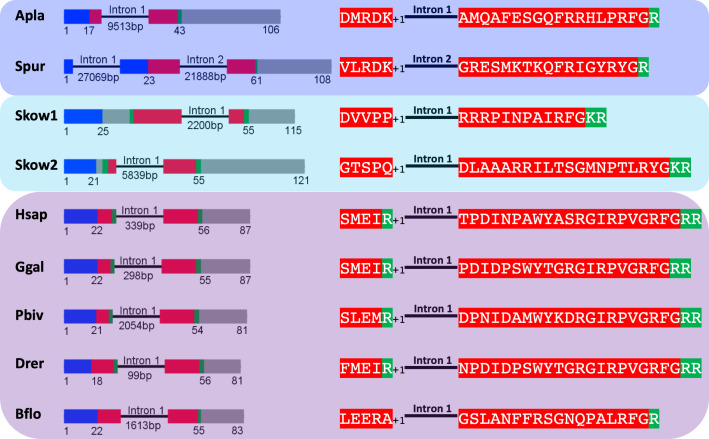
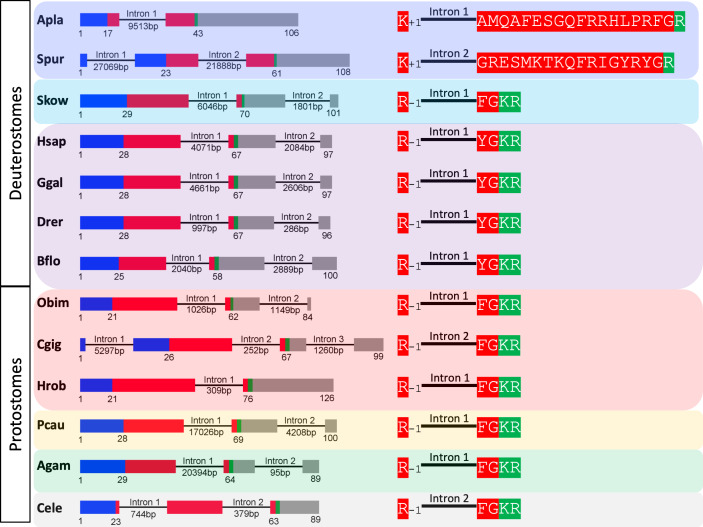
Figure 2. Comparison of exon/intron structure of genes encoding precursors of PrRP-like peptides in echinoderms and hemichordates with precursors of PrRP-type peptides in chordates.
Schematic representations of the gene structures are shown, with protein-coding exons shown as rectangles and introns shown as lines (with intron length stated underneath). The protein-coding exons are colour-coded to show regions that encode the N-terminal signal peptide (blue), the neuropeptide (red), monobasic or dibasic cleavage sites (green) and other regions of the precursor protein (grey). Note that a common characteristic is that an intron interrupts the coding sequence in the N-terminal or central region of the neuropeptide, with the intron consistently located between the first and second nucleotides (phase one intron represented by +1) of the codon for the amino acid shown after intron. Taxa are highlighted in phylum-specific colours: dark blue (Echinodermata), light blue (Hemichordata), purple (Chordata). The full names of the species and the accession numbers of the sequences are listed in Figure 2—source data 1.