Abstract
We report the case of an asymptomatic (no fever, no cough, no dyspnea) 80-year-old woman who had an 18F-FDG PET/CT scan for initial staging of Lieberkühnian adenocarcinoma located on anal canal. Chest analysis incidentally revealed bilateral diffuse patchy ground-glass opacity with mild increasing 18F-FDG uptake, consistent with incidental COVID-19 infection finding during the March 2020 pandemic. The infection was confirmed by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction. It led us to improve patient flow and to undertake broader measures to avoid patient clinical issues and potential disease spreading.
Key Words: COVID-19, FDG, PET/CT
FIGURE 1.
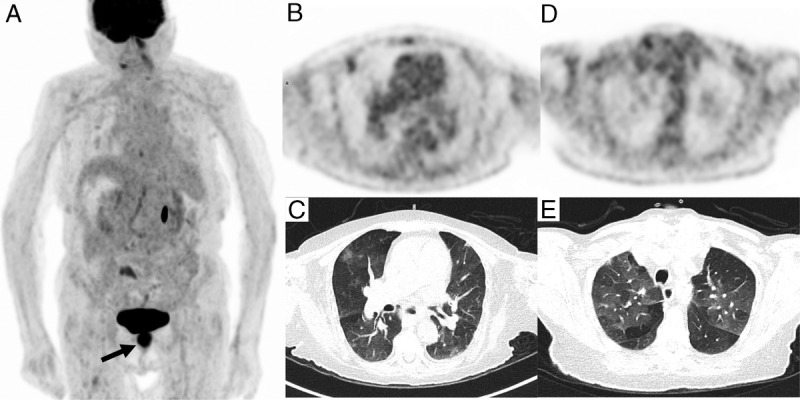
PET/CT acquisition was performed 1 hour after intravenous infusion of 145 MBq of 18F-FDG. A, 18F-FDG PET/CT maximum intensity projection showed an intense uptake (SUVmax 12.8) in anal canal primary neoplasm (black arrow) and increasing uptake in right lung corresponding in axial PET/CT slices to subpleural ground-glass opacity with 18F-FDG increasing uptake in right upper lobe (SUVmax of 2.4) (B, C), associated with patchy, rounded, diffuse, ground-glass opacity with mild FDG uptake (D, E). This incidental lung lesion finding, even in an asymptomatic patient, was consistent with typical appearance of COVID-19 infection during the March 2020 pandemic.1–5 There was no evidence of lymph node FDG uptake compared with some prior reported cases.6,7 The infection was confirmed by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction on nasopharyngeal swab collection.
FIGURE 2.
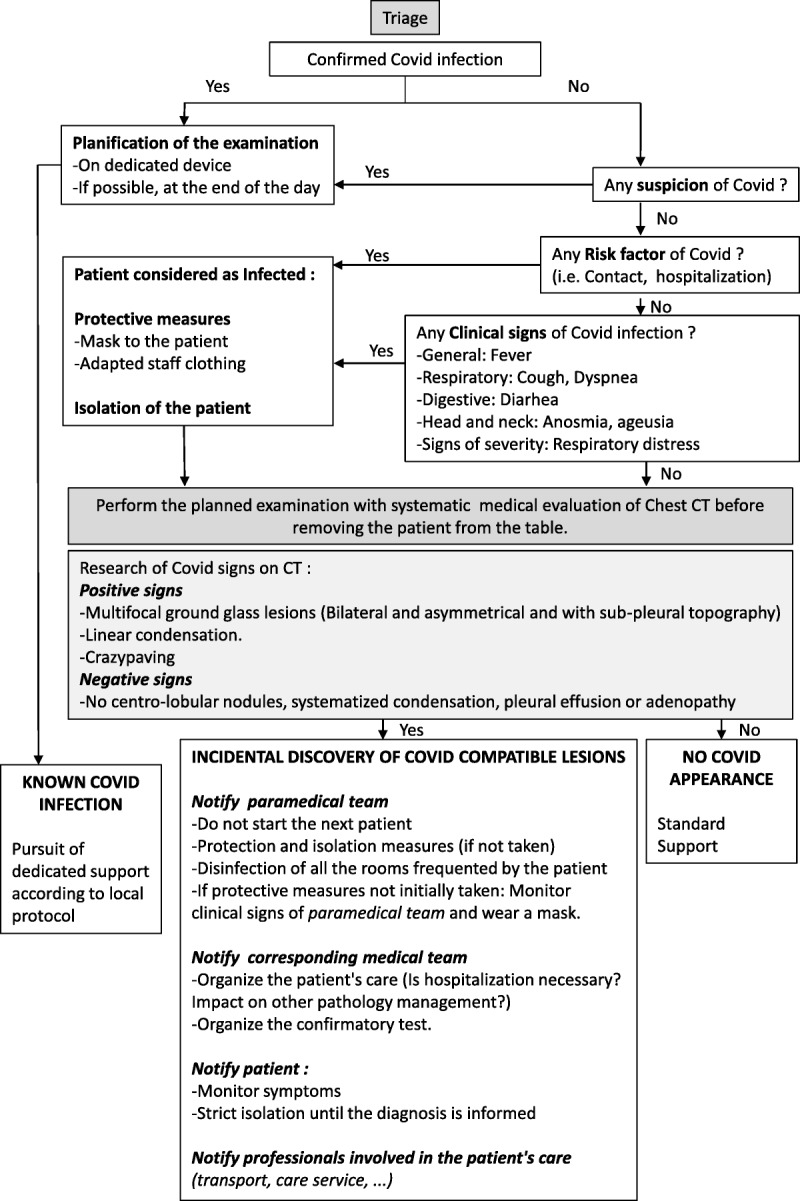
Following this event, we took measures to decrease the risk of disease spreading in our department. They are synthetized in this algorithm. Every patient must be screened for COVID-19 infection risk before and upon entering in the unit. Patients suspicious for COVID-19 infection have to wear surgical mask and to be isolated, combined with transmission droplets-based precautions for the medical staff.8 As chest CT has high sensitivity to detect COVID infection,9 we recommend to analyze chest area before patient leaves camera’s bed. This allows taking hygienic measures (particularly specific COVID camera disinfection) to protect the following patients.10 For that purpose, it is necessary to increase time between examinations. In case of suspected COVID-19 infection scan, it is warmly recommended to notify medical and paramedical staff in order to adapt patient’s care (including transfer and reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction test) and hygienic measures. Patient and contact cases must be warned to strictly adhere to isolation rules and for self-monitoring in case of ambulatory care in asymptomatic form. More generally, it is recommended to cancel nonurgent investigations and to limit contact with other patients.11 These recommendations are all the more important to follow as there is an increased risk of COVID infection (1% vs 0.29%) and more frequent complication (39% vs 8%) in the cancer patient population.12
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest and sources of funding: none declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Kanne JP, Little BP, Chung JH, et al. Essentials for radiologists on COVID-19: an update—Radiology Scientific Expert Panel [published online February 27, 2020]. Radiology. 2020;200527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simpson S, Kay FU, Abbara S, et al. Radiological Society of North America expert consensus statement on reporting chest CT findings related to COVID-19. Endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020;2:e200152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bai HX, Hsieh B, Xiong Z, et al. Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from viral pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology. 2020;200823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qin C, Liu F, Yen TC, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings of COVID-19: a series of four highly suspected cases. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47:1281–1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shi H, Han X, Jiang N, et al. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:425–434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zou S, Zhu X. FDG PET/CT of COVID-19. Radiology. 2020;200770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Deng Y, Lei L, Chen Y, et al. The potential added value of FDG PET/CT for COVID-19 pneumonia [published online March 21, 2020]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.World Health Organization Modes of transmission of virus causing COVID-19: implications for IPC precaution recommendations. 2020.
- 9.Fang Y, Zhang H, Xie J, et al. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology. 2020;200432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tulchinsky M, Fotos JS, Slonimsky E. Incidental CT findings suspicious for COVID-19 associated pneumonia on nuclear medicine exams: recognition and management plan [published online April 9, 2020]. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Skali H, Murthy VL, Al-mallah MH, et al. Guidance and best practices for nuclear cardiology laboratories during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: an information statement from ASNC and SNMMI [published online April 2, 2020]. Open AIR. 2020;1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335–337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


