Abstract
Background
Amanitin-producing mushrooms, mainly distributed in the genera Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota, possess MSDIN gene family for the biosynthesis of many cyclopeptides catalysed by prolyl oligopeptidase (POP). Recently, transcriptome sequencing has proven to be an efficient way to mine MSDIN and POP genes in these lethal mushrooms. Thus far, only A. palloides and A. bisporigera from North America and A. exitialis and A. rimosa from Asia have been studied based on transcriptome analysis. However, the MSDIN and POP genes of many amanitin-producing mushrooms in China remain unstudied; hence, the transcriptomes of these speices deserve to be analysed.
Results
In this study, the MSDIN and POP genes from ten Amanita species, two Galerina species and Lepiota venenata were studied and the phylogenetic relationships of their MSDIN and POP genes were analysed. Through transcriptome sequencing and PCR cloning, 19 POP genes and 151 MSDIN genes predicted to encode 98 non-duplicated cyclopeptides, including α-amanitin, β-amanitin, phallacidin, phalloidin and 94 unknown peptides, were found in these species. Phylogenetic analysis showed that (1) MSDIN genes generally clustered depending on the taxonomy of the genus, while Amanita MSDIN genes clustered depending on the chemical substance; and (2) the POPA genes of Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota clustered and were separated into three different groups, but the POPB genes of the three distinct genera were clustered in a highly supported monophyletic group.
Conclusions
These results indicate that lethal Amanita species have the genetic capacity to produce numerous cyclopeptides, most of which are unknown, while lethal Galerina and Lepiota species seem to only have the genetic capacity to produce α-amanitin. Additionally, the POPB phylogeny of Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota conflicts with the taxonomic status of the three genera, suggesting that underlying horizontal gene transfer has occurred among these three genera.
Keywords: Amanita, Galerina, Lepiota, Cyclopeptide toxin, Prolyl oligopeptidase, Horizontal gene transfer
Background
Amatoxins, which are lethal substances found in mushrooms, have mainly been reported to be present in species from three distinct genera classified into three different families: Amanita (Amanitaceae), Galerina (Hymenogastraceae) and Lepiota (Agaricaceae) [1–4]. Among these amanitin-producing mushrooms, lethal Amanita species are the best-known and most typical mushrooms that produce three primary groups of cyclopeptide toxins: amatoxins, phallotoxins and virotoxins, which are bicyclic octapeptides, bicyclic heptapeptides and monocyclic heptapeptides, respectively [1–4].
The precursor peptide genes of α-amanitin (α-AMA) and phallacidin (PHD) along with multiple related sequences encoding unknown cyclic peptides were first identified and predicted in Amanita bisporigera by genome shotgun sequencing, indicating that amatoxins and phallotoxins are encoded by the same gene family and are biosynthesized on ribosomes [5]. This gene family is referred to as MSDIN in reference to the first five conserved encoded amino acids, and the precursor peptides of its members contain 33–37 amino acids, consisting of two conserved regions, 10 upstream amino acids and 17 downstream amino acids, a highly variable core region, and a 6–10 amino acid sequence that ultimately forms the corresponding cyclopeptide [6]. GmAMA, which is responsible for producing α-AMA, is also found in the genome of Galerina marginata [7]. Galerina marginata is a specific amanitin-containing species in the genus Galerina. Unlike lethal amanitas, G. marginata does not harbour MSDIN-like family genes other than two copies of α-AMA genes. Additionally, α-AMA of Lepiota brunneoincarnata, which is an amanitin-containing mushroom of the genus Lepiota, has been successfully cloned [8]. The genome sequencing of L. venenata, another newly reported amanitin-containing species, has been completed, and it has been shown to harbour α-AMA genes [9]. Precursor peptide sequence alignment of α-AMA sequences from Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota shows high divergence except in the toxin region.
It has been strongly indicated that a prolyl oligopeptidase (POP) plays an important role in the initial processing of MSDIN precursor peptides. Since the core toxin regions are flanked by two highly conserved proline (Pro) residues, this enzyme can cleave the C-terminus of Pro residues and release the peptide chain of the toxin to form a cyclopeptide [10]. It has been reported that there are two types of POP in amatoxin-producing mushrooms: POPA, which behaves like a conventional housekeeping protein that is present in all species, and POPB, which is the enzyme that actually catalyses the cutting and cyclization of precursor peptides [7, 11, 12].
Increasing numbers of MSDIN family members have been published since the first 15 MSDIN genes were found in the A. bisporigera genome, and four were amplified by using degenerate primers in A. phalloides and A. ocreata [5]. Twenty-four MSDIN members were obtained from 6 Amanita species using degenerate primers [13]. Recently, the draft genome sequences of A. palloides and A. bisporigera showed that each species possessed approximately 30 MSDIN members, but only three of these genes were common to the two fungi [6]. Eighteen and twenty-two MSDIN genes were mined from the A. subjunquillea and A. pallidorosea genomes through PacBio and Illumina sequencing, respectively [8]. However, the MSDIN genes of many amanitin-containing Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota mushrooms have not been investigated in depth to date. Lethal Amanita species are classified in section Phalloideae of the genus Amanita [14, 15]. Approximately 50 lethal Amanita species have been reported worldwide, and the species diversity of lethal amanitas is strongly underestimated under the current taxonomy [15, 16]. Many new lethal Amanita and Lepiota species, including A. rimosa, A. subfuliginea, A. subpallidorosea, and L. venenata, have been discovered over the past decade [17–20]. In addition to the 22 known cyclopeptide toxins, some new cyclopeptide substances, such as cycloamanide E and cycloamanide F in A. phalloides and amanexitide in A. exitialis, have been extracted and identified [6, 21, 22]. It has been reported that A. bisporigera and A. phalloides present high potential for the biosynthesis of a variety of cyclopeptides, most of which are unknown according to predictions. Hence, considering the species diversity of amanitin-containing mushrooms and the broad genetic capacity of lethal amanitas to produce unknown cyclopeptides, there are still many new cyclopeptide genes and corresponding cyclopeptides to be discovered.
Alpha-amanitin and toxin-biosyntheic prolyl oligopeptidase B (POPB) genes have been proven to exist in some lethal Amanita [6, 23, 24], Galerina [7] and Lepiota [9] species. The reason that the biosynthetic pathway for α-amanitin is present in these three phylogenetically disjunct genera classified in different families has been studied in recent years. Recent studies reported that horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is the underlying cause of the distribution of MSDIN and POPB genes in Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota on the basis of phylogenetic analysis [8, 9]. The possibility of convergent evolution was negated because the MSDIN and POPB genes in these three genera show similarity and associations, such as a shared conserved gene structure and the encoding of precursor peptides by MSDIN genes [8].
According to previous research, whole-genome sequencing has proven to be the most comprehensive, in-depth method for identifying MSDIN genes or genes related to the cyclopeptide biosynthetic pathway in amanitin-producing mushrooms [6, 8]. Nevertheless, compared with genome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing provides an alternative efficient and low-cost method to obtain functional gene data. To the best of our knowledge, only A. palloides and A. bisporigera from North America and A. exitialis and A. rimosa from Asia have been studied using transcriptome sequencing [6, 25, 26].
In this study, the transcriptomes of seven amanitin-producing mushrooms (A. exitialis, A. fuliginea, A. molliuscula, A. pallidorosea, A. rimosa, A. subpallidorosea and L. venenata) and an Amanita species producing no amanitin (A. oberwinklerana) were sequenced. MSDIN and POP genes were searched and predicted from the transcriptome data. The genomic and coding sequences of the MSDIN and POP genes were cloned and verified. Similarly, MSDIN and POP sequences were cloned from two Galerina strains (G. marginata and G. sulciceps). In addition to the Amanita species mentioned above, MSDIN genes from A. subfuliginea, A. subjunquillea and A. virosa were cloned using specific and degenerate primers. Furthermore, phylogenetic analysis was performed on the obtained toxin and POP genes. Our study was aimed at (a) identifying MSDIN genes from amanitin-producing mushrooms to guide the isolation and identification of new unknown related cyclopeptides and (b) determining the evolutionary relationships of toxin MSDIN and POP genes in amanitin-producing mushrooms.
Results
Data filtering and assembly of transcriptomes
Transcriptome sequencing of seven amanitin-producing mushrooms was performed on the BGISEQ-500 platform using the combinational probe-anchor synthesis sequencing method. After the removal of ambiguous, adaptor-containing and low-quality sequences, clean data were obtained and de novo assembled using Trinity software. The main transcriptomic features and NCBI accession numbers of the transcriptome data obtained in our study are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Features and accession numbers of transcriptomes
| Species | Total clean bases (Gb) | Q30 (%) |
Total number of unigene | Total length of unigene (nt) | Mean length of unigene (nt) | N50 | GC (%) | accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. exitialis | 6.67 | 86.25 | 24,578 | 48,383,999 | 1968 | 2891 | 49.75 | SRR9929233 |
| A. fuliginea | 6.55 | 88.20 | 21,624 | 36,817,429 | 1702 | 2599 | 49.54 | SRR9937194 |
| A. molliuscula | 6.32 | 90.65 | 46,471 | 79,566,952 | 1712 | 3007 | 49.71 | SRR9937646 |
| A. oberwinklerana | 6.59 | 86.87 | 24,326 | 61,864,918 | 2543 | 3993 | 48.83 | SRR9937816 |
| A. pallidorosea | 6.25 | 89.78 | 36,846 | 79,216,743 | 2149 | 3375 | 49.52 | SRR9937866 |
| A. rimosa | 6.57 | 87.93 | 22,532 | 36,712,344 | 1629 | 2648 | 49.05 | SRR9943992 |
| A. subpallidorosea | 10.24 | 91.21 | 42,803 | 110,323,057 | 2577 | 3630 | 49.00 | SRR9943549 |
| L. venenata | 8.47 | 93.83 | 13,859 | 21,738,818 | 1569 | 2994 | 48.88 | SRR9943552 |
MSDIN and POP genes
Through transcriptome sequencing, 110 MSDIN genes (Table 2) were manually identified in 7 lethal Amanita and Lepiota species using known MSDIN members from A. bisporigera as TBLASTN queries. Additionally, 70 MSDIN genes (Table 3) were obtained from 12 lethal Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota species by PCR cloning using degenerate and specific primers. In general, a total of 151 nonrepetitive MSDIN genes were identified at the genomic and transcriptomic levels by using these methods. All the obtained MSDIN genes were predicted to encode 98 cyclopeptides, including α-amanitin (IWGIGCNP), β-amanitin (IWGIGCDP), phallacidin (AWLVDCP), phalloidin (AWLATCP) and 94 unknown peptides. These predicted cyclopeptides were composed of 6–11 amino acids and included 5 hexapeptides, 30 heptapeptides, 73 octapeptides, 22 nanopeptides, 19 decapeptides, and 2 undecapeptides.
Table 2.
MSDIN family members searched from the transcriptomes of seven amanitin-producing mushrooms
| Name | No. | Leader peptide | Core peptide |
Recognition sequence |
Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. exitialis | Ae1 | MTDINDTRLP | FIWLLWIWLP | SVGDDNNILNRGEDLC* | |
| Ae2 | MSDINATRLP | LFFPPDFRPP | CVGDADNFTLTRGENLC* | ||
| Ae3 | MSDVNATRLP | FNFFRFPYP | CIGDDSGSALRLGESLC* | ||
| Ae4 | MSDINTARLP | IPVPPFFIP | FVGDDIDVVLRRGENLC* | ||
| Ae5 | MSDINVTRLP | VFIFFFIPP | CVGDGTADIVRKGENLC* | ||
| Ae6 | MSDINTARLP | VFSLPVFFP | FVSDDIQAVLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ae7 | MSDINTTRLP | FVFVASPP | CVGDDIAMVLTRGENLC* | ||
| Ae8 | MSDINPTRLP | IFWFIYFP | CVSDVDSTLTLCISLS* | ||
| Ae9 | MSDINTARLP | IIWIIGNP | CVSDDVERILTRGESLC* | ||
| Ae10 | MSDINATRLP | IIWAPVVP | CISDDNDSTLTRGQSLC* | ||
| Ae11 | MSDINATRLP | IGRPQLLP | CVGGDVNYILISGENLC* | ||
| Ae12 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | |
| Ae13 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDDVTSVLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | |
| Ae14 | MSDINVIRLP | SMLTILPP | CVSDDASNTLTRGENLC* | ||
| Ae15 | MSDINATRLP | AWLTDCP | CVGDDVNRLLTRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| Ae16 | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDVNRLLTRGESLC* | phallacidin | |
| Ae17 | MSDINLTRLP | GIIAIIP | CVGDDVNSTLTRGQSLC* | ||
| Ae18 | MSDINATRLP | VWIGYSP | CVGDDCIALLTRGEGLC* | ||
| Ae19 | MSDINATRLP | GFLFWA | YVGDDVDYILTRGESLA* | ||
| A. fuliginea | Af1 | MSDINATRLP | IIIVLGLIIP | LCVSDIEMILTRGESLC* | |
| Af2 | MSDLNASRLP | ILSVLGLPVP | HVGEETNSTLARGESLC* | ||
| Af3 | MSDINSARLP | LFFPPIFIPP | CVSDDVQVVLTRGENLC* | ||
| Af4 | MSDINAARLP | FFPFVFIPP | CIGDDATSIVRQAENLC* | ||
| Af5 | MSDINTIRIP | FPWTGPFVP | CVSDDVGSVLMRGESLS* | ||
| Af6 | MSDTNATRLP | IWFIQLQIP | CAGDDVNSSLTRGESLC* | ||
| Af7 | MSDINVTRLP | VLVFIFFPP | YISDDAVNILKQGENLC* | ||
| Af8 | MFDINGSRLP | AFRLIPPP | CVGDDVDSTLTSGESLC* | ||
| Af9 | MSDINATRLP | GILIVFPP | CVGDDVNSTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Af10 | MSDINATRLP | HLFTWIPP | CISDDSTLTRGESFC* | ||
| Af11 | MFDINSSRLP | HLYPNSRP | CVCDDACSTLTSAESLC* | ||
| Af12 | MSDINATRLP | IFWFIYFP | CVGDDVDNTLTRGESLS* | ||
| Af13 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAALITRGEALC* | β-amanitin | |
| Af14 | MSCINATRLP | LPSRPVFP | FVSDAIEVVLGRGEDLC* | ||
| Af15 | MSDINSLRLP | VVNSRFNP | CVGDDVSPTLTRGEGLC* | ||
| Af16 | MSDINASRLP | AWLATCP | CIGDDVNPTITRGESLC* | phalloidin | |
| Af17 | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDVNRLLARGENLC* | phallacidin | |
| Af18 | MSDINATRLP | AWLVTCP | CVGDDINRLLTRGENLC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| A. molliuscula | Am1 | MSDINTARLP | YFLPPIFSPP | CVSDDIEMVLTRGENLC* | |
| Am2 | MTDINATRLP | ILFGFFLLP | CVDGVDNTLHSGENLC* | ||
| Am3 | MSNINASRLP | IWAAFFRFP | CVGDEVDGILRSGESLC* | ||
| Am4 | MSDINATRLA | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | |
| Am5 | MSDINASRLP | RLLVPRYP | CIDEDAEGATYLC* | ||
| Am6 | MSNINAIRLP | GFFAVVP | YLATSITFSLLGRGESLC* | ||
| Am7 | MTDINATRLP | WIFFFPP | CVDDVDNTLHSGENLC* | ||
| Am8 | MSNINALRLP | GFGFIP | YASGDVDYTLTRGESLS* | ||
| Am9 | MSDINATRFP | GKVNPP | YVGDDVDDIIIRGEKLC* | ||
| A. pallidorosea | Ap1 | MADINAARLP | FHGLFPFLPPP | FVDDDATSTLTRGESLC* | |
| Ap2 | MADINASRLP | LNILPFHLPP | CVSDDATSTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap3 | MSDINATRLP | NWHAGPTRPP | CVADDVSLTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap4 | MSDINTARLP | VFFMPPFIPP | CVSDDIQMVLTRGENLC* | ||
| Ap5 | MSDINTARLP | EFIVFGIFP | CVGDDIQTVLTRGEDLC* | ||
| Ap6 | MSDINASRLP | FFPEVGFFP | CVGDDTNPILTRGGSLS* | ||
| Ap7 | MSDLNATRLP | FNLFRFPYP | CIGDDSGSVLTLGEGLC* | ||
| Ap8 | MSDINTIRVP | FPWTGPFVP | CVGDDVGSVLTHGESLS* | ||
| Ap9 | MSDINATRLP | HPFPLGLQP | CAGDVDNLTLFRGEGLC* | ||
| Ap10 | MSDINATRLP | DPRRLLIP | GSSDDVDSALTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap11 | MSDINTTRLP | HFFNLMPP | CVGDDIETVLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap12 | MSDINATRLP | HQHHPFVP | GGSDDVGSTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap13 | MSDMNVVRLP | ISDPTAYP | CVGDDIQAVLGRGESLC* | ||
| Ap14 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTAVLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | |
| Ap15 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDEVAALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | |
| Ap16 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDEVTALITRGEALC* | α-amanitin | |
| Ap17 | MSDINATRLP | LGRPESLP | CVGDDVNYILVSGGNLS* | ||
| Ap18 | MSDINAARLP | LVYMILFP | SVGDDIDVVLGRGENLC* | ||
| Ap19 | MSDVNATRLP | MAFPEFLA | CVGDDVNHTLTRGERLC* | ||
| Ap20 | MSDINTARLP | MHILAPPP | CVSDDIEMVLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap21 | MSDINAARLP | NLFVWIPP | CISDDINSTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ap22 | MSDINTTRLP | YMWDHHLP | CASDDIQMVFTRGENLC* | ||
| Ap23 | MSDINASRLP | AWLATCP | CAGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | phalloidin | |
| Ap24 | MSDINATRLP | AWLMTCP | CVGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| Ap25 | MSDVNATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDINRLLTRGENLC* | phallacidin | |
| A. rimosa | Ar1 | MSDINTSRLP | FIPLGIITILP | CVSDDVNTTITRGESLC* | |
| Ar2 | MTDINDTRLP | FVWILWLWLA | CVGDDTSILNRGEDLC* | ||
| Ar3 | MSDINATRLP | IIIVLGLIIP | LCVSDIEMILTRGESLC* | ||
| Ar4 | MSDVNTTRLP | FNFFRFPYP | CICDDSEKVLELGENLC* | ||
| Ar5 | MSDINATRLP | HPFPLGLQP | CAGDVDNFTVSCHSLC* | ||
| Ar6 | MLDINATRFP | LGRPTHLP | CVGDDVNYILIGNGENLC* | ||
| Ar7 | MSDINASCLP | LILVANGMA | YVSDDVSPTLTRGENLC* | ||
| Ar8 | MPDINVTRLP | LLIIVLLTP | CISDDNNILNRGKDLC* | ||
| Ar9 | MSDIHAARLP | FPTRPVFP | SAGDDMIEVVLGRGEDLC* | ||
| Ar10 | MSDNNAARLP | FYFYLGIP | SDDAHPILTRGESLC* | ||
| Ar11 | MSDINIARLP | IFWFIYFP | CVGDDVDNTLSRGESLS* | ||
| Ar12 | MSDINASRLP | ILKKPWAP | SVCDDVNSTLTRGEGLC* | ||
| Ar13 | MSDINVARLP | ISDPTAYP | CVGDDIQAVVKRGESLC* | ||
| Ar14 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAALTTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | |
| Ar15 | MSDINSTRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEVTALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | |
| Ar16 | MSDINATRLP | AWDSKHP | CVGDDVSRLLTRGESLC* | ||
| Ar17 | MSDINATRVP | AWLAECP | CVGDDISHLLTRGENLC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| Ar18 | MSDINATRVP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDISRLLTRGENLC* | phallacidin | |
| A. subpallidorosea | Asp1 | MTDVNDTRLP | FIWLIWLWLP | SVGDDINILNGGEDLC* | |
| Asp2 | MTDINYARLP | ITLFLFFFIP | CLSDDDNILNRGKDLC* | ||
| Asp3 | MSDINTARLP | YFLPPIFSPP | CVSDDIEMVLTRGENLC* | ||
| Asp4 | MSDINATRLP | HPFPLGLQP | CAGDVDNFTLTKGEDLC* | ||
| Asp5 | MSDINATRLP | GILIVWPP | CVGDDVNFTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Asp6 | MSDINTTRLP | IAFPEFIA | RVGDDIHRTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Asp7 | MSDINVTRLP | IFWFIYFP | CVGDDVDNTLTRGESLS* | ||
| Asp8 | MSDINAIRLP | IGRPENKP | CVGGDVNYILISGEKLC* | ||
| Asp9 | MSDINATRLP | IVFLEFYS | CVGDDVNSTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Asp10 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAAFLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | |
| Asp11 | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEVTALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | |
| Asp12 | MSDINASRLP | VIGLFGLP | YVSDDVQPILTRGDSLC* | ||
| Asp13 | MSDINASRLP | VIPFLLPP | CVSDDVNFTLTRGESLC* | ||
| Asp14 | MSDINATRLP | YFRPAPPP | CVSDDINPILTCGESLC* | ||
| Asp15 | MSDINAARLP | AWITDCP | CVGDDINRILTRGENIC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| Asp16 | MSDINASRFP | AWLATCP | CVGDDVNPTIARGESLC* | phalloidin | |
| Asp17 | MSDINATRLP | AWLVTCP | CVGDDVNFTLTRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| Asp18 | MSDINATRLP | AWLVTCP | CVGDDVNPTITRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | |
| Asp19 | MSDINTIRIP | GPFGFA | YVGDEVENLLKRGESLS* | ||
| L. venenata | Lv1 | MDANATRLP | IWGIGCNP | WTPESVNDTLTKDLS* | α-amanitin |
| Lv2 | MDANSTRLP | IWGIGCNP | WAPESVNDTLTRGKDLC* | α-amanitin |
The MSDIN members with underlined numbers were verified at the genomic level. “Phallotoxin” means a novel heptapeptide similar to the phallotoxin cyclopeptide and capable of containing tryptathione (Trp-Cys)
Table 3.
MSDIN family members cloned from genomic DNA of twelve amanitin-producing mushrooms
| Name | No. | Leader peptide | Core peptide | Recognition sequence |
Product | GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. exitialis | Ae1a | MSDINATRLP | FIWVFGIP | GDIGTVLTRGENLC* | MN318165 | |
| Ae2a | MSDINATRLP | IIWIIGNP | CVSDDVERILTRGESLC* | MN318166 | ||
| Ae3ab | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN264225 | |
| Ae4ab | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDDVTSVLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN264220 | |
| Ae5b | MSDINATRLP | AWLTDCP | CVGDDVNRLLTRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN264235 | |
| Ae6b | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDVNRLLTRGESLC* | phallacidin | MN264231 | |
| Ae7a | MSDINATRLP | VWIGYSP | CVGDDCIALLTRGEGLC* | MN318167 | ||
| Ae8a | MSDINATRLP | GFLFWA | YVGDDVDYILTRGESLA* | MN318168 | ||
| Ae9a | MSDINATRLP | GFLLWA | YVGDDVDYILTRGESLA* | MN318169 | ||
| A. fuliginea | Af1a | MSDINATRLP | FPHFPPYNPP | CVSDDIHMVLTRGENLC* | MN318170 | |
| Af2a | MSDINATRLP | YYLLLILPP | CVSDDLQTVLTRGENLC* | MN318171 | ||
| Af3a | MSDINATRLP | IFWFIYFP | CVGDDVDNTLARGESLS* | MN318172 | ||
| Af4b | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAALITRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN264226 | |
| Af5a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGEDVAALITRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN318173 | |
| Af6a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEVTALLTSGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN318174 | |
| Af7a | MSDINATRLP | LPSRPVFP | FVSDAIEVVLGRGEDLC* | MN318175 | ||
| Af8b | MSDINASRLP | AWLATCP | CIGDDVNPTITRGESLC* | phalloidin | MN264249 | |
| Af9ab | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDVNRLLARGENLC* | phallacidin | MN264232 | |
| A. molliuscula | Am1b | MSDINATRLA | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN264227 |
| A. pallidorosea | Ap1a | MSDINATRLP | LIFIPPFIPP | CVSDDIQMVLTRGENLC* | MN318176 | |
| Ap2a | MSDINAPRLP | LIFIPPFIPP | CVSDDIQMVLTRGEGLC* | MN318177 | ||
| Ap3a | MSDINATRLP | IPFHIPAP | SVGDDIEVVLGRGENLC* | MN318178 | ||
| Ap4a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTAVLTCGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN318179 | |
| Ap5b | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVTAVLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN264228 | |
| Ap6ab | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDEVAALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN264222 | |
| Ap7b | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDEVTALITRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN264221 | |
| Ap8a | MSDINATRLP | AWLATCP | CAGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | phalloidin | MN318180 | |
| Ap9a | MSDINATRLP | AWLMTCP | CVGDDVNPILTRGESVC* | “phallotoxin” | MN318181 | |
| Ap10b | MSDINATRLP | AWLMTCP | CVGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN264236 | |
| Ap11ab | MSDVNATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDINRLLTRGENLC* | phallacidin | MN264233 | |
| A. rimosa | Ar1a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAALATRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN318182 |
| Ar2ab | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAALTTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN264229 | |
| Ar3a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEVTALLASGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN318183 | |
| Ar4ab | MSDINSTRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEVTALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN264223 | |
| Ar5b | MSDINATRVP | AWLAECP | CVGDDISHLLTRGENLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN264237 | |
| A. subfuliginea | Asf1a | MSDINATRLP | HPFPLGLQP | CAGDVDNFTLTKGEGLC* | MN318184 | |
| Asf2a | MSDINATRLP | AIFLAWPP | CVGDNVNSTLTRGESLC* | MN318185 | ||
| Asf3a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVSDDVAALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN318186 | |
| Asf4a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDEVAALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN318187 | |
| Asf5a | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDVNRLITRGENLC* | phallacidin | MN318188 | |
| A. subjunquillea | Asj1a | MSDINATRLP | AYLPLFFIPP | CVSDDIEMVLTRGESLC* | MN318189 | |
| Asj2a | MSDINATRLP | AYLPLFFIPP | CVSDDIEVVLTRGESLC* | MN318190 | ||
| Asj3a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CIGDDVTALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MH142177 | |
| Asj4a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDEVTALLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MH142176 | |
| Asj5a | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | CVGDEVAALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MH142175 | |
| Asj6ab | MSDINATRLP | AWLATCP | CAGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | phalloidin | MN264250 | |
| Asj7a | MSDINATRLP | AWLATCP | CVGDDVNPTLSRGESLC* | phalloidin | MN318191 | |
| Asj8ab | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDINRLLTRGENLC* | phallacidin | MN264234 | |
| A. subpallidorosea | Asp1ab | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCDP | CVGDDVAAFLTRGEALC* | β-amanitin | MN264230 |
| Asp2ab | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEVTALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN264224 | |
| Asp3ab | MSDINAARLP | AWITDCP | CVGDDINRILTRGENIC* | “phallotoxin” | MN272408 | |
| Asp4ab | MSDINASRFP | AWLATCP | CVGDDVNPTIARGESLC* | phalloidin | MN272407 | |
| Asp5a | MSDINATRLP | AWLITCP | CVGDDANPTITRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN318192 | |
| Asp6ab | MSDINATRLP | AWLVTCP | CVGDDVNPTITRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN272409 | |
| Asp7a | MSDINATRLP | AWLVTCP | CVGDDVNSTITRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN318193 | |
| A. virosa | Av1a | MSDINATRLP | FLLFIIPP | CVSDDVNSTLTRGESLC* | MN318194 | |
| Av2a | MSDINATRLP | FYFQPGFP | WSVGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | MN318195 | ||
| Av3b | MSDINATRLP | IWGIGCNP | SVGDEATALLTRGEALC* | α-amanitin | MN272412 | |
| Av4a | MSDINATRLP | SILIVWPP | CVGDDVNSTLTRGESLC* | MN318196 | ||
| Av5a | MSDINATRLP | SILVVWPP | CVSDDVNSTLTRGESLC* | MN318197 | ||
| Av6a | MSDINATRLP | AWLATCP | CVGDDVNPTLARGESLC* | phalloidin | MN318198 | |
| Av7a | MSDINATRLP | AWLVDCP | CVGDDINRLLTRGENLC* | phallacidin | MN318199 | |
| Av8a | MSDINATRLP | AWLVTCP | CVGDDVNPTLTRGESLC* | “phallotoxin” | MN318200 | |
| Av9a | MSDINATRLP | GPFLFFP | FVSDDIEVILRRGEDLC* | MN318201 | ||
| G. marginata | Gm1b | MFDTNATRLP | IWGIGCNP | WTAEHVDQTLASGNDIC* | α-amanitin | MN272413 |
| Gm2b | MFDTNSTRLP | IWGIGCNP | WTAEHVDQTLVSGNDIC* | α-amanitin | MN272414 | |
| G. sulciceps | Gs1b | MFDTNATRLP | IWGIGCNP | WTAEHVDQTLASGNDIC* | α-amanitin | MN272417 |
| Gs2b | MFDTNSTRLP | I*GIGCNP | WTAEHIDQTLVSGNDTC* | MN272418 | ||
| L. venenata | Lv1b | MDANATRLP | IWGIGCNP | WTPESVNDTLTKDLS | α-amanitin | MN272421 |
| Lv2b | MDANSTRLP | IWGIGCNP | WAPESVNDTLTRGKDLC | α-amanitin | MN272422 |
Superscripts a and b are for products cloned with degenerate and specific primers, respectively. “Phallotoxin” means a novel heptapeptide similar to phallotoxin cyclopeptide and capable of containing Tryptathione (Trp-Cys)
Among the MSDIN members found in the 9 lethal species of Amanita sect. Phalloideae included in our study, in addition to the common α-amanitin, β-amanitin, phallacidin and phalloidin (PHA) peptides, several unnamed predicted peptides overlapped among different Amanita species, including “FNFFRFPYP” in A. exitialis and A. rimosa; “FPWTGPFVP” in A. fuliginea and A. pallidorosea; “IIIVLGLIIP” in A. fuliginea and A. rimosa; “YFLPPIFSPP” in A. molliuscula and A. subpallidorosea; “ISDPTAYP” in A. pallidorosea and A. rimosa; “IFWFIYFP” in A. exitialis, A. fuliginea, A. rimosa and A. subpallidorosea; and “ISDPTAYP” in A. pallidorosea, A. rimosa, A. subfuliginea and A. subpallidorosea. The remaining 87 core regions were unique to their corresponding species. The MSDIN genes encoding “AWLTDCP” in A. exitialis; “AWLMTCP” in A. pallidorosea; “AWLECP” in A. rimosa; “AWLVTCP” in A. fuliginea, A. subpallidorosea and A. virosa; and “AWITDCP” and “AWLITCP” in A. subpallidorosea probably produce new unknown phallotoxins because their core regions are similar to those of phallacidin (AWLVDCP) and phalloidin (AWLATCP). As expected, no MSDIN genes were found in A. oberwinklerana, a species belonging to Amanita sect. Lepidella [16] or sect. Roanokenses that dose not contain cyclopeptide toxins [15].
In G. marginata, G. sulciceps and L. venenata, only MSDIN genes encoding α-amanitin were found, and such genes were the only genes common to the amanitin-producing genera Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota. Unlike the situation in lethal Amanita species, no MSDIN genes other than the α-amanitin gene were discovered. Interestingly, an MSDIN gene with the full amino acid sequence MFDTNSTRLPI*GIGCNPWTAEHIDQTLVSGNDTC* (with the core region shown in bold and underlined) was found in G. sulciceps. Due to its similarity to the α-amanitin gene Gs_α-AMA1 (MFDTNATRLPIWGIGCNPWTAEHVDQTLASGNDIC*) in G. sulciceps, it was designated Gs_α-AMA2.
Similarly, 19 POP genes were identified from the transcriptomes of nine Amanita, two Galerina and one Lepiota species using known POPA and POPB genes of A. bisporigera and G. marginata, respectively, as the TBLASTN queries and these sequences were further verified by PCR amplification. Eleven lethal Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota species contained both POPA and POPB genes, but A. oberwinklerana, an Amanita species producing no cyclopeptide toxins, only exhibited the POPA gene. All of the obtained POP sequences and their accession numbers are listed in Table 4.
Table 4.
Gene sequences used in the molecular phylogenetic analyses and their GenBank accession numbers
| Taxon | Gene | Source | GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agaricus bisporus var. bisporus | POP | NCBI | XM006459721 |
| Agaricus bisporus var. burnettii | POP | NCBI | JH971409 |
| Amanita bisporigera | α-AMA1 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – |
| α-AMA2 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| PHA1 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| PHA2 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| POPA | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| POPB | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| Amanita exitialis | α-AMA | Our study | MN264220 |
| β-AMA | Our study | MN264225 | |
| PHA | Our study | MN264231 | |
| “AWLTDCP” | Our study | MN264235 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN264238 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN264244 | |
| Amanita fuliginea | β-AMA | Our study | MN264226 |
| PHA | Our study | MN264232 | |
| PHD | Our study | MN264249 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN264239 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN264245 | |
| Amanita molliuscula | β-AMA | Our study | MN264227 |
| POPA | Our study | MN264240 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN264246 | |
| Amanita muscaria | POPA | NCBI | KN818232 |
| Amanita oberwinklerana | POPA | Our study | MN264241 |
| Amanita pallidorosea | α-AMA1 | Our study | MN264221 |
| α-AMA2 | Our study | MN264222 | |
| β-AMA | Our study | MN264228 | |
| PHA | Our study | MN264233 | |
| “AWLMTCP” | Our study | MN264236 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN264242 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN264247 | |
| Amanita phalloides | α-AMA | Pulman. et al., 2016 | – |
| β-AMA1 | Pulman. et al., 2016 | – | |
| β-AMA2 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| PHA | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| PHD1 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| PHD2 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| PHD3 | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| POPA | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| POPB | Pulman et al., 2016 | – | |
| Amanita rimosa | α-AMA | Our study | MN264223 |
| β-AMA | Our study | MN264229 | |
| “AWLAECP” | Our study | MN264237 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN264243 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN264248 | |
| Amanita subjunquillea | α-AMA | Luo et al., 2018 | – |
| β-AMA1 | Luo et al., 2018 | – | |
| β-AMA2 | Luo et al., 2018 | – | |
| PHA | Our study | MN264234 | |
| PHD | Our study | MN264250 | |
| POPA | Luo et al., 2018 | – | |
| POPB | Luo et al., 2018 | – | |
| Amanita subpallidorosea | α-AMA | Our study | MN264224 |
| β-AMA | Our study | MN264230 | |
| PHD | Our study | MN272407 | |
| “AWITDCP” | Our study | MN272408 | |
| “AWLVTCP” | Our study | MN272409 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN272410 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN272411 | |
| Amanita thiersii | POPA | NCBI | KZ302001 |
| Amanita virosa | α-AMA | Our study | MN272412 |
| Anomoporia bombycina | POP | JGI | – |
| Auriculariopsis ampla | POP | NCBI | VDMD01000002 |
| Bolbitius vitellinus | POP | JGI | – |
| Conocybe apala | POP | NCBI | FJ906819 |
| Coprinellus micaceus | POP | NCBI | QPFP01000027 |
| Coprinopsis cinerea | POP | NCBI | XM001841192 |
| Coprinopsis marcescibilis | POP | NCBI | ML210154 |
| Cortinarius glaucopus | POP | JGI | – |
| Crucibulum laeve | POP | NCBI | ML213591 |
| Cyathus striatus | POP | JGI | – |
| Fistulina hepatica | POP | NCBI | KN881639 |
| Galerina marginata | α-AMA1 | Our study | MN272413 |
| α-AMA2 | Our study | MN272414 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN272415 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN272416 | |
| Galerina sulciceps | α-AMA1 | Our study | MN272417 |
| “α-AMA2” | Our study | MN272418 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN272419 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN272420 | |
| Gymnopilus chrysopellus | POP | JGI | – |
| Gymnopilus dilepis | POP | NCBI | NHYE01005597 |
| Hebeloma cylindrosporum | POP | NCBI | KN831777 |
| Hypholoma sublateritium | POP | NCBI | KN817688 |
| Hypsizygus marmoreus | POP | NCBI | LUEZ02000233 |
| Laccaria amethystina | POP | NCBI | KN838546 |
| Laccaria bicolor | POP | NCBI | DS547115 |
| Lepiota brunneoincarnata | POPA | NCBI | MN912699 |
| Lepiota subincarnata | α-AMA1 | Luo et al., 2018 | – |
| α-AMA2 | Luo et al., 2018 | – | |
| POPB | Luo et al., 2018 | – | |
| Lepiota venenata | α-AMA1 | Our study | MN272421 |
| α-AMA2 | Our study | MN272422 | |
| POPA | Our study | MN272423 | |
| POPB | Our study | MN272424 | |
| Lepista nuda | POP | JGI | – |
| Leucoagaricus sp. | POP | NCBI | KQ962668 |
| Macrolepiota fuliginosa | POP | JGI | – |
| Panaeolus cyanescens | POP | NCBI | NHTK01005903 |
| Pleurotus ostreatus | POP | NCBI | KL198007 |
| Plicaturopsis crispa | POP | JGI | – |
| Pterula gracilis | POP | NCBI | ML178816 |
| Schizophyllum commune | POP | NCBI | GL377318 |
| Termitomyces sp. | POP | NCBI | KQ412502 |
Comparison of MSDIN precursor peptide sequences
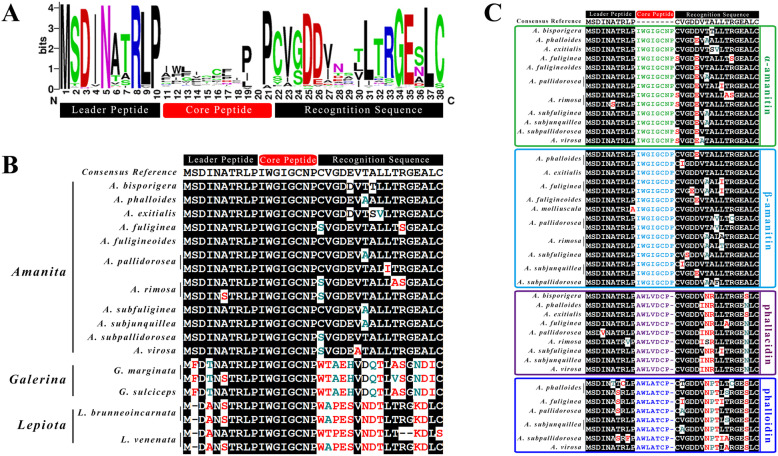
WebLogo alignment was carried out for 145 MSDIN sequences obtained from 9 Amanita species (Fig. 1a). The composition and structure of these sequences and the relative degree of conservation of the amino acids at each point were analysed. As shown in Fig. 1a, the MSDIN precursor peptides of the Amanita species were 31–38 amino acids in length and could be divided into three regions: a highly conserved upstream leader peptide, a relatively conserved downstream recognition sequence and a highly variable core peptide. The core peptide was located between P10 and P21 and included the latter proline, and its ends were the leader peptide and recognition sequence of MSDIN. The leader peptide contained 10 amino acids, and the M1S2D3I4N5R8L9P10 residues were highly conserved, with conservation rates of 100% (145/145), 91.7% (133/145), 97.2% (141/145), 93.1% (135/145), 99.3% (144/145), 99.3% (144/145), 94.5% (137/145) and 99.3% (144/145), respectively. In the leader peptide, P10 was the first cleavage site for prolyl oligopeptidase (POPB) [12]. The recognition sequence usually contained 17 amino acids, beginning with C22V23G24D25D26, with conservation rates of 76.5% (111/145), 79.3% (115/145), 66.2% (96/145), 93.1% (135/145) and 83.4% (121/145), and ending with L31T32R33G34E35L37C38, with conservation rates of 86.9% (126/145), 73.8% (107/145), 82.1% (119/145), 96.6% (140/145), 93.1% (135/145), 97.9% (142/145) and 91.7% (133/145), respectively. In the recognition sequence, L31 and L37 were conducive to the formation of an alpha helix and substrate recognition by the POPB enzyme [28]; additionally, the C-terminal Cys38 (sometimes replaced with Ser) was indispensable for performing the function of POPB [12]. The core peptides were predicted to form cyclopeptides in which the last amino acid, P21 (the second cleavage site for POPB), was highly conserved, with a conservation rate of 94.5% [12].
Fig. 1.
Alignment of MSDIN precursor peptide sequences. a WebLogo [27] alignment of 145 MSDIN members from 9 Amanita species. The letter height of each amino acid represents its conservation degree, and the higher the letter, the more conserved the site. b Alignment of the precursor peptide sequences of α-amanitin from 15 amanitin-producing mushrooms. c Alignment of the precursor peptide sequences of α-, β-amanitin, phallacidin and phalloidin from 12 Amanita species. Letters with white background are variations compared with the consensus sequence. The sequences of A. bisporigera, A. phalloides were from Pulman et al. (2016), the sequences of A. fuligineoides were from Li et al. (2014) and the sequences of L. brunneoincarnata were from Lüli et al. (2019)
The α-AMA precursor peptide sequences of the genera Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota were compared, as shown in Fig. 1b. The α-AMA sequences showed few differences within the same genus but presented more differences between the different genera. The α-AMA leader peptides of the three genera showed few differences and were more conserved than the other sequences. The leader peptides of Amanita and Galerina contained 10 amino acids, while that of the genus Lepiota contained 9, and the sequences of the three genera started with “MSDIN”, “MFDTN”, and “MDAN”, respectively. In the recognition sequences of the three genera, with the exception of several highly conserved amino acids (specifically V, L, G, and LC or LS at the end), many differences were observed. Overall, there were large differences among the α-AMA sequences of Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota, but the Galerina and Lepiota α-AMA sequences were closer to each other than to those of Amanita.
The Amanita MSDIN genes encoding amatoxins (α-, β-amanitin) and phallotoxins (phallacidin and phalloidin), which are the major cyclopeptides in these mushrooms, were aligned, and the highlighted variations were compared to representative consensus sequences (Fig. 1c). In general, the precursor peptide sequences encoding the same toxin shared high identity. There were obviously more variations in the recognition sequences than in the leader peptides. The phallotoxin sequences presented more variations than the amatoxin sequences.
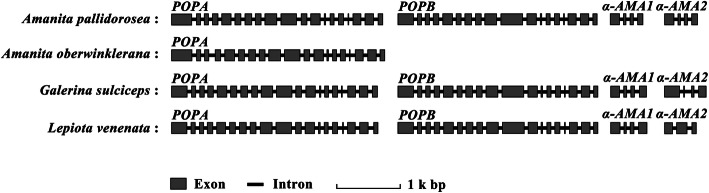
Structures of MSDIN and POP genes
The genomic sequences and coding sequences of the toxin MSDIN and POP genes obtained in this study (Table 2)were subjected to pairwise alignment, and the gene composition of the exons and introns was analysed. As shown in Fig. 2, the POPA genes comprised 19 exons and 18 introns, while the POPB genes comprised 18 exons and 17 introns, which was very similar to other known POP genes. The α-AMA genes of Amanita and Galerina contained three introns, while the α-AMA genes of Lepiota contained two or three introns. In addition to α-AMA, other MSDIN toxin genes in Amanita species, such as β-AMA, PHA and PHD, were also composed of three introns.
Fig. 2.
Structures of α-AMA and POP exemplified by four agaric species
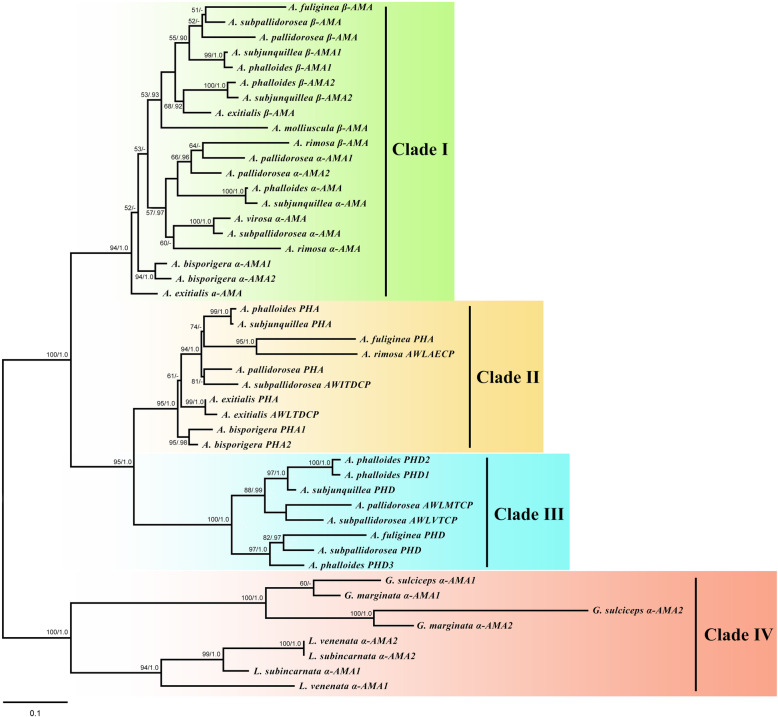
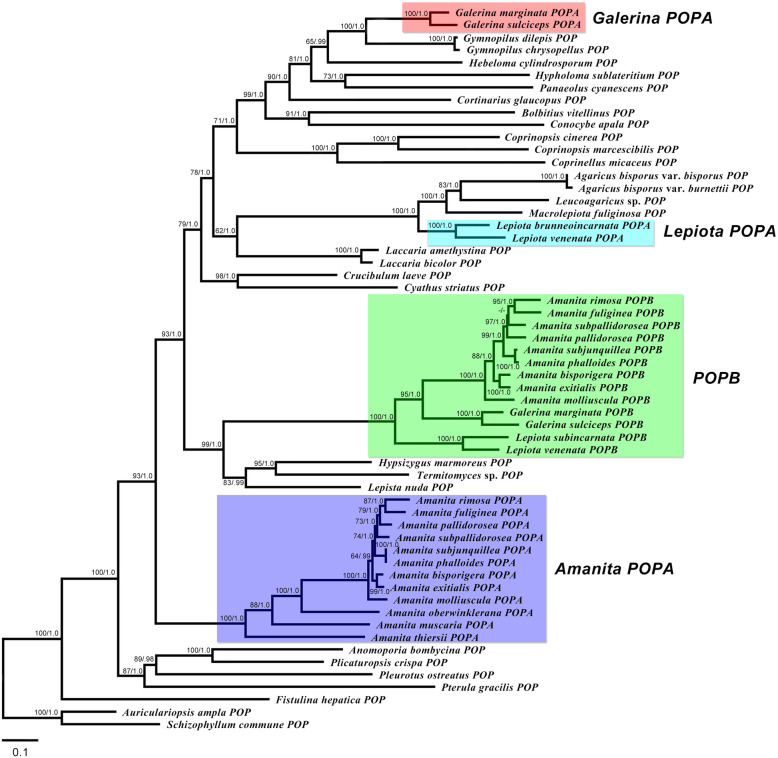
Phylogenetic analysis of MSDIN and POP genes
From the phylogenetic analysis, two maximum likelihood (ML) trees based on 46 MSDIN toxin genes from 14 amanitin-producing mushrooms and 58 POP genes from 46 agaric species were constructed. In the MSDIN toxin gene tree (Fig. 3), all MSDIN toxin gene sequences were distributed in four clades. Clade I contained 10 α-amanitin gene sequences and 10 β-amanitin gene sequences from 10 lethal Amanita species forming a cluster with 95% bootstrap support and a Bayesian posterior probability of 1.0. Clade II contained MSDIN genes encoding AWLVDCP (phallacidin, PHA) and the unknown related variants AWLAECP, AWITDCP and AWLTDCP forming a cluster with 95% bootstrap support and a Bayesian posterior probability of 1.0. Clade III contained MSDIN genes encoding AWLATCP (phalloidin, PHD) and the unknown related variants AWLMTCP and AWLVTCP forming a cluster with a 100% bootstrap and a 1.0 Bayesian posterior probabilities. Clade IV contained α-amanitin genes from Galerina and Lepiota species, including G. marginata, G. sulciceps, L. subincarnata and L. venenata, forming a cluster with a 100% bootstrap and a 1.0 Bayesian posterior probabilities. In the POP gene tree (Fig. 4), POPA sequences from Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota were separated from each other in different groups. Amanita POPA sequences (12) were clustered together as a single group, while Galerina POPA sequences (2) were clustered in a group containing Gymnopilus dilepis and Gymnopilus chrysopellus, and Lepiota POPA sequences (2) were clustered in a group containing Agaricus bisporus var. bisporus, Agaricus bisporus var. burnettii, Leucoagaricus sp. and Macrolepiota fuliginosa. However, POPB sequences (13) belonging to three disjunct genera (Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota) were clustered together forming a monophyletic group.
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic trees generated from maximum likelihood analysis based on toxin MSDIN genes. Bootstrap percentages (> 50%) based on 1000 replications and Bayesian posterior probabilities (> 0.90) are shown at nodes. Bar, a substitution per 10 nucleotides
Fig. 4.
Phylogenetic trees generated from maximum likelihood analysis based on POP genes. Bootstrap percentages (> 50%) based on 1000 replications and Bayesian posterior probabilities (> 0.90) are shown at nodes. Bar, a substitution per 10 nucleotides
Discussion
It has been proven that lethal Amanita species are classified in section Phalloideae of Amanita and that these species contain members of the MSDIN gene family, allowing them to produce many small cyclopeptides, such as α-amanitin, on ribosomes [6, 16]. In the present study, nine lethal Amanita species from China, including A. exitialis, A. fuliginea, A. mulliuscula, A. pallidorosea, A. rimosa, A. subfuliginea, A. subjunquillea, A. subpallidorosea and A. virosa, were proven to contain MSDIN genes, as found in other lethal Amanita species described previously, such as A. bisporigera. These results further suggest that species of the Amanita section Phalloideae are genetically similar and are able to biosynthesize amatoxins, phallotoxins and some other unknown peptides.
Based on the MSDIN gene data from nine lethal Amanita species from China obtained in our study and some other European and North American species, such as A. bisporigera, A. phalloides and A. ocreata [5, 6], most MSDIN genes have not been found to be common and may even be unique among these lethal Amanita species. In species of Amanita section Phalloideae, the MSDIN gene encoding α-amanitin is present in all species, whereas the MSDIN genes encoding β-amanitin, phallacidin and phalloidin are widely distributed but are not common to all species. This findings suggested that each lethal Amanita species exhibits its own independent MSDIN family and that few overlapping MSDIN genes occur among lethal Amanita species.
In addition to species of Amanita section Phalloideae, some Galerina and Lepiota species, such as G. marginata and L. brunneoincarnata, produce amatoxin [2, 29]. In our study, the MSDIN gene-mining results showed that G. marginata and L. venenata only presented two copies of the α-amanitin gene, and no additional MSDIN genes were found, consistent with the results of Luo et al. (2012) and Lüli et al. (2019) [7, 9]. Lethal Galerina and Lepiota species are considered to have two copies of the α-amanitin gene. However, the analysis of the MSDIN genes of another Galerina species, G. sulciceps, showed that G. sulciceps only presented a single copy of the α-amanitin gene, although it also exhibited an MSDIN gene that was extremely similar to the α-amanitin gene with an I*GIGCNP core region. This MSDIN gene seemed to represent an α-amanitin gene mutation, and we speculated that its tryptophan (W) codon, TGG, in the core region has been mutated to a termination codon, TGA, via a single-base substitution, thus inhibiting the proper expression of the gene. In general, only the α-amanitin gene is found in Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota, which indicates that the α-amanitin genes of the three genera might share a common origin or originate from a single genus. Additionally, MSDIN genes including β-AMA, PHA, PHD, etc., were only found in Amanita, which indicated that these MSDIN genes (except for α-AMA) were likely derived from lethal Amanita species. The higher genetic diversity of MSDIN genes in Amanita than in Galernia and Lepiota causes the lethal Amanita species to produce greater amounts of toxic compounds than Galernia and Lepiota species. For this reason, lethal Amanita species present a greater defence ability to prevent their consumption than Galernia and Lepiota species.
Lethal Amanita species contain three primary kinds of peptide toxins: amatoxins, phallotoxins and virotoxins [21]. MSDIN genes encoding amatoxin and phallotoxin were discovered in 2007 [5], but there has been no related evidence of MSDIN genes encoding virotoxins published to date. It has been reported that A. subpallidorosea and A. virosa contain virotoxins [3, 30]. In this study, toxin genes of the two lethal Amanita species were also identified, and no virotoxin genes were found. Nevertheless, the two species both contain MSDIN genes encoding AWLATCP (PHD) and AWLVTCP, which only show a single amino acid difference in the composition of the virotoxins (AWLATSP or AWLVTSP). Therefore, we speculated that virotoxins might be encoded by the PHD gene or the phallotoxin-like gene AWLVTCP and that cysteine (C) is transformed to serine (S) during posttranslational modification.
Phylogenetic analysis showed that the Galerina α-AMA genes and Lepiota α-AMA genes were homologous but were distant from the Amanita α-AMA gene. In the genus Amanita, α-AMA and β-AMA are mixed and clustered in a clade, which indicates that β-AMA might be derived from α-AMA. PHA genes (AWLVDCP) were clustered with MSDIN genes encoding AWLAECP, AWITDCP and AWLTDCP, and PHD genes (AWLATCP) were clustered with MSDIN genes encoding AWLMTCP and AWLVTCP, which indicated that the encoded products of these MSDIN genes were very likely to correspond to new unknown phallotoxins, considering the similarity of their amino acid composition with those of PHA and PHD and their capacity to contain tryptathione (Trp-Cys). These phallotoxin-like genes might be variants derived from PHA and PHD. For example, we found that the PHA gene (AWLVDCP) sequence in A. exitialis was almost the same as the sequence of the MSDIN gene encoding AWLTDCP, with only a two-nucleotide difference in the core region, and the valine (V) codon GTA is likely mutated into the threonine (T) codon ACA. According to this finding, it can be inferred that the MSDIN genes in Amanita evolved faster than those in Galerina and Lepiota, which led to the generation of a variety of new peptide genes and might also be the reason why the Galerina and Lepiota α-AMA genes differed from the Amanita α-AMA genes.
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT), also known as lateral gene transfer, refers to the transmission of genetic material between distinct organisms, specifically across species boundaries [31, 32]. It has been reported that HGT is very common in prokaryotes and may be an important source of their biological evolution, and HGT also occurs in eukaryotes at a lower frequency than in prokaryotes [33–36]. The most recent reports suggest that HGT may be responsible for the α-amanitin biosynthetic pathway found in the three distantly related genera Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota [8, 9]. It has been reported that in amanitin-producing mushrooms, the POPB gene product catalyses the cleavage and cyclization of the toxin precursor peptide, while the POPA gene is a housekeeping gene that is unrelated to toxin biosynthesis [7, 12]. In our study, phylogenetic analysis based on the POP gene showed that the POPA genes of Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota were distributed in three separate groups, but the POPB genes of the three genera were highly homologous forming a highly monophyletic group, which apparently conflicted with the species taxonomic status and could not be explained by conserved gene inheritance. Additionally, the MSDIN and POP genes were proven to exhibit the same exon and intron structures. These results can be considered to represent evidence of HGT events among Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota. For the complete validation of HGT among amanitin-producing mushrooms in the future, the inclusion more related species and their genomic data will be required to perform a phylogenetic analysis with appropriate taxon sampling and tree-building methodologies.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the MSDIN gene family is abundant and diverse. In addition to the peptide toxins α-amanitin, β-amanitin, phallacidin, phalloidin, etc., the MSDIN family encodes a variety of unknown small cyclopeptides. The amanitin-producing species Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota exhibit a common toxin biosynthetic pathway, and their α-amanitin genes and POPB genes may have a common origin that involving HGT among the three distant genera.
Methods
Sample collection and preparation
Samples of seven Amanita species and Lepiota venenata were collected from the wild for RNA extraction and sequencing, and their fresh basidiocarps were cleaned and placed on dry ice then transported back to the lab and stored at − 80 °C. The mushroom samples intended for DNA extraction were dried with silica gel and then stored at 4 °C. The mycelia of two Galerina strains were cultivated to grow material for DNA and RNA extraction. Detailed information for the mushroom materials used in this study is given in Table 5.
Table 5.
Information of the mushroom materials used in this study
| Species name | Locality | Collection time | Specimen no. | GenBank accession no. | Nucleic acid extract |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. exitialis | Guangdong, China | 2017-03-27 | MHHNU 30937 | KR996717 | DNA, RNA |
| A. fuliginea | Hunan, China | 2017-06-06 | MHHNU 9047 | MN061271 | DNA, RNA |
| A. molliuscula | Jilin, China | 2017-08-07 | MHHNU 9142 | MN061272 | DNA, RNA |
| A. oberwinklerana | Hunan, China | 2017-06-09 | MHHNU 9051 | MN061273 | DNA, RNA |
| A. pallidorosea | Shandong, China | 2018-08-13 | MHHNU 31203 | MN061274 | DNA, RNA |
| A. rimosa | Hunan, China | 2017-06-09 | MHHNU 9050 | MN061275 | DNA, RNA |
| A. subfuliginea | Chongqing, China | 2015-07-01 | MHHNU 30946 | MN061276 | DNA |
| A. subjunquillea | Hunan, China | 2012-09-10 | MHHNU 7751 | KR996715 | DNA |
| A. subpallidorosea | Hunan, China | 2017-09-14 | MHHNU 8617 | KU601411 | DNA, RNA |
| A. virosa | Hunan, China | 2016-09-09 | MHHNU 8621 | KY472227 | DNA |
| G. marginata | – | – | MHHNU 8380 | MN061277 | DNA, RNA |
| G. sulciceps | – | – | MHHNU 7669 | KX214585 | DNA, RNA |
| L. venenata | Hubei, China | 2017-9-10 | MHHNU 31031 | MK095189 | DNA, RNA |
G. marginata and G. sulciceps samples were cultured mycelia, and the other mushroom samples were wild fruiting bodies
Nucleic acid extraction and cDNA preparation
Total genomic DNA was extracted using the Fungal DNA Mini Kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, USA). Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) following the TRIzol User Guide. cDNA was synthesized using TransScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMIX (Transgen Biotech, Beijing, China). The DNA and RNA quality and yield were detected using a SmartSpec Plus (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA).
Transcriptome sequencing and de novo assembly
The concentration, purity and integrity of the RNA samples used for next-generation sequencing were further examined using an Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, USA). Qualified RNA samples were used to construct circular single-stranded cDNA libraries, and the libraries were then sequenced on a BGISEQ-500 sequencer (BGI, Shenzhen, China). Clean reads were obtained using the filtering software SOAPnuke to remove reads containing adaptors, reads with more than 5% unknown bases, and low-quality reads (bases with a quality value < 15 accounting for more than 20% of the bases in a read) from the raw reads. These clean reads were de novo assembled using Trinity software. Finally, nonredundant unigenes were obtained using Tgicl software. All of these steps were performed by the Beijing Genomic Institute (BGI)-Wuhan in China.
Retrieval and annotation of MSDIN and POP genes
The unigene data obtained as described above were searched for MSDIN and POP genes (Galerina unigenes were provided by Professor Ping Zhang at Hunan Normal University) by using the known amino acid sequences of the MSDIN family and POP genes from A. bisporigera and G. marginata [5, 7] as queries for the online NCBI TBLASTN tool. Then, unigenes similar to the queries were manually annotated, and the coding sequences were predicted and translated into protein sequences using DNAMAN 7.0 software.
Cloning of MSDIN and POP genes
Partial MSDIN gene sequences were amplified from Amanita genomic DNA using the following degenerate primers: forward (5′-ATGTCNGAYATYAAYGCNACNCG-3′) and reverse (5′-CCAAGCCTRAYAWRGTCMACAAC-3′), according to the method of Li et al. (2014) [13]. The PCR mixtures contained 1× PCR buffer, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dNTPs, each primer at 0.4 μM, 1.25 U of Taq polymerase (Comwin Biotech, Beijing, China), and 1 μL of DNA template in a total volume of 25 μL. PCR was performed with the following program: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 4 min, 35 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, 52 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, and the reaction batches were incubated at 72 °C for 2 min for terminal elongation.
Using the known MSDIN and POP genes from A. bisporigera and G. marginata as reference models [5, 7], specific primers (shown in Table S1) were designed to obtain target products that were close to the full lengths of the genes according to the flanking sequences of the CDS. The genomic DNA and cDNA of the Amanita, Galerina and Lepiota species were used as templates, and PCR was performed as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 4 min, followed by 32 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, 55–60 °C for 30 s (annealing temperature for each target shown in Table S1), and extension at 72 °C (30 s for an MSDIN gene, 2 min for a POP gene), and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min.
All PCR products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis and purified using an EasyPure Quick Gel Extraction Kit (Transgen Biotech, Beijing, China). The purified products were ligated into the pEASY®-Blunt Zero Cloning Vector (Transgen Biotech, Beijing) and transformed into competent cells. Positive clones to be sequenced were selected using Amp-resistant LB medium and were further verified by colony PCR. Finally, all of the obtained genomic and coding sequences of the genes were used to manually predict the corresponding functions and structures by using DNAMAN 7.0 software.
Phylogenetic tree construction of MSDIN and POP genes
Forty-six coding sequences (CDSs) of MSDIN toxin genes and fifty-eight CDSs of POP genes were used for phylogenetic analysis, and their source and GenBank accession numbers are presented in Table 4. These sequences were aligned by using MAFFT v7.374 [37] and then manually adjusted by using BioEdit [38]. HKY + I + G and GTR + I + G were inferred as the best-fit models for the CDSs of the MSDIN and POP genes selected according to the AIC in MrModeltest v2.3 [39]. Maximum likelihood (ML) trees with 1000 bootstrap replicates and Bayesian inferences were generated with RAxML v7 [40] and MrBayes v3.1.2 [41], respectively.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Specific PCR Primers designed for peptide toxins and POP genes.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Dr. Yang ZL and Luo H (Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China) for critically reviewing the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- POP
Prolyl oligopeptidase
- α-AMA
α-amanitin
- β-AMA
β-amanitin
- PHD
Phallacidin
- PHA
Phalloidin
- CDS
Coding sequence
- HGT
Horizontal gene transfer
- ML
Maximum likelihood
Authors’ contributions
ZHC and ZMH conceived and designed the experiments. ZMH and PL carried out the MSDIN and POP genes cloning, FF and SNL carried out the phylogenetic analysis. PZ provided some Amanita materials and identified the species. ZMH and ZHC wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31872616), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Hunan Provincial Education Department, China (Grant no. 18A026). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The mushroom species and related transcriptome data, MSDIN and POP genes used in this study has been deposited at GenBank and their accession numbers can be found in Tables 1, 3, 4 and 5.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12864-020-06857-8.
References
- 1.Wieland T. Peptides of poisonous Amanita mushrooms. New York: Springer; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Enjalbert F, Cassanas G, Rapior S, Chaumont JP. Amatoxins in wood-rotting Galerina marginata. Mycologia. 2004;96:720–729. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2005.11832920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tang SS, Zhou Q, He ZM, Luo T, Zhang P, Cai Q, et al. Cyclopeptide toxins of lethal amanitas: compositions, distribution and phylogenetic implication. Toxicon. 2016;120:78–88. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Walton JD. The cyclic peptide toxins of Amanita and other poisonous mushrooms. New York: Springer; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hallen HE, Luo H, Scott-Craiq JS, Walton JD. Gene family encoding the major toxins of lethal Amanita mushrooms. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:19097–19101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707340104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pulman JA, Childs KL, Sgambelluri RM, Walton JD. Expansion and diversification of the MSDIN family of cyclic peptide genes in the poisonous agarics Amanita phalloides and A bisporigera. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:1038. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3378-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Luo H, Hallen HE, Scott-Craig JS, Walton JD. Ribosomal biosynthesis of α-amanitin in Galerina marginata. Fungal Genet Biol. 2012;49:123–129. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2011.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Luo H, Cai Q, Lüli YJ, Li X, Sinha R, Hallen HE, et al. The MSDIN family in amanitin-produing mushrooms and evolution of the prolyl oligopeptidase genes. IMA Fungus. 2018;9:225–242. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2018.09.02.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lüli YJ, Cai Q, Chen ZH, Sun H, Zhu XT, Li X, et al. Genome of lethal Lepiota venenata and insights into the evolution of toxin-biosynthetic genes. BMC Genomics. 2019;20:198. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5575-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Walton JD, Hallen HE, Luo H. Ribosomal biosynthesis of the cyclic peptide toxins of Amanita mushrooms. Biopolymers. 2010;94:659–664. doi: 10.1002/bip.21416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Luo H, Hallen HE, Scott-Craig JS, Walton JD. Colocalization of amanitin and a candidate toxin-processing prolyl oligopeptidase in Amanita basidiocarps. Eukaryot Cell. 2010;9:1891–1900. doi: 10.1128/EC.00161-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Luo H, Hong SY, Sgambelluri RM, Angelos E, Li X, Walton JD. Peptide macrocyclization catalyzed by a prolyl oligopeptidase involved in α-amanitin biosynthesis. Chem Biol. 2014;21:1610–1617. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.10.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li P, Deng WQ, Li TH. The molecular diversity of toxin gene families in lethal Amanita mushrooms. Toxicon. 2014;83:59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yang ZL. Atlas of the Chinese species of Amanitaceae. Beijing: Science; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cui YY, Cai Q, Tang LP, Liu JW, Yang ZL. The family Amanitaceae: molecular phylogeny, higher-rank taxonomy and the species in China. Fungal Divers. 2018;91:5–230. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cai Q, Tulloss RE, Tang LP, Tolgor B, Zhang P, Chen ZH, et al. Multi-locus phylogeny of lethal amanitas: implications for species diversity and historical biogeography. BMC Evol Biol. 2014;14:143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang P, Chen ZH, Xiao B, Tolgor B, Bao HY, Yang ZL. Lethal amanitas of East Asia characterized by morphological and molecular data. Fungal Divers. 2010;42:119–133. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li HJ, Xie JW, Zhang S, Zhou YJ, Ma PB, Zhou J, et al. Amanita subpallidorosea, a new lethal fungus from China. Mycol Prog. 2015;14:43. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cai Q, Cui YY, Yang ZL. Lethal Amanita species in China. Mycologia. 2016;108:993–1009. doi: 10.3852/16-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cai Q, Chen ZH, He ZM, Luo H, Yang ZL. Lepiota venenata, a new species related to toxic mushroom in China. J Fungal Res. 2018;16:63–69. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Clarke DB, Lloyd AS, Robb P. Application of liquid chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry separation for rapid assessment of toxins in Amanita mushrooms. Anal Methods. 2012;4:1298. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xue JH, Wu P, Chi YL, Xu LX, Wei XY. Cyclopeptides from Amanita exitialis. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2011;1:52–56. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li P, Deng WQ, Li TH. Molecular cloning of α-amanitin and characterization of its expression pattern in different parts and development stages of Amanita exitialis fruitbody. Mycol Prog. 2014;13:1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang CH, Zou JP, Deng WQ, Li TH, Jiang ZD. Molecular cloning and expression pattern of AePOPB involved in the α-amanitin biosynthesis in Amanita exitialis fruiting body. Gene. 2018;662:123–130. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li P, Deng WQ, Li TH, Song B, Shen YH. Illumina-based de novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of Amanita exitialis basidiocarps. Gene. 2013;532:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.He Y, Deng WQ, Zhang CH, Li TH. Diveristy of the MSDIN family in Amannita rimosa. Toxicon. 2019;158:S72. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE. WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004;14:1188–1190. doi: 10.1101/gr.849004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sgambelluri RM, Smith MO, Walton JD. Versatility of prolyl oligopeptidase B in peptide macrocyclization. ACS Synth Biol. 2018;7:145–152. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yilmaz I, Bakirci S, Akata I, Bayram R, Kaya E. Toxin content and toxicological significance in different tissues and development stages of Lepiota brunneoincarnata mushroom. Toxin Rev. 2015;34:109–114. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wei JH, Wu JF, Chen J, Wu BD, He ZM, Zhang P, et al. Determination of cyclopeptide toxins in Amanita subpallidorosea and Amanita virosa by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Toxicon. 2017;133:26–32. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2017.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Keeling PJ, Palmer JD. Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic evolution. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:605–618. doi: 10.1038/nrg2386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Andersson JO. Gene transfer and diversification of microbial eukaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2009;63:177–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.091208.073203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Richards TA, Leonard G, Soanes DM, Talbot NJ. Gene transfer into the fungi. Fungal Biol Rev. 2011;25:98–110. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Richards TA, Soanes DM, Jones MDM, Vasieva O, Leonard G, Paszkiewica K, et al. Horizontal gene transfer facilitated the evolution of plant parasitic mechanisms in the oomycetes. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:15258–15263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105100108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Savory F, Leonard G, Richards TA. The role of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of the oomycetes. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004805. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Dhillon B, Feau N, Aerts AL, Beauseigle S, Bernier L, Foster A, et al. Horizontal gene transfer and gene dosage drives adaptation to wood colonization in a tree pathogen. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:3451–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424293112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Katoh K, Standley DM. A simple method to control over-alignment in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:1933–1942. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Sym Ser. 1999;41:95–98. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nylander JAA. MrModeltest v2.2 Uppsala: evolutionary biology Centre, Uppsala University. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stamatakis A. RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2688–2690. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1572–1574. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Specific PCR Primers designed for peptide toxins and POP genes.
Data Availability Statement
The mushroom species and related transcriptome data, MSDIN and POP genes used in this study has been deposited at GenBank and their accession numbers can be found in Tables 1, 3, 4 and 5.