Abstract
Background
A mutation in the canine multidrug resistance MDR1 gene (also referred as ABCB1), encoding for the multidrug resistance (MDR) P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transponder, causes a pathological condition known as ‘ivermectin toxicosis’. The causative mutation, known since 2001, has been described to affects sheep herding breeds related to collie lineage. The present study is a retrospective investigation of the presence of MDR1 mutated allele in Italian dog populations in a 5 years’ time lapse. The aim of the research is to offer a deep knowledge in MDR1 allelic and genotypic frequencies in canine breeds and populations raised in Italy.
Methods
Genotype data for the 4-bp deletion (c296_299del4) in MDR1 gene from 811 dogs belonging to 32 breeds/populations were collected.
Results
The mutated allele has been found in 9 out of 31 breeds: Rough Collie, Smooth Collie, Border Collie, Bearded Collie, Shetland Sheepdog, Australian Shepherd, White Swiss Shepherd, Old English Sheepdog, Whippet and also in crossbreed. The breeds with the highest allelic mutation frequency are Smooth and Rough Collies with 75 per cent and 66 per cent of mutant MDR1 allele, respectively.
Conclusions
The results support the usefulness of this genetic analysis to optimise medical care in dogs at risk of multidrug resistance and to create an objective basis in breeding programme definition and in the risk evaluation in different breeds.
Keywords: dogs, ivermectint Toxicosisx, MDR1, breeding management, genetic analysis
Introduction
Ivermectin toxicosis is a pathological condition, first observed in shepherd dog breed in the 19th century in UK,1 caused by a mutation in the canine multidrug resistance MDR1 (also referred as ABCB1). This gene encodes for a glycoprotein2: the multidrug resistance (MDR) P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transponder. This is an ATP-driven multidrug efflux carrier2 3 belonging to the group of membrane-bound ATP-binding cassette transponder. The evident clinical signs of the neurotoxic effect promoted by the dysfunction of P-gp, caused by the expression of the mutant MDR1 gene, could even lead to coma and death.3
P-gp plays an important role in physiological barriers. In the blood/brain barrier, it limits drug efflux in the central nervous system whereas in placental trophoblast it reduces drug access to fetal circulation and in Sertoli cells barrier it limits drug entry in gonads.3
Pharmacogenetic investigation of MDR1 gene plays a pivotal role in purebred dog breed studies considering the basic function of P-gp in restricting the xenobiotics’ access.4 The risk of intrinsic and acquired multidrug resistance in clinical therapy with particular attention to cancer treatment has been first described more than 30 years ago by Ueda and colleagues.5
The causative mutation was first described in 2001 by Mealey and colleagues who demonstrated the association of ivermectin sensitivity in collies with a deletion mutation in MDR1 gene. The mutation consists in a 4-bp deletion (c296_299del4), leading to the expression of a truncated P-gp protein (7 per cent of the wild-type P-gp).6
The mutation has been described to affect sheep herding breeds related to collie lineage (Rough Collie—RoC, Smooth Collie—SmC, Border Collie—BoC, Bearded Collie—BeC, Shetland Sheepdog—ShS, Australian Shepherd—AuS) or not (German Shepherd—GeS, White Swiss Shepherd—WSS, Old English Sheepdog—OES); furthermore, MDR1 polymorphism has been described in some sighthounds (Whippet—Whi), in some ENCI-FCI (Ente Nazionale della Cinofilia Italiana—Federation Cynologique International) unofficial breeds (Miniature Australian Shepherd—MAS, Silken Windhund—SiW, Waller—Wal, McNab—McN) and in crossbreed (Cro).3 7
The present study is a retrospective investigation of the presence of MDR1 mutated allele in Italian dogs from 2012 to 2017. At present, it is the first survey about mutation distribution in Italy. The aim of the work is to offer a deep knowledge of the presence of this mutation in canine breeds and in crossbreed in Italy to raise awareness among veterinarians to optimise medical care in dogs at risk of multidrug resistance and to create an objective basis in breeding programme definition and in the risk evaluation in different breeds.
Materials and methods
Genotypic data at MDR1 locus of 811 (M: 382; F: 429) dogs from 32 populations (31 breeds+1 crossbreed) were analysed. Table 1 shows the number of dogs analysed per population.
Table 1.
List of samples tested for MDR1 mutation
| Breed and acronym | Samples |
| N | |
| Afghan Hound AfH | 1 |
| American Staffordshire Terrier AST | 2 |
| Australian Cattle Dog ACD | 2 |
| Australian Kelpie AuK | 3 |
| Australian Shepherd AuS | 202 |
| Bearded Collie BeC | 10 |
| Belgian Shepherd BeS | 4 |
| Bernese Mountain Dog BMD | 1 |
| Border Collie BoC | 208 |
| Borzoi Bor | 2 |
| Central Asia Shepherd Dog CAS | 1 |
| Crossbreed Cro | 31 |
| Czechoslovakian Wolfdog CzW | 2 |
| Dobermann Dob | 1 |
| English Bulldog EnB | 1 |
| Flat Coated Retriever FCR | 1 |
| German Shepherd GeS | 3 |
| Labrador Retriever LaR | 1 |
| Maltese Mal | 1 |
| Mudi Mud | 1 |
| Old English Sheepdog OES | 12 |
| Rottweiler Rot | 1 |
| Rough Collie RoC | 190 |
| Saarloos Wolfhound SaW | 1 |
| Schipperkee Sch | 1 |
| Shetland Sheepdog ShS | 86 |
| Shih Tzu | 1 |
| Smooth Collie SmC | 6 |
| Tibetan Mastiff | 1 |
| Welsh Corgi Pembroke | 2 |
| Whippet Whi | 5 |
| White Swiss Shepherd Dog WSS | 27 |
Sample processing and analysis were carried out by Vetogene SRL, one of the official reference laboratories for the Italian Kennel Club ENCI (FCI associate), who collected all the samples through the years (from 2012 to 2017), and provided the genotyping analysis and data for the present work. Vetogene extracted DNA from 100 to 200 µL whole blood samples using the commercial kit Qiagen DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). All samples were sent for the genetic test analysis by veterinarians who certified the identification of the sample through microchip control. The presence of the causative mutation of 4-bp deletion (c.296_299del4) in the MDR1 gene (GenBank AF045016) was tested by PCR, in Vetogene Lab, using specific primers as described by Baars and colleagues in 2008. Data were analysed using the SAS V.9.4 statistical software package PROC FREQ, a procedure to calculate genotypic and allelic frequencies per breed.8 The obtained results have been classified as the frequencies of MDR1 with homozygous wild type (+/+; clear), heterozygous (+/−; carrier), homozygous mutant (−/−; affected). Moreover, the frequency of the mutated allele MDR1 was calculated in the breed with almost five analysed animals (table 2).
Table 2.
Allelic and genotypic frequencies at MDR1 locus in affected breeds: breed and acronym, number of samples per breed (N), mutant MDR1 (MDR1−) allelic frequency (%), MDR1 genotypes (N; %)
| Breed and acronym | Samples | MDR1–frequency | MDR1+/+ | MDR1+/− | MDR−/− | |||
| N | % mutated allele | N | % genotype | N | % genotype | N | % genotype | |
| Smooth Collie SmC | 6 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 50 | 3 | 50 |
| Rough Collie RoC | 190 | 66 | 22 | 11 | 85 | 45 | 83 | 44 |
| Australian Shepherd AuS | 202 | 35 | 82 | 41 | 97 | 48 | 23 | 11 |
| Shetland Sheepdog ShS | 86 | 23 | 52 | 60 | 29 | 34 | 5 | 6 |
| Whippet Whi | 5 | 10 | 4 | 80 | 1 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Old English Sheepdog OES | 12 | 8 | 10 | 83 | 2 | 17 | 0 | 0 |
| White Swiss Shepherd Dog WSS | 27 | 7 | 23 | 85 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Bearded Collie BeC | 10 | 5 | 9 | 90 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Border Collie BoC | 208 | 4 | 193 | 93 | 15 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Crossbreed Cro | 31 | 15 | 24 | 78 | 5 | 16 | 0 | 6 |
Results
MDR1 mutated allele has been found in nine breeds (SmC, RoC, AuS, ShS, Whi, OES, WSS, BeC, BoC) listed in table 2 together with sample size. The sample size reflects the census of each breed in Italy.
The breeds with the highest mutated allele frequency are SmC and RoC with 75 per cent and 66 per cent of the MDR1 mutated allele, respectively. It is worth mentioning that tested SmC were 6, according to the low number of new registered dogs per year in Italy: 8 puppies entered in the Italian studbook in 2017.
In the sample of 202 AuS analysed dogs, the MDR1 mutated allele showed a frequency of 35 per cent, while 41 per cent of the analysed dogs did not present the mutated allele. The affected dogs are 11 per cent and the frequency of carriers (48 per cent) is one of the highest observed in the Italian analysed breeds. The presence trend of the mutant allele increased since 2012; furthermore, in 2017, AuS is the breed with the highest number of analysed dogs with 67 tested samples on a yearly entry of 2086 puppies in 2017.
In the tested sample of 86 ShS dogs, the frequency of the causative mutation of multidrug resistance gene was 23 per cent, and a much higher value has been reported by Baars and colleague9 in Germany (67 per cent), while a lower frequency (7 per cent–8 per cent) has been recorded in the USA.1 10
In the Italian tested sample, 60 per cent of the ShS dogs analysed were homozygous for the absence of the mutated allele while only 6 per cent of the ShS dogs resulted affected with the MDR1 −/− genotype.
A high number of BoC dogs was tested in Italy (208) and the MDR1 mutant allele frequency was 4 per cent, with 93 per cent of homozygous clear animals and only 7 per cent of carriers. No genetic affected dogs were observed (with −/− genotype).
Going on with collie-related breeds, tested BeC had a mutated allele frequency of 5 per cent and no homozygous mutated genotypes have been recorded in the breed in Italy. Two more breeds from the sheep herders’ group have been recorded to have MDR1 mutated allele: OES and WSS; the first one showed a frequency of mutant allele presence of 8 per cent, the second one 7 per cent; in no one of the two breeds mutant homozygous subjects were found.
The results obtained analysing 5 Whippet samples showed a 10 per cent frequency of the mutant allele, with one carrier dog.
No mutant allele was found in the other 22 breeds tested with a number of samples ranging from 1 to 4 (Afghan Hound—AfH, American Staffordshire Terrier—AST, Australian Cattle Dog—ACD, Australian Kelpie—AuK, Borzoi—Bor, Belgian Shepherd—BeS, Bernese Mountain Dog—BMD, Saarloos Wolfdog—SaW, Central Asia Shepherd Dog—CAS, Czechoslovakian Wolfdog—CzW, Dobermann—Dob, English Bulldog—EnB, Flat Coated Retriever—FCR, German Shepherd—GeS, Labrador Retriever—LaR, Maltese—Mal, Mudi—Mud, Rottweiler—Rot, Schipperkee—Sch, Shih Tzu—ShT, Tibetan Mastiff—TiM, Welsh Corgi Pembroke—WCP).
In the 31 Cro analysed, a mutated allele frequency in MDR1 gene of 15 per cent was recorded and six genotypically affected animals were diagnosed.
Discussion
One hundred nine out of 811 dogs analysed, belonging respectively to RoC (44), AuS (23) and SmC3 breed, are homozygous for the mutated MDR1 allele; moreover, 242 out of 811 are heterozygous for this mutation in 9 breeds and in the analysed crossbreed group. Forty-three per cent of all the tested dogs has at least one copy of the mutated MDR1 allele. These results underline the importance of an accurate knowledge of the genetic asset of canine pure breeds and of crossbreed in every clinical and reproductive approach.
The big sample of analysed Rough collies (n=190) reflects the census of this breed in Italy with 445 new entries in 2017. Only 11 per cent of the tested dogs are homozygous for the absence of the causative mutation, 44 per cent are affected and 45 per cent are carriers.
The mutant allele frequency recorded in Italy in these two breeds (SmC=75 per cent; RoC=66 per cent) is in accordance with those reported in UK by Tappin and colleagues in 2012,4 73 per cent and 71 per cent for SmC and RoC populations, respectively, and also with the 64 per cent reported in French RoC breed.11 Slightly lower results in MDR1 mutant frequency have been recorded in Germany: 59 per cent,7 55 per cent,12 in Japan 58.3 per cent,13 Australia 56 per cent14 and Brazil 61.2 per cent.3
In AuS, the MDR1 mutated allele frequency in Italy was calculated to be 35 per cent, a mean value considering it ranged from 15.7 per cent in Brazil2 to 46 per cent in UK.4 In the USA, the country of origin of AuS breed, Neff et al1 and Mealey and Meurs10 reported a mutant allele frequency of 17 per cent and 29 per cent, respectively. This could be considered a demonstration of the breeders’ attention and probably it is the reason of the low frequency of affected dogs registered in this breed considering, for example, that the highest number of entries in BoC in 2017 (3304) corresponded only to 62 tested dogs. Moreover, it is worth mentioning that the high frequency of carriers needs a careful programming of the reproductive choices in these breeds.
The frequency of Italian ShS affected dogs is really lower than the 33 per cent frequency reported by Kawabata et al in Japan13 and Baars et al in Germany.9 Higher frequencies have been described in Australia with 43 per cent11 and UK with 46 per cent.4 The same four base pair deletion in the canine ABCB1 gene was considered by all the cited authors.
The observed results are intermediate between the reported frequency of 2 per cent in UK and of 6 per cent in Germany.4 9 No MDR1 mutation was found in BoC, as reported by Firdova and colleagues in 201615 considering 13 different European countries. Some variability in the BoC breed results could be supposed to be related to the existing division in two attitude/origin subpopulations: the show type mainly originated in Australian and the working type mainly originated in Great Britain.16
The frequencies observed in BeC are in contrast with those reported by Tappin and colleagues in 20124 from the country of origin of the breed where no mutated alleles were found in BeC. No one of the tested subjects was homozygous for the mutation, anyway it is important to know the presence of the mutated gene in BeC breed considering the reduced number of breeders in the breed (73 puppies entered in 2017 in Italian ENCI studbook).
Dekel reports a 37.5 per cent frequency of mutant allele in OES,17 which is the highest published frequency for the breed.4 7 15 For WSS, a slightly higher frequency was calculated by Gramer and colleagues in 2011 in Germany7 and by Dekel and colleagues in Israel in 2017,17 about 14 per cent and 16.7 per cent, respectively.
About Whi: the mutation has been described in the FCI as unrecognised long-haired whippet SiW in the USA with a 16–18 per cent frequency,1 10 but no mutation was found in the 14 samples analysed in UK by Tappin et al in 20124 and in the 53 samples tested by Monobe and colleagues in Brazil.3
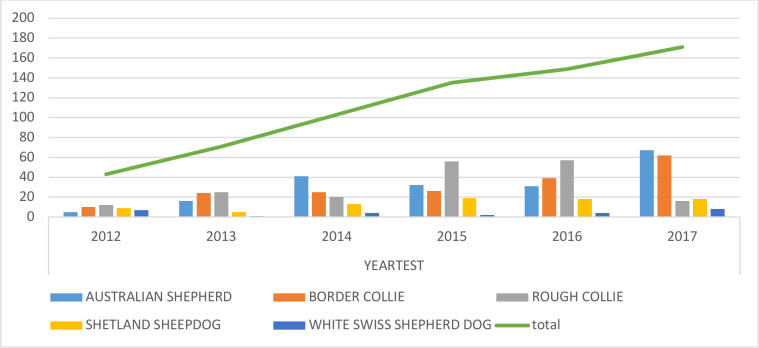
MDR1 mutation test is available since 2008 when the first animals were tested for (2009 n=0, 2010 n=2, 2011 n=3). A clear increase in the number of animals tested has been recorded since 2012 (n=44). In figure 1, the number of animals tested per breed per year and the total tested animal have been reported: a constant increase in the total number of tests has been shown, and a constant positive increase in tested BoC number is described. In the breeds where a negative variation has been recorded, it could be supposed that the produced litters are out of tested parents, so the genetic asset of the litter is known: ‘clear by parentage’. Furthermore, the knowledge of the genetic combination causing ivermectin toxicosis is very important in small effective population sized breeds like SmC where carriers should be bred with mutation clear partners to ensure high levels of genetic variability and to reduce the pathological mutated allele frequency in the next generation. Furthermore, considering the obtained results, MDR1 mutation testing in crossbreed specimens where British sheepherding breeds’ ancestors could be supposed, could be very effective in the definition of appropriate therapeutic treatments.
Figure 1.
Average yearly variation in test frequency per breed per year (2012–2017); %.
In conclusion, the presented results underline the importance of an accurate knowledge of the MDR1 allele distribution in pedigree dogs to optimise clinical treatments and reproductive management. The presence, the prevalence and the effects of the mutation should be taken into consideration in breeding strategy planning aiming to eliminate the causative mutation in the breeding stock, constantly monitoring inbreeding levels and limiting genetic variability losses.2 3 The supplied data could be used both to establish prevention and therapeutic programmes and to trace down selection plans in the presented breeds considering both the differences in breed diffusion and the mutated allele frequencies in the different geographical areas.
Footnotes
Contributors: All the authors contributed in the same way to data collection and analysis and to paper writing.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement: All processed data were supplied By Vetogene SRL, Milan Italy.
References
- 1.Neff MW, Robertson KR, Wong AK, et al. Breed distribution and history of canine mdr1-1Delta, a pharmacogenetic mutation that marks the emergence of breeds from the Collie lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004;101:11725–30. 10.1073/pnas.0402374101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mizukami K, Yabuki A, Kohyama M, et al. Molecular prevalence of multiple genetic disorders in border collies in Japan and recommendations for genetic counselling. Vet J 2016;214:21–3. 10.1016/j.tvjl.2016.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Monobe MM, Junior JPA, Lunsford KV, et al. Frequency of the MDR1 mutant allele associated with multidrug sensitivity in dogs from Brazil. Vet Med 2015;6:111. 10.2147/VMRR.S72373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tappin SW, Goodfellow MR, Peters IR, et al. Frequency of the mutant MDR1 allele in dogs in the UK. Vet Rec 2012;171:72.2–72. 10.1136/vr.100633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ueda K, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Isolation and sequence of the promoter region of the human multidrug-resistance (P-glycoprotein) gene. J Biol Chem 1987;262:17432–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Roulet A, Puel O, Gesta S, et al. MDR1-deficient genotype in Collie dogs hypersensitive to the P-glycoprotein substrate ivermectin. Eur J Pharmacol 2003;460:85–91. 10.1016/S0014-2999(02)02955-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gramer I, Leidolf R, Döring B, et al. Breed distribution of the nt230(del4) MDR1 mutation in dogs. Vet J 2011;189:67–71. 10.1016/j.tvjl.2010.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Institute SAS Base SAS 9.4 procedures guide: statistical procedures. SAS Institute, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baars C, Leeb T, von Klopmann T, et al. Allele-specific polymerase chain reaction diagnostic test for the functional MDR1 polymorphism in dogs. Vet J 2008;177:394–7. 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.05.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mealey KL, Meurs KM. Breed distribution of the ABCB1-1Delta (multidrug sensitivity) polymorphism among dogs undergoing ABCB1 genotyping. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2008;233:921–4. 10.2460/javma.233.6.921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hugnet C, Bentjen SA, Mealey KL. Frequency of the mutant MDR1 allele associated with multidrug sensitivity in a sample of collies from France. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2004;27:227–9. 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2004.00585.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Geyer J, Döring B, Godoy JR, et al. Frequency of the nt230 (del4) MDR1 mutation in Collies and related dog breeds in Germany. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2005;28:545–51. 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2005.00692.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kawabata A, Momoi Y, Inoue-Murayama M, et al. Canine MDR1 gene mutation in Japan. J Vet Med Sci 2005;67:1103–7. 10.1292/jvms.67.1103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mealey KL, Munyard KA, Bentjen SA. Frequency of the mutant MDR1 allele associated with multidrug sensitivity in a sample of herding breed dogs living in Australia. Vet Parasitol 2005;131:193–6. 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Firdova Z, Turnova E, Bielikova M, et al. The prevalence of ABCB1:c.227_230delATAG mutation in affected dog breeds from European countries. Res Vet Sci 2016;106:89–92. 10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.03.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Studdert VP, Mitten RW. Clinical features of ceroid lipofuscinosis in border collie dogs. Aust Vet J 1991;68:137–40. 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1991.tb03156.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dekel Y, Machluf Y, Stoler A, et al. Frequency of canine nt230(del4) MDR1 mutation in prone pure breeds, their crosses and mongrels in Israel—insights from a worldwide comparative perspective. BMC Vet Res 2017;13:333. 10.1186/s12917-017-1251-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]