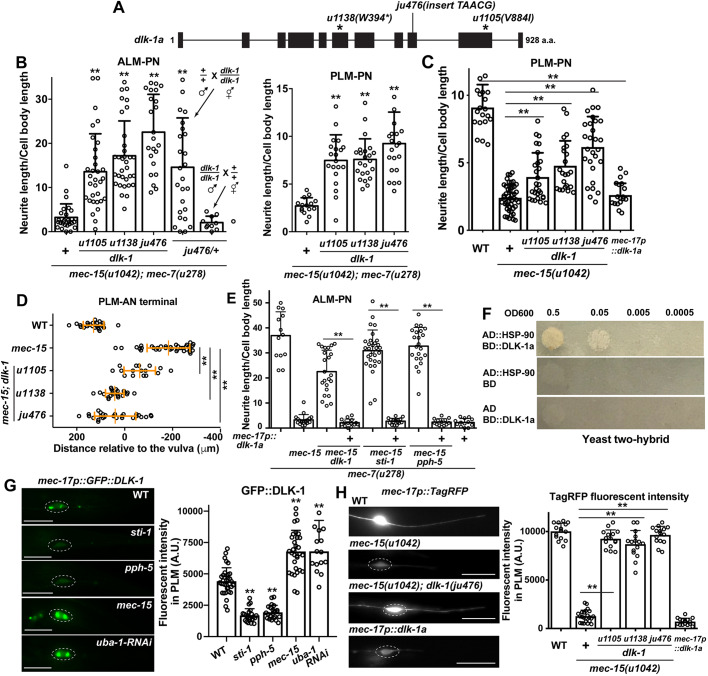
Fig. 5.
DLK-1 acts downstream of the chaperones to destabilize MTs and inhibit neurite growth. (A) Gene structure of the long isoform (a) of dlk-1 and the positions of three lf mutations. (B) Effects of dlk-1 mutations on the normalized neurite length of ALM-PN and PLM-PN in mec-15(u1042); mec-7(u278) animals. The ALM-PN length in ju476/+ animals was examined in male cross progeny. **P<0.01 between the test group and mec-15; mec-7 double mutants. (C) The length of PLM-PN in dlk-1; mec-15 mutants and wild-type animals expressing the mec-17p::dlk-1a transgene. (D) The distance between the PLM-AN terminal and the vulva in the dlk-1; mec-15 mutants grown at 25°C. (E) The length of ALM-PN in mec-7(u278) animals with indicated mutant genotype. Some animals expressed a mec-17p::dlk-1a transgene. The dlk-1(ju476), sti-1(ok3354) and pph-5(ok3498) alleles were used. (F) Yeast two-hybrid assays for the interaction between AD::HSP-90 and BD::DLK-1a. AD means the Gal4 activation domain and BD means the Gal4 DNA-binding domain. (G) Fluorescent intensity of GFP::DLK-1 expressed from the TRN-specific mec-17 promoter in wild type, sti-1(ok3354), pph-5(ok3498) and mec-15(u1042) mutants, and animals carrying the mec-17p::uba-1RNAi transgenes. Dashed circles enclose PLM cell bodies; scale bar: 20 µm. Double asterisks indicate significant difference from the wild type (WT). (H) Fluorescent intensity of TagRFP expressed from mec-17 promoter in dlk-1; mec-15 double mutants and in wild-type animals expressing the mec-17p::dlk-1a transgene. A.U., arbitrary units. Data are mean±s.d. (**P<0.01).