Abstract
Nitrogen (N) deposition is a serious environmental issue for soil fertility and human wellbeing. Studies on various terrestrial ecosystems yielded fragmented information on soil-N status (microbial biomass- and mineral-N) and dynamics (N-mineralization and -leaching) whereas the holistic view on this issue is relatively unknown. A complete understanding of soil-N status and dynamics in response to N deposition is essential for sustainable management of ecosystem structure and function as needed for human wellbeing. Therefore, we conducted an experiment in the N-limited tropical grassland to explore the question whether N-deposition weakens the soil-N status and dynamics; if yes, then what could be the optimum amount of deposited N and the related controlling mechanism? We undertook a 3-year (2013–2016) experimental N fertilization (control, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 kg N ha−1 year−1) study (using urea as a source of N deposition). The data from a total of 72, 1 × 1 m plots (six treatments with 12 replicates) were collected and properly analysed with statistical software. N deposition caused significant differences in the parameters of soil-N status and dynamics. The responses of microbial biomass-N, N-mineralization, and mineral-N to the N deposition were quadratic (maximum values were in N90) whereas N-leaching showed a linear response. Compared to control, N deposition (30–150 kg N) consistently enhanced (29–96%) leaching of N. As a mechanism, acidification induced aluminium toxicity, carbon to nitrogen ratio and litter decomposition governed the soil-N status and dynamics. N deposition over and above 90 kg ha−1 year−1 resulted in a negative feedback to soil N transformation and availability. Hence, N deposition below 90 kg ha−1 year−1 could be a limit for the sustainable functioning of the tropical or similar grasslands.
Subject terms: Ecology, Ecology
Introduction
Globally, N deposition has been identified as a major threat to the functioning of the sensitive ecosystems1,2. Fossil fuel combustion, biomass burning, changes in land use pattern and use of N-fertilizer have been identified as major contributors of atmospheric-N depositions1,2.These N deposition sources doubled the global N cycle over the last century3. Studies have suggested that in 1,860 the reactive-N deposition for terrestrial ecosystems was 15.88 Tg year−1 and at the beginning of the 1990s it was 63.5 Tg year−1 which is four times higher than that in 18604. According to Galloway et al.5 and Zhou et al.6, recently, the global ecosystems are receiving a very high rate of N deposition, often > 100 kg N ha−1 year−1 and it may reach up to 125.2 Tg year−1 by 20504,7. The deposition is expected to increase by a factor of 2.5 over the next century8. In the Asian region, the predicted reactive-N deposition by 2030 would be more than 1.5 times higher (from 67.7 to 105.3 Tg year−1) than that of 20009 and by 2020 it is likely to exceed the combined emissions of North America and Europe10. On the other hand, the global N fertilizer uses in 1960 and 2000 were 3.5 and 87 million metric tons (MT) and by 2050, it would be around 249 million MT1. These estimates indicated that between 1960 and 2000, annual N fertilizer use was 2.09 million MT and by 2050 it would increase by 2.73 million MT annually. To feed the hungry world (through massive food and agriculture production) has been identified as a major reason for tremendous hike in the global N fertilizer use and emission. These studies reflected synchronization of atmospheric-N deposition and N fertilization1,2,11–13 (henceforth, N fertilization is referred to as N deposition).
The N deposition and its associated processes responsible for changes in structure and functioning of the ecosystems constitute a big challenge to the mankind, and in future, the situation would be horrific11–13. Studies from various terrestrial ecosystems showed disturbances in normal soil-N status (NH4+-N, NO3−-N, total mineral-N, microbial biomass nitrogen; MBN) and dynamics (ammonification, nitrification, N mineralization and rate of soil-N leaching) owing to atmospheric N depositions14–19. These perturbed N status and dynamics have changed plant composition, diversity20, productivity and carbon storage capacity of the concerned ecosystems5,21,22. Due to N deposition induced changes in the normal N cycling23, further increasing rate of N deposition is assumed to be one of the main modulators of the global climate change19,24,25 which is seriously threatening the human well-beings5,26–28.
Among the soil N pools, MBN has been observed as an indicator of soil fertility and normal N cycling29,30. Reports suggested decreasing30, increasing31 and no32 effect of N deposition on the MBN. Thus the responses of MBN to N depositions are inconclusive and need more studies to conclude. Therefore, the feedbacks of MBN to the atmospheric-N depositions from diverse ecosystems need urgent study for predicting its impact on the soil health and global N cycling33.
Soil-N mineralization is a fundamental step of soil-N transformation33, governing the status of soil fertility34 and fate of NO3− leaching35. The research on the response of N-mineralization to N-deposition dates back to the early 1970s, since then the results are fragmentry and indecisive; viz: increased36–38, decreased30,39 and no pattern40–42. Hence; similar to MBN, the assessment of N deposition effect on soil-N mineralization from different ecosystems are imperative43.
The excess N deposition leads to high N availability and causes N saturation44, although N deposition may increase soil N-mineralization in the N-limited ecosystems, and decrease the MBN as well as N retention capacity of the soil45. The excess N goes beyond the availability of plants and microbes and is lost through leaching46,47 or gaseous emissions44. Therefore, determination of N deposition threshold of an ecosystem prior to occurrence of negative impacts on its soil-N pools and processes is essential. Determining the N threshold will be helpful to the policymakers for curbing the N loss via gaseous and soil-N leaching23,45.
Temperate and sub-tropical studies have improved our understanding of the fate of soil-N leaching in response to N deposition. These studies suggested increased N-leaching on account of increased N deposition48. This pattern has been argued because of increased N availability and decreased N retention capacity of the soil49. Similar to other parameters of soil-N pools and processes, our understanding on the response of N leaching to the N deposition from the tropical grasslands is not much known. It is expected that the response of N leaching in tropical ecosystems may differ from that of temperate and sub-tropical ecosystems because tropical ecosystems are not limited to N-saturation50 and are characterised by marked seasonality21,22,29. Added to it, the response of inorganic N leaching to the N depositions in natural ecosystem is thought to be complex and non-linear, due to differences in climate, vegetation and soil attributes49. Hence, from the N management view point and prediction of global N-leaching response to the N deposition, information from tropical ecosystems could be valuable50.
The N deposition and its consequences on soil-N status, dynamics and leaching from agroecosystems, grasslands and forests of temperate, tropical and sub-tropical ecosystems are fragmentary4,7,23,51,52. Unfortunately these studies lack the holistic response of soil-N status and dynamics to N deposition53. On one hand, the tropics are major sources and sink of atmospheric N deposition4 compared to other regions50 because of tremendous human pressure on per capita utilization of food and energy7. On the other hand, these regions are losing their biodiversity at an alarming rate due to high biotic pressure54 and N depositions23,55. For example, most tropical grasslands are being converted into shrub, semi-desert and desert like ecosystems which are progressively species poor56. As, N often limits the growth and survival of plants in majority of ecosystems23,55, above situations together with seasonality-governed functioning of the tropical soils21,22,29 prompted us to understand the complete fate of soil-N status and dynamics against the N deposition from N-limited tropical grasslands which are experiencing very high rates of anthropogenic pressure and N deposition.
It has been reported that the soil base and non-base cations, soil acidification and N deposition are directly linked57; therefore, analysis of base and non-base cations could be useful in understanding the mechanism of soil-N pool and processes in response to the atmospheric N deposition. The out-come of this study could be helpful in determining the optimum amount of N required for the sustainability of the tropical grassland. Also, the current study could be valuable in global generalization of soil-N status and dynamics in view of the increasing levels of N deposition because until recently no study has considered holistic approach for understanding the effects of N deposition on the soil-N status and dynamics. However, studies on individual responses of soil-N pools and processes to the N deposition are frequently available19,31,32,48,58.
Looking into the above accounts; we have set a hypothesis that N depositions weaken the soil-N status and dynamics. If the hypothesis is supported, then what could be the optimum amount of deposited N and what could be the controlling mechanism for soil-N status and dynamics for sustainability of tropical grasslands. Specifically, the objectives of the present study were (i) to determine the responses of MBN, rates of N-mineralization, available soil-N and leaching of mineral-N to the N deposition, (ii) to understand the mechanism governing the soil-N pool and processes in relation to the N deposition from a three-year external N-manipulative experiment conducted in a tropical grassland.
Materials and methods
Study location
The study was conducted on 72 plots on the campus of the Banaras Hindu University (24° 18′ N and 83° 03′ E and 76 m m.a.s.l. altitude), during July 2013 to June 2016 in the Indo Gangetic Basin of eastern Uttar Pradesh located in Varanasi district of India (Fig. 1). The climate of the study area is tropical monsoonal with three different seasons; a cold winter (November–February), a hot summer (April–June) and a warm rainy season (July–September). October and March are transitional periods between rainy and winter, and between winter and summer seasons, respectively59. During the study period, mean maximum temperature was 31 °C while mean minimum temperature was 20 °C and the mean annual precipitation was 969 mm. The soil is categorised as Banaras Type III60, alluvial, well-drained, pale brown, silty loam, inceptisol61 and moderately fertile being low in available N and medium in available phosphorus and potassium62 with neutral to alkaline soil pH63.
Figure 1.
Location of the 3-year of experimental nitrogen (N) inputs plots in Tropical grassland on the campus of Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. Map was created by Dr. P. Verma (co-author of the ms) using ArC Map 10.4 (ESRI, Redland, CA, USA) software and https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/.
The campus of the Banaras Hindu University is spread in ≈ 520 ha land area having a luxuriant growth of natural flora. Azadiracta indica, Dalbergia sissoo, Madhuca longifolia, Mangifera indica, Sterculia alata, Tamarindus indica, Tectona grandis, Zizyphys glaberrima, etc. are locally top canopy dominating species while Alysicarpus monilifer, Cynodon dactylon, Cyperus compressus, Desmodium gangeticum, Dichanthium annulatum, Evolvulus nummularius, Imperata cylindrica, Malvastrum coromandelianum, Oplismenus burmannii, Sida acuta are the locally dominating species of ground vegetation21,56.
Experimental design
A 20 × 20 m open area having natural herbaceous vegetation and substantially away from the buildings was selected in the horticulture premise of the University. Within this; 72, 1 × 1 m experimental plots (plot size determined by species-area curve), arranged in 6 parallel rows (12, 1 × 1 m plots in each row) were established. Surface-to-belowground boundary of each 1 × 1 m plot was permanently demarcated by using bricks and cement (10 cm wide and 50 cm depth). A 1 m distance between two 1 × 1 m plots was kept as buffer zone to protect against boundary effects due to the migration of N out of the sampling areas. Six treatments of N, each replicated twelve times, were randomly established on the basis of lottery method: control (without N), N30 (30 kg N ha−1 year−1), N60 (60 kg N ha−1 year−1), N90 (90 kg N ha−1 year−1), N120 (120 kg N ha−1 year−1) and N150 (150 kg N ha−1 year−1)64.
Before the N treatment to the plots; soil bulk density, soil-porosity, -water holding capacity, -sand, -silt and -clay contents for the experimental plots were analysed. Across the plots; values of soil bulk density (g cm−3), percentage soil-porosity, -water holding capacity, -sand, -silt and -clay contents varied from 1.23–1.26, 52–54, 48–49, 8–9, 77–79 and 12–13, respectively. Statistically; none of these soil variables varied due to designated N-levels. Thus, before the initiation of the experiment, the selected plots were homogenous in soil characteristics.
N-inputs
Similar to other studies65,66, urea fertilizer was used as a source of N deposition because it has high (46%) N content, zero phosphorus and potassium and is comparatively inexpensive, stable, and easy to handle and it alone contributed more than 50% of the global atmospheric-N deposition2. The urea was applied in the evening in each month to avoid the N loss due to volatization21,64. For calculating the monthly doses, the total annual N dose of each N level was equally divided into 12 applications. We deliberately used a wide range of N-level with a maximum of 150 kg N ha−1 year−1 to understand the measureable responses of soil-N attributes and threshold tolerance of soil N to the N deposition within the tropical grassland.
Sampling and analyses
The soils were sampled at two depths (0–10 cm and 90–100 cm depths from the soil surface). For each N-level, three soil samples (0 to 10 cm depth) were collected from each 1 × 1 m plot, for each month of the year starting from 2013 to 2016 by using a 5 cm-diameter corer. For each soil depth, the three soil samples collected from each 1 × 1 m plot were combined to form a composite soil sample for each plot. These composite soil samples of 0–10 cm depth were gently homogenized. Carefully, large roots, woods, litters and all fine roots were removed from the composite soil samples.
One part of soil sample was air dried, sieved through 2 mm mesh screen and analyzed soil-pH, total organic-carbon (C), total soil-N (TN), ammonium-N (NH4+-N) and nitrate–N (NO3−-N). Soils of 0–10 cm depth were used for the analysis of soil N mineralization, microbial biomass carbon; MBC and MBN. To understand the leaching; the soils of 90–100 cm depth were collected by inserting a 100 cm long metallic corer into soil by avoiding the root injury. These soil samples were used for the estimation of NH4+-N and NO3−-N67. Total soil-N (TN) was determined by micro-Kjeldahl digestion method68. NH4+-N was extracted by 2 M KCl and analyzed by using the phenate method69. The concentration of NO3−-N was analyzed by the phenol disulphonic acid method after extraction by CaSO468.
For the analysis of litter decomposition, nylon net litter bag (10 × 10 cm) technique70 was adopted. In this analysis, 100 g of air-dried mixed leaf litters of grasses and forbs were used. The mesh size of the litter bags was 1 mm which easily allows the movement and activity of soil microorganisms. Litter decomposition was determined by computing the decay constant (k). The negative exponential decay (k = − ln (Xt/X0)/T) model was used to compute the k71–73. In the equation; X0 is the initial dry weight, Xt the dry weight remaining at the end of the investigation time T (1 month).
The in situ buried bag technique was adopted for N-mineralization. Before incubation, the NH4+-N and NO3−-N concentrations were determined for zero-month sampling. Using a large sealed polythene bag, a portion of fresh soil sample (200 g) was incubated in soil at a depth of 0–10 cm on the same microsite from which the samples had been collected for the analysis of NH4+-N and NO3−-N. After one month of field incubation, the incubated bags were collected for the analysis of NH4+-N and NO3−-N. Again, a portion of fresh soil sample (200 g) was incubated on the same microsite from which the samples had been collected for the analyses of NH4+-N and NO3−-N and after one month of incubation the incubated samples were re-collected and NH4+-N and NO3−-N were re-analyzed. These analyses were repeated for each month of the entire experimental period after an interval of 30 days from 1st July 2013 to 24th June 2016. The increase in the concentrations of NH4+-N and NO3−-N after field incubation is referred to as ammonification and nitrification, respectively and the increase in the amount of NH4+-N plus NO3−-N over the course of field incubation is defined as total N mineralization73.
MBC and MBN were determined by the chloroform fumigation-extraction method using 0.5 M K2SO4 as an extractant74. The organic-C of extract was estimated by oxidation with potassium dichromate. The difference in the organic-C content between the fumigated and unfumigated extracts was converted to MBC by dividing with a conversion factor of 0.4575. The MBN was estimated by micro-Kjeldahl digestion procedure from the extracts. The difference in N content between the fumigated and unfumigated extracts was converted to MBN by dividing with a conversion factor of 0.5476.
For the analysis of soil base cation and non-base cations, dried soil samples in triplicate were homogenized by grinding to fine powder followed by digestion in di-acid (HNO3 and HClO4 in 9:4 ratio) solution77. The contents of soil Na+, K+, Al3+ and Fe3+ were determined with Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer; AAS (Analyst-800, PerkinElmer Inc., Norwalk, CT, USA). For all the metals; blank and standards (Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., India) were run after every five samples to check the accuracy and precision of the results (within 2% of the certified value).
The analyses of litter decay constant, C/N ratio, pH and MBC/MBN ratio were used for explaining the patterns of soil-N pools and dynamics to the N depositions. Similarly, base and non-base cations were used. We used these variables as explanatory variables because under the scenario of N deposition these variables are supposed to be interlinked with the soil-N pools and dynamics.
For understanding the effects of N deposition on the response variables, the effect sizes (response ratio; RR) were computed following the equation of Hedges et al., (1999)78. For a given variable; the RR was estimated as the ratio of its value in the N treatment group (Xt) to that in the control group (Xc). It was transformed in log scale to improve its statistical behaviour, hence the ln RR = ln (Xt/Xc) or ln Xt − ln Xc equation was used. ln RR was assumed to follow a normal distribution79,80. The optimum amount of N deposition (before the negative feedback) required for the maximum beneficial responses of the selected variables of soil-N status and dynamics were computed based on the best-fitted regression equations between the N-levels and corresponding parameters of soil-N status and dynamics.
Statistical analyses
Repeated measures analysis of variance (RANOVA) procedure selecting general linear model (GLM) option in SPSS package81 was used to notice the effects of year, month, and season on the parameters of soil-N status and dynamics. In these analyses, year and season were used as within-subject variable and N-levels as between-subject factor. Tukey’s HSD test was used to determine the significance of differences in the values of these variables between different treatment pairs. Pearson correlation coefficient was established between the different response variables with the help of the SPSS package81. The MBN and N mineralization parameters were linearly regressed with the soil-pH, TN, C/N ratio and decay constant opting linear regression option in SPSS software81. A path analysis was constructed by using AMOS 16.0 software82, which executes the “structural equation modelling/analysis of covariance structures/causal modelling”. It was based on the linear correlation analysis and represented graphically to visualize the direct and indirect interactions among the predictors and the dependent variables83. In the path analysis; MBC/MBN ratio, N mineralization, inorganic-N and leaching of mineral-N were defined as dependent variables. The N-levels, soil-C:N, -pH and litter decay constant were defined as predictor variables.
Results
Soil pH
Season, year, N-levels and their interactions caused significant variations in the soil-pH (Table 1). The soil-pH decreased with the progress of the experimental duration and N-levels. Effect size analysis also indicated a consistent decline of soil-pH due to increasing amount of N deposition (Fig. 2).
Table 1.
Summary of repeated measures analysis of variance (F-value and degree of freedom; df) indicating the effects of year (Y), season (S), nitrogen (N) levels and their interactions on the soil N pools and fluxes during three-year of N manipulated study in a Tropical grassland located on the campus of Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
| Soil variables | Year (Y) | Season (S) | N-levels (N) | Y × S | S × N | Y × N | Y × S × N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1,66 | F1,198 | F5,198 | F2,198 | F5,198 | F5,66 | F10,198 | |
| Soil-pH | 905*** | 6,534*** | 1,017*** | 38.76*** | 69.36*** | 37.38*** | 23.08*** |
| MBN | 28.42*** | 966*** | 89.40*** | 0.78NS | 15.26*** | 1.54NS | 3.67** |
| Ammonification | 2,394*** | 17,392*** | 24.80*** | 486*** | 34.91*** | 66.93*** | 7.62*** |
| Nitrification | 1556*** | 8,144*** | 16.98*** | 151*** | 18.00*** | 37.82*** | 5.89*** |
| N-mineralization | 2,854*** | 14,878*** | 21.20*** | 351*** | 29.84*** | 72.25*** | 5.84*** |
| NH4+-N | 2,924*** | 6,611*** | 137*** | 98.61*** | 56.50*** | 107*** | 15.61*** |
| NO3−-N | 1744*** | 15,327*** | 236*** | 25.16*** | 437*** | 8.00*** | 69.35*** |
| Inorganic-N | 3,392*** | 17,150*** | 175*** | 131*** | 169*** | 58.88*** | 8.71*** |
| Total-N | 21.48*** | 1,469*** | 33.56*** | 14.34*** | 48.72*** | 1.75NS | 3.17** |
| NH4+-N leaching | 680*** | 11,099*** | 74.56*** | 164*** | 80.68*** | 11.85*** | 2.75* |
| NO3−-N leaching | 5,991*** | 54,839*** | 222*** | 959*** | 325*** | 141*** | 36.74*** |
| Inorganic-N leaching | 2,861*** | 27,621*** | 136*** | 449*** | 166*** | 51.95*** | 10.90*** |
MBN microbial biomass nitrogen. *P ≤ 0.01; **P ≤ 0.001; ***P ≤ 0.0001 and NS insignificant.
Figure 2.
Effect size responses of soil pH, decay constant, ratios of microbial biomass carbon (MBC) to the microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) and carbon (C) to nitrogen (N) and various soil N pools and fluxes to the different levels of experimental N input in Tropical grassland, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. Error bars represent the standard deviation. R = Pearson correlation coefficient, P = level of significance.
Concentrations of soil base and non-base cations
Across the N-levels, the concentrations (g Kg−1 of soil) of Na+ and K+ soil base cations ranged from 1.03 to 1.34 and 6.37–7.52, respectively. The concentrations (g Kg−1 of soil) of Al3+ and Fe3+ (non-base cations) varied from 36.63 to 48.79 and 8.95–9.59, respectively (Table 2). The values were greater in N treated plots compared to control plots. The K+ (R = 0.97, P ≤ 0.002) and Al3+ (R = 0.98, P ≤ 0.001) positively responded to the N-levels (Fig. 3). Interestingly, the Al3+ was linearly and negatively related with the soil-pH (Fig. 3).
Table 2.
Yearly, seasonally and nitrogen treatment-wise variations in the soil-N pools and fluxes and soil pH during 3-years of N-manipulative study in a Tropical grassland, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
| Variables | Year | Season | N-levels | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | Rainy | Winter | Summer | Control | 30 N | 60 N | 90 N | 120 N | 150 N | |
| Soil-pH | 7.12c (0.06) | 7.04b (0.06) | 6.92a (0.06) | 6.78a (0.04) | 7.03b (0.04) | 7.26c (0.03) | 7.80f (0.02) | 7.37e (0.03) | 7.15d (0.02) | 6.92c (0.02) | 6.68b (0.03) | 6.22a (0.02) |
| MBN | 66.89b (6.85) | 68.8b (8.90) | 63.42a (6.36) | 55.37a (7.21) | 65.59b (6.33) | 78.16c (8.78) | 51.76b (0.85) | 75.01c (3.00) | 83.01d (3.63) | 88.51e (3.12) | 53.74b (1.47) | 46.22a (1.67) |
| Ammonification | 13.79 b (0.32) | 12.54b (0.30) | 11.36a (0.27) | 18.88c (0.26) | 9.70 b (0.19) | 8.76a (0.17) | 10.17a (0.35) | 12.12abc (0.51) | 13.87cd (0.66) | 14.70d (0.70) | 13.16bcd (1.16) | 11.36ab (0.87) |
| Nitrification | 9.52b (0.25) | 8.80b (0.23) | 7.59a (0.19) | 13.34c (0.20) | 6.80b (0.15) | 5.90 a (0.12) | 6.98 a (0.23) | 8.51c (0.50) | 9.35c (0.58) | 10.18d (0.71) | 8.86cd (0.81) | 7.97ab (0.66) |
| N-Mineralization | 23.31b (0.56) | 21.34b (0.52) | 18.95 a (0.46) | 32.22c (0.45) | 16.50b (0.33) | 14.66a (0.27) | 17.15a (0.58) | 20.63abc (1.00) | 23.22cd (1.21) | 24.88d (1.41) | 22.02bcd (1.97) | 19.33ab (1.53) |
| NH4+-N | 7.11c (0.19) | 6.47b (0.13) | 5.27a (0.15) | 4.22a (0.10) | 6.39b (0.12) | 8.24c (0.16) | 4.61a (0.17) | 5.91c (0.20) | 6.97d (0.20) | 8.59e (0.26) | 6.16cd (0.21) | 5.45b (0.19) |
| NO3—N | 4.34c (0.11) | 3.86b (0.12) | 3.54a (0.10) | 2.60 a (0.05) | 3.77b (0.06) | 5.36c (0.11) | 2.66a (0.09) | 3.68c (0.08) | 4.73e (0.12) | 5.20f (0.19) | 3.99d (0.16) | 3.20b (0.12) |
| Inorganic-N | 11.44c (0.29) | 10.33b (0.23) | 8.81 a (0.24) | 6.83 a (0.13) | 10.16b (0.18) | 13.60c (0.24) | 7.28a (0.25) | 9.59c (0.28) | 11.70e (0.31) | 13.79f (0.43) | 10.15d (0.34) | 8.65b (0.27) |
| Total-N | 1.65a (0.17) | 1.90b (0.21) | 1.79b (0.20) | 2.49c (0.31) | 1.70b (0.20) | 1.15a (0.07) | 1.23a (0.06) | 1.60bc (0.09) | 2.23d (0.10) | 2.44d (0.13) | 1.74c (0.07) | 1.43ab (0.03) |
| NH4+-N Leaching | 1.65a (0.10) | 2.14b (0.14) | 2.50c (0.15) | 4.42c (0.09) | 1.61b (0.06) | 0.26a (0.01) | 1.42a (0.14) | 1.73b (0.16) | 1.90c (0.16) | 2.23d (0.18) | 2.33e (0.19) | 2.97f (0.24) |
| NO3—N Leaching | 2.85a (0.14) | 3.83b (0.19) | 4.54c (0.23) | 6.99c (0.14) | 3.58b (0.08) | 0.64a (0.02) | 2.41a (0.18) | 3.23b (0.23) | 3.74c (0.28) | 4.04d (0.28) | 4.38e (0.31) | 4.62f (0.33) |
| Inorganic-N Leaching | 4.49a (0.24) | 5.97b (0.32) | 7.04c (0.38) | 11.41c (0.22) | 5.19b (0.13) | 0.90a (0.02) | 3.83a (0.32) | 4.96b (0.39) | 5.64c (0.43) | 6.27d (0.46) | 6.71e (0.50) | 7.59f (0.56) |
The rates of ammonification, nitrification and N mineralization are in µg g−1 month−1. The values of soil total-N are in g kg−1 of soil. The values of inorganic-N (NH4+-N, NO3−-N), N-leaching, microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) are in µg g−1. The values in parentheses are ± 1SE. The means within a column superscript with different letters within a predictor variable are significantly different from each other at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 3.
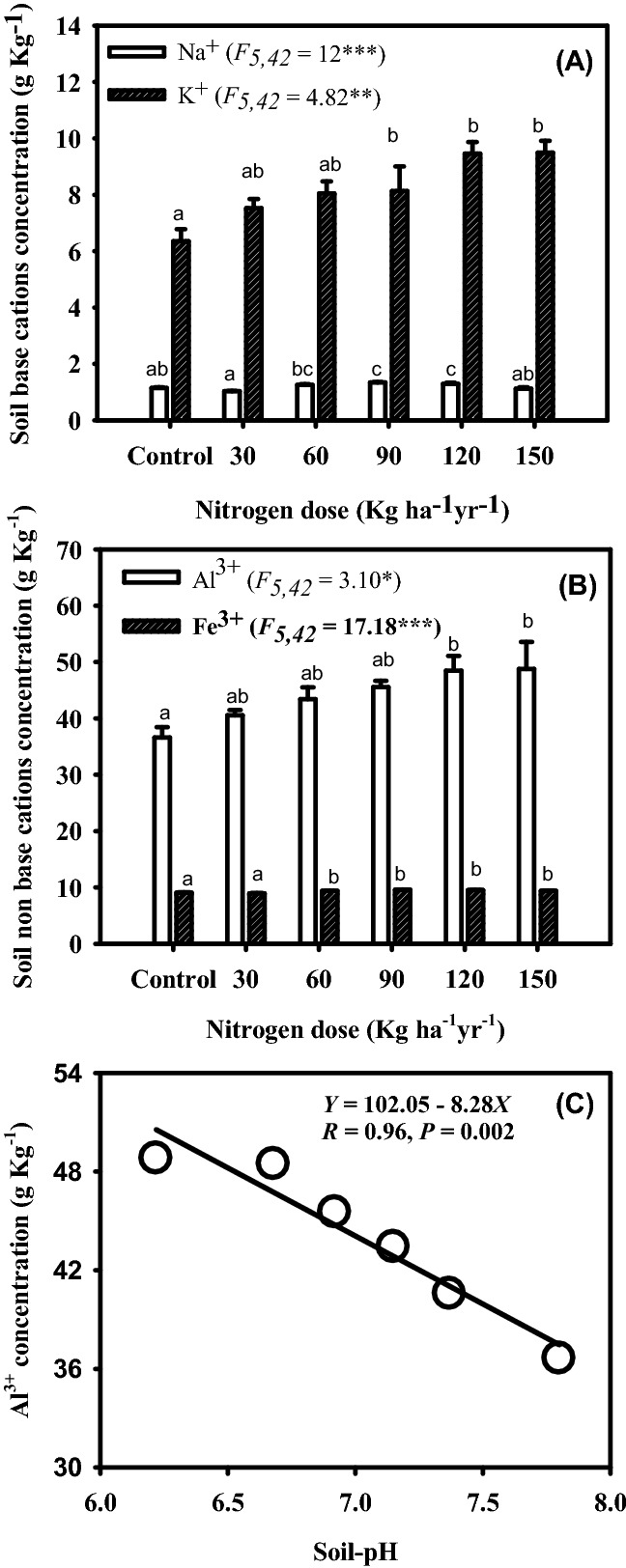
Variations in the soil base (A) and non-base (B) cations due to different levels of N inputs and relationship between concentration of Al3+ and soil pH (C) during 3-year of N manipulative study in Tropical grassland on the campus of Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. The bars within a diagram affixed with different letters are significantly different from each other at P < 0.05.
Soil microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN)
Across the N-levels, MBN (µg g−1) varied from 415; N150 level to 545; N90 level (Table 2). RANOVA showed significant effects of year, season, N-levels, season × year, season × N-levels, year × N-levels and season × year × N-levels on the MBN (Table 1). Yearly, the MBN was maximum in second-year of the experiment and minimum in the third-year of the experiment (Table 2). Tukey’s HSD test showed significant differences in the values of the MBN among the different year-pairs (Table 2). Season-wise, it was minimum in rainy and maximum in the dry season (Table 2). The Tukey’s test yielded a significant difference in the MBN between rainy and winter, between winter and summer and between summer and rainy seasons (Table 2). Response size of the MBN to the N-levels was humped-shape (Fig. 2). Compared to control, the percent change in the MBN for each N-level varied between -11; N150 level and 21; N90 level (Fig. 4).
Figure 4.
A conceptual framework for the percentage change in soil N pool and fluxes at 0 to 10 cm soil depth and proportional change in the leaching of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N to the three-year of N manipulative study in Tropical grassland, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
Rate of N-mineralization
Across the N-levels; ammonification, nitrification and total N-mineralization ranged from 10.17 to 14.70, 6.98–10.18, and 17.15–22.02, respectively (Table 2). The values of these parameters were low in N0 and high in N90 (Table 2). Year wise, the ammonification (µg g−1 month−1), nitrification (µg g−1 month−1) and total N-mineralization (µg g−1 month−1) varied between 11.36 and 13.79, 7.59 and 9.52, and 18.95 and 23.31, respectively. The values were minimum for the third-year of the experiment and maximum for the first-year of the experiment. Minimum values were observed in the dry season and maximum in the rainy season (Table 2). Results showed differences in the values of total N-mineralization as well as its components due to differences in the year, season, N-levels and their possible interactions (Table 1). The Tukey’s test suggested major variations in the values of the third-year N-mineralization with those of the first and second years. Similarly, these parameters varied between different season-pairs (Table 2). The response effect sizes of these parameters to the N-levels were quadratic (Fig. 2). Compared to the N0, the percent changes in ammonification, nitrification and total N-mineralization for each N-level varied from 31 to 93, 19–97 and 27–94. Also, these parameters showed quadratic responses to the N-levels (Fig. 4). The ammonification, nitrification and net N-mineralization were positively related with the decay constant (R = 0.37–0.45, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72), negatively with C/N (− R = 0.54–60, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72) and MBC/MBN ratios (− R = 0.58–0.59, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72) and quadratically with the soil-pH (R = 0.46–0.54, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72).
The ammonification, nitrification and total N-mineralization promptly increased from the end of the dry season to the onset of the rainy season (Fig. 5). Such pattern indicated a quick response of N mineralization to the first-rain event after a period of dry season.
Figure 5.

Comparison of microbial biomass carbon (MBC), nitrogen (MBN) and parameters of N mineralization (µg g−1 month−1) from the end of dry season to the start of rainy season during a 3-year of N manipulative study in Tropical grassland, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
Mineralized N (NH4+-N, NO3−-N, inorganic-N)
Yearly, the amount of NH4+-N, NO3−-N, inorganic-N (µg g−1) varied from 5.27 to 7.11, 3.54–4.31 and 8.81–11.44, respectively (Table 2). In the same order, the seasonal values of these parameters ranged from 4.22 to 8.24, 2.60–5.36 and 6.83–13.60. Across the N-levels, their corresponding values ranged between 4.61 and 8.59, 2.66 and 5.20, and 7.28 and 13.79 (Table 2). The values of these variables were minimum in the third-year of the experiment and maximum in the first-year of the experiment. These results suggested reduction of available-N due to longer period of N deposition. Season-wise, the values of available-N were minimum in the rainy season and maximum in the summer season. Similarly, N level-wise, the values were minimum in the N0 and maximum in the N90 levels (Table 2).
RANOVA showed considerable variations in the NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N due to year, season, N-levels and their interactions (Table 1). Moreover, the mineralized N substantially varied between the years and between the seasons (Table 2). The effect size responses of the mineralized-N to the N-levels were positive and humped-shape (Fig. 2). The results showed synchronization of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N with those of the ammonification, nitrification and total N-mineralization. Thus, it seems that the available-N was controlled by the rates of N-mineralization as also suggested by path analysis (Fig. 6). Interestingly, similar to the N-mineralization attributes; the NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N were positively related with the decay constant (R = 0.74–0.77, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72), negatively with the C/N (− R = 0.76–80, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72) and MBC/MBN ratios (− R = 0.52–0.73, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72) and quadratically with the soil-pH (R = 0.68–0.74, P ≤ 0.001, n = 72).
Figure 6.

Path analysis indicating the direct (bold arrows) and indirect (thin arrows) effects of soil variables on the soil-N pools and fluxes during 3-year of N manipulative study in Tropical grassland, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. The path coefficients are standardized regression coefficients. The values associated with arrows represent standardized path coefficients. *, ** and *** represent significance levels of standardized path coefficients at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively.
Leaching of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N
RANOVA yielded remarkable differences in the leaching of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N due to year, season, N-levels and their interactions (Table 1). Individually, these attributes were one and half times greater in the third-year of the experiment than the first-year of the experiment, 11–17 times greater in the rainy season than the dry season and consistently increased with the N-levels (Table 2). Interestingly, the values were two-fold greater in the N150 than the N0 (Table 2). Also, the effect size analysis indicated increasing pattern of N leaching along the increasing rate of N depositions (Fig. 2). Compared to control, N deposition favoured the leaching of NH4+-N by 20–107%, NO3−-N by 33–95% and inorganic-N by 29–97%. Overall, on average N deposition enhanced leaching of NH4+-N by 56% and NO3−-N by 65% (Fig. 4).
Pearson correlation analysis indicated that the leaching of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N were positively related with TN, decay constant and rates of N-mineralization (Table 3). In contrast to these relations, the N leaching parameters were negatively related with those of soil-pH, MBN, C/N ratio, MBC/MBN ratio, NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N of the 0–10 cm soil depth (Table 3).
Table 3.
Correlation matrix indicating the relationships of nitrogen (N) leaching with the N-levels, soil-pH, decay constant, microbial biomass (MBN), microbial biomass carbon (MBC): MBN, rates of N mineralization, inorganic N, total N and carbon : nitrogen (C:N) during the three-year of N manipulative study in Tropical grassland located on the campus of Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
| Variables | NH4+-N leaching | NO3−-N leaching | Inorganic-N leaching |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-levels | 0.25** | 0.25** | 0.25** |
| pH | − 0.52** | − 0.55** | − 0.55** |
| Decay constant (k) | 0.92*** | 0.94*** | 0.94*** |
| MBN | − 0.33** | − 0.33** | − 0.33** |
| MBC:MBN | − 0.40** | − 0.42** | − 0.42** |
| Ammonification | 0.75*** | 0.69*** | 0.72*** |
| Nitrification | 0.75*** | 0.69*** | 0.72*** |
| N-mineralization | 0.75*** | 0.69*** | 0.72*** |
| NH4+-N | − 0.54** | − 0.56** | − 0.56** |
| NO3−-N | − 0.60*** | − 0.61*** | − 0.62*** |
| Inorganic-N | − 0.59** | − 0.61*** | − 0.61*** |
| Total-N | 0.64*** | 0.66*** | 0.66*** |
| C:N | − 0.40** | − 0.44** | − 0.43** |
Values are Pearson correlation coefficients (R) NSinsignificant, *significant at p ≤ 0.05; **significant at p ≤ 0.01; ***significant at p ≤ 0.001.
Finally; path analysis was performed to identify the direct and indirect effects of soil variables on the parameters of inorganic-N leaching. Results showed that the N-levels, soil-pH, decay constant, N-mineralization and C/N ratio caused direct effects on the leaching of inorganic-N. As a main result; the rate of N deposition and soil-pH mediated by it firmly determined the leaching of inorganic-N (Fig. 6).
Discussion
Soil acidification, soil base and non-base cations
In the present study, N induced reduction of soil-pH along increasing rate of N deposition could be due to increase in Al3+ concentration. It is evident because of negative relationship of Al3+ concentration with soil-pH. Release of carbonic acids during litter decomposition84 and H+ into the soil solutions during nitrification85 could be probable explanation for reduction of soil-pH owing to N deposition. Also, it is known that breakdown of urea fertilizer (similar to other studies65,66, we also used urea fertilizer to simulate N deposition) in presence of soil moisture and uptake of NH4+ through the plant roots decrease the soil-pH21,31,84. In other studies differential buffering and mobilization capacities of base and non-base cations are suggested for soil acidification because of N input57. Reports indicated that reduction of base cations (Na+ and K+) present in soil system usually delays acid-buffering capacity of the soil57,86. Once, these base cations are exhausted, the non-base cations (Al3+ and Fe3+) mobilize and buffer during the N-induced soil acidification57,86. Similar to present study, other studies also reported reduction of soil-pH due to N deposition21,23,55,66.
Microbial biomass-N
Low MBN in the rainy season and high in the dry season suggested seasonality in the MBN of the tropical grassland29,87,88. Significantly positive effect sizes of MBN from low to moderate N-levels (N30-N90), and negative from moderate to high levels of applied N (N120-N150), decline in the third-year of the experiment and humped-shape response across the applied N-levels (by pooling entire data) favoured the assumption that moderate level of N deposition favours maximum MBN while continuous and sufficiently high amount of N depositions retard the conservation of soil-N in microbial biomass89,90. Noticeably, regression analysis revealed 63 kg N ha−1 year−1 as an optimum rate of N deposition for maximum accumulation of N in the microbes of tropical grassland. Using 82 published field studies (considering only highest N application rates), Treseder91 suggested reduction of microbial biomass due to N additions. However, he excluded the data of microcosm or greenhouse-based experiments as well as organic N or urea, or N with phosphorus added data. A recent analysis of Camenzind et al.52, from tropical forest showed inconsistent (no relation to N in lowland forest and positive in montane forests) responses of microbes to the N deposition. In the present study, occurrence of positive relation between MBN and soil inorganic-N pool, and maximum MBN at 63 kg ha−1 year−1 N deposition rate improved our understanding that the N-deposition dependent MBN of the tropical grassland may act as a source for the availability of mineral-N in the soil system.
N mineralization
The occurrence of maximum total N-mineralization in the rainy season and minimum in the dry season suggested a flush of N-mineralization at the start of the rainy season. It may be because of drying and rewetting effects of the dry tropical soils21,29,92,93. Rapid variation in soil water potential because of drying and rewetting possibly exhibited osmotic shocks to the microbes; consequently, there could have microbial cell lysis and release of cell solutes94. The labile-N substrate quickly mineralized through the activities of the remaining microbes; hence, a pulse of N-mineralization was likely95. It might be expected that the microbes have stored a higher amount of N during the dry season and as they receive a rain event their activities get accelerated, consequently, the start of the rainy season yielded a greater mineralised-N29,96.
The study yielded humped-shape curves for the effect sizes of N-mineralization parameters to the N-levels. These curves suggested that the N-mineralization was low at low levels of N depositions (N30–N90), whereas increased to a maximum at a moderate level (N90) then decreased towards the higher rate of N deposition (N90–N150). It could be explained by changes in composition and activities of soil microbes,’ soil-pH and rate of organic matter decomposition in response to N depositions. These patterns are evident due to positive relations of decay constant, negative relations of C/N and MBC/MBN ratios and quadratic relations of soil-pH with those of ammonification, nitrification and total N-mineralization. The path analysis also revealed such mechanisms for the controlling the N-mineralization in the present experiment.
Since the N-mineralization parameters quadratically responded to the N deposition and soil-pH and 90 kg N ha−1 year−1 deposition rate yielded 6.98 soil-pH for maximum N-mineralization, therefore, 90 kg N ha−1 year−1 deposition is thought to be an optimum amount of N for favourable soil-pH that had supported maximum soil N-transformation from organic residues to the mineral-N in the tropical grassland. Similar to the present findings, other temperate studies also suggested moderate level of N deposition for greater soil N-mineralization mediated by microbial communities and their performances36–38,97–99. The poor quality of decomposing materials; high C/N ratio43,84,100, poor growth and activities of oligotrophic decomposers; high MBC/MBN ratio43,101–103 and conditions during the decomposition; low soil-pH and high Al3+ toxicity104, could be major constrains for the transformation of organic residues into the mineralized-N.
Soil mineral-N pool
Similar to present study other temperate studies also suggested positive relationships between soil mineral-N status (NH4+-N, NO3−-N) and the rate of N-mineralization under the N-deposition scenario31,84,105. The synchronisation of NH4+-N and NO3−-N with those of ammonification and nitrification in relation to the N deposition also highlighted that NH4+-N and NO3−-N are low at the low level of N deposition, became maximum at a medium level of N deposition (90 kg N) and decline progressively towards higher N deposition levels. The study inferred that at the low level of N deposition; probably the soil-N was not sufficient for the activities of ammonifiers and nitrifiers to release the NH4+-N and NO3−-N. As soon as amount of N deposition was increased, more ammonifiers and nitrifiers get activated for ammonification and nitrification23, at adequately high level of N deposition, probably there was loss of additional N via volatilization of ammonium106, denitrification of nitrate106–108 and also, possibly consumed by the nitrophilc plants for increasing their biomass23,109–111.
Further, study believes that whatever N is present in the control plot maybe because of biological N2-fixation as well as from the release of N through the microbial decomposition of litters. The N deposition at the rate of 90 kg ha−1 year−1 reduces the N2-fixation for a short time and later on; N2-fixation is increased because of an increased microbial population23. Beyond this limit of N deposition; denitrification (if any); appears to be insignificant; therefore, the loss of extra N may be through volatilization106 and denitrification112, however, at a slow rate. The N deposition at the rate of 150 kg ha−1 year−1 entirely reduces the growth of N2-fixing microbes and N2-fixation as well as activities and the growth of denitrifying microbes106,112. Additionally, a substantial amount of NH4+-N and NO3−-N may be taken by the nitrophilic species23,109,110. In this situation; the quantity of ammonia formation appeared to be reasonably high because of the increased quantity of substrate106,113,114 and most of this ammonia is being transformed into the NO3−-N by nitrifies, whereas remaining ammonia is being volatilized106.
Mineral-N leaching
Significantly positive linear relationships of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and total inorganic-N to the N-levels as well as yearly increased amount of these variables in the 90–100 cm soil depth suggested that the increased amount of N deposition probably exceeded beyond the needs of microbes and plants. Therefore, extra N could have percolated in the 90–100 cm soil depth115–117. In contrast to 0–10 cm soil depth; the amounts of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and inorganic-N at 90–100 cm soil depths were maximum in the rainy season and minimum in the dry season. The emergence of such patterns may be due to the maximum uptake of mineral-N by the plants for their vigorous growth in the rainy season. At the same time, the increased precipitation and slightly warmer condition during rainy season probably increased the microbial activities and the rates of decomposition which in turn could have increased the rate of N-mineralization (because of positive relationship between decay constant and N-mineralization). Thus, the remaining inorganic-N beyond the demands of plants and microbes possibly resulted into the leaching of inorganic-N through the water2. Probably, it could be a reason for high leaching in rainy and low in the dry season.
The percentage change of NO3−-N leaching is approximately one and a half times greater than the NH4+-N. It may be because of greater nitrification and accumulation of NO3−-N (as evident by positive relationship between nitrification and NO3−-N leaching) which were assumed to be over and above the requirements of the plants and nitrifying microbes and less competition between them for NO3−-N118,119. Further, higher NO3−-N leaching rates than that of NH4+-N may be expected because the latter is a preferred form of inorganic N for the biota due to low energetic cost during biological assimilation. Thus, it appears that the high NO3−-N leaching could be a dominant form of N-leaching because of biological assimilation controlled NO3−-N saturation120,121. Also, the possible mechanisms behind it may be explained by the differences in the charges of NH4+ and NO3−. For example, the NH4+ is positively charged and it binds with the negatively charged clay particles while the negatively charged NO3− freely moves with the water molecule until the exchange of anions within the soil is completed122. Thus, the study supported the view that the excess N deposition increases the NO3−-N leaching2,58 in the tropical grassland. Its proper management is warranted; otherwise the excess N deposition may cause soil acidification, leaching of N123 and ultimately participate in the warming of the globe through production of nitrous oxide from soil via nitrification and denitrification by different aerobic and anaerobic microbes124. Overall, the current holistic study revealed that the N deposition below 90 kg ha−1 year−1 could be a substantial limit for the healthy soil-N fertility and its transformation in the tropical grassland.
Conclusions
The continuous, as well as an incremental amount of N-levels decreased the soil-pH and increased the Al3+ concentration within the soil system and changes in these soil variables governed the decomposition of organic materials and N-transformation. Also, the N deposition dependent soil-pH, decay constant and N-mineralization guided the leaching pattern of mineral-N. The N deposition below 90 kg ha−1 year−1 seems to be an optimum limit for the maximum soil-N status and dynamics. The N deposition beyond this limit caused negative feedback to the soil-N fertility and its dynamics. Hence, this holistic approach suggested that the N deposition should not go beyond 90 kg ha−1 year−1 and it should be managed by implementing into a policy for sustainable functioning of the tropical or similar grasslands.
Acknowledgements
RS is thankful to the SERB, New Delhi for the financial support with file number: EEQ/2016/000129. We express our high gratitude to both reviewers who had taken much pain in improving the ms. Dr. Ping He, editorial board member of the journal is deeply acknowledged for his beautiful coordination and healthy communication among the constructive reviewers and us.
Author contributions
P.V. and R.S. conceived the ideas and designed methodology. P.V. conducted experiment and collected data. P.V. and R.S. analysed the data. P.V. drafted and R.S. corrected the manuscript. Both authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Preeti Verma, Email: preetivermakasia@gmail.com.
R. Sagar, Email: sagar@bhu.ac.in
References
- 1.Waldrop MP, Zak DK, Sinsabaugh RL, Gallo M, Lauber C. Nitrogen deposition modifies soil carbon storage through changes in microbial enzymatic activity. Ecol. Appl. 2004;14:1172–1177. doi: 10.1890/03-5120. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhaohui L, Xiaozong S, Lihua J, Haitao L, Yu X, Xinhao G, Fuli Z, Deshui T, Mei W, Jing S, Yuwen S. Strategies for Managing Soil Nitrogen to Prevent Nitrate-N Leaching in Intensive Agriculture System. Jinan: Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fowler D, Coyle M, Skiba U, Sutton MA, Cape JN, Reis S, Sheppard LJ, Jenkins A, Grizzetti B, Galloway JN, Vitousek P, Leach A, Bouwman AF, Butterbach-Bahl K, Dentener F, Stevenson D, Amann M, Voss M. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2013;368:20130164. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Galloway JN, Dentener FJ, Capone DG, Boyer EW, Howarth RW, Seitzinger SP, Asner GP, Cleveland CC, Green PA, Holland EA, Karl DM, Michaels AF, Porter JH, Townsend AR, Vo CJ. Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry. 2004;70:153–226. doi: 10.1007/s10533-004-0370-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle. Science. 2008;320:889–892. doi: 10.1126/science.1136674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhou L, Zhou X, Shao J, Nie Y, He Y, Jiang LL, Wu Z, Bai SH. Interactive effects of global change factors on soil respiration and its components: a metaanalysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2016;22:3157–3169. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Galloway JN. Nitrogen mobilization in Asia. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2000;57:1–12. doi: 10.1023/A:1009832221034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lamarque JF, Kiehl JT, Brasseur GP, Butler I, Cameron-Smith P, Collins WD, Collins WJ, Granier C, Hauglustaine D, Hess PG, Horowitz L, Lawrence MG, McKenna D, Merilees P, Prather MJ, Rasch PJ, Rotman D, Shindell D, Thornton P. Assessing future nitrogen deposition and carbon cycle feedback using a multimodel approach: analysis of nitrogen deposition. J. Geophys. Res. D: Atmos. 2005;110:1–21. doi: 10.1029/2005JD005825. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zheng X, Fu C, Xu X, Yan X, Huang Y, Han S, Hu F, Chen G. The Asian nitrogen cycle case study. Ambio. 2002;31:79–87. doi: 10.1639/0044-7447(2002)031[0079:Tanccs]2.0.Co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Galloway JN. Acid deposition: perspectives in time and space. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995;85:15–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00483685. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tilman D, Fargione J, Wolff B, D’antonio C, Dobson A, Howarth R, Schindler D, Schlesinger WH, Simberloff D, Swackhamer D. Forecasting agriculturally driven global environmental change. Science. 2001;292:281–284. doi: 10.1126/science.1057544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hirel B, Le Gouis J, Ney B, Gallais A. The challenge of improving nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants: towards a more central role for genetic variability and quantitative genetics within integrated approaches. J. Exp. Bot. 2007;58:2369–2387. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schultze-Kraft R, Rao IM, Peters M, Clements RJ, Bai C, Liu G. Tropical forage legumes for environmental benefits: an overview. Trop. Grassl. Forrajes Trop. 2018;6:1. doi: 10.17138/TGFT(6)1-14. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gundersen P, Emmett BA, Kjønaas OJ, Koopmans CJ, Tietema T. Impact of nitrogen deposition on nitrogen cycling in forests: a synthesis of NITREX data. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998;101:37–55. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1127(97)00124-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gundersen P, Schmidt IK, Raulund-Rasmussen K. Leaching of nitrate from temperate forests—effects of air pollution and forest management. Environ. Rev. 2006;14:1–57. doi: 10.1139/a05-015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007;10:1135–1142. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tu LH, Hu HL, Chen G, Peng P, Xiao YL, Hu TX, Zhang J, Li XW, Liu L, Tang Y. Nitrogen addition significantly affects forest litter decomposition under high levels of ambient nitrogen deposition. PLoS ONE. 2014 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.van Groenigen JW, Huygens D, Boeckx P, Kuyper TK, Lubbers IM, Rütting T, Groffman PM. The soil N cycle: new insights and key challenges. Soil. 2015;1:235–256. doi: 10.5194/soil-1-235-2015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dirnböck T, Foldal C, Djukic I, Kobler J, Haas E, Kiese R, Kitzler B. Historic nitrogen deposition determines future climate change effects on nitrogen retention in temperate forests. Clim. Change. 2017;144:221–235. doi: 10.1007/s10584-017-2024-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yang X, Yang Z, Tan J, Li GY, Wan SQ, Jiang L. Nitrogen fertilization, not water addition, alters plant phylogenetic community structure in a semi-arid steppe. J. Ecol. 2018;106:991–1000. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12893. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Verma P, Verma P, Sagar R. Variations in N mineralization and herbaceous species diversity due to sites, seasons, and N treatments in a seasonally dry tropical environment of India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013;297:15–26. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2013.02.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sagar R, Verma P, Verma H, Singh DK, Verma P. Species diversity–primary productivity relationships in a nitrogen amendment experiment in grasslands at Varanasi, India . Curr. Sci. 2015;108:2163–2166. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bobbink R, Hicks K, Galloway J, Spranger T, Alkemade R, Ashmore M, Bustamante M, Cinderby S, Davidson E, Dentener F, Emmett B, Erisman J-W, Fenn M, Gilliam F, Nordin A, Pardo L, De Vries D. Global assessment of nitrogen deposition effects on terrestrial plant diversity: a synthesis. Ecol. Appl. 2010;20:30–59. doi: 10.1890/08-1140.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Suddick EC, Whitney P, Townsend AR, Davidson EA. The role of nitrogen in climate change and the impacts of nitrogen–climate interactions in the United States: foreword to thematic issue. Biogeochemistry. 2013;114:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s10533-012-9795-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boutin M, Corcket E, Alard D, Villar L, Jiménez JJ, Blaix C, Lemaire C, Corriol G, Lamaze T, Pornon T. Nitrogen deposition and climate change have increased vascular plant species richness and altered the composition of grazed subalpine grasslands. J. Ecol. 2017;105:1199–1209. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12743. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Townsend AR, Howarth RW. Fixing the global nitrogen problem. Sci. Am. 2010;302:64–71. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0210-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Davidson EA, David MB, Galloway JN, Goodale CL, Haeuber R, Harrison JA, Howarth RW, Jaynes DB, Lowrance RR, Nolan BT, Peel RJL, Pinder W, Porter E, Snyder CS, Townsend AR, Ward MH. Excess nitrogen in the U.S. environment: trends, risks, and solutions. Issues Ecol. 2012;15:1–16. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Erisman JW, Galloway JN, Seitzinger S, Bleeker A, Dise NB, Petrescu AMR, Leach AM, de Vries W. Consequences of human modification of the global nitrogen cycle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2013;368:20130116. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Singh JS, Raghubanshi AS, Singh RS, Srivastava SC. Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna. Nature. 1989;338:449–500. doi: 10.1038/338499a0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fisk MC, Fahey TJ. Microbial biomass and nitrogen cycling responses to fertilization and litter removal in young northern hardwood forests. Biogeochemistry. 2001;53:201–223. doi: 10.1023/A:1010693614196. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang H, Mo J, Lu X, Xue J, Li J, Fang Y. Effects of elevated nitrogen deposition on soil microbial biomass carbon in major subtropical forests of southern China. Front. For. China. 2009;4:21–27. doi: 10.1007/s11461-009-0013-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang T, Chen HYH, Ruan H. Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes. ISME J. 2018;12:1817–1825. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0096-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang Y, Xu W, Duan P, Cong Y, An T, Yu N, Zou H, Dang X, An J, Fan Q, Zhang Y. Evaluation and simulation of nitrogen mineralization of paddy soils in Mollisols area of Northeast China under waterlogged incubation. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(2):1. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fu MH, Xu XC, Tabatabai MA. Effect of pH on nitrogen mineralization in crop-residue-treated soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 1987;5:115–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00257645. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Perakis SS, Sinkhorn ER. Biogeochemistry of a temperate forest nitrogen gradient. Ecology. 2011;92:1481–1491. doi: 10.1890/10-1642.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brenner RE, Boone RD, Ruess RW. Nitrogen additions to pristine, high-latitude, forest ecosystems: consequences for soil nitrogen transformations and retention in mid and late succession. Biogeochemistry. 2005;72:257–282. doi: 10.1007/s10533-004-0356-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dijkstra FA, Hobbie SE, Reich PB, Knops JMH. Divergent effects of elevated CO2, N fertilization, and plant diversity on soil C and N dynamics in a grassland field experiment. Plant Soil. 2005;272:41–52. doi: 10.1007/s11104-004-3848-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sirulnik AG, Allen EB, Meixner T, Allen MF. Impacts of anthropogenic N additions on nitrogen mineralization from plant litter in exotic annual grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007;39:24–32. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.04.048. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Soon YK, Malhi SS. Soil nitrogen dynamics as affected by landscape position and nitrogen fertilizer. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2005;85:579–587. doi: 10.4141/S04-072. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chappell HN, Prescott CE, Vesterdal L. Long-term effects of nitrogen fertilization on nitrogen availability in coastal Douglas-fir forest floors. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999;63:1448–1454. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1999.6351448x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gilliam FS, Yurish YB, Adams MB. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen transformations in nitrogen-saturated soils of a central Appalachian hardwood forest. Can. J. For. Res. 2001;31:1768–1785. doi: 10.1139/cjfr-31-10-1768. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nohrstedt HÖ. Effects of liming and fertilization (N, P, K) on chemistry and nitrogen turnover in acidic forest soils in SW Sweden. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002;139:343–354. doi: 10.1023/A:1015858922200. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang X, Wang Q, Gilliam FS, Bai W, Han X, Li L. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on net nitrogen mineralization in a grassland soil, northern China. Grass Forage Sci. 2012;67:219–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2494.2011.00836.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Aber J, Mcdowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Berntson G, Kamakea M, McNulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I. Nitrogen saturation in forest ecosystems hypotheses revisited. Bioscience. 1998;48:921–934. doi: 10.2307/1313296. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Herai Y, Kouno K, Hashimoto M, Nagaoka T. Relationships between microbial biomass nitrogen, nitrate leaching and nitrogen uptake by corn in a compost and chemical fertilizer-amended regosol. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2006;52:186–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00031.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rustad LE, Campbell JL, Marion GM, Norby RJ, Mitchell MJ, Hartley AE, Cornelissen J, Gurevitch J, Wright R. A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration, net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming. Oecologia. 2001;126:543–562. doi: 10.1007/s004420000544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Beier C, Emmett B, Penuelas J, Schmidt I, Tietema A, Estiarte M, Gundersen P, Llorens L, Riis-Nielsen T, Sowerby A. Carbon and nitrogen cycles in European ecosystems respond differently to global warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2008;407:692–697. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Crowley KF, Lovett GM. Effects of nitrogen deposition on nitrate leaching from forests of the northeastern United States will change with tree species composition. Can. J. For. Res. 2017;47:997–1009. doi: 10.1139/cjfr-2016-0529. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Braakhekke MC, Rebel KT, Dekker SC, Smith B, Beusen AS, Wassen MJ. Nitrogen leaching from natural ecosystems under global change: a modelling study. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2017;8:1121–1139. doi: 10.5194/esd-8-1121-2017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Matson P, Lohse KA, Hall SJ. The globalization of nitrogen deposition: consequences for terrestrial ecosystems. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2002;31:113–119. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447-31.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fang Y, Zhu W, Gundersen P, Mo J, Zhou G, Yoh M. Large loss of dissolved organic nitrogen from nitrogen-saturated forests in subtropical China. Ecosystems. 2009;12:33–45. doi: 10.1007/s10021-008-9203-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Camenzind T, Hättenschwiler S, Treseder KK, Lehmann A, Rillig MC. Nutrient limitation of soil microbial processes in tropical forests. Ecol. Monogr. 2018;88:4–21. doi: 10.1002/ecm.1279. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhao B, Wang S, Dong X, Wang J, Duan L, Fu X, Hao J, Fu J. Environmental effects of the recent emission changes in China: implications for particulate matter pollution and soil acidification. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013;8(2):1. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.SDG (Sustainable Development Goal). 2019. UN Report: Nature’s Dangerous Decline ‘Unprecedented; Species Extinction Rates ‘Accelerating’. (Assessed on 6th June, 2019); https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/blog/2019/05/nature-decline-unprecedented-report/.
- 55.Stevens CJ, Thompson K, Grime JP, Long CJ, Gowing DJG. Contribution of acidification and eutrophication to declines in species richness of calcifuge grasslands along a gradient of atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Funct. Ecol. 2010;24:478–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2009.01663.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sagar R, Verma P. Effects of soil physical characteristics and biotic interferences on the herbaceous community composition and species diversity on the campus of Banaras Hindu University India. Environmentalist. 2010;30:289–298. doi: 10.1007/s10669-010-9276-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bowman WD, Cleveland CC, Halada L, Hreško J, Baron JS. Negative impact of nitrogen deposition on soil buffering capacity. Nat. Geosci. 2008;1:767–770. doi: 10.1038/ngeo339. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zvomuya F, Rosen J, Russelle P, Gupta C. Nitrate leaching and nitrogen recovery following application of polyolefin-coated urea to potato. J. Environ. Qual. 2003;32:480–489. doi: 10.2134/jeq2003.0480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Verma P, Sagar R, Verma H, Verma P, Singh DK. Changes in species composition, diversity and biomass of herbaceous plant traits due to N amendment in a dry tropical environment of India. J. Plant Ecol. 2015;8:321–332. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtu018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Agrawal RR, Mehrotra CL. Soil Work in Uttar Pradesh. Lucknow: Department of Agriculture; 1952. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Buol SW, Southard RJ, Graham RC, McDaniel PA. Soil Genesis and Classification. 5. Ames, IA: Iowa State Press; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Singh H, Singh KP. Biology and fertility of soils effect of residue placement and chemical fertilizer on soil microbial biomass under tropical dryland cultivation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994;26:695–702. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(94)90261-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sagar R, Singh A, Singh JS. Differential effect of woody plant canopies on species composition and diversity of ground vegetation: a case study. Trop. Ecol. 2008;49:189–197. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Verma P, Sagar R. Responses of diversity, productivity, and stability to the nitrogen input in a tropical grassland. Ecol. Appl. 2020 doi: 10.1002/eap.2037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bai W, Guo D, Tian Q, Liu N, Cheng W, Li L, Zhang W-H. Differential responses of grasses and forbs led to marked reduction in below-ground productivity in temperate steppe following chronic N deposition. J. Ecol. 2015;103:1570–1579. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12468. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Tian D, Niu S. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015;10:1748–9326. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/10/2/024019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lu X, Mao Q, Gilliam FS, Luo Y, Mo J. Nitrogen deposition contributes to soil acidification in tropical ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2014;20:3790–3801. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Jackson M. Soil Chemical Analysis. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1958. [Google Scholar]
- 69.APHA . Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association APHA; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gilbert O, Bocock KL. Changes in leaf litter when placed on the surface of soils with contrasting humus types: I. Losses in dry weight of oak and ash leaf litter. J. Soil Sci. 1960;11:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1960.tb02196.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Olson JS. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology. 1963;44:322–331. doi: 10.2307/1932179. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ezcurra E, Becerra J. Experimental decomposition of litter from the Tamaulipan cloud forest: a comparison of four simple models. Biotropica. 1987;19:290–296. doi: 10.2307/2388624. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Roy S, Singh JS. Consequences of habitat heterogeneity for availability of nutrients in a dry tropical forest. J. Ecol. 1994;82:503–509. doi: 10.2307/2261259. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987;19:703–707. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Wu J, Joergensen RG, Pommerening B, Chaussod R, Brookes PC. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction—an automated procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990;22:1167–1169. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(90)90046-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985;17:837–842. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gaidajis G. Ambient concentrations of Total Suspended Particulate matter and its elemental constituents at the wider area of the mining facilities of TVX Hellas in Chalkidiki, Greece. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2003;38:2509–2520. doi: 10.1081/ESE-120024443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Hedges LV, Gurevitch J, Curtis PS. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology. 1999;80:1150–1156. doi: 10.2307/177062. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Curtis PS, Wang X. A meta-analysis of elevated CO2 effects on woody plant mass, form, and physiology. Oecologia. 1998;113:299–313. doi: 10.1007/s004420050381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Luo Y, Hui D, Zhang D. Elevated CO2 stimulates net accumulations of carbon and nitrogen in land ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Ecology. 2006;87:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.SPSS . SPSS Base 7.5, Applications Guide. Chicago: SPSS; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Arbuckle JL. AMOS 16 User’s Guide. Spring House: AMOS Development Corporation; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Clark JS. Landscape interactions among nitrogen mineralization, species composition, and long-term fire frequency. Biogeochemistry. 1990;11:1–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00000849. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Rao LE, Parker DR, Bytnerowicz A, Allen EB. Nitrogen mineralization across an atmospheric nitrogen deposition gradient in Southern California deserts. J. Arid Environ. 2009;73:920–930. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.04.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Smith SE, Read DJ. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. 3. New York: Academic Press; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 86.McLaughlin SB, Wimmer R. Calcium physiology and terrestrial ecosystem processes. Tansley Review No. 104. New Phytol. 1999;142:373–417. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.1999.00420.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Arunachalam A, Arunachalam K. Influence of gap size and soil properties on microbial biomass in a subtropical humid forest of north-east India. Plant Soil. 2000;223:187–195. doi: 10.1023/A:1004828221756. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Wang R, Creamer CA, Wang X, He P, Xu Z. The effects of a 9-year nitrogen and water addition on soil aggregate phosphorus and sulfur availability in a semi-arid grassland. Ecol. Indic. 2016;61:806–814. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Song B, Niu S, Li L, Zhang L, Yu G. Soil carbon fractions in grasslands respond differently to various levels of nitrogen enrichments. Plant Soil. 2014;384:401–412. doi: 10.1007/s11104-014-2219-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Van Diepen LTA, Frey SD, Landis EA, Morrison EW, Pringle A. Fungi exposed to chronic nitrogen enrichment are less able to decay leaf litter. Ecology. 2017;98:5–11. doi: 10.1002/ecy.1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Treseder KK. Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: a meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol. Lett. 2008;11:1111–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Franzluebbers AJ, Haney RL, Honeycutt CW, Schomberg HH, Hons FM. Flush of carbon dioxide following rewetting of dried soil relates to active organic pools. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000;64:613. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2000.642613x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fierer N, Schimel JP. Effects of drying-rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002;34:777–787. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00007-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 94.van Gestel M, Ladd JN, Amato M. Microbial biomass responses to seasonal change and imposed drying regimes at increasing depths of undisturbed topsoil profiles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1992;24:103–111. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(92)90265-Y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kieft TL, Soroker E, Firestone MK. Microbial biomass response to a rapid increase in water potential when dry soil is wetted. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987;19:119–126. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(87)90070-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Yokobe T, Hyodo F, Tokuchi N. Seasonal effects on microbial community structure and nitrogen dynamics in temperate forest soil. Forests. 2018;9:1–17. doi: 10.3390/f9030153. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Hobbie SE. Interactions between litter lignin and soil nitrogen availability during leaf litter decomposition in a Hawaiian montane forest. Ecosystems. 2000;3:484–494. doi: 10.1007/s100210000042. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Knorr M, Frey SD, Curtis PS. Nitrogen additions and litter decomposition: a meta-analysis. Ecology. 2005;86:3252–3257. doi: 10.1890/05-0150. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Zhang Y, Guo S, Liu Q, Jiang J, Wang R, Li N. Responses of soil respiration to land use conversions in degraded ecosystem of the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2015;74:196–205. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.10.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Vourlitis GL, Zorba G, Pasquini SC, Mustard R. Chronic nitrogen deposition enhances nitrogen mineralization potential of semiarid shrubland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007;71:836. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2006.0339. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Delin S, Lindén B. Relations between net nitrogen mineralization and soil characteristics within an arable field. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2002;52:78–85. doi: 10.1080/090647102321089819. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Campbell BJ, Polson SW, Hanson TE, Mack MC, Schuur EAG. The effect of nutrient deposition on bacterial communities in Arctic tundra soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;12:1842–1854. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bárta J, Tahovská K, Šantrůčková H, Oulehle F. Microbial communities with distinct denitrification potential in spruce and beech soils differing in nitrate leaching. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08554-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Xiao K, Yu L, Xu J, Brookes PC. pH, nitrogen mineralization, and KCl-extractable aluminum as affected by initial soil pH and rate of vetch residue application: results from a laboratory study. J. Soils Sedim. 2014;14:1513–1525. doi: 10.1007/s11368-014-0909-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Mlambo D, Mwenje E, Nyathi P. Effects of tree cover and season on soil nitrogen dynamics and microbial biomass in an African savanna woodland dominated by Colophospermum mopane. J. Trop. Ecol. 2007;23:437–448. doi: 10.1017/S0266467407004233. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Schwab, G. J. & Murdock, L. W. Nitrogen Transformation Inhibitors and Controlled Release Urea. University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Lexington, KY, 40546. AGR185. www.ca.uky.edu (2010).
- 107.Seitzinger S, Harrison JA, Böhlke JK, Bouwman AF, Lowrance R, Peterson B, Drecht GV. Denitrification across landscapes and waterscapes: a synthesis. Ecol. Appl. 2006;16:2064–2090. doi: 10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[2064:DALAWA]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.McCrackin ML, Elser JJ. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition influences denitrification and nitrous oxide production in lakes. Ecology. 2010;91:528–539. doi: 10.1890/08-2210.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Binkley D, Högberg P. Does atmospheric deposition of nitrogen threaten Swedish forests? For. Ecol. Manag. 1997;92:119–152. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1127(96)03920-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lu X, Dong S. Effects of nitrogen deposition on forest biodiversity. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008;28:5532–5548. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2032(09)60012-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Eckert, D. Efficient Fertilizer Use Mannual—Nitrogen. http://www.rainbowplantfood.com/agronomics/efu/nitrogen.pdf (2009).
- 112.Garzio-Hadzick, A. M. Experimental nitrogen deposition influences microbial denitrifying communities and increases denitrification rates in a Northern Hardwood Forest. M.Sc. Thesis, Submitted to the University of Michigan (2012).
- 113.Firestone MK, Firestone RB, Tiedje JM. Nitrous oxide from soil denitrification: factors controlling its biological production. Science. 1980;208:749–751. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4445.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Weier KL, Doran JW, Power JF, Walters DT. Denitrification and the dinitrogen/nitrous oxide ratio as affected by soil water, available carbon, and nitrate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993;57:66–72. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700010013x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Alcoz MM, Hons FM, Haby VA. Nitrogen fertilization timing effect on wheat production, nitrogen uptake efficiency, and residual soil nitrogen. Agron. J. 1993;85:1198–1203. doi: 10.2134/agronj1993.00021962008500060020x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Jemison JM, Fox RH. Nitrate leaching from nitrogen-fertilized and manured corn measured with zero-tension pan lysimeters. J. Environ. Qual. 1994;23:337–343. doi: 10.2134/jeq1994.00472425002300020018x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Andraski TW, Bundy LG, Brye KR. Crop management and corn nitrogen rate effects on nitrate leaching. J. Environ. Qual. 2000;29:1095–1103. doi: 10.2134/jeq2000.00472425002900040009x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Hahne HCH, Kroontje W, Lutz JA. Nitrogen fertilization I. Nitrate accumulation and losses under continuous corn cropping 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977;41:562. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100030028x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Jolley VD, Pierre WH. Profile accumulation of fertilizer-derived nitrate and total nitrogen recovery in two long-term nitrogen-rate experiments with corn 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977;41:373–378. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100020041x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Hartmann TE, Yue S, Schulz R, Chen X, Zhang FS, Müller T. Nitrogen dynamics, apparent mineralization and balance calculations in a maize–wheat double cropping system of the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2014;160:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2014.02.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Yang S, Wang Y, Liu R, Zhang A, Yang Z. Effect of nitrate leaching caused by swine manure application in fields of the yellow river irrigation zone of Ningxia, China . Sci. Rep. 2017;7:13693. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12953-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Ghaly AE, Ramakrishnan VV. Nitrogen sources and cycling in the ecosystem and its role in air, water and soil pollution: a critical review. J. Pollut. Effects Control. 2015;27:1–26. doi: 10.4172/2375-4397.1000136. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Katzensteiner K, Glatzel G, Kazda M. Nitrogen-induced nutritional imbalances—a contributing factor to Norway spruce decline in the Bohemian Forest (Austria) For. Ecol. Manag. 1992;51:29–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(92)90469-P. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Shrawat AK, Carroll RT, Depauw M, Taylor GT, Good AG. Genetic engineering of improved nitrogen use efficiency in rice by the tissue-specific expression of alanine aminotransferase. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008;6:722–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





