Abstract
Purpose
Various clinical outcome assessments (COAs) are used in clinical research to assess and monitor treatment efficacy in pediatric attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) trials. It is unclear whether the concepts assessed are those that are important to patients and their caregivers. The concepts measured by commonly used COAs in this population have not been explicitly compared.
Methods
We conducted reviews of the qualitative literature to extract information on pediatric ADHD-related concepts reported by pediatric patients, parents, and teachers. Using these concepts, we developed a conceptual framework of pediatric ADHD using both the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) criteria and the additional symptoms and behavioral impacts identified in the literature. We searched for COAs that have been used in pediatric ADHD research and mapped their items based on their conceptual underpinning.
Results
Of the 27 COAs found in the empirical literature, 4 COAs assessed only DSM symptoms. The most comprehensive coverage of our conceptual framework was seen in the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale–DSM-IV (SNAP-IV). Eighteen COAs were used in at least 1 clinical trial: ADHD-Rating Scale-IV (ADHD-RS-IV) was used most often (n=77), followed by SNAP-IV (n=50), Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham Scale (SKAMP; n=31), Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale (WFIRS; n=24), and Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale (VADRS; n=15).
Conclusion
We identified symptoms and behavioral impacts from qualitative studies in pediatric ADHD that are not included in DSM-based criteria. Most COAs used in pediatric ADHD clinical trials measure only those symptoms listed in the DSM. While these COAs can measure symptom severity, they may not assess the full range of symptoms and impacts important to patients and their caregivers. Future research is needed to measure all concepts important to patients and caregivers within ADHD clinical trials.
Keywords: clinical outcome assessment, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, children, adolescents, pediatrics, assessment scales, efficacy
Introduction
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a neurodevelopmental condition affecting both children and adults, comprises behavioral symptoms and attentional dysregulation (eg, inattentiveness, impulsivity, overactivity).1 The prevalence of ADHD in the United States is about 6.1 million among children ages 2–17 years.2 ADHD is a lifelong and impairing disorder, resulting in significant challenges to educational and vocational attainment as well as increased risks for negative physical, psychosocial, and financial outcomes, particularly when untreated.3
Although effective interventions for ADHD exist – including stimulant and nonstimulant medications and nonpharmacologic therapies4,5 – evaluation of treatment response can be difficult because of the subjectivity of ADHD symptoms.6 Outcome measures in clinical trials for ADHD treatments are often rating instruments based on symptom criteria defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM).7 The symptoms of ADHD listed in both the Fourth and Fifth Editions (DSM-IV and DSM-5, respectively) are the same; changes between the 2 diagnostic editions were limited to additional examples of symptom manifestations, criteria for age of onset, and minor wording changes (eg, ADHD “types” in the DSM-IV are called “presentations” in the DSM-5).8 However, individuals with ADHD are typically referred for evaluation and treatment because of dysfunction in social, emotional, familial, academic, and/or occupational roles rather than ADHD symptoms alone.9 Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate treatment benefits beyond symptom reduction by using additional clinical outcome assessments (COAs).
COAs, as defined by the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA), are measures that “describe or reflect how a patient feels, functions, or survives.”10 COAs include outcome measures that are patient-reported, observer-reported, or clinician-reported as well as performance outcome measures.10 COA-based outcomes may be influenced by personal choices, judgment, and motivation.11 They should measure treatment benefit on meaningful aspects of how a patient functions, feels, or survives in his/her life.11 As such, the improvement of the concept(s) measured should be meaningful to the patient in his/her usual or typical life (outside of the clinical trial setting).11
Despite a need to assess outcomes meaningful to pediatric patients with ADHD and their caregivers, there has not yet been a formal evaluation of the relevance of concepts measured by COAs commonly used within clinical trials in ADHD. Whether these COAs measure meaningful aspects of pediatric patients’ and their caregivers’ typical lives has also not been examined. In addition, the degree to which COAs used in pediatric ADHD clinical trials to support label claims capture the concepts important to patients has not been examined. The aim of this literature review is to: 1) identify concepts that are important to pediatric patients with ADHD and their caregivers; 2) identify COAs that have been used in pediatric ADHD research and explore the extent to which they align with the identified concepts; and 3) identify the COAs and their frequency of use in clinical trials, including those that have undergone regulatory review to support product label claims.
Methods
We performed separate literature reviews to address 3 questions:
What concepts should be assessed by pediatric ADHD COAs?
How well are these concepts measured by existing COAs used to assess ADHD symptoms and impacts in children/adolescents?
Which COAs are currently used in pediatric ADHD clinical trials, including those that support label claims and have been reviewed by regulatory bodies?
After applying the search strategy, article filtering was conducted in 2 stages: first, on a title/abstract level, followed by a full-text level review of articles retained after the first filtering. We extracted data on the population, methods, and patient- or caregiver-reported concepts from the full-text articles. Each article was analyzed by one reviewer, and the resulting data were assessed by a second reviewer. If any aspect of the data was unclear, both reviewers reassessed the article. For each of the concepts that required additional review, the reviewers discussed the concept until a consensus was reached.
Literature Review of ADHD Concepts
Two searches were conducted in PubMed to identify publications reporting qualitative research on the symptoms or impacts of ADHD in pediatric patients. Search terms for both searches included “quality of life” or “burden” to capture multiple aspects of the ADHD experience. The first search was conducted to assess the experience of ADHD from the perspective of the patient, using the search terms “ADD OR ADHD” AND “Qualitative OR interview OR focus group” AND “Quality of life OR burden.” Results were limited to human studies published in English from 2000 through 2018 and to patients ≤18 years of age. The second literature search explored the experience of ADHD from the viewpoint of the parent, caregiver, or teacher. This search included the terms “ADD OR ADHD” AND “Qualitative OR interview OR focus group” AND “Quality of life OR burden” AND “Parent OR caregiver OR teacher.” Results were limited to human studies published in English from 2000 through 2018.
Concepts reported by patients and their caregivers were analyzed and organized into a conceptual framework12 to describe the experience of ADHD, including symptoms and impacts. The identified concepts were then compared with concepts from each pediatric ADHD COA. COAs were assessed to understand how well each captured the experience of ADHD.
The conceptual framework was first organized according to concepts underlying DSM diagnostic criteria for ADHD,1 including: 1) predominantly inattentive; and 2) predominantly hyperactive/impulsive. Concepts that did not fit within DSM criteria were listed as additional behavioral symptoms or as specific to certain concepts within those categories. A final category of general functional impacts was also created to capture impacts that applied to ADHD more broadly.
Literature Review of Existing ADHD COAs and the Concepts They Measure
A search was conducted in PubMed to identify COAs used in ADHD research. Search terms included “Attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity” [MeSH Major Topic] AND “Patient-reported outcome [Title/Abstract] OR scale [Title/Abstract] OR instrument [Title/Abstract] OR questionnaire [Title/Abstract]” AND “Symptom OR impact OR quality of life.” We limited the search to articles in the English language published within the last 10 years. We extracted specific COA names from the abstracts and then assessed each COA for its relevance to pediatric ADHD. We also examined information about each COA’s development, psychometrics, and interpretation when available.
Literature Review of COAs Used in Clinical Trials and COAs Used to Support Labeling Claims
We conducted a search on ClinicalTrials.gov to identify and review COAs currently used in clinical trials for pediatric ADHD. Individual searches were conducted for each of the COAs identified through the literature review to document their use as outcome measures in clinical trials. We extracted the endpoints (primary, secondary, and exploratory) derived from these COAs.
To ascertain which COAs have been used to make label claims, we examined the medical reviews and product labels for pediatric ADHD medications approved in the past 10 years by the FDA or the European Medicines Agency (EMA). We assessed the reviews and labels of each medication for information about the use of COAs in clinical trials.
Results
ADHD Concepts from the Perspective of Pediatric Patients and Their Caregivers
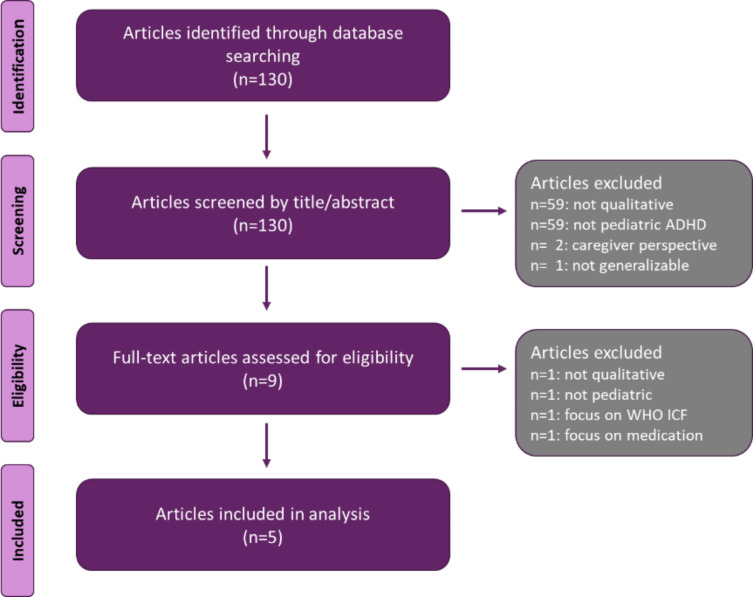
The initial stage of the literature search yielded 130 articles. After excluding articles deemed to be out of scope, 5 articles were included in our analysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Literature review of ADHD concepts (patient perspective).
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; ICF, International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health; WHO, World Health Organization.
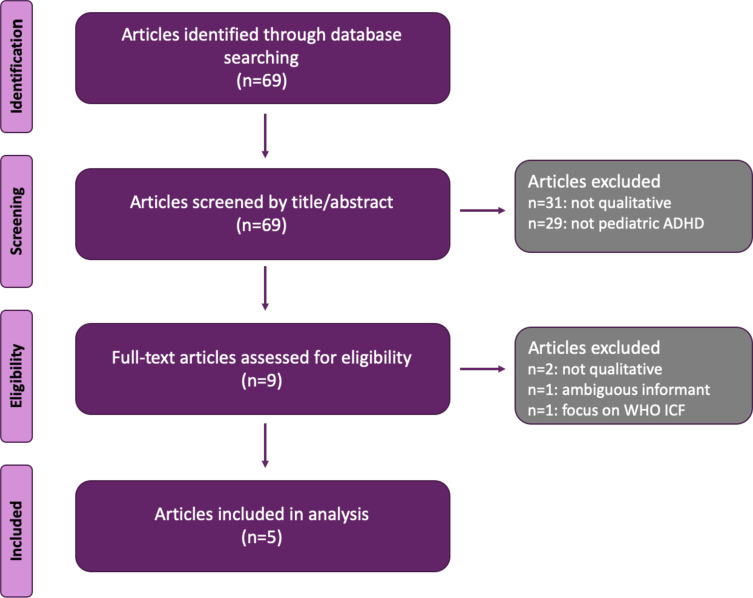
The second stage of the first literature search yielded 69 articles. After excluding articles that were out of scope or had incomplete information, 5 articles were included in our analysis (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Literature review of ADHD concepts (parent, caregiver, or teacher perspective).
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; ICF, International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health; WHO, World Health Organization.
Three articles were captured in both search strategies and reported perspectives from both the patients and caregivers (eg, both children and their teachers provided information), and thus these articles were included in both reviews. In all, 7 unique full-text articles were reviewed (Table 1). Studies were conducted across the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Puerto Rico, and South Africa.
Table 1.
Full-Text Articles from Literature Review of ADHD Concepts
| Authors | Objective | Population | Methods | Patient Concepts | Caregiver Concepts** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bussing et al13 | To understand the perceptions of adolescents, parents, health-care providers, and teachers toward ADHD treatments, including willingness to use different treatment methods and potential negative effects* |
|
Participants were asked one open-ended question: “What other undesirable effects are you concerned about?” All responses were transcribed |
|
|
| Chavez et al14 | To collect adolescents’ assessments of domains important to their QoL in order to develop a Spanish mental health QoL instrument | 60 Latino adolescents (ages 12–18) with diagnoses of either ADHD, CD, ODD, GAD, or MDD. Participants were referred by clinicians in the San Juan metropolitan area. |
|
|
N/A |
| Dewey et al15 | To investigate HRQoL and peer relationships in adolescents with DCD and ADHD | 44 adolescents in Canada (aged 11–18) recruited from a cohort study examining genetics and neurobiology of motor and attention problems
Normally developing: n=19 |
Semistructured interviews exploring various aspects of HRQoL |
|
N/A |
| Hareendran et al16 | To describe the experience of living with ADHD from the perspective of adolescents and their caregivers, for use in the creation of a new self-report instrument |
|
|
|
Teacher interviews:
Caregiver interviews
|
| Laugesen et al17 | A systematic review of the qualitative literature to identify and synthesize reported experiences of parenting a child with ADHD | 21 published research articles that:
|
|
|
|
| Lloyd et al18 | To understand impact of ADHD on HRQoL from the perspective of adolescent patients and their caregivers |
|
|
|
|
| Mofokeng et al19 | To explore the experiences of parents living with a child with ADHD |
|
|
|
|
Notes: *Did not distinguish between patient- and caregiver-reported concepts. **Caregiver perspectives as to impact of their child’s ADHD on their own lives is recorded but not relevant to the aims of this review.
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; CD, conduct disorder; DCD, developmental coordination disorder; DSM-IV, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition; GAD, generalized anxiety disorder; HRQoL, health-related quality of life; MDD, major depressive disorder; N/A, not available; ODD, oppositional-defiant disorder; Tx, treatment; QoL, quality of life.
The conceptual framework was developed using the concepts identified from the literature searches (Table 2). The final conceptual framework comprised 4 areas: symptoms of ADHD as listed in the DSM, additional behavioral symptoms not in the DSM, specific impacts of ADHD symptoms (eg, task-level functioning), and general impacts of ADHD (eg, overall functioning in broad domains such as self-esteem and socialization).
Table 2.
Conceptual Framework: Impacts on Pediatric Patients with ADHD
| DSM | Additional Behavioral Symptoms* | Specific Impacts | General Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
Inattention
|
|
|
|
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
|
|
Note: *Additional behavioral symptoms not included in DSM criteria for ADHD.
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; DSM, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
Existing ADHD COAs and the Concepts Assessed
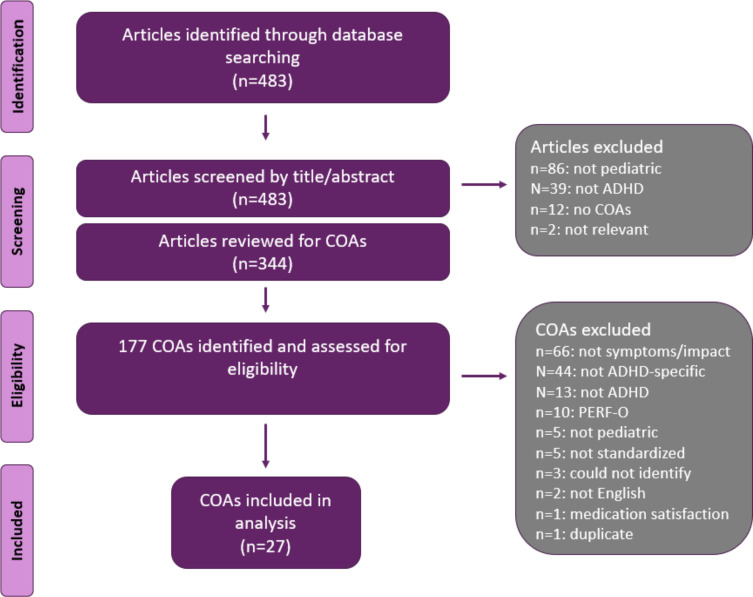
A total of 483 articles were identified through the PubMed search for COAs. After excluding abstracts that were not relevant to pediatric ADHD or did not report the use of any COAs, 344 full-text articles were reviewed and 177 unique COAs were identified (Figure 3). After excluding those that were not relevant to the symptoms or impacts of pediatric ADHD, those that were not written in English, and those that could not be identified, 27 COAs remained. (See Supplemental Table 1 for a listing of identified measures.) Of the 27 relevant COAs, 12 were easily and fully accessible (ie, the full COA was available for review) and were mapped onto the conceptual framework.
Figure 3.
Search of existing ADHD COAs.
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; COAs, clinical outcome assessments; PERF-O, performance outcome measures.
The identified COAs differed in their scope and content; some strictly assessed DSM criteria while others also covered additional behavioral symptoms and impacts.
COAs Evaluating DSM Symptoms
We identified 4 of 12 COAs that assessed only the 18 DSM symptoms of ADHD: ADHD Current Symptoms Scale (ADHD CSS),20 ADHD Rating Scale–DSM-5 (ADHD-RS-5),21 the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale–Adolescent Edition (ASRS-Adolescent),22 and the Strengths and Weaknesses of ADHD Symptoms and Normal Behavior (SWAN) Rating Scale.23
ADHD Current Symptoms Scale (ADHD CSS)
The ADHD CSS,20 also known as the Barkley Current Symptoms Scale, is both a self-report and parent-report measure of current ADHD symptoms. Each item provides 4 answer choices about experienced/observed behaviors: never or rarely, sometimes, often, and very often.
ADHD Rating Scale–DSM-5 (ADHD-RS-5)
The ADHD Rating Scale–DSM-IV (ADHD-RS-IV) and the updated version based on the DSM-5 (ADHD-RS-5)21 both measure the frequency of ADHD symptoms. Although the ADHD-RS-IV is more frequently cited in the literature than the ADHD-RS-5 because of the publication dates of the studies (ie, DSM-5 was released in 2013), the ADHD-RS-5 was used for this review because the purpose of the ADHD-RS-5 is to supersede the ADHD-RS-IV. The ADHD-RS-5 includes separate scales for children and adolescents in both the home (parent-report) and the school (teacher-report) setting. There are 4 answer choices for each item, ranging from 0 to 3. Depending on the phrasing of the question, these scores are described as never or rarely, sometimes, often, and very often, or as no problem, minor problem, moderate problem, and severe problem.
Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale–Adolescent Edition (ASRS-Adolescent)
The ASRS-Adolescent22 is a self-report measure of current ADHD symptoms. It is typically used in adults but has also been used in adolescent populations. Item responses include never, rarely, sometimes, often, and very often.
Strengths and Weaknesses of ADHD Symptoms and Normal Behavior (SWAN) Rating Scale
Lastly, the SWAN23 is a self-, observer- (parent or teacher), or clinician-reported scale to assess ADHD symptom severity. Unlike the other 3 COAs that assess DSM symptoms, the SWAN uses positively worded scale items (eg, “Gives close attention to detail” rather than “Struggles to give attention to detail”). In addition to assessing DSM criteria, it also asks the rater to consider the child’s behavior in comparison with other children. Item responses include far below average, below average, slightly below average, average, slightly above average, above average, and far above average.
COAs Evaluating Additional Concepts
Eight of 12 measures assessed symptoms and impacts not included in the DSM. These COAs include items referring to specific behavioral symptoms and/or specific or general impacts related to the ADHD subtypes. Some of these measures also included items measuring symptom criteria from the DSM, to varying degrees. Where available, we collected information on the item generation process, item reduction process, classical test theory criteria, responsiveness criteria, and Rasch measurement theory criteria.
The ADHD Functional Impairment Questionnaire (ADHD-FX)
The ADHD-FX is a 32-item, observer-reported measure of the level of functional impairment a child experiences related to his or her ADHD.24 Response options include not at all, a little, quite a bit, a lot, and do not know. As shown in Table 3, the scale assesses 3 DSM inattention symptoms and 3 hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms as well as a few specific and general impacts. It has demonstrated adequate reliability and convergent and divergent validity.25
Table 3.
Mapping of Pediatric ADHD COAs Onto the Pediatric ADHD Conceptual Framework
| Measure | DSM Symptoms Assessed | Additional Behavioral Symptoms Not Assessed in DSM Criteria for ADHD | Specific Impacts Assessed | General Impacts Assessed | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADHD-FX24 | Inattention
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
Difficulty regulating emotion Disrespectful/argumentative |
Needs reminders Disruptions in class |
Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others | Addresses some nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms Addresses some functional impairment Has established reliability and validity |
| AIM-C42 | Inattention
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
N/A | Getting to school on time | Poor academic performance Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others |
Includes items on the child’s treatment history and other demographics Has established reliability and validity Addresses some functional impairment |
| DAYAS27 | Inattention
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
Easy to anger Frustration Difficulty regulating emotion Disrespectful/argumentative |
N/A | Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others | Has established reliability and validity Addresses many DSM-5 symptoms of both ADHD subtypes Addresses some functional impairment Assesses intensity of symptoms and behaviors |
| IRS28 | N/A | N/A | Disruptions in class | Poor academic performance Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others Low self-confidence and self-esteem |
Has established validity Addresses some functional impairment |
| SKAMP30,31 | Inattention
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
Disrespectful/argumentative | N/A | Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others | Has been used extensively in clinical trials in a laboratory classroom Addresses some functional impairment |
| SNAP-IV34 | Inattention
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
Easy to anger Frustration Difficulty regulating emotion Disrespectful/argumentative |
Poor performance on/neglecting to do tasks Disruptions in class Difficulty settling down (eg, in class, to sleep) |
Poor academic performance Difficulty communicating Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others Low self-confidence and self-esteem |
Includes items to address oppositional defiant disorder Has established reliability and validity Addresses all 18 DSM-5 symptoms of both subtypes of ADHD Addresses several nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms Addresses many specific and general functional impairments |
| VADRS40 | Inattention
Hyperactivity/impulsivity
|
Easy to anger Frustration Disrespectful/argumentative |
Disruptions in class | Poor academic performance Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others Low self-confidence and self-esteem |
Includes items to address oppositional defiant disorder as well as depression and anxiety symptoms Has established reliability and validity Addresses all 18 DSM-5 symptoms of both ADHD subtypes Addresses several nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms Addresses several general functional impairments |
| WFIRS41 (Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance, 2011) | N/A | N/A | Needing reminders Disruptions in class Getting to school on time Difficulty settling down (eg, in class, to sleep) |
Poor academic performance Difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others Low self-confidence and self-esteem |
Has established reliability and validity Addresses several specific and general functional impairments |
Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; ADHD-FX, ADHD Functional Impairment Questionnaire; AIM-C, ADHD Impact Module–Child; DAYAS, Day Profile of ADHD Symptoms; DSM, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; IRS, Impairment Rating Scale; N/A, not available; SKAMP, Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham Scale; SNAP-IV, Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale–DSM-IV; VADRS, Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale; WFIRS, Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale.
ADHD Impact Module–Child (AIM-C)
The AIM-C is a parent-completed measure of the impact of ADHD on a child’s functioning and at-home quality of life.42 The scale is divided into 2 sections: Child Scale and Home Scale. The Child Scale consists of 8 items and measures the child’s well-being, including emotional functioning and school performance. The Home Scale has 10 items and measures the impact of the child’s ADHD on family life. The AIM-C also includes general questions regarding the child’s treatment history and other demographic information. Items were generated using patient input and literature reviews and were refined with additional patient and expert input. Mean scores have been shown to be significantly worse for children with ADHD-combined subtype than for those with ADHD-inattention subtype.26 Items on the AIM-C have little conceptual coverage of ADHD symptoms as listed in the DSM (Table 3).
Day Profile of ADHD Symptoms (DAYAS)
The DAYAS scale is a parent- or teacher-completed form (DAYAS-P and DAYAS-T, respectively) that measures the intensity of ADHD symptoms and problematic behaviors.27 The measure consists of 17 (DAYAS-P) or 15 (DAYAS-T) items. Answer choices are not at all, just a little, pretty much, and very much. Information about the original item generation was not reported, but patient input was used to reduce the number of items included in the final scale. As shown in Table 3, it provides better coverage of DSM symptoms than the ADHD-FX and AIM-C but is not comprehensive. In addition to nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms, the DAYAS addresses impairment in social relationships but not in other general or specific areas.
Impairment Rating Scale (IRS)
The IRS is a parent- or teacher-completed measure of child functioning across multiple clinically relevant domains: peer, sibling, parent, teacher, academics, self-esteem, classroom/family, and global.28 The IRS Parent consists of 8 items and the IRS Teacher has 7 items. Items are scored on a 7-point scale ranging from no problem (definitely does not need treatment or special services) to extreme problem (definitely needs treatment or special services). Each item on the IRS also includes a space for the respondent to provide an open-ended written answer. It is unclear what sources were used to generate the items on this scale. The IRS does not measure DSM symptoms or additional behavioral symptoms for either ADHD subtype. Items on the IRS assess only 1 specific impact of hyperactivity/impulsivity and 3 of the 4 identified general impacts of ADHD from the conceptual framework (Table 3).
Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham Scale (SKAMP)
The SKAMP is a 13-item observer-rated measure of the child’s impairment on various ADHD-related behaviors.29–33 It is used in laboratory classrooms and scored by trained observers. Responses are given on a 7-point scale, ranging from 0 (no impairment) to 6 (maximal impairment). The SKAMP measures some but not all DSM symptoms as well as some nondiagnostic behaviors and general impacts identified in the conceptual framework (Table 3).
Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale–DSM-IV (SNAP-IV)
The SNAP-IV34 measures the child’s problematic behavior. It is derived from the DSM-IV ADHD criteria and includes 10 questions assessing behaviors typical of oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), as the 2 disorders are often comorbid. Items on the scale were developed from the older SNAP questionnaire, with additional input from the Conners Index Questionnaire and the IOWA Conners Questionnaire. The scale must be completed by a parent or teacher and consists of 90 items in total. Item response choices include not at all, just a little, quite a bit, and very much. The SNAP-IV covers nearly all of the concepts included in the conceptual framework, including all DSM-specific symptoms for both ADHD subtypes, as well as many nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms and specific and general ADHD impacts (Table 3).
Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale (VADRS)
The VADRS is based on DSM-IV symptoms35 and is used by teachers or parents to determine whether a child should be evaluated for a diagnosis of ADHD.36 The latter half of the scale addresses the presence of ODD symptoms as well as symptoms of anxiety or depression. There are 45 items in total. The first 35 items are answered on a 4-point scale: never, occasionally, often, and very often. The remaining 10 items ask for a rating on a 5point scale, from problematic to above average. The VADRS includes all 18 DSM-5 criteria for both subtypes of ADHD, numerous nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms, one specific impact (ie, disruption in class), and several general impacts (Table 3).
Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale (WFIRS)
Finally, the WFIRS measures a child’s functioning in a variety of domains, including family, school, social activity, and life skills.37 Items on this parent- and self-report form were developed using a conceptual framework. There are 46 total items; item responses are never or not at all, sometimes or somewhat, often or much, very often or very much, and N/A (not applicable). The parent form may be used to differentiate 5-to-19-year-olds with and without ADHD based on functional impairment.38 The WFIRS includes none of the DSM diagnostic criteria, nor does it focus on any nondiagnostic behavioral symptoms; rather, it includes items that address both the specific and general impacts listed in our conceptual framework (Table 3).
Conners Rating Scales, Third Edition (Conners 3)
Although not part of our mapping to the pediatric ADHD conceptual framework due to lack of access to the full COA, the Conners 339 is a commonly used measure in pediatric ADHD clinical trials (Table 6). This COA assesses ADHD symptoms and common comorbid conditions (eg, full criteria for DSM-IV conduct disorder and ODD; screening questions for anxiety and depression) in children and adolescents ages 6–18 years. It includes all 18 items of both subtypes of DSM-IV ADHD. Subscales also provide assessments of ADHD-related problems or areas of concern, including learning difficulties, problems with executive functioning, aggression, and peer and family relations. Versions are available for parents (Conners 3-P), teachers (Conners 3-T), and the child self-reports (Conners 3-SR) and come in both long and short forms.
Table 6.
Efficacy COAs in Pediatric ADHD Used in Clinical Trials and Regulatory Information
| COA Name and Completion | Number of Items | Coverage of DSM Concepts | Coverage of Other Concepts | Use in Clinical Trials (n) (January 2019) |
Use in FDA Labels for Reviewed Drugs in Pediatric ADHD (n) (January 2019) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADHD-FX | 32 | 5/18 | 7/17 | 1 | 0 |
| ADHD-RS-IV | 18 | 18/18 | 0/17 | 77 | 4 |
| AIM-C | 47 | 3/18 | 3/17 | 3 | 0 |
| ASRS | 24 | 18/18 | 0/17 | 3 | 0 |
| Brown ADD Scale | * | * | * | 2 | 0 |
| CGI-ADHD S | * | * | * | 18 | 0 |
| Conners 3 | * | * | * | 83 | 0 |
| Conners–Wells | * | * | * | 1 | 0 |
| DPREMB | * | * | * | 2 | 0 |
| DAYAS | 17 | 8/18 | 6/17 | 1 | 0 |
| FSI | * | * | * | 2 | 0 |
| FTF | * | * | * | 2 | 0 |
| IRS | 15 | 0/18 | 4/17 | 13 | 0 |
| SKAMP | 10 | 6/18 | 3/17 | 31 | 6 |
| SNAP-IV | 90 | 18/18 | 16/17 | 50 | 0 |
| SWAN | 30 | 18/18 | 0/17 | 6 | 0 |
| Vanderbilt scale | 43 | 18/18 | 9/17 | 15 | 0 |
| WFIRS | 50 | 0/18 | 7/17 | 24 | 0 |
Note: *Did not have full text of COA to review.
Abbreviations: ADD, attention-deficit disorder; ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; ADHD CSS, ADHD Current Symptoms Scale; ADHD-FX, ADHD Functional Impairment Questionnaire; ADHD-RS-IV, ADHD Rating Scale–DSM-IV; AIM-C, ADHD Impact Module–Child; ASRS, Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale–Adolescent Edition; CGI-ADHD-S, Clinical Global Impressions–ADHD-Severity; COA, clinical outcome assessment; DPREMB, Daily Parent Rating of Evening and Morning Behavior; DAYAS, Day Profile of ADHD Symptoms; FSI, Family Strain Index; FTF, Five to Fifteen; IRS, Impairment Rating Scale; SKAMP, Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham Scale; SNAP-IV, Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale–DSM-IV; SWAN, Strengths and Weaknesses of ADHD Symptoms and Normal Behavior; WFIRS, Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale.
COAs Used in Clinical Trials and Regulatory Labels
We searched ClinicalTrials.gov for each of the 27 COAs identified through the PubMed review. Eighteen of these COAs were used in at least one clinical trial as a primary or secondary endpoint. We extracted data on each study, including a description of the endpoint measured by the COA (Table 4). We did not include information on the informant completing the COA (ie, self, parent, or teacher), as it was not consistently reported on ClinicalTrials.gov.
Table 4.
Review of COAs in Clinical Trials
| COA | Ages Included | Primary Endpoint (n) | Definition of Primary Endpoint | Secondary Endpoint (n) | Definition of Secondary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADHD-FX | 5–12 | 1 |
|
0 | N/A |
| ADHD-RS | 3–29 | 55 |
|
22 |
|
| AIM-C | 6–12 | 0 | N/A | 3 |
|
| ASRS | 3–18 | 1 |
|
2 |
|
| Brown ADD Scale | 6–18 | 0 | N/A | 2 |
|
| CGI-ADHD S | 6–18 | 1 |
|
17 |
|
| Conners 3 | 3–18 | 32 (used as both primary and secondary in 9 studies) |
|
60 (used as both primary and secondary in 9 studies) |
|
| Conners–Wells | 6–17 | 0 | N/A | 1 |
|
| DPREMB | 6–17 | 2 (used as both primary and secondary in 2 studies) |
|
2 (used as both primary and secondary in 2 studies) |
|
| DAYAS | 6–12 | 0 | N/A | 1 |
|
| FSI | 3–10 | 0 | N/A | 2 |
|
| FTF | 7–15 | 0 | N/A | 2 |
|
| IRS | 5–15 | 6 (used as both primary and secondary in 1 study) |
|
8 (used as both primary and secondary in 1 study) |
|
| SKAMP | 6–17 | 24 (used as both primary and secondary in 14 studies) |
|
21 (used as both primary and secondary in 14 studies) |
|
| SNAP-IV | 5–20 | 28 (used as both primary and secondary in 6 studies) |
|
28 (used as both primary and secondary in 6 studies) |
|
| SWAN | 6–17 | 3 |
|
3 |
|
| VADRS | 5–18 | 12 (used as both primary and secondary in 2 studies) |
|
5 (used as both primary and secondary in 2 studies) |
|
| WFIRS | 6–18 | 2 (used as both primary and secondary in 2 studies) |
|
24 (used as both primary and secondary in 2 studies) |
|
Abbreviations: ADD, attention-deficit disorder; ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; ADHD CSS, ADHD Current Symptoms Scale; ADHD-FX, ADHD-Functional Impairment Questionnaire; ADHD-RS-IV, ADHD Rating Scale–DSM-IV; AIM-C, ADHD Impact Module–Child; ASRS, Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale–Adolescent Edition; CGI-ADHD S, Clinical Global Impressions–ADHD-Severity; DPREMB, Daily Parent Rating of Evening and Morning Behavior; DAYAS, Day Profile of ADHD Symptoms; FSI, Family Strain Index; FTF, Five to Fifteen; IRS, Impairment Rating Scale; N/A, not available; ODD, oppositional defiant disorder; SKAMP, Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham Scale; SNAP-IV, Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale–DSM-IV; SWAN, strengths and weaknesses of ADHD symptoms and normal behavior; VADRS, Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale; WFIRS-P, Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale-Parent Form.
We reviewed product labels of pediatric ADHD products approved by the FDA. Table 5 summarizes the COAs used in clinical trials that support FDA-approved product labels.
Table 5.
COAs Cited in Labels
| FDA Label | Product |
|---|---|
| ADHD-RS-IV | Adezenys XR-ODT™ (amphetamine extended-release orally disintegrating tablets) Aptensio XR™ (methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release) Intuniv® (guanfacine) Mydayis® (mixed salts of a single-entity amphetamine product) Quillivant XR® (methylphenidate hydrochloride) |
| SKAMP (although not noted in label, PERMP was collected and used to determine items on the SKAMP) | Adezenys XR-ODT™ (amphetamine extended-release orally disintegrating tablets) Aptensio XR™ (methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release) Contempla XR-ODT (methylphenidate extended-release orally disintegrating tablets) DYANAVEL™ XR (amphetamine) Quillichew ER® (methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release chewable tablets) Quillivant XR® (methylphenidate hydrochloride for extended release oral suspension) |
| PERMP | Adezenys XR-ODT™ (amphetamine extended-release orally disintegrating tablets) Mydayis® (mixed salts of a single-entity amphetamine product) |
| CGI-I | Mydayis® (mixed salts of a single-entity amphetamine product) Quillivant XR® (methylphenidate hydrochloride for extended-release oral suspension; secondary endpoint) |
| CGI-S | Quillivant XR® (methylphenidate hydrochloride for extended-release oral suspension; secondary endpoint) |
Abbreviations: ADHD-RS-IV, ADHD Rating Scale–DSM IV; CGI-I, Clinical Global Impression of Improvement; CGI-S, Clinical Global Impression of Severity; COA, clinical outcome assessment; FDA, US Food & Drug Administration; PERMP, permanent product measure of performance; SKAMP, Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham Scale.
Table 6 summarizes the COAs identified through our literature search that were also used in clinical trials (from ClinicalTrials.gov) and regulatory information.
Discussion
A number of COAs are available to assess symptoms and impacts of pediatric ADHD, and some have been used to assess treatment benefits in clinical trials. The need to measure treatment benefits meaningful to the patient in his/her normal life within clinical trials has been increasingly recognized.4,9,11 However, there has not yet been a formal evaluation of whether the concepts measured by the various ADHD COAs are of relevance to pediatric patients with ADHD and/or their caregivers. In this review, we set out first to identify the conceptual areas of the ADHD experience important to pediatric patients and their caregivers based on existing qualitative research and then to evaluate the extent to which COAs used in pediatric ADHD research align with these identified concepts. Finally, we identified the subset of COAs that have been used in clinical trials, including those that have undergone regulatory review to support product label claims.
We found that most outcome measures used in ADHD studies are a reflection of DSM symptoms, a finding that extends those of previous literature reviews of outcome assessments in pediatric ADHD.7,9 Epstein and Weiss reviewed measures used to assess treatment response in individuals with ADHD across the life span.9 Although findings were not stratified into adults versus children/adolescents, the review reported that most studies assessing ADHD treatment effects used DSM-based symptom measures. The investigators also proposed that additional domains, including functional impairment, quality of life, adaptive life skills, and executive functioning, should be evaluated to determine treatment effect.9 Another literature review corroborated that DSM-based rating scales were most frequently used to measure treatment outcomes.7
Although DSM criteria measure symptom severity, they may not assess the full range of symptoms and/or impacts important to patients and their caregivers. Hence, relying on DSM-based outcome measures may result in a failure to assess treatment benefit in ADHD comprehensively. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that patients’ and families’ perspectives be considered to sustain appropriate treatments and achieve long-term successful treatment outcomes.4 In contrast with previous literature reviews, our approach was to first determine symptoms and impacts important to the patient and caregiver (eg, teacher, parent) through a review of existing qualitative literature in order to construct a more comprehensive conceptual framework against which assessment tools could be mapped.
In addition to DSM-defined symptoms, we identified many patient-, parent-, and teacher-reported concepts that may be important to consider when evaluating treatment benefits in pediatric ADHD. For the inattention subtype category of ADHD, we identified 5 additional concepts: poor listening, poor planning, frequently procrastinating, needing reminders to perform activities, and poor performance on/neglecting to do tasks. For the hyperactivity and Impulsivity subtype category, there were 8 additionally identified concepts: easy to anger, frustration, difficulty regulating emotion, disrespectful/argumentative, clumsy/accident-prone, disruptions in class, difficulty getting to school on time, and difficulty settling down. Additional general impacts included poor academic performance, difficulty communicating, difficulty in social situations/poor relationships with others, and low self-confidence/self-esteem.
Our work on patient- and caregiver-reported ADHD concepts and the resulting conceptual framework based on these concepts (Table 1) is important because it elucidates the extent to which certain COAs accurately and thoroughly capture patient and caregiver experiences of ADHD, which may inform their potential use in clinical trials.
We found that some COAs were used as endpoints in the registration trials of currently marketed pediatric ADHD medications. Among DSM-based scales, the ADHD-RS-IV was most frequently used in pediatric ADHD clinical trials and was mentioned in 4 pediatric ADHD product labels. The SKAMP was also mentioned in many product labels (n = 6) and was used to assess outcomes in 31 clinical trials. The SKAMP may be preferred because it is a rating scale that is completed in a classroom setting;30,31 ADHD medications are often designed to reduce symptoms during the school day or improve other activities that require focus and concentration that a parent may not be able to observe.43 The SKAMP may have been used in clinical trials of ADHD medications, including registration trials, specifically to obtain evidence of these treatment benefits (ie, attention and behaviors in simulated academic settings, which may permit an understanding of time-course effects). The use of the ADHD-RS-IV or ADHD-RS-5 and the SKAMP in registration studies may suggest their acceptance by regulatory bodies.
Of the outcome measures we evaluated; the SNAP-IV appears to have the most comprehensive coverage of the concepts listed in our conceptual framework. The SNAP-IV not only assesses DSM symptoms but also most of the additional concepts identified in our framework (Table 3). Although the SNAP-IV was widely used in clinical trials (n=50), it has not been used in registration trials and it was not found in any product labels.
The FDA has published guidance on the use of COAs, which include patient- and observer-reported outcomes, as clinical trial efficacy endpoints to support labeling claims.10,12 Whether some of the COAs evaluated in this review meet the criteria stated in the FDA guidance will need to be further examined.
Limitations
Our study is limited by the use of publications instead of collecting data directly from patients and their caregivers. For example, we were not able to assess how questions were asked or the environment in which the qualitative studies were conducted. Instead, we assumed the studies used to form our conceptual framework were conducted with good qualitative methods. Our study also did not include a review of the psychometric properties of each COA, but rather aimed at assessing content validity from a patient-centric perspective.
Conclusion
The need to measure treatment benefits meaningful to the patient in his/her usual or typical life has been increasingly recognized.4,9,11 A number of COAs are available to assess symptoms and/or impacts of pediatric ADHD, but the concepts they measure vary. In this review, we set out to first identify a conceptual framework of the ADHD experience important to pediatric patients and their caregivers based on existing qualitative research. We mapped the existing ADHD COAs used in pediatric ADHD research to the conceptual framework and summarized the extent to which these COAs align with the identified concepts. The registration trials of currently available pediatric ADHD medications frequently used ADHD-RS-IV or ADHD-RS-5 to assess DSM symptoms and the SKAMP, administered in the classroom to assess symptoms and functional impairments during the school day. Future research is needed to understand the best way to measure all concepts important to patients and caregivers within clinical trials in ADHD.
Acknowledgments
Editorial support for this article was provided by Kai I. Cheang, PharmD, MS, BCPS, and Emily Kuhl, PhD, of the Global Outcomes Group. This study, as well as editorial support, was funded by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc.
Disclosure
Jessica T Markowitz and Alissa Rams are employees of Modus Outcomes, which was commissioned by Otsuka to conduct this work. Dorothee Oberdhan is an employee of Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. Sharon Wigal is a consultant to, member of the scientific advisory boards of, or received speaker fees and/or research support from Akili, Arbor, Attentiv, Cingulate Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Ironshore, Neos, Neurovance, NLS Pharma, Noven, Otsuka, Pfizer, Purdue, Rho, Rhodes, Shire, Sunovion, Supernus, TouchPoint, and Tris. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data and statistics about ADHD. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html. Accessed September5, 2019.
- 3.Hamed AM, Kauer AJ, Stevens HE. Why the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder matters. Front Psychiatry. 2015;6:168. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00168 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wolraich M, Brown L, Brown RT, et al. ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2011;128(5):1007–1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Feldman ME, Charach A, Belanger SA. ADHD in children and youth: part 2-treatment. Paediatr Child Health. 2018;23(7):462–472. doi: 10.1093/pch/pxy113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coghill D, Seth S. Effective management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) through structured re-assessment: the Dundee ADHD Clinical Care Pathway. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2015;9:52. doi: 10.1186/s13034-015-0083-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Woods D, Wolraich M, Pierce K, Dimarco L, Muller N, Sachdeva R. Considerations and evidence for an ADHD outcome measure. Acad Pediatr. 2014;14(5):54–60. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2014.06.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Epstein JN, Loren REA. Changes in the definition of ADHD in DSM-5: subtle but important. Neuropsychiatry. 2013;3(5):455–458. doi: 10.2217/npy.13.59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Epstein JN, Weiss MD. Assessing treatment outcomes in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a narrative review. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;14(6):1–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Clinical outcome assessments (COA): frequently asked questions. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/clinical-outcome-assessments-coa-frequently-asked-questions#COADefinition. Accessed September5, 2019.
- 11.Walton MK, Powers JH, Hobart J, et al. Clinical outcome assessments: conceptual foundation-report of the ISPOR clinical outcomes assessment-emerging good practices for outcomes research task force. Value Health. 2015;18(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2015.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: patient-reported outcome measures–use in medical product development to support labeling claims. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/77832/download. Accessed September16, 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Bussing R, Koro-Ljungberg M, Noguchi K, Mason D, Mayerson G, Garvan CW. Willingness to use ADHD treatments: A mixed methods study of perceptions by adolescents, parents, health professionals and teachers. Soc Sci Med. 2012;74(1):92––100.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chavez L, Mir K, Canino G. Starting from Scratch: The Development of the Adolescent Quality of Life-Mental Health Scale (AQOL-MHS). Cult Med Psychiatry. 2012;36(3):465––479.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dewey D, Volkovinskaia A. Health-related quality of life and peer relationships in adolescents with developmental coordination disorder and attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2018;60(7):711––717.. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hareendran A, Setyawan J, Pokrzywinski R, Steenrod A, Madhoo M, Erder MH. Evaluating functional outcomes in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: development and initial testing of a self-report instrument. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13:133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Laugesen B, Groenkjaer M. Parenting experiences of living with a child with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Reports. 2015;13(11):169––234.. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lloyd A, Hodgkins P, Sasane R, et al. Estimation of utilities in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder for economic evaluations. Patient. 2011;4(4):247–257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mofokeng M, van der Wath AE. Challenges experienced by parents living with a child with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2017;29(2):137–145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Barkley RA, Murphy KR. Current symptoms self-report scale In: Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Clinical Workbook. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 21.DuPaul GJ, Power TJ, Anastopoulos AD, Reid R. ADHD Rating Scale-5 for Children and Adolescents: Checklists, Norms, and Clinical Interpretation. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Adler L, Kessler R, Spencer T. Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale-V1. 1 (ASRS-V1. 1) Symptom Checklist. New York, NY: World Health Organization; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Swanson J, Schuck S, Porter M, et al. Categorical and dimensional definitions and evaluations of symptoms of ADHD: history of the SNAP and the SWAN rating scales. Int J Educ Psychol Assess. 2012;10(1):51–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Haack LM, Gerdes AC, Lawton KE, Schneider BW. Understanding and measuring functional impairment in diverse children with ADHD: development of the ADHD-FX scale with an at-risk, community sample. J Atten Disord. 2016;20(6):487–500. doi: 10.1177/1087054714527791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Haack LM, Gonring K, Harris M, Gerdes A, Pfiffner L. Assessing impairment in childhood ADHD: validation of the parent and teacher ADHD-FX rating scale in a dual-site clinical sample. J Atten Disord. 2019;23(6):541–552. doi: 10.1177/1087054716659360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Landgraf JM, Rich M, Rappaport L. Measuring quality of life in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and their families: development and evaluation of a new tool. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2002;156(4):384–391. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.156.4.384 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Breuer D, Gortz-Dorten A, Rothenberger A, Dopfner M. Assessment of daily profiles of ADHD and ODD symptoms, and symptomatology related to ADHD medication, by parent and teacher ratings. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011;20(Suppl 2):S289–96. doi: 10.1007/s00787-011-0206-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.DefiniPoint. Impairment rating scale. Available from: https://www.attentionpoint.com/x_upload/media/images/definipoint_instrument_overview_130423.pdf. Accessed February15, 2019.
- 29.Swanson JM, Lerner M, Wigal T, et al. The use of a laboratory school protocol to evaluate concepts about efficacy and side effects of new formulations of stimulant medications. J Atten Disord. 2002;6(Suppl 1):S73–88. doi: 10.1177/070674370200601S10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wigal SB, Gupta S, Guinta D, Swanson JM. Reliability and validity of the SKAMP rating scale in a laboratory school setting. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1998;34(1):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wigal SB, Wigal TL. The laboratory school protocol: its origin, use, and new applications. J Atten Disord. 2006;10(1):92–111. doi: 10.1177/1087054705286049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wigal SB. Laboratory school protocol mini-review: use of direct observational and objective measures to assess ADHD treatment response across the lifespan. Front Psychol. 2019;10:1796. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01796 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Swanson JM, Alger D, Fineberg E, et al. UCI laboratory school protocol for PK/PD studies. In: Greenhill L, Osman B (eds), Ritalin: Theory and Practice, 2nd Edition.Larchmont, NY: Mary Ann Liebert: 1999;405–460. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Swanson J. The SNAP-IV teacher and parent rating scale In: Fine A, Kotkin R, eds. Therapist’s Guide to Learning and Attention Disorders. Elsevier; 2003:487–500. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wolraich ML, Feurer ID, Hannah JN, Baumgaertel A, Pinnock TY. Obtaining systematic teacher reports of disruptive behavior disorders utilizing DSM-IV. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1998;26(2):141–152. doi: 10.1023/A:1022673906401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Futures B. Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic teacher rating scale. Available from: https://www.brightfutures.org/mentalhealth/pdf/professionals/bridges/adhd.pdf. Accessed September16, 2019.
- 37.Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance. Weiss functional impairment rating scale - Parent Report (WFIRS-P). Available from: https://www.caddra.ca/pdfs/caddraGuidelines2011_Toolkit.pdf. Accessed September16, 2019.
- 38.Thompson T, Lloyd A, Joseph A, Weiss M. The Weiss functional impairment rating scale-parent form for assessing ADHD: evaluating diagnostic accuracy and determining optimal thresholds using ROC analysis. Qual Life Res. 2017;26(7):1879–1885. doi: 10.1007/s11136-017-1514-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Conners CK, Pitkanen J, Rzepa SR. Conners 3rd edition (Conners 3; Conners 2008) In: Kreutzer JS, DeLuca J, Caplan B, editors. Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology. New York, NY: Springer; 2011:675–678. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Futures Bright. Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Teacher Rating Scale. Available from: https://www.brightfutures.org/mentalhealth/pdf/professionals/bridges/adhd.pdf. Accessed September 16, 2019.
- 41.Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance. Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale - Parent Report (WFIRS-P). Available from: https://www.caddra.ca/pdfs/caddraGuidelines2011_Toolkit.pdf. Accessed September 16, 2019.
- 42.HealthAct CHQ. AIM-C: ADHD impact module - childTM. Available from: https://www.healthactchq.com/survey/aim-c. Accessed September16, 2019.
- 43.Daughton JM, Kratochvil CJ. Review of ADHD pharmacotherapies: advantages, disadvantages, and clinical pearls. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2009;48(3):240–248. doi: 10.1097/CHI.0b013e318197748f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Citations
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data and statistics about ADHD. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html. Accessed September5, 2019.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Clinical outcome assessments (COA): frequently asked questions. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/clinical-outcome-assessments-coa-frequently-asked-questions#COADefinition. Accessed September5, 2019.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: patient-reported outcome measures–use in medical product development to support labeling claims. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/77832/download. Accessed September16, 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- DefiniPoint. Impairment rating scale. Available from: https://www.attentionpoint.com/x_upload/media/images/definipoint_instrument_overview_130423.pdf. Accessed February15, 2019.
- Futures B. Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic teacher rating scale. Available from: https://www.brightfutures.org/mentalhealth/pdf/professionals/bridges/adhd.pdf. Accessed September16, 2019.
- Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance. Weiss functional impairment rating scale - Parent Report (WFIRS-P). Available from: https://www.caddra.ca/pdfs/caddraGuidelines2011_Toolkit.pdf. Accessed September16, 2019.
- HealthAct CHQ. AIM-C: ADHD impact module - childTM. Available from: https://www.healthactchq.com/survey/aim-c. Accessed September16, 2019.