Carbon nanoparticles, carrying small interfering RNA, enter plant cells to silence genes in plants.
Abstract
Posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS) is a powerful tool to understand and control plant metabolic pathways, which is central to plant biotechnology. PTGS is commonly accomplished through delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) into cells. Standard plant siRNA delivery methods (Agrobacterium and viruses) involve coding siRNA into DNA vectors and are only tractable for certain plant species. Here, we develop a nanotube-based platform for direct delivery of siRNA and show high silencing efficiency in intact plant cells. We demonstrate that nanotubes successfully deliver siRNA and silence endogenous genes, owing to effective intracellular delivery and nanotube-induced protection of siRNA from nuclease degradation. This study establishes that nanotubes could enable a myriad of plant biotechnology applications that rely on RNA delivery to intact cells.
INTRODUCTION
Plants are central in providing more than 25% of our most clinically relevant drugs, are at the core of our sustainability efforts, and will benefit from genetic engineering to feed our growing population in the midst of climate change. Plant biotechnology is currently limited by the cost, ease, and throughput of methods for probing plant genetics and by the complexity of plant biosynthetic pathways. Consequently, less than a dozen complete biosynthetic pathways are known for plant natural products that have been reconstituted heterologously, compared to the ~1000 known biosynthetic pathways in bacteria and fungi (1). RNA interference (RNAi) is sequence-specific inhibition of gene expression at the messenger RNA (mRNA) level and can consist of either transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) or posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS). In PTGS, small RNA molecules—microRNA or small interfering (siRNA)—direct enzyme complexes to degrade mRNA molecules, hence suppressing their activity by preventing translation.
PTGS has shown to be a prominent tool in plants for genotype-phenotype mapping (2), discovery of new biosynthetic pathways (3), increased production of valuable small molecules (4), understanding of the functions of genes and proteins (5), and conferring of resistance to plant diseases (6). One common way of using PTGS in plants is to directly deliver siRNA molecules into cells. However, plants have a cell wall that presents a barrier to exogenous biomolecule delivery, whereby the plant cell wall size exclusion limit is ~5 to 20 nm (7). Consequently, viral vectors combined with Agrobacterium tumefaciens delivery is the preferred method to deliver siRNA into intact plant cells. Viral vectors present the advantage of directly and strongly expressing the siRNA without relying on plant transformation; however, most viruses are limited in their host range (8), often do not result in uniform silencing of the gene (and thus levels of silencing can vary between plants and experiments) (9), and might inadvertently result in the suppression of nontarget genes. Similarly, Agrobacterium-mediated delivery is also limited to use in certain plant species, often yields random DNA integration that can adversely and unpredictably affect the cell operation (10), results in constitutive expression of siRNA (thus limiting temporal control over gene silencing), and can be difficult to scale or multiplex for high-throughput or multigene target applications (11).
While nanomaterial-mediated delivery of RNA and therapeutics has been extensively explored in animals, its potential for plant systems remains understudied (12). Several previous studies take advantage of nanomaterials to deliver plasmid DNA (13–17) or proteins (18) to intact plant cells. Polymeric nanoparticles have shown promise for siRNA delivery to cell wall–free plant protoplasts, but polymeric nanoparticles have not been shown to traverse the cell wall for gene silencing in intact plant cells (8). A recent study has shown that clay nanosheets can facilitate delivery of pathogen-specific double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) into intact plant cells for virus resistance (19). Topical application of clay nanosheets enabled silencing of homologous RNA to provide sustained 20-day viral protection on the leaf surface. Clay nanosheet platform is a promising use of nanoparticles for delivery of RNAi into plants, paving the way toward future developments in plant bionanotechnology.
For many applications, particularly biosynthetic pathway mapping, direct and strong but also transient gene silencing is desired within all cellular layers of plant leaves while also mitigating against RNA degradation. In this study, we demonstrate the delivery of a different RNAi molecule—single-stranded siRNA—into intact cells of plant leaves using high–aspect ratio one-dimensional carbon nanomaterials: single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). SWNTs are biocompatible allotropes of carbon that have a high–aspect ratio cylindrical nanostructure with diameters of 0.8 to 1.2 nm and lengths of 500 to 1000 nm. SWNTs are capable of passively crossing the extracted chloroplast envelope (20) and plant cell membranes (21) because of their high–aspect ratio morphology, uniquely high stiffness, and small dimensions. SWNTs are among the few nanomaterials that can be synthesized to have the smallest dimension (~1 nm) below the plant size exclusion limit of ~20 nm while also providing a large cylindrical surface area from the extrusion of their one dimension out to ~500 nm. The resulting large surface area to volume ratio is thus amenable to facile loading of appreciable quantities of biological cargoes such as siRNA. In contrast, spherical nanoparticles must often exceed the plant cell wall size exclusion limit to load necessary quantities of bio-cargoes because of the reduced scaling of the spherical nanoparticle surface area to volume. Furthermore, when bound to SWNTs, biomolecules are protected from degradation in mammalian systems (22), exhibiting superior biostability compared to free biomolecules; a phenomenon we show here can extend to plants. Moreover, SWNTs have strong intrinsic near-infrared (nIR) fluorescence (23) within the biological tissue transparency window and beyond the chlorophyll autofluorescence range and thus enable tracking of cargo-nanoparticle complexes deep in plant tissues.
Previous usage of SWNTs in plant systems is limited to studies of SWNT biocompatibility (20, 24, 25), to sensing of small molecules (21, 26), and for delivery of plasmid DNA for genetic transformations (16, 17). To date, there has yet to be a nanoparticle-based delivery platform for siRNA molecules into intact plant cells. Here, we develop a SWNT-based siRNA delivery platform for the efficient silencing of an endogenous Nicotiana benthamiana gene in plant leaves. We show that SWNTs enable passive delivery (without external mechanical aid) and fluorescent tracking of siRNA molecules in plant tissues. SWNTs present a nontoxic platform for siRNA delivery that uses a minimal siRNA dose to achieve strong silencing that starts 1 day after treatment and reduces in intensity until the silencing completely disappears by 7 days after treatment, whereby silencing can be sustained upon reinfiltration of the siRNA-SWNT dose. With SWNT-mediated siRNA delivery, we achieve 95% gene silencing efficiency at the mRNA level, and show a substantial delay in siRNA nuclease degradation in cells, and also at the single-molecule level, through protection by SWNTs. Altogether, SWNT-based delivery platform is rapid, scalable, facile to multiplex for multiple gene silencing targets, and species independent (16, 24, 27–29). In sum, this study establishes that SWNTs could be a promising resource to overcome plant RNA delivery limitations and could enable a variety of plant biotechnology applications based on RNAi.
RESULTS
Preparation and characterization of siRNA-SWNTs
In this study, we aim to validate SWNTs as a passive and effective siRNA delivery and gene silencing platform for use in intact cells of mature plants. To this end, we aim to silence green fluorescent protein (GFP) transgene expression in transgenic mGFP5 N. benthamiana (Nb) plants by delivering siRNA molecules into leaves with SWNT nanocarriers and also demonstrate silencing of an endogenous plant gene, ROQ1. mGFP5 Nb plants constitutively express GFP targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum under the control of the Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter (DNA sequences for the promoter and GFP gene can be found in data S1) (30). Here, we tested two separate siRNA sequences (a-siRNA and b-siRNA), which target two slightly different regions of the mGFP5 gene for GFP silencing (Fig. 1A).
Fig. 1. siRNA-SWNT preparation and characterization.
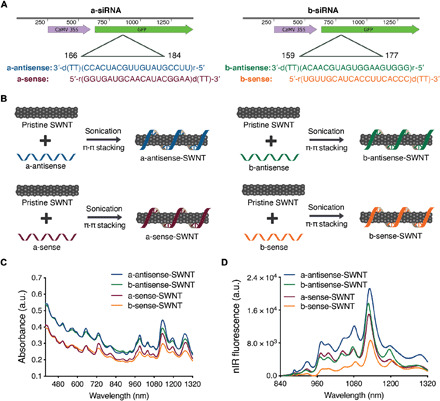
(A) Two sets of siRNA sequences targeting the GFP gene of transgenic mGFP5 Nb were separately tested in this study. Sequences on the left were chosen from Tang et al. (46), and sequences on the right were designed specifically for this study. (B) Suspension of pristine SWNTs with sense and antisense ssRNA sequences via probe-tip sonication. (C) Absorbance spectra of all RNA-SWNT suspensions. (D) nIR spectra of all RNA-SWNT suspensions. a.u., arbitrary units.
Loading of siRNA on SWNTs was accomplished by probe-tip sonication of each siRNA single strand (sense and, separately, antisense) with pristine SWNTs for both a-siRNA and b-siRNA sequences (Fig. 1B). With this method, sense and antisense strands of siRNA were noncovalently adsorbed on SWNTs via π-π stacking of RNA nitrogen bases with the π bonds of sp2-hybridized carbons in SWNTs. The adsorption of RNA on SWNTs was confirmed for each sequence (a-antisense-SWNT, a-sense-SWNT, b-antisense-SWNT, and b-sense-SWNT) through the emergence of characteristic peaks in the individually suspended SWNT absorbance (Fig. 1C) and nIR fluorescence emission spectra (Fig. 1D). We hypothesize and later verify that upon infiltration of an equimolar mixture of sense and antisense suspended SWNTs, these complementary siRNA strands desorb from the SWNT surface and hybridize to each other inside plant cells to form the active double-stranded siRNA silencing complex.
As a negative control for all siRNA silencing studies, we used SWNTs suspended with a nontargeting scrambled RNA sequence (s-RNA-SWNT; table S3) (31), which is not complementary to the mGFP5 mRNA. Successful suspension of SWNTs with nontargeting RNA sense and antisense strands was confirmed by absorbance and fluorescence spectra of individually suspended s-RNA-SWNTs (fig. S1). Furthermore, the atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterization of single-stranded RNA (ssRNA)–suspended SWNTs reveals an average ssRNA-SWNT conjugate length of 776.6 nm and an average conjugate height of 1.567 nm (fig. S1), which agrees with the expected values for undamaged and individually suspended ssRNA-SWNTs.
Internalization of siRNA-SWNTs into mature plant leaves
We first tested the internalization of ssRNA-SWNTs into intact mGFP5 Nb leaf cells. All internalization studies were performed with a-antisense-SWNT suspension as a representative strand to demonstrate the internalization ability of ssRNA-loaded SWNTs into intact walled plant leaf cells. Cy3 fluorophore–tagged RNA-SWNTs [100 nM siRNA and SWNTs (2 mg/liter)] and Cy3-tagged free RNA (100 nM) solutions were introduced into the intact plant leaves by infiltrating the abaxial surface of the leaf lamina with a needleless syringe (Fig. 2A). Following 6 hours of incubation, infiltrated mGFP5 Nb leaves were imaged with confocal microscopy to quantify Cy3 fluorescence inside leaf cells and in the extracellular area. Leaves infiltrated with Cy3-RNA-SWNTs showed a high degree of colocalization (70 ± 8%, mean ± SD) between the intracellular (cytosolic) GFP and Cy3 fluorescence originating from the nanocarriers, which confirms efficient internalization of RNA-SWNTs into intact cells (Fig. 2B). Conversely, leaves infiltrated with Cy3-RNA show minimal colocalization between the GFP and Cy3 channels (12 ± 10%, mean ± SD), and Cy3 fluorescence is observed mostly around the guard cells, suggesting that free RNA is not able to internalize into intact plant cells efficiently (Fig. 2B). Additional confocal images of Cy3-RNA-SWNT– and Cy3-RNA–infiltrated leaves with representative higher and lower colocalization percentages are presented in fig. S2. To note, a typical plant cell contains an organelle called the vacuole, which performs many functions in plants (32), and is filled with water, thus occupying ~80% of the cell volume. Therefore, fluorescence localized in the cytoplasm follows the cytosolic cell contour shape (fig. S3).
Fig. 2. ssRNA-SWNT internalization into transgenic mGFP5 N. benthamiana leaves.
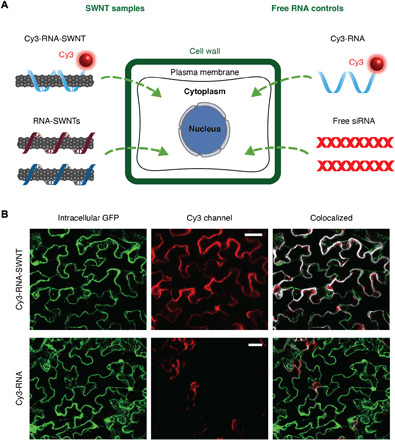
(A) Schematic showing samples tested for internalization into mGFP5 Nb leaves (Cy3-tagged RNA-SWNTs and Cy3-tagged free RNA as a control) and samples subsequently tested for silencing of a constitutively expressed GFP gene (RNA-SWNTs and free siRNA as a control). (B) Representative confocal images of Cy3-RNA-SWNT– and Cy3-RNA–infiltrated Nb leaves; intracellular GFP (green), Cy3 (red), and colocalization (white) channels. All scale bars, 20 μm.
To investigate the effect of SWNT length on the cell internalization efficiency, we prepared short SWNTs through excessive probe-tip sonication. AFM images revealed that these short SWNTs have an average length of 250 nm; they are significantly shorter than SWNTs obtained with regular preparation (776 nm). We then loaded these short SWNTs with Cy3-RNA as before and checked internalization efficiency into mGFP5 Nb cells with confocal microscopy. We found that short SWNTs have lower plant cell internalization efficiency compared to the longer ones, shown by respective average colocalization percentages of 47 and 70% (fig. S4).
In addition to confocal imaging of fluorophore-tagged ssRNA-SWNTs, we verified internalization of SWNT nanocarriers into intact leaf cells by leveraging the intrinsic SWNT nIR fluorescence. mGFP5 Nb leaves were infiltrated with ssRNA-SWNTs or free RNA without a fluorophore (Fig. 2A). Following 6 hours of incubation, we imaged the infiltrated leaves with a custom-built nIR microscope equipped with a Raptor Ninox VIS-SWIR 640 camera, a 721-nm SWNT excitation laser, and a white lamp and appropriate filters to image GFP (see Materials and Methods). In leaves infiltrated with ssRNA-SWNTs, commensurate with Cy3-tagged confocal imaging results, we observe a high degree of colocalization between intracellular GFP and the nIR fluorescence of SWNTs (fig. S5), further substantiating efficient internalization of SWNTs into intact plant cells. No colocalization was observed in leaves treated with unlabeled free RNA. The internalization of SWNT nanocarriers into plant cells is also supported by the nIR fluorescence spectra of ssRNA-SWNTs. Compared to as-prepared ssRNA-SWNTs, the nIR fluorescence spectra of ssRNA-SWNTs that infiltrated into leaves show a 6-nm solvatochromic shift and a relative change in intensity of small bandgap nanotubes upon cell membrane crossing (fig. S5). These differences in SWNT nIR spectra upon infiltration into leaves are possibly the result of the local dielectric environment change and exposure to intracellular biomolecules (33–35).
Thermodynamic analysis of RNA desorption and hybridization
After confirming that ssRNA-adsorbed SWNTs can efficiently be uptaken by plant cells, we analyzed the thermodynamics of sense and antisense strand desorption from the SWNT surface and their subsequent propensities for hybridization in the extracellular and intracellular conditions. According to our analysis (see the Supplementary Materials), in the in vitro and extracellular area of the leaf tissue, sense and antisense strand desorption from the SWNT surface and hybridization is not thermodynamically favorable (∆G > 0) because of a high free-energy cost of bare SWNTs in an aqueous environment (Fig. 3A). This unfavorable RNA desorption energy facilitates maintenance of intact RNA-SWNT conjugates in the extracellular environment until RNA-SWNTs enter cells. Once intracellular, sense and antisense strand desorption from the SWNT surface and hybridization is thermodynamically favorable (∆G < 0) because intracellular proteins, lipids, and other membrane and cytosolic biomolecules can occupy the SWNT surface and lower the associated free-energy costs of RNA desorption (Fig. 3B).
Fig. 3. Thermodynamic analysis of RNA desorption from SWNTs: Hybridization in extracellular and intracellular conditions and proposed gene silencing mechanism.
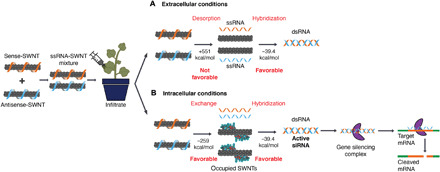
(A) An equimolar mixture of sense-SWNT and antisense-SWNT suspensions are infiltrated into transgenic Nb leaves with a needleless syringe. In the extracellular area of leaf tissue, RNA desorption and hybridization are not thermodynamically favorable because of the high free-energy cost of bare SWNTs. (B) Inside cells, RNA desorption from SWNTs and hybridization are thermodynamically favorable because molecules can occupy the bare SWNT surface and lower the RNA desorption free-energy cost. Upon desorption from SWNTs, double-stranded active siRNA assembles with the gene silencing complex and complexes with target mRNA for cleavage and gene silencing.
Hybridization and desorption of sense and antisense RNA strands were verified with an in vitro experiment, where we mixed and incubated an equimolar mixture of a-sense-SWNT and a-antisense-SWNT suspensions for 3 hours at room temperature either in water or in plant cell lysate solution (fig. S6). We then eluted the desorbed siRNA and quantified it via absorbance at 260 nm. The results confirm that an insignificant amount of siRNA is desorbed when RNA-SWNTs incubated in water, whereas 66% of the siRNA is desorbed when incubated in plant cell lysate solution. We then ran the eluted RNA from the cell lysate sample on an agarose gel and showed that it is double stranded, which verifies the formation of double-stranded siRNA in the cell cytosol. In addition, zeta potential measurements of a-siRNA-SWNTs before and after hybridization in water and removal of desorbed RNA show unchanged nanoparticle zeta potential, suggesting that there is no significant amount of RNA hybridization and desorption from SWNT surface in water (fig. S6).
Once hybridized, double-stranded active siRNA can merge with the gene silencing complex, whereby the antisense strand of siRNA directs the complex to the endogenous target mRNA. Upon hybridization of the antisense strand with the complementary target mRNA, a protein in the gene silencing complex (Argonaute) cleaves the target mRNA and prevents translation of GFP proteins (Fig. 3B).
siRNA-SWNT mediated gene silencing in intact plants
Following verification of SWNT internalization and formation of active siRNA complexes in plant cells, we next infiltrated transgenic mGFP5 Nb leaves with siRNA-SWNTs and control solutions to determine the gene silencing efficiency of this platform. Silencing studies were conducted with the following samples at 100 nM final siRNA and final SWNT concentration (2 mg/liter): nontreated leaves, s-RNA-SWNT (nontargeting), free siRNA, a-siRNA-SWNT, and b-siRNA-SWNT (see table S3 for sequences). We have shown that 100 nM siRNA on SWNTs is an optimal dose to be used in mGFP5 silencing studies (fig. S7). Transgenic Nb leaves that constitutively express GFP were imaged via confocal microscopy to quantify GFP silencing at the protein level. Representative confocal images of the leaves 2 days after infiltration reveal that both a-siRNA-SWNTs and b-siRNA-SWNTs lead to significant reduction of GFP in cells, whereas GFP expression in leaves infiltrated with s-RNA-SWNT and free siRNA appears similar to GFP expression in nontreated leaves (Fig. 4A). Quantification of GFP fluorescence intensity from the confocal images of s-RNA-SWNTs and a-siRNA-SWNTs (see Materials and Methods) reveals that a-siRNA-SWNT–infiltrated leaves have 38 ± 3.2% (mean ± SD) less GFP protein 3 days after infiltration compared to the s-RNA-SWNT–infiltrated leaves. At 7 days after infiltration, a-siRNA-SWNT shows roughly the same amount of GFP, 106.6 ± 4.1% (mean ± SD), as s-RNA-SWNT–infiltrated leaves (Fig. 4B), as expected since gene silencing with siRNA is a transient process due to rapid RNA degradation in cells (36). GFP silencing with a-siRNA-SWNT was also verified with Western blot analysis, where GFP extracted from the Nb leaves infiltrated with a-siRNA-SWNT is 42.6 ± 2.8% (mean ± SD) less than GFP extracted from s-RNA-SWNT–infiltrated leaves at both 1 and 2 days after infiltration (Fig. 4C).
Fig. 4. GFP gene silencing with RNA-SWNTs at the mRNA transcript and protein level.
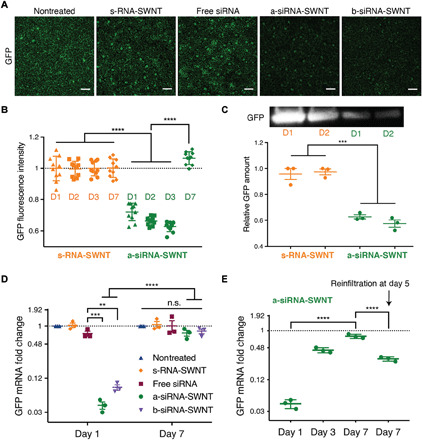
(A) Representative confocal microscopy images of nontreated and s-RNA-SWNT–, free siRNA–, a-siRNA-SWNT–, and b-siRNA-SWNT–infiltrated transgenic Nb leaves 2 days after infiltration. Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Quantitative fluorescence intensity analysis of confocal images for s-RNA-SWNT and a-siRNA-SWNT at 1, 2, 3, and 7 days after infiltration. ****P < 0.0001 in one-way ANOVA. Error bars, SD (n = 10). (C) Representative Western blot for GFP extracted from s-RNA-SWNT– and a-siRNA-SWNT–infiltrated Nb leaves 1 and 2 days after infiltration and quantification of GFP protein. ***P = 0.0001 in one-way ANOVA; error bars, SEM (n = 3). (D) qPCR analysis for GFP mRNA fold change at days 1 and 7 after infiltration for all samples tested. **P = 0.0016; ***P = 0.0008; ****P < 0.0001 in two-way ANOVA (n.s., nonsignificant). All error bars, SEM (n = 3). (E) qPCR analysis for GFP mRNA fold change at days 1, 3, and 7 and day 7 with reinfiltration at day 5 for a-siRNA-SWNT–treated Nb leaf sample. ****P < 0.0001 in one-way ANOVA; all error bars, SEM (n = 3). All qPCR data for GFP expression are normalized with respect to housekeeping gene elongation factor 1 (EF1) and a control sample of a nontreated leaf.
We corroborated the GFP reduction results obtained with confocal imaging and Western blot analysis by performing quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) at the mRNA transcript level. One day after infiltration of leaves with s-RNA-SWNT, free siRNA, a-siRNA-SWNT, and b-siRNA-SWNT, we extracted total RNA from the leaves and quantified the GFP mRNA transcript levels in each sample at days 1 and 7. qPCR demonstrates that s-RNA-SWNT– and free siRNA–infiltrated leaves have the same amount of GFP mRNA transcript as the nontreated leaf, whereby a-siRNA-SWNT– and b-siRNA-SWNT–infiltrated leaves show 95 ± 4.1% (mean ± SD) and 92 ± 6.2% (mean ± SD) reduction in the GFP mRNA transcript levels at day 1, respectively (Fig. 4D). Similar to the confocal results, we found that mRNA transcript levels return back to the baseline levels as observed in nontreated leaves by day 7 in all samples as a result of transient silencing (Fig. 4D). In addition, we show that we can recover GFP silencing at day 7 by up to 71 ± 2.9% (mean ± SD) by reinfiltrating the leaf with a second 100 nM a-siRNA-SWNT dose at day 5 (Fig. 4E). With the same technique, we also demonstrated the silencing of a functional endogenous Nb gene called ROQ1, which has implications in disease resistance against many plant pathogens (fig. S8) (37). Our results verify that SWNTs can also silence an endogenous plant gene, ROQ1, efficiently, and suggest that other endogenous genes may be targeted for down-regulation with SWNT-based siRNA delivery.
SWNT scaffold delays intracellular RNA degradation
It is likely that SWNT scaffolding improves internalization of siRNA and also protects siRNA from degradation once intracellular. To explore this hypothesis, we performed single-molecule total internal reflection fluorescence (smTIRF) microscopy to probe single siRNA strand susceptibility to degradation by ribonuclease A (RNase A) when adsorbed on SWNTs, compared to single free siRNA. To do so, we labeled the a-antisense strand of GFP siRNA with a 5′ terminal Cy3 fluorophore and immobilized RNA-Cy3 and RNA-Cy3-SWNTs onto parallel channels of a microfluidic slide (see Materials and Methods). We measured the Cy3 fluorescence in each channel before and after treatment with RNase A, whereby percent decrease in the number of Cy3 molecules was used as a proxy for the percent siRNA degraded (Fig. 5A). Our TIRF results show that 98 ± 0.3% (mean ± SD) of the initial Cy3-RNA immobilized on the channel surface is degraded after incubation with RNase A, whereas only 16 ± 4.9% (mean ± SD) of Cy3-RNA is degraded when it is bound to SWNTs, suggesting that SWNTs protect the siRNA cargo from enzymatic degradation inside cells (Fig. 5B). Negative controls in which only salt buffer is flown through, or empty bovine serum albumin (BSA)–passivated channels, do not show appreciable changes in fluorescence or fluorescence counts, respectively (fig. S9).
Fig. 5. RNA protection from enzymatic degradation and SWNT biocompatibility analysis.
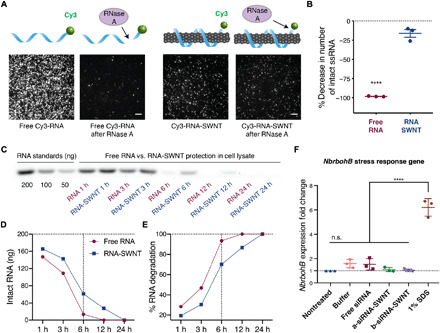
(A) smTIRF microscopy of Cy3-labeled RNA and Cy3-labeled RNA-SWNTs before and after incubation with RNase A. Scale bars, 5 μm. (B) Quantification of percent decrease in number of intact RNA molecules upon RNase A treatment. Error bars, SEM (n = 3). ****P < 0.0001 in two-tailed unpaired t test. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of free RNA and RNA-SWNTs incubated in plant cell lysate for 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours. (D) Quantification of intact RNA from the agarose gel in (C). (E) Quantification of percent RNA degradation from the agarose gel in (C). (F) qPCR analysis of NbrbohB following a 3-hour exposure to samples. ****P < 0.0001 in one-way ANOVA; error bars, SEM (n = 3).
Intracellular stability of ssRNA-suspended SWNTs and free ssRNA was also assessed by incubating ssRNA-SWNT conjugates with total proteins extracted from plant leaves (i.e., plant cell lysate). Agarose gel electrophoresis of free ssRNA versus ssRNA-SWNTs incubated in plant cell lysate for 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours demonstrates that free ssRNA is degraded substantially faster in cell lysate compared to ssRNA adsorbed on SWNTs (Fig. 5C). Band intensity quantification of this agarose gel reveals that both free ssRNA and ssRNA on SWNTs start degrading immediately in cell lysate solution. By 6 hours, 94% of free ssRNA and 70% of ssRNA on SWNTs are degraded (Fig. 5, D and E). Results show that by 12 hours, all free ssRNA is completely degraded, whereas 14% of the ssRNA on SWNTs remains intact. By 24 hours, ssRNA on SWNTs is completely degraded (Fig. 5, D and E), which corresponds to a 12-hour increase in the residence time of siRNA strands in cells when delivered with SWNTs. We hypothesize that this increased residence time gives rise to prolonged and increased silencing efficiency, as siRNA strands in cells have a higher chance of hybridizing into the active siRNA duplex before getting degraded by plant nucleases if delivered with SWNTs. With a similar in vitro cell lysate degradation experiment, we also show that after hybridization and desorption from SWNTs, about a quarter of the originally delivered double-stranded siRNA persists in cells by 4 days. Results show that, by 24 hours, half of the double-stranded siRNA and, by 96 hours, almost all of the double-stranded siRNA are degraded in cells (fig. S10).
SWNT biocompatibility analysis in plant leaves
SWNT biocompatibility, at the concentrations used in this study, was tested by qPCR analysis of a commonly used stress gene and by tissue damage analysis via confocal microscopy. For qPCR toxicity analysis, we checked the up-regulation of the respiratory burst oxidase homolog B (NbrbohB) gene (Fig. 5F). NbrbohB up-regulation in Nb leaves represents stress response to many factors such as mechanical, light, or heat damage (38). qPCR results show that RNA-SWNT (2 mg/liter)–treated areas in leaves do not up-regulate NbrbohB gene compared to buffer-treated adjacent areas within the same leaves. SDS (1%) solution was used as a positive toxicity control and up-regulated NbrbohB gene by sixfold 3 hours after infiltration (Fig. 5F). Tissue damage in the RNA-SWNT– and 1% SDS–infiltrated leaves was also monitored via confocal microscopy, and no tissue or cell damage was detected in RNA-SWNT–infiltrated leaves, whereas significant distortion of cell morphology and tissue integrity can be seen in the SDS-treated areas (fig. S11). Given the unchanged expression levels of stress gene NbrbohB and healthy leaf tissue of RNA-SWNT–infiltrated plants, we can conclude that RNA-SWNTs (2 mg/liter) are biocompatible for in planta RNAi applications.
DISCUSSION
Nanomaterials have shown much promise for plasmid (16, 17) and protein (18) delivery to plants, motivating their use for plant delivery of RNAi, as has proven quite fruitful for human therapeutics. We demonstrate here that high–aspect ratio one-dimensional SWNTs can successfully deliver siRNA molecules to efficiently silence a GFP gene in transgenic Nb mature plant leaves through a combination of (i) effective intracellular delivery and (ii) protection of the siRNA cargo from nuclease degradation. We found that RNA-adsorbed SWNTs rapidly and efficiently internalize into the full leaf thickness of mature walled plant cells within 6 hours, in contrast to free RNA internalization, which is minimal. We further found that π-π adsorption of siRNA on the SWNT surface delays intracellular siRNA degradation and thus prolongs silencing.
Here, we developed a platform for siRNA delivery using nanoparticles well suited for cellular delivery in plant tissues with intact cell walls. This platform uses SWNTs, to which single-stranded sense and antisense siRNAs are adsorbed separately, enabling thermodynamically favorable siRNA hybridization once intracellular for subsequent gene silencing mechanisms. We show that ssRNA is protected from degradation for up to 24 hours when adsorbed to SWNTs, whereas free ssRNA is almost completely degraded by 6 hours. We show a similar siRNA protection phenomenon with smTIRF microscopy of individual siRNA molecules either free or adsorbed to SWNTs. With this rapid and facile SWNT delivery platform, we achieve transient and DNA-free silencing of genes in mature plant leaves with a low siRNA-SWNT dose, showing mRNA knockdown efficiencies of up to 95% within 1 day after infiltration, returning to native transcript levels by day 7. We further show that it is possible to retain gene silencing for longer periods of time with a reinfiltration of another siRNA-SWNT dose at day 5, for applications in which sustained silencing is desired. Applications that require the introduction of repeated doses of siRNA-SWNTs may cause some long-term toxicity due to nanoparticle accumulation in cells (39). For these applications, studies should be undertaken to investigate the long-term effects of SWNT accumulation in plant cells.
The commonly used cationic nanoparticles for the delivery of negatively charged siRNA through electrostatic interactions have shown appreciable cellular toxicity to cells for certain effective concentrations and/or charge densities (40). The pristine noncharged SWNT surface eliminates this problem and makes it possible to scale up the delivery of siRNA for higher doses or systemic administration. In addition, the platform could be adapted to loading multiple siRNA sequences to multiplex gene silencing targets by delivering a mixture of SWNTs suspended with multiple siRNA sequences or loading a single SWNT sample with multiple siRNA sequences. Furthermore, SWNT internalization and polynucleotide delivery into plants is hypothesized to be species independent and can be used with monocots, nonmodel species, and hard-to-transform species, and cargo-carrying SWNTs are expected to diffuse into the full thickness of leaves, providing a uniform transformation profile (16).
Given the aforementioned advantages, we believe that there is a broad range of applications of our siRNA delivery platform. The process of RNA adsorption to SWNTs is based on π-π adsorption and is thus agnostic to the function of the RNA cargo. In addition to the more traditional applications of RNAi in plants, such as disease/virus resistance, discovery of biosynthetic pathways, increasing the yield of small-molecule production, and understanding protein functions, SWNT-mediated gene silencing could also potentially be used for efficient and DNA-free delivery of other synthetic ribonucleic acids. For instance, SWNTs could aid nuclease-based genome editing in plants by delivery of single-guide RNAs and/or mRNAs for controlled and transient nuclease expression and subsequent genome editing. Another potential application of SWNT-based RNA delivery is for increasing homology-directed repair rates in plants for gene knock-in applications, which could possibly be achieved by suppressing the expression of the genes required for competitive nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) repair pathways (41). Because the efficient suppression of these genes is only desirable for the few-day time window in which genome editing takes place, our SWNT-mediated gene silencing platform could enable such control over transient siRNA delivery. Hence, SWNT-based delivery of polynucleic acids is a useful resource to expand the plant biotechnology toolkit.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Preparation of chemicals
Super-purified HiPCO SWNTs (lot no. HS28-037) were purchased from NanoIntegris, and SWNTs samples were extensively purified before use (42). ssRNA strands, Cy3-tagged ssRNA strands, and all primer sequences were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies and dissolved in 0.1 M NaCl before use. 100K MWCO Amicon spin filters were purchased from Fisher Scientific. The following chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich: SDS (molecular biology grade), sodium chloride, tris-HCl, EDTA, NP-40, glycerol, BSA-biotin, and NeutrAvidin. RNase A was purchased from Takara Bio. All PCR reagents and materials and molecular biology–grade agarose were purchased from Bio-Rad. UltraPure DNase/RNase-free distilled water from Invitrogen was used for qPCR, and EMD Millipore Milli-Q water was used for all other experiments.
Plant growth
Transgenic mGFP5 Nb seeds were provided by the Staskawicz Lab, University of California, Berkeley. The seeds were germinated and grown in Sun Gro Sunshine LC1 Grower soil mix for 4 to 6 weeks before experiments in a growth chamber, 12-hour light at 24°C and 12-hour dark at 18°C cycle. All experiments were done with intact leaves attached to plants, where plants were incubated in the growth chamber until the time of data collection.
RNA-SWNT and Cy3-RNA-SWNT preparation
SWNTs were suspended with ssRNA polymers or Cy3-tagged ssRNA sequences through probe-tip sonication as previously described (43). See table S3 for all RNA sequences used in this study. Briefly, RNA was dissolved in 0.1 M NaCl at a concentration of 100 mg/ml. Dry HiPCO SWNTs (1 mg) were added to 20 μl of dissolved RNA, and the solution volume was completed to 1 ml with 0.1 M NaCl. The mixture of SWNTs and RNA was bath-sonicated for 10 min at room temperature. Then, it was probe-tip–sonicated with a 3-mm tip at 50% amplitude (~7 W) for 30 min in an ice bath. The sonicated solution was incubated at room temperature for 30 min and centrifuged at 16,100g for 1 hour to remove bundled SWNT and any leftover metal catalyst precursor from SWNT synthesis. Any RNA that was not bound to SWNTs was removed by spin-filtering eight times with 100K Amicon filters, and the SWNT concentration of RNA-SWNTs was determined by measuring the carbon nanotube absorbance at 632 nm. Absorbance spectra of RNA-SWNTs were collected with Shimadzu UV-3600 Plus, and fluorescence spectra of RNA-SWNTs were collected with a nIR spectrometer (Princeton Instruments IsoPlane 320 coupled to a liquid nitrogen–cooled Princeton Instruments PyLoN-IR 1D array of InGaAs pixels). RNA concentration on suspended SWNTs was determined by measuring the amount of RNA in flow-through solutions after each spin-filter step via absorbance at 260 nm and by subtracting the total amount of free RNA washed from the total amount of RNA added.
In more detail, for each suspension, we start with 1 mg of SWNTs and 2 mg of RNA in 1 ml of 0.1 M NaCl solution. After the probe-tip sonication and centrifugation, we end up with approximately 40 μg/ml SWNTs, meaning that our SWNT yield is 40 μg/1000 μg = 4%. In terms of siRNA yield, after the probe-tip sonication, centrifugation, and removal of free RNA, we end up with 640 μg/ml RNA on SWNTs, meaning that our RNA yield is 640 μg/2000 μg = 32%. These values can slightly change from experiment to experiment; therefore, we made sure to use the same final diluted concentration of siRNA-SWNTs for every experiment at 100 nM siRNA and SWNT (2 mg/liter).
AFM characterization
AFM characterization of RNA-SWNTs was performed as described in (16).
Infiltration of leaves with RNA-SWNTs and control solutions
Healthy and fully developed leaves from mGFP5 Nb (4 to 6 weeks old) plants were selected for experiments. A small puncture on the abaxial (bottom) surface of the leaf was introduced with a pipette tip, and ~100 μl of the RNA-SWNT solution was infiltrated from the hole with a 1-ml needleless syringe with caution not to damage the leaf.
Internalization imaging with confocal and nIR fluorescence microscopy
The a-antisense siRNA strand was used in the internalization study. After infiltration of 100 nM RNA carrying RNA-SWNTs (2 mg/liter), plants with attached infiltrated leaves were left in the plant growth chamber to allow internalization for 6 hours and imaged with confocal microscopy to track Cy3-tagged RNA-SWNTs in leaves. A Zeiss LSM 710 confocal microscope was used to image the plant tissue with 488-nm laser excitation with an enhanced GFP (eGFP) filter cube to detect intracellular GFP and 543-nm laser excitation with an appropriate filter cube to detect Cy3 fluorescence. The emission window of Cy3 was adjusted to 550 to 600 nm to avoid cross-talk between Cy3 and leaf chlorophyll autofluorescence. For nIR imaging, RNA-SWNTs (40 mg/liter) were infiltrated into leaves, and plants with attached infiltrated leaves were left in the plant growth chamber to allow internalization for 6 hours and imaged with nIR microscopy to track intrinsic SWNT nIR fluorescence in leaves. RNA-SWNT leaf internalization images were captured using a custom-built microscope equipped with a Raptor Ninox VIS-SWIR 640 camera. A 1050-nm long-pass filter was used to avoid chlorophyll autofluorescence, and a white lamp with an appropriate filter cube was used to image GFP. GFP and Cy3 (or nIR) images were analyzed with the ImageJ colocalization program to demonstrate internalization of RNA-SWNTs into cells.
In vitro RNA hybridization and desorption assay
The a-sense-SWNT and a-antisense-SWNT solutions were prepared according to the “RNA-SWNT and Cy3-RNA-SWNT preparation” section. Equimolar mixtures of these suspensions each containing RNA (600 ng/μl) on SWNTs were incubated either in water or in plant cell lysate for 3 hours at room temperature to allow hybridization and desorption. Next, hybridized dsRNA in solution was eluted with 100K spin filters, and the concentration of RNA in the elute was measured via absorbance at 260 nm with NanoDrop. For zeta potential measurements in fig. S4C, an equimolar mixture of a-sense-SWNT and a-antisense-SWNT suspensions was incubated in water for 3 hours at room temperature to allow hybridization and desorption. Next, hybridized dsRNA in solution (if any) was eluted with 100K spin filters, and the zeta potential of the remaining RNA-SWNT mixture was measured with Malvern Zetasizer.
Confocal imaging for silencing and quantitative fluorescence intensity analysis of GFP expression
mGFP5 Nb leaves were infiltrated with s-RNA-SWNT, free siRNA, a-siRNA-SWNT, and b-siRNA-SWNT at the same RNA concentration of 100 nM and SWNT concentration of 2 mg/liter. Infiltrated plant leaves were prepared for confocal imaging 1, 2, 3, and 7 days after infiltration as described in (16). For each sample, mean fluorescence intensity value was normalized with respect to the mean GFP fluorescence intensity of a nontreated leaf. The same imaging parameters and quantification analyses were applied to samples imaged on different days.
Quantitative Western blot experiments and data analysis
Whole leaves fully infiltrated with samples were harvested 24 and 48 hours after infiltration, and total proteins were extracted as described in (16). After quantification of the total extracted proteins by the Pierce 660-nm Protein Assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, product no. 22660), 0.5 μg of normalized total proteins from each sample was analyzed by 12% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. The membrane was blocked for 1 hour using 7.5% BSA in PBST (phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20) buffer and incubated overnight at 4°C with the primary GFP antibody as required (1:2000 dilution; Abcam, ab290). After extensive washing, the corresponding protein bands were probed with a goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase–conjugated antibody (1:5000 dilution; Abcam, ab205718) for 30 min. The membrane was then developed by incubation with chemiluminescence (Amersham ECL Prime Kit) plus and imaged by ChemiDoc XRS+ System. The intensity of GFP bands was quantified with ImageJ software.
qPCR experiments for gene silencing
Two-step qPCR was performed to quantify GFP gene silencing in transgenic Nb plants as described in (16). The target gene in our qPCR was mGFP5 (GFP transgene inserted into Nb) and EF1 (elongation factor 1) as our housekeeping (reference) gene. Primers for these genes can be found in table S3. An annealing temperature of 60°C and 40 cycles were used for qPCR. qPCR data were analyzed by the ΔΔCt method (44) as described in (16). For each sample, qPCR was performed as three reactions from the same isolated RNA batch, and the entire experiment consisting of independent infiltrations and RNA extractions from different plants was repeated three times (three biological replicates).
smTIRF to image RNA protection by SWNTs
The a-antisense siRNA strand was used in this assay. 5′-Labeled Cy3-RNA (10 μM) was added to an equal mass of SWNTs. The RNA-SWNT suspension and removal of unbound RNA followed the same protocol as described in the previous section. The positive control comprised the same sequence that was 5′ Cy3–labeled and 3′ biotin–labeled. Six-channel μ-slides (ibidi, μ-Slide VI 0.5 Glass Bottom) were initially washed by pipetting 100 μl of 100 mM sterile NaCl solutions into one reservoir and removing 60 μl of the other end, leaving just enough solution to fully wet the channel. Each subsequent step involved depositing the desired solution volume into the reservoir and removing the equivalent volume from the other end of the channel. Slide preparation was done as described by Kruss et al. (45) with some modifications. Briefly, 50 μl of BSA-biotin (0.25 mg/ml) was added to coat the surface of the glass slide for 5 min. Next, 50 μl of NeutrAvidin (0.05 mg/ml) was added, followed by 50 μl of RNA-SWNT (1.0 mg/liter), which nonspecifically adsorbs to NeutrAvidin. For the positive control, 50 μl of 200 pM biotinylated Cy3-RNA was added in place of RNA-SWNT. The addition of each component comprised a 5-min incubation period, followed by flushing the channel with 50 μl of NaCl solution to remove specimens that were not surface-immobilized. Each channel was exposed to 50 μl of RNase A (10 μg/ml) for 15 min at room temperature. The reaction was stopped by rinsing the channel with 50 μl of NaCl solution. Slides were imaged with a Zeiss ELYRA PS.1 microscope immediately following incubation with RNase A.
RNA protection gel assay
To determine whether SWNT-adsorbed RNA is protected from nuclease degradation, we performed an agarose gel electrophoresis–based RNA protection assay as described in (16). Free RNA (200 ng) and RNA-SWNTs (carrying 200 ng of RNA) were each incubated with cell lysate proteins obtained from one Nb leaf to mimic the intracellular degradation conditions for 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours.
After incubation in cell lysate, all RNA (intact or not) was desorbed from the SWNT surface by heating at 95°C for 1 hour in 2% SDS and 1.5 M NaCl solution. Desorbed RNA and cell lysate–treated free RNA were run on a 1% agarose gel with RNA standards (200, 100, and 50 ng) to measure the intact versus degraded RNA in each sample lane. RNA amounts on the agarose gel were quantified by using band intensity as a proxy (ImageJ GelAnalyzer) and normalized with the lanes containing known RNA quantities.
dsRNA degradation gel assay
The a-sense and a-antisense siRNA strands were hybridized by heating at 95°C for 5 min and 37°C for 1 hour. Hybridized double-stranded siRNA samples were incubated in nuclease-free water and cell lysate solutions at room temperature for 16, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours, and solutions were run on 2% agarose gel. Quantification of the RNA bands from the gel was done using ImageJ gel analyzer tool. All band intensities were normalized with respect to the hybridized RNA band intensity at time zero without any treatment.
Plant biocompatibility analysis
qPCR was used to determine the expression levels of an oxidative stress gene (NbrbohB) (38) in Nb plants treated with RNA-SWNTs and control solutions (primer sequences in table S3). The samples tested for toxicity were buffer (0.1 M NaCl), 100 nM free siRNA, a-siRNA-SWNT, b-siRNA-SWNT [each containing 100 nM siRNA and SWNT (2 mg/liter)], and 1% SDS (as a positive toxicity control), and the qPCR was performed 3 hours after the infiltration of these samples. EF1 gene was used as a housekeeping gene with an annealing temperature of 60°C for 40 cycles. The same ΔΔCt method was used to analyze the qPCR data (16).
Statistics and data analysis
GFP silencing confocal data
N = 10 technical replicates (10 different fields of view from the same leaf per sample infiltration) were imaged. Confocal images reported in Fig. 4A are representative images chosen from 10 replicates of day 2 data. Data are expressed as each mean from the 10 replicates, together with error bars indicating SD. Significance is measured with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. In Fig. 4B, F = 124.3 and P < 0.0001.
Western blot experiment
N = 3 replicates are independent experiments, and Fig. 4C denotes the results from a representative blot. Relative GFP amount data determined from the Western blot are expressed as mean from the three independent experiments, together with error bars indicating SEM. Significance is measured with one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. F = 54.65, s-RNA-SWNT versus a-siRNA-SWNT, P = 0.0001.
qPCR experiments
For GFP mRNA fold change experiments in Fig. 4D, N = 3 replicates are independent experiments, starting with RNA extraction from different leaves through the qPCR amplifications. Each qPCR in three independent experiments is performed in triplicate. GFP mRNA fold change data are expressed as each mean from the three independent experiments, together with error bars indicating SEM. Significance is measured with two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. Free siRNA versus a-siRNA-SWNT, P = 0.0008; free siRNA versus b-siRNA-SWNT, P = 0.0016; and siRNA-SWNT day 1 versus day 7, P < 0.0001.
For qPCR results reported in Fig. 4E, N = 3 replicates are independent experiments; three separate leaves were infiltrated per sample and each was measured with qPCR. Each sample in each independent experiment consisted of three technical replicates of the qPCR. Data are expressed as each mean from the three independent experiments, together with error bars indicating SEM. Significance is measured with one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. F = 143.7, day 1 versus day 7, P ≤ 0.0001, and day 7 versus day 7 (reinfiltration at day 5), P ≤ 0.0001.
smTIRF microscopy data
For each sample, N = 3 replicates are three channels on a microfluidic slide that were prepared independently. Each channel was imaged to obtain 30 fields of views (technical replicates). In Fig. 5B, data are expressed as each mean from the three independent channels, together with error bars indicating SEM. Significance is measured with a two-tailed unpaired t test. F = 317.6 and P < 0.0001.
Toxicity qPCR data
N = 3 replicates are independent experiments with separate infiltrations of SWNT solutions for each replicate. For the toxicity plot in Fig. 5F, 1% SDS versus all other samples, P < 0.0001 in one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, F = 82.95.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding: We acknowledge support of a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award at the Scientific Interface (CASI), a Stanley Fahn PDF Junior Faculty Grant with award no. PF-JFA-1760, a Beckman Foundation Young Investigator Award, a USDA AFRI award, a USDA NIFA award, the Moore Foundation, and an FFAR New Innovator Award (to M.P.L.). M.P.L. is a Chan Zuckerberg Biohub investigator. G.S.D. is supported by a Schlumberger Foundation Faculty for the Future Fellowship. We acknowledge the support of University of California Berkeley Molecular Imaging Center, the QB3 Shared Stem Cell Facility, and the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI). Author contributions: G.S.D. and M.P.L. conceived the project, designed the study, and wrote the manuscript. G.S.D. performed most of the experiments and data analysis. H.Z. performed Western blot studies and helped with qPCR experiments. N.S.G. performed TIRF experiments and analyzed TIRF data. R.L.P. contributed to the thermodynamic analysis of RNA desorption and hybridization. R.C. prepared some of the RNA-SWNT suspensions used in the studies. All authors have edited and commented on the manuscript and have given their approval of the final version. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Data and materials availability: The DNA sequence of the GFP gene silenced in this study is added as data S1 file in the FASTA format. The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/6/26/eaaz0495/DC1
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Lau W., Sattely E. S., Six enzymes from mayapple that complete the biosynthetic pathway to the etoposide aglycone. Science 349, 1224–1228 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Casacuberta J. M., Devos Y., du Jardin P., Ramon M., Vaucheret H., Nogué F., Biotechnological uses of RNAi in plants: Risk assessment considerations. Trends Biotechnol. 33, 145–147 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dhaka N., Sharma R., MicroRNAs as targets for engineering biofuel feedstock Sorghum. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 22, 484–492 (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sukenik S. C., Karuppanan K., Li Q., Lebrilla C. B., Nandi S., McDonald K. A., Transient recombinant protein production in glycoengineered Nicotiana benthamiana cell suspension culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1205 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Small I., RNAi for revealing and engineering plant gene functions. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 18, 148–153 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Duan C.-G., Wang C.-H., Guo H.-S., Application of RNA silencing to plant disease resistance. Silence 3, 5 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schwab F., Zhai G., Kern M., Turner A., Schnoor J. L., Wiesner M. R., Barriers, pathways and processes for uptake, translocation and accumulation of nanomaterials in plants—Critical review. Nanotoxicology 10, 257–278 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silva A. T., Nguyen A., Ye C., Verchot J., Moon J. H., Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for effective siRNA delivery to tobacco BY-2 protoplasts. BMC Plant Biol. 10, 291 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Burch-Smith T. M., Anderson J. C., Martin G. B., Dinesh-Kumar S. P., Applications and advantages of virus-induced gene silencing for gene function studies in plants. Plant J. 39, 734–746 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.A. Anand, T. J. Jones, in Agrobacterium Biology: From Basic Science to Biotechnology, S. B. Gelvin, Ed. (Springer International Publishing, 2018), pp. 489–507. [Google Scholar]
- 11.N. J. Baltes, J. Gil-Humanes, D. F. Voytas, Genome engineering and agriculture: Opportunities and challenges, in Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science (Academic Press, 2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Demirer G. S., Landry M. P., Delivering genes to plants. Chem. Eng. Prog. 113, 40–45 (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chang F.-P., Kuang L.-Y., Huang C.-A., Jane W.-N., Hung Y., Hsing Y. C., Mou C.-Y., A simple plant gene delivery system using mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 1, 5279–5287 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hussain H. I., Yi Z., Rookes J. E., Kong L. X., Cahill D. M., Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a biomolecule delivery vehicle in plants. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1676 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martin-Ortigosa S., Valenstein J. S., Sun W., Moeller L., Fang N., Trewyn B. G., Lin V. S.-Y., Wang K., Parameters affecting the efficient delivery of mesoporous silica nanoparticle materials and gold nanorods into plant tissues by the biolistic method. Small 8, 413–422 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Demirer G. S., Zhang H., Matos J. L., Goh N. S., Cunningham F. J., Sung Y., Chang R., Aditham A. J., Chio L., Cho M.-J., Staskawicz B., Landry M. P., High aspect ratio nanomaterials enable delivery of functional genetic material without DNA integration in mature plants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 456–464 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kwak S.-Y., Salim Lew T. T., Sweeney C. J., Koman V. B., Wong M. H., Bohmert-Tatarev K., Snell K. D., Seo J. S., Chua N.-H., Strano M. S., Chloroplast-selective gene delivery and expression in planta using chitosan-complexed single-walled carbon nanotube carriers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 447–455 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Martin-Ortigosa S., Peterson D. J., Valenstein J. S., Lin V. S.-Y., Trewyn B. G., Lyznik L. A., Wang K., Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-mediated intracellular Cre protein delivery for maize genome editing via loxP site excision. Plant Physiol. 164, 537–547 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mitter N., Worrall E. A., Robinson K. E., Li P., Jain R. G., Taochy C., Fletcher S. J., Carroll B. J., Lu G. Q., Xu Z. P., Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses. Nat. Plants 3, 16207 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wong M. H., Misra R. P., Giraldo J. P., Kwak S.-Y., Son Y., Landry M. P., Swan J. W., Blankschtein D., Strano M. S., Lipid exchange envelope penetration (LEEP) of nanoparticles for plant engineering: A universal localization mechanism. Nano Lett. 16, 1161–1172 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Giraldo J. P., Landry M. P., Faltermeier S. M., McNicholas T. P., Iverson N. M., Boghossian A. A., Reuel N. F., Hilmer A. J., Sen F., Brew J. A., Strano M. S., Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing. Nat. Mater. 13, 400–408 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wu Y., Phillips J. A., Liu H., Yang R., Tan W., Carbon nanotubes protect DNA strands during cellular delivery. ACS Nano 2, 2023–2028 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang H., Koleilat G. I., Liu P., Jiménez-Osés G., Lai Y.-C., Vosgueritchian M., Fang Y., Park S., Houk K. N., Bao Z., High-yield sorting of small-diameter carbon nanotubes for solar cells and transistors. ACS Nano 8, 2609–2617 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu Q., Chen B., Wang Q., Shi X., Xiao Z., Lin J., Fang X., Carbon nanotubes as molecular transporters for walled plant cells. Nano Lett. 9, 1007–1010 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Serag M. F., Kaji N., Gaillard C., Okamoto Y., Terasaka K., Jabasini M., Tokeshi M., Mizukami H., Bianco A., Baba Y., Trafficking and subcellular localization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in plant cells. ACS Nano 5, 493–499 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wong M. H., Giraldo J. P., Kwak S. Y., Koman V. B., Sinclair R., Lew T. T. S., Bisker G., Liu P., Strano M. S., Nitroaromatic detection and infrared communication from wild-type plants using plant nanobionics. Nat. Mater. 16, 264–272 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang P., Lombi E., Zhao F.-J., Kopittke P. M., Nanotechnology: A new opportunity in plant sciences. Trends Plant Sci. 21, 699–712 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nair R., Varghese S. H., Nair B. G., Maekawa T., Yoshida Y., Kumar D. S., Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci. 179, 154–163 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khodakovskaya M., Dervishi E., Mahmood M., Xu Y., Li Z., Watanabe F., Biris A. S., Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth. ACS Nano 3, 3221–3227 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kalantidis K., Tsagris M., Tabler M., Spontaneous short-range silencing of a GFP transgene in Nicotiana benthamiana is possibly mediated by small quantities of siRNA that do not trigger systemic silencing. Plant J. 45, 1006–1016 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Agaësse G., Barbollat-Boutrand L., El Kharbili M., Berthier-Vergnes O., Masse I., p53 targets TSPAN8 to prevent invasion in melanoma cells. Oncogenesis 6, e309 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shimada T., Takagi J., Ichino T., Shirakawa M., Hara-Nishimura I., Plant vacuoles. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 69, 123–145 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Choi J. H., Strano M. S., Solvatochromism in single-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 223114 (2007). [Google Scholar]
- 34.T. V. Galassi, P. V. Jena, J. Shah, G. Ao, E. Molitor, Y. Bram, A. Frankel, J. Park, J. Jessurun, D. S. Ory, A. Haimovitz-Friedman, D. Roxbury, J. Mittal, M. Zheng, R. E. Schwartz, D. A. Heller, An optical nanoreporter of endolysosomal lipid accumulation reveals enduring effects of diet on hepatic macrophages in vivo. 10, eaar2680 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Williams R. M., Lee C., Galassi T. V., Harvey J. D., Leicher R., Sirenko M., Dorso M. A., Shah J., Olvera N., Dao F., Levine D. A., Heller D. A., Noninvasive ovarian cancer biomarker detection via an optical nanosensor implant. Sci. Adv. 4, eaaq1090 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bartlett D. W., Davis M. E., Insights into the kinetics of siRNA-mediated gene silencing from live-cell and live-animal bioluminescent imaging. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 322–333 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schultink A., Qi T., Lee A., Steinbrenner A. D., Staskawicz B., Roq1 mediates recognition of the Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas effector proteins XopQ and HopQ1. Plant J. 92, 787–795 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yoshioka H., Numata N., Nakajima K., Katou S., Kawakita K., Rowland O., Jones J. D. G., Doke N., Nicotiana benthamiana gp91phox homologs NbrbohA and NbrbohB participate in H2O2 accumulation and resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell 15, 706–718 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yuan H., Hu S., Huang P., Song H., Wang K., Ruan J., He R., Cui D., Single walled carbon nanotubes exhibit dual-phase regulation to exposed Arabidopsis mesophyll cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 44 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Goodman C. M., McCusker C. D., Yilmaz T., Rotello V. M., Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjug. Chem. 15, 897–900 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Qi Y., Zhang Y., Zhang F., Baller J. A., Cleland S. C., Ryu Y., Starker C. G., Voytas D. F., Increasing frequencies of site-specific mutagenesis and gene targeting in Arabidopsis by manipulating DNA repair pathways. Genome Res. 23, 547–554 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Del Bonis-O’Donnell J. T., Beyene A., Chio L., Demirer G., Yang D., Landry M. P., Engineering molecular recognition with bio-mimetic polymers on single walled carbon nanotubes. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, e55030 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Beyene A. G., Demirer G. S., Landry M. P., Nanoparticle-templated molecular recognition platforms for detection of biological analytes. Curr. Protoc Chem. Biol. 8, 197–223 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schmittgen T. D., Livak K. J., Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1101–1108 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kruss S., Landry M. P., Vander Ende E., Lima B. M. A., Reuel N. F., Zhang J., Nelson J., Mu B., Hilmer A., Strano M., Neurotransmitter detection using corona phase molecular recognition on fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 713–724 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tang W., Samuels V., Whitley N., Bloom N., DeLaGarza T., Newton R. J., Post-transcriptional gene silencing induced by short interfering RNAs in cultured transgenic plant cells. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2, 97–108 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Johnson R. R., Johnson A. T. C., Klein M. L., Probing the structure of DNA−carbon nanotube hybrids with molecular dynamics. Nano Lett. 8, 69–75 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Das A., Sood A. K., Maiti P. K., Das M., Binding of nucleobases with single-walled carbon nanotubes: Theory and experiment. Chem. Phys. Lett. 453, 266–273 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- 49.Salvador-Morales C., Flahaut E., Sim E., Sloan J., Green M. L. H., Sim R. B., Complement activation and protein adsorption by carbon nanotubes. Mol. Immunol. 43, 193–201 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Harvey J. D., Jena P. V., Baker H. A., Zerze G. H., Williams R. M., Galassi T. V., Roxbury D., Mittal J., Heller D. A., A carbon nanotube reporter of microRNA hybridization events in vivo. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 1, 0041 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pinals R. L., Yang D., Lui A., Cao W., Landry M. P., Corona exchange dynamics on carbon nanotubes by multiplexed fluorescence monitoring. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 1254–1264 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shen J.-W., Wu T., Wang Q., Kang Y., Induced stepwise conformational change of human serum albumin on carbon nanotube surfaces. Biomaterials 29, 3847–3855 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yang Z., Wang Z., Tian X., Xiu P., Zhou R., Amino acid analogues bind to carbon nanotube via π-π interactions: Comparison of molecular mechanical and quantum mechanical calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 136, 025103 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rajesh C., Majumder C., Mizuseki H., Kawazoe Y., A theoretical study on the interaction of aromatic amino acids with graphene and single walled carbon nanotube. J. Chem. Phys. 130, 124911 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Beyene A. G., Alizadehmojarad A. A., Dorlhiac G., Goh N., Streets A. M., Král P., Vuković L., Landry M. P., Ultralarge modulation of fluorescence by neuromodulators in carbon nanotubes functionalized with self-assembled oligonucleotide rings. Nano Lett. 18, 6995–7003 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.J. Kuriyan, B. Konforti, D. Wemmer, The Molecules of Life: Physical and Chemical Principles (Garland Science, 2012). [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lu N., Sui Y., Ding Y., Tian R., Li L., Liu F., Adsorption of human serum albumin on functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes reduced cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 295, 64–72 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Brocchieri L., Karlin S., Protein length in eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 3390–3400 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/6/26/eaaz0495/DC1


