Abstract
Background and study aims Colonoscopy is an invasive procedure that may cause patients pain and discomfort. Routine use of sedation, while effective, is expensive and requires logistical planning. Virtual reality (VR) offers immersive, three-dimensional experiences that distract the attention and might comfort patients. We performed a pilot study to investigate the feasibility of VR distraction during colonoscopy.
Patients and methods Adults referred for colonoscopy were considered for inclusion and divided over two groups: with and without VR glasses. The main outcome was patient acceptance of wearing VR glasses during colonoscopy without compromising the technical success of the procedure. Secondary outcomes were patient comfort, pain, and anxiety before, during and after the procedure, using validated patient questionnaires. Patient comments were collected through a qualitative interview.
Results We included 19 patients, 10 of whom were offered VR glasses. All patients accepted VR glasses without prolonging procedural time. No disadvantages of the VR glasses were reported in terms of communication or change of position of the patient. We found that patient comfort, pain, anxiety, and satisfaction in relation to the procedure were similar in both groups. Patients described a pleasant distracting effect using VR glasses.
Conclusion VR glasses during colonoscopy are accepted by patients and do not compromise endoscopic technical success. Patients reported that the VR experience was pleasant and distracting.
Introduction
Use of colonoscopy as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool is likely to rise. This is mainly a result of implementation and expansion of colorectal cancer screening projects, targeting ever younger patients 1 . Endoscopic procedures are associated with embarrassment, pain, and discomfort 2 . This proves an important barrier to undergoing colonoscopy and may subsequently make patients less willing to be subjected to repeat surveillance colonoscopies 3 4 .
Indeed, a relevant proportion of patients (18 % to 29 %) experience anxiety due to concerns related to preparation for, execution of, and anticipation of the result of colonoscopy 5 . Sedation to relieve anxiety is the method of choice used to mitigate the discomfort patients experience during colonoscopy 6 . However, drug-induced sedation comes with adverse effects related to suppression of pulmonary and circulatory function 7 8 . There is a higher post-procedural risk of pneumonia in elderly patients 9 . Deep sedation even puts patients at increased risk for procedure-related complication of perforation 10 . Also, monitoring patients during and after sedation is both logistically demanding and costly 11 .
Therefore, several studies have examined non-pharmacological interventions to reduce anxiety and pain during endoscopy 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 . These studies used a mix of visual 13 15 18 19 or auditory stimuli 12 14 18 and found that while true efficacy is not fully established, combined visual and auditory distraction is better at reducing discomfort than auditory distraction alone 18 .
Virtual reality (VR) integrates computer-generated visual and auditory signals to recreate an illusionary perception of the actual physical world 20 21 . The distraction that comes with immersive VR induces an analgesic effect and has been used as an adjunct to control pain and anxiety during operative procedures 22 23 . VR technology has become more affordable and portable, adding to its immersive qualities 24 . VR reduces pain during burn wound debridement 25 26 27 , and discomfort during dental procedures 28 .
A questionnaire study found that up to 25 % patients are willing to undergo colonoscopy with VR glasses instead of sedation. Key patient motive is the reduction in sedative use, which allows patients to drive their cars home themselves afterwards 29 .
But still unknown is patient acceptance (e. g. feasibility) of performing colonoscopy on patients actually wearing VR glasses. Wearing VR glasses could potentially be disadvantageous to the colonoscopy procedure, as it could obstruct communication with patients. Conversely, the procedure itself might compromise the VR effect, as positional changes of the patient are sometimes necessary. Therefore, we set out in this pilot study to investigate use of VR distraction during colonoscopy. The primary aim was to assess patient acceptance of wearing VR glasses while undergoing colonoscopy. We were also interested in whether VR reduces discomfort, pain, and anxiety and increases satisfaction in patients compared to the standard practice.
Patients and methods
This experiment was designed as a pilot study to evaluate patient acceptance and practical feasibility. A control group was designed to allow evaluation of procedural and patient-related outcomes. The sample size was set at 12 subjects per group. This computation was based on a rule of thumb for pilot studies 30 . Ethical permission from the Radboudumc Ethics Committee was obtained prior to commencement of the study (number 2016–2750). The trial was registered with the Dutch trial Registry (NTR6175).
Patients
We screened patients who were already scheduled for outpatient colonoscopy. Inclusion criteria of the study were adult age and any elective indication of colonoscopy. Exclusion criteria of the study were visual and/or auditory impairments, dementia, limited Dutch language skills, and a diagnosis of balance disorders or epilepsy.
After evaluation of the above criteria, informed consent was obtained from all participants and they were allocated to the VR (intervention) or non-VR (control) group. Allocation was based on the day the colonoscopy was planned. Participants were informed about the group to which they were allocated on the day of the procedure.
Intervention
The hardware we used to generate VR distraction was the Samsung Gear VR (Consumer Edition–SM-R322, combined with Galaxy S7). This is an inexpensive ($ 172) off-the-shelf wide field-of-view, three-dimensional VR headset that projects video and rendered graphics into two independent lenses. The current model is the size of a small pair of ski goggles, with a combined weight of 470 g, and is positioned on the head with elastic straps. The video content that was visualized on the VR hardware consisted of several short clips (with a total length 19 minutes, 59 seconds) of moving 360-degree cameras featuring tropical islands and forests in the Caribbean (supported by VR firm Visyon, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The VR content had not audio, to allow optimal communication with the patient. The authors considered the chosen VR content to be of a relaxing and not overly thrilling character, generating an adequate level of distraction for all participants.
Study design
At T1, all participants filled out a baseline form on a tablet with information about demography, prior experience undergoing colonoscopy, prior VR experience, and a validated general health questionnaire (RAND-36) 31 . On T2, the day of colonoscopy, about 15 minutes before the procedure, all patients received a second form that included validated questionnaires on anxiety (STAI) and pain (NRS) 32 33 . Patients in the intervention group also tested the VR glasses before colonoscopy. During colonoscopy, T3, one researcher (NK) observed the patient’s well-being and positioning together with several procedural aspects e. g., time to cecul intubation and time of total procedure. All patients received conscious sedation with midazolam and/or alfentanyl according to the standard of care, with the dose increased at physician discretion. After colonoscopy, patients completed a set of questionnaires at T4, including questions about anxiety (STAI), pain (NRS), net promoter score, and willingness-to-return questions. A short qualitative interview was held with the patients in the intervention group to explore their experiences with VR glasses.
Measures
Primary outcome
The main outcome was patient acceptance of wearing VR glasses during the procedure. That included adequate positioning of the VR glasses during the entire procedure, even during patient repositioning. In addition, we recorded cecal intubation rate, cecum and total procedure time as well as administered sedatives and analgesics.
Secondary outcomes
Patient comfort
Patient comfort was measured using a five-point Gloucester Comfort scale: 1, comfortable and 5, severe discomfort 34 .
Patient pain
An 11-point numeric rating scale (NRS) was used to measure pain of the patient before and during the procedure: 0, no pain and 10, highest imaginable pain 32 .
Patient anxiety
The State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was used to measure patient anxiety before and after the procedure. The 20-item STAI is widely used with scores ranging from 20 (absence of anxiety) to 80 (high anxiety) 33 .
Patient satisfaction
The general health of the participants was measured using the RAND 36 questionnaire 31 . Net Promoter Score (NPS) 35 and an 11-point scale of willingness to return: 0, no willing at all and 10, definitely willing, were used to measure participant satisfaction with the procedure.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 22 (International Business Machines Corporation, Armonk, New York, United States). Mann Whitney U-tests were used to test whether the median scores for, i. e., age, pain, dose of medication, duration of the procedure, anxiety, satisfaction, NPS, and willingness to return, of the VR (intervention) and non-VR (control) group were comparable to each other. Fisher’s Exact tests were used to test categorical data. P ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
In total 24 patients entered the trial ( Fig. 1 ). Patients were recruited at the endoscopy outpatient clinic. There were 55 eligible patients scheduled for colonoscopy within a 4-week timeframe and we invited 38 consecutive patients, 24 of whom accepted our invitation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. After allocation, two patients in the VR (intervention) group and three patients in the non-VR (control) group were excluded (three patients cancelled the scheduled appointment, one was admitted to the hospital, and in one patient there was a technical problem with the endoscopy equipment). As a result, 19 patients were included in the final analysis, 10 in the VR group and nine in the non-VR group. All patients in the intervention group used the VR glasses during the whole procedure ( Fig. 2 ). No adverse events associated with VR distraction in combination with medication were observed. One endoscopist performed all the procedures (FV) except one in the VR group (BvH). FV had > 5 years of experience, BvH > 3 years.
Fig. 1.
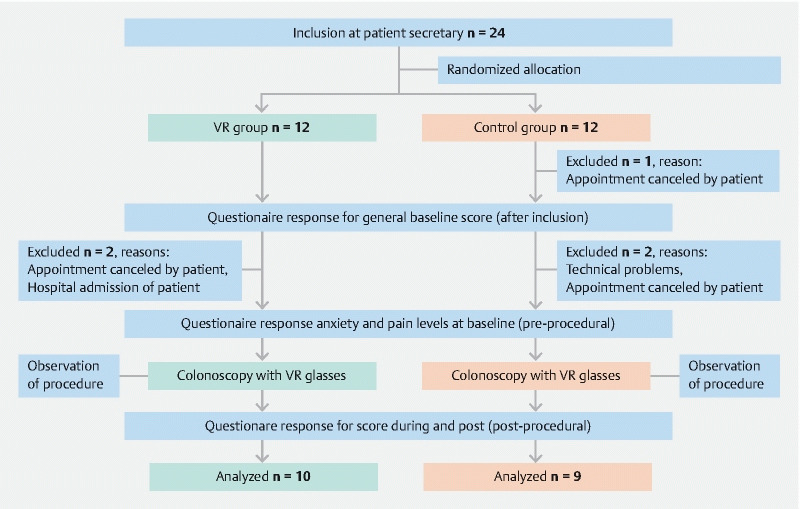
Study flowchart.
Fig. 2.
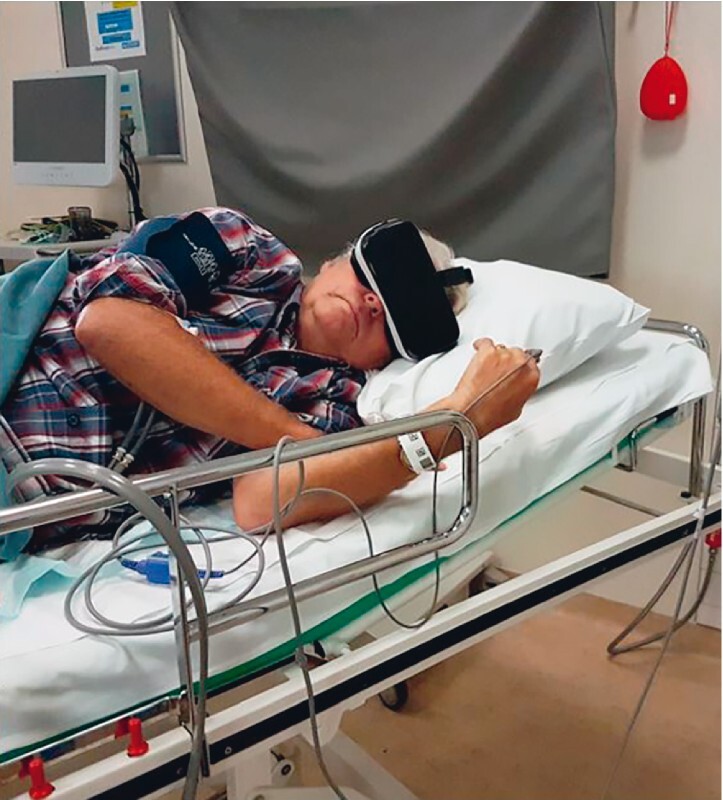
Samsung Gear VR shown on a patient during colonoscopy (with permission).
Baseline characteristics
No significant differences were observed in baseline characteristics of the two groups, i. e., gender (55.6 % women in the control group, versus 60 % women in the intervention group), age (median, 64, versus 65 years), level of education, RAND-36, previous colonoscopy, and prior experience with VR ( Table 1 ).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics.
| Control (non-VR) (n = 9) |
Intervention (VR) (n = 10) |
P value | |
| Age (years) 1 | 64 [47.5; 67.5] | 65 [62, 67] | 0.414 2 |
| Gender (male:female) | 4:5 | 4:6 | 1.000 3 |
| RAND-36 | |||
| Physical functioning 1 | 90 [70, 100] | 82.5 [72.5; 95] | 0.549 2 |
| Role limitations due to physical health 1 | 87.5 [68.75; 100] | 68.75 [50; 84.38] | 0.156 2 |
| Role limitations due to emotional problems 1 | 100 [53.13; 81.25] | 83.33 [47.92; 100] | 0.133 2 |
| Energy/ fatique 1 | 75 [72.5; 90] | 59.38 [48.44; 81.25] | 0.497 2 |
| Emotional well-being 1 | 85 [75, 100] | 75 [50; 81.25] | 0.113 2 |
| Social functioning 1 | 100 [73.47; 94.9] | 81.25 [62.5; 100] | 0.113 2 |
| Pain 1 | 89.79 [73.47; 67.5] | 72.45 [67.35; 100] | 0.497 2 |
| General health 1 | 55 [35; 67.5] | 57.5 [52.5; 66.25] | 0.497 2 |
| Health change 1 | 50 [25; 62.5] | 37.5 [25, 50] | 0.549 2 |
| Number of previous colonoscopy 1 | 2.5 [1.75; 5] | 2 [1.25; 3.75] | 0.515 2 |
| Level of education | 0.733 4 | ||
| Primary school | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Lower vocational education | 0 (0) | 10 (1) | |
| Lower general secondary school | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Intermediate general secondary school | 11.1 (1) | 10 (1) | |
| Intermediate vocational education | 22.2 (2) | 20 (2) | |
| Upper general secondary school | 22.2 (2) | 10 (1) | |
| Higher vocational education | 33.3 (3) | 50 (5) | |
| University | 11.1 (1) | 0 (0) | |
| Prior experience with VR (yes) % (n) | 22.2 (2) | 30 (3) | 1.000 3 |
VR, virtual reality
Variables are denoted as median (interquartile range).
Mann-Whitney U test.
Fisher’s Exact test.
Chi-square test.
Procedure characteristics
There were no differences in procedural characteristics. The time to reach the cecum (median 10.48 minutes in the control group, versus 6.83 minutes in the intervention group), time to complete procedure (median 21.20 minutes in the control group, versus 22.60 minutes in the intervention group), and completed colonoscopies (100 % in the control group, versus 90 % in the intervention group) were comparable in the two groups ( Table 2 ).
Table 2. Procedure characteristics.
| Control (non VR) (n = 9) |
Intervention (VR) (n = 10) |
P value | |
| Dose midazolam, in mg 1 | 2.5 [2.5; 3] min 2; max 3.75 |
2.5 [2.38; 3] min 2.5; max 3 |
0.842 2 |
| Dose alfentanyl, in mg 1 | 0.25 [0.25; 0.50] min 0.25; max 0.50 |
0.25 [0.25; 0.5] min 0.25; max 0.50 |
0.278 2 |
| Completed colonoscopies % (n) | 100 (9) | 90 (9) | 1.000 3 |
| Patient acceptance of VR glasses % (n) | n/a | 100 (10) | n/a |
| Time to reach the cecum, in minutes 1 | 10.48 [8.65; 13.80] min 6.10; max 19.00 |
6.83 [5.75; 10.77] min 2.66; max 11.92 |
0.094 2 |
| Time to complete procedure, in minutes 1 | 21.20 [19.72; 35.15] min 19.18; max 44.07 |
22.60 [16.25; 25.45] min 9.95; max 26.43 |
0.340 2 |
VR, virtual reality
Variables are denoted as median (interquartile range).
Mann-Whitney U test.
Fisher’s Exact test.
Similarly, both groups were comparable in terms of initial intravenous bolus of sedatives and analgesics, i. e., dose of midazolam (median, 2.5 mg in both groups), dose of alfentanyl (median, 0.25 mg in both groups).
Patient pain, comfort and anxiety
Results of pain scores, patient comfort, and anxiety scores are summarized in Table 3 . Median pain score before (0 in both groups) and during (3 in both groups) the procedure was similar in both groups. The Gloucester Comfort scale did not reveal significant differences in patient comfort between the two groups (4 patients [44 %] in the control group were rated comfortable, versus 4 patients [40 %] in the intervention group). No significant difference was observed in median anxiety score prior to the procedure (49 in the control group, versus 48.5 in the intervention group). Median baseline anxiety score (trait) was similar in the intervention group and the control group (29 in the control group, versus 35 in the intervention group). Median anxiety score increased after the procedure (50 and 50).
Table 3. Pain, patient comfort and anxiety results.
| Control (non-VR) (n = 9) |
Intervention (VR) (n = 10) |
P value | |
| Pain score (pre-procedure) 1 | 0 [0, 3] | 0 [0; 1.75] | 0.968 2 |
| Pain score (during procedure) 1 | 3 1 4 | 3 [1.5; 5.5] | 0.661 2 |
| Gloucester comfort scale % (n) | 0.699 3 | ||
| Comfortable | 44.4 (4) | 40 (4) | |
| Minimal | 44.4 (4) | 30 (3) | |
| Mild | 11.1 (1) | 20 (2) | |
| Moderate | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Severe | 0 (0) | 10 (1) | |
| STATE (Pre-procedure) 1 | 49 [48, 50] | 48.5 [45.75; 50.25] | 0.497 2 |
| TRAIT 1 | 29 [21; 36.5] | 35 [28; 41.5] | 0.156 2 |
| STATE (Post-procedure) 1 | 50 [48; 52.5] | 50 [47.75; 51.25] | 0.549 2 |
VR, virtual reality
Variables are denoted as median (interquartile range).
Mann-Whitney U test.
Chi-square test.
Patient satisfaction
No differences were observed between the two groups in patient satisfaction. All patients scored high satisfaction rates in the scales that were used (median score was of 9 out of 10 in both groups). Results on patient satisfaction are summarized in Table 4 .
Table 4. Satisfaction results.
| Control (non-VR) (n = 9) |
Intervention (VR) (n = 10) |
P value | |
| Patient satisfaction 1 | 9 8 10 | 9 [6.5; 10] | 0.905 2 |
| NPS 1 | 9 8 10 | 9 [7.75; 10] | 0.905 2 |
| Willingness to return 1 | 9 [7.5; 10] | 9 [6.75; 10] | 0.720 2 |
VR, virtual reality.
NPS, net promoter score.
Variables are denoted as median [interquartile range].
Mann-Whitney U test.
Qualitative comments
The majority of patients (9/10) rated use of VR glasses as positive. Four patients indicated that they preferred to select the VR content themselves. Two patients complained about the quality of the movie and one patient indicated that the resolution of the VR movie was too low. The physician who performed the colonoscopy was able to communicate with all patients in the intervention group and did not experience any limitations with use of VR.
Discussion
Our pilot study shows that it feasible to use VR distraction during colonoscopy as we observed complete patient acceptance of the device during all procedures. Procedural time was not longer as a result of our intervention.
Comfort, pain, anxiety and patient satisfaction were not affected by VR, but patients reported a positive distracting effect of the VR glasses.
This pilot study indicates that there are no obstacles to investigating VR glasses further in a larger sample of patients. Important to the design of subsequent trials from the endoscopist perspective is that use of VR glasses did not interfere with the completion colonoscopy.
Various studies have found that visual and/or auditory distraction during endoscopic procedures reduces pain and improves satisfaction as a result 13 15 18 . In this pilot we were not able to identify these advantages for VR. This is similar to outcomes in two trials of VR in burn wound victims in which the authors suggested resolving this issue by developing a better-customized VR system instead of off-the-shelf VR sets 36 37 .
Indeed, patients reported that the effect of the VR distraction was less immersive probably because of the content shown. Other studies have found that content is relevant to the level of distraction 12 15 . Low pixel resolution of the VR content influenced the experience of at least one participant and previous studies hhave shown that low-resolution videos reduce the quality of the experience 38 .
The literature on VR for patients in endoscopy is scarce. A retrospective study of 190 patients found that VR allowed unsedated transnasal gastroscopy in children and young adults. In this study, VR-assisted transnasal gastroscopy was safe and cost-effective for staging of eosinophilic esophagitis 39 . The argument has been made that VR makes it possible to avoid sedation for colonoscopy, which fuels patient experience 40 . Therefore it is probable that in selected patients, VR during colonoscopy will be the preferred option 29 .
Strengths and limitations
Our study was performed in a real-life setting and a representative sample of patients, which add to its external validity. By using Samsung Gear VR to provide distraction, we chose a widely available and relatively inexpensive VR device, enhancing the generalizability of the results.
Our study also comes with limitations. First, the small sample size does not allow robust statements on clinically relevant endpoints like reducing anxiety or pain or improving patient satisfaction. Also, recent literature suggests that our sample size computation carries the risk of overestimation of the required sample size when designing a main trial to confirm our results 41 . Second, the physicians who performed the procedure were not blinded, because the patients in the control group did not wear VR glasses. Although we did not observe a difference in administration of drugs in the control and intervention groups, this could have affected the choice and dose of sedatives. The ideal set-up is a direct comparison of sedation vs VR, instead of VR combined with sedation as done in our pilot.
We used patient-reported measures for pain and comfort after patients were recovering from sedative administration. The post-amnesia effect of midazolam might have had some effect, but the Gloucester scale rated by the nursing staff revealed no differences between groups.
Because of the low costs of the VR device, VR distraction may easily be deployed in colonoscopy. There are several technical shortcomings such as low resolution, orientation, and content, which if resolved may improve the distractive effect and help ensure enhanced patient comfort and satisfaction.
To achieve a maximal immersive effect, VR content must be developed that provides specific targeted distraction for colonoscopy, such as relaxing colors, relaxing music, and properly selected visualizations.
Conclusion
In summary, patients accepted VR distraction undergoing colonoscopy, without compromising the technical success of the procedure. Future studies are justified to evaluate the possible substitution of sedation with VR. Patients reported that the VR experience was pleasant and distracting, facilitating recruitment for these trials.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Fia Voogd (FV) and Dr. Björn van Heumen (BvH) as the participating endoscopists in this trial.
Footnotes
Competing interests Funding for the trial was supported by Radboudumc. Visyon (supplier of hardware) had no role in the funding of this trial, nor in design and conduct of the study or in the writing and submission of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Peterse E FP, Meester R GS, Siegel R L et al. The impact of the rising colorectal cancer incidence in young adults on the optimal age to start screening: Microsimulation analysis I to inform the American Cancer Society colorectal cancer screening guideline. Cancer. 2018;124:2964–2973. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lauriola M, Tomai M, Palma R et al. Intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety-related dispositions predict pain during upper endoscopy. Frontiers Psychol. 2019;10:1112. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brandt L J. Patients' attitudes and apprehensions about endoscopy: how to calm troubled waters. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:280. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bynum S A, Davis J L, Green B L et al. Unwillingness to participate in colorectal cancer screening: examining fears, attitudes, and medical mistrust in an ethnically diverse sample of adults 50 years and older. Am J Health Promotion. 2012;26:295–300. doi: 10.4278/ajhp.110113-QUAN-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shafer L A, Walker J R, Waldman C et al. Factors associated with anxiety about colonoscopy: the preparation, the procedure, and the anticipated findings. Digest Dis Sci. 2018;63:610–618. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-4912-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cohen L B, Delegge M H, Aisenberg J et al. AGA Institute review of endoscopic sedation. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:675–701. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cote G A, Hovis R M, Ansstas M A et al. Incidence of sedation-related complications with propofol use during advanced endoscopic procedures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:137–142. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee L A, Caplan R A, Stephens L S et al. Postoperative opioid-induced respiratory depression: a closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology. 2015;122:659–665. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kollmann C M, Schmiegel W, Brechmann T. Gastrointestinal endoscopy under sedation is associated with pneumonia in older inpatients-results of a retrospective case-control study. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018;6:382–390. doi: 10.1177/2050640617735059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wernli K J, Brenner A T, Rutter C M et al. Risks associated with anesthesia services during colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:888–894; quiz e818. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lin O S. Sedation for routine gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures: a review on efficacy, safety, efficiency, cost and satisfaction. Intest Res. 2017;15:456–466. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.4.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.El Hassan H, McKeown K, Muller A. Clinical trial: music reduces anxiety levels in patients attending for endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Therap. 2009;30:718–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee D, Chan A, Wong S et al. Can visual distraction decrease the dose of patient-controlled sedation required during colonoscopy? A prospective randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2004;36:197–201. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-814247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martindale F, Mikocka-Walus A A, Walus B P et al. The effects of a designer music intervention on patients' anxiety, pain, and experience of colonoscopy: a short report on a pilot study. Gastroenterol Nursing. 2014;37:338–342. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0000000000000066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Umezawa S, Higurashi T, Uchiyama S et al. Visual distraction alone for the improvement of colonoscopy-related pain and satisfaction. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:4707. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nomura T, Higuchi K, Yu H et al. Slow‐wave photic stimulation relieves patient discomfort during esophagogastroduodenoscopy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:54–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fanti L, Gemma M, Passaretti S et al. Electroacupuncture analgesia for colonoscopy: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:312–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lembo T, Fitzgerald L, Matin K et al. Audio and visual stimulation reduces patient discomfort during screening flexible sigmoidoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1113–1116. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sjolander A, Jakobsson Ung E, Theorell T et al. Hospital design with nature films reduces stress-related variables in patients undergoing colonoscopy. HERD. 2019;12:186–196. doi: 10.1177/1937586719837754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gold J I, Belmont K A, Thomas D A. The neurobiology of virtual reality pain attenuation. CyberPsychol Behav. 2007;10:536–544. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2007.9993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoffman H G, Richards T L, Van Oostrom T et al. The analgesic effects of opioids and immersive virtual reality distraction: evidence from subjective and functional brain imaging assessments. Anes Analg. 2007;105:1776–1783. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000270205.45146.db. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chapman C R, Nakamura Y. Hypnotic analgesia: A constructivist framework. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 1998;46:6–27. doi: 10.1080/00207149808409987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McCaul K D, Malott J M. Distraction and coping with pain. Psychol Bull. 1984;95:516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dascal J, Reid M, IsHak W W et al. Virtual reality and medical inpatients: a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2017;14:14–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeffs D, Dorman D, Brown S et al. Effect of virtual reality on adolescent pain during burn wound care. J Burn Care Res. 2014;35:395–408. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0000000000000019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Maani C V, Hoffman H G, Morrow M et al. Virtual reality pain control during burn wound debridement of combat-related burn injuries using robot-like arm mounted VR goggles. J Trauma. 2011;71:S125. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31822192e2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Das D A, Grimmer K A, Sparnon A L et al. The efficacy of playing a virtual reality game in modulating pain for children with acute burn injuries: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Ped. 2005;5:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-5-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Furman E, Jasinevicius T R, Bissada N F et al. Virtual reality distraction for pain control during periodontal scaling and root planing procedures. J Am Dental Assoc. 2009;140:1508–1516. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2009.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Blokzijl S J, Lamberts K F, van der Waaij L A et al. Short article: Willingness to undergo colonoscopy with virtual reality instead of procedural sedation and analgesia. Europ J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;31:334–339. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Julious S A. Sample size of 12 per group rule of thumb for a pilot study. Pharm Stat. 2005;4:287–291. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Vander Zee K I, Sanderman R, Heyink J W et al. Psychometric qualities of the RAND 36-Item Health Survey 1.0: a multidimensional measure of general health status. Int J Behav Med. 1996;3:104–122. doi: 10.1207/s15327558ijbm0302_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Breivik H, Borchgrevink P, Allen S et al. Assessment of pain. Br J Anaesthesia. 2008;101:17–24. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Spielberger C D. Plato Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press; 1987. Manual for the State‐Trait anxiety inventory (form Y) [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rostom A, Ross E D, Dubé C et al. Development and validation of a nurse-assessed patient comfort score for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Reichheld F F. The one number you need to grow. Harvard Bus Rev. 2003;81:46–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kipping B, Rodger S, Miller K et al. Virtual reality for acute pain reduction in adolescents undergoing burn wound care: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Burns. 2012;38:650–657. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2011.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Morris L D, Louw Q A, Crous L C. Feasibility and potential effect of a low-cost virtual reality system on reducing pain and anxiety in adult burn injury patients during physiotherapy in a developing country. Burns. 2010;36:659–664. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2009.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McCarthy J D, Sasse M A, Miras D. Vienna, Austria: Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems; 2004. Sharp or smooth? comparing the effects of quantization vs. frame rate for streamed video. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nguyen N, Lavery W J, Capocelli K E et al. Transnasal endoscopy in unsedated children with eosinophilic esophagitis using virtual reality video goggles. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.01.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Terruzzi V, Paggi S, Amato A et al. Unsedated colonoscopy: A neverending story. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;4:137–141. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i4.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Whitehead A L, Julious S A, Cooper C L et al. Estimating the sample size for a pilot randomised trial to minimise the overall trial sample size for the external pilot and main trial for a continuous outcome variable. Stat Methods Med Res. 2016;25:1057–1073. doi: 10.1177/0962280215588241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


