ABSTRACT
Background. Recently isolated Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains have displayed multiple antibiotic resistance. Alternatives to conventional antibiotics are needed, especially for the multiple-antibiotic–resistant V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strain.
Methods. A bacteriophage, designated pVp-1, showed effective infectivity for multiple-antibiotic–resistant V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus, including V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strains. The therapeutic potential of the phage was studied in a mouse model of experimental infection using a multiple-antibiotic–resistant V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strain. We monitored the survivability and histopathological changes, quantified the bacterial and phage titers during phage therapy, and observed the immune response induced by phage induction.
Results. Phage-treated mice displayed protection from a V. parahaemolyticus infection and survived lethal oral and intraperitoneal bacterial challenges.
Conclusions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of phage therapy in a mouse model against a multiple-antibiotic–resistant V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strain infection.
Keywords: Vibrio parahaemolyticus, bacteriophage, pVp-1, pandemic strains
Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a gram-negative marine bacterium, is one of the most important causes of gastroenteritis associated with consumption of raw oysters [1]. Vibrio parahaemolyticus pandemic strains, such as O3:K6, are responsible for current pandemics in many countries [2]. Emergence of Vibrio species that are resistant to multiple antibiotics has been recognized as a serious global clinical problem [3]. Recently isolated V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strains have displayed multiple antibiotic resistance, increasing concerns about possible treatment failure [4].
Bacteriophages (phages) can be used to treat infectious diseases both in humans and animals [5–10]. Phages display an effective bacteriolytic activity and possess several advantages over other antimicrobial agents, and no serious side effects of phage therapy have been described to date [9, 11]. All isolated V. parahaemolyticus strains have exhibited resistance to a broad variety of commercial antibiotics, and we previously noted that alternatives to conventional antibiotics are needed [4].
In this study, we isolated and characterized 1 lytic Siphoviridae phage, designated pVp-1 [12], that infects V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strains. Our aim was to determine whether this phage could be suitable for therapeutic use in a mouse model of a multiple-antibiotic–resistant V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strain.
METHODS
Bacterial Strains
Vibrio parahaemolyticus American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) 33844 was used as the host bacterial strain for phage isolation and amplification. CRS 09-17 (isolated from a patient with diarrhea; V. parahaemolyticus new O3:K6 pandemic strain) [4] was used to evaluate its therapeutic potential.
Electron Microscope Examination
Phage particles were negatively stained with 2% uranyl acetate. Electron micrographs were taken using a Zeiss TEM EM902.
One-Step Growth
The one-step growth curve of pVp-1 was determined according to the method of Verma et al [13]. Ten microliters of phage suspension was added to 10 mL of the mid-exponential host bacterial culture (ATCC 33844, 8.0 × 106 CFU/mL). The mixture was then centrifuged and the pellet resuspended in 20 mL of trypticase soy broth. Samples (100 μL) were taken at 5-minute intervals and subjected to phage titration.
Phage Stability
Phage stability tests were conducted as described elsewhere [13], with modifications. Briefly, phage stability to various conditions such as organic solvents (chloroform, ethanol, and diethylether; 25% of total volume), pH (3, 5, 7, 9, and 11), temperature (20, 25, 30, 37, 50, and 65°C), and ultraviolet (UV) light (30 cm from the UV-C, 253.7 nm; Sankyo Denki, Japan) was evaluated after 1 hour incubation at 25°C (except for the temperature test). After incubation, the phage titer was estimated by the double-agar layer method.
Host Cell Lysis
The bacteriolytic effect of the phage on V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 was observed by determining viable bacteria counts throughout the incubation period. The phage was added to the early exponential phase (optical density [OD]600 nm = 0.1; 8.0 × 106 CFU/mL) of CRS 09-17 at the indicated multiplicity of infection (MOI); the change in OD was monitored for 24 hours.
Ethics Statement
Specific pathogen-free BALB/c female mice (8-weeks-old) were used with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea (reg. no. SNU-120602-1). All animal care and experimental protocols were performed according to the guidelines of the Animal Ethical Committee, Seoul National University.
Induction of V. parahaemolyticus Infection in Mice
To determine the 50% lethal dose (LD50), V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 was diluted with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to a range of 2.0 × 106 to 2.0 × 108 CFU per mouse in 200 μL and was administered by either the intraperitoneal (IP) or orogastric route (orally). Five mice were used for each concentration. The survival rate of mice was recorded until 7 days post-infection. Mice inoculated with CRS 09-17 were observed for their state of infection based on several clinical signs, including ruffled fur, hunchback moribund, and partially closed eyes. The experiment was replicated 3 times.
Kinetics of Phage in Mice
A phage in vivo kinetic assessment was performed as previously described [13], with several modifications. First, between the 2 groups, with each group composed of 21 mice, 1 group was given an IP injection, while the other group was orally given the phage preparation (2.0 × 108 PFU/mouse). Second, the 2 groups (7 mice per group) were given an IP injection or were administered a heat-inactivated (65°C, 2 hours) phage suspension orally as the negative control. Finally, at appropriate time intervals, 4 mice (3 test mice and 1 control mouse) from the IP and oral groups were euthanized, and phage titers were determined from their organs.
Treatment of Bacteremic Mice With Phage pVp-1
The efficacy of phage therapy was evaluated in 2 experiments using the V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 infection mouse model. In the first experiment, 2 groups of mice (control/treatment; 5 mice in each group) were challenged by an IP injection of an LD50 of CRS 09-17. Each mouse was treated with a single IP injection of phage pVp-1 (2.0 × 108 PFU per mouse) or PBS 1 hour after the bacterial challenge (2.0 × 107 CFU per mouse).
In the second experiment, all conditions were similar to those of the first study except that the bacterial challenge (2.0 × 107 CFU per mouse) and phage treatment (2.0 × 108 PFU per mouse) were administered orally. Both experiments were repeated 5 times, and the health of the mice was monitored for 72 hours.
In an additional study, 2 groups (5 mice per group) were not challenged with bacteria and received only phage (2.0 × 1011 PFU per mouse) by IP and oral routes. The health of these mice was monitored for 28 days.
Quantitative Analysis of V. parahaemolyticus/Phage in Mouse Organs
All conditions were similar to those of the phage treatment experiment described above. Three mice from each group were euthanized at 0, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 hours post-treatment. As the main target organs of gastroenteritis, the stomach and intestine were removed and homogenized to quantify viable bacteria and phage. Bacterial and phage counts were normalized by organ weight when the organs were halved and processed for histopathological examination. A selective medium (CHROMagar Vibrio-containing resistant antibiotics) was used for the enumeration of V. parahaemolyticus, as described previously [4]. This experiment was repeated 3 times.
Histopathology of Organs
A portion (one-half) of the stomach and intestine was fixed and cut by a standardized method and placed in tissue cassettes for further processing. Slides of hematoxylin-eosin–stained tissues were prepared and observed for histopathology by microscopic examination. Histopathology was examined for severity in a blinded manner.
Measuring Phage Immune Response
Mice were immunized using an IP injection of phage (2.0 × 1010 PFU per mouse) at intervals of 0, 4, 6, and 8 weeks, as described previously [14]. At various times, the sera from 5 mice were prepared and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed, as previously described [15]. Immunoglobulins were detected with goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin M (IgM)- or IgG-specific antibodies.
Statistical Analyses
Statistically significant differences in all of the experiments were determined using Student t test. The SPSS statistical software package, version 16.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL), was used for all statistical analyses.
RESULTS
Characterization of Vibrio Phage pVp-1
The Vibrio phage pVp-1 formed small plaques (average diameter, 1 mm) in a lawn of V. parahaemolyticus ATCC 33844 and it had a latent period of approximately 15 minutes with a burst size of 47 PFU/cell (see Supplementary Data).
The pVp-1 was sensitive to organic solvents. After 1 hour of incubation in chloroform, diethylether, and ethanol, phage activity decreased to 37.7%, 33%, and 56.6%, respectively. However, no effect on phage activity was observed within a pH range of 5–11, and the activity remained at a high level (94.9%) at pH 3. In addition, the phage was relatively heat stable over a temperature range of 20°C–37°C, and no loss in activity was observed, although phage activity decreased to 3.3% at 50°C and to 0% at 65°C. Upon exposure to UV light, a complete inactivation of pVp-1 at approximately 45 minutes was observed (see Supplementary Data).
Phage Therapeutic Application on Pandemic Clinical Strain
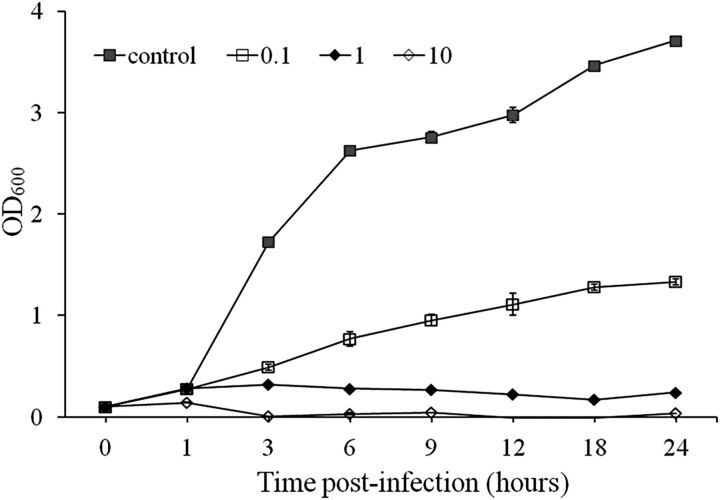
The bacteriolytic effect of pVp-1 was tested on an early exponential phase culture of V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 (Figure 1). When the culture was not infected by pVp-1 (control), the OD600 value continued to increase throughout the incubation period. In contrast, bacterial growth induced by pVp-1 was apparently retarded at an MOI of 0.1, 1, and 10 until 24 hours. Bacterial growth was properly inhibited at an MOI of 1 and 10, whereas the OD600 value at an MOI of 0.1 increased gradually and reached 1.0 after 9 hours.
Figure 1.
The bacteriolytic effect of pVp-1 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17. Early exponential phase cultures of V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 were cocultured with pVp-1 at multiplicity of infections of 0, 0.1, 1, and 10. The results are shown as the mean ± standard deviation from triplicate experiments.
In animal experiments, invalidism and the wellness of the animals were measured using the following 4 criteria: physical condition, survival rate, CFU per gram of target organs (stomach/intestine), and histopathology of target organs (stomach/intestine). The LD50 of V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 was examined using IP and oral routes of administration. The LD50 of the IP and oral routes were between 2.0 × 106 and 2.0 × 107 CFU per mouse (data not shown). The IP and oral mouse infection model was an acute death model; all mortality occurred within 36 hours. Thirty-six hours post-infection, mice that survived entered the recovery stage.
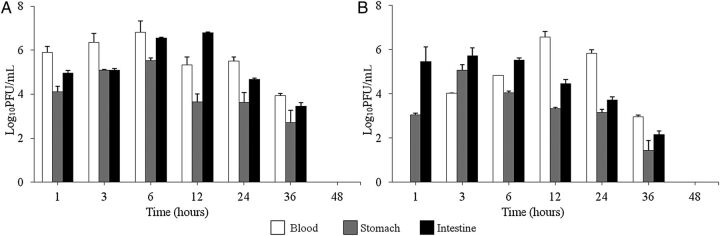
To examine in vivo kinetics, a pVp-1 kinetic analysis was performed in mice treated by IP and oral administration (Figure 2). In the IP group, the maximum PFU values were observed at 6 hours (blood/stomach) and 12 hours (intestine) of inoculation. In the group receiving the oral administration, the maximum PFU values were obtained at 3 hours (stomach/intestine) and 12 hours (blood) of inoculation. In every experimental group, there was a gradual fall in the titer thereafter; after 48 hours of inoculation, pVp-1 became undetectable. During the experiment, all mice were healthy and in normal condition. In addition, the administration of a high dose (2.0 × 1011 PFU/mouse) of pVp-1 alone did not affect the physical condition or survival during 28 days of observation.
Figure 2.
Kinetics of pVp-1 in the mouse model. Phage was injected via the intraperitoneal (A) or orogastric route (B) at 108 PFU/mouse. After 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 hours of phage inoculations, blood, stomach, and intestine were removed and their phage titers were estimated. Titers are presented as the mean of 3 experiments performed in triplicate, and the error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3).
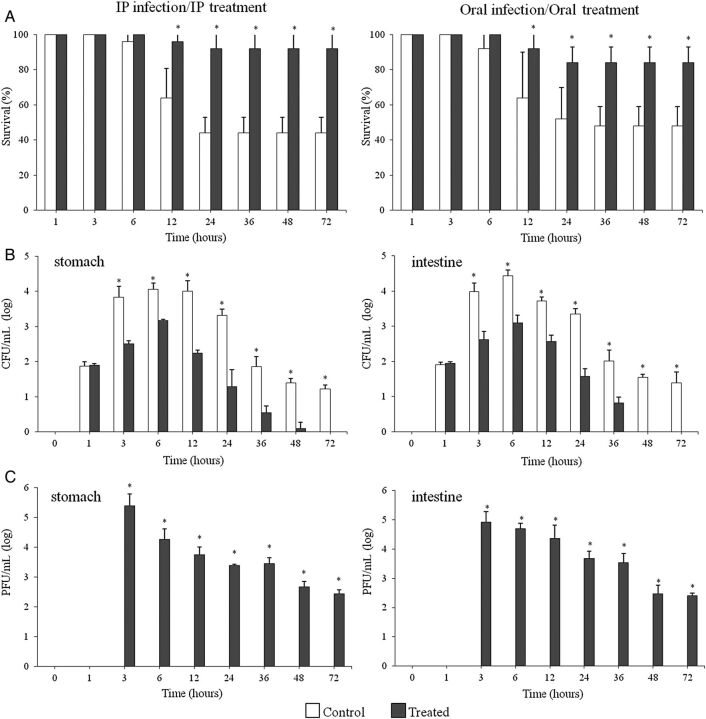
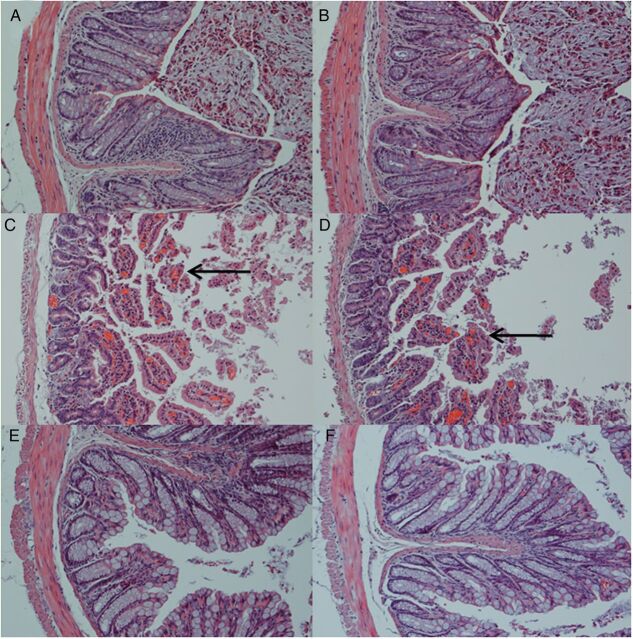
To determine whether phage pVp-1 could treat a CRS 09-17 infection, pVp-1 was administered by IP and oral routes 1 hour after a CRS 09-17 challenge (Figure 3). After 6 hours of infection, all control (infected but not phage-treated) mice were visibly ill, lethargic, and scruffy. The control group fatality rate was 56% (IP) and 52% (oral) within 36 hours. The stomachs and intestines of control mice contained high levels of bacteria (stomach, 1.0 × 104 CFU/g; intestine, 5.3 × 103 CFU/g) until 12 hours post-infection (Figure 3). In contrast, phage treatment resulted in excellent protection in terms of all 4 criteria. The phage-treated mice appeared to be only slightly ill and were protected up to 92% (IP) and 84% (oral) from the lethal infection induced by CRS 09-17 (2.0 × 107 CFU) after the administration of a single dose of purified pVp-1 of 2.0 × 108 PFU (Figure 3). The stomach/intestine CFU and histopathological features were improved by phage treatment. In the IP treatment group, a decrease in stomach/intestine CFU was obtained with the increased phage titer at 12 hours post-infection, 1.7 × 102/3.7 × 102 CFU/g and 5.7 × 103/2.3 × 104 PFU/g (Figure 3). In the oral treatment group, the maximum CFU and PFU values of the stomach/intestine, which were observed at experimental onset, gradually decreased (data not shown). In addition, the histopathological features demonstrated that the V. parahaemolyticus infection significantly damaged the intestinal tract as observed by the hematoxylin-eosin stain (Figure 4C and 4D) but not in the gastric region (data not shown). Severe destruction of the histologic structure of the colon was accompanied by a thinning of the wall, enterohemorrhage, and loss of crypts in the mucosal layer (Figure 4C and 4D). However, treatment with phage ameliorated the histological damage in the colon. The histopathological examination of the colon of the phage-treated mice revealed a significant recovery in the destruction of the intestinal wall and crypts, hemorrhages, and inflammation after both IP and oral treatment (Figure 4E and 4F). This suggests that phage-treated animals showed strongly reduced infection severity and could survive a lethal bacterial challenge.
Figure 3.
Effect of phage treatment on Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in mice. A, The survival rate of mice in the control (treated with phosphate buffered saline) and treated (phage-treated) groups. The 50% lethal dose of V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 (2.0 × 107 CFU/mouse) was required to induce an acute death model by way of the intraperitoneal (IP) and oral routes. The phage, pVp-1 (2.0 × 108 PFU/mouse), was applied by IP injection and oral administration after a 1-hour CRS 09-17 challenge because the maximum effect of cell lysis was examined at a multiplicity of infection of 10. B, CFU per gram of target organs (stomach/intestine) in the experimental mice through IP infection/IP treatment. C, The PFU per gram of target organs (stomach/intestine) in the experimental mice through IP infection/IP treatment. In the oral infection/oral treatment group, the maximum CFU and PFU values of stomach/intestine were determined at the experimental onset, and the values were gradually decreased. The bars show the mean, and the error bars show the standard error. Significant differences (P < .05) were observed at various time points (shown with asterisks).
Figure 4.
Histopathological features of the intestines of mice at 24 hours of phage inoculations, infected with Vibrio parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17 and treated with the phage pVp-1. The micrographs depict the histologic features of the mice from the experiment. A, A healthy mouse that only received a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) IP injection. B, A healthy mouse that only received PBS oral administration. C, A control mouse (IP infection/no phage treatment). D, A control mouse (oral infection/no phage treatment). Deteriorated crypts are indicated in C and D. E, A phage-treated mouse (IP infection/IP treatment). F, A phage-treated mouse (oral infection/oral treatment). The phage-treated mice demonstrated the protected morphology of the crypt in both the IP and oral treatment groups. Sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin and observed at a magnification of × 200.
Immune Response to Phage pVp-1
After the fourth phage induction in a series of phage injections in mice, titers of IgG and IgM against the phage increased above background levels by 170-fold and 50-fold, respectively (see Supplementary Data). No anaphylactic reactions, changes in physical condition, or adverse events were observed during the course of these multiple injections of phage.
DISCUSSION
Based on the morphological analysis, pVp-1 was classified into the family Siphoviridae and demonstrated a broad host range. This differs from a prior finding that Siphoviridae phages are generally considered to have restricted host ranges [16]. The phage infected 74% (20/27) of all multiple-antibiotic–resistant V. parahaemolyticus strains used in this study, including the 2 pandemic strains CRS 09-17 and CRS 09-72. Interestingly, pVp-1 infected the V. parahaemolyticus clinical isolate CRS 09-17 from a patient with diarrhea, which represents a multiple-antibiotic–resistant new O3:K6 pandemic strain (tdh+, ORF8+, toxRS/new+) [4]. The results obtained from pVp-1 showed its lytic nature with a latent period and a large burst size. Full genome sequencing of pVp-1 identified no similarity match with lysogenic or phage integrase-related genes (considered as markers of temperate phages), indicating that it is a novel, newly isolated lytic phage [12]. This result emphasizes the potential of pVp-1 as a therapeutic agent, as described by Gutiérrez et al [11], who regarded lytic phages as more suitable phages for therapy. Furthermore, the stability of pVp-1 over a wide range of pH (3–11) and temperature (20°C –37°C) clearly indicates that pVp-1 would be highly stable in the human body.
Current analyses show that the search for new antibiotics conducted by pharmaceutical companies is becoming more and more restricted due to the increasing costs of conducting the appropriate trials, low profits, and high risk of the investment, precisely because of the possibility of a rapid acquisition of resistance to the new drug [17–20]. We hypothesize that phage therapy can be useful, especially in epidemics caused by multiple-antibiotic–resistant pandemic strains. To evaluate the therapeutic potential of pVp-1, we used a mouse model of V. parahaemolyticus CRS 09-17. In the cell lysis test of pVp-1, the growth of CRS 09-17 was apparently inhibited after pVp-1 inoculations at MOIs of 1 and 10, although pVp-1 partially inhibited the bacterial growth at an MOI of 0.1.
Because the route of phage inoculation is important, in vivo phage kinetics were ascertained following IP and oral administration of pVp-1. To apply pVp-1 at an MOI of 10 (CRS 09-17, 2.0 × 107 CFU per mouse), where the maximum effect of cell lysis was examined, kinetic tests were performed with pVp-1 at 2.0 × 108 PFU per mouse. Phage titers in the stomach as well as the intestine indicated that pVp-1 was maintained at higher concentrations in these 2 organs and could prevent V. parahaemolyticus infections. These findings suggest that pVp-1 might be efficacious for a prophylactic approach. In blood, pVp-1 reached a high titer within the first hour following IP injection. In contrast, no phage was detected until after 1 hour, and it took longer to reach a higher titer when it was administered orally. Moreover, the highest titer in each organ was also much higher in the IP route of administration compared with the oral route of administration. Therefore, we speculate that the IP route of administration would be the more suitable route.
Phage treatment trials in the mouse model for CRS 09-17 demonstrated that the application of pVp-1 can protect from a V. parahaemolyticus infection in all 4 criteria and that pVp-1 can be used as a therapeutic agent to reduce the impact of epidemics caused by multiple-antibiotic–resistant pandemic strains. The current phage treatment revealed the unique advantage of phage therapy, that is, that the normal microbial flora can be preserved in contrast to antibiotic use, which may lead to secondary symptoms by the disruption of normal flora, as previously reported [5, 21–23]. In the present study, mice were treated with phage pVp-1 at 1 hour post-infection in order to induce complete infection by V. parahaemolyticus. However, the progression of disease in our model was extremely rapid, and the delayed treatment with phages resulted in decreased efficacy of protection [21]. Furthermore, even if the Vibrios and phages were administered to mice simultaneously, they may not come into contact until some time after injection [21]. In order to achieve a higher level of protection, administration soon after infection is required.
While pVp-1 invoked an immune response in mice, the antibodies raised over the course of repeated injections were not associated with anaphylaxis or other adverse reactions. These experiments were designed as a model for acute human infections, where antibiotics are no longer effective and a single course of phage treatment may rescue the patient. If phages are to be employed repeatedly (eg, for chronic infections), selection use and phage display may produce phage variants that are less prone to induce an immune response [5].
In 2006, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of a commercial phage cocktail (List-Shield; Intralytix, Inc.) as a biocontrol agent. This is confirmation that the FDA's view of phages is that they are safe for human use and opens the doors for phage commercialization for human applications [24]. Despite no reports of significant adverse reactions during the long history of phage administration in humans, phage therapy still needs to gain credibility to overcome the regulatory hurdles facing its adoption in mainstream clinical practice [24]. Moreover, it is necessary to establish adequate phage preparation methodologies such as the purification and removal of endotoxins for safety in phage therapy to prevent anaphylactic responses [25–28].
Supplementary Material
Notes
Financial support. This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (2013R1A1A2006794).
Potential conflict of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts.
All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
References
- 1.Daniels NA, MacKinnon L, Bishop R, et al. Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections in the United States, 1973–1998. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:1661–6. doi: 10.1086/315459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Matsumoto C, Okuda J, Ishibashi M, et al. Pandemic spread of an O3:K6 clone of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and emergence of related strains evidenced by arbitrarily primed PCR and toxRS sequence analyses. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:578–85. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.2.578-585.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Okoh AI, Igbinosa EO. Antibiotic susceptibility profiles of some Vibrio strains isolated from wastewater final effluents in a rural community of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jun JW, Kim JH, Choresca CH, et al. Isolation, molecular characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Korean seafood. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2012;9:224–31. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2011.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Biswas B, Adhya S, Washart P, et al. Bacteriophage therapy rescues mice bacteremic from a clinical isolate of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Infect Immun. 2002;70:204–10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.204-210.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bruttin A, Brűssow H. Human volunteers receiving Escherichia coli phage T4 orally: a safety test of phage therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:2874–8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.2874-2878.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chhibber S, Kaur S, Kumari S. Therapeutic potential of bacteriophage in treating Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055-mediated lobar pneumonia in mice. J Med Microbiol. 2008;57:1508–13. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.2008/002873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kumari S, Harjai K, Chhibber S. Efficacy of bacteriophage treatment in murine burn wound infection induced by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;19:622–8. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0808.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sulakvelidze A, Kutter E. Bacteriophage therapy in humans. In: Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A, editors. Bacteriophages: biology and applications. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2005. pp. 381–436. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vinodkumar CS, Neelagund YF, Kalsurmath S. Bacteriophage in the treatment of experimental septicemic mice from a clinical isolate of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Commun Dis. 2005;37:18–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gutiérrez D, Martínez B, Rodríguez A, García P. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages infecting Staphylococcus epidermidis. Curr Microbiol. 2010;61:601–8. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9659-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim JH, Jun JW, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE, Park SC. Complete genome sequence of a novel marine siphovirus, pVp-1, infecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Virol. 2012;86:7013–4. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00742-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Verma V, Harjai K, Chhibber S. Characterization of a T7-like lytic bacteriophage of Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055: a potential therapeutic agent. Curr Microbiol. 2009;59:274–81. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9430-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sunagar R, Patil SA, Chandrakanth RK. Bacteriophage therapy for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Res Microbiol. 2010;161:854–60. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Harlow E, Lane D. Using antibodies, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wichels A, Biel SS, Gelderblom HR, Brinkhoff T, Muyzer G, Schűtt C. Bacteriophage diversity in the North Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998;64:4128–33. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.11.4128-4133.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Clarke T. Drug companies snub antibiotics as pipeline threatens to run dry. Nature. 2003;425:225. doi: 10.1038/425225a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Norrby SR, Nord CE, Finch R European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Lack of development of new antimicrobial drugs: a potential serious threat to public health. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:115–9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(05)01283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wenzel RP. The antibiotic pipeline-challenges, costs, and values. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:523–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp048093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Summers WC. Bacteriophage therapy. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:437–51. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cerveny KE, DePaola A, Duckworth DH, Gulig PA. Phage therapy of local and systemic disease caused by Vibrio vulnificus in iron-dextran-treated mice. Infect Immun. 2002;70:6251–62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6251-6262.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Merril CR, Biswas B, Carlton R, et al. Long-circulating bacteriophage as antibacterial agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:3188–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smith HW, Huggins MB. Successful treatment of experimental Escherichia coli infections in mice using phage: its general superiority over antibiotics. J Gen Microbiol. 1982;128:307–18. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Housby JN, Mann NH. Phage therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14:536–40. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2009.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boratynski J, Syper D, Weberdabrowska B, Lusiak-Szelachowska M, Pozniak G, Gorski A. Preparation of endotoxin-free bacteriophages. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2004;9:253–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Merabishvili M, Pirnay JP, Verbeken G, et al. Quality-controlled small-scale production of a well-defined bacteriophage cocktail for use in human clinical trials. PLoS One. 2009;4:e4944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Skurnik M, Strauch E. Phage therapy: facts and fiction. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006;296:5–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Skurnik M, Pajunen M, Kiljunen S. Biotechnological challenges of phage therapy. Biotechnol Lett. 2007;29:995–1003. doi: 10.1007/s10529-007-9346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.