Figure 1.
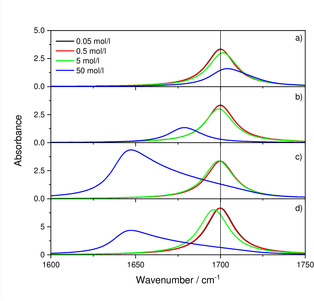
Absorbance for different concentrations of 0.05, 0.5, 5 and 50 mol/l of the hypothetical substance assuming c ⋅ d=5 ⋅ 103 cm ⋅ mol/l. a) conventional dispersion formula. b) conventional dispersion formula assuming additionally a redshift according to . c) Lorentz‐Lorenz formula [Eq. (10)] in combination with Equation (18). d) Same as c) but with hypothetical solvent (please note the change concerning the range of the y‐axis for d).
