFF file showing the geographic locations of fires, and five separate data files:
Dataset_citations.csv: Comma-delimited ASCII text file containing the main citation for each contributed dataset in the Fire and Tree Mortality (FTM) database.
Dataset_primary_contacts.csv: Comma-delimited ASCII text file containing dataset names as they appear in the FTM database and the associated primary contact information.
FTM_fires.csv: Comma-delimited ASCII text file containing fire names, year, dataset contact, and location for fires in the FTM database.
FTM_trees.csv: Comma-delimited ASCII text file containing tree-level records of fire injury, tree size, and bark beetle attack.
Species_BarkThickness.csv: Comma-delimited ASCII text file containing the list of species found in the FTM database and the bark thickness information used to evaluate FOFEM version 6.4 model accuracy.
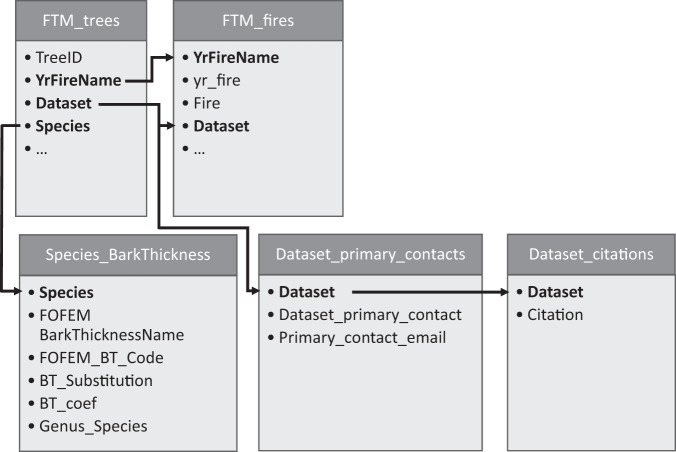
Figure 3 shows the common fields and connections among each of the five data files.
Fig. 3.
Fire and Tree Mortality (FTM) database structure showing individual files contained in the FTM database. Bold arrows indicate common fields that can be used to join files.
Technical Validation
The data used to build the FTM database primarily come from high-quality data sources that have been used in other analyses and peer-reviewed publications, or from long-term institutional monitoring studies. The majority of individual-tree observations are derived from peer-reviewed studies6–8,15,17,18,27,34–74. Data were contributed by corresponding authors, or came from archived datasets from completed projects28,40,75–78. Twelve additional datasets were not peer reviewed, but were summarized in professional reports or theses79–82 or represent ongoing research or monitoring by land management professionals26,83–89. The contributed database with the largest sample of fires is from the National Park Service Fire Effects Monitoring Program, a long-term institutional monitoring program in which permanent field plots are resampled on a standardized schedule with trained staff and established quality controls26. These studies and monitoring projects were designed for a range of purposes, listed in the FTM_Fires.csv file, including modelling post-fire tree mortality6,7,15,17,18,40,42,47,48,50,58,71,74,79,90–92, understanding the effectiveness of prescribed fire at reducing fuel loading, future fire severity, restoring historical forest structure38,39,56,57,59–61,66,67,69,82,93, tracking post-fire successional dynamics43,45,59,62,63,90,94, developing remote sensing indices to understand landscape fire effects46,70,95, carbon emission modeling65, plant physiological research36,53–55, and research on interactions between fire and bark beetles4,7,10,18,34,35,37,41,43,44,49,51,81. The file Dataset_citations.csv provides the primary citations for each contributed dataset in the FTM database.
Usage Notes
We developed the FTM database to validate existing models of individual-stem and tree-scale post-fire tree mortality96 and to support development of new models. Researchers may find additional uses for these data, but we urge caution in their use. For any use, researchers should consider possible sources of error. Despite multiple procedures for quality control, there are likely to be errors of observation and calculation present in the final FTM database. For example, many post-fire injury measurements, such as crown volume scorch, are subjective field estimates, and may vary among observers (although consistency within a study is likely to be higher than consistency across studies). Data from studies that included repeated measurements over time will be more accurate than those based on a single post-fire measurement. Common errors that can be identified and corrected through repeated measurements include misidentified species, duplicate or missing records, incorrect diameter measurements, and incorrect tree status (e.g., mistakenly identifying trees as dead). We excluded trees that were dead prior to fires, and we excluded ingrowth that reached minimum measurement sizes after the fire that were recorded in longitudinal datasets. For studies where plots were measured post-, but not pre-fire, there may be errors in pre-fire status if trees that died shortly before the fire were erroneously coded as alive. Any calculations of carbon stores from this dataset could only include pre-fire live carbon, since contributed datasets did not consistently include measurements of trees that were dead before the fire, and therefore we did not include any trees that were dead before the fire in the database.
Crown injury variables derived from field observations are also susceptible to errors. Most derived variables are based on simple calculations (detailed above) and after each calculation we checked for impossible values. If found, these were coded as “NA”. The most common error of this sort occurred when pre-fire crown base height was slightly higher than post-fire crown base height (resulting in a negative value for crown length scorch). This error likely reflects varying precision in the measurement of crown base height before and after the fire, but it could also reflect a data collection or data entry error. For crown volume scorch and crown volume killed (Eqs. 5 and 6), the equation, based on assumptions of tree crown shape and crown length, may introduce error. For transparency, we coded which observations were based on field observations and which were derived from the crown volume equation. Percentages of crown length and crown volume are positively correlated but are not the same or interchangeable15, and models using field-based measurements perform better96. In addition, users should be aware that observations of crown scorch typically imply that the scorched portions of the crown are killed by the fire (i.e., bud kill or crown kill). However, this is not always true for species with large buds or epicormic sprouting4. Thus, the FTM database crown scorch values should be understood to represent the proportion of the tree’s leaves that were killed by fire, but not the extent of bud mortality or the potential for branch recovery. For studies that differentiated between crown scorch and crown kill levels, the percentage of crown scorched must always be greater than or equal to the percentage of crown killed.
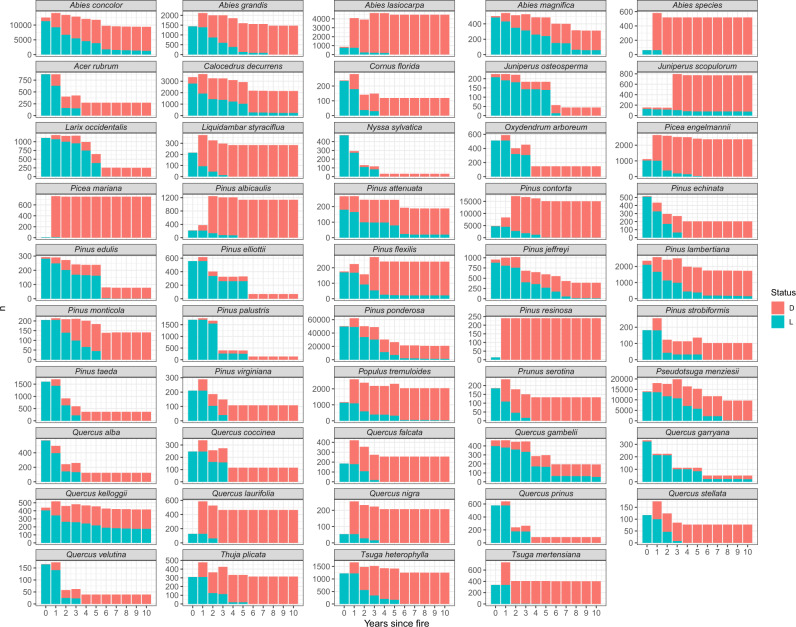
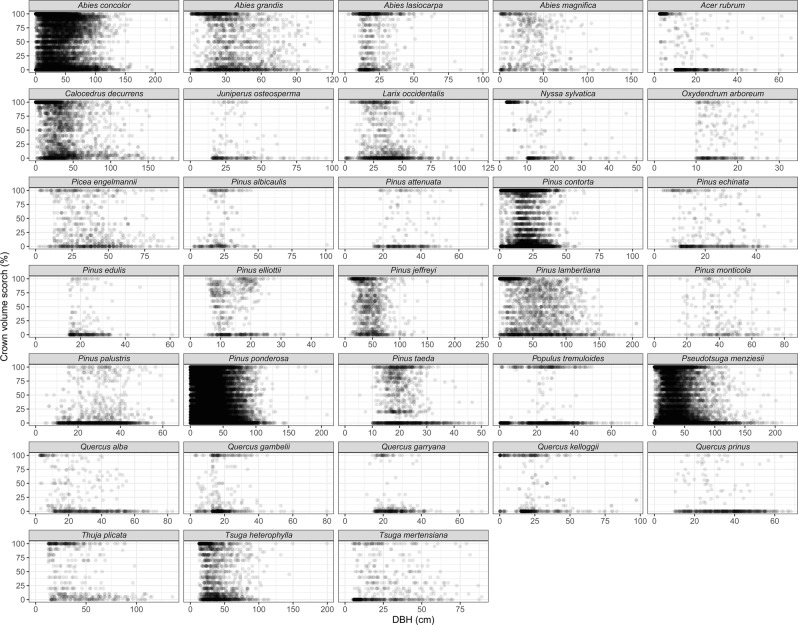
For tree mortality and top-kill modelling, we note three limitations in particular. First, because different combinations of injury variables were measured in each study, there are many missing values in the FTM database. Second, tree status observations decline—particularly observations of live trees—as time since fire increases (Fig. 4). Because we extrapolated tree status for years when plots were not measured, modeling of plot-scale proportional mortality would not be an appropriate use of the data. Third, in building empirical models, it is important to consider the data range for the variables used, and not simply for the individual variables, but for the combined predictor space represented in the dataset97 (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4.
Number of tree-status observations (n) by years since fire for live (L) and dead (D) trees. Only species with ≥200 samples are shown. We filled in missing values for tree status when possible (e.g., dead trees remained dead after monitoring ceased; live trees were coded as live in previous years). The longer the time since fire, the more likely a database will contain only dead trees for a given species.
Fig. 5.
Scatterplots of tree diameter at breast height (DBH) vs. percentage crown volume scorch (CVS) for species with ≥200 observations of both variables. These data displays can show gaps in information, such as small or large trees or species for which there are few or no combinations of DBH and CVS.
The FTM database includes information on sampling design, and where applicable, plot size and minimum tree diameter sampled. The best use for the fire-scale and plot-scale identifiers is understanding and accounting for the spatial aggregation or nesting of many of the observations (e.g., by using hierarchical or mixed-effects models)98. Although plot-level metrics, such as stem density, basal area, or stand density index can be generated from some datasets, we did not develop the FTM database explicitly for plot-level modeling. Plot-level measurements can be used to quantify variation in forest structure or intensity of competition, but with caution due to variation in how trees were sampled among studies. There are several possible types of unaccounted variation in plot-level statistics: (1) individual tree records that were incomplete and removed from contributed datasets before transfer to the current study; (2) undocumented procedures for subsampling different tree diameter classes; and (3) undocumented exclusion of species (e.g., angiosperms) or growth forms (e.g., tall woody shrubs or hardwoods) that would have influenced stem densities or indices of competition.
Plots were not the sampling units in all contributed datasets. For many studies—particularly physiology and bark beetle studies—the individual tree was the sampling unit. In other studies, plots were used to structure the sampling, but not all trees were measured within a plot (e.g., only the first three stems of a given species or size class were sampled or only a particular species was sampled). When trees were fully censused within a plot, the minimum DBH differed among studies (noted in the FTM_fires.csv file), thus cross-study comparisons of plot-level statistics must be made with caution.
Because the FTM database was developed to support individual-tree scale modeling, we devoted considerable effort to identifying incomplete or duplicate records. These were detectable only in datasets with repeated measurements (e.g., National Park Service datasets). However, optimizing for complete and non-duplicate records may produce erroneous plot-level metrics (e.g., tree density). Finally, for all datasets, tree locations within plots were not recorded, thus indices of neighborhood competition at the individual-tree scale (or any finer scale than the plot) cannot be calculated. Users can refer to the primary literature contained in Dataset_citations.csv for additional information on study designs and dataset contents.
Pooling data from across the United States incorporates taxa that are not well represented in previous studies, such as junipers and oaks. Nevertheless, geographic and taxonomical gaps remain. Data are primarily from the western USA, with some representation of the southeastern USA (Fig. 1). Gymnosperms are better represented than angiosperms (Online-only Table 1). We encourage researchers to identify geographic or taxonomic gaps in the existing data and to target sampling to fill those gaps. We plan to update the FTM database as additional data are collected and made available from the USA and internationally.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge funding from the Joint Fire Science Program under project JFSP 16-1-04-8. Additional support was provided by USDA Forest Service Forest Health Protection, USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, the National Fire Plan, and our current institutions. Comments from Erik Jules, and two anonymous reviewers improved this manuscript. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. The FTM database would not exist without the hard work of hundreds of individuals who collected data in the field. Thank you.
Online-only Table
Author contributions
C. Alina Cansler solicited data contributions, co-developed the database structure, reformatted all contributed data, developed the fire-location database, entered and formatted hard-copy data, and co-wrote the manuscript. Sharon M. Hood conceived of the database idea, solicited data contributions, provided input into the database structure and development, co-wrote the manuscript and provided data. Phillip J. van Mantgem and J. Morgan Varner co-developed the project, solicited data contributions, provided input into the database structure and development, assisted with reformatting contributed data, contributed to writing the manuscript, and provided data. Michelle C. Agne, Robert A. Andrus, Matthew P. Ayres, Jonathan D. Bakker, Michael A. Battaglia, Barbara J. Bentz, Carolyn R. Breece, Daniel R. Cluck, Tom W. Coleman, R. Greg Corace III, Douglas S. Cram, James B. Cronan, Adrian J. Das, Ryan S. Davis, Darci M. Dickinson, Jim L. Hanula, Brian J. Harvey, MaryBeth Keifer, Tara L. Keyser, Leda N. Kobziar, Karen E. Kopper, Andrew P. Lerch, Virginia L. McDaniel, Joseph J. O’Brien, Daniel D.B. Perrakis, Susan J. Prichard, Robert A. Progar, John P. Roccaforte, Brendan M. Rogers, Carolyn H. Sieg, Rebecca J. Smith, Mary Steuver, Jens T. Stevens, Nicole M. Vaillant and Douglas J. Westlind, oversaw data collection and analysis of original data, contributed data to the database, helped inform data reformatting, reviewed the FTM database, and contributed to the manuscript. Timothy M. Shearman, Lindsay M. Grayson and Micah Wright helped conduct and inform data reformatting. Bruce D. Ayres, James K. Brown, W. Wallace Covington, Joseph E. Crouse, Stephen A. Fitzgerald, Lisa M. Ganio, Charles B. Halpern, J. Kevin Hiers, David W. Huffman, Tom E. Kolb, Crystal A. Kolden, Jason R. Kreitler, Jesse K. Kreye, Andrew M. Latimer, Maria J. Lombardero, Charles W. McHugh, Joel D. McMillin, Jessica J. Page, David W. Peterson, Kenneth F. Raffa, Elizabeth D. Reinhardt, Joe C. Restaino, Kevin C. Ryan, Hugh D. Safford, Alyson E. Santoro, Alice M. Shumate, Sheri Smith, Nathan L. Stephenson, Michael T. Stoddard, Walter G. Thies, Shelby A. Weiss and Travis J. Woolley oversaw original data collection and analysis and contributed to the manuscript.
Code availability
Fire and Tree Mortality Database (FTM) is available from Forest Service Research Data Archive 10.2737/RDS-2020-0001. All reformatting of contributed data was completed in R version 3.6.199. Original contributed data are only available by contacting data contributors. The code used to reformat the data may be obtained contacting C. A. Cansler.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors jointly supervised this work: C. Alina Cansler, Sharon M. Hood, J. Morgan Varner, Phillip J. van Mantgem.
Contributor Information
C. Alina Cansler, Email: acansler@uw.edu.
Sharon M. Hood, Email: sharon.hood@usda.gov
References
- 1.Kane JM, Varner JM, Metz MR, van Mantgem PJ. Characterizing fire-disturbance interactions and their potential impacts on tree mortality in western U.S. forests. For. Ecol. Manage. 2017;405:188–199. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rollins, M. G. & Frame, C. K. The LANDFIRE Prototype Project: Nationally Consistent and Locally Relevant Geospatial Data for Wildland Fire Management. Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-175. (U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, 2006).
- 3.LANDFIRE Mapping Team. LANDFIRE/GAP Land Cover Map Unit Descriptions. Modified by GAP/USGS to incorporate descriptions for all LANDFIRE Map Units, and the 2015 NVC Hierarchy Jan. 4, 2016. Based on NatureServe Ecological Systems Version 1.13 Data Date: Oct. 23, 2009. 1377 (2016).
- 4.Hood SM, Varner JMM, van Mantgem P, Cansler CA. Fire and tree death: understanding and improving modeling of fire-induced tree mortality. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018;13:113004. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Woolley T, Shaw DC, Ganio LM, Fitzgerald S. A review of logistic regression models used to predict post-fire tree mortality of western North American conifers. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2012;21:1. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grayson LM, Progar RA, Hood SM. Predicting post-fire tree mortality for 14 conifers in the Pacific Northwest, USA: Model evaluation, development, and thresholds. For. Ecol. Manage. 2017;399:213–226. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hood S, Bentz B. Predicting postfire Douglas-fir beetle attacks and tree mortality in the northern Rocky Mountains. Can. J. For. Res. 2007;37:1058–1069. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Keyser TL, et al. Short-term stem mortality of 10 deciduous broadleaved species following prescribed burning in upland forests of the Southern US. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2018;27:42. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ryan KC, Reinhardt ED. Predicting postfire mortality of seven western conifers. Can. J. For. Res. 1988;18:1291–1297. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ryan, K. & Amman, G. Interactions between fire-injured trees and insects in the Greater Yellowstone Area. Plants their Environ. Proc. First Bienn. Sci. Conf. Gt. Yellowstone Ecosyst., 259–271, https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/barkbeetles/169/ (1994).
- 11.Reinhardt, E., Keane, R. E. & Brown., J. K. First Order Fire Effects Model: FOFEM 4.0 User’s Guide. General Technical Report INT-GTR-344, USDA Forest Service (1997).
- 12.Lutes, D., Keane, R. E. & Reinhardt, E. D. FOFEM 6.0 User Guide. (USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, 2012).
- 13.Reinhardt, E. & Crookston, N. L. Fire and Fuels Extension to the Forest Vegetation Simulator. Gen. Tech. Rep. - Rocky Mt. Res. Station. USDA For. Serv. (2003).
- 14.Andrews PL. Current status and future needs of the BehavePlus Fire Modeling System. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2014;23:21–33. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hood SM, Smith SL, Cluck DR. Predicting mortality for five California conifers following wildfire. For. Ecol. Manage. 2010;260:750–762. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Menges ES, Deyrup MA. Postfire survival in south Florida slash pine: Interacting effects of fire intensity, fire season, vegetation, burn size, and bark beetles. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2001;10:53–63. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sieg CH, et al. Best predictors for postflre mortality of ponderosa pine trees in the intermountain west. For. Sci. 2006;52:718–728. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Breece C, Kolb T, Dickson B, Mcmillin J, Clancy K. Prescribed fire effects on bark beetle activity and tree mortality in southwestern ponderosa pine forests. For. Ecol. Manage. 2008;255:119–128. [Google Scholar]
- 19.van Mantgem PJ, Falk DA, Williams EC, Das AJ, Stephenson NL. Pre-fire drought and competition mediate post-fire conifer mortality in western U.S. National Parks. Ecol. Appl. 2018;28:1730–1739. doi: 10.1002/eap.1778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.van Mantgem PJ, et al. Climatic stress increases forest fire severity across the western United States. Ecol. Lett. 2013;16:1151–1156. doi: 10.1111/ele.12151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nesmith, J. C. B., Das, A. J., Hara, K. L. O. & Mantgem, P. J. V. The influence of prefire tree growth and crown condition on postfire mortality of sugar pine following prescribed fire in Sequoia National Park. 919, 910–919 (2015).
- 22.Keane, R. E., Loehman, R. A. & Holsinger, L. M. The FireBGCv2 landscape fire and succession model: a research simulation platform for exploring fire and vegetation dynamics. (U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station), 10.2737/RMRS-GTR-255 (2011).
- 23.Thonicke K, et al. The influence of vegetation, fire spread and fire behaviour on biomass burning and trace gas emissions: Results from a process-based model. Biogeosciences. 2010;7:1991–2011. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sturtevant, B. R., Scheller, R. M., Miranda, B. R., Shinneman, D. & Syphard, A. Simulating dynamic and mixed-severity fire regimes: A process-based fire extension for LANDIS-II. Ecol. Modell, 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.07.030 (2009).
- 25.Cansler CA, 2020. Fire and Tree Mortality Database (FTM) Forest Service Research Data Archive. [DOI]
- 26.US Department of the Interior National Park Service. Fire Monitoring Handbook. 274 (2003).
- 27.Hood S, Lutes D. Predicting post-fire tree mortality for 12 western us conifers using the first order fire effects model (FOFEM) Fire Ecol. 2017;13:66–84. [Google Scholar]
- 28.McIver JD, 2016. Data for National Fire and Fire Surrogate study: environmental effects of alternative fuel reduction treatments. Forest Service Research Data Archive. [DOI]
- 29.Hood, S., Bentz, B., Gibson, K., Ryan, K. & DeNitto, G. Assessing post-fire Douglas-fir mortality and Douglas-fir beetle attacks in the northern Rocky Mountains. USDA Forest Service - General Technical Report RMRS-GTR, 10.2737/RMRS-GTR-199 (2007).
- 30.Ryan, K. C. In Proceedings of the symposium: Fire, its field effects, 19–21 October 1982, Jackson, Wyoming. 1–11 (Intermountain Fire Council, Missoula, MT, 1982).
- 31.Peterson DL, Ryan KC. Modeling postfire conifer mortality for long-range planning. Environ. Manage. 1986;10:797–808. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hood, S. M., Cluck, D. R., Smith, S. L. & Ryan, K. C. Using bark char codes to predict post-fire cambium mortality. Fire Ecol. 4, 57–73, ST-Using bark char codes to predict post- (2008).
- 33.Google Inc. Google Earth Pro. Version 7.1.1.188. (2013).
- 34.Agne MC, Woolley T, Fitzgerald S. Fire severity and cumulative disturbance effects in the post-mountain pine beetle lodgepole pine forests of the Pole Creek Fire. For. Ecol. Manage. 2016;366:73–86. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Andrus RA, Veblen TT, Harvey BJ, Hart SJ. Fire severity unaffected by spruce beetle outbreak in spruce-fir forests in southwestern Colorado. Ecol. Appl. 2016;26:700–711. doi: 10.1890/15-1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lombardero MJ, Ayres MP, Ayres BD. Effects of fire and mechanical wounding on Pinus resinosa resin defenses, beetle attacks, and pathogens. For. Ecol. Manage. 2006;225:349–358. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Santoro AE, Lombardero MJ, Ayres MP, Ruel JJ. Interactions between fire and bark beetles in an old growth pine forest. For. Ecol. Manage. 2001;144:245–254. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Harrod, R. J., Peterson, D. W., Povak, N. A. & Dodson, E. K. Thinning and prescribed fire effects on overstory tree and snag structure in dry coniferous forests of the interior Pacific Northwest. For. Ecol. Manage, 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.05.011 (2009).
- 39.Battaglia MA, Smith FW, Shepperd WD. Can prescribed fire be used to maintain fuel treatment effectiveness over time in Black Hills ponderosa pine forests? For. Ecol. Manage. 2008;256:2029–2038. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Brown JK, DeByle NV. Fire damage, mortality, and suckering in aspen. Can. J. For. Res. 1987;17:1100–1109. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Davis RS, Hood S, Bentz BJ. Fire-injured ponderosa pine provide a pulsed resource for bark beetles. Can. J. For. Res. Can. Rech. For. 2012;42:2022–2036. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Engber EA, Varner JM. Predicting Douglas-fir Sapling Mortality Following Prescribed Fire in an Encroached Grassland. Restor. Ecol. 2012;20:665–668. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Harvey BJ, Donato DC, Romme WH, Turner MG. Influence of recent bark beetle outbreak on fire severity and postfire tree regeneration in montane Douglas-fir forests. Ecology. 2013;94:2475–2486. doi: 10.1890/13-0188.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Harvey BJ, Donato DC, Turner MG. Recent mountain pine beetle outbreaks, wildfire severity, and postfire tree regeneration in the US Northern Rockies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014;111:15120–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411346111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Harvey, B. J., Donato, D. C., Romme, W. H. & Turner, M. G. Fire severity and tree regeneration following bark beetle outbreaks: The role of outbreak stage and burning conditions. Ecol. Appl., 10.1890/13-1851.1 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Harvey, B. J., Donato, D. C. & Turner, M. G. Drivers and trends in landscape patterns of stand-replacing fire in forests of the US Northern Rocky Mountains (1984–2010). Landsc. Ecol., 10.1007/s10980-016-0408-4 (2016).
- 47.Hood SM, McHugh CW, Ryan KC, Reinhardt E, Smith SL. Evaluation of a post-fire tree mortality model for western USA conifers. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2007;16:679. [Google Scholar]
- 48.McHugh CW, Kolb TE. Ponderosa pine mortality following fire in northern Arizona. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2003;12:7. [Google Scholar]
- 49.McHugh CW, Kolb TE, Wilson JL. Bark Beetle Attacks on Ponderosa Pine Following Fire in Northern Arizona. Environ. Entomol. 2003;32:510–522. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kobziar L, Moghaddas J, Stephens SL. Tree mortality patterns following prescribed fires in a mixed conifer forest. Can. J. For. Res. 2006;36:3222–3238. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lerch AP, Pfammatter JA, Bentz BJ, Raffa KF. Mountain pine beetle dynamics and reproductive success in post-fire lodgepole and ponderosa pine forests in Northeastern Utah. PLoS One. 2016;11:1–22. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.McDaniel VL, Perry RW, Koerth NE, Guldin JM. Evaluation of FOFEM Fuel Loads and Consumption Estimates in Pine-Oak Forests and Woodlands of the Ouachita Mountains in Arkansas, USA. For. Sci. 2016;62:307–315. [Google Scholar]
- 53.O’Brien JJ, Hiers JK, Mitchell RJ, Varner JM, Mordecai K. Acute physiologicaal stress and mortality following fire in a long-unburned longleaf pine ecosystem. Fire Ecol. 2010;6:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Perrakis DDB, Agee JK, Eglitis A. Effects of Prescribed Burning on Mortality and Resin Defenses in Old Growth Ponderosa Pine (Crater Lake, Oregon): Four Years of Post-Fire Monitoring. Nat. Areas J. 2011;31:14–25. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Perrakis DD, Agee JK. Seasonal fire effects on mixed-conifer forest structure and ponderosa pine resin properties. Can. J. For. Res. 2006;36:238–254. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Trappe MJ, et al. Interactions among prescribed fire, soil attributes, and mycorrhizal community structure at Crater Lake National Park, Oregon, USA. Fire Ecol. 2009;5:30–50. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Prichard SJ, Peterson DL, Jacobson K. Fuel treatments reduce the severity of wildfire effects in dry mixed conifer forest, Washington, USA. Can. J. For. Res. 2010;40:1615–1626. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ganio LM, Progar RA. Mortality predictions of fire-injured large Douglas-fir and ponderosa pine in Oregon and Washington, USA. For. Ecol. Manage. 2017;390:47–67. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Roccaforte JP, et al. Delayed tree mortality, bark beetle activity, and regeneration dynamics five years following the Wallow Fire, Arizona, USA: Assessing trajectories towards resiliency. For. Ecol. Manage. 2018;428:20–26. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Huffman DW, et al. Effectiveness of fuel reduction treatments: Assessing metrics of forest resiliency and wildfire severity after the Wallow Fire, AZ. For. Ecol. Manage. 2014;334:43–52. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Roccaforte, J. P. et al. Forest structure and fuels dynamics following ponderosa pine restoration treatments, White Mountains, Arizona, USA. For. Ecol. Manage., 10.1016/j.foreco.2014.11.001 (2015).
- 62.Stoddard, M. T., Huffman, D. W., Fulé, P. Z., Crouse, J. E. & Sánchez Meador, A. J. Forest structure and regeneration responses 15 years after wildfire in a ponderosa pine and mixed-conifer ecotone, Arizona, USA. Fire Ecol., 10.1186/s42408-018-0011-y (2018).
- 63.Stoddard, M. T., Sánchez Meador, A. J., Fulé, P. Z. & Korb, J. E. Five-year post-restoration conditions and simulated climate-change trajectories in a warm/dry mixed-conifer forest, southwestern Colorado, USA. For. Ecol. Manage., 10.1016/j.foreco.2015.07.007 (2015).
- 64.Korb, J. E., Fulé, P. Z. & Stoddard, M. T. Forest restoration in a surface fire-dependent ecosystem: An example from a mixed conifer forest, southwestern Colorado, USA. For. Ecol. Manage., 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.01.002 (2012).
- 65.Rogers, B. M. et al. Quantifying fire-wide carbon emissions in interior Alaska using field measurements and Landsat imagery. J. Geophys. Res. G Biogeosciences, 10.1002/2014JG002657 (2014).
- 66.Safford HD, Stevens JT, Merriam K, Meyer MD, Latimer AM. Fuel treatment effectiveness in California yellow pine and mixed conifer forests. For. Ecol. Manage. 2012;274:17–28. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Stevens JT, Safford HD, Latimer AM. Wildfire-contingent effects of fuel treatments can promote ecological resilience in seasonally dry conifer forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2014;44:843–854. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Das AJ, Stephenson NL, Davis KP. Why do trees die? Characterizing the drivers of background tree mortality. Ecology. 2016;97:2616–2627. doi: 10.1002/ecy.1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.van Mantgem, P. J., Stephenson, N. L., Knapp, E., Battles, J. & Keeley, J. E. Long-term effects of prescribed fire on mixed conifer forest structure in the Sierra Nevada, California. For. Ecol. Manage., 10.1016/j.foreco.2010.12.013 (2011).
- 70.McCarley, T. R. et al. Landscape-scale quantification of fire-induced change in canopy cover following mountain pine beetle outbreak and timber harvest. For. Ecol. Manage., 10.1016/j.foreco.2017.02.015 (2017).
- 71.Varner JM, et al. Overstory tree mortality resulting from reintroducing fire to long-unburned longleaf pine forests: the importance of duff moisture. Can. J. For. Res. 2007;37:1349–1358. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Thies WG, Westlind DJ, Loewen M, Brenner G. Prediction of delayed mortality of fire-damaged ponderosa pine following prescribed fires in eastern Oregon, USA. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2006;15:19–29. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hanula JL, Meeker JR, Miller DR, Barnard EL. Association of wildfire with tree health and numbers of pine bark beetles, reproduction weevils and their associates in Florida. For. Ecol. Manage. 2002;170:233–247. [Google Scholar]
- 74.McDaniel, V. L. et al. Tree mortality following a drought-year lightning ignition in the Ouachita Mountains, Arkansas: 2 years postburn. Proc. 18th Bienn. South. Silvic. Res. Conf. 206–213 (2016).
- 75.Brown, J. K. & Debyle, N. V. Aspen Mortality and Response. Supplement to Study Plan No. 2108-103 and 1751-24. Fire as a management tool in the western aspen ecosystem - Prescription development and postburn vegetative response in western Wyoming. USDA Forest Service (1982).
- 76.Schwilk DW, et al. The National Fire and Fire Surrogate study: effects of fuel reduction methods on forest vegetation structure and fuels. Ecol. Appl. 2009;19:285–304. doi: 10.1890/07-1747.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Finney, M. A. Fire-related mortality in ponderosa pine in eastern Montana. Unpublished Report INT-93800-RJVA. (USDA Forest Service, RMRS Fire Sciences Laboratory, Missoula., 1999).
- 78.Hanula, J. L. Unpublished data. Post-fire tree data from the 1998 Oak fire, FL, USA. (2018).
- 79.Stuever, M. Fire induced mortality of Rio Grande Cottonwood. (M.S. Thesis. Department of Biology, University of New Mexico, 1997).
- 80.Weiss, S. A. & Corace, R. G. III Rapid Ecological Assessment of Forest Cover and Fire Effects at Driggs River Road Prescribed Fire. (2014).
- 81.Ayres, M. P., Lombardero, M. J., Ayres, B. D., Shumate, A. M. & Santoro, A. E. The biology and management of bark beetles in old growth pine forests of Itasca State Park. Gt. Lakes Inst. Pine Ecosyst. Res. 128 pp. (1999).
- 82.Cram, D. S., Baker, T. T. & Boren, J. C. Wildland Fire Effects in Silviculturally Treated vs. Untreated Stands of New Mexico and Arizona. Res. Pap. RMRS-RP-55. USDA For. Serv. Rocky Mt. Res. Stn. 28 (2006).
- 83.Kopper, K. E. Unpublished data. Rapid Assessment Plots from the 2016 Paradise fire, Olympic National Park, WA, USA. (2017).
- 84.Hood, S. M. Unpublished data on file at USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. (2019).
- 85.Dickinson, D. M. Unpublished data. Post-fire tree data from the WWETAC project in the Carlton Complex fire, WA, USA. (2019).
- 86.Coleman, T. W. Unpublished data. Post-fire tree injury data from the 2013 Mountain wildfire and 2015 Wooded Hill prescribed fire, CA, USA. (2018).
- 87.Cluck, D. R. Unpublished data. Post-fire tree data from 2013 fires in California. (2018).
- 88.Kreye, J., Cronan, J., Ottmar, R., Restaino, J. & Pulido-Chavez, F. Pre- and post-burn fuel characterization and tree mortality assessment for the Forest Resiliency Burning Pilot. Report to the Washington Department of Natural Resources. (2017).
- 89.Roccaforte, J. P. Evaluating treatment effectiveness following the 2014 San Juan Fire, White Mountains, Arizona. ERI Fact Sheets. Ecological Restoration Institute, Northern Arizona University. 3 p. (2016).
- 90.Battaglia M, Smith FW, Shepperd WD. Predicting mortality of ponderosa pine regeneration after prescribed fire in the Black Hills, South Dakota, USA. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 2009;18:176–190. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ryan, K. C. & Amman, G. D. Bark Beetle Activity and Delayed Tree Mortality in the Greater Yellowstone Area Following the 1988 Fires. Ecol. Implic. fire Gt. Yellowstone Proceedings. Int. Assoc. Wildliand Fire, Fairland, WA 151–158 (1996).
- 92.Keyser TL, Smith FW, Lentile LB, Shepperd WD. Modeling postfire mortality of ponderosa pine following a mixed-severity wildfire in the Black Hills: The role of tree morphology and direct fire effects. For. Sci. 2006;52:530–539. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fiedler CE, Metlen KL, Dodson EK. Restoration treatment effects on stand structure, tree growth, and fire hazard in a ponderosa pine/douglas-fir forest in Montana. For. Sci. 2010;56:18–31. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Harvey BJ, Donato DC, Turner MG. High and dry: Post-fire tree seedling establishment in subalpine forests decreases with post-fire drought and large stand-replacing burn patches. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016;25:655–669. [Google Scholar]
- 95.McCarley, T. R. et al. Multi-temporal LiDAR and Landsat quantification of fire-induced changes to forest structure. Remote Sens. Environ., 10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.022 (2017).
- 96.Cansler, C. A., Hood, S. M., Mantgem, P. van & Varner, J. M. A large database supports the use of simple models of post-fire tree mortality in the continental United States. In prep. Fire Ecol.
- 97.Shearman TM, Varner JM, Hood SM, Cansler CA, Hiers JK. Modelling post-fire tree mortality: Can random forest improve discrimination of imbalanced data? Ecol. Modell. 2019;414:108855. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Gelman, A. & Hill, J. Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel/Hierarchical Models. (Cambridge University Press, 2006).
- 99.R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Version 3.1.2 (2014-10-31). (2014).
- 100.Ryan, K. C. & Noste, N. V. Evaluating prescribed fires. in Proceedings - symposium and workshop on wilderness fire. Missoula, MT, 15-18 November 1983. Gen. Tech. Rep. INT-182. (eds. Lotan, J., Kilgore, B. M., Fischer, W. C. & Mutch, R. W.) 230–238 (U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station, 1985).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Citations
Data Availability Statement
Fire and Tree Mortality Database (FTM) is available from Forest Service Research Data Archive 10.2737/RDS-2020-0001. All reformatting of contributed data was completed in R version 3.6.199. Original contributed data are only available by contacting data contributors. The code used to reformat the data may be obtained contacting C. A. Cansler.