Abstract
Background
Ten-eleven translocation (Tet) methyl-cytosine dioxygenases (including Tet1/2/3)-mediated 5mC oxidation and DNA demethylation play important roles in embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis. The expression of Tet2 and Tet3 genes are relatively abundant in the adult murine kidneys while Tet1 gene is expressed at a low level. Although Tet3 has been shown to suppress kidney fibrosis, the role of Tet2 in kidney physiology as well as renal ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury is still largely unknown.
Results
Tet2−/− mice displayed normal kidney morphology and renal function as WT mice while the expression of genes associated with tight junction and adherens junction was impaired. At 24 h post-renal IR, Tet2−/− mice showed higher SCr and BUN levels, more severe tubular damage, and elevated expression of Kim1 and Ngal genes in the kidney in comparison with WT mice. Moreover, the transcriptomic analysis revealed augmented inflammatory response in the kidneys of Tet2−/− mice.
Conclusions
Tet2 is dispensable for kidney development and function at baseline condition while protects against renal IR injury possibly through repressing inflammatory response. Our findings suggest that Tet2 may be a potential target for the intervention of IR-induced acute kidney injury (AKI).
Keywords: Tet2, Kidney, Cell junctions, Ischemia-reperfusion injury, Inflammatory response
Introduction
Ten-eleven translocation (Tet) family methyl-cytosine dioxygenases (Tet1, Tet2, and Tet3) are key enzymes to convert 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC) [1–3]. Tet protein-catalyzed 5mC oxidation generates new epigenetic modifications and initiates active and passive DNA demethylation [4]. Emerging evidence has shown that Tet family genes and 5mC oxidation are critical for not only embryonic development but also the maintenance of adult tissue homeostasis [5]. Tet1–3 have differential expression pattern in the kidney, with relatively high expression of Tet2 and Tet3 and low expression of Tet1 [6, 7]. We have previously shown that Tet2 is dramatically downregulated in the IR-injured kidney, which is accompanied by a reduction of the global 5hmC level [7]. By performing hydroxymethylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (hMeDIP-seq) analysis, we also revealed that 5hmC was enriched in the gene body regions of renal IR injury-associated genes [8]. In addition, a few studies have shown that Tet3 confers protection against kidney fibrosis [9–11].
These above-mentioned studies suggest that Tet family genes as well as 5mC oxidation may play important roles in regulating the physiological and pathophysiological processes in the kidney. However, the functional importance of Tet2 gene in the kidney as well as renal IR injury remains unknown. Using a unique Tet2−/− mouse model, here, we determined the impact of Tet2 deficiency on the function of the kidney at baseline as well as in response to renal IR injury. Our findings suggest that Tet2 is dispensable for kidney development but limits kidney damage following IR. Mechanistically, we identified that Tet2 regulates a specific set of genes that are involved in cell junctions and inflammatory response. Thus, our findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanism regulating kidney homeostasis and renal IR injury.
Results
Tet2 deficiency does not influence kidney development and normal renal function
Tet2−/− mice could spontaneously develop chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) in their adult stage (starting from 2–4 months) [12–15]. To avoid the secondary effect of Tet2 depletion-induced hematopoietic dysfunction on the kidney, we used 6-week-old male mice in the current study. Indeed, there were no CMML-like pathological changes in the peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow of Tet2−/− mice at a young age (data not shown). Importantly, there was no difference in the morphology and histological structure of kidneys between WT and Tet2−/− groups of mice (Fig. 1a–c). Moreover, the SCr and BUN levels (two plasma markers of renal dysfunction) in Tet2−/− mice were also comparably low as those in WT mice (Fig. 1d, e).
Fig. 1.
Tet2 deficiency does not influence kidney development and normal renal function. a Morphology of the kidneys and spleens from WT and Tet2−/− mice at 6 weeks old. b, c H&E staining of the kidneys from WT and Tet2−/− mice at 6 weeks old. d, e Serum creatinine (d) and blood urea nitrogen (e) concentrations of WT and Tet2−/− mice under baseline conditions. N = 3 in each group
Tet2 deficiency impairs the expression of genes associated with cell junctions in the kidney
To understand the role of Tet2 in the kidney, we performed RNA-seq analysis of the transcriptomes in WT and Tet2−/− mice kidneys. Compared with WT mice, 452 differentially expressed genes (24 upregulated genes and 428 downregulated genes) were identified in the kidneys of Tet2−/− mice (Fig. 2a). KEGG pathway analysis revealed that “fructose and mannose metabolism,” “tight junction,” and “proteoglycans in cancer” were the top three enriched terms in the downregulated genes (Fig. 2b). Gene set enrichment analyses (GSEA) revealed that the downregulated genes in the kidney tissues of Tet2−/− mice were significantly enriched for the “adherens junction” and “tight junction” gene sets (Fig. 2c, d). Moreover, key regulators in the above biological processes, i.e., Cldn8 and Tjp1, were validated by RT-qPCR (Fig. 2e).
Fig. 2.
Tet2 deficiency impairs the expression of genes associated with cell junctions in the kidney. The kidneys from WT and Tet2−/− mice (n = 3 in each genotype) were subjected to RNA-seq analysis. a Scatter plotting of the differentially expressed genes in the kidneys between WT and Tet2−/− mice. Green dot, downregulated gene; red dot, upregulated gene. b Top 10 terms of the pathway analysis of the downregulated genes. c, d Gene set enrichment analyses (GSEA) of RNA-seq data for WT and Tet2−/− mouse kidneys, revealing the association of the gene program in Tet2−/− mouse kidneys with the “tight junction” (c) and “adherens junction” (d) gene signature. e qRT-PCR analysis of two representative genes (Tjp1 and Cldn8) in the kidneys from WT and Tet2−/− mice. *P < 0.05. N = 3 in each group
Tet2 deficiency exacerbates renal IR injury in mice
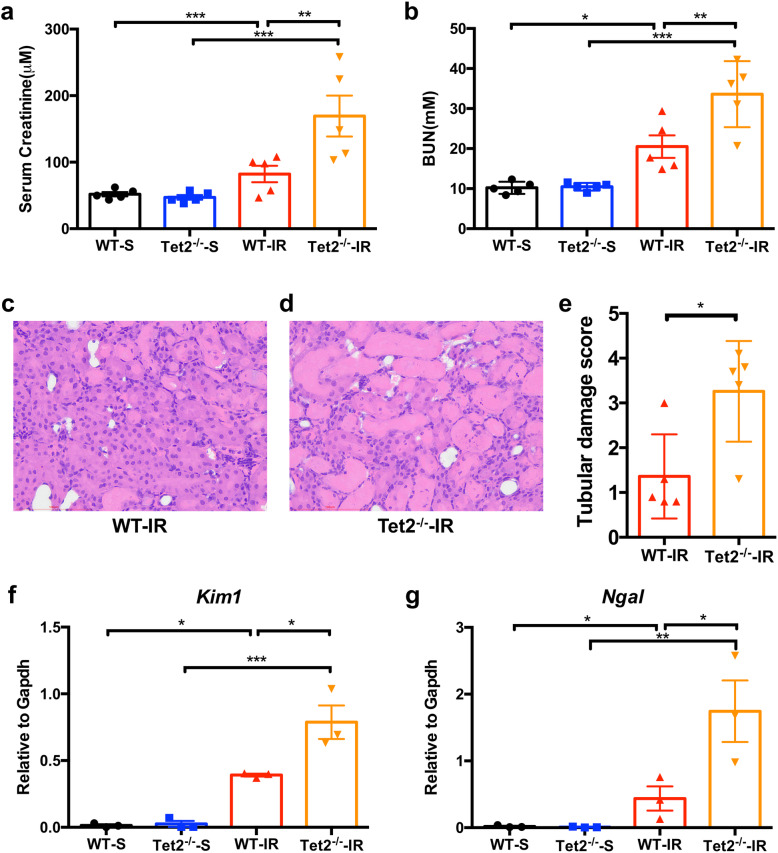
We then examined whether Tet2 depletion affects the response of the kidney to pathological stimulus. WT and Tet2−/− mice were subjected to sham operation or renal IR. Compared with the sham group, IR significantly increased SCr and BUN levels in WT mice, both of which were further elevated in Tet2−/− mice in response to renal IR (Fig. 3a, b). As revealed by H&E staining, IR caused tubular detachment, foamy degeneration, and necrosis in the kidneys from both genotypes of mice (Fig. 3c, d). However, Tet2−/− mice displayed more severe tubular damage than WT mice (Fig. 3c–e). Moreover, the mRNA levels of Kim1 and Ngal, two well-known renal IR injury marker genes [16, 17], were significantly higher in the IR-insulted kidneys from Tet2−/− mice than those from WT mice (Fig. 3f, g).
Fig. 3.
Tet2 deficiency exacerbates renal IR injury in mice. Mice were subjected to sham operation or 60 min of warm kidney ischemia. Blood and kidney tissues were collected at 24 h after reperfusion for the following analyses. S, sham-operated; IR, ischemia-reperfusion injury; WT, wild type; Tet2−/−, Tet2 knockout mice. a, b Serum creatinine (a) and blood urea nitrogen (b) concentrations of WT and KO mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. N = 5 in each group. c, d Representative micrographs showing the morphology of the IR-insulted kidneys from WT (c) and Tet2−/− (d) mice. Arrows show the injury. e Quantitative assessment of tubular damage. *P < 0.05. N = 5 in each group. f, g The mRNA levels of Kim1 and Ngal were measured by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. N = 3 in each group
Tet2 deficiency boosts inflammation in kidney upon IR injury
To determine the potential molecular mechanism underlying the protective role of Tet2 in the kidney, we profiled the transcriptomes of the IR-insulted kidneys from WT and Tet2−/− mice. Compared to the counterparts from WT mice, the IR-insulted kidneys from Tet2−/− mice displayed 928 upregulated genes and 1092 downregulated genes (Fig. 4a). KEGG pathway analyses for the upregulated genes identified “leukocyte aggregation,” “cellular response to cytokine stimulus,” “negative regulation of hemostasis,” and “positive regulation of inflammatory response” in the top 10 enriched terms (Fig. 4b). Persisting inflammation contributes to renal damage following IR. We found that the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory genes (Il6, Tnf-alpha, and Il1-beta) and chemokine genes (Cxcl2, Ccl6, and Ccl2) are significantly higher in the IR-insulted kidneys from Tet2−/− mice than those from WT mice (Fig. 4c). The changes in Il6 and Tnf-alpha mRNAs were validated by qRT-PCR (Fig 4d, e). Consistently, higher expression levels of macrophage markers (CD14 and CD11b) and neutrophil markers (S100a8 and S100a9) were also observed in the IR-insulted kidneys from Tet2−/− mice (Fig. 4c). For the downregulated genes, metabolism processes (such as catabolic process, metabolic process, and biosynthetic process) were enriched (Fig. 4f), suggesting that Tet2 deficiency may dampen the renal metabolism during IR injury.
Fig. 4.
Tet2 deficiency boosts inflammation in the kidney upon IR injury. The IR-insulted kidney tissues from WT and Tet2−/− mice (n = 3 in each genotype) were subjected to RNA-seq analysis. a Scatter plotting of the differentially expressed genes in the IR-insulted kidney tissues from WT and Tet2−/− mice. Green dot, downregulated genes; red dot, upregulated genes. b Top 10 terms of the pathway analysis of the upregulated DEGs in the IR-insulted kidney between WT and Tet2−/− mice. c Heatmap showing the augmented expression of renal inflammation-related genes. d, e The mRNA levels of IL6 (d) and TNF-alpha (e) were measured by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. N = 3 in each group. f Top 10 terms in the pathway analysis of downregulated DEGs in the IR-insulted kidney between WT and Tet2−/− mice
Discussion
In the current study, we used WT and Tet2−/− mice as a comparative model to explore the functional role of Tet2 in the kidney and demonstrated that Tet2 deficiency impairs the expression of genes associated with cell junctions and exacerbates IR-induced AKI. These findings extended our understanding of the physiological and pathophysiological function of Tet2, a key regulator of DNA demethylation. To our knowledge, this work for the first time establishes the functional role of Tet2 in the kidney.
Since Rao and colleagues identified TET1 as the first 5mC dioxygenase in 2009, TET family genes have attracted increasing attention regarding their physiological function in various contexts [1, 4]. Our data uncover that Tet2 gene is dispensable for kidney development and physiological function as its deficiency does not alter the morphology, histological structure, or functional markers of mouse kidney. This observation is consistent with the results of previous studies that Tet2 knockout mice had no significant phenotype despite hematological lineage dysregulation in the adult age [12, 14, 18]. While the loss of Tet2 does not impair kidney development and function, our transcriptomic analysis revealed that a panel of genes associated with cell junctions were inhibited in the kidneys of Tet2−/− mice. Cell junctions (including tight junction (TJ), adherens junction (AJ), gap junction (GJ), desmosomes, and hemidesmosomes) play important roles in the epithelial homeostasis [19, 20]. For instance, tight junctions at the most apical part of the basolateral plasma membrane create a selective diffusion barrier for epithelium [21]. Consistently, a recent study has shown that Tet2 depletion increases the intestinal permeability (especially the jejunum), leading to microbial leaky and chronic inflammation, which function as an extrinsic non-cell-autonomous factor for leukemia onset [22]. Therefore, the aberrant expression of cell junction genes indicates that Tet2 depletion may influence kidney function under stress conditions.
Our previous work has shown that Tet2 gene expression was downregulated in murine kidneys insulted by IR injury [7]. Therefore, we evaluated the impact of Tet2 deficiency on renal IR injury in this study and uncovered that Tet2 deficiency increases the susceptibility to renal IR injury. Miao et al. have reported that Tet2 knockout worsened ischemic brain injury in a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mouse model [23]. Their work together with ours indicates that Tet2 plays a protective role against IR injury and that such effect is not limited to a specific organ.
During the renal IR injury, oxidative stress induces necrosis of endothelial or epithelial cells, leading to sterile inflammation and amplified acute kidney injury [24]. Consistent with more severe AKI, we observed much higher expression levels of pro-inflammatory genes and immune cell markers in the IR-insulted kidneys from Tet2−/− mice. It has been reported that Tet2 knockout macrophages were more sensitive to lipopolysaccharide-induced IL6 production [25]. However, it is unclear whether such a stronger immune response in the IR-insulted kidneys of Tet2−/− mice is due to a direct effect of Tet2 loss on the immune system or rather a consequence of more severe renal tubule injury.
As one of the key epigenetic regulators, TET2 has 5mC dioxygenase activity and exerts its function in regulating chromatin structure and gene transcription through two mechanisms [4]. First, TET2 can convert 5mC to 5hmC/5fC/5caC and thereby initiate passive or active DNA demethylation. TET2 deficiency may impair gene transcription due to aberrant DNA hypermethylation on the regulatory regions such as promoters and enhancers [26, 27]. Alternatively, TET2 functions as a transcriptional co-repressor through recruiting SIN3A and HDAC1/2 histone deacetylases to chromatin and triggers histone deacetylation, which in turn inhibits gene transcription [28]. Given that both up- and downregulated genes were observed in the kidneys of Tet2−/− mice compared to WT mice, our findings indicate that both epigenetic regulatory mechanisms are likely to be involved in the renal protective role of TET2.
As one of the hotspots mutated genes in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs) of the elderly population, which was also known as clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) [29–31], TET2 mutation is associated with an increased risk for atherosclerosis and cardiac diseases [32]. However, the impact of hematopoietic TET2 mutation on the risk of acute or chronic kidney diseases in elder people is still unclear. In general, old patients are more vulnerable to IR-induced AKI than young ones [33]. Given that 5hmC (an index of TET activity) level was reduced in the kidney during aging [34], our findings indicate that the age-associated decline in TET activity may contribute to the increased risk of AKI and chronic kidney diseases in elderly patients. Since recent studies have shown that vitamin C could work as a direct regulator of Tet activity in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) [35, 36], it will be of great interest to determine whether vitamin C exerts its substantial clinical benefits on renal IR injury partially through activation of Tet2.
Conclusion
Taken together, our study demonstrates that Tet2 deficiency impairs the expression of genes associated with cell junctions in mouse kidney and increases the susceptibility to renal IR injury. These findings highlight a protective role of Tet2 in the kidney against IR-induced AKI and indicate that Tet2 may be a potential target for the prevention and therapy of perioperative AKI.
Methods
Animals
Breeding pairs of Tet2+/− mice with a C57BL/6J background were kindly provided by Dr. Guoliang Xu (State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) [37]. Wild-type (WT) and Tet2−/− (KO) mice were generated according to the half-sib mating and housed under specific pathogen-free conditions and a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle at 21–23 °C with ad libitum food and water. A total of 26 male mice (13 WT and 13 Tet2−/−) at a young age (6 weeks old) were used in the current study. Three pairs of mice were used for baseline condition analysis, and ten pairs of mice were used for renal IR injury as well as sham operation. All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (protocol no. 20170207), and conformed to the Animal Research-Reporting In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines.
Renal IR injury
WT and Tet2−/− male mice at around 6 weeks old were subjected to renal IR injury or sham operation. The renal IR injury model was performed as described previously [38]. In brief, mice were anesthetized with isoflurane. After an abdominal incision was made, IR injury was induced by clamping the renal pedicle of the right kidney for 60 min. After the clamps were released, the left kidney was removed. Before the wounds were sutured, 2 ml of saline was infused into the peritoneal cavity to keep the animals well hydrated. During the procedure, mice were warmed on a heating pad (36 °C) to maintain their body temperature. The mice under sham operation experienced a similar procedure except for renal ischemia. At the end of the experiment (24 h post-operation), all animals were euthanized by overdose (100 mg kg−1) of sodium pentobarbital and the blood and tissues were collected for the analyses of serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), RNA-seq, qRT-PCR, and histology.
RNA analysis
Total RNA was isolated from the kidney using TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
RNA-seq
RNA-seq library was constructed and sequenced by WuXi NextCODE (Shanghai). RNA-seq reads were aligned to the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) mouse genome mm9 using STAR. The tag directories were established. The raw read counts were measured with RefSeq genes using Homer, and the differential gene expression analysis was carried out using edgeR. The differential expression genes (DEGs) between WT and Tet2−/− kidneys were defined by over 1 or − 1 in the difference FPKM log2 value and FDR P value less than 0.05. Gene ontology (GO) and KEGG pathway analyses for DEGs were performed using DAVID functional annotation tools. Gene set enrichment analyses (GSEA) were performed according to the instructions. The raw RNA-seq data have been deposited in NCBI’s GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) and are accessible through the GEO Series accession number GSE151260.
RT-qPCR
Reverse transcription (RT) of cDNA was performed using the PrimeScript RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa). Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was conducted with SYBR Premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa) on the Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System. Levels of Gapdh were used as an internal control for the normalization of RNA quantity and quality differences among the samples. The sequence information of PCR primers is shown in the supplementary data (Table 1).
Table 1.
The sequences of qRT-PCR primers
| GeneBank ID | Gene symbol | Primer sequence (forward/reverse) |
|---|---|---|
| NM_008084 | Gapdh |
5′-GTGTTCCTACCCCCAATGTGT-3′ 5′-ATTGTCATACCAGGAAATGAGCTT-3′ |
| NM_009386 | Tjp1 (ZO-1) |
5′-CCACCTCTGTCCAGCTCTTC-3′ 5′-CACCGGAGTGATGGTTTTCT-3′ |
| NM_018778 | Cldn8 |
5′-TCCCAAGGCGTACAGATTTC-3′ 5′-CACTCTCCACTGAGGCATGA-3′ |
| NM_134248 | Kim1 (Havcr1) |
5′-AGCTCAGGGTCTCCTTCACA-3′ 5′-ACCACCCCCTTTACTTCCAC-3′ |
| NM_008491 | Ngal (Lcn2) |
5′-CTGAATGGGTGGTGAGTGTG-3′ 5′-GGAGTGCTGGCCAAATAAGA-3′ |
| NM_031168 | Il-6 |
5′-AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA-3′ 5′-TCCACGATTTCCCAGAGAAC-3′ |
| NM_013693 | Tnf-alpha |
5′-GAAAAGCAAGCAGCCAACCA-3′ 5′-CGGATCATGCTTTCTGTGCTC-3′ |
Assessment of renal function
Blood was centrifuged to collect serum. Serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were measured as markers of renal function using Creatinine Assay Kit (QuantiChrom, DICT-500) and Urea Assay Kit (QuantiChro, DIUR-500).
Histology
Formalin-fixed kidney sections were cut into 4 μm slides and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The percentage of tubules in the cortical-medullary junction that displayed cellular necrosis, loss of brush border, cast formation, and tubular dilatation was counted and scored in a blinded manner as follows: 0, none; 1, 0–10%; 2, 11–25%; 3, 26–45%; 4, 46–75%; and 5, > 75%. At least 10 high-power fields (HPFs, × 200 magnification) per section for each sample were examined. The pathologists who scored the degree of the injury were blinded.
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used for statistical analyses and graphs. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean). An unpaired t test was applied for two-group analyses. One-way ANOVA with Turkey’s test was applied for four-group analyses. For all analyses, P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Guoliang Xu (Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. R. China) for providing the Tet2 knockout mice, and Dr. Zhanggang Xue for critically reading the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- Tet2
Ten-eleven translocation 2
- 5hmC
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine
- IR
Ischemia-reperfusion
- AKI
Acute kidney injury
- SCr
Serum creatinine
- BUN
Blood urea nitrogen
- CMML
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
- TJ
Tight junction
- AJ
Adherens junction
- GJ
Gap junction
- DEGs
Differential expression genes
- CHIP
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential
- PMBCs
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Authors’ contributions
HW conceived the idea and designed the study. HW and JC supervised the study. HY and YL performed the experimental work. LT and NH performed bioinformatics and data analysis. HY, LT, and HW wrote the manuscript. All authors were involved in the final approval of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (81301615) to HW.
Availability of data and materials
Based on a reasonable request, the data from the current research analysis can be obtained from the corresponding author. The raw RNA-seq data are available through the GEO Series accession code GSE151260.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (protocol no. 20170207) and conformed to the Animal Research-Reporting In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines.
Consent for publication
We confirm that all authors agree with the submissions currently (and thereafter).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Huan Yan, Li Tan and Yuqi Liu contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Tahiliani M, Koh KP, Shen Y, Pastor WA, Bandukwala H, Brudno Y, et al. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science. 2009;324:930–935. doi: 10.1126/science.1170116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.He YF, Li BZ, Li Z, Liu P, Wang Y, Tang Q, et al. Tet-mediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA. Science. 2011;333:1303–1307. doi: 10.1126/science.1210944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB, Swenberg JA, et al. Tet proteins can convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine. Science. 2011;333:1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1210597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tan L, Shi YG. Tet family proteins and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in development and disease. Development. 2012;139:1895–1902. doi: 10.1242/dev.070771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Scott-Browne JP, Lio CJ, Rao A. TET proteins in natural and induced differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017;46:202–208. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ito S, D'Alessio AC, Taranova OV, Hong K, Sowers LC, Zhang Y. Role of Tet proteins in 5mC to 5hmC conversion, ES-cell self-renewal and inner cell mass specification. Nature. 2010;466:1129–1133. doi: 10.1038/nature09303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huang N, Tan L, Xue Z, Cang J, Wang H. Reduction of DNA hydroxymethylation in the mouse kidney insulted by ischemia reperfusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;422:697–702. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.05.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang H, Huang N, Liu Y, Cang J, Xue Z. Genomic distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse kidney and its relationship with gene expression. Ren Fail. 2016;38:982–988. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2016.1172973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tampe B, Tampe D, Muller CA, Sugimoto H, LeBleu V, Xu X, et al. Tet3-mediated hydroxymethylation of epigenetically silenced genes contributes to bone morphogenic protein 7-induced reversal of kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:905–912. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013070723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tampe B, Steinle U, Tampe D, Carstens JL, Korsten P, Zeisberg EM, et al. Low-dose hydralazine prevents fibrosis in a murine model of acute kidney injury-to-chronic kidney disease progression. Kidney Int. 2017;91:157–176. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.07.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tampe B, Tampe D, Zeisberg EM, Muller GA, Bechtel-Walz W, Koziolek M, et al. Induction of Tet3-dependent epigenetic remodeling by low-dose hydralazine attenuates progression of chronic kidney disease. EBioMedicine. 2015;2:19–36. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2014.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li Z, Cai X, Cai CL, Wang J, Zhang W, Petersen BE, et al. Deletion of Tet2 in mice leads to dysregulated hematopoietic stem cells and subsequent development of myeloid malignancies. Blood. 2011;118:4509–4518. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-325241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pronier E, Almire C, Mokrani H, Vasanthakumar A, Simon A, da Costa Reis Monte Mor B, Masse A, Le Couedic JP, Pendino F, Carbonne B, et al: Inhibition of TET2-mediated conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine disturbs erythroid and granulomonocytic differentiation of human hematopoietic progenitors. Blood. 2011;118:2551–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Moran-Crusio K, Reavie L, Shih A, Abdel-Wahab O, Ndiaye-Lobry D, Lobry C, et al. Tet2 loss leads to increased hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and myeloid transformation. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Quivoron C, Couronne L, Della Valle V, Lopez CK, Plo I, Wagner-Ballon O, et al. TET2 inactivation results in pleiotropic hematopoietic abnormalities in mouse and is a recurrent event during human lymphomagenesis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:25–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wasung ME, Chawla LS, Madero M. Biomarkers of renal function, which and when? Clin Chim Acta. 2015;438:350–357. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alge JL, Arthur JM. Biomarkers of AKI: a review of mechanistic relevance and potential therapeutic implications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10:147–155. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12191213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dawlaty MM, Breiling A, Le T, Raddatz G, Barrasa MI, Cheng AW, et al. Combined deficiency of Tet1 and Tet2 causes epigenetic abnormalities but is compatible with postnatal development. Dev Cell. 2013;24:310–323. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.12.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Denker BM, Sabath E. The biology of epithelial cell tight junctions in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:622–625. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010090922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Macara IG, Guyer R, Richardson G, Huo Y, Ahmed SM. Epithelial homeostasis. Curr Biol. 2014;24:R815–R825. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hou J. The kidney tight junction (review) Int J Mol Med. 2014;34:1451–1457. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Meisel M, Hinterleitner R, Pacis A, Chen L, Earley ZM, Mayassi T, et al. Microbial signals drive pre-leukaemic myeloproliferation in a Tet2-deficient host. Nature. 2018;557:580–584. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0125-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Miao Z, He Y, Xin N, Sun M, Chen L, Lin L, et al. Altering 5-hydroxymethylcytosine modification impacts ischemic brain injury. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:5855–5866. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bonventre JV, Yang L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4210–4221. doi: 10.1172/JCI45161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang Q, Zhao K, Shen Q, Han Y, Gu Y, Li X, et al. Tet2 is required to resolve inflammation by recruiting Hdac2 to specifically repress IL-6. Nature. 2015;525:389–393. doi: 10.1038/nature15252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hon GC, Song CX, Du T, Jin F, Selvaraj S, Lee AY, et al. 5mC oxidation by Tet2 modulates enhancer activity and timing of transcriptome reprogramming during differentiation. Mol Cell. 2014;56:286–297. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kong L, Tan L, Lv R, Shi Z, Xiong L, Wu F, et al. A primary role of TET proteins in establishment and maintenance of De novo bivalency at CpG islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:8682–8692. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Williams K, Christensen J, Pedersen MT, Johansen JV, Cloos PA, Rappsilber J, et al. TET1 and hydroxymethylcytosine in transcription and DNA methylation fidelity. Nature. 2011;473:343–348. doi: 10.1038/nature10066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Genovese G, Kahler AK, Handsaker RE, Lindberg J, Rose SA, Bakhoum SF, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis and blood-cancer risk inferred from blood DNA sequence. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2477–2487. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, et al. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2488–2498. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1408617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xie M, Lu C, Wang J, McLellan MD, Johnson KJ, Wendl MC, et al. Age-related mutations associated with clonal hematopoietic expansion and malignancies. Nat Med. 2014;20:1472–1478. doi: 10.1038/nm.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fuster JJ, MacLauchlan S, Zuriaga MA, Polackal MN, Ostriker AC, Chakraborty R, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis associated with TET2 deficiency accelerates atherosclerosis development in mice. Science. 2017;355:842–847. doi: 10.1126/science.aag1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yokota LG, Sampaio BM, Rocha EP, Balbi AL, Sousa Prado IR, Ponce D. Acute kidney injury in elderly patients: narrative review on incidence, risk factors, and mortality. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2018;11:217–224. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S170203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Heylen L, Thienpont B, Busschaert P, Sprangers B, Kuypers D, Moisse M, et al. Age-related changes in DNA methylation affect renal histology and post-transplant fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2019;96:1195–1204. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sasidharan Nair V, Song MH, Oh KI. Vitamin C facilitates demethylation of the Foxp3 enhancer in a Tet-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2016;196:2119–2131. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blaschke K, Ebata KT, Karimi MM, Zepeda-Martinez JA, Goyal P, Mahapatra S, et al. Vitamin C induces Tet-dependent DNA demethylation and a blastocyst-like state in ES cells. Nature. 2013;500:222–226. doi: 10.1038/nature12362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hu X, Zhang L, Mao SQ, Li Z, Chen J, Zhang RR, et al. Tet and TDG mediate DNA demethylation essential for mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in somatic cell reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:512–522. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nezu M, Souma T, Yu L, Suzuki T, Saigusa D, Ito S, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 hyperactivation in early-phase renal ischemia-reperfusion injury prevents tubular damage progression. Kidney Int. 2017;91:387–401. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.08.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Based on a reasonable request, the data from the current research analysis can be obtained from the corresponding author. The raw RNA-seq data are available through the GEO Series accession code GSE151260.