Abstract
Background
The Mulam are an ethnic group native to Guangxi, and nearly 80% of the Mulam population lives in Luocheng Mulam Autonomous County, northern Guangxi, southern China. They have accumulated rich medicinal folk knowledge through practice and experience in their long-term struggles with disease and the harsh natural environment. However, their traditional medicinal knowledge is threatened due to a lack of written records, conservative inheritance patterns, and rapid economic development. Therefore, the investigation and documentation of medicinal plants and their associated indigenous wisdom are necessary.
Method
Ethnobotanical data were collected from 12 villages and five communities in Luocheng County from January 2013 to April 2017. A total of 128 informants were interviewed through semistructured interviews, field observations, group discussions, and guided field walks. Quantitative indices such as use categories, preference ranking exercises, the informant consensus factor (ICF), and the fidelity level (FL) were used to evaluate the importance of medicinal plant species. Additionally, group discussions were conducted about the conservation of and threats to medicinal plants and traditional knowledge.
Results
A total of 456 medicinal plant species from 350 genera and 132 families were recorded and documented in our ethnobotanical investigation. Most of them (335 species, 73.47%) were obtained from wild habitats. Most of the documented species (246) were herbaceous (54%), followed by shrubs, with 76 species (17%), lianas, with 75 species (16%), and trees, with 59 species (13%). The most common method of administration was oral administration, which was used for 390 species (62.70%). The most common method of preparation was decoction (316 species, 54.11%). The plants were used to treat 312 human diseases in 12 disease categories, and most of the categories had a high ICF value. The highest ICF value was recorded for gynecological ailments (0.92), followed by nervous and psychosomatic problems (0.90) and digestive system diseases (0.89). Traditional medicinal knowledge and medicinal plants are under threat due to conservative inheritance processes and anthropogenic pressures for various reasons.
Conclusion
A rich diversity of medicinal plants is distributed in the Mulam area, and these plants play an important role in healthcare among the Mulam people. Mulam people are skilled in using the plants in their surroundings to treat diseases in their daily lives. However, their traditional medicinal knowledge and medicinal plants are greatly threatened by rapid economic development for various reasons. Thus, policies and practices for the conservation of medicinal plants and the associated traditional knowledge are necessary.
Keywords: Medicinal plants, Mulam people, Traditional medicinal knowledge, Luocheng County
Background
Medicinal plants have been used for many centuries not only in rural areas but also increasingly by urban citizens in both developing and developed countries [1–7]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 80% of populations worldwide depend on herbal medicine for their healthcare needs, especially in rural areas [8]. In developing countries, traditional medicines provide an inexpensive source of primary health care due to the lack of modern health facilities [9, 10].
Herbal medicines have been widely accepted in China since ancient times. Shennong Bencao Jing (Shennong’s Herbal Classic) was the first book that systematically introduced and described traditional medicinal plant knowledge in the Eastern Han Dynasty (25 AD–220 AD) [11]. Traditional medicinal plants currently play an important role in protecting people’s lives and health in ethnic minority regions, especially in remote and less-developed areas [12–17].
Guangxi is an autonomous region of ethnic minorities, with Zhuang as the main group, and of multiethnic groups living together. The herbal medicinal markets during the Dragon-Boat Festival are very famous in the Zhuang and Yao communities of Guangxi [18–20]. Most members of ethnic minorities live in mountainous or hilly areas, and they are very good at using and naming the medicinal plants in their surroundings [21–25].
The Mulam are an ethnic group native to Guangxi, with a population of more than 210,000 [26]. Nearly 80% of the Mulam people live in Luocheng Mulam Autonomous County, Guangxi [26, 27]. Mulam people believe that human beings are an organic combination of “lingqi” (the energy that sustains living organisms), blood, tissue, bone, and muscle. They advocate “the unity of nature and man,” that is, harmony among people and between people and nature, with attention paid to both physical and mental health. “The unity of nature and man” is expressed in daily life as, for example, family members of all ages poking fun each other and through collective activity, such as the lion dance, dragon dance, monkey jumping, “zoupo” (antiphonal folk song singing by young people), and so on; these activities are beneficial to mental and physical health [28]. In their long history, Mulam people have accumulated rich folk medicinal knowledge and described many unique experiences in treating common local diseases (e.g., traumatic injuries, cough, diarrhea). Mulam folk medicinal knowledge has been enriched and developed through the process of use; this knowledge plays an important role in local daily life but has not been scientifically reported or studied. In addition, traditional medicinal knowledge is greatly threatened due to the lack of a written record and to conservative inheritance patterns. Young people prefer to look for higher-income jobs in urban areas and are not interested in traditional medicinal knowledge. Therefore, the investigation and documentation of medicinal plants and the associated indigenous wisdom are necessary. This study investigated medicinal plants and related traditional knowledge of the Mulam people, analyzed their ethnic medicinal characteristics and current threats, and proposed conservation strategies.
Methods
Study area
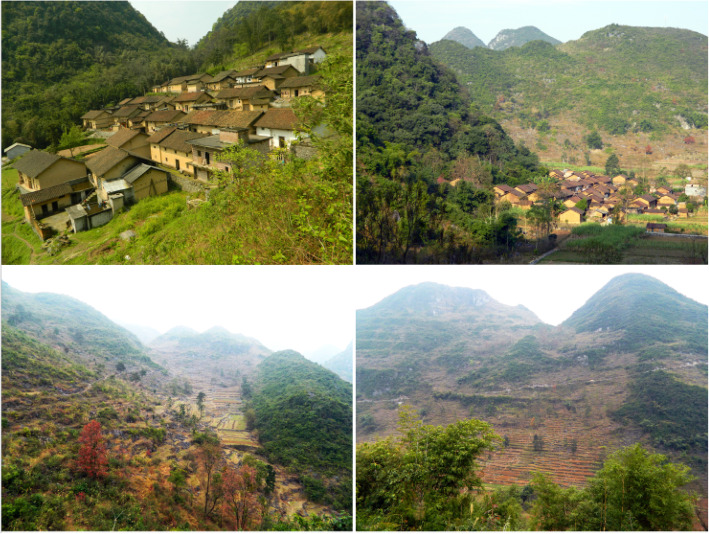
The study area is Luocheng Mulam Autonomous County, where the Mulam people live. Luocheng Mulam Autonomous County is situated in the subtropical zone between 24° 38′ and 25° 12′ east longitude and between 108° 29′ and 109° 10′ north latitude, with an annual average temperature of 19 °C and annual rainfall of 1566 mm. The vegetation category is the subtropical evergreen montane forest [26, 28]. Most Mulam villages are located on small strips of flat land or slopes in the karst mountainous area of southern Luocheng Mulam Autonomous County (Fig. 1). Based on the characteristics of traditional Mulam settlements and suggestions from local government officials, 12 villages (Xinan, Maan, Lining, Shuangzhai, Dashan, Youdong, Pingluo, Dafu, Lee, Dashanjiao, Deyin, Sanjia) and five townships (Dongmen, Xiali, Siba, Xiaochangan, Qiaotou) were selected as the investigation sites (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
Mulam villages and the surrounding farming fields
Fig. 2.
A sketch map of the study area
Mulam settled in Luocheng during the Pre-Qin Dynasty (twenty-first century BC–221 BC) [26, 27]. The Mulam language is part of the Dong-Shui branch of the Zhuang-Dong language group in the Chinese-Tibetan language family. The Mulam language has its own independent and complete language system and preserves the language of the ancient Yue people [29]. Mulam people have multiple beliefs. They believe that every village or region is protected by a deity, so they have constructed temples around their villages, such as “Shewang,” “Powang,” “Tuzhu,” “Zaowang,” and “God of Mountain” [28]. They also believe in Taoism and Buddhism. They grow rice, corn, and potatoes as staple foods. Cats and snakes are their taboo foods. Most Mulam people engage in traditional agriculture and can identify common herbal medicines and treat common diseases. For example, they use Artemisia argyi for traumatic injuries, Lobelia chinensis for wound healing, Sarcandra glabra for the common cold, and so on [28].
Ethnobotanical data collection
A total of 128 informants (81 males and 47 females) were interviewed in the study area. Among them, 84 informants were selected using the snowball method from the herbal medicinal market and Mulam villages, and 44 key informants were selected purposively and systematically after visiting local officers, village leaders, agricultural technicians, and other people in the study area via a reconnaissance survey prior to data collection. Local healers were automatically qualified as key informants who are custodians of indigenous knowledge of medicinal plants [30]. The informants were local inhabitants aged between 32 and 86 years old. Before each interview, prior informed consent was requested, and throughout the study, international codes of ethics were respected. After obtaining consent, various strata of participants (traditional healers, farmers, village leaders, religious leaders, and health officials) were interviewed.
Ethnobotanical data were collected from January 2013 to April 2017. Information about the medicinal use of plants was collected through semistructured interviews, observations, field visits, and group discussions in the investigation area [22, 31–33]. Interviews and discussions were performed based on a checklist of questions prepared in Chinese and translated into the Mulam language. The local names of the plants, the ailments treated by the plants, the plant parts used, the condition of the plant material, the modes of preparation, and the routes of administration were carefully recorded during the interviews with the informants. Vegetation categorization information was also requested and recorded. Other information, including the name, age, occupation, and education level of the informants, was collected in detail. Furthermore, we also recorded the geographic locality and date of the interview. Group discussions were conducted about the conservation of and threats to medicinal plants and traditional knowledge. In addition, the key informants were asked to perform preference ranking exercises.
Specimen collection and identification
Field observations were performed with traditional healers to identify the morphological features and habitats of each medicinal plant species. Voucher specimens and photographs of the local medicinal plants were collected from the field and from home gardens, and the habits and habitats of these plants were recorded. For future reference, voucher specimens were made and deposited in the Herbarium of Guangxi Institute of Botany (IBK), Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guilin, Guangxi, China.
Voucher specimens and photographs were identified and confirmed according to Flora of China, Flora of Guangxi, and botanical websites (e.g., http://www.tropicos.org/, http://www.cvh.ac.cn/search, http://www.plant.csdb.cn/). Finally, the identified specimens were reaffirmed by taxonomic experts from IBK, and the inventory of medicinal plants was completed.
Data analysis
Data analysis was carried out by using ethnobotanical investigation and descriptive statistical methods, such as frequency and percentage, to evaluate the importance of the plant species mentioned in the study area.
Preference ranking exercises [32–34] were conducted by asking informants to rank the most important medicinal plants that were frequently used by the local people based on their preference and the importance of the plant in the community. The plants in this exercise were shortlisted by the key informants, and then their importance in managing diseases was discussed. The ranking was based on the efficacy of the medicinal plants. If a medicinal plant was believed to be the most effective for a disease, it was given the highest value of 10 for the selected disease. In contrast, the least-effective plant would be given a value of 1. Each plant species was given a ranking based on its total score. The total ranking for the preference exercise was obtained by summing the number of informants who participated [28].
The informant consensus factor (ICF) was calculated to determine the effectiveness of the medicinal plants in each ailment category according to Heinrich et al. [31]. The formula is provided below:
nur is the number of individual reports of a plant use for a particular illness category and nt is the total number of species used by all informants for this illness category.
The fidelity level (FL) was calculated for each of the 15 preferred species for their popularity according to the key informants who cited them in the treatment of particular ailments [31, 35, 36]. The formula is provided below:
Ip is the number of informants who suggested the use of a species for the same major purpose (therapeutic use) and Iu is the total number of informants who mentioned the plant species for any use.
Results
Demographics of the informants
A total of 128 informants, 84 of whom were general informants and 44 of whom were key informants, from Luocheng County agreed to participate in this study. The distribution of informants by age, gender, and education level is shown in Table 1. The age of the informants ranged from 32 to 86 years old. Among them, 82.3% of informants were over 40 years old, 58.59% of informants had only a primary education, and 12.5% were illiterate. There were more male informants (81, 63.28%) than female informants.
Table 1.
Demographic profile of informants
| Indicator | Description | General informants | Key informants | Total | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 30–39 | 12 | 1 | 13 | 10.16 |
| 40–49 | 23 | 4 | 27 | 21.09 | |
| 50–59 | 25 | 17 | 42 | 32.81 | |
| 60–69 | 12 | 16 | 28 | 21.88 | |
| 70–79 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 7.81 | |
| ≧ 80 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 6.25 | |
| Gender | Male | 43 | 38 | 81 | 63.28 |
| Female | 41 | 6 | 47 | 36.72 | |
| Education | Illiteracy | 11 | 5 | 16 | 12.50 |
| Primary | 53 | 22 | 75 | 58.59 | |
| Secondary | 20 | 13 | 33 | 25.78 | |
| Tertiary | 0 | 4 | 4 | 3.13 |
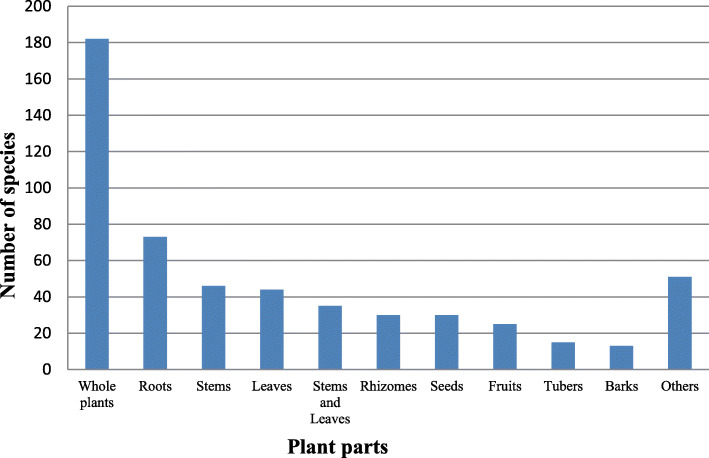
Medicinal plants recorded
From the study sites, a total of 456 medicinal plant species belonging to 350 genera and 132 families were documented. Ethnomedicinal information for each species, including its scientific name, Chinese name, Mulam name, family name, habit, habitat, plant parts used, cited sources, preparation, and use, is listed in Table 2.
Table 2.
Inventory of medicinal plants traditionally used by Mulam people
| Scientific name | Chinese name | Mulam name | Family | Habit | Habitat | Parts used | Preparation and uses | Cited sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abelmoschus sagittifolius (Kurz) Merr. | Jianyeqiukui箭叶秋葵 | – | Malvaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for kidney deficiency, backache | 451225130608007 |
| Abrus cantoniensis Wall. ex Wightet Arn. | Guangdongxiangsizi广州相思子 | hɣɔk8ci1kwət7 | Fabaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for jaundice hepatitis, stomachache, scrofula. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, painful swelling | 451225130719008 |
| Acalypha australis L. | Tiexiancai铁苋菜 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and promoting diuresis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for hemostasis with astringents | 451225130517008 |
| Achyranthes aspera L. | Tuniuxi土牛膝 | – | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for clearing away heat and toxic material, diuresis, treating for ascites, nephritis, sweating | 451225130517018 |
| Achyranthes bidentata Blume | Niuxi牛膝 | mai4cen1tən2 | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Wild | Root, Rhizome | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, traumatic injury. Decoction; taken orally for sore throat, urinary urgency, dysuria, furuncle and carbuncle | 451225130101019 |
| Achyranthes longifolia Makino | Liuyeniuxi柳叶牛膝 | – | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for calculosis | 451225130517052 |
| Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux | Wutou乌头 | – | Ranunculaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for hyperosteogeny | 451225130607001 |
| Acorus calamus L. | Changpu菖蒲 | – | Acoraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath, treating for carbuncle, headache | 451225130607020 |
| Acorus gramineus Soland. | Jinqianpu金钱蒲 | sik8tshja:ŋ1pu2 | Acoraceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for epilepsy, phlegm heat, abdominal distension, abdominal pain. Powdered, applied on the affected area for traumatic injury | 451225130310058 |
| Adina rubella Hance | Xiyeshuituanhua细叶水团花 | – | Rubiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for treating tracheitis | 451225130310001 |
| Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. | Longyacao龙芽草 | ma4ljen6a:n1 | Rosaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for stanching bleeding, cool the blood, dissipate blood stasis, diarrhea | 451225130719003 |
| Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. subsp. australis (Diels) T. Shimizu | Baimutong白木通 | – | Lardizabalaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Decoction; taken orally for nephritis | 451225130428026 |
| Alangium chinense (Lour) Harms. | Bajiaofeng八角枫 | pa:t7kak7foŋ1 | Cornaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem, Leaf, Root | Decoction; medicinal bath for treating rheumatism, numbness of limbs, internal lesion caused by overexertion, traumatic injury, dissipate blood stasis, relieve pain | 451225130421036 |
| Albizia julibrissin Durazz. | Hehuan合欢 | thəu5mu2kwa:n1tɔ1 | Fabaceae | Tree | Wild | Bark | Decoction; taken orally for treating restlessness, insomnia and dreaminess, ADHD. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for abscess, traumatic injury | 451225130430033 |
| Alchornea trewioides (Benth.) Muell. Arg. | Hongbeishanmagan红背山麻杆 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Medicinal bath, treating for eczema | 451225130307019 |
| Alisma orientale (Samuel) Juz. | Dongfangzexie东方泽泻 | – | Alismataceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for enteritis | 451225131107033 |
| Allium fistulosum L. | Cong葱 | thɔŋ1pa:k8 | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Home garden | Bulb | Decoction; taken orally for typhoid, headache, abdominal pain, constipation, urinary stoppage, diarrhea, abscess | 451225131107034 |
| Allium macrostemon Bge. | Yongbai薤白 | kɣo3ceu4 | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem | Decoction; taken orally for thoracic obstruction, diarrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle | 451225130729012 |
| Allium sativum L. | Suan蒜 | kɣo3hɣɔ2 | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Home garden | Bulb | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating fever, headache, angina, hiccough, anorexia, poor appetite, furuncle, carbuncle | 451225130311031 |
| Allium tuberosum Rottler ex Spreng. | Jiu韭 | ha:i5la:k8 | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed, Leaf | Fried; taken orally directly for treating impotence, nocturnal emission, frequent micturition, enuresis, diarrhea, leukorrhea, turbidity, infantile convulsion | 451225130723008 |
| Alocasia cucullata (Lour.) Schott | Jianweiyu尖尾芋 | – | Araceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction after slicing and drying; taken orally for hepatocirrhosis | 451225130425003 |
| Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. | Luhui芦荟 | ma1ləm6 | Xanthorrhoeaceae | Herb | Home garden | Leaf juice | Taken orally directly for treating constipation, infantile convulsion, infatile malnutrition with fever, ringworm, hemorrhoid complicated by anal fistula, scrofula | 451225131107017 |
| Alyxia sinensis Champ. ex Benth. | Lianzhuteng链珠藤 | – | Apocynaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for treating bladder cancer, uterine cancer | 451225130807002 |
| Amaranthus spinosus L. | Cixian刺苋 | – | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Home garden | Root | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for piles | 451225130606018 |
| Amomum tsaoko Crevost et Lemarie | Caoguo草果 | – | Zingiberaceae | Herb | both | Seed | Taken orally directly for aid digestion | 451225130728017 |
| Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch | Huamoyu花磨芋 | ɣa:k7la:i4 | Araceae | Herb | both | Tuber | Decoction after slicing and drying; taken orally for cough. Powdered, applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, furuncle, erysipelas | 451225130519009 |
| Amygdalus persica L. | Tao桃 | hwi1tɔ2la:k8 | Rosaceae | Tree | Home garden | Seed | Taken orally directly for treating dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain, traumatic injury, abscess of lung, intestinal carbuncle, constipation due to intestinal dryness | 451225130424017 |
| Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees | Chuanxinlian穿心莲 | tshjøn5təm1ljen2 | Acanthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for influenza, sore throat, tracheitis, pneumonia | 451225121230008 |
| Anredera cordifolia (Ten.) Steenis | Luokuishu落葵薯 | – | Basellaceae | Herb | Home garden | Tuber, Stem and leaf | Stewed with pork bone and drunk the soup for supplementary blood and nutrition. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area for dissipate blood stasis | 451225121230001 |
| Arachis hypogaea L. | Luohuasheng落花生 | ti6tau6 | Fabaceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed | Taken orally directly for treating irritating dry cough, stomachache, hypertension, dizziness due to deficiency of blood | 451225130606021 |
| Aralia chinensis L. | Huangmaocongmu黄毛楤木 | khai1mai4 | Araliaceae | Shrub | Wild | Bark or Stem | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath, treating for rheumatic arthritis, nephritis edema, ascites due to cirrhosis, hepatitis, stomachache, turbidity, metrorrhagia, traumatic injury, abscess | 451225130518021 |
| Arctium lappa L. | Niupang牛蒡 | tən2ha5la:k8 | Asteraceae | Herb | both | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for treating wind-heat type common cold, cough, sore throat, eczema | 451225130428019 |
| Ardisia crenata Sims | Zhushagen朱砂根 | – | Primulaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root, Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism | 451225130308012 |
| Ardisia gigantifolia Stapf. | Zoumatai走马胎 | ça:u1tsha:m3ma4 | Primulaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism, dispelling wind, remove dampness, removing blood stasis, traumatic injury, waist-leg weakness, carbuncle ulcer | 451225130610040 |
| Ardisia lindleyana D. Dietr. | Xiaoluosan小罗伞 | mai4ta:n5niŋ5 | Primulaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root or Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating rheumatoid arthritis, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225130311035 |
| Ardisia japonica (Thunb) Blume | Zijinniu紫金牛 | te3ti6tsa2 | Primulaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally and medicinal bath for treating chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis, nephritis, hypertension, swollen toxin, hernia | 451225130722002 |
| Areca catechu L. | Binglang槟榔 | – | Arecaceae | Tree | Home garden | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for liver ascites | 451225130610033 |
| Arisaema erubescens (Wall.) Schott | Yibasannanxing一把伞南星 | – | Araceae | Herb | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials | 451225130311032 |
| Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zuce. | Madongling马兜铃 | mai4həu1mɣa:ŋ1 | Aristolochiaceae | Liana | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for relieve pain, detoxifcation detumescence, blood pressure lowering | 451225130729011 |
| Aristolochia fordiana Hemsl. | Tongchenghu通城虎 | – | Aristolochiaceae | Liana | both | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for anti-inflammatory, gastritis, enteritis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite | 451225121204039 |
| Armeniaca mume Sieb. | Mei梅 | u5məi6 | Rosaceae | Tree | Home garden | Fruit | Taken orally directly for treating diarrhea, hemafecia, cough with lung heat, sore throat, depriving ascarid | 451225130426040 |
| Artemisia anomala S. Moore. | Qihao奇蒿 | pɛ:k8hwa1wəi1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for treating amenorrhea, abdominal distention, postpartum blood stasis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, carbuncle toxin | 451225130427037 |
| Artemisia argyi H. Lév. et Vaniot | Ai艾 | ŋa:i6fa5 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Leaf | Moxibustion; Treating for tocolysis, dysmenorrhea, irregular menses, leukorrhea, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis | 451225130720008 |
| Artemisia capillaris Thunb. | Yinchenhao茵陈蒿 | mau5hɣɔk8 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Stem and leaf | Taken orally directly for treating damp and hot jaundice, dysuria, sores | 451225130102009 |
| Artemisia carvifolia Buch.-Ham. ex Roxb. | Qinghao青蒿 | ŋa:i6həu1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating malaria, diarrhea, jaundice. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for scabies, pruritus | 451225130610003 |
| Artemisia indica Willd. | Wuyueai五月艾 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for dispelling wind and removing dampness | 451225130427028 |
| Artemisia scoparia Waldst. et Kit. | Zhumaohao猪毛蒿 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for treating stomachache | 451225130518018 |
| Arundo donax L. | Luzhu芦竹 | – | Poaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for pharyngitis, nephritis, edema | 451225130611004 |
| Asarum caudigerum Hance | Weihuaxixin尾花细辛 | – | Aristolochiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, for relieve pain, toothache, gout | 451225130309040 |
| Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr | Tianmendong天门冬 | mən6tɔŋ1 | Asparagaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for cough, hemoptysis, pneumalgia, sore throat | 451225130428020 |
| Bauhinia championii (Benth.) Benth. | Longxuteng龙须藤 | ça:u1ma6jin5 | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for gastritis, rheumatism, traumatic injury, bone fracture | 451225121231022 |
| Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. | Shegan射干 | məm6kwət7hɣɔk8 | Iridaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for sore throat, abscess, amenorrhea | 451225130428054 |
| Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn. | Donggua冬瓜 | tɔŋ5kwa1ŋɣa2 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Peel | Decoction; taken orally for nephritis edema, poor urination | 451225130430039 |
| Bidens bipinnata L. | Popozhen婆婆针 | la:i4tshəm1hɣɔk8 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for acute appendicitis, mastalgia, bacillary dysentery, angina, kidney deficiency, backache, nephritis, migraine. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite, traumatic injury | 451225130608021 |
| Bidens pilosa L. | Guizhencao鬼针草 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for degerming and anti-inflammatory | 451225130608026 |
| Bischofia javanica Blume | Qiufeng秋枫 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Tree | both | Root | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for piles | 451225131108037 |
| Bletilla formosana (Hayata) Schltr. | Xiaobaiji小白及 | – | Orchidaceae | Herb | Wild | Tuber | Stewed with pork bag and taken orally directly for tumour | 451225130309006 |
| Bletilla striata (Thunb. ex A. Murray) Rchb. f. | Baiji白及 | – | Orchidaceae | Herb | Wild | Tuber | Decoction; taken orally for gastric ulcer, tuberculosis | 451225130307037 |
| Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich. | Zhuma苎麻 | pə6ma6ta:ŋ1 | Urticaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for internal hemorrhage, hemokelidosis, threatened abortion, poor urination. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for poisoned sore, snake and insect injury | 451225130421030 |
| Botrychium lanuginosum Wall. | Rongmaoyindijue绒毛阴地蕨 | – | Ophioglossaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for lunacy, settle fright and quiet the spirit | 451225131107031 |
| Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. | Jiecai芥菜 | – | Brassicaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for calculosis | 451225130307031 |
| Bryophyllum pinnatum (L. f. ) Oken | Luodishenggen落地生根 | – | Crassulaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for detumescence relieve pain, detoxicating and generating muscles | 451225130607009 |
| Buchnera cruciata Buch. Mutis ex. L. f. Hamilt. | Heicao黑草 | hɣɔk8nam1 | Orobanchaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating eruptive disease, typhoid, epilepsy, painful swelling | 451225130310048 |
| Buddleja officinalis Maxim. | Mimenghua密蒙花 | – | Scrophulariaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for ascites due to cirrhosis, jaundice hepatitis | 451225130310013 |
| Callerya reticulata (Benth.) Schot | Wangluojixueteng网络鸡血藤 | – | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or rinsed, treating for rheumatism, free the channels and network vessels, osteoporosis | 451225130722005 |
| Callerya speciosa (Champ. ex Benth.) Schot | Meilijixueteng美丽鸡血藤 | – | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating tracheitis, osteoporosis | 451225130607039 |
| Callicarpa macrophylla Vahl | Dayezizhu大叶紫珠 | – | Verbenaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc, hyperosteogeny, rheumatism | 451225130607013, 451225130722004 |
| Camellia oleifera Abel | Youcha油茶 | tsa:i6jəu2 | Theaceae | Tree | Wild | Oil from seeds | Taken orally directly treating for abdominal pain, depriving ascarid, intestinal dryness and nodding. Applied on the affected area, treating for scabies, scald | 451225130421041 |
| Campanumoea javanica Blume Bijdr. | Jinqianbao金钱豹 | – | Campanulaceae | Herb | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for lung heat, dry cough | 451225130608018 |
| Canarium album (Lour.) Rauesch. | Ganlan橄榄 | ka:n3la:n3 | Burseraceae | Tree | Home garden | Fruit | Taken orally directly for sore throat, cough hemoptysis, bacillary dysentery, alleviate a hangover | 451225130609002 |
| Canna indica L. | Meirenjiao美人蕉 | tɔŋ6fa5 | Cannaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem, Flower | Decoction; taken orally for acute jaundice hepatitis, protracted dysentery, leukorrhea, irregular menses, hypertension. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, abscess | 451225130518003 |
| Canscora lucidissima (Levl. et Vant.) Hand.-Mazz. | Chuanxincao穿心草 | hɣɔk8tshjøn5təm1 | Gentianaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for hepatopathy, cough with lung heat, hepatitis, jaundice, pectoralgia, stomachache, traumatic injury | 451225130311007 |
| Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medic. | Jicai荠菜 | ma1ja4 | Brassicaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, edema, gonorrhea, internal hemorrhage, red eyes painful swelling | 451225130608022 |
| Cardiospermum halicacabum L. | Daodiling倒地铃 | – | Sapindaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally directly or pounded fresh part applied on the affected area for expelling parasite, relieve pain | 451225130519053 |
| Carica papaya L. | Fanmugua番木瓜 | – | Caricaceae | Tree | Home garden | Peel | Stewed with pork bone and drunk the soup, treating for osteoporosis | 451225130312001 |
| Cassytha filiformis L. | Wugenteng无根藤 | ça:u1khu5mɛ2ni4 | Lauraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diuresis, detumescence, cough with lung heat, jaundice, diarrhea, internal hemorrhage, abscess, scabies, scald | 451225130311062 |
| Catalpa ovata G. Don | Zi梓 | – | Bignoniaceae | Tree | Wild | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for hepatopathy | 451225130424024 |
| Cayratia albifolia C. L. Li | Baimaowulianmei白毛乌蔹莓 | ça:u1mu5mai4 | Vitaceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Leaf | Root: medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatic arthritis. Leaf: pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for unknown swollen toxin; Chewing, treating for toothache. | 451225130426036 |
| Cayratia japonica (Thunb.) Gagnep. | Wulianmei乌蔹莓 | ŋɔ4fa5mwa:i2 | Vitaceae | Liana | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for rheumatoid arthritis, jaundice, diarrhea, hematuria, gonorrhea, furuncle abscess, erysipelas | 451225130606003 |
| Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. | Nansheteng南蛇藤 | ta6pɣa1lɔŋ2 | Celastraceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Decoction; taken orally for arthralgia and myalgia, numbness of limbs, infantile convulsion, measles syndrome, diarrhea | 451225130430008 |
| Celosia argentea L. | Qingxiang青葙 | ja4ci1kon1hwa1 | Amaranthaceae | Herb | both | Seed | Medicinal bath for insecticidal | 451225130518039, 451225130608024 |
| Celosia cristata L. | Jiguanhua鸡冠花 | ci1kon1hwa1 | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Home garden | Inflorescence | Decoction; taken orally for internal hemorrhage, leukorrhea | 451225130607049 |
| Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. | Jixuecao积雪草 | chøt7pa:k7won3 | Apiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for prostatitis, eruptive disease, diarrhea, jaundice, internal hemorrhage, measles. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle abscess, traumatic injury | 451225130424011 |
| Centipeda minima (L.) A. Br. et Aschers. | Shihusui石胡荽 | hɣɔk8ŋa:n6khu5tsa:n1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for dissipate blood stasis, dispelling wind detumescence, hepatitis, common cold, pharyngitis, pertussis cough, diarrhea, malaria, nasosinusitis, hemorrhoids | 451225130611010 |
| Cephalotaxus fortunei Hook. | Sanjianshan三尖杉 | tau6la:n3sa1 | Cephalotaxaceae | Tree | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for dry cough, dry pharynx | 451225130430030 |
| Chenopodium hybridum L. | Zapeili杂配藜 | phɣə:t7nən1jəu1 | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for sore abscess, irregular menses, internal hemorrhage, enteritis, bacillary dysentery | 451225130425013 |
| Chloranthus henryi Hemsl. | Kuanyejinsulan宽叶金粟兰 | ti5phjen5ŋwa4 | Chloranthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism, arthralgia and myalgia, traumatic injury | 451225130723006 |
| Choerospondias axillaris (Roxb.) B. L. Burtt et A. W. Hill | Nansuanzao南酸枣 | – | Anacardiaceae | Tree | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for encephalemia | 451225130426037 |
| Chrysanthemum indicum L. | Yeju野菊 | cy6hwa1ja4 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Flower | Decoction; taken orally for anti-inflammatoryy, enteritis, rheumatism, wind-heat type common cold, pneumonia, diphtheritis, hypertension, furuncle, aptha, erysipelas, eczema | 451225121205038 |
| Chrysopogon aciculatus (Retz.) Trin. | Zhujiecao竹节草 | – | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diuresis detumescence, clearing away heat and toxic materials | 451225130611024 |
| Cibotium barometz (L.) J. Sm. | Jinmaogou金毛狗 | cəm1mɔ2ŋwa1 | Cibotiaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for hemiplegia, backache, rheumatism, urinary frequency, spermatorrhea, leukorrhea | 451225121204014, 451225130728003 |
| Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl | Zhang樟 | – | Lauraceae | Tree | both | Stem, Root | Decoction; taken orally for hepatosplenomegaly, edema, hepatitis | 451225130430032 |
| Cipadessa baccifera (Roth) Miq. | Huimaojiangguolian灰毛浆果楝 | – | Meliaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Medicinal bath for thermolysis, anti-inflammatory | 451225121230031 |
| Cirsium chinense Gardner et Champ. | Xiaoji小蓟 | ci1niŋ5 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant or Root | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating internal hemorrhage, irregular menses, damp and hot, jaundice. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound, furuncle, swollen toxin | 451225130422019 |
| Cirsium japonicum Fisch. ex DC. | Daji大蓟 | ci1lo4 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant or Root | Decoction; taken orally for internal hemorrhage, scald, mumps, jaundice, costalgia, intestinal carbuncle | 451225130422019 |
| Cissus pteroclada Hayata | Yijingbaifenteng翼茎白粉藤 | ça:u1ti5teŋ2 | Vitaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor or decoction; taken orally for activate collaterals, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury | 451225130310068 |
| Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. et Nakai | Xigua西瓜 | te1kwa1ŋɣa2 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Bark | Decoction; taken orally for hotness and polydipsia, oliguresis, edema | 451225130606028 |
| Citrus maxima (Burm.) Merr. | You柚 | – | Rutaceae | Tree | Home garden | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for sweating | 451225130426008 |
| Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck | Tiancheng甜橙 | ka:m5tsən2ŋɣa2 | Rutaceae | Tree | Home garden | Peel | Taken orally directly for abdominal distention, nausea, vomit | 451225131108015 |
| Citrus tangerina Hort. et Tanaka. | Fuju福橘 | cy6fa5 | Rutaceae | Tree | Home garden | Peel | Taken orally directly for costalgia, acute mastitis, lump of breast | 451225140408015 |
| Citrus trifoliata L. | Ji枳 | tsi2la:k8 | Rutaceae | Tree | Home garden | Fruit | slicing and drying, decoction; taken orally for rib expansion, dyspeptic retention, hiccup, alo laxata, rectal prolapse, uterine prolapse | 451225130721012 |
| Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels. | Huangpi黄皮 | ŋɣa2ŋa:n3hwi1la:k8 | Rutaceae | Tree | Home garden | Fruit | Taken orally directly for removing jaundice,hepatitis, dyspeptic retention, cough asthma | 451225130422041 |
| Clematis chinensis Osbeck. | Weilingxian威灵仙 | hɣɔk8məm4mut8 | Ranunculaceae | Liana | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for gout, obstinate arthralgia, barbiers, malaria, tetanus, painful swelling | 451225121205044 |
| Clerodendrum bungei Steud. | Choumudan臭牡丹 | ȵin1lɔ2ta:n1 | Lamiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for tuberculosis, carbuncle, furuncle, eczema, piles, rectal prolapse, infantile convulsion | 451225130426029 |
| Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum Turcz. | Daqing大青 | – | Lamiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded and heated the fresh part, applied on the affected area, treating for hyperosteogeny | 451225130729016 |
| Clerodendrum japonicum (Thunb.) Sweet | Chengtong赪桐 | – | Lamiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for rheumatism | 451225130606025 |
| Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson. | Shechuang蛇床 | twi2pho5la:k8 | Apiaceae | Herb | Wild | Fruit | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating impotence, rheumatoid arthritis, hemorrhoids eczema. Decoction; taken orally and medicinal bath for eczema scrotum, leukorrhea, pruritus vulvae, infertility | 451225130421020 |
| Coix lacryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen (Rom. Caill.) Stapf | Yimi薏米 | hɣɔk8lak8khau5 | Poaceae | Herb | both | Seed | Stewed; taken orally directly for dysuria, edema, inchacao, invigorating spleen, diarrhea, rheumatoid arthritis, abscess of lung, intestinal carbuncle | 451225130310025 |
| Commelina diffusa Burm. | Jiejiecao节节草 | – | Commelinaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for lithangiuria, clearing liver and eyesight, removing dampness | 451225130519005 |
| Coriandrum satiuum L. | Yuansui芫荽 | jøn6tok8 | Apiaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for measles, poor appetite, stomach cold | 451225130519021 |
| Corydalis saxicola Bunting | Yanhuanglian岩黄连 | pa:i2lε5huŋ6ljen2 | Papaveraceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for anti-inflammatory | 451225130426020 |
| Corydalis sheareri S. Moore | Dijinmiao地锦苗 | hu5təm1mwɔ5 | Papaveraceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Taken orally directly or pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for stomach heat, damp and hot jaundice, edema, traumatic injury, furuncle and carbuncle | 451225130307005 |
| Crassocephalum crepidioides (Benth.) S. Moore | Yetonghao野茼蒿 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for hyperplasia of mammary glands | 451225130519023 |
| Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N. E. Br. | Shanlihong山里红 | pɣa1tsa1 | Rosaceae | Tree | both | Fruit | Taken orally directly for abdominal distension, anorexia, abdominal pain | 451225130729010 |
| Crinum asiaticum L. var. sinicum (Roxb. ex Herb.) Baker | Wenshulan文殊兰 | khɣɛ1lɔŋ2ma4 | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Wild | Leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for abscess, traumatic injury, joint pain | 451225130430048 |
| Cucumis sativus L. | Huanggua黄瓜 | – | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Root, Seed | Root: Decoction; taken orally for rheumatism, removing jaundice, jaundice, hepatitis. Seed: taken orally directly for treating heart disease | 451225130609003 |
| Cucurbita moschata (Duch. ex Lam.) Duch. ex Poiret | Nangua南瓜 | cəm1kwa1piŋ5 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Peel, pedicel, Seed | Peel: Decoction; taken orally for stone. Pedicellus cucurbitae: Decoction; taken orally for treating stone, carbuncle, furuncle, scald, threatened abortion. Seed: taken orally directly, treating for tapeworm, depriving ascarid, postpartum blood stasis, piles | 451225130718020 |
| Cupressus funebris Endl. | Baimu柏木 | – | Cupressaceae | Tree | both | Bark | Decoction; taken orally for liver ascites | 451225130517006 |
| Curculigo orchioides Gaertn. | Xianmao仙茅 | pɣa1jyn6 | Hypoxidaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Stir-fry until dry after soaking with wine, then decoction or medicinal liquor for treating impotence, aconuresis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for carbuncle, scrofula | 451225130309002 |
| Curcuma longa L. | Jianghuang姜黄 | – | Zingiberaceae | Herb | both | Tuber | Slicinged and heated applied on the affected area for dissipate blood stasis, dredging collaterals | 451225130430037 |
| Curcuma phaeocaulis Valeton | Eshu莪术 | – | Zingiberaceae | Herb | both | Tuber | Decoction; medicinal bath for dissipate blood stasis, dysmenorrhea | 451225130501009 |
| Cyclea hypoglauca (Schauer) Diels | Fenyelunhuanteng粉叶轮环藤 | ça:u1phəp7 | Menispermaceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Stem, Leaf | Root: Decoction; taken orally for soothe throats, suppressing cough. Stem: Decoction; taken orally for expectorant. Leaf: Decoction; taken orally for sore throat, abdominal pain | 451225130310018 |
| Cynanchum amplexicaule (Sieb. et Zucc.) Hemsl. var. castaneum Makino | Zihuahezhangxiao紫花合掌消 | – | Apocynaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cool blood detoxifcation, hepatitis | 451225130424025 |
| Cynanchum atratum Bunge | Baiwei白薇 | – | Apocynaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for skin disease | 451225130523002 |
| Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. | Gouyagen狗牙根 | khɣət7tjen5hɣɔk8 | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for rheumatism, hemiplegia, over-strained hemoptysis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, bleeding wound, carbuncle | 451225130610024 |
| Cyperus rotundus L. | Xiangfuzi香附子 | hɣɔk8ti6cəu3 | Cyperaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; medicinal liquor; taken orally for clearing and activating the channels and collaterals, rheumatism, ostealgia, stomachache, asthma in children | 451225130606020 |
| Daemonorops jenkinsiana (Griffith) Martius | Huangteng黄藤 | ça:u1ŋa:n3 | Arecaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem or root | Decoction; taken orally for food-poisoning, constipation, diarrhea, infectious hepatitis, carbuncle, sore throat | 451225130311001 |
| Damnacanthus indicus C. F. Gaertn. | Huci虎刺 | – | Rubiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for treating stone, diuresis, nephropathy | 451225121230021 |
| Datura metel L. | Baimantuoluo白曼陀罗 | ma:n4tho6lo5 | Solanaceae | Herb | Home garden | Flower, Leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for alopecia. Decoction; medicinal bath, treating for cough with asthma, arthralgia, inchacao, rectal prolapse | 451225130523001 |
| Davallia divaricata Dutch et Tutch. | Dayegusuibu大叶骨碎补 | – | Davalliaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, for treating rheumatism, strengthening the bones and muscles, traumatic injury | 451225130307006 |
| Dendrobium nobile Lindl. | Shihu石斛 | hɣɔk8ŋa:n3 | Orchidaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem | Decoction; taken orally for febrile diseases, asthenia fever after illness | 451225130427039 |
| Desmodium gangeticum (L.) DC. | Dayeshanmahuang大叶山蚂蝗 | – | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diuresis | 451225121230019 |
| Desmodium racemosum (Thunb.) DC. | Shanmahuang山蚂蝗 | pɣa1miŋ2 | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for stomachache, infantile malnutrition | 451225131109003 |
| Desmodium multiflorum DC. | Dongmahuang饿蚂蝗 | – | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, anti-itch, infantile malnutrition | 451225130726004 |
| Dichondra repens Forst. | Matijin马蹄金 | ma1luk7 | Convolvulaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for throat inflammation, enteritis, liver ascites, jaundice, costalgia, urinary urgency, dysuria, irregular menses. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225130610014 |
| Dicliptera chinensis (L.) Juss. | Gougancai狗肝菜 | ma1tap7ŋwa1 | Acanthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for dizziness, tinnitus, bacillary dysentery hemafecia, dysuria, pyretic stranguria, measles | 451225130606001 |
| Dimocarpus longan Lour. | Longyan龙眼 | ȵøn2sik8 | Sapindaceae | Tree | Home garden | Aril | Taken orally directly for weakness of spleen and stomach, anorexia, diarrhea, insomnia dreaminess, palpitation, postpartum hypogalactia | 451225130101009 |
| Dioscorea bulbifcra L. | Huangdong黄独 | kɣa2ŋa:n3la:k8 | Dioscoreaceae | Liana | Wild | Tuber | Decoction; taken orally for antral gastritis, enteritis, thyroid disease, cough with lung heat, pudendal ulcer | 451225130430035 |
| Dioscorea cirrhosa Lour. | Shuliang薯莨 | – | Dioscoreaceae | Liana | Wild | Tuber | Stir-fry with rice; taken orally for fever in children | 451225130101027, 451225130430011 |
| Dioscorea esquirolii Prain et Burkill | Qiyeshuyu七叶薯蓣 | – | Dioscoreaceae | Liana | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; medicinal bath, treating for herpes, hyperthyreosis | 451225130312023 |
| Diospyros kaki Thunb. | Shi柿 | ca:u1ma3kai5 | Ebenaceae | Tree | both | Persistent calyx | Decoction; taken orally for vomiting, relieve hiccup | 451225130421035, 451225130428004 |
| Drynaria roosii Nakaike | Hujue槲蕨 | çiŋ1mu6lau2 | Polypodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decocted with water, slicing, drying, medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating kidney deficiency, backache, rheumatoid arthritis, toothache, tinnitus, traumatic injury, bone injury, appendicitis, pelada, heloma | 451225130311014, 451225130421012 |
| Dryopteris championii (Benth.) C. Chr. | Kuolinlinmaojue阔鳞鳞毛蕨 | kon5tsɔŋ1 | Dryopteridaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for anemopyretic cold ecchymosis, internal hemorrhage, leukorrhea, enteric verminosis | 451225130421053 |
| Duchesnea indica (Andr.) Focke. | Shemei蛇莓 | təm6twi2 | Rosaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for fever, cough, spitting blood, angina, diarrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for abscessfuruncle, snake bite, scald. | 451225130311059, 451225130424009 |
| Dysosma versipellis (Hance) M. Cheng | Bajiaolian八角莲 | – | Berberidaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for poisonous insect bite | 451225130612002 |
| Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin et Clemants | Tujingjie土荆芥 | ma1ȵin1 | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal bath or pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for treating for rheumatism painful swelling, eczema, poisonous insect bite | 451225130607023 |
| Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv. | Bai稗 | – | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diuresis detumescence, quiet the spirit | 451225130718016 |
| Eclipta Prostrata L. | Lichang鳢肠 | hɣɔk8ma1ha:n5 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating internal hemorrhage, premature graying hair, diphtheritis, turbidity, leukorrhea, pudendal eczema. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound, snake bite | 451225130421003, 451225130501038 |
| Elaeagnus glabra Thunb. | Manhutuizi蔓胡颓子 | – | Elaeagnaceae | Liana | Wild | Leaf, Fruit, Root | Leaf: Decoction; taken orally for calm panting and suppress cough. Fruit: Taken orally directly for anti-diarrhea | 451225131108045 |
| Elephantopus scaber L. | Didancao地胆草 | hɣɔk8tsja:k7ta:ŋ1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating gastritis, dental ulcer, pharyngitis, inchacao edema, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, furuncle | 451225130806001 |
| Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. | Niujincao牛筋草 | tən2cen1hɣɔk8 | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for fever, damp and hot jaundice, abdominal distention, lumbar muscle injury | 451225130610023 |
| Eleutherococcus nodiflorus (Dunn) S. Y. Hu | Xizhuwujia细柱五加 | ŋɔ4ca1ŋɣa2 | Araliaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root bark | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, cramp | 451225121205001 |
| Eleutherococcus trifoliatus (L.) S. Y. Hu | Baiha白簕 | – | Araliaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Root and leaf: Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, nephritis, renal tuberculosis, edema; pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for stanching bleeding; Stem: medicinal liquor; taken orally for rheumatism | 451225121205030 |
| Elsholtzia rugulosa Hemsl. | Baibeixiangru白背香薷 | ma1mɣa:ŋ1 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant with flower | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for headache fever, abdominal pain, vomit, diarrhea, edema, inchacao | 451225130608041 |
| Embelia parviflora Wall. ex A. DC. | Dangguiteng当归藤 | – | Primulaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for diuresis, edema | 451225121204018 |
| Emilia sonchifolia DC. | Yidianhong一点红 | nə5tjem3la:n3 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for urinary tract infection, kidney deficiency, sore throat, cough, urinary urgency, furuncle, herpes, eczema | 451225130312002 |
| Epimedium sagittatum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim. | Sanzhijiuyecao三枝九叶草 | hɣɔk8ta:n1ŋa5cəu3fa5 | Berberidaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Medicinal liquor or stewed with bone and drunk the soup, treating for impotence, dripping discharge of urine, soreness and weakness of waist and knees, rheumatoid arthritis | 451225121231009 |
| Equisetum diffusum D. Don | Pisanmuzei披散木贼 | – | Equisetaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, for anti-inflammatory, detumescence. Decoction; taken orally for nephritis, diuresis stranguria, renomegaly, clearing heat and improving eyesight | 451225130721013 |
| Equisetum hiemale L. | Muzei木贼 | hɣɔk8pət7tha:p7 | Equisetaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for conjunctivitis, sore throat, abdominal pain, hemafecia, edema | 451225131108023 |
| Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. | Pipa枇杷 | pε:k8pa2fa5 | Rosaceae | Tree | both | Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for ascites due to cirrhosis, cough with lung heat, hemoptysis, clearing away heat and toxic materials | 451225130426034 |
| Eriocaulon buergerianum Koern. | Gujingcao谷精草 | hɣɔk8muŋ4la1 | Eriocaulaceae | Herb | Wild | Inflorescence | Decoction; taken orally for nyctalopia, headache, toothache, pharyngitis, hemorrhinia | 451225130428017 |
| Erycibe obtusifolia Benth. | Dinggongteng丁公藤 | ça:u1kɔŋ1pɔ1 | Convolvulaceae | Shrub | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for rheumatism, hemiplegia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for painful swelling from knocks and falls | 451225130611027 |
| Eucalyptus globulus Labill. | Lanan蓝桉 | a:n5mai4fa5lo4 | Myrtaceae | Tree | both | Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for stomachache, prostatitis, wind-heat type common cold, cough, urinary urgency, dysuria. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle, skin itch, eczema | 451225130425026 |
| Eucalyptus robusta Sm. | An桉 | – | Myrtaceae | Tree | both | Seed | Decoction; taken orally for prostatitis, stomachache | 451225130310004 |
| Eucommia ulmoides oliv. | Dongzhong杜仲 | tshja3ti1ŋɣa2 | Eucommiaceae | Tree | both | Bark | Stewed with pig kidney and taken orally directly, treating for kidney deficiency, backache, frequent micturition, hypertension. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for breaking of muscle and tendon, bone fracture | 451225130426035 |
| Eulaliopsis binata (Retz.) C. E. Hubb. | Nijinmao拟金茅 | – | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for clearing liver and eyesight | 451225130607032 |
| Euonymus fortunei (Turcz.) Hand.-Mazz. | Fufangteng扶芳藤 | ça:u1fu6səu3 | Celastraceae | Liana | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism, ostealgia, traumatic injury, bone fracture. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound, | 451225130428013 |
| Euonymus nitidus Benth. | Zhonghuaweimao中华卫矛 | – | Celastraceae | Tree | Wild | Stem and leaf | Medicinal bath for relieve pain | 451225130307032 |
| Eupatorium fortunei Turcz. | Peilan佩兰 | hɣɔk8la:n6 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for acute gastritis and enteritis, blood blight | 451225131109021 |
| Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. | Linzelan林泽兰 | thjen1mɛ1hɣam5 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for treating wind-heat type common cold, swelling and aching of gum, cough due to lung heat | 451225130427017 |
| Euphorbia esula L. | Rujiangdaji乳浆大戟 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for degerming; put it on the bed, treating for chills, fever | 451225130306004 |
| Euphorbia helioscopia L. | Zeqi泽漆 | na:u3pa3ta:n5 | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for edematous asthma, malaria, bacillary dysentery, scrofula, kerion, osteomyelitis | 451225130426030 |
| Euphorbia hirta L. | Feiyangcao飞扬草 | nɛ6hɣo5hɣɔk8lo4 | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, hematuria, dysuria, herpes eczema | 451225121206004 |
| Euphorbia humifusa Willd. ex Schltdl. | Dijin地锦 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite | 451225130306004 |
| Euphorbia hypericifolia L. | Tongnaicao通奶草 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for diarrhea | 451225130420011 |
| Euphorbia thymifolia L. | Qiangencao千根草 | nɛ6hɣo5hɣɔk8niŋ5 | Euphorbiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for diarrhea, hemafecia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for eczema, kerion, pruritus | 451225140420070 |
| Euryale ferox Salisb. | Qian芡 | kɣo3ci1ja4 | Nymphaeaceae | Herb | Home garden | Fruit | Taken orally directly for enuresis, spermatorrhea, leukorrhea, diarrhea | 451225140412008 |
| Evodia lepta (Spreng.) Merr. | Sanyaku三桠苦 | – | Rutaceae | Tree | Wild | Root, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for clearing away heat and toxic materials, anti-itch | 451225131109030 |
| Fagopyrum dibotrys (D. Don) H. Hara | Jinqiaomai金荞麦 | – | Polygonaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for mammitis before suppuration | 451225130519008 |
| Ficus carica L. | Wuhuaguo无花果 | khu5mɛ2hwa1hwi1 | Moraceae | Shrub | both | Receptacle | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, constipation, piles, sore throat, cough with lung heat | 451225130430049 |
| Ficus hirta Vahl | Cuyerong粗叶榕 | ŋɔ4nja2la:k8mɔ6tɔ2 | Moraceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for stomachache, cough, abdominal distension, edema, leukorrhea, rheumatoid arthritis, lumbago | 451225130307034 |
| Ficus microcarpa L. f. | Rongshu榕树 | – | Moraceae | Tree | Wild | Root, Aerial root | Root: medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating raumatic injury, hyperosteogeny, catagma. Aerial root: Decoction with old bamboo and drunk the soup, treating for hemiplegia | 451225130430036 |
| Ficus sarmentosa Buch.-Ham. ex J. E. Sm. var. lacrymans (Levl. Vant.) Corner | Baoyepatengrong薄叶爬藤榕 | – | Moraceae | Liana | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for numbness of bone, rheumatism | 451225130423027 |
| Ficus tikoua Bur. | Diguo地果 | ti6ɔŋ5 | Moraceae | Liana | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for anemopyretic cold, edema, jaundice, rheumatism, piles, amenorrhea, leukorrhea, indigestion, traumatic injury, treating for abdominal paindiarrhea, diarrhea, dizziness due to blood deficiency, leukorrhea, hemorrhinia | 451225130423009 |
| Ficus tinctoria G. Forst. subsp. gibbosa (Blume) Corner | Xieyerong斜叶榕 | – | Moraceae | Tree | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for clearing away heat and toxic materials | 451225121205032, 451225130519013, 451225130519028 |
| Ficus pumila L. | Bili薜荔 | – | Moraceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction with the root of Melastoma malabathricum; medicinal bath for foot pain | 451225121231023, 451225130311072 |
| Flemingia macrophylla (Willd.) Kuntze ex Prain | Dayeqianjinba大叶千斤拔 | – | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath, treating for caligo of old people | 451225130427015 |
| Flemingia prostrata Roxb. f. ex Roxb. | Qianjinba千斤拔 | – | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, arthritis, traumatic injury, relaxing tendons and strengthening bones, waist-leg weakness | 451225130606029 |
| Flueggea virosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) Voigt | Baifanshu白饭树 | – | Phyllanthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for eczema, anti-itch | 451225130519010, 451225130606029 |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Huixiang茴香 | ma1mɣa:ŋ1niŋ5 | Apiaceae | Herb | Home garden | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for heart and chest pain, abdominal distension, abdominal pain | 451225130430031 |
| Galium aparine L. var. echinospermum (Wallr.) Farw. | Lalateng拉拉藤 | hɣɔk8pak7ta:n5 | Rubiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for treating turbidity, hematuria. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, abscess | 451225131108001 |
| Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis | Zhizi栀子 | lak8mwɔ2 | Rubiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for jaundice with damp-heat pathogen. Incinerated; taken orally with water for treating internal hemorrhage. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for sore, oliguria with reddish urine, painful swelling | 451225130422008 |
| Gelsemium elegans (Gardn. et Champ.) Benth. | Gouwen钩吻 | – | Gelsemiaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem and leaf | Frying into carbon shape, decoction; taken orally for treating cancer | 451225121204028, |
| Geum japonicum Thunb. var. chinense F. Bolle | Roumaolubianqing柔毛路边青 | tshjøn5məm6mai4 | Rosaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for intestinal carbuncle, diarrheabacillary dysentery, toothache, traumatic injury, pudendal pruritus, skin eczema | 451225131108027 |
| Ginkgo biloba L. | Yinxing银杏 | la:k8ho3pa:k8 | Ginkgoaceae | Tree | Home garden | Seed | Decoction; taken orally for cough, asthma, nocturnal emission, turbid urine | 451225131108049 |
| Glechoma longituba (Nakai) Kuprian. | Huoxuedan活血丹 | hɣɔk8tjen2ljen6 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for commom cold, fever, cough, heatstroke, eruptive disease. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, cool the blood, dispelling wind detumescence, painful swelling from knocks and falls | 451225130309028 |
| Gleditsia sinensis Lam. | Zaojia皂荚 | thjem1teŋ1 | Fabaceae | Tree | Wild | Thorn | Powdered; applied on the affected area, treating for abscess, sore, kerion, enteritis | 451225130308006 |
| Glochidion eriocarpum Champ. ex Benth. | Maoguosuanpanzi毛果算盘子 | – | Phyllanthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for nephritis, edema | 451225130421057, 451225130430045, 451225130421057 |
| Glochidion puberum (L.) Hutch. | Suanpanzi算盘子 | ton5pon2.la:k8 | Phyllanthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Fruit, Stem and leaf | Taken orally directly for malaria, hernia, turbidity, backache. Decoction; medicinal bath for insecticidal anti-itch | 451225130608029 |
| Gnetum parvifolium (Warb.) Chun | Xiaoyemaimateng小叶买麻藤 | – | Gnetaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for rheumatism, activating blood circulation to dissipate blood stasis | 451225130310009 |
| Gomphrena globosa L. | Qianrihong千日红 | thjen1fan1la:n3 | Amaranthaceae | Herb | Home garden | Inflorescence or Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for headache, giddiness. Decoction; taken orally for cough and asthma | 451225130501040 |
| Gonostegia hirta (Bl.) Miq. | Nuomituan糯米团 | hu3kɣœ3ça:u1 | Urticaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, leukorrhea, infantile malnutrition, spitting blood. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle, abscess, scrofula, bleeding wound | 451225130427019 |
| Gossypium herbaceum L. | Caomian草棉 | mjεn2hwa1ta:ŋ1 | Malvaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for weakness cough with asthma, hernia, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, uterine prolapse | 451225130501004 |
| Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino | Jiaogulan绞股蓝 | thət7fa5mwɔ5 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for relieve fever, anti-inflammator, chronic tracheitis, cough and asthma, stomachache, insomnia, headache | 451225131109006 |
| Gynura japonica (Thunb.) Juel | Jusanqi菊三七 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, piles | 451225130608031 |
| Gynura bicolor (Roxb. ex Willd.) DC. | Hongfengcai红凤菜 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for aid digestion, hypertension | 451225130608021 |
| Hedyotis diffusa Willd. | Baihuasheshecao白花蛇舌草 | hɣɔk8ma2twi2 | Rubiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cough with lung heat, sore throat, jaundice, pelvic inflammation. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for carbuncle, snake bite | 451225130427036 |
| Helianthus annuus L. | Xiangrikui向日葵 | la:k8thəu5fan1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed, Receptacle | Seed: taken orally directly for treating constipation, bloody dysentery, hemafecia, measles, furuncle. Receptacle: Decoction; taken orally for tinnitus, dizziness, hypertension, dysmenorrhea, constipation | 451225121205003 |
| Helicteres angustifolia L. | Shanzhima山芝麻 | – | Malvaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, detumescence anti-itch, poor urination, removing stasis | 451225121205014 |
| Hemerocallis fulva L. | Xuancao萱草 | ŋa:n3hwa1ma1ta:ŋ1 | Xanthorrhoeaceae | Herb | both | Root | Decoction; taken orally for edema, dysuria, turbidity, leukorrhea, jaundice, hemafecia, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, mammary abscess | 451225130729014 |
| Hibiscus mutabilis L. | Mufurong木芙蓉 | mai4fu6juŋ6 | Malvaceae | Shrub | Wild | Flower, Leaf, Root | Decoction; taken orally for cough with lung heat, infantile convulsion, leukorrhagia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle, scald | 451225121206003 |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa L. | Meiguiqie玫瑰茄 | – | Malvaceae | Herb | Home garden | Root | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for acute appendicitis | 451225121230028 |
| Hibiscus sgriacus L. | Mujin木槿 | mai4cen1ŋɣa2 | Malvaceae | Shrub | Home garden | Bark or Root bark | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, hemoptysis, rectal prolapse, piles, eczema, stubborn dermatitis | 451225130519029, 451225130722009 |
| Hordeum vulgare L. | Damai大麦 | mε:k8ŋa2 | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for treating dyspeptic retention, abdominal distention, poor appetite, vomit diarrhea | 451225121230036 |
| Houttuynia cordata Thunb. | Jicai蕺菜 | ma1wat7 | Saururaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for gynecological disease, tracheitis in children, bronchitis, pneumonia, stone, dermatitis | 451225130425034 |
| Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides Lam. | Tianhusui天胡荽 | – | Apiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for jaundice hepatitis, lithangiuria | 451225121231004 |
| Hypericum japonicum Thunb. | Didongcao地耳草 | ça:ŋ1tsən2 | Clusiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for gynecological inflammation, liver ascites, damp and hot jaundice, intestinal carbuncle. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite, furuncle abscess | 451225130423003, 451225130427018, 451225130610029 |
| Hypericum sampsonii Hance | Yuanbaocao元宝草 | hɣɔk8ȵen6pɔ1 | Clusiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for internal hemorrhage, irregular menses, dysmenorrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225130426017, 451225130518027 |
| Ilex asprella (Hook. et Arn.)_champ. ex Benth. | Chengxingshu秤星树 | mai4ja4həu1 | Aquifoliaceae | Tree | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for bitter taste, common cold, eruptive disease, abscess of lung, hemoptysis, sore throat, gonorrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for carbuncle toxin, traumatic injury | 451225121231014 |
| Ilex rotunda Thunb. | Tiedongqing铁冬青 | cəu5lai3çen1 | Aquifoliaceae | Tree | Wild | Bark | Decoction; taken orally for fever, sore throat, damp and hot diarrhea, stomachache, hemoptysis, spitting blood, hemafecia, hematuria. Powdered; applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225130101003 |
| Illicium verum Hook. f. | Bajiao八角 | – | Schisandraceae | Tree | both | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for facial skin disease | 451225130430031 |
| Impatiens balsamina L. | Fengxianhua凤仙花 | – | Balsaminaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant, Seed | Decoction; medicinal bath for rheumatoid arthritis, contracture of bones and muscles, inchacao, tinea sores | 451225130519022 |
| Imperata cylindrica (L.) Raeusch. | Baimao白茅 | juŋ3nɔ3 | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for edema, jaundice, pancreatitis, mastitis, internal hemorrhage, edema, damp and hot jaundice | 451225130101017 |
| Ipomoea nil (Linnaeus ) Roth | Qianniu牵牛 | chen1tən2la:k8 | Convolvulaceae | Herb | Wild | Seed | Taken orally directly for treating edema, inchacao, constipation | 451225121206008, 451225130718012 |
| Isatis tinctoria L. | Songlan崧蓝 | lo4sən3fa5 | Brassicaceae | Herb | Home garden | Root | Decoction; taken orally for influenza, epidemic encephalitis B, sore throat, mumps, red eyes, pneumonia, erysipelas, herpes | 451225130102011 |
| Ixeris polycephala Cass. | Kumaicai苦荬菜 | ma1kam1 | Asteraceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for abscess of lung, mammary abscess, bloody stranguria, furuncle. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225130424008 |
| Jasminum nudiflorum Lindl. | Yingchunhua迎春花 | jin6tshən1hwa1 | Oleaceae | Shrub | Home garden | Flower | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating fever headache, painful voidings of hot urine, carbuncle eczema | 451225130307012 |
| Jasminum sambac (L.) Aiton | Molihua茉莉花 | – | Oleaceae | Shrub | both | Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism | 451225130307014 |
| Juglans regia L. | Hutao胡桃 | hwi1tɔ2 | Juglandaceae | Tree | Home garden | Seed | Taken orally directly for kidney deficiency, dyspnea with cough, backache, impotence, spermatorrhea, frequent micturition, dry feces | 451225130307017 |
| Juncus effusus L. | Dengxincao灯心草 | hɣɔk8fi1taŋ1 | Juncaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for insomnia, prostatitis, lithangiuria | 451225130422017, 451225130501023 |
| Justicia adhatoda L. | Yazuihua鸭嘴花 | – | Acanthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc, snake bite, traumatic injury | 451225130307025 |
| Justicia ventricosa Wall. ex Sims. | Heiyexiaobogu黑叶小驳骨 | – | Acanthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, hyperosteogeny, protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc, scald | 451225130607011 |
| Kadsura coccinea (Lem.) A. C. Smith | Heilaohu黑老虎 | ça:u1kon3kɔk8 | Schisandraceae | Liana | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for liver ascites, rheumatism, ostealgia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, bone fracture, furuncle, wound infection | 451225130307040 |
| Kadsura longipedunculata Finet et Gagnep. | Nanwuweizi南五味子 | – | Schisandraceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Stem, Fruit | Root and stem: Decoction; taken orally for gastritis. Fruit: medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, stomachache | 451225130308007 |
| Kalimeris indica (L.) Sch. Bip. | Malan马兰 | – | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for removing blood stasis, clearing away heat and toxic materials | 451225130309013 |
| Kummerowia striata (Thunb.) Schindl. | Jiyancao鸡眼草 | hɣɔk8ci1la1 | Fabaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cold and fever, vomiting and diarrhea, malaria, diarrhea, infectious hepatitis | 451225130608028 |
| Kyllinga polyphylla Kunth | Shuiwugong水蜈蚣 | hɣɔk8nəm4cε3khɣap7 | Cyperaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant or Root | Decoction; taken orally for fever, cough, diarrhea bacillary dysentery. Medicinal liquor; taken orally for traumatic injury, rheumatism | 451225130309030 |
| Kyllinga nemoralis (J. R. Forster & G. Forster) Dandy ex Hutchinson & Dalziel | Dansuishuiwugong单穗水蜈蚣 | – | Cyperaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for commom cold, cough, clearing and activating the channels and collaterals, pneamopathy, renomegaly | 451225130519004 |
| Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet | Biandong扁豆 | tau6pɔp7 | Fabaceae | Liana | Home garden | Seed | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, vomit, bacillary dysentery | 451225130309043 |
| Lantana camara L. | Mayingdan马缨丹 | ŋɔ4sak7hwa1 | Verbenaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Branch and leaf: Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for itchy skin, eczema, traumatic injury, painful swelling. Root: Decoction; taken orally for treating kidney stone | 451225130429022 |
| Laportea violacea Gagnep. | Putaoyeaima葡萄叶艾麻 | – | Urticaceae | Herb | Wild | Root | Stewed with pig spleen and drunk the soup, treating for ascites due to cirrhosis | 451225130310042 |
| Lemmaphyllum microphyllum C. Presl var. obovatum (Harr.) C. Chr. | Daoluanyefushijue倒卵叶伏石蕨 | – | Polypodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for infantile malnutrition | 451225130311011 |
| Leonurus japonicus Houtt. | Yimucao益母草 | mau6mai4hɣɔk8 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for irregular menses, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, postpartum blood stasis, abdominal pain, persistent lochia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for edema, abscess, pruritus, traumatic injury | 451225130426002, 451225130518028, 451225130606006 |
| Lespedeza cuneata (Dum.-Cours.) G. Don | Jieyetiesaozhou截叶铁扫帚 | mu2kwa:n1tɔ1 | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for dissipate blood stasis detumescence | 451225130311017 |
| Ligustrum lucidum Ait. | Nvzhen女贞 | tsɔŋ1tsən5la:k8 | Oleaceae | Tree | both | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for liver ascites, soreness and weakness of waist and knees, tinnitus and dizziness | 451225130718011 |
| Ligustrum quihoui Carr. | Xiaoyenvzhen小叶女贞 | – | Oleaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Medicinal bath, treating for clearing away heat and toxic materials | 451225130311048 |
| Lilium brownii F. E. Br. ex Miellez | Yebaihe野百合 | – | Liliaceae | Herb | Wild | Bulb | Stewed with meat and taken orally directly for cough with lung heat, expectoration, dysphoria, palpitation, insomnia | 451225130518030, 451225130519050 |
| Lindera aggregata (Sims) Kosterm. | Wuyao乌药 | u1kɣa2 | Lauraceae | Tree | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for abdominal distention, abdominal pain, urinary frequency | 451225130312003 |
| Liquidambar formosana Hance | Fengxiangshu枫香树 | mai4hɣəu1la:k8 | Altingiaceae | Tree | Wild | Fruit | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for rheumatism, removing blood, spasm of hand and foot. Decoction; taken orally for stomachache, edema, carbuncle, anal fistula, eczema | 451225130312012 |
| Liriope spicata (Thunb.) Lour. | Shanmaidong山麦冬 | – | Asparagaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for hepatopathy. Stewed with meat and drank the soup for treating jaundice hepatitis | 451225130312016 |
| Litchi chinensis Sonn. | Lizhi荔枝 | li6tsi1la:k8 | Sapindaceae | Tree | Home garden | Aril, Seed | Seed: taken orally directly for epigastralgia, hernia, dysmenorrhea, eliminating stagnation. Fruit: taken orally directly for polydipsia, hiccup | 451225130730006 |
| Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Per. | Shanjijiao山鸡椒 | – | Lauraceae | Tree | Wild | Root, Stem, Leaf | Stewed with meat and drunk the soup, treating for removing wind and dispersing cold, smooth circulation and stop pains | 451225130310026, 451225130430046, 451225130519032, 451225130610028 |
| Litsea pungens Hemsl. | Mujiangzi木姜子 | ja4mai4tsja:ŋ5la:k8 | Lauraceae | Tree | Wild | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for anemofrigid cold, abdominal distention, poor appetite. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225130421018 |
| Lobelia chinensis Lour. | Banbianlian半边莲 | mɣa:ŋ6pjen1ljen2 | Campanulaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for jaundice, edema, abdominal distension, diarrhea, diarrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite, furuncle abscess, sprain | 451225130501028, 451225130606026 |
| Lonicera confusa (Sweet) DC. | Huananrendong华南忍冬 | cəm1ȵen2ça:u1 | Caprifoliaceae | Liana | both | Stem, Bud | Stem: Medicinal bath, treating for abscess, rheumatism. Flower: Decoction; taken orally for treating for fever, bloody flux, carbuncle, swollen toxin, scrofula, hemorrhoid complicated by anal fistula | 451225130422035 |
| Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. | Guxianrendong菰腺忍冬 | – | Caprifoliaceae | Liana | Both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for headache, liver ascites, skin disease | 451225130421045, 451225130719005 |
| Lophatherum gracile Brongn. | Danzhuye淡竹叶 | kwan1ta:m6fa5 | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for tongue and mouth sores, dysuria, cough with lung heat, infantile convulsions, insomnia, uterine bleeding, apoplexy, threatened abortion | 451225130422050 |
| Loranthus sp. | Sangjishengshuyizhong桑寄生属一种 | – | Loranthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for treating inchacao, rheumatoid arthritis, postpartum hypogalactia | 451225130423005 |
| Loranthus sp. | Sangjishengshuyizhong桑寄生属一种 | – | Loranthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cough, cold | 451225130423015 |
| Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem. | Sigua丝瓜 | thjen1la2hɣə:n5 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Peel | Decoction; taken orally for cough with lung heat, testicle painful swelling, amenorrhoea, promoting lactation | 451225130423016 |
| Lycopodium japonicum Thunb. | Shisong石松 | hɣɔk8hɣaŋ4cen1 | Lycopodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor ; taken orally or applied on the affected area, for treating rheumatoid arthritis, numbness of limbs, edema, traumatic injury | 451225130424032 |
| Lycopus lucidus Turcz. ex Benth. | Disun地笋 | tsek8la:m2 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for amenorrhea abdominal pain, edema, traumatic injury, carbuncle, swelling and pain | 451225130425002 |
| Lycoris radiata (L’Hey.) Herb. | Shisuan石蒜 | hɣɔ2mən1 | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Wild | Bulb | Decoction; taken orally for anemofrigid cold, cough. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for edema | 451225130425021 |
| Lygodium japonicum (Thunb.) Sw. | Haijinsha海金沙 | – | Lygodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for kidney stone, clearing heat and diuresis, stranguria. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area for anaesthesia | 451225121204033, 451225130311055, 451225130606031 |
| Lygodium microphyllum (Cav.) R. Br. | Xiaoyehaijinsha小叶海金沙 | – | Lygodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for kidney stone, heat-clearing and diuresis, stranguria | 451225130425040 |
| Lysionotus pauciflorus Maxim. | Diaoshijutai吊石苣苔 | – | Gesneriaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225130723003 |
| Maclura cochinchinensis (Lour.) Corner | Gouji构棘 | ta:ŋ1lyn1cet7 | Moraceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatoid arthralgia, traumatic injury. Decoction; taken orally for jaundice, turbidity, menostasis, hemoptysis, furuncle abscess | 451225131108028 |
| Magnolia liliflora Desr. | Xinyi辛夷 | çin5tshən6hwa1 | Magnoliaceae | Tree | Home garden | Flower | Decoction; taken orally for headache, nasosinusitis | 451225130426014 |
| Mahonia bealei (Fortune) Carrière | Kuoyeshidagonglao阔叶十大功劳 | ŋa:n3mai4ljen2 | Berberidaceae | Shrub | Wild | Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and resolving fire, treating for headache, cough, jaundice | 451225130728014 |
| Mahonia sp. | Shidagonglaoshu十大功劳属 | – | Berberidaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and reducing fire, internal thermal, pneumonia | 451225130427006 |
| Mallotus paniculatus (Lam.) Muell. Arg. | Baiqiu白楸 | fa5ləu2pa:k8 | Euphorbiaceae | Tree | Wild | Root, Leaf | Root: Decoction; taken orally for leukorrhea, infertility. Leaf: pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound, traumatic injury, thrush, bedsore | 451225130427007 |
| Malva verticillata L. var. crispa L. | Dongkui冬葵 | tɔŋ6thəu5fan1 | Malvaceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed | Decoction; taken orally for constipation, poor urination, insufficient lactation | 451225130427013 |
| Marsilea quadrifolia L. Sp. | Ping苹 | – | Marsileaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for liver ascites | 451225130425012, 451225130519011 |
| Melastoma dodecandrum Lour. | Dinie地菍 | – | Melastomataceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for hepatopathy | 451225130422007 |
| Melastoma malabathricum L. | Yemudan野牡丹 | – | Melastomataceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Medicinal bath for painful swelling of feet | 451225130422005, 451225130610026, 451225131109025 |
| Melia azedarach L. | Lian楝 | mai4khu1ljen6ta:ŋ1ŋɣa2 | Meliaceae | Tree | Wild | bark | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating for depriving ascarid, enterobiasis, measles, hemorrhoids | 451225130611026 |
| Mentha canadensis L. | Baohe薄荷 | po6o5 | Lamiaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for treating affection of exogenous wind-heat, headache, fever, red eyes, measles | 451225130427024 |
| Millettia pachyloba Drake | Hainanyadouteng海南崖豆藤 | ça:u1tɔk8məm6 | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Stem, Leaf | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for scabies, wet leprosy, rheumatic arthritis | 451225130428018 |
| Mimosa pudica L. | Hanxiucao含羞草 | hɣɔk8khɣə:n5jɛ6 | Fabaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for gastritis, enteritis, insomnia, infantile malnutrition, herpes zoster | 451225130428034 |
| Miscanthus sinensis Andersson | Mang芒 | – | Poaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for relieve pain, stanching bleeding, enteritis | 451225130310057 |
| Momordica charantia L. | Kugua苦瓜 | ku1li5fa5 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for stomachache, diarrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for eczema, prickly heat | 451225130718020 |
| Morinda officinalis How. | Bajitian巴戟天 | hɣɔk8ci1khɣe3 | Rubiaceae | Liana | Wild | Root | Powdered; taken orally with water or liquor, treating for impotence, aconuresis, rheumatoid arthritis, soreness and weakness of waist and knees | 451225130428047 |
| Morus alba L. | Sang桑 | saŋ5la:k8 | Moraceae | Shrub | Home garden | Whole plant | Root: Decoction; taken orally for diuresis. Branch: medicinal liquor; taken orally or rinsed the affected area, treating for rheumatism. Leaf: Decoction; taken orally for clear wind-heat. Fruit: taken orally directly or medicinal liquor and taken orally for tonifying liver and kidney | 451225130311060, 451225130421060 |
| Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack. | Qianlixiang千里香 | – | Rutaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root, Stem | Decoction; taken orally for heart disease | 451225121231001, 451225130311022 |
| Musa basjoo Sieb. et Zucc. | Bajiao芭蕉 | fja:k7ta:ŋ1 | Musaceae | Herb | Home garden | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for jaundice, edema, inchacao, bloody stranguria, metrorrhagia, furuncle, erysipelas | 451225130429011 |
| Mussaenda erosa Champ. ex Benth. | Nanteng楠藤 | – | Rubiaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for clearing away heat and relieving exterior syndrome, infertility | 451225130421042, 451225130430005 |
| Nandina domestica Thunb. | Nantianzhu南天竹 | – | Berberidaceae | Shrub | both | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for cooling blood | 451225130102005, 451225130426025 |
| Nelumbo nucifera gaerth. | Lian莲 | ŋau4la:k8təm1 | Nelumbonaceae | Herb | Home garden | Leaf, Seed, Germ | Leaf: Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, vertigo, edema, internal hemorrhage. Seed: Taken orally directly for upset, spitting blood, spermatorrhea, swelling and pain of eye | 451225130429017 |
| Neolepisorus fortunei (T. Moore) Li Wang | Jiangnanxingjue江南星蕨 | – | Polypodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for rheumatism | 451225121205019 |
| Nepeta cataria L. | Jingjie荆芥 | mai4jin1 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for fever commom cold, headache, sore throat, internal hemorrhage, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, postpartum anemic fainting, abscess, sores, scrofula | 451225130430022 |
| Nervilia plicata (Andrews) Schltr. | Maoyeyulan毛叶芋兰 | həu1ljen2 | Orchidaceae | Herb | Wild | Leaf, Tuber | Decoction; taken orally for tuberculosis, cough with lung heat, hemoptysis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for scrofula, swollen toxin, traumatic injury | 451225130430041 |
| Ocimum basilicum L. | Luole罗勒 | – | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant, Seed | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for dispelling wind detumescence, dissipate blood stasis relieve pain | 451225130430048 |
| Onychium japonicum (Thunb.) Kze. | Yezhiweijinfenjue野雉尾金粉蕨 | – | Pteridaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for calculosis | 451225130102002 |
| Ophiopogon intermedius D. Don | Jianxingyanjiecao间型沿阶草 | mε:k8tɔŋ1 | Asparagaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Stewed with meat and taken orally directly for treating irritating dry cough, hemoptysis, angina, abscess of lung, diabetes, constipation due to intestinal dryness | 451225130501003 |
| Opuntia dillenii (Ker Gawl.) Haw. | Xianrenzhang仙人掌 | tɔŋ6pən6tsja:ŋ3 | Cactaceae | Shrub | both | Root, Stem | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for abdominal pain, diarrhea, scald, snake bite | 451225130728015 |
| Oryza sativa L. | Dao稻 | hu3kɔk7ŋa2 | Poaceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed-bud | Decoction; taken orally for treating dyspeptic retention, indigestion | 451225130501036 |
| Oxalis corniculata L. | Zhajiangcao酢浆草 | ma1khɣəm3 | Oxalidaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for diarrhea, gonorrhea, leukorrhea, measles, internal hemorrhage, sore throat, abscess, piles, rectal prolapse. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, scald | 451225130721007 |
| Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merr. | Jishiteng鸡矢藤 | ça:u1cɛ3ci1 | Rubiaceae | Liana | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite, itching | 451225130102016 |
| Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merr. var. tomentosa (Bl.) Hand.-Mazz. | Maojishiteng毛鸡矢藤 | ça:u1ci1cɛ3pa:k8 | Rubiaceae | Liana | Wild | Root or Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for jaundice, diarrhea, dyspeptic retention, amenorrhea | 451225130501037 |
| Pandanus austrosinensis T. L. Wu | Ludongcao露兜草 | – | Pandanaceae | Herb | Wild | Fruit | Leaf: Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for renomegaly, diuresis, sweating, anti-inflammatory. Fruit: Decoction; taken orally for cough, nephritis | 451225130310036 |
| Paris polyphylla Sm. var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara | Qiyeyizhihua七叶一枝花 | thət7fa5ljen2 | Trilliaceae | Herb | both | Rhizome | Powdered, taken orally or applied on the affected area for abscess furuncle, scrofula, sore throat, chronic tracheitis, infantile convulsion, snake bite | 451225130518006 |
| Passiflora papilio H. L. Li | Hudieteng蝴蝶藤 | – | Passifloraceae | Liana | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor or decoction; taken orally for rheumatism, paralysis, indigestion | 451225130726016 |
| Patrinia villosa (Thunb.) Juss. | Pandaozeng攀倒甑 | hɣɔk8ja:ŋ6tsja:ŋ5 | Caprifoliaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating intestinal carbuncle, diarrhea, leukorrhea, abdominal pain, red eyes swollen toxin, abscess, hemorrhoids | 451225130718007, 451225131108012 |
| Paulownia fortunei (Seem) Hemsl. | Baihuapaotong白花泡桐 | mai5phɔ5tɔŋ2 | Scrophulariaceae | Tree | Wild | Bark | Decoction; taken orally for treating rheumatism, arthritis, edema, toxic heat, scabies | 451225130518011 |
| Pentarhizidium orientale Hayata | Dongfangjiaguojue东方荚果蕨 | – | Onocleaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for hepatitis, carditis | 451225130518012 |
| Penthorum chinense Pursh | Chegencai扯根菜 | – | Penthoraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225130518034 |
| Pericampylus glaucus (Lam.) Merr. | Xiyuanteng细圆藤 | ça:u1nam2fɔŋ1 | Menispermaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem or root | Decoction; taken orally for infantile convulsions | 451225130423031, 451225130611009 |
| Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton | Zisu紫苏 | – | Lamiaceae | Herb | Home garden | Stem, Leaf, Seed | Taken orally directly for dissipate wind-cold, relieve stasis and dissipate phlegm, ichthyotoxin, fish poison, turtle poison | 451225130519025 |
| Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton var. purpurascens (Hayata) H. W. Li | Yeshengzisu野生紫苏 | – | Lamiaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Taken orally directly for cold. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, promoting wound healing | 451225130518038 |
| Perilla frutescensc (L.) Britt. var. crispa (Thunb.) Hand-Mazz. | Huihuisu回回苏 | lau5ma1fa5 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Home garden | Whole plant | Root: Decoction; taken orally for anemofrigid cold, cough, abdominal distention, threatened abortion, fish poison, turtle poison. Seed: Taken orally directly for cough and asthma, constipation due to intestinal dryness. Stem: Decoction; taken orally for threatened abortion, abdominal distension | 451225130426018 |
| Pholidota chinensis Lindl. | Shixiantao石仙桃 | hwi1tɔ2fa5 | Orchidaceae | Herb | Wild | Tuber or Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cough, hemoptysis, cough with lung heat, nocturnal emission. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for scrofula, traumatic injury | 451225130101026 |
| Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. | Luwei芦苇 | kɣo3ŋɔ4 | Poaceae | Shrub | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for prostatitis, nephritis, vomiting due to stomach heat, nausea, abscess of lung, oliguria with reddish urine | 451225130606041 |
| Phyllanthus urinaria L. | Yexiazhu叶下珠 | – | Phyllanthaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for detumescence improving eyesight, diuresis | 451225130611023, 451225130718026, 451225130611023 |
| Phyllodium pulchellum (L.) Desv. | Paiqianshu排钱树 | pa:i2tjen2hɣɔk8 | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and relieving exterior syndrome. Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating removing blood and dissipate blood stasis | 451225130607012 |
| Physalis angulata L. | Kuta苦蘵 | – | Solanaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, expectorants up pressing cough | 451225130718031 |
| Physalis peruviana L. | Denglongguo灯笼果 | tɔŋ6kwi5pɔm1 | Solanaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for common cold, sore throat, hernia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for poisoned sore | 451225130429006 |
| Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. | Shanglu商陆 | lən1ləm6tjeu1 | Phytolaccaceae | Herb | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for edema, antral gastritis, gastric bleeding, constipation, diuresis, abscess | 451225130429035, 451225130518026 |
| Phytolacca americana L. | Chuixushanglu垂序商陆 | – | Phytolaccaceae | Herb | Wild | Root | Decoction; medicinal bath for skin disease | 451225130609004 |
| Pilea cavaleriei H. Lév. | Shiyoucai石油菜 | pi2ma1mu5 | Urticaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cough due to tuberculosis, cough with lung heat. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for scald, sores painful swelling | 451225130608032 |
| Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit. | Banxia半夏 | ma1ɣa:k7la:k8 | Araceae | Herb | Wild | Tuber | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle abscess | 451225130306013 |
| Pinus massoniana Lamb. | Maweisong马尾松 | tsuŋ6pε:k7jəu2 | Pinaceae | Tree | Wild | Stem tubercle, Leaf | Branchlet tubercle: medicinal liquor, taken orally or rinsed the affected area, treating for rheumatic arthritis, tuberculous arthritis, blood stasis. Leaf: Decoction; taken orally and rinsed for rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury, insomnia, edema, eczema, hemorrhoids | 451225130610011 |
| Piper kadsura (Choisy) Ohwi. | Fengteng风藤 | ta6pɣa1lɔŋ2fa5lo4 | Piperaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatoid arthritis, joint pain, vessel contracture syndromes etc., traumatic injury | 451225130610012 |
| Piper nigrum L. | Hujiao胡椒 | hu2tjeu1 | Piperaceae | Herb | Wild | Fruit | Taken orally directly for cold phlegm and dyspepsia, nausea, vomit, diarrhea, cold type dysentery, food-poisoning | 451225130610017 |
| Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz. | Shinanteng石南藤 | – | Piperaceae | Liana | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, ostealgia, waist-leg weakness, cough and asthma | 451225130310071, 451225130425006 |
| Plantago asiatica L. | Cheqian车前 | tu3mu5ma1 | Plantaginaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for enriching blood, clearing away heat and dampness, diuresis stranguria, hematuria, urinary tract infection, nephritis | 451225130309004 |
| Platycladus orientalis (L.) Franco | Cebai侧柏 | pə6fa5 | Cupressaceae | Tree | both | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for piles, internal hemorrhage, hemorrhoidal hamorrhage, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, bacillary dysentery, cough, seborrhoeic dermatitis, alopecia | 451225130611007 |
| Plumbago zeylanica L. | Baihuadan白花丹 | – | Plumbaginaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath, treating for edema, infantile malnutrition | 451225121205037, 451225130606038 |
| Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. | Guanghuoxiang广藿香 | khɔ6mɣa:ŋ1 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Taken orally with saline water for abdominal distention, poor appetite, nausea, vomit | 451225130611029 |
| Polygala japonica Houtt. | Guazijin瓜子金 | hɣɔk8kwa1la:k8 | Polygalaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant or Root | Decoction; taken orally for sore throat, cough with copious phlegm, pertussis cough, abscess, traumatic injury, insomnia | 451225130804002 |
| Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua | Donghuahuangjing多花黄精 | ci1ŋa:n3ma1 | Asparagaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Slicing and decoction; taken orally directly for tuberculosis hemoptysi, weakness, soreness and weakness of waist and knee, rheumatoid arthritis | 451225000000000 |
| Polygonum chinense L. | Huotanmu火炭母 | – | Polygonaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for relieve pain and inflammation, ulcer | 451225130501031 |
| Polygonum hydropiper L. | Shuiliao水蓼 | – | Polygonaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for killing parasites to relieve itshing, eczema | 451225130718008 |
| Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. | Heshouwu何首乌 | ma1tap7twi2 | Polygonaceae | Liana | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for insomnia, profuse sweating, skin eruption, kidney deficiency, premature graying of the hair, dizzy of the head and dim of sight, soreness and weakness of waist and knees, spermatorrhea, chronic hepatitis, abscess, constipation due to intestinal dryness | 451225130428007 |
| Polygonum orientale L. | Hongliao红蓼 | la:n3la6lja:u5 | Polygonaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for hyperosteogeny, abdominal distension, ascites due to cirrhosis, gastric distention, diarrhea, neck lymphatic tuberculosis | 451225130718024 |
| Polygonum Perfoliatum L. | Gangbangui杠板归 | hɣɔk8twi2khu5ta6 | Polygonaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for damp and hot jaundice, diarrhea, bacillary dysentery, poor urination, stranguria with turbid discharge, hemorrhoids, eczema, pemphigus, anti-itch | 451225000000000 |
| Polygonum plebeium R. Br. | Xijianliao习见蓼 | pjen5jøn6 | Polygonaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for pyretic stranguria, jaundice, leukorrhea, depriving ascarid, malnutrition, hemorrhoids, eczema | 451225130721005 |
| Portulaca oleracea L. | Machixian马齿苋 | tɔŋ6fan1ma4 | Portulacaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for bacillary phthisis, diarrhea, bacillary dysentery, fever, cough, internal hemorrhage, eczema | 451225130718010 |
| Pothos chinensis (Raf.) Merr. | Shiganzi石柑子 | – | Araceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism, traumatic injury, numbness of meridians and collaterals | 451225130308016 |
| Prunella vulgaris L. | Xiakucao夏枯草 | ha5khu1hɣɔk8 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Infructescence | Decoction; taken orally for scrofula, mammary abscess, breast cancer, dizziness, arthralgia and myalgia, tuberculosis, acute icteric hepatitis, metrorrhagia, leukorrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225130420001, 451225130425023 |
| Psidium guajava L. | Fanshiliu番石榴 | – | Myrtaceae | Tree | both | Leaf, Fruit, Bark | Taken orally directly for stanching bleeding, hepatitis, hepatopathy | 451225130724006 |
| Psychotria rubra (Lour.) Poir. | Jiujie九节 | mai4ta:n5lo4 | Rubiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, bone fracture, rheumatism, ostealgia, swollen toxin, sore throat | 451225130307033, 451225130501013, 451225130519040, 451225130608001 |
| Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn var. latiusculum (Desv.) Underw. ex Heller | Jue蕨 | – | Dennstaedtiaceae | Herb | Wild | Leaf | Medicinal bath for clearing heat and toxic materials | 451225130726011 |
| Pteris vittata L. | Wugongcao蜈蚣草 | – | Pteridaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for eczema, epilation | 451225130727001 |
| Pteris multifida Poir. | Jinglanfengweijue井栏凤尾蕨 | hɣɔk8ci1jem1 | Pteridaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant or Root | Decoction; taken orally for abdominal pain, diarrhea, bacillary dysentery, hemafecia, dysuria, urinary urgency. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225130311019 |
| Pterolobium punctatum Hemsl. | Laohuci老虎刺 | – | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for hepatitis, duodenal ulcer | 451225130727011 |
| Pueraria montana (Loureiro) Merrill var. lobata (Willdenow) Maesen & S. M. Almeida ex Sanjappa & Predeep | Ge葛 | ɔ6mε:k8ça:u1 | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for alleviate a hangover, vertebral syndrom, clearing away heat and relieving exterior syndrome, stimulate saliva and reduce thirst, measles, diarrhea | 451225130804006 |
| Punica granatum L. | Shiliu石榴 | sik8ləu2ŋɣa2 | Lythraceae | Tree | Home garden | Peel | Taken orally directly for diarrhea, bacillary dysentery, protracted dysentery, hemafecia, rectal prolapse, leukorrhea, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, parasitic accumulation abdominal pain | 451225130805001 |
| Pyrrosia lingua (Thunb.) Farwell | Shiwei石韦 | twi2hwi2 | Polypodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound, gunshot wounds. Decoction; taken orally for clearing heat, calculosis, promoting diuresis and relieving stranguria | 451225130806004 |
| Pyrrosia tonkinensis (Giesenh.) Ching | Zhongyueshiwei中越石韦 | – | Polypodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for nephritis, urinary stone | 451225131107008 |
| Pyrrosia calvata (Baker) Ching | Guangshiwei光石韦 | – | Polypodiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism | 451225121205015 |
| Quisqualis indica L. | Shijunzi使君子 | – | Combretaceae | Liana | both | Seed | Decoction; taken orally for stomachache | 451225131107011 |
| Raphanus sativus L. | Luobo萝卜 | lak8pak8la:k8 | Brassicaceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed | Taken orally directly for treating cough, dyspeptic retention and qi stagnatio, bosom frowsty abdominal distension, diarrhea | 451225131107013 |
| Reynoutria japonica Houtt. | Huzhang虎杖 | cəu3lɔŋ2ta:ŋ1 | Polygonaceae | Shrub | Wild | Rhizome | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, traumatic injury. Decoction; taken orally for damp and hot jaundice, stranguria, leukorrhea, menostasis, postpartum blood stasis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, burn and scald, malignant sore and tinea | 451225130608004 |
| Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Aiton) Hassk. | Taojinniang桃金娘 | – | Myrtaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root, Leaf, Fruit | Taken orally directly or Medicinal liquor; taken orally for astringing to stop diarrhea, dispelling wind and activating collaterals | 451225130608030 |
| Rhus chinensis Mill. | Yanfumu盐肤木 | kwa6hu3mai4 | Anacardiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for cool the blood, cough, sore throat, jaundice, night sweat, diarrhea, kerion, carbuncle toxin, head-wind white scaling | 451225131107018 |
| Rhynchosia volubilis Lour. | Luhuo鹿藿 | – | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for aid digestion | 451225130723004 |
| Ricinus communis L. | Bima蓖麻 | la:k8ma6la:k8 | Euphorbiaceae | Shrub | both | Seed | Decoction after frying; taken orally for carbuncle, pharyngitis, edema, scrofula, constipation. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for scabies | 451225121230004 |
| Rohdea japonica Roth. | Wannianqing万年青 | hwa:n6mɛ1həu1 | Asparagaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for palpitation, pectoralgia, edema, sore throat. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225131107022 |
| Rosa chinensis Jacq. | Yuejihua月季花 | mwa:n4ci5hwa1 | Rosaceae | Liana | Home garden | Bud | Decoction; taken orally for irregular menses, leukorrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225131107025 |
| Rosa laevigata Miehx. | Jinyingzi金樱子 | la:k8muŋ3ta:ŋ1 | Rosaceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Fruit | Root: Decoction; taken orally or rinsed for spermatorrhea, enuresis, diarrhea, diarrhea, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, leukorrhea, uterine prolapse, hemorrhoid complicated by anal fistula, scald. Fruit: medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating spermatorrhea, enuresis, frequent micturition, diarrhea due to spleen deficiency, spontaneous sweating, night sweat, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, leukorrhea, rectal prolapse | 451225130517014, 451225130519046 |
| Rosa multiflora Thunb. | Yeqiangwei野蔷薇 | tshja:ŋ6wəi6ta:ŋ1 | Rosaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for abscess of lung, diarrhea, arthritis, internal hemorrhage, irregular menses, furuncle, hemorrhoids. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, acariasis | 451225131108002 |
| Rosa sp. | Meigui玫瑰 | məi6ji1hwa1 | Rosaceae | Shrub | Home garden | Flower | Taken orally directly for spitting blood, hemoptysis, irregular menses, leukorrhea, diarrhea, mastalgia, swollen toxin | 451225131107030 |
| Rotala rotundifolia (Buch.-Ham. ex Roxb.) Koehne | Yuanyejiejiecai圆叶节节菜 | – | Lythraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cough | 451225130425036 |
| Rubia cordifolia L. | Qiancao茜草 | hɣɔk8la:n3ta:ŋ1 | Rubiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for treating rheumatism, internal hemorrhage, amenorrhea, jaundice, chronic bronchitis. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury, painful swelling | 451225130311033 |
| Rubus alceifolius Poir. | Cuyexuangouzi粗叶悬钩子 | – | Rosaceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for clearing heat, stanching bleeding, promoting blood circulation for removing blood stasis | 451225130608042, 451225130730004 |
| Rubus corchorifolius L. f. | Shanmei山莓 | – | Rosaceae | Liana | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for ascites due to cirrhosis, prostatitis, tracheitis | 451225130308013, 451225130310029, 451225130425022 |
| Rubus phoenicolasius Maxim. | Dongxianxuangouzi多腺悬钩子 | – | Rosaceae | Liana | Wild | Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism | 451225131108010 |
| Rubus rosifolius Smith | Kongxinpao空心泡 | – | Rosaceae | Herb | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for ascites due to cirrhosis | 451225131108017 |
| Salix babylonica L. | Chuiliu垂柳 | ja:ŋ6liu3ŋa5 | Salicaceae | Tree | Home garden | Stem | Decoction; taken orally for rheumatoid arthritis, gonorrhea, gonorrhea, urinary stoppage, infectious hepatitis B, pemphigus, erysipelas, decayed tooth, swelling and aching of gum | 451225131109002 |
| Salvia chinensis Benth. | Huashuweicao华鼠尾草 | twi2nən1tshøn1 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for menostasis, leukorrhea, swelling and pain, costalgia, damp and hot jaundice | 451225140504030 |
| Sambucus chinensis Lindl. | Jiegucao接骨草 | – | Adoxaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for dispelling wind and remove dampness | 451225130426004 |
| Sanguisorba offieinalis L. | Diyu地榆 | tsi3phɣə:t7kɣa2 | Rosaceae | Herb | Wild | Root, Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for internal hemorrhage, diarrhea, anal fistula. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for scald | 451225140505011 |
| Sapium sebiferum (L.) Roxb. | Wujiu乌桕 | u4tsin5 | Euphorbiaceae | Tree | Wild | Bark | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle, eczema, pruritus, bleeding wound. Decoction; taken orally for edema, constipation, abdominal distension, eczema | 451225130519026 |
| Sarcandra glabra (Thunb.) Nakai | Caoshanhu草珊瑚 | cəu3kwət7tsa2 | Chloranthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; taken orally for sore throat, wind-heat type common cold, diarrhea bacillary dysentery. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism, traumatic injury | 451225130518041 |
| Sargentodoxa cuneata (Oliv.) Rehder et E. H. Wilson | Daxueteng大血藤 | ça:u1phɣə:t7lo4 | Lardizabalaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, ostealgia, backache, traumatic injury, beadache due to deficiency of blood, intestines carbuncle | 451225131108025 |
| Saururus chinenisi (Lour.) Baill. | Sanbaicao三白草 | hɣɔk8ta:m1pɛ:k8 | Saururaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath for damp and hot, edema, stranguria with turbid discharge, leukorrhea, carbuncle, inchacao | 451225130426027 |
| Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin | Ezhangchai鹅掌柴 | – | Araliaceae | Tree | Wild | Bark, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for rheumatism, rheumatoid, sweating | 451225121204025, 451225130309015 |
| Tacca plantaginea (Hance) Drenth | Lieguoshu裂果薯 | nəm4lak8pak8 | Dioscoreaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for gastrosis | 451225130422026, 451225130429009 |
| Scutellaria barbata D.Don. | Banzhilian半枝莲 | mɣa:ŋ6ŋa5ljen6 | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cancer, ascites due to cirrhosis, internal hemorrhage, sore throat, jaundice. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for snake bite, carbuncle toxin, traumatic injury | 451225130718028 |
| Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | Huangqin黄芩 | – | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for hepatitis, nephritis | 451225140504021 |
| Sedum lineare Thunb. | Fojiacao佛甲草 | hɣɔk8fu6cap7 | Crassulaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for sore throat, jaundice, diarrhea. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for abscess, furuncle, erysipelas, scald, snake bite | 451225130422042 |
| Sedum sarmentosum Bge. | Chuipencao垂盆草 | hɣɔk8pa:i2pən2 | Crassulaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for damp and hot jaundice. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for skin and external diseases, snake bite, scald | 451225140506013 |
| Selaginella tamariscina (Beauv.) Spring. | Juanbai卷柏 | kon3pɛ:k8 | Selaginellaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for stimulating saliva, internal hemorrhage, cough, asthma, jaundice, leukorrhea, stranguria. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for edema, scald | 451225140508012 |
| Selaginella uncinata (Desv.) Spring. | Cuiyuncao翠云草 | tshəi4jyn6hɣɔk8 | Selaginellaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for jaundice, diarrhea, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, hemoptysis, sore throat, anal fistula, cold sweat. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound, scald | 451225121230022, 451225130311029, 451225130612003 |
| Semiaquilegia adoxoides (DC.) Mak. | Tiankui天葵 | mən1khwəi6la:k8 | Ranunculaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for cough, asthma, edema, stranguria. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle and carbuncle, traumatic injury | 451225130306014 |
| Semiliquidambar cathayensis H. T. Chang | Banfenghe半枫荷 | – | Altingiaceae | Tree | Wild | Root, bark | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatoid arthritis, lumbar muscle degeneration | 451225131109028 |
| Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don | Qianliguang千里光 | ça:u1jɛ5 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for rhinitis, hepatitis, clearing away heat and toxic materials, sore throat, swelling and pain, pruritus | 451225121204007 |
| Senna occidentalis (L.) Link | Wangjiangnan望江南 | moŋ6ca:ŋ1na:m2 | Fabaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for cough, asthma, bloody stranguria, constipation, headache, red eyes. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle swollen toxin, snake bite | 451225140507003 |
| Senna tora (L.) Roxb. | Jueming决明 | – | Fabaceae | Herb | both | Seed | Decoction; taken orally for clearing liver and eyesight, diuresis, anti-hypertensive | 451225131107001 |
| Serissa japonica (Thunb.) Thunb. | Liuyuexue六月雪 | – | Rubiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Decoction; taken orally for nephropathy, pharyngitis, urinary stone | 451225140508032 |
| Sesamum indicum L. | Zhima芝麻 | yəu6ma2nam1 | Pedaliaceae | Herb | Home garden | Seed | Powdered, taken orally with water for premature graying hair, dizzy of the head and dim of sight, constipation due to intestinal dryness | 451225130726012 |
| Setaria italica (L.) Beauv. var. germanica (Mill.) Schrad. | Su粟 | – | Poaceae | Tree | Home garden | Stigma, Pulp of infructescence | Decoction; taken orally for diuresis stranguria, removing jaundice detumescence | 451225130306003 |
| Sigesbeckia pubescens (Makino) Makino | Xiangengxixian腺梗豨莶 | çi1tshjen1hɣɔk8 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for rheumatism, numbness of limbs, apoplexy, abscess, eczema pruritus, hypertension | 451225130429025 |
| Smilax biumbellata T. Koyama | Xinanbaqia西南菝葜 | ça:u1cəm1ka:ŋ1 | Smilacaceae | Liana | Wild | Rhizome | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, for treating dispelling wind and remove dampness, rheumatism, traumatic injury, scrofula | 451225130423029 |
| Smilax china L. | Baqia菝葜 | – | Smilacaceae | Liana | Wild | Tuber | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for tonifying kidney, general fatigue, cough | 451225130430025 |
| Smilax glabra Roxb. | Tufuling土茯苓 | hu3kɔk7ta:ŋ1 | Smilacaceae | Liana | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for syphilis, turbidity, inchacao, furuncle, abscess, scrofula | 451225130501042, 451225130611002 |
| Solanum melongena L. | Qie茄 | ca6la:i4ta:ŋ1 | Solanaceae | Herb | Home garden | Root, Stem | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for rheumatic arthritis, protracted dysentery, hemafecia, inchacao. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for chilblain, toothache | 451225131109029 |
| Solanum nigrum L. | Longkui龙葵 | tɔŋ6taŋ1lɔŋ2 | Solanaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, diuresis detumescence, anticancer. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle, traumatic injury | 451225130307003 |
| Solanum verbascifolium L. | Jiayanyeshu假烟叶树 | jen1ja4fa5 | Solanaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for rheumatism, toothache, scrofula, metrorrhagia. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury, furuncle abscess, eczema | 451225121205029 |
| Solena heterophylla Lour. | Maogua茅瓜 | – | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area or medicinal bath, treating for pedal edema | 451225130606028 |
| Solidago decurrens Lour. | Yizhihuanghua一枝黄花 | nə5ŋa5ŋa:n3hwa1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for common cold with headache, sore throat, cough, jaundice; medicinal bath, treating for infantile convulsions, traumatic injury, furuncle, eczema itch | 451225130307026 |
| Sophora flavescens Alt. | Kucan苦参 | sən5kam1 | Fabaceae | Herb | both | Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, ostealgia. Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for infantile malnutrition, toxic heat, discharging fresh blood stool, jaundice, leukorrhea, acute tonsillitis, hemorrhoid complicated by anal fistula, rectal prolapse, pruritus, scald | 451225130719007 |
| Sophora japonica L. | Huai槐 | hwa:i6mai4hwa1 | Fabaceae | Shrub | Home garden | Flower | Decoction; taken orally for piles, internal hemorrhage, hypertension. Stewed with tail of pig intestine and drunk the soup, treating for syphilis | 451225130428048 |
| Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep. | Yuenanhuai越南槐 | – | Fabaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root | Taken orally directly for sore throat, gastric cancer, stomachache, gastric ulcer, prostatitis, diuresis | 451225130311063 |
| Spatholobus suberectus Dunn. | Mihuadong密花豆 | ça:u1ci1phɣə:t7 | Fabaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating dizziness due to deficiency of blood, soreness of waist, paralysis, irregular menses | 451225130429024 |
| Speranskia cantonensis (Hance) Pax et Hoffm. | Guangdongdigouye广东地构叶 | – | Euphorbiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; medicinal bath, treating for ague or fever | 451225130428050 |
| Spirodela polyrhiza (Linnaeus) Schleiden | Ziping紫萍 | ȵai3 | Araceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for affection of exogenous wind-heat, measles, pruritus, edema | 451225130429034 |
| Stachytarpheta jamaicensis (L.) Vahl | Jiamabian假马鞭 | – | Verbenaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, diuresis stranguria, stone, urinary tract infection | 451225131108026 |
| Stahlianthus involucratus (King ex Bak.) Craib | Tutianqi土田七 | – | Zingiberaceae | Herb | Home garden | Tuber | Stewed with meat and eated directly for bodily weakness | 451225130607010 |
| Stellaria alsine Grimm | Queshecao雀舌草 | – | Caryophyllaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for clearing away heat and toxic materials, diuresis, detumescence relieve pain | 451225130307021 |
| Stemona tuberosa Lour. | Dabaibu大百部 | – | Stemonaceae | Herb | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for relieving thirst and asthma, insecticidal relieve pain, cough with lung heat, tuberculosis | 451225130423020 |
| Stephania japonica (Thunb.) Miers | Qianjinteng千金藤 | ça:u1thjen1can1 | Menispermaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem or root, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for sore blister, diarrhea, rheumatism, edema, stranguria with turbid discharge, sore throat, abscess, furuncle | 451225130805003 |
| Striga asiatica (L.) O. Ktze. | Dongjiaojin独脚金 | na:u3tin1cəm1 | Orobanchaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for infantile malnutrition, edema | 451225130721002 |
| Strobilanthes cusia (Nees) Kuntze | Banlan板蓝 | lo4həu1fa5 | Acanthaceae | Herb | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc, snake bite, traumatic injury. Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for fever, headache, sore throat, mumps, furuncle, miliaria, eczema | 451225130726001 |
| Strychnos nux-vomica L. | Maqianzi马钱子 | – | Loganiaceae | Shrub | both | Seed | Chewing, treating for toothache | 451225130501039 |
| Talinum paniculatum (Jacq.) gaertn. | Turencan土人参 | tɔŋ6ma1pi2 | Talinaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Stewed with meat and drunk the soup, treating for weakness of spleen and stomach, poor appetite, cough hemoptysis, spontaneous sweating, palpitation, irregular menses | 451225130422044 |
| Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz. | Pugongying蒲公英 | ma1pa:k8hɣɔk8 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for treating toxic heat, abscess of lung, intestinal carbuncle, mammary abscess | 451225130519001 |
| Taxillus chinensis (DC.) Danser | Guangjisheng广寄生 | – | Loranthaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for rheumatism, activate collaterals, lumbar muscle degeneration, paralysis | 451225130424027 |
| Taxus wallichiana Zucc. var. mairei (Lemée et H. Lév.) L. K. Fu et Nan Li | Nanfanghongdongshan南方红豆杉 | – | Taxaceae | Tree | both | Stem pith | Decoction; taken orally for heart disease, hepatopathy | 451225131108003 |
| Tetrastigma planicaule (Hook. f.) Gagnep. | Biandanteng扁担藤 | ça:u1pjɛn3 | Vitaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem, Root | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or rinsed, treating for ischialgia, rheumatism, hemiplegia | 451225130727009 |
| Teucrium viscidum Bl. | Xuejianchou血见愁 | – | Lamiaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for difficult labour | 451225130718001 |
| Tinospora sagittata (Oliv.) Gagnep. | Qingniudan青牛胆 | – | Menispermaceae | Liana | Wild | Rhizome | Decoction; taken orally for hepatitis, prostatitis. Taken orally directly for abdominal pain | 451225130423033 |
| Tinospora sinensis (Lour.) Merr. | Zhonghuaqingniudan中华青牛胆 | ça:u1hɣa:ŋ4cen1 | Menispermaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for breaking of muscle and tendon, rheumatism, ostealgia. Medicinal liquor; taken orally for activate collaterals | 451225121231021 |
| Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. | Feilongzhangxue飞龙掌血 | lən1phɣə:t7ta:n5 | Rutaceae | Liana | Wild | Root or Root bark | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism, traumatic injury. Powder and applied on the affected area, treating for bleeding wound | 451225121205031 |
| Toona sinensis (Juss.) Roem. | Xiangchun香椿 | mai4jam4ŋɣa2pa:k8 | Meliaceae | Tree | both | Bark or Root bark | Decoction; taken orally for chronic diarrhea, protracted dysentery, hemorrhoidal hemafecia, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, leukorrhea, spermatorrhea, gonorrhea, malnutrition, depriving ascarid, tinea sores | 451225130611026 |
| Torilis scabra (Thunb.) DC. | Qieyi窃衣 | – | Apiaceae | Herb | Wild | Seed | Stewed with pork liver and taken orally directly for treating blurred vision, heloma | 451225130420004 |
| Toxicodendron succedaneum (L.) Kuntze | Yeqi野漆 | – | Anacardiaceae | Tree | Wild | Leaf | Decoction; Medicinal bath for treating dermatitis | 451225130311047 |
| Toxicodendron vernicifluum (Stokes) F. A. Barkley | Qi漆 | – | Anacardiaceae | Tree | both | Leaf | Decoction; Medicinal bath for treating dermatitis | 451225130519035 |
| Trachelospermum jasminoides (Lindl.) Lem. | Luoshi络石 | lɔ6twi2ça:u1 | Apocynaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem and leaf | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatism, traumatic injury, muscle and vessel contracture etc syndromes, swelling and pain. Decoction; taken orally for spitting blood, postpartum lochia | 451225121205021, 451225130429013 |
| Tradescantia pallida (Rose) D. R. Hunt | Zizhumei紫竹梅 | – | Commelinaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal bath for sterilization and anti-itch | 451225130607017 |
| Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. | Gualou栝楼 | thjen1la2pən5 | Cucurbitaceae | Liana | both | Root | Root: Decoction; taken orally for cough with lung heat, jaundice, pemphigus; Fruit: Decoction; taken orally for cough, palpitation, costalgia, marasmus, frequent micturition | 451225130518025 |
| Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. | Leigongteng雷公藤 | ça:u1ləi6pɣa3 | Celastraceae | Liana | Wild | Root, Leaf, Flower | Medicinal liquor; Applied on the affected area, treating for scabies, eczema, rheumatic arthritis | 451225130309033 |
| Tupistra sp. | Kaikoujian开口箭 | – | Asparagaceae | Herb | both | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for bone injury | 451225131108040 |
| Typha domingensis Persoon | Changbaoxiangpu长苞香蒲 | pu2ŋa:n3 | Typhaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for internal hemorrhage, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, dysmenorrhea, menostasis, postpartum blood stasis, bloody stranguria | 451225130608027 |
| Uncaria rhynchophylla (Miq.) Miq. ex Havil. | Gouteng钩藤 | ça:u1kau1 | Rubiaceae | Liana | Wild | Hooked stem | Hooked stem: Decoction; taken orally for blood pressure lowering, epilepsy, dizziness. Root: Medicinal liquor; taken orally for treating rheumatism | 451225130430001 |
| Urena lobata L. | Ditaohua地桃花 | – | Malvaceae | Shrub | Wild | Root, Leaf | Decoction; taken orally for bacillary phthisis, cough, anti-inflammato | 451225130427023, 451225130606027 |
| Verbena officinalis L. | Mabiancao马鞭草 | hɣɔk8ma4pjen1 | Verbenaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for commom cold, tonsillitis, acute nephritis, sore throat, damp and hot jaundice. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for mastitis, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury | 451225130421046, 451225130427025 |
| Vernicia fordii (Hemsl.) Airy Shaw | Youtong油桐 | mai4tɔŋ6lau5 | Euphorbiaceae | Tree | both | Whole plant | Decoction; taken orally for scrofula, hemorrhoids, scald, crusted tetter, erysipelas, dyspeptic retention abdominal distension, urinary stoppage and constipation, rheumatism, ostealgia | 451225130425010 |
| Viburnum taitoense Hayata | Taidongjiasan台东荚蒾 | – | Adoxaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Pounded fresh part with salt applied on the affected area, treating for hyperosteogeny, protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc, relieve pain, traumatic injury | 451225130429025 |
| Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek | Lvdong绿豆 | lɔk8tau6 | Fabaceae | Liana | Home garden | Seed | Taken orally directly or pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for polydipsia, carbuncle, crotonism | 451225130606005 |
| Vigna umbellata (Thunb.) Ohwi et H. Ohashi | Chixiaodong赤小豆 | tau6la:n3niŋ5 | Fabaceae | Liana | Home garden | Seed | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for edema, inchacao, jaundice, toxic heat, carbuncle | 451225130723004 |
| Viola japonica Langsd. | Litoucao犁头草 | hɣɔk8kɣo3khɣəi1 | Violaceae | Herb | Wild | Whole plant or Root | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for furuncle, acute mastitis, intestinal carbuncle, erysipelas, red eyes, snake bite | 451225130306012 |
| Viscum articulatum Burm. F. | Bianzhihujisheng扁枝槲寄生 | – | Santalaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Pounded fresh part with the feet of crab applied on the affected area, treating for fractura | 451225130612005 |
| Vitex negundo L. | Huangjing黄荆 | mai4jin1la:k8 | Lamiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Fruit | Decoction; taken orally for commom cold, cough, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, stomachache, hernia, malaria, anal fistula | 451225130729004 |
| Vitex negundo L. var. cannabifolia (Sieb. et Zucc.) Hand.-Mazz. | Mujing牡荆 | – | Lamiaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for commom cold, cough, rheumatism, eliminating stagnation | 451225130729006 |
| Vitis balansana Planchon | Xiaoguoputao小果葡萄 | pɣa2pɣa1məm4 | Vitaceae | Liana | Wild | Tendril | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or rinsed, for treating swollen sore, traumatic injury, rheumatism | 451225130309044 |
| Vitis heyneana Roem. et Schult. | Maoputao毛葡萄 | ça:u1lak8jyt7ja4 | Vitaceae | Liana | Wild | Stem | Medicinal liquor; taken orally or applied on the affected area, treating for rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury, sore swollen toxin | 451225130722008 |
| Vitis vinifera L. | Putao葡萄 | – | Vitaceae | Liana | Home garden | Fruit | Taken orally directly for anti-inflammatory, hepatopathy, hepatitis | 451225130518017 |
| Wikstroemia indica (L.) C. A. Mey | Liaogewang了哥王 | – | Thymelaeaceae | Shrub | Wild | Stem and leaf | Decoction; medicinal bath for killing parasites to relieve itshing | 451225130428014 |
| Xanthium sibiricum Patr. ex Widd | Cangdong苍耳 | hɣɔk8tsha:ŋ5khɣa1 | Asteraceae | Herb | Wild | Seed, Stem, Leaf | Seed: Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for anemofrigid headache, nasosinusitis, rheumatoid arthritis, scabies, pruritus. Stem and leaf: Decoction; medicinal bath, treating for rheumatoid arthritis | 451225130607021 |
| Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC. | Liangmianzhen两面针 | – | Rutaceae | Shrub | Wild | Whole plant | Medicinal liquor; taken orally for rheumatism, relieve pain. Decoction; taken orally for gastric ulcer, stomachache, prostatitis | 451225130312018 |
| Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. | Huajiao花椒 | hwa5tsja:u5 | Rutaceae | Shrub | both | Peel | Stewed with meat and Taken orally directly for invigorating spleen, cold pain in abdomen, vomit, diarrhea, rheumatoid arthritis, colic; taken orally directly for depriving ascarid, enterobiasis; Medicinal bath for pruritus vulvae, pemphigus | 451225130421062 |
| Zea mays L. | Yushushu玉蜀黍 | jəu6mɛ4mut8 | Poaceae | Herb | Home garden | Stigmata | Decoction; taken orally for nephrotic syndrome, edema, jaundice, hypertension, damp and hot jaundice, diabetes | 451225130518032 |
| Zephyranthes carinata Herbert | Jiulian韭莲 | – | Amaryllidaceae | Herb | Wild | Bulb | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, for stanching bleeding | 451225130517016 |
| Zingiber lingyunense D. Fang | Wujiang乌姜 | – | Zingiberaceae | Herb | Wild | Tuber | Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area, treating for traumatic injury | 451225130607040 |
| Zingiber officinale Roscoe | Jiang姜 | çiŋ1khɣɔ3 | Zingiberaceae | Herb | Home garden | Tuber | Decoction; taken orally or medicinal bath for cough, hemoptysis, hiccough, anemofrigid cold, vomit, cough, reduce phlegm | 451225130519031 |
Mulam name: as written in the international phonetic alphabet (IPA)
Among the families that contributed more medicinal species were Fabaceae and Asteraceae, represented by 29 species (6.36%) in each family, Lamiaceae with 21 species (4.61%), Rosaceae with 16 species (3.51%), Poaceae with 15 species (3.29%), Euphorbiaceae with 14 species (3.07%), Rubiaceae with 13 species (2.85%), and Rutaceae with ten species (2.19%). The other 309 species (67.76%) came from 124 families that were mostly represented by one or two species (Table 3).
Table 3.
Taxonomic diversity of medicinal plants in the study area
| Family | Number of medicinal plant species | Percentage of species (%) | Number of genera | Percentage of genus (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asteraceae | 29 | 6.36 | 20 | 5.71 |
| Fabaceae | 29 | 6.36 | 21 | 6.00 |
| Lamiaceae | 21 | 4.61 | 15 | 4.29 |
| Rosaceae | 16 | 3.51 | 10 | 2.86 |
| Poaceae | 15 | 3.29 | 15 | 4.29 |
| Euphorbiaceae | 14 | 3.07 | 9 | 2.57 |
| Rubiaceae | 13 | 2.85 | 12 | 3.43 |
| Rutaceae | 10 | 2.19 | 6 | 1.71 |
| Amaranthaceae | 9 | 1.97 | 6 | 1.71 |
| Cucurbitaceae | 9 | 1.97 | 9 | 2.57 |
| Moraceae | 9 | 1.97 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Malvaceae | 8 | 1.75 | 6 | 1.71 |
| Polygonaceae | 8 | 1.75 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Amaryllidaceae | 7 | 1.54 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Vitaceae | 7 | 1.54 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Apiaceae | 6 | 1.32 | 6 | 1.71 |
| Araceae | 6 | 1.32 | 6 | 1.71 |
| Asparagaceae | 6 | 1.32 | 6 | 1.71 |
| Polypodiaceae | 6 | 1.32 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Solanaceae | 6 | 1.32 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Zingiberaceae | 6 | 1.32 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Acanthaceae | 5 | 1.10 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Berberidaceae | 5 | 1.10 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Lauraceae | 5 | 1.10 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Menispermaceae | 5 | 1.10 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Orchidaceae | 5 | 1.10 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Primulaceae | 5 | 1.10 | 2 | 0.57 |
| Anacardiaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Apocynaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Araliaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Brassicaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Celastraceae | 4 | 0.88 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Dioscoreaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 2 | 0.57 |
| Myrtaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Oleaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 2 | 0.57 |
| Phyllanthaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 3 | 0.86 |
| Urticaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Verbenaceae | 4 | 0.88 | 4 | 1.14 |
| Others | 142 | 31.14 | 122 | 34.86 |
| Total | 456 | 100.00 | 350 | 100.00 |
Habit, plant parts used, and habitat
The results of the habit analysis of the medicinal plants showed that herbaceous plants constituted the highest proportion (246 species (54%)), while there were 76 (17%) shrubs, 75 (16%) lianas, and 59 (13%) tree species (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
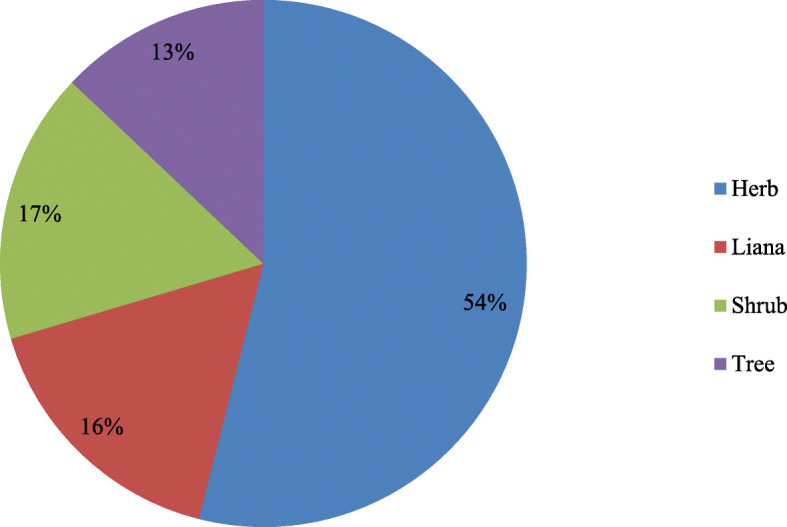
Habits of medicinal plants in the study area
Mulam people use different plant parts in the preparation of traditional drugs (e.g., leaves, stems, roots, seeds, bark, flowers, and fruits). Many of the herbal medicines are made by using whole plants (182 species, 33.46%), followed by roots (73 species, 13.42%), stems (46 species, 8.46%), leaves (44 species, 8.09%), a combination of stems and leaves (35 species, 6.43%), rhizomes (30 species, 5.51%), seeds (30 species, 5.51%), fruits (25 species, 4.60%), tubers (15 species, 2.76%), bark (13 species, 2.39%), and 26 other plant parts (e.g., bulbs, flowers, root bark, aril, stigma; 16%) (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Plant parts used in the treatment of human ailments
A total of 456 species of medicinal plants were collected from the study area, most of which (335 species, 73.47%) were obtained from wild habitats; 68 (14.91%) species were from home gardens, and 53 (11.62%) species were both from home gardens and wild habitats (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
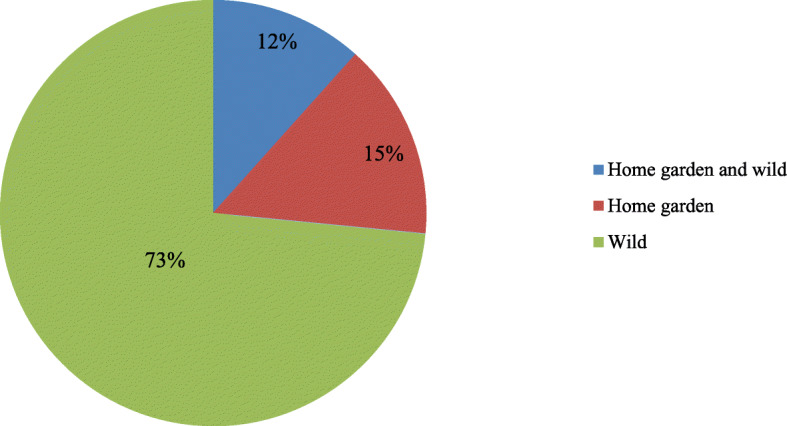
Habitats of medicinal plants in the study area
Preparation and application methods
There are numerous different ways to prepare medicinal plants to treat human ailments. In the study area, the most common methods of preparation of traditional medicines from plant material were decoction (54.11%), followed by pounding (20.48%), preparing a medicinal liquor (9.64%), raw (9.64%), stewing (2.75%), and others (Table 4).
Table 4.
Ways of preparation of medicinal plants
| Method of preparation | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Decoction | 316 | 54.11 |
| Pounded | 119 | 20.48 |
| Medicinal liquor | 56 | 9.64 |
| Natural | 56 | 9.64 |
| Stewed | 16 | 2.75 |
| Others (powdered, drying, frying, slicing) | 18 | 3.48 |
Table 5 shows that the traditional medicines are used in four main ways. The most common method is oral administration (390 plant species, 62.70%), followed by external application (143 species, 22.99%), a medicated bath or rinsing (87 species, 13.99%), and chewing (two species, 0.32%).
Table 5.
Application method by local Mulam people
| Application method | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Oral taking | 390 | 62.70 |
| External application | 143 | 22.99 |
| Medicinal bath or rinsed | 87 | 13.99 |
| Chewing | 2 | 0.32 |
Diseases treated in the study area
Based on our investigation and records, medicinal plants were used to treat 312 human ailments in the study area. Based on the statistical analysis, rheumatism was the most common disease treated with 84 medicinal plant species, followed by traumatic injury (71 species), cough (68 species), diarrhea (54 species), jaundice (47 species), abscesses (42 species), furuncles (38 species), edema (36 species), sore throat (34 species), carbuncles (33 species), and eczema (30 species).
Ranking and informant consensus factor of medicinal plants
Among all of the ailments in the study area, rheumatism was the most common disease and was treated by a high number of medicinal plants (82 species). Ten medicinal plant species were used effectively to treat rheumatism according to key informants. The results revealed that Semiliquidambar cathayensis was the most preferred medicinal plant for rheumatism, followed by Tetrastigma planicaule, Bauhinia championii, and Millettia lasiopetala (Table 6).
Table 6.
Preference ranking to medicinal plants used to treat rheumatism
| List of medicinal plants | Informants | Total | Rank | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | |||
| Ardisia crenata | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 37 | 8 |
| Ardisia gigantifolia | 5 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 43 | 6 |
| Bauhinia championi | 9 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 74 | 3 |
| Cibotium barometz | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 30 | 9 |
| Clerodendrum japonicum | 4 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 38 | 7 |
| Kadsura coccinea | 6 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 59 | 5 |
| Maclura cochinchinensis | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 26 | 10 |
| Millettia lasiopetala | 7 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 70 | 4 |
| Semiliquidambar cathayensis | 10 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 93 | 1 |
| Tetrastigma planicaule | 8 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 80 | 2 |
R represented respondents; scores in the table indicated ranks given to medicinal plants based on their scarcity. Highest number (10) is for the medicinal plants which informants thought most preferred in the area and the lowest number (1) for the least preferred medicinal plant
Twelve ailment categories were identified based on the eight systems of the human body and the medication characteristics of the Mulam people. The ICF was calculated for each ailment category, and the range was from 0.51 to 0.92 (Table 7). The highest ICF (0.92) was reported for gynecological ailments, with 12 species and 138 use reports, followed by nerves and psychosomatic problems (0.90), digestive system diseases (0.89), urinary system diseases (0.88), skin diseases (0.88), and circulatory system diseases (0.88).
Table 7.
Informant consensus factor by categories of diseases in the study area
| Category | Specific conditions | nur | nt | ICF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gynecological aliments | Leukorrhea (28), metrorrhagia and metrostaxis (8), irregular menses (12), dysmenorrhea (9), postpartum blood stasis (5), etc. | 138 | 12 | 0.92 |
| Nerves and psychosomatic problems | Headache (17), insomnia (10), dizziness (8), hemiplegia (5), etc. | 83 | 9 | 0.90 |
| Digestive system | diarrhea (54), jaundice (47), abdominal pain (18), stomachache (19), abdominal distension (18), constipation (17), etc. | 314 | 36 | 0.89 |
| Urinary system | diuresis (21), stranguria (19), calculosis (17), urinary frequency (13), dysuria (5), etc. | 105 | 13 | 0.88 |
| Skin diseases | abscess (42), pruritus (42), furuncle (38), eczema (30), scald (19), inchacao (12), piles (11), scabies (9), etc. | 233 | 28 | 0.88 |
| circulatory system | internal hemorrhage (25), clearing away heat and toxic materials (23), hypertension (13), hemoptysis (15) , etc. | 124 | 16 | 0.88 |
| Respiratory system | cough (68), sore throat (34), common cold (30), abscess of lung (8), etc. | 189 | 42 | 0.78 |
| Traumatic injury and sprain and bleeding wound | traumatic injury (71), bleeding wound (32), bone fracture (7), wound infection, etc. | 129 | 33 | 0.75 |
| Inflammation | nephritis (16), prostatitis (9), enteritis (10), tracheitis (10), erysipelas (9), cancer (7), dermatitis (5), gastritis (5), pneumonia (5), etc. | 129 | 33 | 0.75 |
| Rheumatic problems | Rheumatism (60), rheumatoid arthritis (24), etc. | 92 | 43 | 0.53 |
| Strong body and relieve pain | numbness of limbs (6), backache (8), soreness and weakness of waist and knees (4), stop pains (8), etc. | 71 | 35 | 0.51 |
| Other Uses | edema (36), male problems (36), pediatric disease (22), scrofula (15), toothache (8), hyperosteogeny (7), etc. | 152 | 36 | 0.77 |
Fidelity levels of most commonly used plants by key informants
For each of the 15 most commonly used plant species as ranked by key informants, the fidelity level (FL) (Table 8) was calculated to quantify their importance in treating a major ailment [31, 35]. The results showed a high FL of greater than 50% for 12 plant species, which highlights the importance of these species in the treatment of the frequently mentioned diseases in the study area. Polygonum multiflorum, Semiliquidambar cathayensis, Zingiber officinale, and Striga asiatica had FLs of 100% for strengthening the body and treating rheumatism, infantile malnutrition and cough.
Table 8.
Fidelity Levels (FL) of most commonly used plants by key informants
| Plant species | Therapeutic uses | Ip | Iu | FL% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artemisia carvifolia | Malaria | 11 | 33 | 33.33 |
| Camellia oleifera | Scald | 16 | 25 | 64.00 |
| Curculigo orchioides | Impotence | 12 | 21 | 57.14 |
| Eriobotrya japonica | cough | 36 | 38 | 94.74 |
| Gynostemma pentaphyllum | Anti-inflammatory | 34 | 42 | 80.95 |
| Lygodium japonicum | Renal calculus | 16 | 28 | 57.14 |
| Polygonum multiflorum | Premature graying of the hair | 39 | 39 | 100.00 |
| Pueraria montana var. lobata | Hangover alleviation | 16 | 44 | 36.36 |
| Ricinus communis | Scabies | 12 | 18 | 66.67 |
| Rosa laeuigata | Spermatorrhea | 18 | 44 | 40.91 |
| Sarcandra glabra | Common cold | 36 | 43 | 83.72 |
| Semiliquidambar cathayensis | Rheumatism | 35 | 35 | 100.00 |
| Sophora tonkinensis | Stomachache | 23 | 25 | 92.00 |
| Striga asiatica | Malnutritional stagnation | 26 | 26 | 100.00 |
| Zingiber officinale | Cough | 42 | 42 | 100.00 |
Threats to traditional medicinal knowledge and medicinal plants
According to our investigation (Table 1), more than 80% of key informants who showed mastery of rich traditional medicinal knowledge were over 50 years old, and more than 60% of key informants were illiterate or had only received a primary education. Currently, Mulam children spend most of their time in schools, where they receive mainstream culture and education and have no chance to study traditional medicinal knowledge. In addition, young people prefer to look for jobs in urban areas to earn higher incomes. Furthermore, Mulam healers are unwilling to pass on their traditional medicinal knowledge to young people under 30 years old. During our surveys, we found that one-third of doctors did not have a successor. The inheritance process of traditional Mulam medicinal knowledge is experiencing a dilemma. In addition, due to the lack of a written language, basic information on the use of plants, the parts used, drug preparation methods, diseases treated, and other information may be lost or discarded in the transmission process.
According to our field investigation and the group discussions, most of the medicinal plants were found to be under threat from anthropogenic pressure, such as agricultural activities, firewood collection, overgrazing, and logging. Most Mulam villages are located on small strips of flat land or slopes in karst mountainous areas, and most Mulam people engage in traditional agriculture (Fig. 1). Informants ranked agricultural activities as the most serious threat to medicinal plants, followed by firewood collection and overgrazing. The overharvesting of wild medicinal plants was also a key threat because Mulam people prefer to collect whole plants, roots, stems, and rhizomes. This collection method damages or totally destroys the plant and diminishes the sustainability of medicinal plant use.
Discussion
Characteristics of informants and their traditional knowledge
Our study included a similar number of men and women as general informants, who have less traditional medicinal knowledge than key informants. Most informants only knew a small number of medicinal plants for treating some common ailments, such as traumatic injuries, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Every key informant knew more than 60 species and more therapeutic methods for different diseases than the general informants. Most of the key informants were male because Mulam women mainly perform housework and farm work. According to the customary inheritance practice, local traditional medicinal knowledge is typically passed on from an older herbalist to a male successor, rather than a female successor. The number and use methods of medicinal plants reported increased with informant age. Older informants possess more traditional knowledge of medicinal plants than younger people. Local herbalists are unwilling to pass on traditional medicinal knowledge to people who are under 30 years old because they believe that young people are too immature to seriously learn the traditional knowledge. Differences in knowledge of medicinal plants among age and gender groups were also reported in other studies from China and other countries [10, 14, 37, 38].
Most informants in our study have attained low levels of education. Only 33 informants received secondary education, and four informants received tertiary education. Currently, highly educated people tend to prefer modern medicinal technology to traditional knowledge. They are not interested in studying or practicing ethnomedicinal knowledge, especially younger generations. Similar results from other studies also reported that most traditional medicinal herbalists and inheritors worldwide have low formal education levels [10, 15, 17, 22].
Methods of medicinal plant collection and patient diagnosis and treatment
According to our investigation, local herbalists believe that it is much better to collect medicinal plants from noon to evening in autumn or winter because many medicinal plants may enter dormancy and have relatively dry bodies with the highest efficacy. The herbalists also said that if they met a pregnant woman or someone combing their hair on their way to pick medicinal plants, the collected medicinal plants would have a negative impact on the medication made from the plant. Therefore, the herbalist would not go to collect medicinal plants on that day. They reported that if the first herb were obtained very easily, all of the medicinal plants collected on the same day would have good efficacy. In addition, when Mulam healers collect medicinal plants, there is a tradition of “keeping a line,” that is, they will put money and rice under the roots of the collected plant and leave a few organs rather than collecting the whole plant.
The Mulam herbalists would let their patients rest for 10–20 min to allow their heart rhythm to normalize before feeling their pulse and inquiring about their condition. Many herbalists would diagnose the disease in combination with the hospital’s inspection report. They would ask patients to go to the hospital for a recheck to ensure that the disease would be cured by the end of their therapy. The key informants believed that when patients filled their prescriptions, if the herbalist were smoking or going out with a hoe, the medicine would not be effective. However, if the herbalist were eating or drinking, the medicine would have good efficacy. To prevent their prescriptions from being stolen and to maintain a sense of mystery, the doctors often made the medicines into granules or pills for patients.
Diversity of medicinal plants
A total of 456 medicinal plant species belonging to 350 genera and 132 families were documented and identified for treating human ailments. Both Fabaceae and Asteraceae (with 29 species) occupied the highest proportion (6.36%), followed by Lamiaceae, Rosaceae, Poaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Rubiaceae, and Rutaceae. Various studies in China showed a similar result, in which these families contain many medicinal species [19, 20, 22, 37, 39]. Most of the families were represented in the study area by one or two species, and the distribution of medicinal plant species in the various families was relatively scattered; this finding reflects the rich biodiversity of the medicinal plants used by Mulam people.
Mulam people believe that wild medicinal plants have stronger efficacy than those from home gardens; therefore, most of the mentioned medicinal plants were harvested from the wild (335 species, 73.47%). Similar findings were reported by other studies from southern China [22, 25, 37, 39]. The herbalists grew a few plants in their home gardens that have multiple uses, are critically endangered in the field, or are urgently needed, such as Paris polyphylla var. chinensis and Cynanchum atratum.
The medicinal plants most widely used by Mulam people were obtained from herbs, which constituted the largest habit category with 246 species (54%). This finding is consistent with other results [37, 39–41]. To explain this phenomenon, Moa et al. suggested that herbs are more widely distributed (roadsides, home gardens, farmlands, and wild habitats) than plants with other habits, such as trees, shrubs, and lianas [30]. In addition, herbs are more easily gathered than tree species [41].
Mulam people like to use whole plants (182 species, 33.46%) in the preparation of traditional drugs, and similar results were found in the neighboring Maonan, Yao, and Zhuang communities [24, 38, 40–42]. The use of roots (73 species, 13.42%), stems (46 species, 8.46%), and rhizomes (30 species, 5.51%) was also common in the study area. However, a clear relationship exists between plant parts collected or the collection method and the impact on the harvested plant [42]. The collection of whole plants, roots, stems, and rhizomes damages or totally destroys the plant and negatively affects the sustainable use of the species. Mulam healers believe that different parts of the same plant may have different medicinal efficacy. The root and stem of Kadsura longipedunculata, for example, are decocted and taken orally for gastritis, and a medicinal liquor made from the fruit is taken orally to treat rheumatism and stomachache. The herbalists also reported that different parts of different plants may have the same medicinal purpose. For instance, the stem of Sargentodoxa cuneata, the root of Semiliquidambar cathayensis, the stem of Tetrastigma planicaule, and the whole plant of Zanthoxylum nitidum could be used to treat rheumatism.
Mulam healers are skilled at using the principle of “lingqi” and have a tradition of “treating diseases using medicine with a similar shape or color.” The herbalists reported using medicines from hollow-stem plants such as Equisetum hyemale, Siegesbeckia orientalis, Leonurus japonicus, and Coix lacryma-jobi var. ma-yuen to treat edema based on the aeration of the hollow stems. The branch joints of Achyranthes bidentata, Polygonum capsicum, and Taxillus chinensis are similar to human joints and are often used to treat arthritis. Black soya bean, black sesame seed, mulberry, black ants, and black fungus have black “lingqi” and can be used for treating prematurely white hair.
Methods of medicinal plant preparation and application
In the study area, various methods used by the local Mulam people for the preparation and administration of medicinal plants were investigated and documented. Decoction (316 species involved, 54.11%) is the most common application method for Mulam people. Mulam people and herbalists believe that decoction accelerates the absorption of medicinal ingredients and improves the taste of medicinal plants. Decoction is cited as the most common method of preparation of herbal remedies and is used widely by other ethnic groups [10, 22, 43–47]. Pounding also had a high frequency (119) and percentage (20.48%).
Mulam people and herbalists prefer to prepare fresh materials directly through decoction or pounding. They believe that the raw medicinal plants possess better efficacy than cooked plants. In addition, the rich plant diversity around Mulam villages provides a material basis for the use of raw medicinal plants. Additionally, the raw material may maintain its volatile oils and other ingredients [22]. However, the utilization of fresh plant parts may threaten the plants due to frequent collection, including in dry seasons [30]. Certain measures and methods should be taken immediately to guide and encourage local people to grow medicinal herbs and to store commonly consumed medicinal materials.
Oral administration (390 species involved, 62.7%) is the most common method of administration of traditional medicine by Mulam people. Oral use was considered popular because it is a simple administration method. It has also been found to be widely applied in other studies [10, 22, 43–47]. Different additives, such as alcohol, honey, salt, and sugar, are widely used by Mulam healers to improve the flavor, taste, and general acceptability of certain orally administered remedies. In addition, Mulam people often stew animal bones, innards, or meat with medicinal plants. Mulam healers believe that animal organs can nourish the corresponding parts of the human body. For example, chicken liver and Buddleja officinalis, Senecio scandens, and Centipeda minima cooked together can be used to treat hepatitis. Pork kidney and Eucommia ulmoides and Allium tuberosum cooked together are used to improve renal function. They also believe that improving patient nutrition can improve the efficacy of medicinal plants for patients.
Medicinal baths were frequently mentioned during our investigations. Mulam people reported that medicinal baths are safe, simple to perform, and did not result in side effects as an external treatment method. A medicinal bath is usually used for sweating, fever reduction, activating blood circulation to dissipate blood stasis, expelling wind to relieve excess gas, and providing itching relief [18]. Medicinal baths can treat diseases and can also prevent diseases. When taking a medicinal bath, the skin is fully exposed to the medicinal bath water so that the bath constituents with medicinal value can be absorbed [48, 49]. Hot water can also stimulate blood capillaries and metabolism. Medicinal baths are commonly used by the Yao and Zhuang people who live in humid mountainous areas of southern and southwestern China [18, 37, 49–51].
Diseases, ranking, and informant consensus factor of medicinal plants
Based on our investigations, 312 human ailments are treated with medicinal plants by Mulam people. According to our statistical analysis, rheumatism had the highest number (84 species) of medicinal plants used for its treatment. Mulam people living in humid and mountainous areas engage in heavy manual labor to survive. Thus, rheumatism is the most common disease in the study area. Because of the complexity of rheumatism, its pathogenesis has not been fully clarified [52]. Rheumatism is common all over the world and has been studied by different research institutions and organizations [52–55]. Numerous medicinal plants are used by Mulam herbalists to treat rheumatism. Ten medicinal plant species are widely used to treat rheumatism according to the key informants. In the preference ranking exercise, Semiliquidambar cathayensis was the most preferred medicinal plant. S. cathayensis is mainly used to treat rheumatism, lumbar muscle injury, hemiplegia, traumatic injury, and other conditions [56]. It is a very popular and effective traditional local medicine for rheumatism in Yao communities [37]. Mulam healers prefer to use the roots and bark of S. cathayensis collected from the wild to treat rheumatism. The large-scale collection of roots and bark threatens the sustainable development of S. cathayensis. Alternative plant parts or species for treating rheumatism urgently need to be discovered and studied.
Most of the ailment categories had a high ICF value (greater than 0.7), such as gynecological ailments (0.92), nerves and psychosomatic problems (0.90), digestive system ailments (0.89), and urinary system ailments (0.88). The higher the ICF value is, the higher the diversity of plant species used by herbalists to treat the disease. The lower the ICF value is, the lower the number of plant species used by herbalists to treat the disease [31]. The high ICF for gynecological ailments can probably be attributed to the local people preferring to obtain medicinal plants from wild habitats nearby, inheriting traditional medicinal knowledge from their parents or grandparents, and having little communication with other people to prevent others from stealing relevant prescriptions. The category of plants used to strengthen the body and release pain had the lowest degree of consensus (0.51) because most of these medicinal plants are easily obtained and used for multiple purposes, such as foods, vegetables, and tea substitutes.
Fidelity levels of the most commonly used plants by key informants
Polygonum multiflorum, Semiliquidambar cathayensis, Zingiber officinale, and Striga asiatica have the highest fidelity level (FL) values (100.00%). Eriobotrya japonica (94.74%) and Sophora tonkinensis (92.00%) also have high FL values. The remedies for frequently reported ailments have the highest FL values, and those with a low number of reports have the lowest FL values [36]. Obviously, these medicinal plants were very effective in the treatment of premature hair graying, rheumatism, infantile malnutrition, cough, and stomachache, which are frequently reported in the Mulam district and widely used by Mulam healers. Additionally, E. japonica (38), Gynostemma pentaphyllum (42), P. multiflorum (39), Pueraria montana var. lobata (44), Rosa laevigata (44), Sarcandra glabra (43), and Z. officinale (42) have high Iu values, showing that these medicinal plants were widely applied by Mulam healers and have high medicinal value.
Comparison with traditional Chinese medicine and previous ethnobotanical studies
To assess the novelty of the ethnomedicinal use of the encountered species, we chose 33 frequently or uniquely used medicinal plant species and compared their use with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and previously published reports from neighboring areas of southern China (Table 9) [18–20, 22, 25, 37, 39, 50, 51, 57–66].
Table 9.
Comparison with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and previous ethnobotanical studies
| Plant species | Diseases treated by Mulam | Diseases treated in traditional Chinese medicine and previous ethnobotanical studies |
|---|---|---|
| Achyranthes longifolia | Calculosis | Traumatic injury, rheumatism, dysentery, diphtheria, sore throat, sore carbuncle, stranguria, edema, removing blood stasis, kidney empty lumbago, dysmenorrhea, hypertension |
| Acorus gramineus | Epilepsy, phlegm heat, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, traumatic injury | Epilepsy, phlegm heat, rheumatism, beautifying, bellyache, tummy bug, numbness of limbs, hemorrhoids, diarrhea, gall, injuries from falls, dysmenorrhea |
| Artemisia argyi | Tocolysis, dysmenorrhea, irregular menses, leukorrhea, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis | Irregular menstruation, spitting blood, uterine bleeding, postpartum hemorrhage, carbuncle and scabies, stopping bleeding by warming meridians, expel cold and alleviate pain |
| Artemisia carvifolia | Malaria, diarrhea, jaundice, scab capillaris ies, pruritus | Malaria, sunstroke, dysentery, jaundice, scabies, pruritus |
| Camellia oleifera | Abdominal pain, depriving ascarid, intestinal dryness, scabies, scald | Acute laryngopharyngitis, cold, diarrhea, stomachache, pruritus |
| Clerodendrum bungei | Tuberculosis, carbuncle, furuncle, eczema, piles, rectal prolapse, infantile convulsion | Carbuncle, furuncle, eczema, enriching the blood |
| Corydalis saxicola | Anti-inflammatory | Acute or chronic hepatitis, scabies swelling poison |
| Cupressus funebris | Liver ascites | Children with high fever, vomiting blood, burns, hemorrhoids, dysentery |
| Curculigo orchioides | Impotence, aconuresis, carbuncle, scrofula | Impotence, urinary incontinence, uterine bleeding, ulcer, scrofula, headache due to common cold, rheumatic arthritis, rheumatism, nourishing, strengthening muscles and bones |
| Dioscorea bulbifcra | Antral gastritis, enteritis, thyroid disease, cough with lung heat, pudendal ulcer | Goiter, lymphatic tuberculosis, sore throat, hematemesis, hemoptysis, whooping cough, cancer, sore furuncle, epistaxis, pneumonia |
| Eriobotrya japonica | Ascites due to cirrhosis, cough with lung heat, hemoptysis, clearing away heat and toxic materials | Pertussis, cough, hematemesis, emesis |
| Euphorbia esula | degerming, chills, fever | – |
| Ficus hirta | Stomachache, cough, abdominal distension, edema, leukorrhea, rheumatoid arthritis, lumbago | Consumption, cough, abdominal distention, edema, rheumatism arthralgia, hepatitis, leucorrhea, no milk after delivery |
| Flemingia macrophylla | Caligo of old people | Rheumatic, lumbar muscle strain, hemiplegia and impotence |
| Gynostemma pentaphyllum | Relieve fever, anti-inflammator, chronic tracheitis, cough, asthma, stomachache, insomnia, headache | Cough, chronic gastroenteritis, rheumatism, bronchitis, stomachache |
| Hedyotis diffusa | Lung heat, sore throat, jaundice, pelvic inflammation, carbuncle, snake bite | Appendicitis, sphagitis, jaundice, adverse urination, dysentery, tumors, boils swelling, snake bite, hepatitis, cough, bronchitis, tonsillitis, toothache, cancer |
| Laportea violacea | Ascites due to cirrhosis | Rheumatic arthritis, urticaria, eczema, stomachache, malnutrition, epilepsy, sciatica |
| Lygodium japonicum | Kidney stone, clearing heat and diuresis, stranguria. Pounded fresh part applied on the affected area for anaesthesia | Stranguria, gonorrhea, leukorrhea, hepatitis, sorethroat, enteritis, dysentery, eczema, shingles, hematemesis, bleeding wound, jaundice, itch, diuresis, calculus, rheumatism, chronic ulcer, skin infection, furuncle, foot rot |
| Pinus massoniana | Rheumatic arthritis, tuberculous arthritis, blood stasis, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury, insomnia, edema, eczema, hemorrhoids | Vertigo, stomachache, dysentery, traumatic hemorrhage, eczema, skin erosion, measles |
| Polygonum multiflorum | Insomnia, profuse sweating, skin eruption, kidney deficiency, premature graying of the hair, dizzy of the head and dim of sight, soreness and weakness of waist and knees, spermatorrhea, chronic hepatitis, abscess, constipation due to intestinal dryness | Vertigo, tinnitus, premature graying of the hair, lumbar and knee pain, limb numbness, neurasthenia, hyperlipidemia, carbuncle, rubella, constipation, spermatorrhea, malaria, dysentery, chronic hepatitis, scrofula, intestinal wind, hemorrhoid, kidney deficit, dizziness, insomnia, postpartum bellyache, retention of blood in uteru |
| Pueraria montana var. lobata | Alleviate a hangover, vertebral syndrom, clearing away heat and relieving exterior syndrome, stimulate saliva and reduce thirst, measles, diarrhea | Fever, headache, diarrhea, hypertension, stenocardia, epicophosis |
| Ricinus communis | Carbuncle, pharyngitis, edema, scrofula, constipation, scabies | Rheumatoid arthralgia, tetanus, epilepsy, schizophrenia, ulcer, pharyngitis, scrofula, scald, scabies |
| Rosa laevigata | Spermatorrhea, enuresis, diarrhea, diarrhea, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, leukorrhea, hemorrhoid complicated by anal fistula, scald, frequent micturition, diarrhea due to spleen deficiency, spontaneous sweating, night sweat, leukorrhea, rectal prolapse | Spermatorrhea, enuresis, diarrhea, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, leukorrhea, uterine prolapse, rectal prolapse, hemorrhoid, scald, spontaneous sweating, night sweat, bone fracture, traumatic injury, appendicitis, enteritis, stomachache |
| Sarcandra glabra | Sore throat, wind-heat type common cold, diarrhea bacillary dysentery, rheumatism, traumatic injury | Rheumatic arthralgia, traumatic injury, fracture, pneumonia, appendicitis, tumour, bacillary dysentery, cholecystitis, abscess, sore throat, rheumatism, promoting blood circulation, heat clearing and detoxifying |
| Schefflera heptaphylla | Rheumatism, rheumatoid, sweating | Fever, rheumatism, traumatic injury, sore throat, for eczema, allergic dermatitis, dermatitis, eczema |
| Semiliquidambar cathayensis | Rheumatoid arthritis, lumbar muscle degeneration | Rheumatism, rheumatoid, traumatic injury, relaxing tendons and activating collaterals, promoting blood circulation, postpartum recovery, skin disease |
| Sophora tonkinensis | Sore throat, gastric cancer, stomachache, gastric ulcer, prostatitis, diuresis | Sorethroat, swelling and aching of gum, jaundice, diarrhea, hemorrhoids, scabies, snake bite, acute pharyngitis, tonsillitis, cough, constipation, clearing heat and detoxifying, diminishing inflammation, relieving pain |
| Striga asiatica | Nfantile malnutrition, edema | Pacify liver and clear heat, remove food retention, infantile malnutrition, dampness-heat constitution, diarrhea, jaundiced hepatitis |
| Toddalia asiatica | Rheumatism, traumatic injury, bleeding wound | Rheumatism, traumatic injury, stomachache, bleeding wound, amenorrhea, algomenorrhea, furuncle, intercostal neuralgia, skin disease, relieving pain, hemiplegia |
| Toxicodendron vernicifluum | Dermatitis | Traumatic injury, traumatic bleeding, sore carbuncle |
| Viburnum taitoense | Hyperosteogeny, protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc, relieve pain, traumatic injury | – |
| Zanthoxylum nitidum | Rheumatism, relieve pain, gastric ulcer, stomachache, prostatitis | Traumatic injury, rheumatism, stomachache, toothache, snakebite, diarrhea, malaria, chronic gastricism |
| Zingiber officinale | Cough, hemoptysis, hiccough, anemofrigid cold, vomit, cough, reduce phlegm | Cold, vomiting, cough, release superficies, warm the middle, resolve phlegm and stop cough |
The comparison showed that the diseases treated with the most frequently used plants by Mulam people were similar to those found in previous ethnobotanical studies and TCM. For example, Acorus tatarinowii was the most frequently used plant for epilepsy, phlegm heat, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, and traumatic injury in the study area. Similarly, it is used to treat epilepsy and phlegm heat in TCM [57]. In addition, this plant is used for rheumatism and beautification in the Yao communities of Longsheng County, Northern Guangxi [25], and it is used to treat stomachache, stomach flu, limb numbness, hemorrhoids, diarrhea, gall, injuries from falls, and dysmenorrhea and as an invigorant by Yao people in Jinping County, southeastern Yunnan [50]. In Guangdong, this plant is used to treat flu, detumescence, and pain by Hakka people [59]. There are some similarities and differences in the diseases treated with A. tatarinowii, and it is used in different places and by different groups of people. However, some unique medicinal plant species (e.g., Achyranthes longifolia, Cupressus funebris, Euphorbia esula, Flemingia macrophylla, Laportea violacea, Pinus massoniana, Toxicodendron vernicifluum, Viburnum taitoense) had completely novel medicinal functions reported in our study area that had never been reported in other investigations or recorded in TCM. For example, A. longifolia was reported in the present study as only being used for calculosis, whereas it is used for traumatic injury, rheumatism, dysentery, diphtheria, sore throat, sore carbuncle, stranguria, and edema in TCM [57]. In southern and southwestern China, this plant was used to treat blood stasis, empty-kidney lumbago, sore throat, dysmenorrhea, hypertension, and traumatic injury by Yao and Miao people [20, 58]. Euphorbia esula is another species mentioned for the first time. It was reportedly used as a disinfectant and to treat chills and fever in a medicinal bath or by placing it on the patient’s bed. Previous studies conducted in other areas mentioned the use of Euphorbia spp. to treat rheumatism, promote blood circulation, cure furuncles, and treat inflammations of unknown origin [22, 61]. V. taitoense is a Viburnum medicinal species mentioned for the first time. It was reported as being used to treat hyperosteogeny, protrusion of the lumbar intervertebral disc, pain, and traumatic injury in the current study. Previous studies conducted in other areas mentioned treatment with Viburnum spp. for toxicoderma, rheumatism, traumatic injury, and to stop bleeding [25, 61]. The pharmacological activity of these plants is a novel finding that has only been reported for such medicinal purposes in this area. Our investigation found that traumatic injury, bacterial infection, calculosis, hyperosteogeny, cough, and fever were the most common diseases in Mulam villages. Mulam people are skilled in using plants from their surroundings to treat diseases in their daily lives. They not only make full use of the surrounding plant resources but also continuously communicate and learn from other ethnic groups in their long-term struggle with the natural environment and diseases.
Threats to traditional medicinal knowledge and medicinal plants
Our investigation and group discussions revealed that traditional medicinal knowledge is greatly threatened due to the lack of a written record, conservative inheritance patterns, and low interest in traditional medicinal knowledge from young people. In addition, agricultural activities, firewood collection, overgrazing, logging, and overharvesting of medicinal plants resulted in a decrease in medicinal plant resources and associated traditional knowledge. Additionally, the superstition and the mystery surrounding the Mulam healers’ traditional medicinal knowledge are also regarded as obstacles to dissemination and promotion. Thus, policies to improve the conservation, development, and sustainable use of Mulam medicinal plants and associated traditional knowledge are essential. First, further investigation and documentation of traditional Mulam medicinal knowledge is imperative. Books and databases of medicinal plants, animals, and minerals should be published, with free access provided to local healers and those (especially young people) who are interested in Mulam ethnomedicine. Second, advanced theories and methods of pharmacology, chemistry, and molecular biology should be applied to study the traditional Mulam medicinal knowledge and enhance Mulam people’s understanding and confidence. Third, it is also necessary to encourage the Mulam people to conserve medicinal plants in situ and ex situ, such as by planting endangered and preferred medicinal species in their home gardens or farmlands.
Conclusions
A total of 456 medicinal plant species used by Mulam people to treat 312 human ailments were investigated and recorded. This result reflects the rich diversity of medicinal plants in the Mulam area. These medicinal plants play an important role in the Mulam healthcare system. Most of the plants (335 species, 73.47%) were obtained from wild habitats, and the herbaceous habit was the most common growth habit (246 species, 54%). The most common method of administration was oral administration, which was used for 390 species (62.70%), and the most common method of preparation was decoction (316 species, 54.11%). Mulam people are skilled in using the plants in their surroundings to treat diseases in their daily lives. Additionally, they continuously communicate and learn from other ethnic groups in their long-term struggle to survive the natural environment and diseases. However, traditional medicinal knowledge and medicinal plants are greatly threatened by rapid economic development for various reasons. Thus, policies and practices for the conservation of medicinal plants and their associated traditional knowledge are necessary.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the traditional healers and local people of the study area for sharing their knowledge, cooperation, and hospitality. The authors would like to thank Changsong He from the Central Hospital of Dongmen Township in Luocheng, Guangxi for providing guidance and local language translation in our field investigations. We are also grateful to Jing Liu, Yusong Huang, Xinyi Huang, and Zhaocen Lu from Guangxi Institute of Botany, Guangxi Region and Chinese Academy of Sciences for participating in the field investigations.
Abbreviations
- ICF
Informant consensus factor
- FL
Fidelity levels
- TCM
Traditional Chinese medicine
Authors’ contributions
YL and CLL conceived of and designed the study. RCH, CRL, and WBX conducted data collection. RCH and CRL integrated the inventory and its analysis. RCH, YL, CLL, CRL, and WBX identified the plants. HRC wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Special Funds for Local Science and Technology Development Guided by the Central Committee (ZY1949013), Ethnobotany Study of Baikuyao in Nandan, Guangxi (2018GXNSFBA281162), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870316, 31560088 & 31761143001), Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (2019HJ2096001006), Key Laboratory of Ethnomedicine (Minzu University of China) of Ministry of Education of China (KLEM-ZZ201904 & KLEM-ZZ201906), the 2018 Chinese Medicine Public Health Service Subsidy Special “National Chinese Medicine Resources Census Project” (GXZYZYPC18-3-2), Jiansheng Fresh Herb Medicine R & D Foundation (JSYY-20190101-043), and Biodiversity Survey, Observation and Assessment Program of Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (8-3-7-20-5).
Availability of data and materials
We have already included all data in this manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Permissions were provided by all participants in this study, including the local Mulam people and healers. Consent was obtained from the local communities prior to the field investigations. The authors have all copyrights.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Renchuan Hu, Email: hrcgxmi@163.com.
Chunrui Lin, Email: linchunrui@gxib.cn.
Weibin Xu, Email: xwb@gxib.cn.
Yan Liu, Email: gxibly@163.com.
Chunlin Long, Email: long@mail.kib.ac.cn, Email: long.chunlin@muc.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Huai HY, Pei SJ. Medicinal ethnobotany and its advances. Chin Bull Bot. 2002;2(19):129–136. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhu YP, Woerdenbag HJ. Traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Pharm World Sci. 1995;17(4):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01872386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brandão MGL, Acúrcio FA, Montemor RLM, Marlière LDP. Complementary/alternative medicine in Latin America: Use of herbal remedies among a Brazilian metropolitan area population. J Complem Integr Med. 2006;3(1). 10.2202/1553-3840.1025.
- 4.Sheldon JW, Balick MJ, Laird SA. Medicinal plants: can utilization and conservation coexist? Econ Bot. 1997;12:1–104. https://www.jstor.org/stable/4256213.
- 5.World Health Organization . WHO traditional medicine strategy 2002-2005. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Burton A, Smith M, Falkenberg T. Building WHO's global strategy for traditional medicine. Eur J Integr Med. 2015;7(1):13–5. 10.1016/j.eujim.2014.12.007.
- 7.Aati H, El-Gamal A, Shaheen H, Kayser O. Traditional use of ethnomedicinal native plants in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15(1):2. 10.1186/s13002-018-0263-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.WHO. Traditional medicine, 2008. Fact sheet 2009. p. 322.
- 9.Bannerman RH, Burton J, Chen WC. Traditional medicine and health care coverage: a reader for health administrators and practitioners. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aziz M, Adnan M, Khan A, Shahat A, Al-Said M, Ullah R. Traditional uses of medicinal plants practiced by the indigenous communities at Mohmand agency, FATA. Pakistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2018;14(2):2–16. 10.1186/s13002-017-0204-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Sun X, Yu J, Qian HN. Research progress and prospect of Shennong Bencao Jing. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. 2014;32:9. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liu Y, Dao Z, Yang C, Liu Y, Long CL. Medicinal plants used by Tibetans in Shangri-la, Yunnan, China. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2009;5(1):15. http://www.ethnobiomed.com/content/5/1/15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Ahmad M, Sultana S, Fazl-i-Hadi S, Ben Hadda T, Rashid S, Zafar M, Khan MA, Khan MPZ, Yaseen G. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in high mountainous region of Chail valley (District Swat-Pakistan). J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2014;10(1):36. http://www.ethnobiomed.com/content/10/1/36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Tugume P, Kakudidi EK, Buyinza M, Namaalwa J, Kamatenesi M, Mucunguzi P, Kalema J. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plant species used by communities around Mabira Central Forest Reserve, Uganda. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2016;12(1):5. 10.1186/s13002-015-0077-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Tewelde F, Mesfin M, Tsewene S. Ethnobotanical survey of traditional medicinal practices in LaelayAdi-Yabo District, Northern Ethiopia. Int J Ophthalmol Visual Sci. 2017;2(4):80–7. 10.11648/j.ijovs.20170204.11.
- 16.Aziz MA, Khan AH, Adnan M, Izatullah I. Traditional uses of medicinal plants reported by the indigenous communities and local herbal practitioners of Bajaur Agency, Federally Administrated Tribal Areas, Pakistan. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;198:268–81. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Kidane L, Gebremedhin G, Beyene T. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in Ganta Afeshum District, Eastern Zone of Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2018;14. 10.1186/s13002-018-0266-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Yang C, Long CL, Shi Y, Wang Y, Wang H. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal market during Dragon Boat Festival in Jingxi County, southwestern Guangxi region. J CUN (Nat Sci Ed). 2009;18(2):16–26.
- 19.Lin CR, Liu Y, Xu WB, Liang YY. Diversity of medicinal plant resources on traditional medicinal market in Jingxi, Guangxi. Lishizhen Med Mat Med Res. 2010;21(12):3286–3288. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lin CR, Lu ZC, Liu J, Huang YS, Xu WB, Liu Y. Investigation of medicinal plants on medicinal market during Dragon-Boat Festival in Gongcheng Yao Autonomous County of Guangxi. Mod Chin Med. 2016;18(6):730–736. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Su SL, Zhang TT, Zhang B, Huang K, Zeng XB. Ethnobotany study in the minority area of Baise region. Anhui Agri Sci Bull. 2011;17(23):123–124. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hong LY, Guo ZY, Huang KH, Wei SJ, Liu B, Meng SW, Long CL. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal plants used by Maonan people in China. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2015;11. 10.1186/s13002-015-0019-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Cao M, Su LY, Ming X, Chen JS. Ethnobotany survey on traditional medicinal plants used by Yao people in Nanping town, Shangsi County, guangxi. J Inner Mongol Norm U (Nat Sci Ed) 2016;45:218–223. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Du Q, Wei WM, Mi DQ. Knowledge and existing status of medicinal ethnobotany of mangrove among Jing People in Guangxi. Guihaia. 2016; 36(4):405–12. 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201508008.
- 25.Chen JS, Cao LM, Su XZ, Cao M. Ethnobotany knowledge of traditional medicinal plants among Hong-Yao in Longsheng, Guangxi. Guihaia. 2019;39(3):375–85. 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201805052.
- 26.Deng QY, Wang CC, Wang XQ, Wang LX, Wang ZY, Wu WJ, Li H, Consortium G. Genetic affinity between the Kam-Sui speaking Chadong and Mulam people. J Syst Evol. 2013;51(3):263–70. 10.1111/jse.12009.
- 27.The Population Census Office of the State Counci and National Bureau of Statistics Population and Employment Statistics Division . Tabulation on the population census of the people’s republic of china by county. Beijing: China Statistics Press; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pan Q, Yin JJ, Long DB. General History of Mulam. Beijing: The Ethnic Press; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wen YT. Exploration on the origin of Mulam. Guangxi Ethnic Study. 2010;2:131–135. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Megersa M, Asfaw Z, Kelbessa E, Beyene A, Woldeab B. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in Wayu Tuka district, east Welega zone of oromia regional state, West Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013;9(1):68. 10.1186/1746-4269-9-68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Wang YH, Wang C. Common Research Methods of Ethnobotany. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Education Publishing House; 2017.
- 32.Martin GJ. Ethnobotany: A Method Manual. London: Chapman and Hall; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bernard HR. Research methods in cultural anthropology (4th ed) Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Teklay A, Abera B, Giday M. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used in Kilte Awulaelo District, Tigray Region of Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013;9(1):65. 10.1186/1746-4269-9-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Friedman J, Yaniv Z, Dafni A, Palewitch D. A preliminary classification of the healing potential of medicinal plants, based on a rational analysis of an ethnopharmacological field survey among Bedouins in the Negev Desert, Israel. J Ethnopharmacol. 1986;16(2-3):275-287. 10.1016/0378-8741(86)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 36.Ugulu I. Fidelity level and knowledge of medicinal plants used to make therapeutic Turkish baths. J Altern Complement Med. 2010;16(3):313–22. 10.1089/acm.2009.0040. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 37.Luo BS, Liu YJ, Liu B, Liu SZ, Zhang BX, Zhang LH, Lin CR, Liu Y, Kennelly EJ, Guo ZY, Long CL. Yao herbal medicinal market during the Dragon Boat Festival in Jianghua County, China J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 2018;14. 10.1186/s13002-018-0260-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Abbasi AM, Khan MA, Shah MH, Shah MM, Pervez A, Ahmad M. Ethnobotanical appraisal and cultural values of medicinally important wild edible vegetables of Lesser Himalayas-Pakistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013;9. http://www.ethnobiomed.com/content/9/1/66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Lee S, Xiao C, Pei S. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants at periodic markets of Honghe Prefecture in Yunnan Province, SW China. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;117(2):362–77. 10.1016/j.jep.2008.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 40.Chekole G, Asfaw Z, Kelbessa E. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in the environs of Tara-gedam and Amba remnant forests of Libo Kemkem District, northwest Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2015;11. http://www.ethnobiomed.com/content/11/1/4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Huang J, Pei SJ, Long CL. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by the Lisu people in Nujiang, northwest Yunnan, China. Econ Bot. 2004;58(1):S253–64. 10.2307/4256922.
- 42.Cunningham AB. Recommendations for multiple use zones and development alternatives around Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda. People & Plants Working paper. 1996;4.
- 43.Polat R, Cakilcioglu U, Kaltalioglu K, Ulusan MD, Tuurkmen Z. An ethnobotanical study on medicinal plants in Espiye and its surrounding (Giresun-Turkey) J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;163:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Phumthum M, Srithi K, Inta A, Junsongduang A, Tangjitman K, Pongamornkul W, Trisonthi C, Balslev H. Ethnomedicinal plant diversity in Thailand. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;214:90–8. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45.Hirt HM, M’pia B. Natural medicine in the Tropics. Thirdth ed. Kisubi, Uganda: Marianum Press; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Scherrer AM, Motti R, Weckerle CS. Traditional plant use in the areas of monte vesole and ascea, cilento national park (Campania, Southern Italy). J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;97(1):129–43. 10.1016/j.jep.2004.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 47.Bano A, Ahmad M, Hadda TB, Saboor A, Sultana S, Zafar M, Khan MPZ, Arshad M, Ashraf MA. Quantitative ethnomedicinal study of plants used in the skardu valley at high altitude of Karakoram-Himalayan range, Pakistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2014;10(1):43. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-10-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.van Tubergen A, van der Linden S. A brief history of spa therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(3):273–5. 10.1136/ard.61.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Wang J, Zhu M, Xiang L, Xiao Y. Chinese medicinal bath for psoriasis vulgaris. J Chin Phys. 2002;4:96–97. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Long CL, Li R. Ethnobotanical studies on medicinal plants used by the Red-headed Yao People in Jinping, Yunnan Province, China. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;90(2-3):389–95. 10.1016/j.jep.2003.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 51.Li SM, Long CL, Liu F, Lee S, Guo Q, Li R, Liu Y. Herbs for medicinal baths among the traditional Yao communities of China. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;108(1):59–67. 10.1016/j.jep.2003.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Zhang XP, Li YZ, Li SS, Luo JY. An overview of rheumatoid arthritis therepeutic drugs. Drug Eval Res. 2018;41(10):1906–1910. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Alamanos Y, Drosos AA. Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4(3):130–6. 10.1016/j.autrev.2004.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 54.Hou Y, Zhao Y. Progress on diagnosis and treatment for rheumatoid arthritis [J] Pract J Clin Med. 2011;2:8–10. doi: 10.17816/clinpract218-10. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhou X, Han L, Ye Y, Wang R, Zhang Y, Bai C. Progress on treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with ethnodrugs. China J Chin Mat med. 2017;42(12):2398–2407. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Xie SY, Yao KL, Wu XJ, Lin XG, Han CL, Ling FX, Lian HM. Overview of pharmacological research on Semiliquidambar cathayensis H. T. Chang. J Fujian For Sci Tech. 2018;45(4):122–127. [Google Scholar]
- 57.State Administrative Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine . Chinese Materia Medica. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Jia MR, Li XW. National Medicine of China. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Au DT, Wu J, Jiang Z, Chen H, Lu G, Zhao Z. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by Hakka in Guangdong, China. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;117(1):0-50. 10.1016/j.jep.2008.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 60.Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine . The Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jin B, Liu YJ, Xie JX, Luo BS, Long CL. Ethnobotanical survey of plant species for herbal tea in a Yao autonomous county (Jianghua, China): Results of a 2-year study of traditional medicinal markets on the Dragon Boat Festival. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2018;14. 10.1186/s13002-018-0257-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 62.Pan YM, Liu HM, Xu ZF. Traditional beverage plants used by Dai villagers in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China. Acta Bot Yunnanica. 2006;28(6):653–664. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tang AL, Wei YX, Tang GX, Liu XF, Luo ZH, Ou XH, Chen SY, Qin HY. Primary research on the chemical constituents of Laportea violacea Gagnep. Strait Pharm J. 2008;20:121–3.
- 65.Liu YJ, Ahmed S, Long CL. Ethnobotanical survey of cooling herbal drinks from southern China. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013;9:82. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-9-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ghorbani A, Langenberger G, Feng L, Sauerborn J. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants utilised by Hani ethnicity in Naban River Watershed National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;134(3):651–67. 10.1016/j.jep.2011.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
We have already included all data in this manuscript.