Abstract
Between March 26 and April 6, among 80 patients who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT in our department (Brescia, Italy), 4 showed the presence of an interstitial pneumonia suspected for COVID-19 with reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction confirmation. All patients except one had bilateral ground-glass opacities and/or lung consolidations in at least 2 pulmonary lobes. Inferior lobes and basal segments were the most frequent site of disease. All lung lesions had an increased FDG uptake corresponding to the interstitial pneumonia, and in one case, mediastinal nodal involvement was registered.
Key Words: COVID-19, PET/CT, pneumonia, 18F-FDG
FIGURE 1.
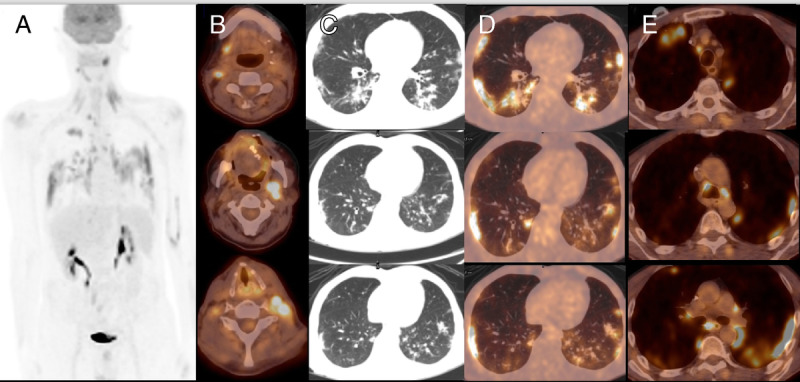
A 59-year-old man with a previous history of oral cavity cancer treated with surgery underwent an 18F-FDG PET/CT for restaging purpose. PET/CT was positive, showing the presence of local relapse at the right side of the tongue and several laterocervical lymph nodes (A and B). Moreover, FDG-positive plural diffuse interstitial alterations with ground-glass opacities (GGOs) appearance were registered with SUVmax of 13.8 (C and D). Concomitant mediastinal nodes with increased FDG uptake were present (E). A subsequent chest radiographs confirmed a diffuse interstitial pneumonia; reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was positive, and the patient was hospitalized for specific therapy.
FIGURE 2.
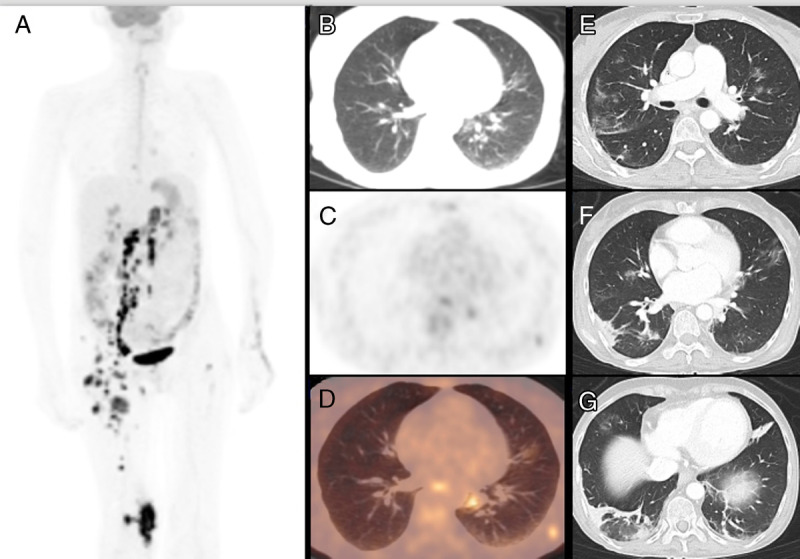
A 47-year-old woman affected by an advanced stage anaplastic large-cell lymphoma relapsed after 2 chemotherapy regimen lines and was hospitalized for starting new chemotherapy cycle. Before starting, she did a nasopharyngeal swap with RT-PCR positive for COVID-19. 18F-FDG PET/CT confirmed the metabolic progression of disease with nodal, muscular, and skeletal hypermetabolic localizations (A). A moderate FDG uptake (SUVmax, 5.6) was showed in small GGOs, especially in the left inferior lobe (B–D). A subsequent chest CT demonstrated a progression of interstitial pneumonia with massive lung involvement (E–G).
FIGURE 3.
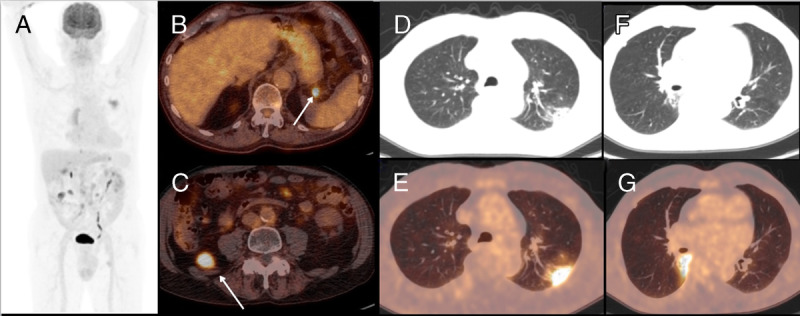
An asymptomatic 77-year-old man with non–Hodgkin lymphoma treated previously with one line of chemotherapy underwent an 18F-FDG PET/CT showing increased FDG uptake to several abdominal nodes consistent of relapse (A–C) and the presence of bilateral pleural thickening and FDG-avid GGOs with SUVmax of 10.2 (D–G). After the appearance of dyspnea and breathing difficulty, he went to the emergency unit and was hospitalized and started treatment with hydroxychloroquine.
FIGURE 4.
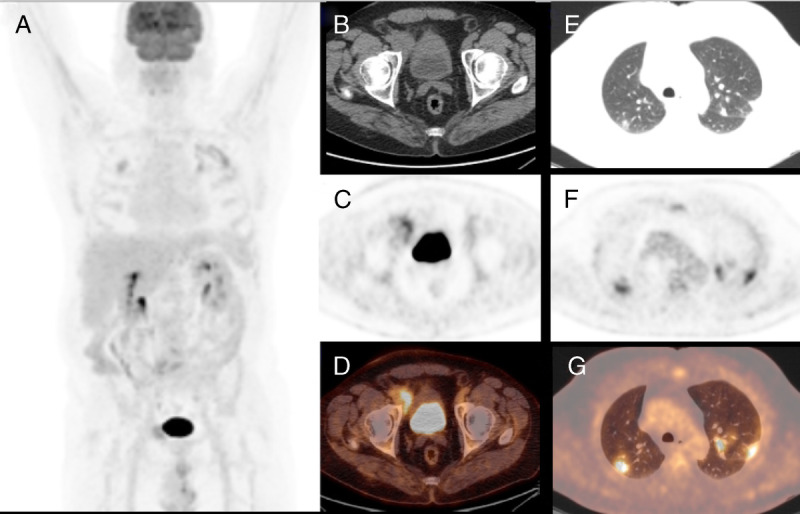
A 62-year-old man affected by follicular lymphoma underwent PET/CT scan for evaluating treatment response after 6 cycles of chemotherapy, and PET/CT showed a partial metabolic response with persistence of increased FDG uptake to an inguinal node (A–D) and the appearance of several bilateral lung consolidative and FDG-avid nodular areas, especially in the superior lobes with SUVmax of 9 (E–G). Being the pattern atypical for COVID-19, the patient started new chemotherapy regimen, but after the early onset of cough and dyspnea, RT-PCR test was done with positive finding for COVID-19. Chest radiographs and CT is the preferred examinations for screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of COVID-19 pneumonia.1–3 In this setting, the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT is still unclear with only few cases present.4–10 18F-FDG PET/CT is a noninvasive tool with a significant role in evaluating several phlogistic and infectious pulmonary diseases, such as sarcoidosis and tuberculosis.11 However, usually lesions presenting as GGOs are unlikely to have FDG uptake.12 In agreement with previous articles,6–8 our patients were characterized by the presence of bilateral peripheral consolidative areas and/or GGOs. All had increased FDG uptake higher than blood pool activity. COVID-19 do not seem to be associated with lymph node involvement; however, Qin et al6 reported an increased nodal FDG uptake in 3 of 4 cases. Of course 18F-FDG PET/CT is not routinely recommended for pulmonary lung inflammatory diseases and not indicated in an emergency setting, but our findings underline that COVID-19 pneumonia are characterized by high 18F-FDG uptake in most cases despite GGOs appearance.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest and sources of funding: none declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, et al. CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology. 2020;295:202–207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Borghesi A, Zigliani A, Massullo R, et al. Radiographic severity index in COVID-19 pneumonia: relationship to age and sex in 783 Italian patients. Radiol Med. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kanne JP, Little BP, Chung JH, et al. Essentials for radiologists on COVID-19: an update radiology scientific expert panel. Radiology. 2020;200527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deng Y, Lei L, Chen Y, et al. The potential added value of FDG PET/CT for COVID-19 pneumonia. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zou S, Zhu X. FDG PET/CT of COVID-19. Radiology. 2020;6:200770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Qin C, Liu F, Yen TC, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings of COVID-19: a series of four highly suspected cases. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47:1281–1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Polverari G, Arena V, Ceci F, et al. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in patient with asymptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (coronavirus disease 2019) referred to positron emission tomography/computed tomography for NSCLC restaging. J Thorac Oncol. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Albano D, Bertagna F, Bertoli M, et al. Incidental findings suggestive of COVID-19 in asymptomatic patients undergoing nuclear medicine procedures in a high prevalence region. J Nucl Med. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tulchinsky M, Fotos JS, Slonimsky E. Incidental CT findings suspicious for COVID-19 associated pneumonia on nuclear medicine exams: recognition and management plan. Clin Nucl Med. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lutje S, Marinova M, Kutting D, et al. Nuclear medicine in SARS-CoV-2 pandemia: 18F-FDG-PET/CT to visualize COVID-19. Nuklearmedizin. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Capitanio S, Nordin AJ, Noraini AR, et al. PET/CT in non oncological lung diseases: current applications and future perspectives. Eur Respir Rev. 2016;25:247–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jacobson FL, Tarascio JN, Fox SW. Can PET/CT help manage ground glass nodules? J Surg Oncol. 2018;117:457–458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


