Fig. 1. Hypoxia Causes HIF-Independent Histone Hypermethylation.
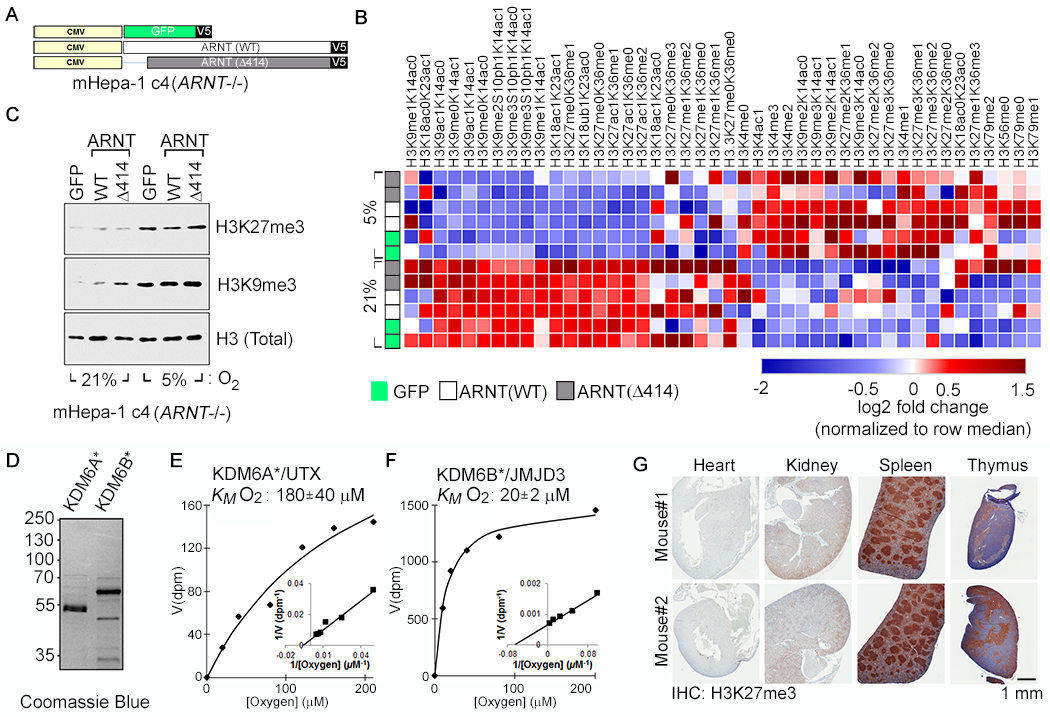
(A-C) Vector schematic (A), Histone modification profiling by mass spectrometry (B), and Histone immunoblot analysis (C) of Arnt-deficient mouse Hepatoma (mHepa-1 c4) cells that were lentivirally transduced to produce the indicated V5-tagged proteins and cultured at the indicated oxygen levels for 4 days. In (B), rows represent two biological replicates of the indicated samples and the color in each cell represents log2 fold change relative to all samples in the column, normalized for total histone using an internal control peptide (Histone H3: residues 41-49). (D-F) Coomassie blue staining (D) and biochemical analysis of baculovirally expressed and purified JumonjiC (JmjC) catalytic domains of KDM6A [KDM6A*] (E) and KDM6B [KDM6B*] (F). KM values are mean +/− SD (N=3). (G) Immunohistochemical analysis of the indicated tissues derived from representative male and female age-matched mice
