Abstract
Within a few months, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a pandemic with more than 2 million patients infected and a high mortality rate. Early detection of COVID-19 in oncologic patients is crucial in order to rapidly apply isolation measures and avoid nosocomial spread. However, early diagnosis may be challenging, especially in cancer patients under treatment with immunotherapy as drug-induced pneumonitis can present similar clinical and radiological features. We describe the findings of a SARS-CoV-2 infection on PET/CT with 18F-FDG in a 51-year-old man with metastatic renal cell carcinoma under treatment with nivolumab.
Key Words: FDG, PET/CT, COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, pneumonitis, nivolumab
FIGURE 1.
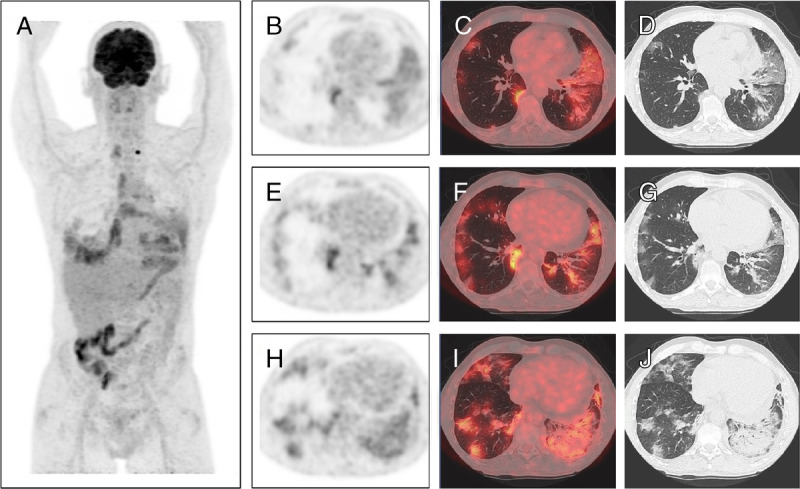
We present herein a 51-year-old man with a renal cell carcinoma diagnosed 8 years ago, initially treated with radical nephrectomy. Since then, and due to contralateral renal agenesis, the patient is dialyzed 3 times a week. During the last 6 years, he received multiple lines of systemic therapies (sunitinib, axitinib, everolimus, and nivolumab) with retroperitoneal lymph node and pleuropulmonary metastatic spread. Patient was referred to our department to perform an 18F-FDG PET/CT for response assessment 4 months after the start of nivolumab. At consultation before scan, patient presented with fatigue grade II and anorexia grade I, initially classified as adverse effects of nivolumab. FDG PET/CT demonstrated a complete metabolic response of pleural lesions, metabolically stable retroperitoneal and mediastinal lymph nodes, and a known left thyroid nodule (A, PET MIP images). Images also showed the appearance of multiple moderately hypermetabolic ground glass opacities (GGO) in both lungs of mainly peripheric distribution (E–G, axial PET, fused, and CT images), interlobular septal thickening also called “crazy paving” in the lingula (B–D, axial PET, fused, and CT images), and basal consolidation in the left lung with air bronchogram (H–J, axial PET, fused, and CT images). This pattern is highly suspicious for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as previously reported.1 However, nivolumab-induced pneumonitis can also present with similar findings on chest CT.2 With these images, the patient was hospitalized for differential diagnosis, even if he presented no other previously reported frequent COVID-19 signs.3 Nasopharyngeal swab test was performed, and blood test at admission showed increased LDH level (365 U/L) and decreased lymphocyte count (1.16 × 103/mm3), which again could be related to both COVID-19 and nivolumab toxicity. C-reactive protein levels were high (167 mg/L), which finally oriented toward the infectious hypothesis. At 24 hours, RT-PCR (reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction) confirmed a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, and hydroxychloroquine and piperacillin/tazobactam treatment was started. Within a few months, COVID-19 has become a pandemic with more than 2 million patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and a mortality rate of 3.4%.4 Oncologic patients are at higher risk for severe clinical events, mainly due to frequent comorbidities and compromised immune system, with a case fatality rate of 5.6% compared with 2.3% in the general population.5 Early diagnosis is crucial in order to rapidly apply isolation measures and avoid nosocomial spread in cancer clinics. However, frequent unspecific clinical presentation and a false-negative rate of up to 30% for nasopharyngeal swab RT-PCR can delay diagnosis.6 When performing routine PET/CT during COVID-19 pandemic, special and systematic attention should be given to the lung images before discharging the patient, as previously unsuspected active disease could be easily detected in asymptomatic patients.7 This case illustrates the added complexity of COVID-19 diagnosis in cancer patients, particularly while on active treatment with immunotherapy, as adverse effects of checkpoint inhibitors can present with similar clinical and radiological findings. Indeed, both conditions can induce interstitial lung opacities consisting of massive amounts of activated immune cells, which are highly hypermetabolic on FDG PET.8,9
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest and sources of funding: none declared.
Contributions: Dr Artigas read the PET/CT images, followed up on the case, and drafted the manuscript. Dr Lemort acted as an expert consultant for the CT images and revised the manuscript. Dr Mestrez and Dr Gil clinically followed the patient and revised the manuscript. Dr Flamen revised the manuscript for important intellectual content.
REFERENCES
- 1.Zhou Z, Guo D, Li C, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019: initial chest CT findings. Eur Radiol. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baba T, Sakai F, Kato T, et al. Radiologic features of pneumonitis associated with nivolumab in non-small-cell lung cancer and malignant melanoma. Future Oncol. 2019;15:1911–1920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1708–1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.World Health Organization Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 46. Data as reported by national authorities by 10AM CET 06 March 2020. Available at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200306-sitrep-46-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=96b04adf_2. Accessed April 8, 2020.
- 5.Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fang Y, Zhang H, Xie J, et al. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology. 2020;200432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tulchinsky M, Fotos JS, Slonimsky E. Incidental CT findings suspicious for Covid-19 associated pneumonia on nuclear medicine exams: recognition and management plan. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:420–422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Delaunay M, Prévot G, Collot S, et al. Management of pulmonary toxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur Respir Rev. 2019;28:190012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


